Fibrinogen-like Protein 1 as a Predictive Marker for the Incidence of Severe Acute Pancreatitis and Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
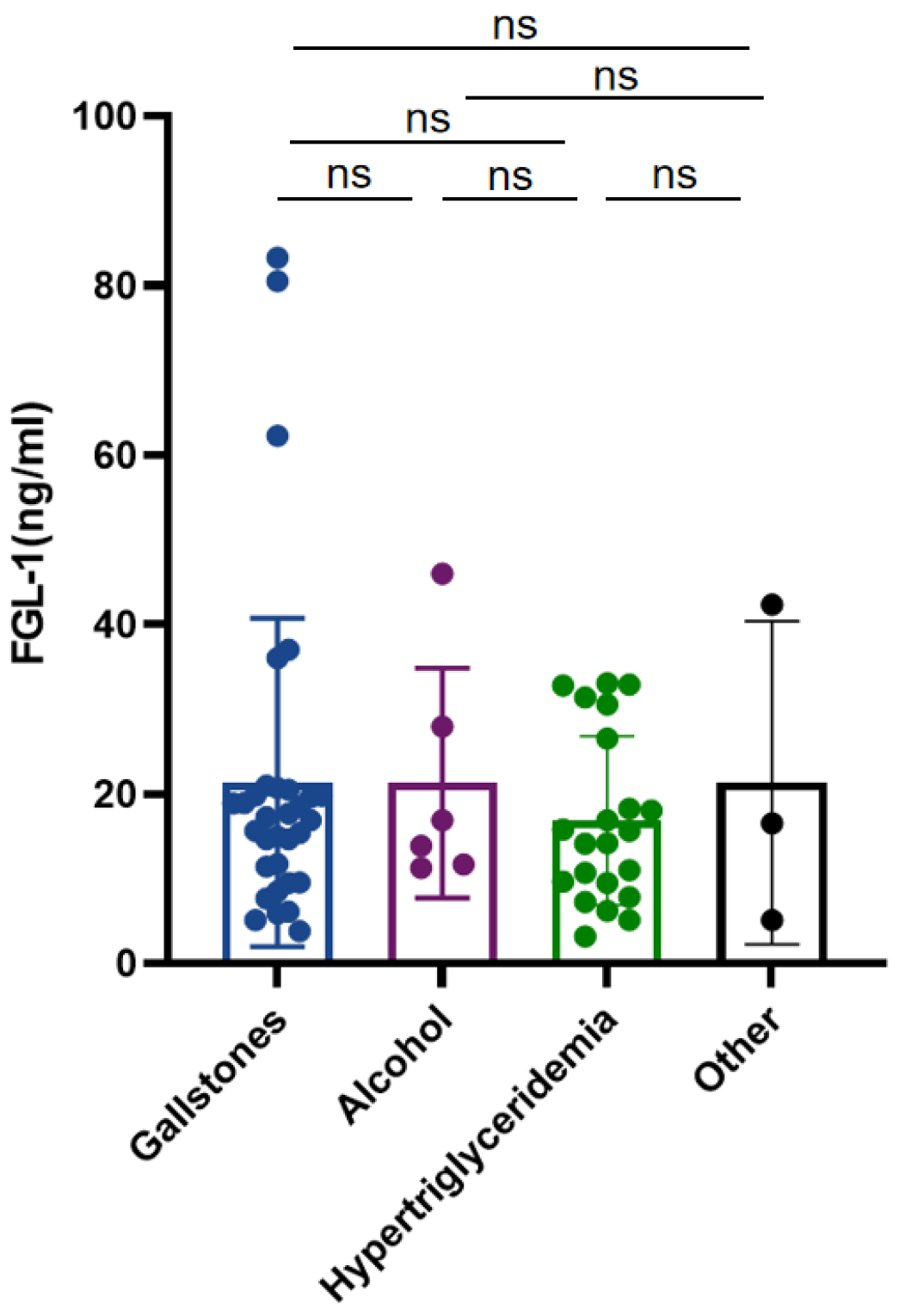
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. FGL-1 and PCT Shows Excellent Diagnostic Power in SAP
3.3. FGL-1 and CRP Shows Better Diagnostic Power in IPN
3.4. Combination of FGL-1 and PCT Improves the Predictive Capability for SAP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S. Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarin, G.; Romano, L.; Coletti, G.; Di Sibio, A.; Vicentini, V.; Fatayer, M.W.A.; Schietroma, M.; Pessia, B.; Leone, M.; Carlei, F.; et al. Branch Duct—IPMN and PanIN, in IgG4-Autoimmune pancreatitis: A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 10, 2111–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewijkx, P.J.; Besselink, M.G.; Witteman, B.J.; Schepers, N.J.; Gooszen, H.G.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Bakker, O.J.; Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group. Nutrition in acute pancreatitis: A critical review. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 10, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gukovskaya, A.S.; Gukovsky, I.; Algül, H.; Habtezion, A. Autophagy, inflammation, and immune dysfunction in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1212–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylänpää, M.L.; Repo, H.; Puolakkainen, P.A. Inflammation and immunosuppression in severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 2867–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matull, W.R.; Pereira, S.P.; O’Donohue, J.W. Biochemical markers of acute pancreatitis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 59, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, A.K.; Meher, S.; Prakash, S.; Tiwary, S.K.; Singh, U.; Srivastava, A.; Dixit, V.K. Comparison of Ranson, Glasgow, MOSS, SIRS, BISAP, APACHE-II, CTSI Scores, IL-6, CRP, and Procalcitonin in Predicting Severity, Organ Failure, Pancreatic Necrosis, and Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis. HPB Surg. 2013, 2013, 367581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neoptolemos, J.P.; Kemppainen, E.A.; Mayer, J.M.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Raraty, M.G.; Slavin, J.; Beger, H.G.; Hietaranta, A.J.; Puolakkainen, P.A. Early prediction of severity in acute pancreatitis by urinary trypsinogen activation peptide: A multicentre study. Lancet 2000, 355, 1955–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.M.; Noh, M.H.; Kim, B.G.; Hsing, C.T.; Han, J.S.; Ryu, S.H.; Seo, J.M.; Yoon, H.A.; Jang, J.S.; Choi, S.R.; et al. Comparison of serum procalcitonin with Ranson, APACHE-II, Glasgow and Balthazar CT severity index scores in predicting severity of acute pancreatitis. