Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: New Developments from Molecular Diagnosis to Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Presentation and Prognostic Factors
3. Diagnosis and Classification
4. New Molecular Insight
5. Differential Diagnosis
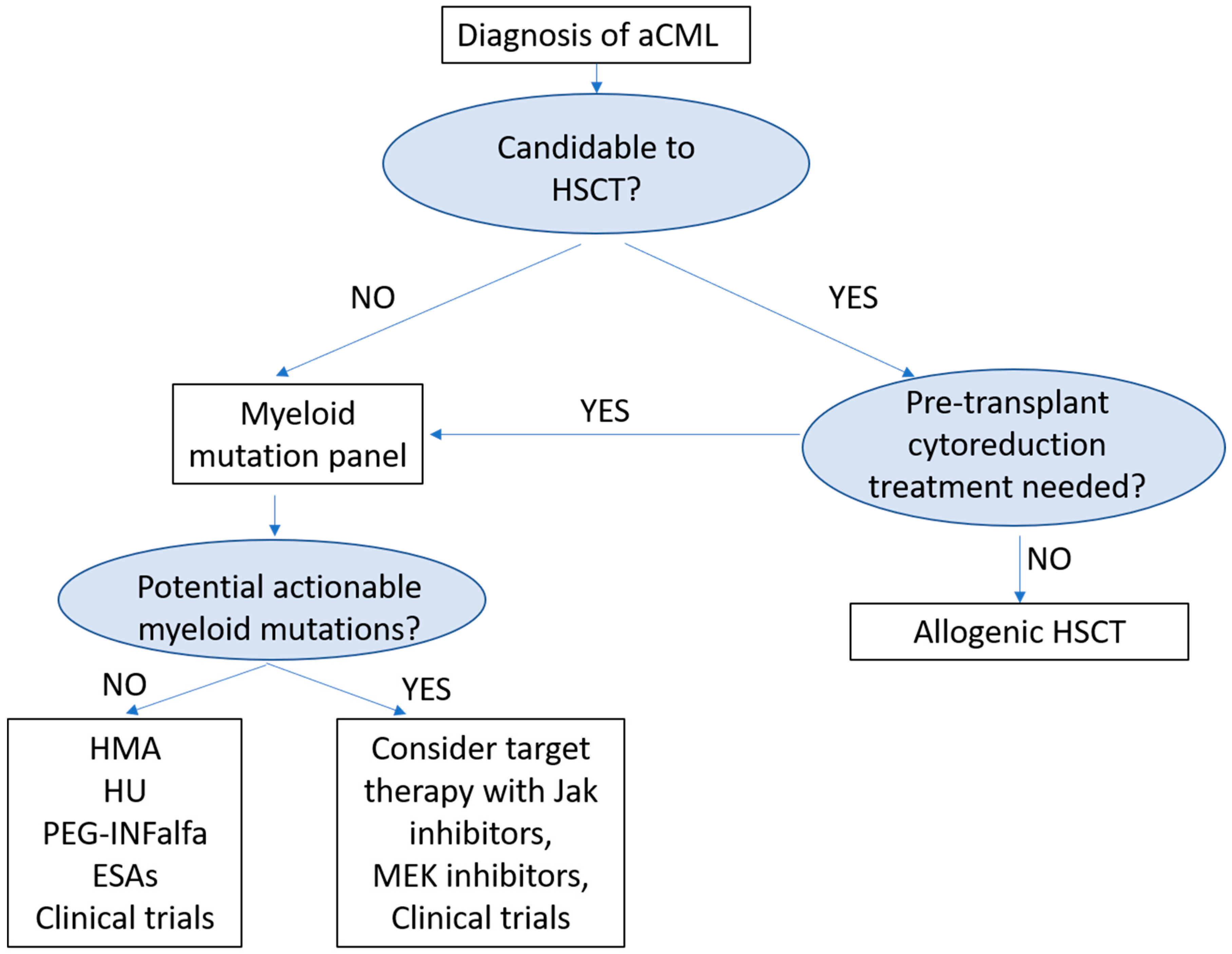
6. Treatment
6.1. Allogenic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (Allo-HSCT)
6.2. Cytoreductive Drugs and Erythropoiesis Stimulation
6.3. New Target Therapies
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swerdlow, S.H.C.E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Patnaik, M.M.; Barraco, D.; Lasho, T.L.; Finke, C.M.; Reichard, K.; Hoversten, K.P.; Ketterling, R.P.; Gangat, N.; Tefferi, A. Targeted next generation sequencing and identification of risk factors in World Health Organization defined atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisà, E.; Nicolosi, M.; Ferri, V.; Favini, C.; Gaidano, G.; Patriarca, A. Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Where Are We Now? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardiman, J.W.; Thiele, J.; Arber, D.A.; Brunning, R.D.; Borowitz, M.J.; Porwit, A.; Harris, N.L.; Le Beau, M.M.; Hellström-Lindberg, E.; Tefferi, A.; et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: Rationale and important changes. Blood 2009, 114, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breccia, M.; Biondo, F.; Latagliata, R.; Carmosino, I.; Mandelli, F.; Alimena, G. Identification of risk factors in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2006, 91, 1566–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Fox, P.S.; Rogers, H.J.; Geyer, J.T.; Chabot-Richards, D.; Weinzierl, E.; Hatem, J.; Jaso, J.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; et al. Atypical chronic myeloid leukemia is clinically distinct from unclassifiable myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2014, 123, 2645–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Pathak, R.; Martin, M.G.; Bhatt, V.R. Characteristics and survival of BCR/ABL negative chronic myeloid leukemia: A retrospective analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2015, 6, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhakal, P.; Gundabolu, K.; Amador, C.; Rayamajhi, S.; Bhatt, V.R. Atypical chronic myeloid leukemia: A rare entity with management challenges. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozd-Sokołowska, J.; Mądry, K.; Waszczuk-Gajda, A.; Biecek, P.; Szwedyk, P.; Budziszewska, K.; Raźny, M.; Dutka, M.; Obara, A.; Wasilewska, E.; et al. Atypical chronic myeloid leukaemia: A case of an orphan disease-A multicenter report by the Polish Adult Leukemia Group. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannella, L.; Breccia, M.; Latagliata, R.; Frustaci, A.; Alimena, G. Clinical and prognostic features of patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative syndrome categorized as unclassified (MDS/MPD-U) by WHO classification. Leuk Res. 2008, 32, 514–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzrock, R.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Kantarjian, H.; Freireich, E.; Tucker, S.L.; Siciliano, M.; Pilat, S.; Talpaz, M. BCR Rearrangement–Negative Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Revisited. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 2915–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoi, K.; Cross, N.C. Molecular pathogenesis of atypical CML, CMML and MDS/MPN-unclassifiable. Int. J. Hematol. 2015, 101, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández, J.M.; del Cañizo, M.C.; Cuneo, A.; García, J.L.; Gutiérrez, N.C.; González, M.; Castoldi, G.; San Miguel, J.F. Clinical, hematological and cytogenetic characteristics of atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Ann. Oncol. 