IL-33 in Mental Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
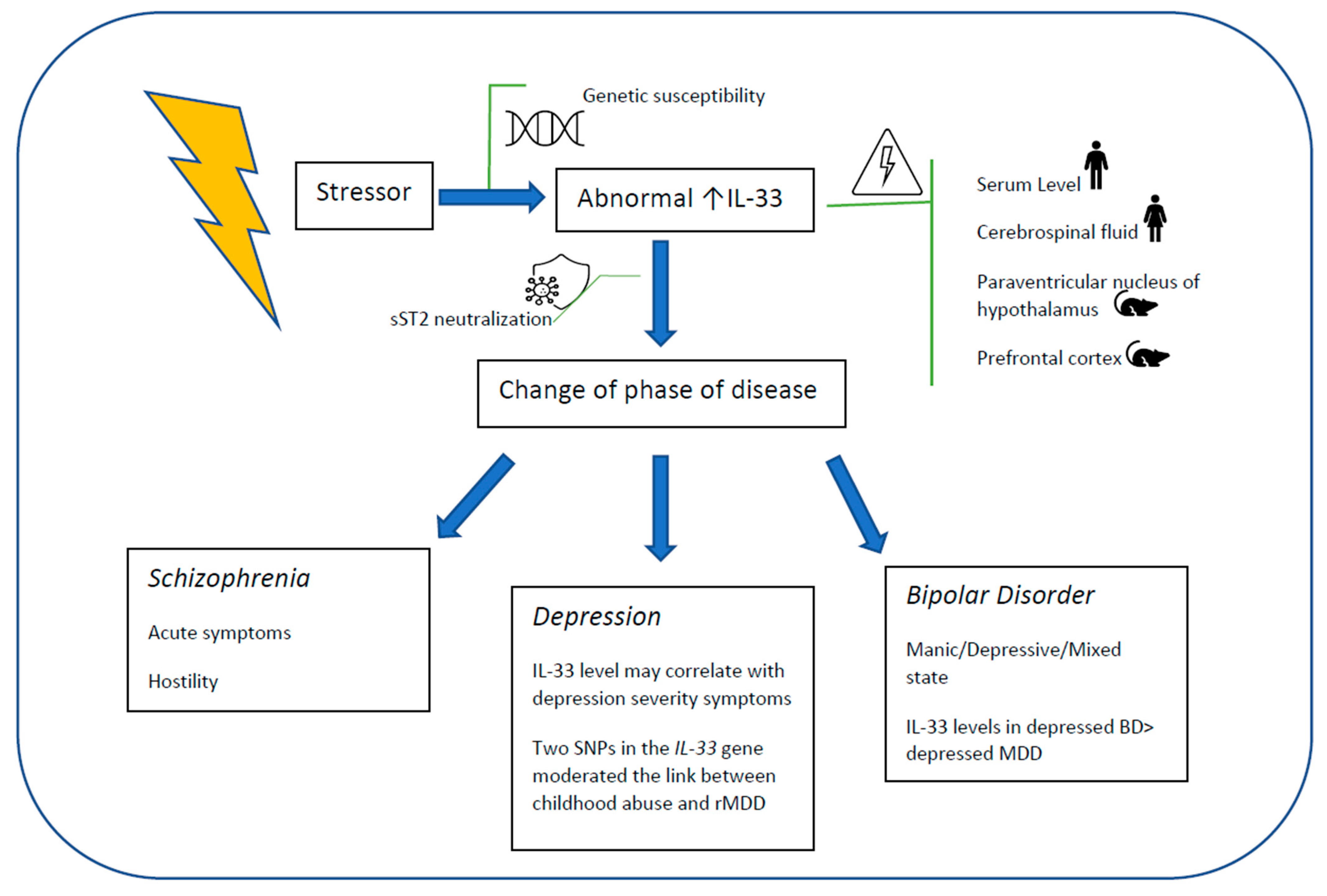
3. Results
3.1. Affective Disorders
3.1.1. Depression
3.1.2. Bipolar Disorder
3.1.3. Bipolar Disorders and Major Depressive Disorder
3.2. Schizophrenia
3.3. Autism Spectrum Disorders
4. Discussion
IL-33, Mental Health and Immune System
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carcrini, L. WHO (EURO) Mental Health Services in Pilot Study Areas: Report on a European Study. Copenhagen, WHO Regional Office for Europe, 1987,578 Pages, Price (Sw.Fr) 70.—. Int. J. Health Plan. Manag. 1989, 4, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 0-89042-555-8. [Google Scholar]
- Momen, N.C.; Plana-Ripoll, O.; Agerbo, E.; Benros, M.E.; Børglum, A.D.; Christensen, M.K.; Dalsgaard, S.; Degenhardt, L.; de Jonge, P.; Debost, J.-C.P.G.; et al. Association between Mental Disorders and Subsequent Medical Conditions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, G. The Need for a New Medical Model: A Challenge for Biomedicine. Science 1977, 196, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatasubramanian, G.; Keshavan, M.S. Biomarkers in Psychiatry—A Critique. Ann. Neurosci. 2016, 23, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ho, R.C.-M.; Mak, A. Interleukin (IL)-6, Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) and Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptors (SIL-2R) Are Elevated in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 139, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmady, S.V.; Venkatasubramanian, G.; Shivakumar, V.; Gautham, S.; Subramaniam, A.; Jose, D.A.; Maitra, A.; Ravi, V.; Gangadhar, B.N. Relationship between Interleukin-6 Gene Polymorphism and Hippocampal Volume in Antipsychotic-Naïve Schizophrenia: Evidence for Differential Susceptibility? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidese, S.; Hattori, K.; Sasayama, D.; Tsumagari, T.; Miyakawa, T.; Matsumura, R.; Yokota, Y.; Ishida, I.; Matsuo, J.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Neuroplasticity-Associated Protein Levels in Patients with Psychiatric Disorders: A Multiplex Immunoassay Study. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Minhajuddin, A.; Gadad, B.S.; Chin Fatt, C.; Trivedi, M.H. Higher S100B Levels Predict Persistently Elevated Anhedonia with Escitalopram Monotherapy Versus Antidepressant Combinations: Findings from CO-MED Trial. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli, F.; Misiak, B.; Crocamo, C.; Carrà, G. Glial and Neuronal Markers in Bipolar Disorder: A Meta-Analysis Testing S100B and NSE Peripheral Blood Levels. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 101, 109922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayana, P.; Colpo, G.D.; Simões, L.R.; Giridharan, V.V.; Teixeira, A.L.; Quevedo, J.; Barichello, T. A Systematic Review of Evidence for the Role of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Bipolar Patients. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 92, 160–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Dai, J.; Liu, C. Inflammation-Related Biomarkers in Major Psychiatric Disorders: A Cross-Disorder Assessment of Reproducibility and Specificity in 43 Meta-Analyses. