Clinical Performance of Short Expandable Dental Implants for Oral Rehabilitation in Highly Atrophic Alveolar Bone: 3-year Results of a Prospective Single-Center Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Informed Consent
2.3. Study Population and Measures
2.4. Implants
2.5. Surgical and Prosthetic Protocol
2.6. Clinical and Radiological Follow-up
2.7. Data Gathering and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Oral Health-Related Quality of Life
3.3. Biomechanical Implant Stability
3.4. Crestal Bone Changes
4. Discussion
4.1. Oral Health-Related Quality of Life
4.2. Implant Stability under Difficult Conditions
4.3. Peri-Implant Crestal Bone Loss
4.4. Limitations of the Study and External Validity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fretwurst, T.; Nack, C.; Al-Ghrairi, M.; Raguse, D.; Stricker, A.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Nelson, K.; Nahles, S. Long-term retrospective evaluation of the peri-implant bone level in onlay grafted patients with iliac bone from the anterior superior iliac crest. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeven, J.W.; Rujiter, J.; Cune, M.S.; Terlou, M.; Zoon, M. Onlay grafts in combination with endosseous implants in severe mandibular atrophy: One year results of a prospective, quantitative radiological study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2000, 11, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkenke, E. Short implants. Do they replace reconstruction of the alveolar crest? Der MKG-Chirurg 2013, 6, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Barausse, C.; Pistilli, R.; Sammartino, G.; Grandi, G.; Felice, P. Short implants versus bone augmentation for placing long implants in atrophic maxillae: One-year post-loading results of a pilot randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 8, 257–268. [Google Scholar]
- Schincaglia, G.P.; Thoma, D.S.; Haas, R.; Tutak, M.; Garcia, A.; Taylor, T.D.; Hämmerle, C.H. Randomised controlled multicenter study comparing short dental implants (6 mm) versus longer dental implants (11–15 mm) in combination with sinus floor elevation procedures. Part 2: Clinical and radiographic outcomes at 1 year of loading. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Vazquez, L.; Rieder, P.; Moraguez, O.; Bernard, J.P.; Belser, U.C. Survival rates of short (6 mm) micro-rough surface implants: A review of literature and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014, 25, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotte, C.; Grønningsaeter, A.; Halmøy, A.M.; Öhrnell, L.O.; Mordenfeld, A.; Isaksson, S.; Johansson, L.Å. Four-millimeter-long posterior-mandible implants: 5-year outcomes of a prospective multicenter study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17 (Suppl. 2), e385–e395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, D.S.; Haas, R.; Tutak, M.; Garcia, A.; Schincaglia, G.P.; Hämmerle, C.H. Randomised controlled multicenter study comparing short dental implants (6 mm) versus longer dental implants (11–15 mm) in combination with sinus floor elevation procedures. Part 1: Demographic and patient-reported outcomes at 1 year of loading. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentschel, A.; Herrmann, J.; Glauche, I.; Vollmer, A.; Schlegel, K.A.; Lutz, R. Survival and patient satisfaction of short implants during the first 2 years of function: A retrospective cohort study with 694 implants in 416 patients. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierrisnard, L.; Renouard, F.; Renault, P.; Barquins, M. Influence of implant length and bicortical anchorage on implant stress distribution. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2003, 5, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.P.; Tan, K.B.; Liu, G.R. Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: A review of the literature. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggi, L.; Capelloni, I.; Di Girolamo, M.; Maceri, F.; Vairo, G. The influence of implant diameter and length on stress distribution of osseointegrated implants related to crestal bone geometry: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 100, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes, S.L.; Verri, F.R.; Santiago, J.F., Jr.; Almeida, D.A.; De Mello, C.C.; Pellizzer, E.P. A 3-D finite element study of the influence of crown-implant ratio on stress distribution. Braz. Dent. J. 2013, 24, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, S.L.; Pellizzer, E.P.; Verri, F.R.; Santiago, J.F., Jr.; Silva, J.V. Three-dimensional finite element analysis on stress distribution in retention screws of different crown-implant ratios. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 18, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, C.S.; Williams, J.L. Comparative evaluation of implant designs: Influence of diameter, length, and taper on strains in the alveolar crest. A three-dimensional finite-element analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanos, G.E.; Kuyunov, O.; Sacks, D.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Delgado-Ruiz, R. Apical stability of implants with progressive thread design in vitro, based on clinicians with different level of experience. J. Periodontol. 2019, 90, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.; Almeida, R.F.; Felino, A.C.; Malo, P.; Nobre, M. The influence of crown-to-implant ratio on short implant marginal bone loss. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2016, 31, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, M.; Brandt, J.; Lauer, H.C. Prothetische Versorgung auf kurzen Implantaten. Zahnmed. up2date 2014, 2, 123–142. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eitner, S.; Wichmann, M.; Schlegel, K.A.; Kollmannberger, J.E.; Nickenig, H.J. Oral health-related quality of life and implant therapy: An evaluation of preoperative, intermediate, and post-treatment assessments of patients and physicians. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawood, J.I.; Howel, R.A. A classification of edentulous jaws. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1988, 17, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Pinas, L.; Escuer-Artero, V.; Fernandez, R.S.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Short dental implants in patients with oral lichen planus: A long-term follow-up. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngyen, T.T.H.; Eo, M.Y.; Cho, Y.J.; Myoung, H.; Kim, S.M. 7-mm-long dental implants: Retrospective clinical outcome in medically compromised patients. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 45, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edher, F.; Ngyen, C.T. Short dental implants: A scoping review of literature for patients with head and neck cancer. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, W.; Schweyen, R.; Heinzelmann, C.; Hey, J.; Al-Nawas, B.; Eckert, A.W. Novel expandable short dental implants in situations with reduced vertical bone height—Technical note and first results. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2017, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Weber, H.P.; Lang, N.P. Tissue integration of non-submerged implants. 1-year results of a prospective study with 100 ITI hollow-cylinder and hollow-screw implants. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 1990, 1, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karoussis, I.K.; Brägger, U.; Salvi, G.E.; Bürgin, W.; Lang, N.P. Effect of implant design on survival and success rates of titanium oral implants: A 10-year prospective cohort study of the ITI dental implant system. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2004, 15, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.T.; Micheelis, W.; Biffar, R. Reference values in oral health-related quality of life for the abbreviated version of the Oral Health Impact Profile. Schweiz. Monatsschr. Zahnmed. 2004, 114, 784–791. [Google Scholar]
