Abstract
Background: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by the presence of β-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, while Lewy body dementia (LBD) is characterized by α-synuclein (α-syn) inclusions. Some authors examine α-syn protein in the neurodegeneration process of AD and propose to consider cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) α-syn as a possible additional biomarker to the so-called “core” of AD. Objective: To determine whether there is a correlation between α-syn levels and “core” AD biomarkers in patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Materials and methods: In total, 81 patients in the early stages of MCI were selected from the outpatient dementia consultation in Alicante General Hospital. Using a cross-sectional case–control design, patients were analyzed in four groups: stable MCI (MCIs; n = 25), MCI due to AD (MCI-AD; n = 32), MCI due to LBD (MCI-LBD; n = 24) and a control group of patients with acute or chronic headache (Ctrl; n = 18). Correlation between CSF protein levels in the different groups was assessed by the Rho Spearman test. Results: We found positive correlations between T-tau protein and α-syn (ρ = 0.418; p value < 0.05) and p-tau181p and α-syn (ρ = 0.571; p value < 0.05) exclusively in the MCI-AD group. Conclusion: The correlation found between α-syn and tau proteins in the first stages of AD support the involvement of α-syn in the pathogenesis of AD. This result may have clinical and diagnostic implications, as well as help to apply the new concept of “precision medicine” in patients with MCI.
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most frequent cause of dementia, followed by Lewy body dementia (LBD). Pathophysiologically, AD is typically characterized by the presence of β-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, while LBD is characterized by α-synuclein (α-syn) inclusions. However, some authors examine α-syn protein in the neurodegeneration process of AD and propose to consider cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) α-syn as a possible additional biomarker to the so-called “core” of AD (Aβ42, T-tau and p-tau181p).
Quantification of α-syn protein in the CSF of AD patients is not usual practice. However, it has been studied by different authors [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Most of the published results indicate that CSF α-syn, in combination with the “core” AD CSF biomarkers, have clinical value in the differential diagnosis of AD and LBD at the stage of dementia, but few authors have not found a role for CSF α-syn as a useful biomarker for AD [3].
In experimental studies, the “in vivo” interaction between β-amyloid, tau and α-syn pathways has been demonstrated, promoting both aggregation and accumulation among themselves and accelerating cognitive dysfunction [10,11,12]. Moreover, there are some studies in humans that demonstrate this interaction in AD patients [2,13].
The aim of this study was to examine the relationship between α-syn levels with “core” AD CSF biomarkers in patients at the stage of mild cognitive impairment (MCI), who, after a long clinical follow-up, developed AD, LBD or remained stable.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
This cross-sectional monocenter case–control study was conducted in the outpatient dementia consultation of Neurology Service at the University General Hospital of Alicante (Spain) between 2008 and 2017. MCI was assessed following the Petersen criteria [14].
Patients’ inclusion criteria were: age over fifty-five, with concordant clinical and neuropsychological diagnosis, particularly an MMSE test score ≥ 24 and an IQCODE over 78. Informed consent was obtained before inclusion in this study and before performing the lumbar puncture (LP). Exclusion criteria were as follows: the presence of dementia or other neurological, psychiatric or medical disease, which could provoke cognitive deterioration; anticoagulant therapy; failure to obtain informed consent; and a score greater than five using Yesavage scale of depression.
All included patients underwent physical and neurological examination, neuropsychological study, cerebral magnetic resonance, blood test, LP and cerebral DAT-SCAN when LBD was suspected. Enrolled patients were reviewed every 6–12 months regarding the development of clinical dementia criteria during almost 4 years of follow-up.
The clinical criteria followed for considering conversion of MCI to AD (MCI-AD) were the NIA-AA criteria [15], while the McKeith criteria were used for conversion to LBD (MCI-LBD) [16]. Stable MCI (MCIs) was considered when patients remained free of dementia for almost 4 years after LP or until death.
Following these criteria, 24 patients were included in the MCI-LBD group with abnormal DAT-SCAN and non-AD CSF criteria. To avoid differences in age with the other MCI groups, 32 patients were selected in the MCI-AD group, fulfilling both the clinical criteria and the new biological NIA-AA criteria [17]. Likewise, 25 patients were included in the MCIs group. Finally, we included a control group (n = 18) composed of subjects with acute or chronic headache (n = 12) or pain syndromes (n = 6) who did not develop cognitive decline during a follow-up period of 4 years.