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, I.E.; de Witte, L.; Begemann, M.; Kahn, R.S. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Schizophrenia: Ready for Practice or a Good Start? A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2011, 73, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, M.; Kishimoto, T.; Müller, N.; Weiser, M.; Davidson, M.; Kane, J.M.; Correll, C.U. Adjunctive Use of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs for Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analytic Investigation of Randomized Controlled Trials. Schizophr. Bull. 2013, 39, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.F.; Rocha, D.Q.C.; McIntyre, R.S.; Mesquita, L.M.; Köhler, C.A.; Hyphantis, T.N.; Sales, P.M.G.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Berk, M. Adipokines as Emerging Depression Biomarkers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 59, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-W.; Su, K.-P. Using Psychoneuroimmunity against COVID-19. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, L.; Shen, T.; Peng, D. HMGB1 Involved in Stress-Induced Depression and Its Neuroinflammatory Priming Role: A Systematic Review. Gen. Psychiatry 2019, 32, e100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, C.E.; Fisk, J.D.; Bernstein, C.N.; Berrigan, L.I.; Bolton, J.M.; Graff, L.A.; Hitchon, C.A.; Marriott, J.J.; Peschken, C.A.; Sareen, J.; et al. Comorbid Anxiety, Depression, and Cognition in MS and Other Immune-Mediated Disorders. Neurology 2019, 92, e406–e417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangemi, S.; Casciaro, M.; Trapani, G.; Quartuccio, S.; Navarra, M.; Pioggia, G.; Imbalzano, E. Association between HMGB1 and COPD: A Systematic Review. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 164913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbalzano, E.; Quartuccio, S.; Di Salvo, E.; Crea, T.; Casciaro, M.; Gangemi, S. Association between HMGB1 and Asthma: A Literature Review. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbalzano, E.; Mandraffino, G.; Casciaro, M.; Quartuccio, S.; Saitta, A.; Gangemi, S. Pathophysiological Mechanism and Therapeutic Role of S100 Proteins in Cardiac Failure: A Systematic Review. Heart Fail. Rev. 2016, 21, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Salvo, E.; Casciaro, M.; Quartuccio, S.; Genovese, L.; Gangemi, S. Do Alarmins Have a Potential Role in Autism Spectrum Disorders Pathogenesis and Progression? Biomolecules 2018, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannetti, A.; Straface, E.; Rosato, E.; Casciaro, M.; Pioggia, G.; Gangemi, S. Role of Alarmins in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavaresco, D.V.; da Rosa, M.I.; Uggioni, M.L.R.; Ferraz, S.D.; Pacheco, T.R.; Toé, H.C.Z.D.; da Silveira, A.P.; Quadros, L.F.A.; de Souza, T.D.; Varela, R.B.; et al. Increased Inflammatory Biomarkers and Changes in Biological Rhythms in Bipolar Disorder: A Case-Control Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 271, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunoni, A.R.; Supasitthumrong, T.; Teixeira, A.L.; Vieira, E.L.; Gattaz, W.F.; Benseñor, I.M.; Lotufo, P.A.; Lafer, B.; Berk, M.; Carvalho, A.F.; et al. Differences in the Immune-Inflammatory Profiles of Unipolar and Bipolar Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 262, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, K.A.; McDonald, E.; Moffat, F.; Tutino, M.; Castelino, M.; Barton, A.; Cavanagh, J.