FGF-23 and Phosphate in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in Kazakhstan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Ethics Approval
2.3. Procedures and Laboratory Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
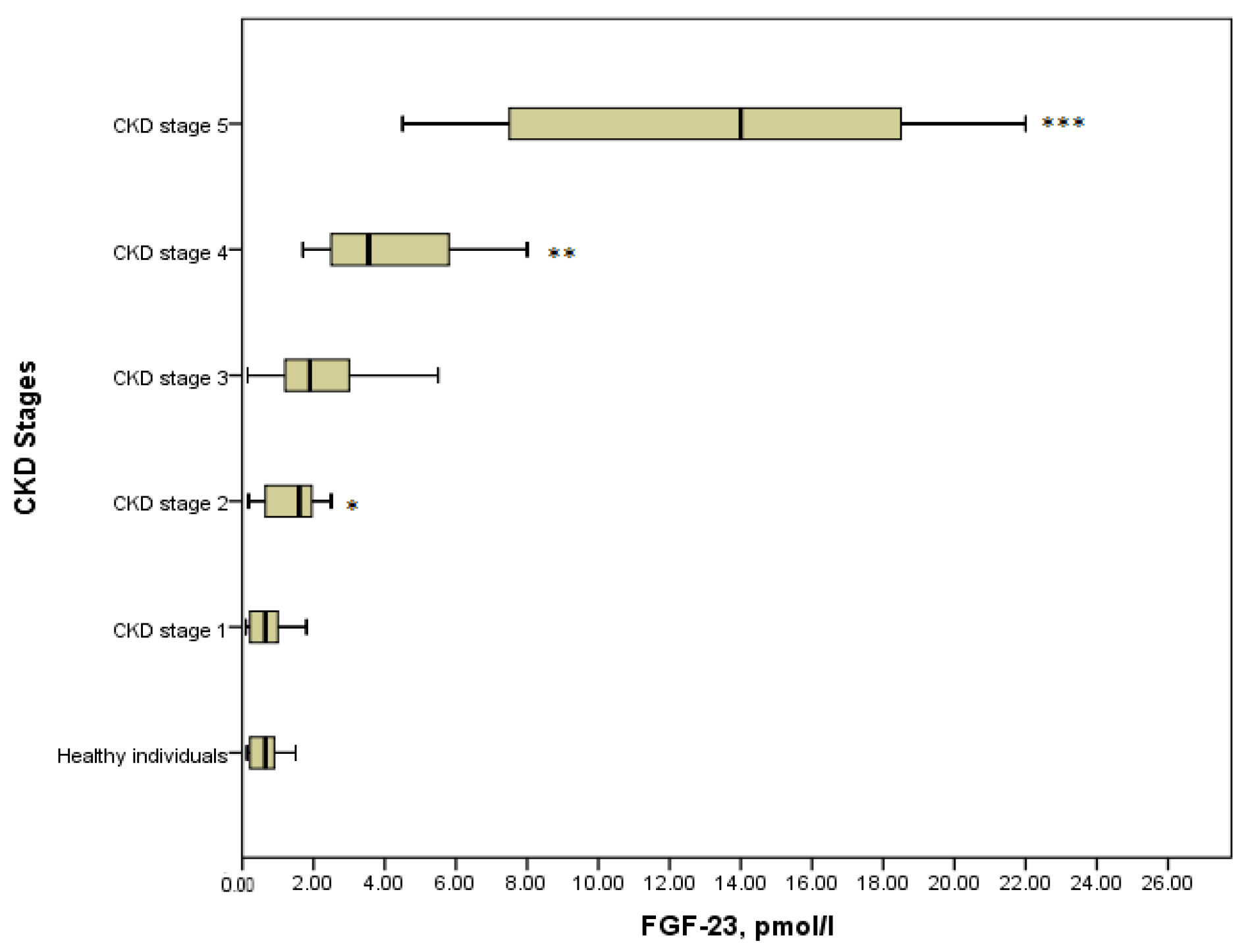
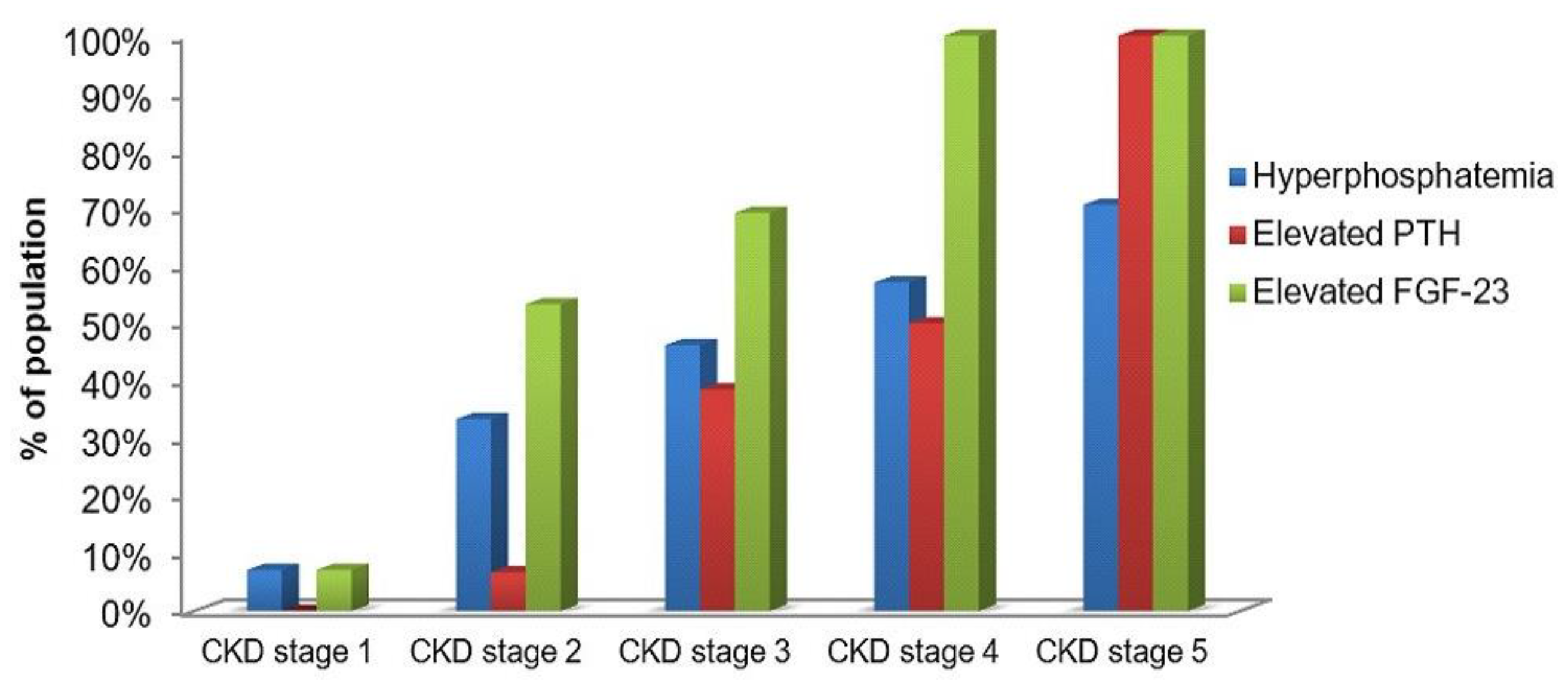
3.2. FGF-23 in Children with CKD
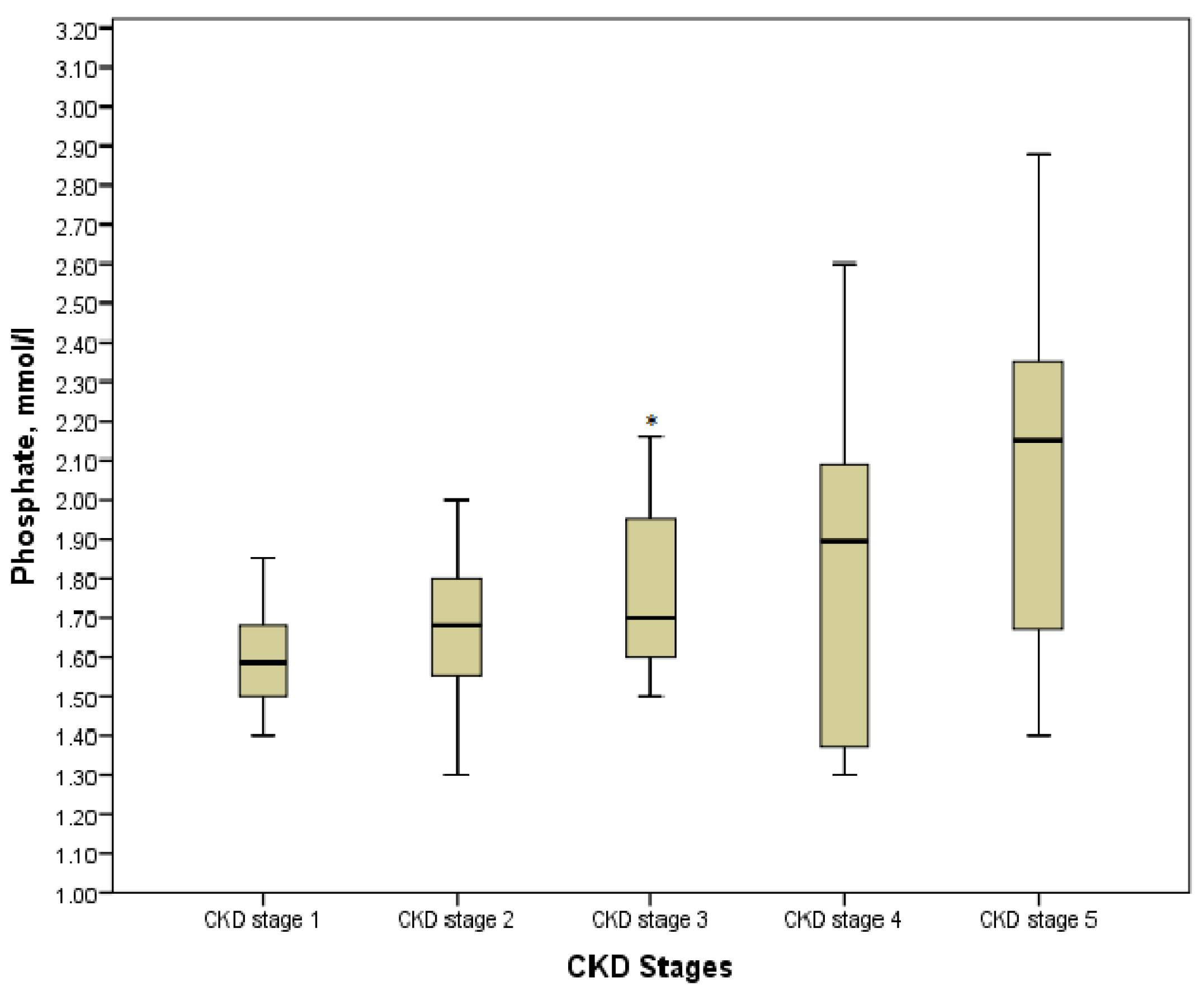
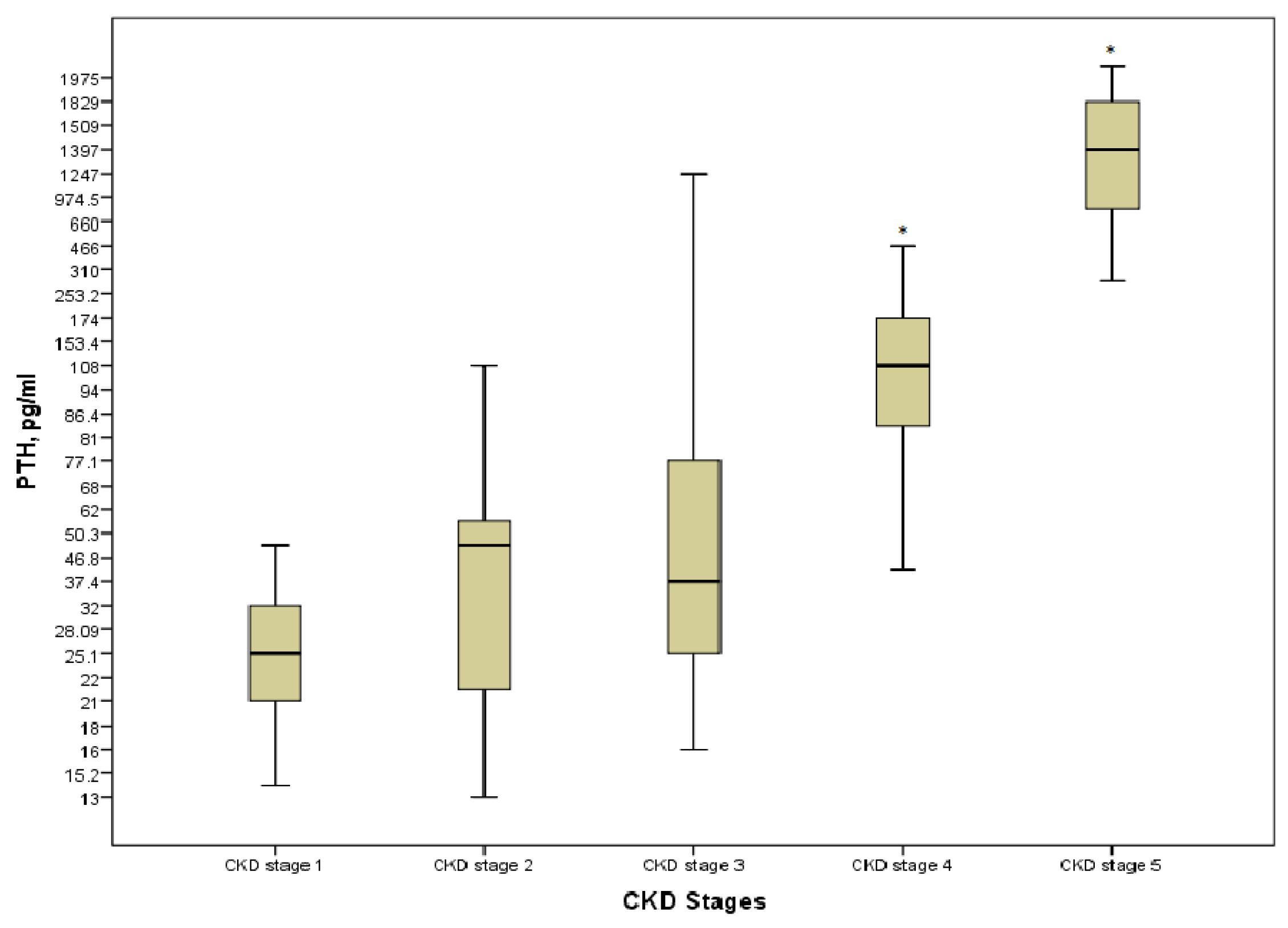
3.3. Phosphate, PTH and 25-OH Vitamin D in Children with CKD
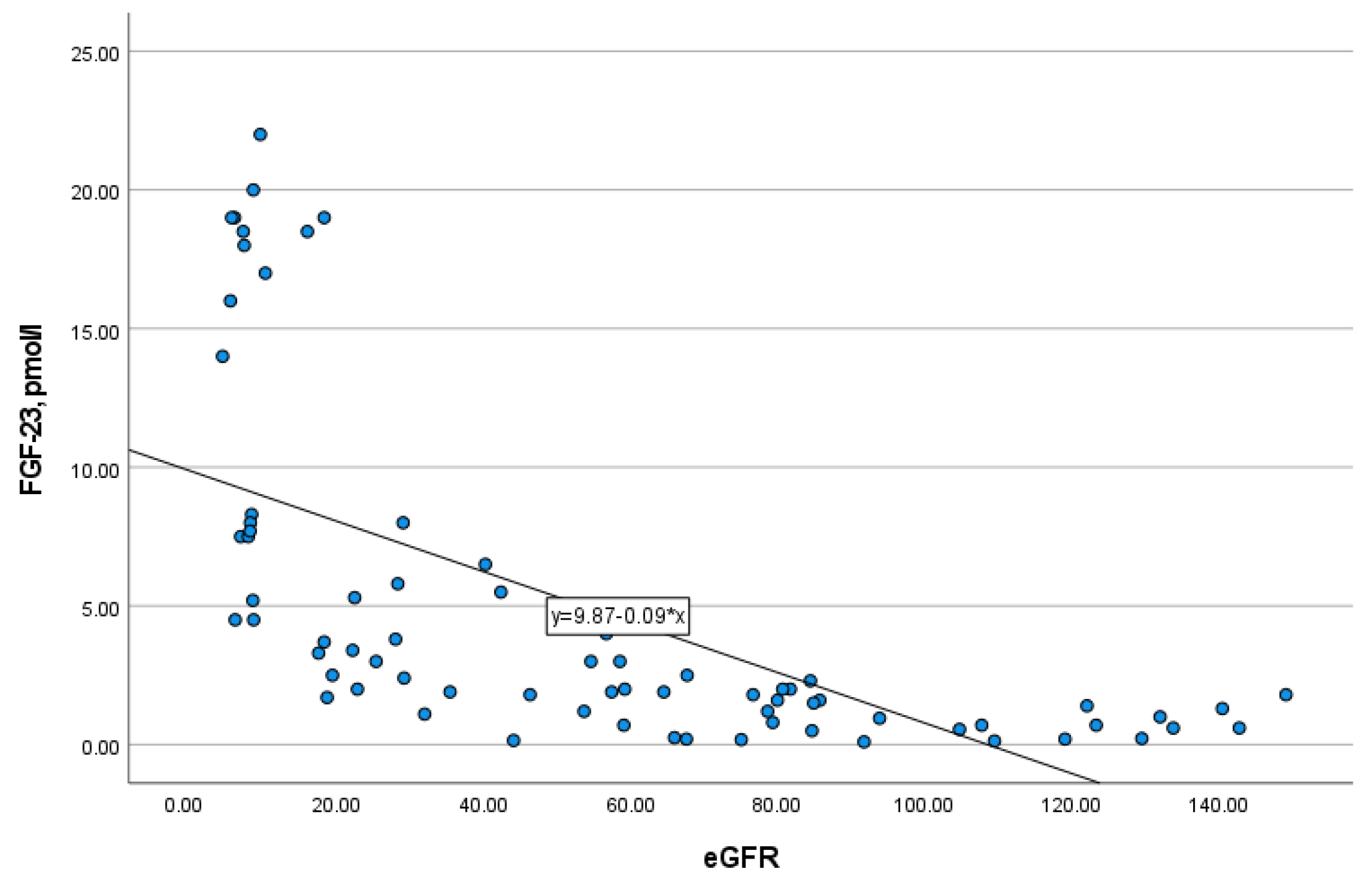
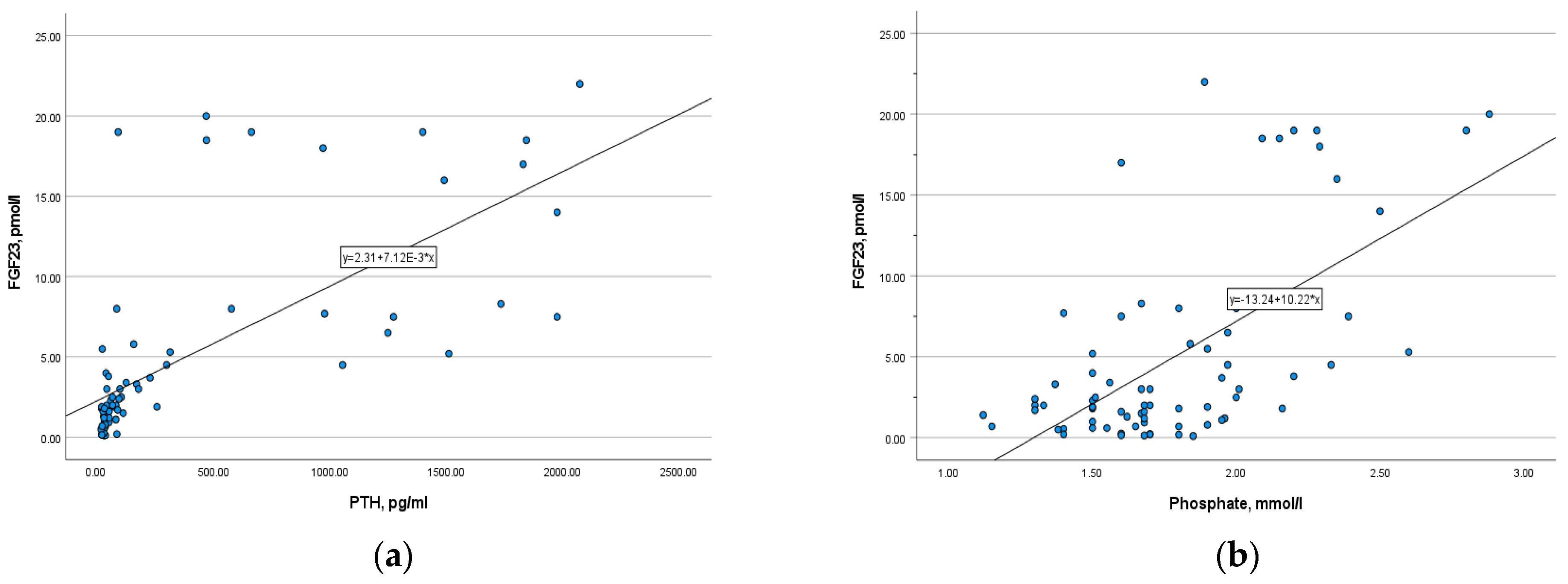
3.4. Correlations of FGF-23 with Other Bone Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Research and Publication Ethics
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brück, K.; Stel, V.S.; Fraser, S.; De Goeij, M.C.M.; Caskey, F.; Abu-Hanna, A.; Jager, K.J. Translational research in nephrology: Chronic kidney disease prevention and public health. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikbov, B.; Purcell, C.A.; Levey, A.S.; Smith, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abebe, M.; Adebayo, O.M.; Afarideh, M.; Agarwal, S.K.; Agudelo-Botero, M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanifer, J.W.; Muiru, A.; Jafar, T.H.; Patel, U.D. Chronic kidney disease in low- and middle-income countries. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2016, 31, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becherucci, F.; Roperto, R.M.; Materassi, M.; Romagnani, P. Chronic kidney disease in children. Clin. Kidney J. 2016, 9, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanatbayeva, A.B.; Kabulbayev, K.A.; Naushabayeva, A.E.; Nurbekova, A.A. Results of the screening for chronic kidney disease in population of Almaty-city. Nephrol. Dial. 2012, 14, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Gansevoort, R.T.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Jafar, T.H.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Mann, J.F.; Matsushita, K.; Wen, C.P. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet 2013, 382, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, B. Growth and Development of the Child with Renal Disease. In Pediatric Nephrology, 7th ed.; Avner, E., Harmon, W., Niaudet, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 637–665. [Google Scholar]
- Siomou, E.; Stefanidis, C.J. FGF-23 in children with CKD: A new player in the development of CKD—Mineral and bone disorder. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seiler, S.; Heine, G.H.; Fliser, D. Clinical relevance of FGF-23 in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, S34–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Hu, M.C. Klotho/FGF23 axis in chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease. Kidney Dis. 2017, 3, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattineni, J.; Bates, C.; Twombley, K.; Dwarakanath, V.; Robinson, M.L.; Goetz, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Baum, M. FGF23 Decreases renal NaPi-2a and NaPi-2c expression and induces hypophosphatemia in vivo predominantly via FGF receptor 1. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 297, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.C.; Kuro-o, M.; Moe, O.W. Klotho and chronic kidney disease. Contrib. Nephrol. 2013, 180, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M. Update on fibroblast growth factor 23 in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean, G.; Terrat, J.C.; Vanel, T.; Hurot, J.M.; Lorriaux, C.; Mayor, B.; Chazot, C. High