2000, 11, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiat, P.; Michaux, J.L.; Rodhain, J. Philadelphianegative (Ph-) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): Comparison with Ph1 CML and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. The Groupe Francais de Cytogenetique Hematologique. Blood 1991, 78, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minakuchi, M.; Kakazu, N.; Gorrin-Rivas, M.J.; Abe, T.; Copeland, T.D.; Ueda, K.; Adachi, Y. Identification and characterization of SEB, a novel protein that binds to the acute undifferentiated leukemia-associated protein SET. Eur J Biochem. 2001, 268, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lasho, T. Atypical CML- the role of morphology and precision genomics. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2020, 33, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggendorfer, M.; Bacher, U.; Alpermann, T.; Haferlach, C.; Kern, W.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Haferlach, T.; Schnittger, S. SETBP1 mutations occur in 9% of MDS/MPN and in 4% of MPN cases and are strongly associated with atypical CML, monosomy 7, isochromosome i(17)(q10), ASXL1 and CBL mutations. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1852–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggendorfer, M.; Haferlach, T.; Alpermann, T.; Jeromin, S.; Haferlach, C.; Kern, W.; Schnittger, S. Specific molecular mutation patterns delineate chronic neutrophilic leukemia, atypical chronic myeloid leukemia, and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2014, 99, e244–e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gotlib, J. How I treat atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2017, 129, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maxson, J.E.; Luty, S.B.; MacManiman, J.D.; Paik, J.; Gotlib, J.; Greenberg, P.L.; Bahamadi, S.; Savage, S.L.; Abel, M.L.; Eide, C.A.; et al. The colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor T640N mutation Is oncogenic, sensitive to JAK inhibition, and mimics T618I. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartels, S.; Lehmann, U.; Büsche, G.; Schlue, J.; Hussein, K.; Debatin, D.; Karcher, A.; Andrulis, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Kreipe, H. De novo CSF3R mutation associated with transformation of myeloproliferative neoplasm to atypical CML. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 1255–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passerini, C.G.; Donadoni, C.; Parmiani, A.; Pirola, A.; Redaelli, S.; Signore, G.; Piazza, V.; Malcovati, L.; Fontana, D.; Spinelli, R.; et al. Recurrent ETNK1 mutations in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2015, 125, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittal, P.; Saliba, R.M.; Giralt, S.A.; Shahjahan, M.; Cohen, A.I.; Karandish, S.; Onida, F.; Beran, M.; Champlin, R.E.; De Lima, M. Allogeneic transplantation: A therapeutic option for myelofibrosis, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and Philadelphia-negative/BCR-ABL-negative chronic myelogenous leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004, 33, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-N.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, S.D.; Kang, Y.-A.; Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-H. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood Res. 2013, 48, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onida, F.; de Wreede, L.C.; van Biezen, A.; Eikema, D.J.; Byrne, J.L.; Iori, A.P.; Schots, R.; Jungova, A.; Schetelig, J.; Finke, J.; et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with atypical chronic myeloid leukaemia: A retrospective study from the chronic malignancies working party of the European Society for blood and marrow transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 177, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koldehoff, M.; Beelen, D.W.; Trenschel, R.; Steckel, N.K.; Peceny, R.; Ditschkowski, M.; Ottinger, H.; Elmaagacli, A.H. Outcome of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004, 34, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Koldehoff, M.; Steckel, N.K.; Hegerfeldt, Y.; Ditschkowski, M.; Beelen, D.W.; Elmaagacli, A.H. Clinical course and molecular features in 21 patients with atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2012, 34, e3–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talati, C.; Padron, E. An Exercise in Extrapolation: Clinical Management of Atypical CML, MDS/MPN-Unclassifiable, and MDS/MPN-RS-T. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2016, 11, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzrock, R.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Shtalrid, M.; Gutterman, J.U.; Talpaz, M. Philadelphia chromosome-negative chronic myelogenous leukemia without breakpoint cluster region rearrangement: A chronic myeloid leukemia with a distinct clinical course. Blood 1990, 75, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costello, R.; Lafage, M.; Toiron, Y.; Brunel, V.; Sainty, D.; Arnoulet, C.; Mozziconacci, M.-J.; Bouabdallah, R.; Gastaut, J.-A.; Maraninchi, D.; et al. Philadelphia chromosome-negative chronic myeloid leukaemia: A report of 14 new cases. Br. J. Haematol. 1995, 90, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefusco, E.; Alimena, G.; Coco, F.L.; De Cuia, M.R.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Spiriti, M.A.A.; Mancini, F.; Cedrone, M.; Mandelli, F. Ph-negative and bcr-negative atypical chronic myelogenous leukemia: Biological features and clinical outcome. Ann. Hematol. 1992, 65, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H.; Cortes, J.; Thomas, D.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Ferrajoli, A.; Faderl, S.; Richie, M.A.; Beran, M.; Giles, F.; et al. PEG-IFN-α-2b therapy in BCR-ABL–negative myeloproliferative disorders. Cancer 2007, 110, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, K.-H.T.; Tyner, J.W. What’s different about atypical CML and chronic neutrophilic leukemia? Hematology 2015, 2015, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; O’Brien, S.; Cortes, J.; Giles, F.J.; Faderl, S.; Issa, J.-P.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Rios, M.B.; Shan, J.; Andreeff, M.; et al. Results of decitabine (5-aza-20deoxycytidine) therapy in 130 patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer 2003, 98, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, D.; Liu, J.; Su, C. Efficacy and side-effects of decitabine in treatment of atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1911–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wu, Z.; Ren, L.; Tao, D.; Tong, H. Decitabine for the treatment of atypical chronic myeloid leukemia: A report of two cases. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hausmann, H.; Bhatt, V.R.; Yuan, J.; Maness, L.J.; Ganti, A.K. Activity of single-agent decitabine in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 22, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; You, L.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Ye, X.; Tong, H.Y. The First Case of Decitabine Successfully in Treatment of Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia with CEBPA Double Mutation. Chemother. Open Access 2013, 2, 114. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, C.; Kiladjian, J.-J.; Al-Ali, H.K.; Gisslinger, H.; Waltzman, R.; Stalbovskaya, V.; McQuitty, M.; Hunter, D.S.; Levy, R.; Knoops, L.; et al. JAK inhibition with Ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for myelofibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verstovsek, S.; Mesa, R.A.; Gotlib, J.; Levy, R.S.; Gupta, V.; DiPersio, J.F.; Catalano, J.V.; Deininger, M.; Miller, C.; Silver, R.T.; et al. A doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vannucchi, A.M.; Kiladjian, J.-J.; Griesshammer, M.; Masszi, T.; Durrant, S.; Passamonti, F.; Harrison, C.N.; Pane, F.; Zachee, P.; Mesa, R.; et al. Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia Vera. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleischman, A.G.; Maxson, J.E.; Luty, S.B.; Agarwal, A.; Royer, L.R.; Abel, M.L.; MacManiman, J.D.; Loriaux, M.M.; Druker, B.J.; Tyner, J.W. The CSF3R T618I mutation causes a lethal neutrophilic neoplasia in mice that is responsive to therapeutic JAK inhibition. Blood 2013, 122, 3628–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dao, K.H.; Solti, M.B.; Maxson, J.E.; Winton, E.F.; Press, R.D.; Druker, B.J.; Tyner, J.W. Significant clinical response to JAK1/2 inhibition in a patient with CSF3R-T618I-positive atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res. Rep. 2015, 3, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freedman, J.L.; Desai, A.V.; Bailey, L.C.; Aplenc, R.; Burnworth, B.; Zehentner, B.; Teachey, D.; Wertheim, G. Atypical chronic myeloid leukemia in two pediatric patients. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, R.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Cortes, J.E.; Pemmaraju, N.; Wang, X.; Nogueras-Gonzalez, G.; Jabbour, E.; Bose, P.; Kadia, T.; et al. A phase II trial of ruxolitinib in combination with azacytidine in myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maxson, J.E.; Gotlib, J.; Pollyea, D.A.; Fleischman, A.G.; Agarwal, A.; Eide, C.A.; Bottomly, D.; Wilmot, B.; McWeeney, S.K.; Tognon, C.E.; et al. Oncogenic CSF3R mutations in chronic neutrophilic leukemia and atypical CML. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, J.; Greshock, J.; Holbrook, J.D.; Gilmartin, A.; Zhang, X.; McNeil, E.; Conway, T.; Moy, C.; Laquerre, S.; Bachman, K.; et al. Comprehensive predictive biomarker analysis for MEK inhibitor GSK1120212. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgess, M.R.; Hwang, E.; Firestone, A.; Huang, T.; Xu, J.; Zuber, J.; Bohin, N.; Wen, T.; Kogan, S.C.; Haigis, K.M.; et al. Preclinical efficacy of MEK inhibition in Nras-mutant AML. Blood 2014, 124, 3947–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthakur, G.; Popplewell, L.; Boyiadzis, M.; Foran, J.; Platzbecker, U.; Vey, N.; Walter, R.B.; Olin, R.; Raza, A.; Giagounidis, A.; et al. Activity of the oral MEK inhibitor trametinib in RAS-mutant relapsed or refractory myeloid malignancies. Cancer 2016, 122, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanna, V.; Pierce, S.T.; Dao, K.-H.T.; Tognon, C.E.; Hunt, D.E.; Junio, B.; Tyner, J.W.; Druker, B.J. Durable disease control with MEK inhibition in a patient with NRAS-mutated atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Curēus 2015, 7, e414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramaswamy, K.; Spitzer, B.; Kentsis, A. Therapeutic re-activation of protein phosphatase 2A in acute myeloid leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coccaro, N.; Tota, G.; Zagaria, A.; Anelli, L.; Specchia, G.; Albano, F. SETBP1 dysregulation in congenital disorders and myeloid neoplasms. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 51920–51935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| aCML | CNL | CMML | MDS/MPN-RS-T | MDS/MPN-U |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB leukocytosis (WBC ≥ 13 × 10 × 9/L), (neutrophilia and increased myeloid precursors) | PB leukocytosis (WBC ≥ 25 × 10 × 9/L) | Persistent PB monocytosis ≥1 × 109/L | Persistent Thrombocytosis (plts ≥ 450 × 109/L) | Mixed MDS and MPN features at onset, not meeting diagnostic criteria for any other MDS/MPN, MDS, or MPN neoplasm |
| Myeloid precursors ≥ 10% of WBC | Myeloid precursors < 10%; segmented and banded neutrophil ≥ 80% of WBC | Plts ≥ 450 × 109/L | Plts ≥ 450 × 109/L with BM megakaryocytic proliferation and/or WBC ≥ 13 × 10 × 9/L | |
| No or minimal absolute monocytosis; monocytes < 10% of WBC | Monocyte count < 1 × 109/L | Monocytes ≥ 1 × 109/L and ≥10% of the WBC | ||
| <20% blasts in PB and BM | Blasts rarely in PB and <5% blasts in BM | <20% blasts in PB and BM | <1% blasts in PB and <5% blasts in BM | <20% blasts in PB and BM |
| No or minimal absolute basophilia; basophils < 2% of WBC | ||||