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Siebert, S.; McInnes, I.B.; et al. Alopecia Areata Is Characterized by Dysregulation in Systemic Type 17 and Type 2 Cytokines, Which May Contribute to Disease-associated Psychological Morbidity. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.S.; Sakowicz, A.; Roy, A.; Yang, A.; Sullivan, J.T.; Grobman, W.A.; Wisner, K.L. Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Inflammatory Cytokines in Perinatal Depression. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 220, 271.e1–271.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogłodek, E.A.; Just, M.J. The Association between Inflammatory Markers (INOS, HO-1, IL-33, MIP-1β) and Depression with and without Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 70, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovcanin, M.M.; Janicijevic, S.M.; Jovanovic, I.P.; Gajovic, N.; Arsenijevic, N.N.; Lukic, M.L. IL-33/ST2 Pathway and Galectin-3 as a New Analytes in Pathogenesis and Cardiometabolic Risk Evaluation in Psychosis. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunoni, A.R.; Padberg, F.; Vieira, E.L.M.; Teixeira, A.L.; Carvalho, A.F.; Lotufo, P.A.; Gattaz, W.F.; Benseñor, I.M. Plasma Biomarkers in a Placebo-Controlled Trial Comparing TDCS and Escitalopram Efficacy in Major Depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 86, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudinova, A.Y.; Deak, T.; Hueston, C.M.; McGeary, J.E.; Knopik, V.S.; Palmer, R.H.C.; Gibb, B.E. Cross-Species Evidence for the Role of Interleukin-33 in Depression Risk. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2016, 125, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saresella, M.; Piancone, F.; Marventano, I.; Zoppis, M.; Hernis, A.; Zanette, M.; Trabattoni, D.; Chiappedi, M.; Ghezzo, A.; Canevini, M.P.; et al. Multiple Inflammasome Complexes Are Activated in Autistic Spectrum Disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 57, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, I.G.; Rodrigues, D.H.; Rocha, N.P.; da Cunha Sousa, L.F.; Vieira, E.L.M.; Simões-e-Silva, A.C.; Kummer, A.; Teixeira, A.L. Plasma Levels of Alarmin IL-33 Are Unchanged in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Preliminary Study. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 278, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, I.G.; Morato, I.B.; de Miranda, A.S.; Bauer, M.E.; Soares, J.C.; Teixeira, A.L. A Preliminary Report of Increased Plasma Levels of IL-33 in Bipolar Disorder: Further Evidence of pro-Inflammatory Status. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 157, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos-Carli, S.M.; Miranda, A.S.; Dias, I.C.S.; de Oliveira, A.; Cruz, B.F.; Vieira, É.L.M.; Rocha, N.P.; Barbosa, I.G.; Salgado, J.V.; Teixeira, A.L. Serum Levels of Interleukin-33 and Its Soluble Form Receptor (SST2) Are Associated with Cognitive Performance in Patients with Schizophrenia. Compr. Psychiatry 2017, 74, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbanna, M.; Shivakumar, V.; Venugopal, D.; Narayanaswamy, J.C.; Berk, M.; Varambally, S.; Venkatasubramanian, G.; Debnath, M. Impact of Antipsychotic Medication on IL-6/ STAT3 Signaling Axis in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Drug-naive Schizophrenia Patients. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 74, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavò, S.; Riso, G.; Casciaro, M.; Di Salvo, E.; Gangemi, S. Oxidative Stress Involvement in Psoriasis: A Systematic Review. Free Radic. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, D.; Miller, V.M.; Lawrence, D.A. Aberrant Immune Responses in a Mouse with Behavioral Disorders. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M.; Saitta, S.; Sirufo, M.M.; Mannucci, C.; Casciaro, M.; Ciccarelli, F.; Gangemi, S. Interleukin-33 Serum Levels in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timur, S.; Sahin, N.H. The Prevalence of Depression Symptoms and Influencing Factors among Perimenopausal and Postmenopausal Women. Menopause 2010, 17, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohi, E.; Choi, E.Y.; Rose, I.V.L.; Murata, A.S.; Chow, S.; Niwa, M.; Kano, S. Behavioral Changes in Mice Lacking Interleukin-33. eNeuro 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, M.; Takase, K.; Hayakawa, M.; Hayakawa, H.; Tominaga, S.; Ohmori, T. Altered Behavior in Mice Overexpressing Soluble ST2. Mol. Brain 2020, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Reference | Objective | Mental Disorder | Subjects | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [24] | Biological rhythms in bipolar disorder (BD) and inflammatory biomarkers | BD | 36 BD and 46 healthy controls | No statistically significant differences in IL-33 (interleukin 33) levels between the BD group and the control group (p value = 0.959) |
| [25] | Differences in immune profiles between BD and major depressive disorder (MDD) patients | MDD, BD | 245 MDD and 59 BD patients in an acute depressive episode of moderate severity | IL-33 was significantly higher in BD than MDD (p < 0.001) |
| [11] | Biomarkers and antipsychotic medications | Schizophrenia (SCZ) | 27 drug-naive schizophrenia patients | no statistically significant difference in IL-33 plasma levels before and after treatment. |
| [26] | To investigate the association between cytokines and depression in patients affected by alopecia areata (AA) | Anxiety and Depression symptoms | 39 patients with AA, 23 Psoriatic arthritis, 26 healthy controls | IL-33 and IL-31 were significantly higher in patients with AA than HCs, no significative correlations with psychiatric symptoms. |
| [27] | Perinatal depression and cytokine levels in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid | Perinatal Depression | 76 patients with depressive symptoms without AD medications | In term pregnant woman IL-33 was significantly associated with an MD episode. |
| [28] | Biomarkers in depressed patient with and without post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) | Depression comorbid with PTSD | Each study group comprised 60 patients: mild depression (MiD), moderate depression (MoD), severe depression (SeD), MiD and PTSD (MiD + PTSD), MoD and PTSD (MoD + PTSD), SeD and PTSD (SeD + PTSD), PTSD, and 40 HC | Depression alone or comorbid with PTSD was associated with high levels of IL-33, with higher levels when in presence of comorbid PTSD. IL-33 levels were reported to increase as depression became more severe both in males and females. Although not significant, there was a trend in females towards higher concentration levels of this parameter than males. |