levels of serum fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-23 are associated with increased mortality in long haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 2792–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, O.M. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and the last mile. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 1355–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouma-de Krijger, A.; Vervloet, M.G. Fibroblast growth factor 23: Are we ready to use it in clinical practice? J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, M.D.; Turner, C.; Dalton, R.N.; Rasmussen, P.; Waller, S.; Booth, C.J.; Goldsmith, D.J. Investigating FGF-23 concentrations and its relationship with declining renal function in paediatric patients with pre-dialysis CKD stages 3-5. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2012, 27, 4361–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Alvarez-elías, A.C.; Wile, B.; Belostotsky, V.; Filler, G. Deviations from the expected relationship between serum FGF23 and other markers in children with CKD: A cross-sectional study. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Husen, M.; Fischer, A.K.; Lehnhardt, A.; Klaassen, I.; Möller, K.; Müller-Wiefel, D.E.; Kemper, M.J. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and bone metabolism in children with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Magnusson, P.; Hansson, S.; Swolin-Eide, D. A prospective study of fibroblast growth factor-23 in children with chronic kidney disease. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2010, 70, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E.; Bilous, R.W.; Coresh, J.; de Francisco, A.L.M.; de Jong, P.E.; Griffith, K.E.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Iseki, K.; Lamb, E.J.; et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Portale, A.A.; Wolf, M.; Jüppner, H.; Messinger, S.; Kumar, J.; Wesseling-Perry, K.; Schwartz, G.J.; Furth, S.L.; Warady, B.A.; Salusky, I.B. Disordered FGF23 and Mineral Metabolism in Children with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Smith, C.; Shah, V.; Gullet, A.; Wells, D.; Rees, L.; Shroff, R. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and soluble klotho in children with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2013, 28, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viaene, L.; Bammens, B.; Meijers, B.K.I.