Ayurgenomics and Modern Medicine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Studies on the Genetic Basis of Prakriti
3. Studies on Physiology, Disease and Prakriti
4. Theoretical Papers
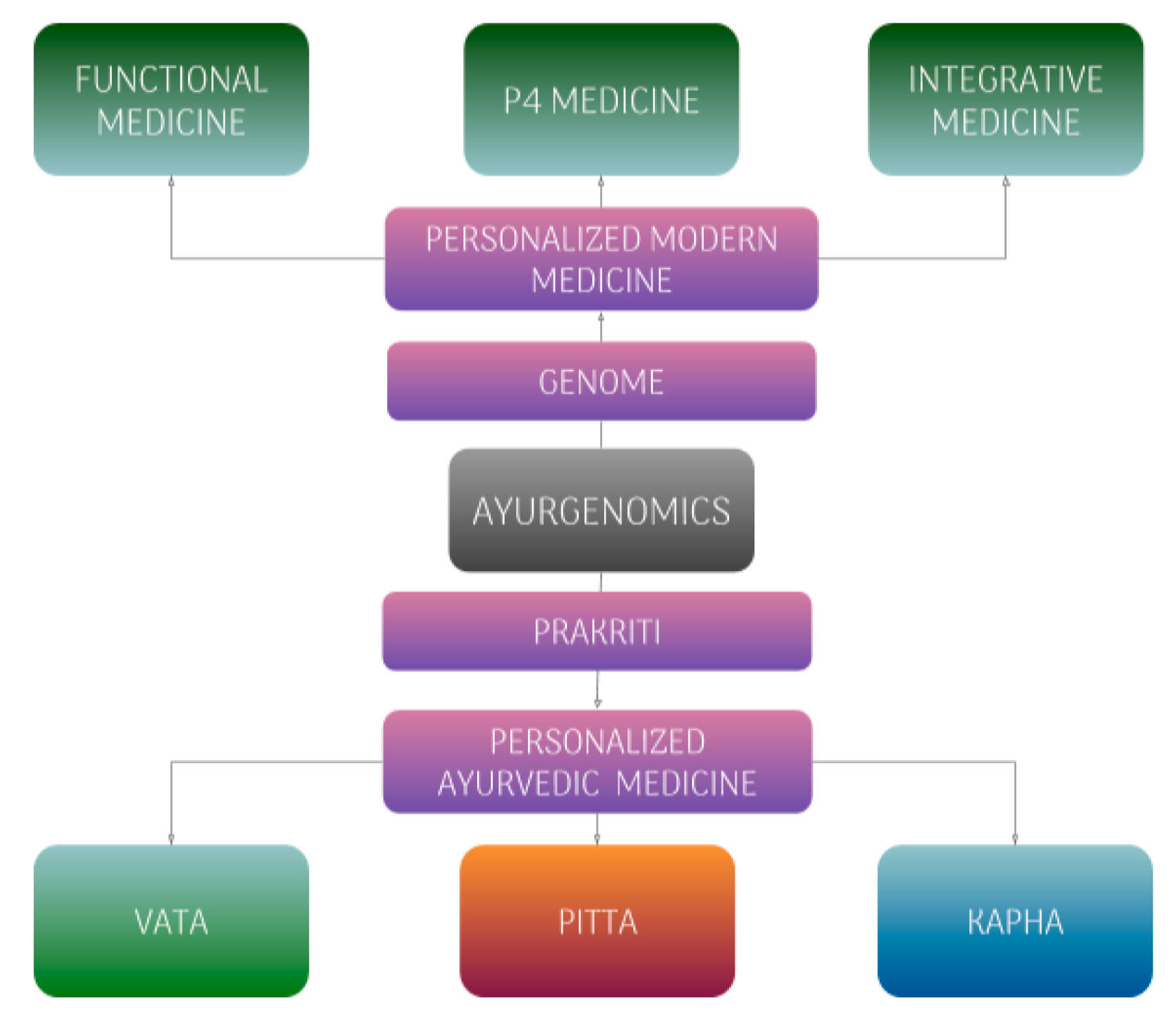
5. Modern Medicine and Ayurgenomics
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dash, B.; Sharma, R.K. Charaka Samhita; Caukhambha Orientalia: Varanasi, India, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Patwardhan, B.; Joshi, K.; Chopra, A. Classification of Human population based on HLA Gene Polymorphism and the Concept of Prakriti in Ayurveda. J. Altern. Complementary Med. 2005, 11, 349–353. [Google Scholar]
- Prasher, B.; Negi, S.; Aggarwal, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Sethi, T.P.; Deshmukh, S.R.; Purohit, S.G.; Sengupta, S.; Khanna, S.; Mohammad, F.; et al. Whole Genome Expression and Biochemical Correlates of Extreme Constitutional Types Defined in Ayurveda. J. Transl. Med. 2008, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.; Negi, S.; Jha, P.; Singh, P.K.; Stobdan, T.; Pasha, M.A. Indian genome variation consortium. EGLN1 involvement in high-altitude adaptation revealed through genetic analysis of extreme constitution types defined in Ayurveda. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18961–18966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodke, Y.; Joshi, K.; Patwardhan, B. Traditional medicine to modern pharmacogenomics: Ayurveda Prakriti type and CYP2C19 gene polymorphism associated with the metabolic variability. Evid. Based Complementary Alternat. Med. 2011, 249528. [Google Scholar]
- Rotti, H.; Guruprasad, K.P.; Nayak, J.; Kabekkodu, S.P.; Kukreja, H.; Mallya, S.; Nayak, J.; Bhradwaj, R.C.; Gangadharan, G.G.; Prasanna, B.V.; et al. Immunophenotyping of normal individuals classified on the basis of human dosha prakriti. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2014, 5, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Juyal, R.C.; Negi, S.; Wakhode, P.; Bhat, S.; Bhat, B.; Thelma, B.K. Potential of ayurgenomics approach in complex trait research: Leads from a pilot study on rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaraj, P.; Nizamuddin, S.; Sharath, A.; Jyothi, V.; Rotti, H.; Raval, R.; Nayak, J.; Bhat, B.K.; Prasanna, B.V.; Shintre, P.; et al. Genome-wide analysis correlates Ayurveda Prakriti. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotti, H.; Mallya, S.; Kabekkodu, S.P.; Chakrabarty, S.; Bhale, S.; Bharadwaj, R.; Bhat, B.K.; Dedge, A.P.; Dhumal, V.R.; Gangadharan, G.G.; et al. DNA methylation analysis of phenotype specific stratified Indian population. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Gheware, A.; Agrawal, A.; Ghosh, S.; Prasher, B.; Mukerji, M.; Indian Genome Variation Consortium. Combined genetic effects of EGLN1 and VWF modulate thrombotic outcome in hypoxia revealed by Ayurgenomics approach. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, R.K.; Kurup, P.A. Hypothalamic digoxin, hemispheric chemical dominance, and the tridosha theory. Int. J. Neurosci. 2003, 113, 657–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Gehlot, S.; Tiwari, S.K.; Singh, G. Effect of walking (aerobic isotonic exercise) on physiological variants with special reference to Prameha (diabetes mellitus) as per Prakriti. Ayu 2012, 33, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalerao, S.; Deshpande, T.; Thatte, U. Prakriti (Ayurvedic concept of constitution) and variations in Platelet aggregation. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotti, H.; Raval, R.; Anchan, S.; Bellampalli, R.; Bhale, S.; Bharadwaj, R.; Bhat, B.K.; Dedge, A.P.; Dhumal, V.R.; Gangadharan, G.G.; et al. Determinants of prakriti, the human constitution types of Indian traditional medicine and its correlation with contemporary science. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2014, 5, 167e75. [Google Scholar]