| [29] | IL-33 and soluble ST2 (sST2) in different stages of schizophrenia | SCZ | 77 drug naïve patients with first episode psychosis (FEP) 45 schizophrenia in relapse (SC in relapse) 27 schizophrenia in remission (SC in remission) 18 healthy controls (HC) |
|
| [30] | To investigate plasma biomarkers in a placebo-controlled trial comparing tDCS and escitalopram efficacy in major depression | MMD | 236 patients | No association between IL-33 levels and depression improvement, also controlling for age. |
| [31] | Data from three complimentary studies that support the role of, interleukin-33 in depression risk | MMD (single episode vs. recurrent) | Study 1: recurrent MDD = 76 single episode of MDD = 40 no MDD n = 125; Study 2: recurrent MDD = 10 single episode of MDD = 10 no MDD = 20 | two-SNP haplotypes in the IL-33 gene (rs11792633 and rs7044343) moderated the link between women’s history of childhood abuse and history of recurrent MDD. Patients with recurrent MDD had higher peripheral levels of IL-33 and IL-1β compared to women with a single MDD episode or no history of MDD. Acute stressor increased IL-33 expression in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. |
| [32] | To investigate the inflammasomes activity in autism spectrum disorders (ASD) | ASD | 25 ASD 23 unaffected siblings of the ASD patients 30 HC | Increased production of IL-1β and IL-18 that was associated with a consistent reduction of IL-33 in ASD |
| [33] | To evaluate plasma levels of IL-33 in ASD | ASD | 30 patients with ASD 18 HC | Patients did not differ from controls in IL-33 levels |
| [34] | Plasma levels of IL-33 and ST2 in bipolar disorder | Bipolar disorder | 46 BD patients | Increased plasma levels of IL-33 in bipolar disorder |
| [35] | Involvement of IL-33 in schizophrenia and its association with cognitive performance | Schizophrenia | 40 patients 40 controls | Patients with schizophrenia and controls presented similar serum levels of IL-33 and sST2. Levels of both markers were positively correlated with better cognitive performance in patients with schizophrenia. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pandolfo, G.; Genovese, G.; Casciaro, M.; Muscatello, M.R.A.; Bruno, A.; Pioggia, G.; Gangemi, S. IL-33 in Mental Disorders. Medicina 2021, 57, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57040315
Pandolfo G, Genovese G, Casciaro M, Muscatello MRA, Bruno A, Pioggia G, Gangemi S. IL-33 in Mental Disorders. Medicina. 2021; 57(4):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57040315
Chicago/Turabian StylePandolfo, Gianluca, Giovanni Genovese, Marco Casciaro, Maria Rosaria Anna Muscatello, Antonio Bruno, Giovanni Pioggia, and Sebastiano Gangemi. 2021. "IL-33 in Mental Disorders" Medicina 57, no. 4: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57040315
APA StylePandolfo, G., Genovese, G., Casciaro, M., Muscatello, M. R. A., Bruno, A., Pioggia, G., & Gangemi, S. (2021). IL-33 in Mental Disorders. Medicina, 57(4), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57040315