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 5, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isman, F.K.; Zulfikaroglu, B.; Isbilen, B.; Ozalp, N.; Ozmen, M.M.; Bilgic, I.; Koc, M. Copeptin is a predictive biomarker of severity in acute pancreatitis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 31, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofidi, R.; Suttie, S.A.; Patil, P.V.; Ogston, S.; Parks, R.W. The value of procalcitonin at predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis and development of infected pancreatic necrosis: Systematic review. Surgery 2009, 146, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.T.; Chen, S.C.; Fan, K.C.; Kuo, C.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Chang, C.J.; Li, H.Y. Targeting fibrinogen-like protein 1 is a novel therapeutic strategy to combat obesity. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 2958–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ukomadu, C. Fibrinogen-like protein 1, a hepatocyte derived protein is an acute phase reactant. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 365, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, R.T.; Lugea, A.; Gulla, A.; Pandol, S.J. Proteomic Identification of Novel Plasma Biomarkers and Pathobiologic Pathways in Alcoholic Acute Pancreatitis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Brady, M.; Shokuhi, S.; Christmas, S.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Slavin, J. Inflammatory mediators in acute pancreatitis. J. Pathol. 2000, 190, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Wong, F.L.; Cao, Y.; Lau, H.Y.; Huang, J.; Puneet, P.; Chevali, L. Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2005, 5, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widdison, A.L.; Karanjia, N.D. Pancreatic infection complicating acute pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 1993, 80, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillip, V.; Steiner, J.M.; Algül, H. Early phase of acute pancreatitis: Assessment and management. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2014, 5, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, S.; Mishra, T.S.; Sasmal, P.K.; Rath, S.; Sharma, R.; Rout, B.; Sahu, M.K. Role of Biomarkers in Diagnosis and Prognostic Evaluation of Acute Pancreatitis. J. Biomark. 2015, 2015, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Zhan, Y.Q.; Yu, M.; Ge, C.H.; Li, C.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, X.H.; Ge, Z.Q.; Yang, X.M. Hepassocin activates the EGFR/ERK cascade and induces proliferation of L02 cells through the Src-dependent pathway. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Cao, C.Z.; Xu, W.X.; Cao, M.M.; Yang, F.; Dong, L.; Yu, M.; Zhan, Y.Q.; Gao, Y.B.; Li, W.; et al. Recombinant human hepassocin stimulates proliferation of hepatocytes in vivo and improves survival in rats with fulminant hepatic failure. Gut 2010, 59, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvaruso, V. Hepassocin as a treatment for fulminant hepatic failure: Will it translate from rats to human? Gut 2010, 59, 