Use of Ultra-Widefield Fluorescein Angiography to Guide the Treatment to Idiopathic Retinal Vasculitis, Aneurysms, and Neuroretinitis—Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
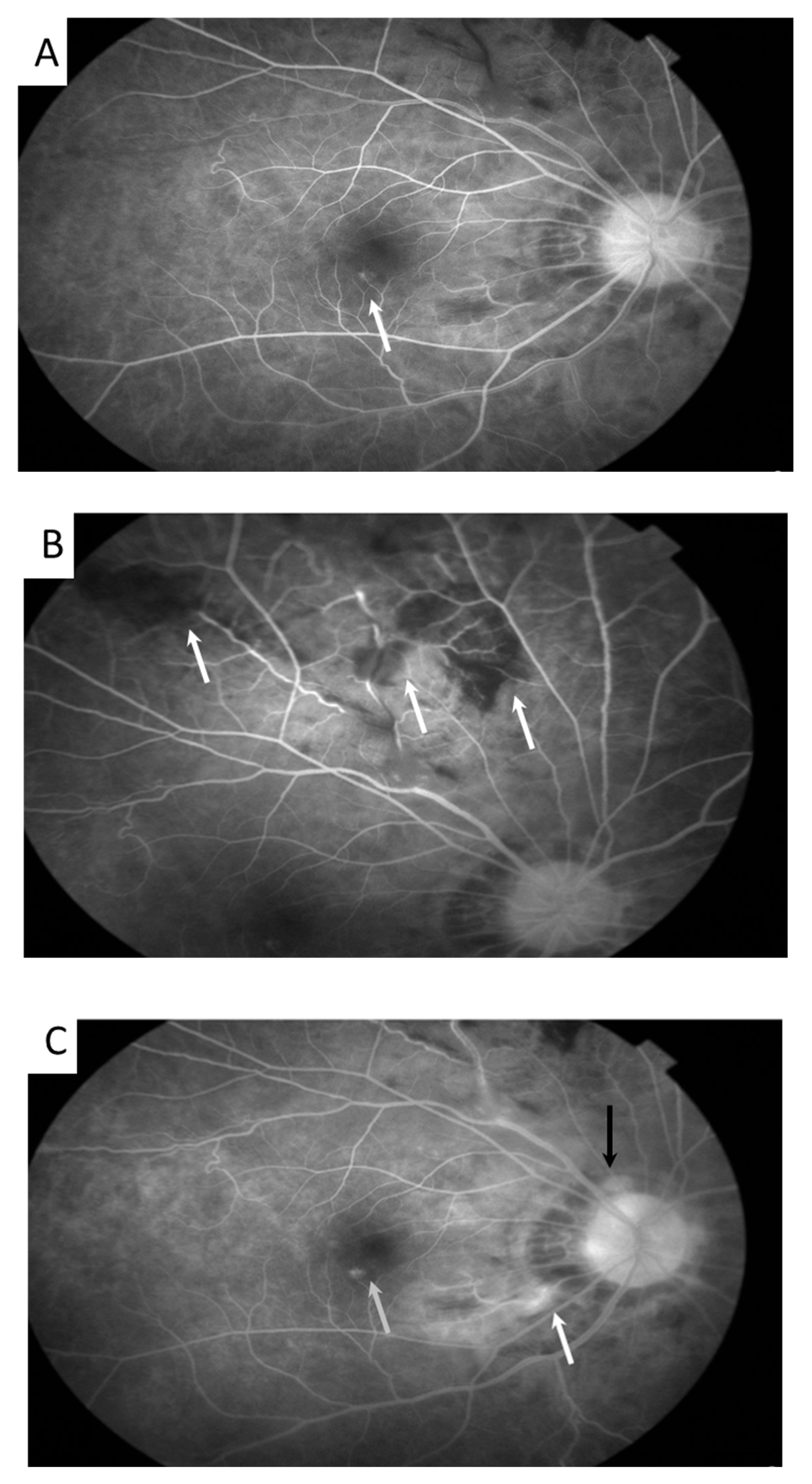
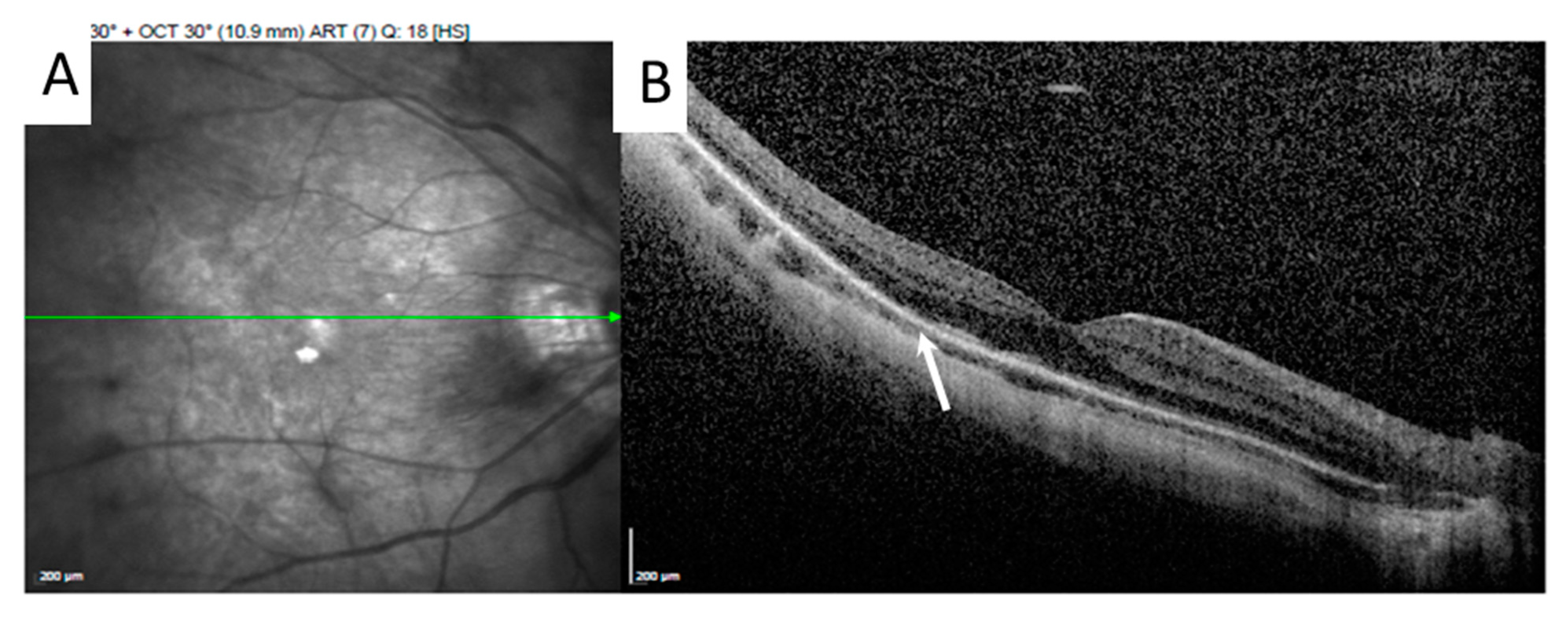
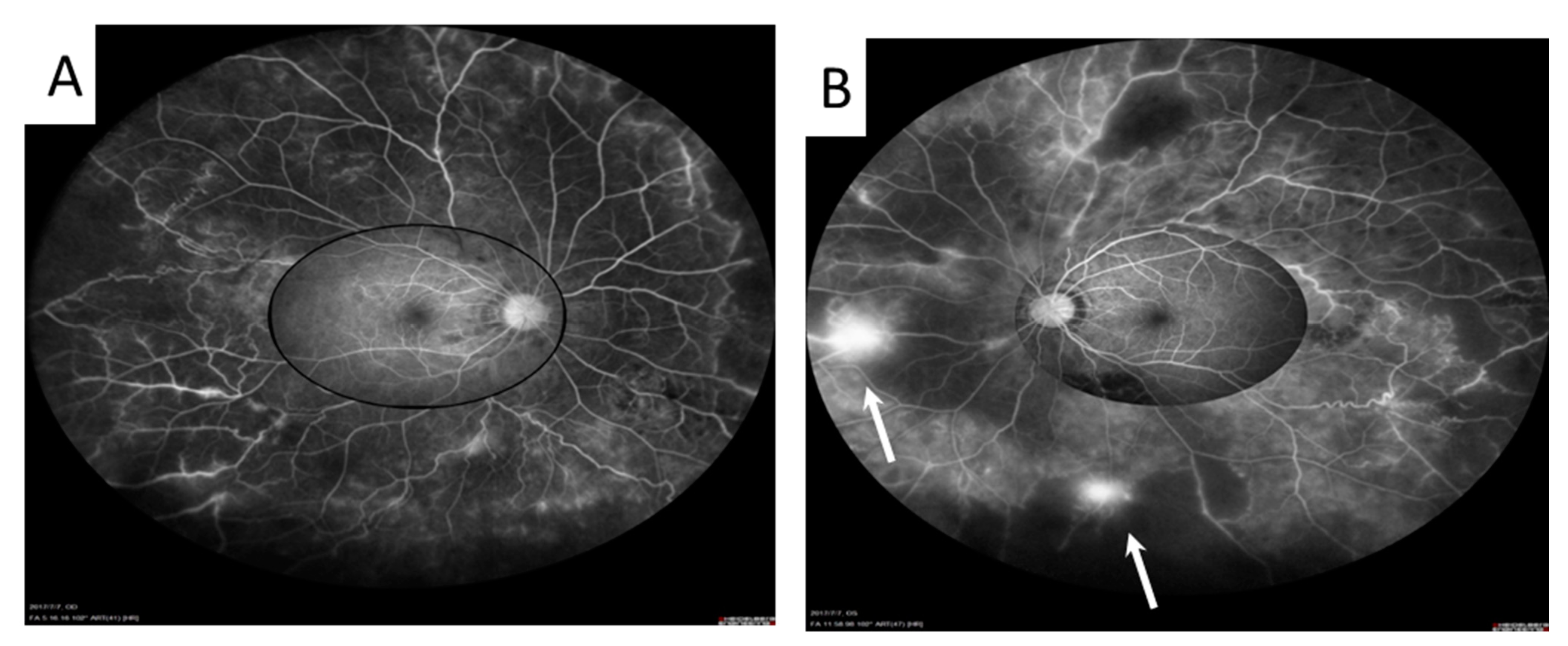
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bajgai, P.; Katoch, D.; Dogra, M.R.; Singh, R. Idiopathic retinal vasculitis, aneurysms, and neuroretinitis (IRVAN) syndrome: Clinical perspectives. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 11, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, M.A.; Equi, R.A.; Chang, T.S.; Mieler, W.; Jampol, L.M.; Hay, D.; Yannuzzi, L.A. Idiopathic retinitis, vasculitis, aneurysms, and neuroretinitis (IRVAN): New observations and a proposed staging system. Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 1526–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Central Vein Occlusion Study Group. A randomized clinical trial of early panretinal photocoagulation for ischemic central retinal vein occlusion: The Central Vein Occlusion Study Group N report. Ophthalmology 1995, 102, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.S.; Aylward, G.W.; Davis, J.L.; Mieler, W.F.; Oliver, G.L.; Maberley, A.L.; Gass, J.D.M.; Callanan, D.; Duker, J.S.; Drouilhet, J.H.; et