- Rapolu, S.B.; Kumar, M.; Singh, G.; Patwardhan, K. Physiological variations in the autonomic responses may be related to the constitutional types defined in Ayurveda. J. Humanitas Med. 2015, 5, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalle, N.P.; Kulkarni, M.V.; Pendse, N.M.; Naik, S.S. Association of constitutional type of Ayurveda with cardiovascular risk factors, inflammatory markers and insulin resistance. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2012, 3, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.K.; Patwardhan, K.; Singh, G. The basic cardiovascular responses to postural changes, exercise and cold pressor test: Do they vary in accordance with the dual constitutional types of Ayurveda? Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2011, 201, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyam, B.V.; Kumar, A. Ayurvedic constitution (prakruti) identifies risk factor of developing Parkinson’s disease. J. Altern. Complementary Med. 2013, 19, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirolkar, S.G.; Tripathi, R.K.; Rege, N.N. Evaluation of prakṛti and quality-of-life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Ancient science of life. J. Altern. Complementary Med. 2015, 34, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.S.; Pandey, R.; Mondal, A.K.; Gupta, S.; Verma, M.K.; Jain, S.; Ahmed, V.; Patil, R.; Agarwal, D.; Girase, B.; et al. Western Indian Rural Gut Microbial Diversity in Extreme Prakriti Endo-Phenotypes Reveals Signature Microbes. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jnana, A.; Murali, T.S.; Guruprasad, K.P.; Satyamoorthy, K. Prakriti phenotypes as a stratifier of gut microbiome: A new frontier in personalized medicine? J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2020, 11, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.K. The Microbiome in Health and Disease from the Perspective of Modern Medicine and Ayurveda. Medicina 2020, 56, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, B.; Bodeker, G. Ayurvedic genomics: Establishing a genetic basis for mind-body typologies. J. Altern. Complementary Med. 2008, 14, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; Ghodke, Y.; Shintre, P. Traditional medicine and genomics. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2010, 1, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo-Sierra, C.V. Ayurvedic genomics, constitutional psychology, and endocrinology: The missing connection. J. Altern. Complementary Med. 2011, 17, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, B.; Pancholi, J. Prakriti-based medicine: A step towards personalized medicine. Ayu 2011, 32, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukerji, M.; Prasher, B. Ayurgenomics: A New Approach in Personalized and Preventive Medicine. Sci. Cult. 2011, 77, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sethi, T.P.; Prasher, B.; Mukerji, M. Ayurgenomics: A New Way of Threading Molecular Variability for Stratified Medicine. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, J. Ayurveda research: Ontological challenges. J. Altern. Complementary Med. 2012, 3, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Pahwa, P. Prakriti and its associations with metabolism, chronic diseases, and genotypes: Possibilities of new born screening and a lifetime of personalized prevention. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2014, 5, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.D. Pharmacogenetics, pharmacogenomics and Ayurgenomics for personalized medicine: A paradigm shift. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Debnath, P.; Debnath, P.K. Ayurnutrigenomics: Ayurveda-inspired personalized nutrition from inception to evidence. J. Tradit. Complementary Med. 2015, 5, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasher, B.; Gibson, G.; Mukerji, M. Genomic insights into ayurvedic and western approaches to personalized medicine. J. Genet. 2016, 95, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukerji, M.; Prasher, B. Genomics and traditional Indian ayurvedic medicine. In Genomics and Society: Ethical, Legal, Cultural and Socioeconomic Implications; Kumar, D., Chadwick, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 271–292. [Google Scholar]