709–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, H.; Yoshimura, H.; Uchida, S.; Toyoda, Y.; Aoki, M.; Sakai, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Shiokawa, K. Molecular cloning and functional expression analysis of a cDNA for human hepassocin, a liver-specific protein with hepatocyte mitogenic activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1520, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijken, D.C.; Dirkx, S.P.; Luider, T.M.; Leebeek, F.W. Hepatocyte-derived fibrinogen-related protein-1 is associated with the fibrin matrix of a plasma clot. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 350, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Li, J.; Shen, J.; Du, F.; Wu, X.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Cho, C.H.; Li, X.; Xiao, Z.; et al. The role of Fibrinogen-like proteins in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Qi, L.W.; Alolga, R.N.; Liu, Q. Implication of the hepatokine, fibrinogen-like protein 1 in liver diseases, metabolic disorders and cancer: The need to harness its full potential. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Datar, I.; Su, T.T.; Ji, L.; Sun, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Yin, W.; et al. Fibrinogen-like Protein 1 Is a Major Immune Inhibitory Ligand of LAG-3. Cell 2019, 176, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, Y.; Lu, L.; Lu, J.; Ke, M.; Xu, T.; Lu, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Kong, D.; et al. Fibrinogen-Like Protein 1 Is a Novel Biomarker for Predicting Disease Activity and Prognosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 579228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L.; Qiao, L.C.; Gong, J.; Wen, K.; Xu, Z.Z.; Yang, B.L. Proteomics identifies a novel role of fibrinogen-like protein 1 in Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 5946–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Hu, J.S.; Ji, L.; Li, Y.L.; Tian, F.Y.; Sun, B. Plasma D-Dimer Level Is an Early Predictor of Severity of Acute Pancreatitis Based on 2012 Atlanta Classification. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 9019–9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rau, B.M.; Kemppainen, E.A.; Gumbs, A.A.; Büchler, M.W.; Wegscheider, K.; Bassi, C.; Puolakkainen, P.A.; Beger, H.G. Early assessment of pancreatic infections and overall prognosis in severe acute pancreatitis by procalcitonin (PCT): A prospective international multicenter study. Ann. Surg. 2007, 245, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.H.; Chen, T.Z.; Huai, J.P.; Lu, G.R.; Zhuge, X.J.; Chen, R.P.; Chen, W.J.; Wang, C.; Huang, Z.M. Correlation of fibrinogen-like protein 2 with progression of acute pancreatitis in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2492–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| SAP (n = 12) | No SAP (n = 51) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age—years | 50.5 (39.8–62.0) | 49.0 (41.0–64.0) | 0.951 |
| Gender—M/F | 8/4 | 31/20 | 0.706 |