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Vanderschueren, D.; Evenepoel, P. Residual renal function is an independent determinant of serum FGF-23 levels in dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2012, 27, 2017–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| All Patients (n = 73) | |
|---|---|
| Age (year) | 7.5 (4.0–11.0) |
| Female/male | 35 (47.9)/38 (52.1) |
| CKD cause | |
| CAKUT | 51 (69.9) |
| Glomerular diseases | 13 (17.8) |
| Nephrolithiasis and nephrocalcinosis | 4 (5.5) |
| HUS | 3 (4.1) |
| Cystic kidney diseases | 2 (2.7) |
| CKD stage | |
| Stage 1 | 14 (19.2) |
| Stage 2 | 15 (20.5) |
| Stage 3 | 13 (17.8) |
| Stage 4 | 14 (19.2) |
| Stage 5 | 17 (23.3) |
| HD | 8 (11) |
| PD | 9 (12.3) |
| Growth and development | |
| Normal | 52 (71.2) |
| Delay | 21(28.8) |
| CKD-MBD | 27 (37) |
| Renal anemia | 25 (34.2) |
| Variable | Healthy Individuals | CKD Stage 1 eGFR >90 mL/min/1.73 m2 (n = 14) | CKD Stage 2 eGFR 60–89 mL/min/1.73 m2 (n = 15) | CKD Stage 3 eGFR 30–59 mL/min/1.73 m2 (n = 13) | CKD Stage 4 eGFR 15–29 mL/min/1.73 m2 (n = 14) | CKD Stage 5 eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m2 (n = 17) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creatinine, mg/dL | N/A | 0.4 ± 0.08 | 0.73 ± 0.19 | 1.11 (0.81–1.62) | 2.32 ± 0.82 | 7.95 ± 2.43 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m² | N/A | 121.46 ± 17.94 | 77.17 ± 7.39 | 49.17 ± 9.61 | 22.5 ± 4.69 | 7.5 ± 1.55 |
| Urea, mmol/L | N/A | 3.68 ± 0.92 | 5.29 ± 1.44 | 6.5 (4.64–10.0) | 14.48 ± 6.0 | 22.06 ± 4.6 |
| Phosphate, mmol/L | 1.52 ± 0.05 | 1.54 ± 0.21 | 1.66 ± 0.2 | 1.76 ± 0.21 a,f | 1.8 ± 0.41 a | 2.08 ± 0.45 a,c |
| Calcium, mmol/L | N/A | 2.23 (2.0–2.39) | 2.1 (2.0–2.2) | 2.16 (2.05–2.25) | 2.15 (2.06–2.32) | 1.8 (1.45–2.04) a,d |
| Ionized calcium, mmol/L | N/A | 1.2 (1.0–1.5) | 1.2 (1.01–1.4) | 1.25 (1.0–1.3) | 1.26 (1.21–1.3) | 1.1 (0.87–1.15) a,e |
| Alkaline phosphatase, U/L | N/A | 244.86 ± 74.7 | 300.76 ± 69.06 a | 250.56 ± 85.52 | 328.39 ± 119.95 | 495.6 ± 303.2 c |
| PTH, pg/mL | 25.5 (21.25–44.75) | 25.5 (21.0–32.0) | 46.8 (21.7–54.0) | 37.4 (21.7–85.55) | 110.34 (83.28–186.5) b,f | 1397 (814–1836) e,f |
| 25-OH vitamin D, ng/mL | N/A | 29.4 ± 14.49 | 24.51 ± 10.64 | 21.16 ± 10.17 | 20.2 ± 14.37 | 20.08 ± 16.27 |
| FGF-23, pmol/L | 0.65 (0.22–0.98) | 0.65 (0.22–1.08) | 1.6 (1.5–1.8) a,f | 1.9 (1.15–3.5) | 3.55 (2.48–6.35) c | 14.0 (7.5–18.75) d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balmukhanova, A.; Kabulbayev, K.; Alpay, H.; Kanatbayeva, A.; Balmukhanova, A. FGF-23 and Phosphate in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in Kazakhstan. Medicina 2021, 57, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57010015
Balmukhanova A, Kabulbayev K, Alpay H, Kanatbayeva A, Balmukhanova A. FGF-23 and Phosphate in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in Kazakhstan. Medicina. 2021; 57(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalmukhanova, Altynay, Kairat Kabulbayev, Harika Alpay, Assiya Kanatbayeva, and Aigul Balmukhanova. 2021. "FGF-23 and Phosphate in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in Kazakhstan" Medicina 57, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57010015
APA StyleBalmukhanova, A., Kabulbayev, K., Alpay, H., Kanatbayeva, A., & Balmukhanova, A. (2021). FGF-23 and Phosphate in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in Kazakhstan. Medicina, 57(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57010015