2.2. Obtention of CSF
All the CSF samples were obtained between 10:00 and 14:00. LP was performed by a neurologist with a 20 × 3.5 gauge needle. CSF was collected in standard tubes and centrifuged 10 min at 1500× g and then aliquoted in propylene tubes. Samples were stored at −80 °C until analyzed. Only those samples with fewer than 50 red blood cells/µL were included.
2.3. Measurement of Core AD CSF Biomarkers
Aβ1–42, T-tau and p-tau181p were measured using a commercial ELISA kit (Innotest, Innogenetic/Fujirebio, Ghent, Belgium) following manufacturer´s instructions. Assays were tested blind with respect to clinical diagnosis.
2.4. Measurement of CSF α-Synuclein
Determination of α-synuclein levels in CSF was performed using the LEGEND MAX human α-synuclein ELISA kit with a precoated plate (BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA), according to manufacturer´s instructions. This assay has been previously validated in a European-wide inter-laboratory study [18]. Luminiscence detection was carried out with BMG Labtech LUMIstar Optima. Assays were tested blind with respect to clinical diagnosis.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used to analyze the distribution of each variable. A Student’s t-test for parametric variables and a Mann–Whitney U test for non-parametric variables were employed for comparisons between two groups. ANOVA was used for parametric variables and the Kruskal–Wallis test was used for non-parametric variables for comparisons between groups. Correlation between CSF protein levels was assessed by the Rho Spearman test. In all hypotheses, a p value of less than 0.05 determined statistical significance. The statistical package SPSS 21.0 was employed.
2.6. Ethical Criteria
The project was approved by the Ethical Committee of the University General Hospital of Alicante (ref. nº: PI2019/111).
3. Results
3.1. Clinical, Demographic Characteristics and Levels of CSF Biomarkers
The clinical and demographic features of each subject group were described in a previous publication [19]. In brief, no significant differences in age, gender, antecedents of hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, depression, Folstein MMSE score, onset of the symptoms, IQCODE score, years of schooling or NPI score were observed between the MCI groups. There was a small difference in age between the control group and the MCI groups and, in the clinical follow-up, that was larger in the stable MCI group than in the other groups. In the MCI-AD and MCI-LBD groups, Aβ42 levels were lower than in control and stable MCI patients, but Aβ42 did not discriminate between MCI-AD and MCI-LBD patients. T-tau and p-tau181p levels were higher in MCI-AD patients compared to the other groups, with no differences between control, stable MCI and MCI-LBD. Finally, α-syn levels were statistical different between the four groups (Table 1).

Table 1.
Clinical, demographic characteristics and levels of CSF biomarkers in the AD, LBD, stable MCI and control groups.
3.2. Total Population
Taking the population as a whole, α-syn CSF levels were positively correlated with both T-tau (ρ = 0.509, p-value < 0.01) and p-tau181p (ρ = 0.528, p-value < 0.01). As expected, there was a strong positive correlation between T-tau and p-tau181p protein levels (ρ = 0.882, p value < 0.01) and a slight negative correlation between Aβ1–42 protein and T-tau (ρ = −0.475, p-value < 0.01) and p-tau181p (ρ = −0.478, p-value < 0.01) (Figure 1).
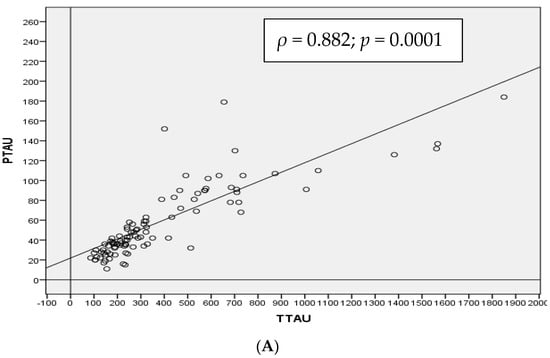
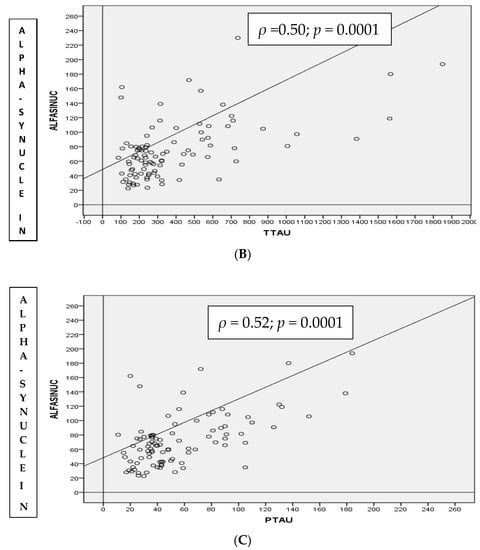
Figure 1.