- John, M.T.; Miglioretti, D.L.; LeResche, L.; Koepsell, T.D.; Hujoel, P.; Micheelis, W. German short forms of the Oral Health Impact Profile. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2006, 34, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Climent, M.; Santos-Garcia, R.; Jaramillo-Santos, R.; Romero-Ruis, M.M.; Fernandez-Palacin, A.; Lazaro-Calvo, P.; Bullon, P.; Rios-Santos, J.V. Assesment of osstell isq‘s reliability for implant stability measurement: A cross-sectional clinical study. Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Cir. Buccal 2013, 18, e877–e882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennerby, L. 20 Jahre Erfahrung mit der Resonanzfrequenzanalyse. Implantologie 2013, 21, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indikationsklassen für Implantatversorgung zur Regelversorgung. Konsensuskonferenz Implantologie. Available online: www.konsensuskonferenz-implantologie.eu (accessed on 5 May 2014).
- Lekholm, U.; Zarb, G.A. Patient selection and preparation. In Tissue Integrated Prostheses: Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry, 1st ed.; Branemark, P.I., Zarb, G.A., Albrektsson, T., Eds.; Quintessence: Chicago, IL, USA, 1985; pp. 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Sclar, A.G. Chirurgische Techniken zur Versorgung der Periimplantären Weichgewebe. In Weichgewebe und Ästhetik in der Implantologie, 1st ed.; Quintessence Publishung: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. 46–49. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Oh, T.J.; Misch, C.E.; Wang, H.L. Occlusal considerations in implant therapy: Clinical guidelines with biomechanical rationale. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, M.D. Occlusion in implant dentistry. A review of the literature of prosthetic determinants and current consepts. Aust. Dent. J. 2008, 53 (Suppl. 1), S60–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Roman, G.; Schulte, W.; D’Hoedt, B.; Axman-Krcmar, D. The Frialit-2 implant system: Five-year clinical experience in single-tooth and immediately postextraction applications. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1997, 12, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Linkevicius, T. Zero Bone Loss Consepts, 1st ed.; Quintessence Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, I.; Desai, S.R.; Singh, R. Short implants: A systematic review. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2012, 16, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, E.; Keceli, H.G.; Uysal, S.; Güngör, H.; Muhtarogullari, M.; Tözüm, T.F. Management of limited vertical bone height in the posterior mandible: Short dental implants versus nerve lateralization with standard length implants. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2016, 27, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrom, H.; Gupta, B.; Ghanem, A.; Cacciato, R.; Ren, Y.; Romanos, G.E. Success rate of short dental implants supporting single crowns and fixed bridges. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, P.; Pistilli, R.; Barausse, C.; Bruno, V.; Pestilli, V.; Piattelli, M.; Ippolito, D.R.; Esposito, M. Posterior atrophic jaws rehabilitated with prostheses supported by 6 mm long and 4 mm wide implants or by longer implants in augmented bone. 3-year post-loading results from a randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2018, 11, 175–187. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, F.; Lang, N.P.; Ricci, E.; Ferraioli, L.; Baldi, N.; Botticelli, D. Long-term follow-up of single crowns supported by short, moderately rough implants—A prospective 10-year cohort study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, A.; Jolette, J. Bone toolbox: Biomarkers, imaging tools, biomechanics, and histomorphometry. Toxicol. Pathol. 2018, 46, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Rotta, R.F.; Lindh, C.; Castro Pereira, A.; Rohlin, M. Ambiguity in bone tissue characteristics as presented in studies on dental implant planning and placement: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsa, A.; Ibrahim, N.; Hassan, B.; van der Stelt, P.; Wismeijer, D. Bone quality evaluation at dental implant site using multislice CT, micro-CT, and Cone beam-CT. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triches, D.F.; Alonso, F.R.; Mezzomo, L.A.; Schneider, D.R.; Villaronho, E.A.; Rockenbach, M.I.; Teixeira, E.R.; Shinkai, R.S. Relation between insertion torque and tactile, visual, and rescaled gray value measures of bone quality: A cross-sectional clinical study with short implants. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2019, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechara, S.; Kubilius, R.; Veronesi, G.; Pires, J.T.; Shibli, J.A.; Mangano, F.G. Short (6-mm) dental implants versus sinus floor elevation and placement of longer (≥10 mm) dental implants: A randomized controlled trial with a 3-year follow-up. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reißmann, D.R.; Krautz, M.; Schierz, O.; John, M.T.; Rudolph, M.; Szentpétery, A. Was ist klinisch relevant bei Veränderungen der Mundgesundheit? Ergebnisse der deutschen Kurzversion des Oral Health Impact Profiles (OHIP-G14). Dtsch. Zahnärztl. Z. 2008, 63, 668–679. (in German). [Google Scholar]
- Polyzois, G.; Lagouvardos, P.; Partalis, C.; Zoidis, P.; Polyzois, H. Short-term assessment of the OHIP-14 scale on denture wearers using adhesives. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 24, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.R.; Li, D.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Chen, S.J.; Guan, S.M.; Kong, L. Evaluation of fixation of expandable implants in the mandibles of ovarectomized sheep. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 71, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowzari, H.; Chee, W.; Tuan, A.; Abou-Rass, M.; Landesman, H.M. Clinical and microbiological aspects of the Sargon immediate load implant. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 1998, 19, 686–689. [Google Scholar]
- Pommer, B.; Hingsammer, L.; Haas, R.; Mailath-Pokorny, G.; Busenlechner, D.; Watzek, G.; Fürhauser, R. Denture-related biomechanical factors for fixed partial dentures retained on short dental implants. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 28, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, A.; D’Isidoro, O.; Bambini, F.; Putignano, A. Potential bone to implant contact area of short versus standard implants: An in vitro micro-computed tomography analysis. Implant Dent. 2016, 25, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.R.; Li, Y.F.; Guan, S.M.; Song, L.; Xu, L.X.; Kong, L. The biomechanical analysis of simulation implants in function under osteoporotic jawbone by comparing cylindrical, apical tapered, neck tapered, and expandable type implants: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, e273–e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, H.J.; Park, J.C.; Yun, J.H.; Jung, U.W.; Kim, C.S.; Choi, S.H.; Cho, K.S. A short-term clinical study of marginal bone level change around microthreded and platform-switched implants. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2011, 41, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.K.; Padmanabhan, T.V. Resonance frequence analysis. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2011, 22, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, W.; Becker, B.E.; Hujoel, P.; Abu Raz, Z.; Goldstein, M.; Smidt, A. Prospective clinical trial evaluating a new implant system for implant survival, implant stability and radiographic bone changes. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Pérez-Albacete Martinez, C.; Piattelli, A.; Shibli, J.A.; Markovic, A.; Calvo Guirado, J.L. The influence of three different apical implant designs at stability and osseointegration process: Experimental study in rabbits. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, P.G.; Jimbo, R.; Tovar, N.; Bonfante, E.A. Osseointegration: Hierarchical designing encompassing the macrometer, micrometer, and nanometer length scales. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitua, E.; Flores, J.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Transcrestal sinus lift using platelet concentrates in association to short implant placement: A retrospective study of augmented bone height remodeling. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.H.; Neiva, R.; Coelho, P.G.; Lukasz, W.; Tovar, N.M.; Lo, I.C.; Gil, L.F.; Torroni, A. Alveolar ridge expansion: Comparison of osseodensification and conventional osteotome techniques. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 30, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Serrano, J.; Molinero-Mourelle, P.; Pardal-Peláez, B.; Sáez-Alcaide, L.M.; Ortega, R.; López-Quiles, J. Influence of short implants geometry on primary stability. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2018, 23, e602–e607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerapong, K.; Sirimongkolwattana, S.; Sastraruji, T.; Khongkhunthian, P. Comparative study of immediate loading on short dental implants and conventional dental implants in the posterior mandible: A randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2019, 34, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.B.; Wu, T.X.; Guo, Y.C.; Zhou, X.D.; Lei, Y.L.; Xu, X.; Mo, A.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yuan, Q. Marginal bone loss around non-submerged implants is associated with salivary microbiome during bone healing. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 9, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martellacci, L.; Quaranta, G.; Patini, R.; Isola, G.; Gallenzi, P.; Masucci, L. A literature review of metagenomics and culturomics of the peri-implant microbiome: Current evidence and future perspectives. Materials 2019, 12, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martellacci, L.; Quaranta, G.; Fancello, G.; D’Addona, A.; Sanguinetti, M.; Patini, R.; Masucci, L. Characterizing peri-implant and sub-gingival microbiota through culturomics. First isolation of some species in the oral cavity. A pilot study. Pathogens 2020, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Pesce, P.; Patini, R.; Antonacci, D.; Tommasato, G. What are the effects of different abutment morphologies on peri-implant hard and soft tissue behavior? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 33, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruta, K.; Ayukawa, Y.; Matsuzaki, T.; Kihara, M.; Koyano, K. The influence of implant-abutment connection on the screw loosening and microleakage. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2018, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Neilands, J.; Davies, J.R.; Ekestubbe, A.; Friberg, B. A randomized, controlled clinical study on a new titanium oxide abutment surface for improved healing and soft tissue health. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streckbein, P.; Streckbein, R.G.; Wilbrand, J.F.; Malik, C.Y.; Schaaf, H.; Howaldt, H.P.; Flach, M. Non-linear 3D evaluation of different oral implant-abutment connections. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzer, E.P.; De Mello, C.C.; Santiago Junior, J.F.; De Souza Batista, V.E.; de Faria Almeida, D.A.; Verri, F.R. Analysis of the biomechanical behavior of short implants: The photo-elasticity method. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 55, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, N.; Rodrigues, S.; Shenoy, S.; Saldanha, S.; Pai, U.; Shetty, T.; Srikant, N.; Mahesh, M.; Hegde, P. A comparative evaluation of stress distribution with two attachment systems of varying heights in a mandibular implant-supported overdenture: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, e795–e805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimmelmayr, M.; Stangl, M.; Edelhoff, D.; Beuer, F. Clinical prospective study of a modified technique to extend the keratinized gingiva around implants in combination with ridge augmentation: One-year results. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2011, 26, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Miron, R.J. Health, maintenance, and recovery of soft tissues around implants. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 618–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.L.; Masri, R.M.; Williams, D.A.; Ji, C.; Romberg, E. Free gingival grafts for implants exhibiting lack of keratinised mucosa: A prospective controlled randomized clinical study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felice, P.; Pistilli, R.; Barausse, C.; Bruno, V.; Trullenque-Eriksson, A.; Esposito, M. Short implants as an alternative to crestal sinus lift: A 1-year multicentre randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 8, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felice, P.; Barausse, C.; Pistilli, R.; Ippolito, D.R.; Esposito, M. Short implants versus longer implants in vertically augmented posterior mandibles: Results at 8 years after loading from a randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2018, 11, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
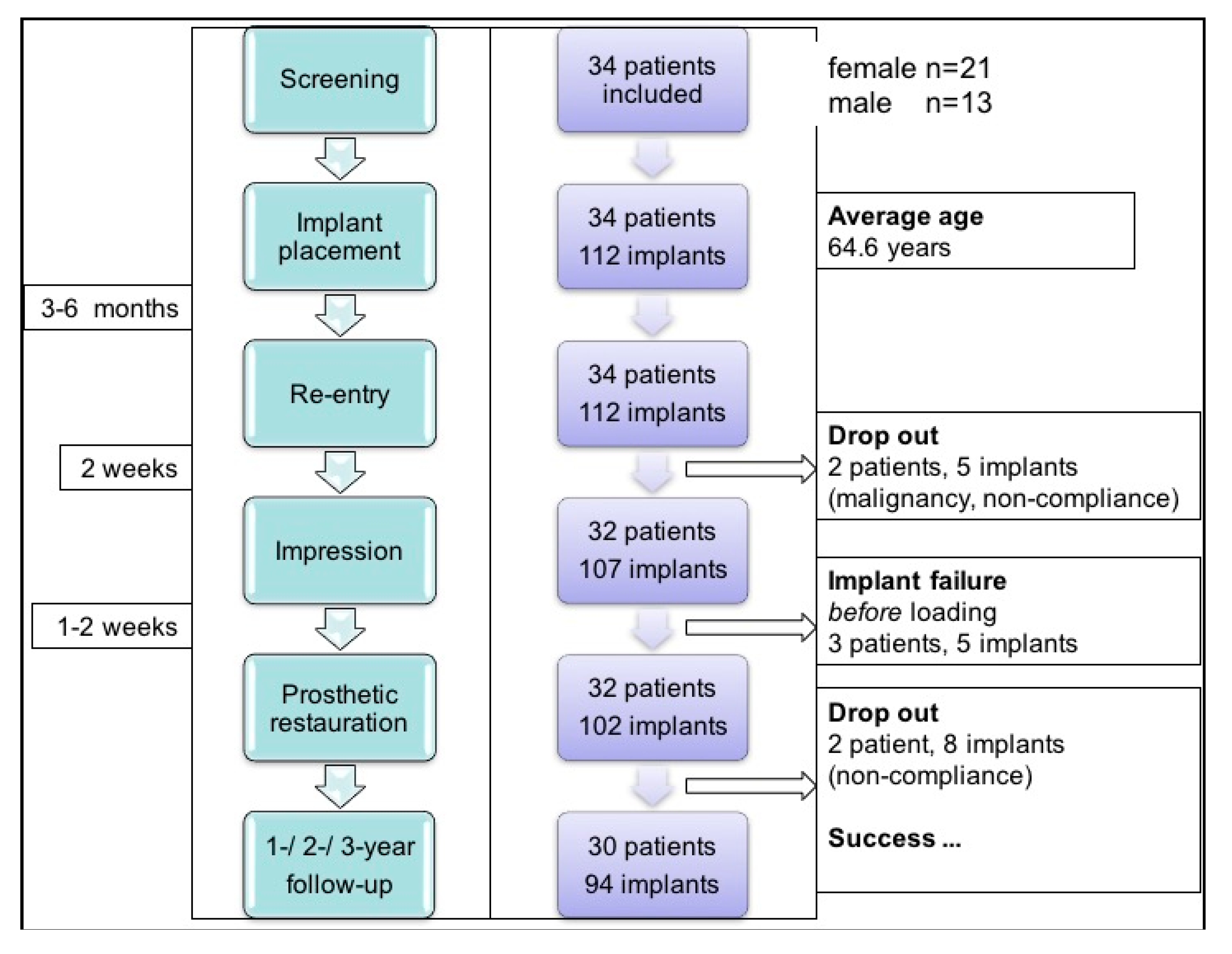

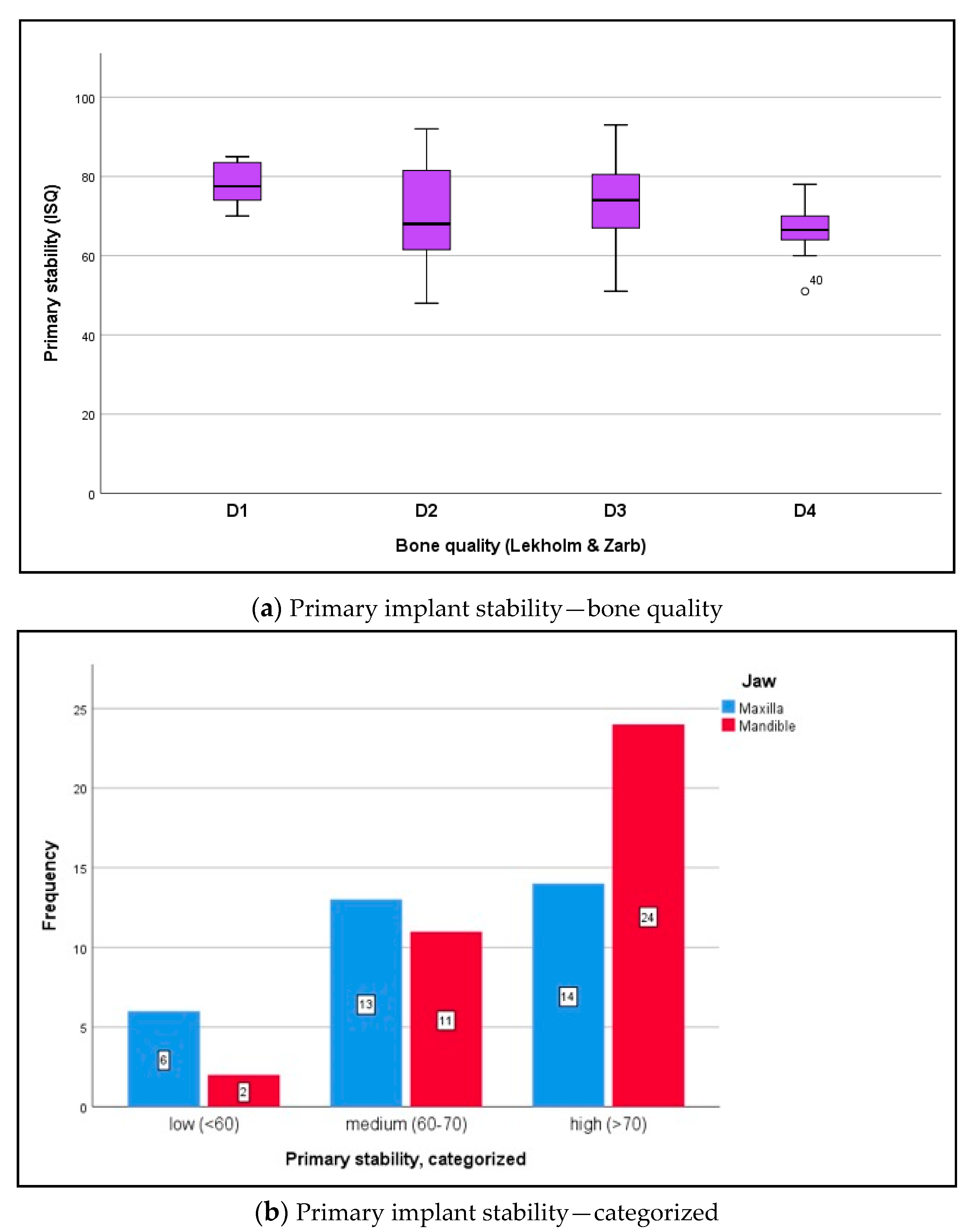
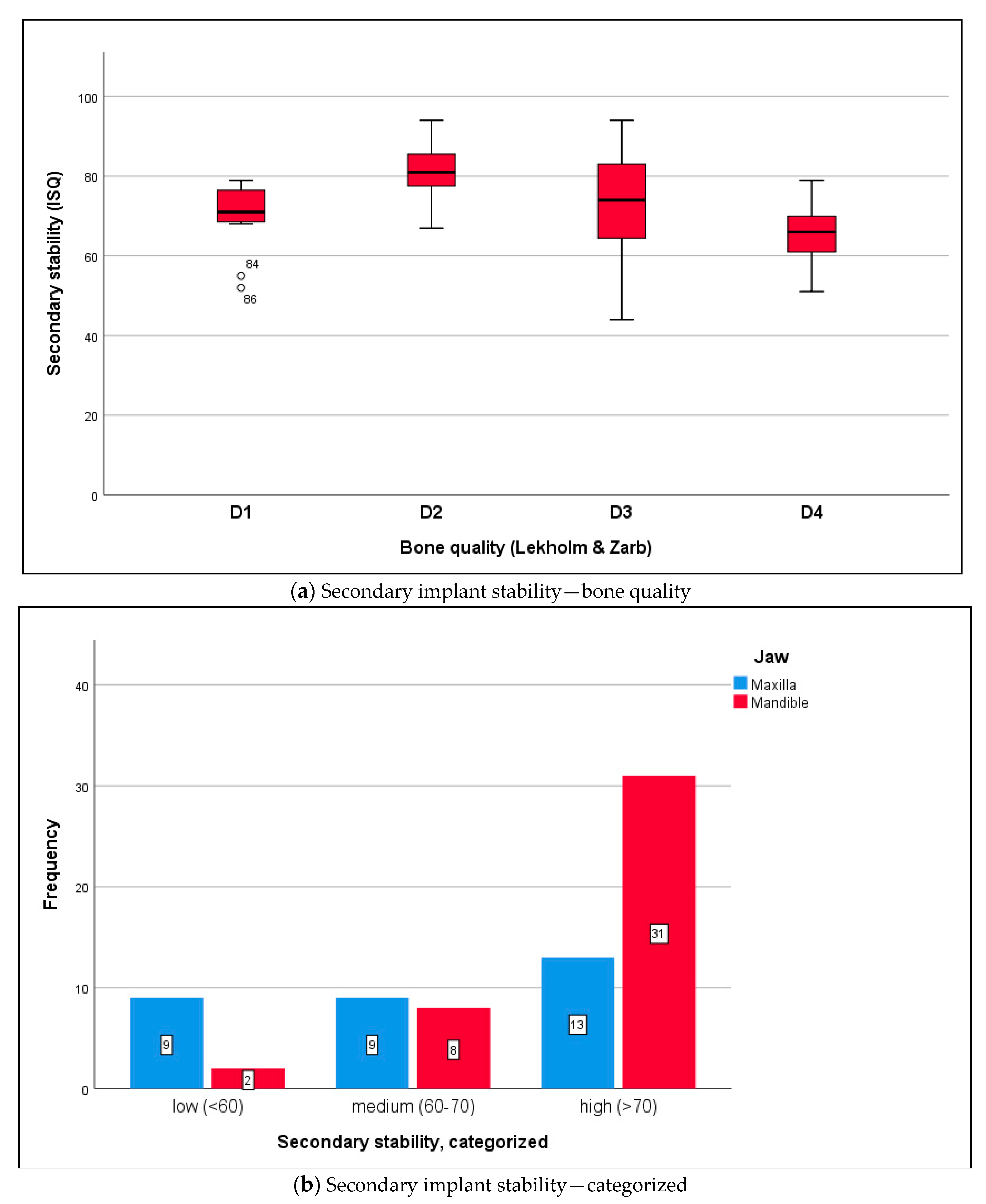


| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Adult patients | Comorbidity ASA score > III |
| Partially or totally edentulous | Pregnancy, bruxism |
| Alveolar process atrophy (Cawood and Howell category III–IV) | Smoking ≥10 cigarettes/d |
| Minimum alveolar bone height of 7–9 mm for placement of short implants (5–7 mm length) | Patients with a significant risk of developing osteo(radio)necrosis of the jaw (radiotherapy ≥50 Gy, intravenous bisphosphonate therapy) |
| Patients that were not willing to accept vertical alveolar bone augmentation | Neurological and psychiatric comorbidities likely to influence the course of treatment |
| First implantological treatment | Untreated or poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, immunosuppression |
| Comorbidity ASA score I–III | Highly atrophic jaws that required vertical augmentation (Cawood and Howell category > IV) |
| Surgical Protocol | Bone Quality | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 (large homogenous cortical bone, little trabecular bone) | D2 (thick cortical bone, dense trabecular bone) | D3 (thin cortical bone, dense trabecular bone) | D4 (thin cortical bone, sparse trabecular bone) | |
| last drill | last drill | second-to-last drill | second-to-last drill (cortical bone only) |
| - | - | - | analog to last drill |
| ||||