| Comorbidities—no. (%) | |||
| Heart disease | 1/12 (8.33%) | 9/51 (17.65%) | 0.427 |
| Diabetes | 2/12 (16.67%) | 14/51 (27.45%) | 0.440 |
| Hypertension | 4/12 (33.33%) | 13/51 (25.49%) | 0.582 |
| hLOS—days | 26.0 (10.5–34.8) | 8.0 (6.0–12.0) | <0.001 |
| Etiology—no. (%) | |||
| Gallstones | 4/12 (33.33%) | 28/51 (54.90%) | 0.327 |
| Alcohol | 2/12 (16.67%) | 4/51 (7.84%) | 0.349 |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 5/12 (41.67%) | 17/51 (33.33%) | 0.586 |
| Other | 1/12 (8.33%) | 2/51 (3.92%) | 0.518 |
| Smoking history—no. (%) | 4/12 (33.33%) | 12/39 (30.77%) | 0.483 |
| IPN (n = 9) | No IPN (n = 54) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age—years | 44.0 (39.0–56.0) | 49.0 (41.0–64.0) | 0.298 |
| Gender—M/F | 7/2 | 32/22 | 0.290 |
| Comorbidities—no. (%) | |||
| Heart disease | 0/9 (0%) | 9/54 (16.67%) | 0.225 |
| Diabetes | 3/9 (33.33%) | 13/54 (24.07%) | 0.555 |
| Hypertension | 2/9 (22.22%) | 15/54 (27.78%) | 0.728 |
| hLOS—days | 18.5 (33.0–50.0) | 8.0 (5.75–11.25) | <0.001 |
| Etiology—no. (%) | |||
| Gallstones | 3/9 (33.33%) | 29/54 (53.70%) | 0.258 |
| Alcohol | 1/9 (11.11%) | 5/54 (9.26%) | 0.861 |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 4/9 (44.44%) | 18/54 (33.33%) | 0.517 |
| Other | 1/9 (11.11%) | 2/54 (3.70%) | 0.334 |
| Smoking history—no. (%) | 2/9 (22.22%) | 14/54 (25.93%) | 0.910 |
| Severity | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | n = 63 | SAP (n = 12) | No-SAP (n = 51) | X2 | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| WBC (109/mL) | 0.459 | 0.549 | - | - | - | |||
| ≤10 | 27 | 4 | 23 | |||||
| >10 | 36 | 8 | 28 | |||||
| HCT (%) | 0.165 | 0.685 | - | - | - | |||
| ≤45 | 45 | 8 | 37 | |||||
| >45 | 18 | 4 | 14 | |||||
| Blood glucose (mmol/L) | 0.932 | 0.334 | - | - | - | |||
| ≤7 | 19 | 5 | 14 | |||||
| >7 | 44 | 7 | 37 | |||||
| Ca2+ (mmol/L) | 1.281 | 0.285 | - | - | - | |||
| <2.25 | 42 | 10 | 32 | |||||
| ≥2.25 | 21 | 2 | 19 | |||||
| FIB (g/L) | 0.466 | 0.496 | - | - | - | |||
| ≤4.66 | 37 | 6 | 31 | |||||
| >4.66 | 26 | 6 | 20 | |||||
| APTT (s) | 0.046 | 0.830 | - | - | - | |||
| ≤27.2 | 28 | 5 | 23 | |||||
| >27.2 | 35 | 7 | 28 | |||||
| PCT (ng/mL) | 9.908 | 0.002 | 0.047 | 0.002~0.991 | 0.049 | |||
| ≤0.5 | 31 | 1 | 30 | |||||
| >0.5 | 32 | 11 | 21 | |||||
| CRP (mg/dL) | 4.632 | 0.031 | 2.241 | 0.165~30.384 | 0.544 | |||
| ≤150 | 28 | 2 | 26 | |||||
| >150 | 35 | 10 | 25 | |||||
| FGL-1 (ng/mL) | 32.029 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.001~0.157 | 0.001 | |||
| ≤23.78 | 49 | 2 | 47 | |||||
| >23.78 | 14 | 10 | 4 | |||||
| IPN | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | n = 63 | IPN (n = 9) | No-IPN (n = 54) | X2 | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| WBC (109/mL) | 0.389 | 0.533 | - | - | - | |||
| ≤10 | 27 | 3 | 24 | |||||
| >10 | 36 | 6 | 30 | |||||
| HCT (%) | 0.117 | 0.733 | - | - | - | |||
| ≤45 | 45 | 6 | 39 | |||||
| >45 | 18 | 3 | 15 | |||||
| Blood glucose (mmol/L) | 0.050 | 0.823 | - | - | - | |||