al. Idiopathic retinal vasculitis, aneurysms, and neuro-retinitis. The retinal vasculitis study. Ophthalmology 1995, 102, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Asrar, A.M.A.; Herbort, C.P.; Tabbara, K.F. Differential diagnosis of retinal vasculitis. Middle East Afr. J Ophthalmol. 2009, 16, 202–218. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, C.S.; Vitale, A.T. Diagnosis and Treatment of Uveitis, 2nd ed.; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2012; pp. 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Khairallah, M.; Khochtal, S.; Ksiaa, I. Is there a true neuroretinitis in idiopathic retinal vasculitis, aneurysms, and neuroretinitis (IRVAN) Syndrome. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2022, 30, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameratunga, R.; Donaldson, M. Treatment of idiopathic retinal vasculitis, aneurysms, and neuroretinitis (IRVAN) with photocoagulation in combination with systemic immunosuppression. Retin. Cases Brief Rep. 2020, 14, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannis, D.; Soumplis, V.; Georgalas, I.; Kandarakis, A. Ranibizumab for idiopathic retinal vasculitis, aneurysms, and neuroretinitis: Favorable results. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 20, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheema, R.A.; Al-Askar, E.; Cheema, H.R. Infliximab therapy for idiopathic retinal vasculitis, aneurysm, and neuroretinitis syndrome. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 27, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouvas, A.; Nikita, E.; Markomichelakis, N.; Theodossiadis, P.; Pharmakakis, N. Idiopathic retinal vasculitis, arteriolar macroaneurysms and neuroretinitis: Clinical course and treatment. J. Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2013, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.P.; Leder, H.A.; Sepah, Y.J.; Gan, T.; Dunn, J.P.; Hatef, E.; Cho, B.; Ibrahim, M.; Bittencourt, M.; Channa, R.; et al. Wide-field retinal imaging in the management of noninfectious posterior uveitis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 154, 908–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leder, H.A.; Campbell, J.P.; Sepah, Y.J.; Gan, T.; Dunn, J.P.; Hatef, E.; Cho, B.; Ibrahim, M.; Bittencourt, M.; Channa, R.; et al. Ultra-wide-field retinal imaging in the management of non-infectious retinal vasculitis. J. Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2013, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, P.-P.; Lin, C.-J.; Hsia, N.-Y.; Lai, C.-T.; Bair, H.; Lin, J.-M.; Chen, W.-L.; Tsai, Y.