| Patient * (Gender) | Age (Years) | ASA Score/ Systemic Disease | Surgery (Year) | Oral Disease/ Smoking | Implant Position (FDI; Σ) | Indication Category ** | Bone Quality (Lekholm and Zarb) | Alveolar Process Atrophy (Cawood and Howell) | Prosthetic Treatment | Implant Failure | Follow-up Period (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. # (female) | 80 | 2/ Diabetes mellitus, bronchitis, arterial hypertension | 2014 | None/ no | Maxilla | IIa | D4 | IV | Telescope | 1 (before loading) ## | 64 |
| 2. # (female) | 64 | 1/ Osteoporosis | 2014 | None/ no | Maxilla 14, 12, 22, 24 (Σ = 4) | IIIa | D4 | IV | Jaw bar | None | 61 |
| 3. # (male) | 53 | 2/ Cured squamous-cell carcinoma (floor of the mouth) | 2014 | History of marginal periodontitis/ yes | Maxilla (Σ = 3) | IIb | D3 | IV | Ball attachment | 2 (under loading) ## | 60 |
| 4. (male) | 67 | 1 | 2015 | None/ no | Maxilla 17(2x, | IIIa | D3-D4 | IV | Jaw bar | 3 (before loading) ## | 55 |
| 5. (female) | 62 | 1 | 2015 | History of mid-facial trauma/ no | Maxilla 16, 14, 12, 22, 24, 26 (Σ = 6) | IIIa | D4 | IV | Jaw bar | None | 52 |
| 6. (male) | 54 | 2/ Cured squamous-cell carcinoma (tongue) | 2016 | Chronic mucositis/ yes | Maxilla 14, 12, 22, 24 (Σ = 4) | IIIa | D3 | IV | Ball attachment | None | 40 |
| 7. (male) | 50 | 1 | 2017 | History of marginal periodontitis/ yes | Maxilla 15, 13, 23, 25 (Σ = 4) | IIIa | D3 | III | Ball attachment | None | 32 |
| 8. # (female) | 44 | 1 | 2014 | None/ no | Maxilla 16, 15, 14 (Σ = 3) | IIa | D3 | III | Bridge | None | 60 |
| 9. (male) | 76 | 1 | 2015 | None/ no | Maxilla 16, 15, 14 (Σ = 3) | IIb | D3 | III | Bridge | None | 56 |
| 10. (male) | 61 | 1 | 2015 | None/ no | Maxilla 24, 25 (Σ = 2) | IIb | D2 | III | Bridge | None | 51 |
| 11. (female) | 62 | 1 | 2015 | History of marginal periodontitis/ no | Maxilla 16, 15, 25, 26 (Σ = 4) | IIb | D4 | IV | Bridge | None | 48 |
| 12. (male) | 57 | 1 | 2015 | History of marginal periodontitis/ no | Maxilla 26, 27 (Σ = 2) | IIb | D3 | III | Bridge | None | 47 |
| 13. (male) | 53 | 1 | 2016 | None/ no | Maxilla 25, 26 (Σ = 2) | IIb | D3 | III | Bridge | None | 46 |
| 14. (female) | 58 | 2/ Cured HCV infection | 2016 | History of marginal periodontitis/ yes | Maxilla 16, 14, 25, 26 (Σ = 4) | IIb | D3-D4 | III | Bridge | None | 41 |
| 15. # (female) | 65 | 2/ Chronic bronchitis, arterial hypertension | 2014 | None/ no | Mandible 34, | IIIb | D1 | IV | Ball attachment | 1 (under loading) ## | 61 |
| 16. # (female) | 72 | 2/ Osteoarthrosis | 2015 | History of marginal periodontitis/ no | Mandible 42, 44, 46 (Σ = 3) | IIb | D2 | IV | Ball attachment | None | 50 |
| 17. (female) | 74 | 3/ Congestive heart failure, arterial hypertension, sicca syndrome | 2016 | None/ no | Mandible 34, 32, 42, 44 (Σ = 4) | IIIb | D3 | IV | Ball attachment | None | 43 |
| 18. (male) | 69 | 3/ Cured squamous-cell cancer (oropharynx) | 2016 | Chronic mucositis/ yes | Mandible 34, 32, 42, 44 (Σ = 4) | IIIb | D2 | IV | Jaw bar | None | 41 |
| 19. (female) | 63 | 2/ Hypothyroidism | 2016 | None/ no | Mandible 34, 32, 42, 44 (Σ = 4) | IIIb | D3 | IV | Jaw bar | None | 41 |
| 20. (female) | 66 | 2/ Osteoporosis | 2016 | History of marginal periodontitis/ no | Mandible 35, 45 (Σ = 2) | IIb | D3 | IV | Ball attachment | None | 40 |
| 21. (male) | 76 | 3/ Arteriosclerosis, hemiplegia | 2016 | None/ yes | Mandible 34, 32, 42, 44 (Σ = 4) | IIIb | D2 | IV | Jaw bar | None | 37 |
| 22. (male) | 59 | 2/ Venous thrombosis | 2016 | None/ no | Mandible 34, 32, | IIIb | D2 | IV | Ball attachment | 1 (under loading) ## | 37 |
| 23. (female) | 80 | 3/ Coronary arteriosclerosis, congestive heart failure | 2017 | None/ no | Mandible 34, 32, 42, 44 (Σ = 4) | IIIb | D2 | IV | Ball attachment | None | 32 |
| 24. (female) | 83 | 3/ Cured squamous-cell carcinoma (maxilla) | 2017 | Leukoplakia/ no | Mandible 34, 32, 42, 44 (Σ = 4) | IIIb | D2 | IV | Ball attachment | None | 32 |