| ≤7 | 19 | 3 | 16 | |||||
| >7 | 44 | 6 | 38 | |||||
| Ca2+ (mmol/L) | 2.333 | 0.127 | - | - | - | |||
| <2.25 | 42 | 8 | 34 | |||||
| ≥2.25 | 21 | 1 | 20 | |||||
| FIB (g/L) | 0.884 | 0.347 | - | - | - | |||
| ≤4.66 | 37 | 4 | 33 | |||||
| >4.66 | 26 | 5 | 21 | |||||
| APTT (s) | 0.525 | 0.469 | - | - | - | |||
| ≤27.2 | 28 | 3 | 25 | |||||
| >27.2 | 35 | 6 | 29 | |||||
| PCT (ng/mL) | 14.860 | <0.001 | 0.447 | 0.038~5.264 | 0.522 | |||
| ≤3.5 | 57 | 5 | 52 | |||||
| >3.5 | 6 | 4 | 2 | |||||
| CRP (mg/dL) | 13.585 | <0.001 | 0.060 | 0.006~0.649 | 0.021 | |||
| ≤430 | 50 | 3 | 47 | |||||
| >430 | 13 | 6 | 7 | |||||
| FGL-1 (ng/mL) | 20.935 | <0.001 | 0.034 | 0.003~0.384 | 0.006 | |||
| ≤23.78 | 50 | 2 | 48 | |||||
| >23.78 | 13 | 7 | 6 | |||||
| AUC (95% CI) | Cut-Off | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | LR+ | LR− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCT (ng/mL) | 0.89 (0.77–1.00) | 1.26 | 83.33% | 88.24% | 62.50% | 95.74% | 7.09 | 0.19 |
| FGL-1 (ng/mL) | 0.88 (0.75–1.00) | 23.78 | 83.33% | 94.12% | 76.92% | 96.00% | 19.23 | 0.24 |
| FGL-1 + PCT | 0.96 (0.88–1.00) | - | 91.67% | 98.04% | 91.67% | 98.04% | 46.77 | 0.08 |
| AUC (95% CI) | Cut-Off | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | LR+ | LR− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.94 (0.87–1.00) | 397 | 100% | 79.63% | 45.00% | 100% | 4.91 | 0 |
| FGL-1 (ng/mL) | 0.84 (0.70–0.99) | 23.79 | 77.78% | 87.04% | 50.00% | 95.92% | 6.00 | 0.26 |
| FGL-1 + CRP | 0.94 (0.87–1.00) | - | 100% | 79.63% | 91.67% | 98.04% | 4.91 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sui, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, G.; Liu, L.; Tan, H.; Sun, B.; Li, L. Fibrinogen-like Protein 1 as a Predictive Marker for the Incidence of Severe Acute Pancreatitis and Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis. Medicina 2022, 58, 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58121753
Sui Y, Zhao Z, Zhang Y, Zhang T, Li G, Liu L, Tan H, Sun B, Li L. Fibrinogen-like Protein 1 as a Predictive Marker for the Incidence of Severe Acute Pancreatitis and Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis. Medicina. 2022; 58(12):1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58121753
Chicago/Turabian StyleSui, Yuhang, Zhongjie Zhao, Yang Zhang, Tao Zhang, Guanqun Li, Liwei Liu, Hongtao Tan, Bei Sun, and Le Li. 2022. "Fibrinogen-like Protein 1 as a Predictive Marker for the Incidence of Severe Acute Pancreatitis and Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis" Medicina 58, no. 12: 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58121753
APA StyleSui, Y., Zhao, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, T., Li, G., Liu, L., Tan, H., Sun, B., & Li, L. (2022). Fibrinogen-like Protein 1 as a Predictive Marker for the Incidence of Severe Acute Pancreatitis and Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis. Medicina, 58(12), 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58121753