-Y. Use of Ultra-Widefield Fluorescein Angiography to Guide the Treatment to Idiopathic Retinal Vasculitis, Aneurysms, and Neuroretinitis—Case Report and Literature Review. Medicina 2022, 58, 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101467
Meng P-P, Lin C-J, Hsia N-Y, Lai C-T, Bair H, Lin J-M, Chen W-L, Tsai Y-Y. Use of Ultra-Widefield Fluorescein Angiography to Guide the Treatment to Idiopathic Retinal Vasculitis, Aneurysms, and Neuroretinitis—Case Report and Literature Review. Medicina. 2022; 58(10):1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101467
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Ping-Ping, Chun-Ju Lin, Ning-Yi Hsia, Chun-Ting Lai, Henry Bair, Jane-Ming Lin, Wen-Lu Chen, and Yi-Yu Tsai. 2022. "Use of Ultra-Widefield Fluorescein Angiography to Guide the Treatment to Idiopathic Retinal Vasculitis, Aneurysms, and Neuroretinitis—Case Report and Literature Review" Medicina 58, no. 10: 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101467
APA StyleMeng, P.-P., Lin, C.-J., Hsia, N.-Y., Lai, C.-T., Bair, H., Lin, J.-M., Chen, W.-L., & Tsai, Y.-Y. (2022). Use of Ultra-Widefield Fluorescein Angiography to Guide the Treatment to Idiopathic Retinal Vasculitis, Aneurysms, and Neuroretinitis—Case Report and Literature Review. Medicina, 58(10), 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101467