Spearman correlation (ρ) in the whole cohort between CSF T-tau and p-tau181p (A), α-synuclein and T-tau (B) and α-synuclein and p-tau181p (C) proteins in total population.
3.3. MCI-AD Group
In this group, there were statistically significant correlations between α-syn levels with T-tau (ρ = 0.418, p-value < 0.01) (Figure 2B), particularly with p-tau181p (ρ = 0.571, p-value < 0.001) (Figure 2C).
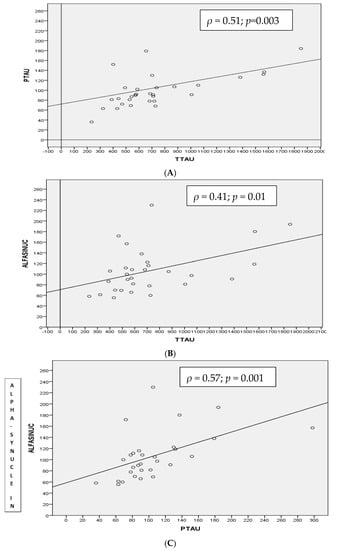
Figure 2.
Spearman correlation (ρ) between CSF T-tau and p-tau181p (A), α-synuclein and T-tau (B) and α-synuclein and p-tau181p (C) proteins in MCI-AD group.
T-tau and p-tau181p CSF levels were positively correlated (ρ = 0.511, p-value < 0.003) (Figure 2A) but no other correlations were found between the “core” biomarkers with either of the CSF α-syn levels.
3.4. Control Group
There was only a statistically significant correlation between T-tau and p-tau181p in the control group (ρ = 0.797, p-value < 0.0001). The low correlation between α-syn and T-tau (ρ = 0.288) or p-tau181p (ρ = 0.276) did not reach statistical significance in this group.
No other correlations were found between the “core” biomarkers with either of the α-syn CSF levels.
3.5. MCIs Group
In this group, there was a statistically positive correlation between T-tau and p-tau181p (ρ = 0.562, p-value < 0.003). No other significant correlations were found between the “core” biomarkers in either of the α-syn CSF levels.
3.6. MCI-LBD Group
There was a strong positive correlation between T-tau and p-tau181p (ρ = 0.822, p value < 0.0001) in this group. The correlations between α-syn and both T-tau (ρ = 0.21) and p-tau181p (ρ = 0.29) were low and without statistical significance. No other significant correlations were found between the “core” biomarkers with either of the α-syn CSF levels.
4. Discussion
The most significant finding of this work was the strong relationship we found between T-tau and p-tau181p with α-syn levels in the MCI-AD group. These results agree with previous publications in which a positive correlation between tau proteins and α-syn in AD patients was described [2,13]. However, these correlations disappeared in LBD patients and control subjects [2,13].
In animal models, α-syn has been related with the pathophysiology of AD due to its association with AD-triggering effectors Aβ1–42 and p-tau [10,11,12]. A synergic mechanism between them should lead to neurodegeneration [10,11,12].
Tau protein and α-syn share common properties and potentially even spreading mechanisms. Stabilization of microtubules, localization at the same cellular region, solubility and the shape of insoluble aggregates that provoke cellular dysfunction have been described; these similarities may explain their relationship in dysfunction and AD pathogenesis [20,21]. Otherwise, α-syn may initiate the fibrillization of tau and stimulate tangle production [22].
No relations were found between tau proteins and α-syn CSF levels in MCI-LBD patients in this study. However, some this relation has been previously described in a more advanced stage of the illness. Considering α-syn as a protein with a synaptic function, its higher levels could be related to more advanced neurodegeneration stages [4,23] in which different pathogenic pathways might be involved [2,4]. The synaptic loss may provoke an increase in tau protein and α-syn levels and subsequent clinical deterioration. However, the AD patients with a higher rate of progression showed an increase in p-tau and a decrease in α-syn CSF levels, suggesting a mixed pathophysiology [13]; these data may be important for prognostic purposes.