| 25. (female) | 55 | 1 | 2018 | None/ no | Mandible 35, 31/41, 45 (Σ = 3) | IIIb | D2 | IV | Ball attachment | None | 21 |
| 26. # (male) | 76 | 1 | 2014 | None/ no | Mandible 35, 36, 37 (Σ = 3) | IIb | D1 | III | Bridge | None | 60 |
| 27. # (female) | 52 | 1 | 2015 | History of marginal periodontitis/ no | Mandible 35, 36, 37 (Σ = 3) | IIb | D2 | III | Bridge | None | 56 |
| 28. # (female) | 59 | 1 | 2015 | None/ no | Mandible 35, 36 (Σ = 2) | IIb | D2 | IV | Bridge | None | 51 |
| 29. (female) | 59 | 2/ Gastric ulcer | 2016 | None/ no | Mandible 47 (Σ = 1) | Ib | D2 | III | Crown | None | 44 |
| 30. (female) | 48 | 1 | 2016 | None/ yes | Mandible 35, 36 (Σ = 2) | IIb | D2 | III | Bridge | None | 37 |
| OHIP-14 Dimension | Variables | Baseline Median (IQR) | Post-Rehabilitation Median (IQR) | Statistics (Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test for Paired Samples) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Functional limitation | Have you had trouble pronouncing any words because of problems with your teeth, mouth, or dentures? | 1 (0–2.5) | 0 (0–0.5) | p = 0.059 |
| Have you felt that your sense of taste has worsened because of…? | 0 (0–1.5) | 0 (0–0) | p = 0.194 | |
| Physical pain | Have you experienced painful aching in your mouth? | 2 (0–2) | 0 (0–1.5) | p = 0.168 |
| Have you found it uncomfortable to eat any foods? | 3 (1–3.5) | 1 (0–1.5) | p = 0.039 * | |
| Psychological discomfort | Have you been self-conscious about…? | 2 (0.5–3) | 0 (0–0) | p = 0.026 * |
| Have you felt tense? | 2 (0–2.5) | 0 (0–1) | p = 0.031 * | |
| Physical disability | Has your diet been unsatisfactory? | 2 (0.5–3.5) | 0 (0–2) | p = 0.071 |
| Have you had to interrupt meals? | 2 (0.5–2.5) | 0 (0–0) | p = 0.027 * | |
| Psychological disability | Have you found it difficult to relax? | 1 (0.5–2.5) | 0 (0–1) | p = 0.071 |
| Have you been slightly embarrassed? | 1 (0.5–2) | 0 (0–0) | p = 0.015 * | |
| Social disability | Have you been slightly irritable around other people? | 1 (0.5–2) | 0 (0–0) | p = 0.023 * |
| Have you found it difficult to perform your usual jobs? | 1 (0–2) | 0 (0–0.5) | p = 0.068 | |
| Handicap | Have you felt that life in general was less satisfying? | 2 (2–3) | 0 (0–2) | p = 0.041 * |
| Have you been totally unable to function? | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–0) | p = 0.157 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reich, W.; Schweyen, R.; Hey, J.; Otto, S.; Eckert, A.W. Clinical Performance of Short Expandable Dental Implants for Oral Rehabilitation in Highly Atrophic Alveolar Bone: 3-year Results of a Prospective Single-Center Cohort Study. Medicina 2020, 56, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56070333
Reich W, Schweyen R, Hey J, Otto S, Eckert AW. Clinical Performance of Short Expandable Dental Implants for Oral Rehabilitation in Highly Atrophic Alveolar Bone: 3-year Results of a Prospective Single-Center Cohort Study. Medicina. 2020; 56(7):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56070333
Chicago/Turabian StyleReich, Waldemar, Ramona Schweyen, Jeremias Hey, Sven Otto, and Alexander Walter Eckert. 2020. "Clinical Performance of Short Expandable Dental Implants for Oral Rehabilitation in Highly Atrophic Alveolar Bone: 3-year Results of a Prospective Single-Center Cohort Study" Medicina 56, no. 7: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56070333
APA StyleReich, W., Schweyen, R., Hey, J., Otto, S., & Eckert, A. W. (2020). Clinical Performance of Short Expandable Dental Implants for Oral Rehabilitation in Highly Atrophic Alveolar Bone: 3-year Results of a Prospective Single-Center Cohort Study. Medicina, 56(7), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56070333