| Dysgranulopoiesis, which may include abnormal chromatin clumping | No dysgranulopoiesis | |||
| Hypercellular BM with granulocytic proliferation and granulocytic dysplasia, with or without dysplasia in the erythroid and megakaryocytic lineages | Hypercellular BM with increased % of neutrophil, but neutrophil maturation appears normal | Dysplasia in 1 or more myeloid lineages * | Erythroid-lineage dysplasia, with or without multilineage dysplasia, ≥15% ring sideroblasts | Clinical and morphological features of one of MDS |
| No BCR-ABL1 fusion. No evidence of PDGFRA, PDGFRB, or FGFR1 rearrangement, or PCM1-JAK2 fusion | ||||
| Not meeting WHO criteria for BCR-ABL1+ CML, PMF, PV or ET | ||||
| Presence of CSF3R T618I or other activating CSF3R mutation ** | Presence of SF3B1 mutation *** No t(3,3)(q21.3; q26.2), inv(3)(q21.3; q26.2), or del(5q) | No history of recent cytotoxic or growth factor therapy that could explain the MDS/MPN features | ||
| ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier | Title | Phase | Drugs Investigated | Mechanism of Action | Setting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03862157 | A Phase I/II Study of Azacitidine, Venetoclax and Pevonedistat in Adults With Newly Diagnosed Secondary or Therapy-Related AML | I/II | Azacitidine Venetoclax Pevonedistat | HMA BCL2 inhibition NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) inhibition | Untreated AML, aCML, MDS, and MDS/MPN overlap syndromes |
| NCT03878524 | Serial Measurements of Molecular and Architectural Responses to Therapy (SMMART) Trial: PRIME | Ib | Different combinations of novel drugs | Relapsed refractory hematological malignancies and solid cancers | |
| NCT04637009 | A Phase 1 Study of Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Preliminary Activity of TAS1553 in Subjects With Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), and Other Myeloid Neoplasms | I/II | TAS1553 | Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) inhibition | Untreated AML, secondary AML, accelerated phase MPN, chronic/accelerated phase MPN-unclassifiable and MDS-MPN, and aCML |
| NCT01787487 | Evaluation of Ruxolitinib and Azacytidine Combination as a Therapy for Patients With Myelofibrosis and Myelodysplastic Syndrome/Myeloproliferative Neoplasm | II | Azacitidine Ruxolitinib | HMA Jak2 inhibition | myelofibrosis or myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasm |
| NCT02158858 | A Phase 1/2 Study of CPI-0610, a Small Molecule Inhibitor of BET Proteins: Phase 1 (in Patients With Hematological Malignancies) and Phase 2 (Dose Expansion of CPI-0610 With and Without Ruxolitinib in Patients With Myelofibrosis) | I/II | CPI-0610 | BET protein inhibition | previously treated Acute Leukemia, Myelodysplastic Syndrome, and Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms and Myelofibrosis |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castellino, A.; Santambrogio, E.; Rapezzi, D.; Massaia, M. Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: New Developments from Molecular Diagnosis to Treatment. Medicina 2021, 57, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101104
Castellino A, Santambrogio E, Rapezzi D, Massaia M. Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: New Developments from Molecular Diagnosis to Treatment. Medicina. 2021; 57(10):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101104
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastellino, Alessia, Elisa Santambrogio, Davide Rapezzi, and Massimo Massaia. 2021. "Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: New Developments from Molecular Diagnosis to Treatment" Medicina 57, no. 10: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101104
APA StyleCastellino, A., Santambrogio, E., Rapezzi, D., & Massaia, M. (2021). Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: New Developments from Molecular Diagnosis to Treatment. Medicina, 57(10), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101104