There is no agreement on whether the additional α-syn measurement to the “core” AD CSF biomarkers improves the differential diagnosis between AD and LBD [2,8,19]. In our previous publication [19], we found that diagnosis validity was high for both α-syn and p-tau181p, and their combination improved the discrimination of MCI-AD from the other three groups. For that reason, we and others [9] consider that combined measurements could provide a pathophysiological report that would be highly important for the new concept of “precision medicine” in degenerative dementia [24].
This is study has some limitations. First, this study is unicentric and we did not perform anatomopathological verification. Otherwise, DAT-SCAN was performed exclusively in MCI-LBD patients, but no clinical signs or symptoms of LBD were observed in the rest of the groups included during clinical follow-up.
5. Conclusions
The correlation found between α-synuclein and tau proteins in the first stages of AD corroborates the involvement of this protein in the pathogenesis of the illness. This result may have clinical and diagnostic implications, and it may be helpful in the application of “precision medicine” to patients with mild cognitive impairment.
Author Contributions
Collection of clinical data: V.M.-G., R.G.-B., R.R.-L., J.-A.M.-A. laboratory analysis: M.-S.G.-A., J.S.-V., F.N.-R., J.M.-R., M.A.C.-G. statistical analysis: J.S.-P. final manuscript: all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
For the acquisition of the reagents by Novartis Spain, Nutricia Spain, KRKA Spain and Neuraxpharm Spain. “This study was funded in part by the Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria y Biomédica de Alicante (ISABIAL; grant 190258)”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethical Comittée of the University General Hospital of Alicante (protocol code: PI2019/111 on the 26 February 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All the data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the outpatients Unit and the Biobanc in the General Hospital of Alicante. We also acknowledge support for the acquisition of the reagents by Novartis Spain, Nutricia Spain, KRKA Spain and Neuraxpharm Spain. We also thank Wiley for permission to include Table 1 in this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest for this publication.
Abbreviations
Aβ42: Aβ1–42; AD; Alzheimer’s disease; AT(N), β-amyloid deposition; pathologic tau and neurodegeneration; CSF; cerebrospinal fluid; IQCODE; informant questionnaire on cognitive decline in the elderly; LBD; Lewy body disease; LP; lumbar puncture; MCI; mild cognitive impairment; MMSE; mini-mental state examination; NIA-AA; National Institute on Aging and Alzheimer’s Association; NPI; neuropsychiatric inventory test.
References
- Korff, A.; Liu, C.; Ginghina, C.; Shi, M.; Zhang, J. α-Synuclein in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 36, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slaets, S.; Vanmechelen, E.; Le Bastard, N.; Decraemer, H.; Vandijck, M.; Martin, J.-J.; De Deyn, P.P.; Engelborghs, S. Increased CSF α-synuclein levels in Alzheimer’s disease: Correlation with tau levels. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2014, 10, S290–S298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berge, G.; Sando, S.B.; Albrektsen, G.; Lauridsen, C.; Møller, I.; Grøntvedt, G.R.; Bråthen, G.; White, L.R. Alpha-synuclein measured in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment, or healthy controls: A two year follow-up study. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llorens, F.; Schmitz, M.; Varges, D.; Kruse, N.; Gotzmann, N.; Gmitterová, K.; Mollenhauer, B.; Zerr, I. Cerebrospinal α-synuclein in α-synuclein aggregation disorders: Tau/α-synuclein ratio as potential biomarker for dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiasserini, D.; Biscetti, L.; Eusebi, P.; Salvadori, N.; Frattini, G.; Simoni, S.; De Roeck, N.; Tambasco, N.; Stoops, E.; Vanderstichele, H.; et al. Differential role of CSF fatty acid binding protein 3, α-synuclein, and Alzheimer’s disease core biomarkers in Lewy body disorders and Alzheimer’s dementia. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Tang, L.; Toledo, J.; Ginghina, C.; Wang, H.; Aro, P.; Jensen, P.H.; Weintraub, D.; Chen-Plotkin, A.S.; Irwin, D.J.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein contributes to the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Stewart, T.; Toledo, J.B.; Ginghina, C.; Tang, L.; Atik, A.; Aro, P.; Shaw, L.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Galasko, D.R.; et al. A Longitudinal Study of Total and Phosphorylated α-Synuclein with Other Biomarkers in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 61, 1541–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bousiges, O.; Philippi, N.; Lavaux, T.; Perret-Liaudet, A.; Lachmann, I.; Schaeffer-Agalède, C.; Anthony, P.; Botzung, A.; Rauch, L.; Jung, B.; et al. Differential diagnostic value of total alpha-synuclein assay in the cerebrospinal fluid between Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies from the prodromal stage. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.H.; Kang, M.J.; Suh, J.W.; Pyun, J.-M.; Ryoo, N.; Park, Y.H.; Youn, Y.C.; Jang, J.-W.; Jeong, J.H.; Park, K.W.; et al. CSF total tau/α-synuclein ratio improved the diagnostic performance for Alzheimer’s disease as an indicator of tau phosphorylation. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.E.; Sherman, M.A.; Greimel, S.; Kuskowski, M.; Schneider, J.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Lesné, S.E. Soluble -Synuclein Is a Novel Modulator of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathophysiology. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 10253–10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clinton, L.K.; Blurton-Jones, M.; Myczek, K.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; LaFerla, F.M. Synergistic Interactions between Aβ, Tau, and -Synuclein: Acceleration of Neuropathology and Cognitive Decline. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 7281–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vergallo, A.; Bun, R.-S.; Toschi, N.; Baldacci, F.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Cavedo, E.; Lamari, F.; Habert, M.-O.; Dubois, B.; et al. Association of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein with total and phospho-tau181protein concentrations and brain amyloid load in cognitively normal subjective memory complainers stratified by Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toledo, J.B.; Korff, A.; Shaw, L.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Zhang, J. CSF α-synuclein improves diagnostic and prognostic performance of CSF tau and Aβ in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Artero, S.; Petersen, R.; Touchon, J.; Ritchie, K. Revised criteria for mild cognitive impairment: Validation within a longitudinal population study. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2006, 22, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKeith, I.G.; Dickson, D.W.; Lowe, J.; Emre, M.; O’Brien, J.; Feldman, H.; Cummings, J.; Duda, J.E.; Lippa, C.; Perry, E.K.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Third report of the DLB consortium. Neurology 2005, 65, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, N.; Persson, S.; Alcolea, D.; Bahl, J.M.; Baldeiras, I.; Capello, E.; Chiasserini, D.; Chiavetto, L.B.; Emersic, A.; Engelborghs, S.; et al. Validation of a quantitative cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein assay in a European-wide interlaboratory study. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 2587–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ayllón, M.; Monge-Argilés, J.; Monge-García, V.; Navarrete, F.; Cortés-Gómez, M.; Sánchez-Payá, J.; Manzanares, J.; Gasparini-Berenguer, R.; Leiva-Santana, C.; Sáez-Valero, J. Measurement of CSF α-synuclein improves early differential diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2019, 150, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pace, M.C.; Xu, G.; Fromholt, S.; Howard, J.; Crosby, K.; Giasson, B.I.; Lewis, J.; Borchelt, D.R. Changes in proteome solubility indicate widespread proteostatic disruption in mouse models of neurodegenerative disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 919–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duka, T.; Sidhu, A. The neurotoxin, MPP+, induces hyperphosphorylation ofTau, in the presence of α-Synuclein, in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Neurotox. Res. 2006, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasson, B.I.; Forman, M.S.; Higuchi, M.; Golbe, L.I.; Graves, C.L.; Kotzbauer, P.T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Initiation and Synergistic Fibrillization of Tau and Alpha-Synuclein. Science 2003, 300, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Msc, I.V.S.; Majbour, N.; Msc, N.N.V.; Berendse, H.W.; Van Der Flier, W.M.; van de Berg, W.; Teunissen, C.E.; Lemstra, A.W.; El-Agnaf, O.M. α-Synuclein species as potential cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for dementia with lewy bodies. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1724–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yiannopoulou, K.G.; Papageorgiou, S.G. Current and Future Treatments in Alzheimer Disease: An Update. J. Central Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2020, 12, 117957352090739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).