- Prasher, B.; Varma, B.; Kumar, A.; Khuntia, B.K.; Pandey, R.; Narang, A.; Tiwari, P.; Kutum, R.; Guin, D.; Kukreti, R.; et al. Ayurgenomics for stratified medicine: TRISUTRA consortium initiative across ethnically and geographically diverse Indian populations. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 197, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukerji, M.; Sagner, M. Genomics and Big Data Analytics in Ayurvedic Medicine. Prog. Prev. Med. 2019, 4, e0021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Kutum, R.; Sethi, T.; Shrivastava, A.; Girase, B.; Aggarwal, S.; Patil, R.; Agarwal, D.; Gautam, P.; Agrawal, A.; et al. Recapitulation of Ayurveda constitution types by machine learning of phenotypic traits. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasundar, R. If systems approach is the way forward, what can the Ayurvedic theory of Tridosha teach us? Curr. Sci. 2017, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Bhargava, S.; Ganeshan, S.; Kaur, R.; Sethi, T.; Sharma, M.; Chauhan, M.; Chauhan, N.; Chauhan, R.; Chauhan, P.; et al. Big Data Analysis of Traditional Knowledge-based Ayurveda Medicine. Prog. Prev. Med. 2018, 3, e0020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhande, S.; Salunkhe, P. Ayurgenomics. Inter. J. Res. Sci. Innov. 2018, V, 322–326. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Gehlot, S.; Agrawal, N.K. Basis of Disease Manifestation: A Molecular and Ayurvedic Approach with an Integrated Concept of Ayurgenomics. J. Nat. Remedies 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H. Ayurveda: Science of life, genetics, and epigenetics. Ayu 2016, 37, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemonnier, N.; Zhou, G.B.; Prasher, B.; Mukerji, M.; Chen, Z.; Brahmachari, S.K.; Noble, D.; Auffray, C.; Sagner, M. Traditional knowledge-basedmedicine: A review of history, principles, and relevance in the present context of P4 systems medicine. Prog. Prev. Med. 2017, 7, e0011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.; Heath, J.R.; Phelps, M.E.; Lin, B. Systems biology and new technologies enable predictive and preventative medicine. Science 2004, 306, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, A.D.; Hood, L. Systems biology, proteomics, and the future of healthcare: Toward predictive, preventative, and personalized medicine. J. Proteome Res. 2004, 3, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, L.; Balling, R.; Auffray, C. Revolutionizing medicine in the 21st century through systems approaches. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, M.; Glusman, G.; Brogaard, K.; Price, N.D.; Hood, L. P4 medicine: How systems medicine will transform the healthcare sector and society. Pers. Med. 2013, 10, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Prakriti Type | Gene Expression | Disease |
|---|---|---|
| Kapha/Vata | EGLN 1 higher | High Altitude Pulmonary Edema |
| Pitta | EGLN 1 lower | more adaptive for higher altitudes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wallace, R.K. Ayurgenomics and Modern Medicine. Medicina 2020, 56, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120661
Wallace RK. Ayurgenomics and Modern Medicine. Medicina. 2020; 56(12):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120661
Chicago/Turabian StyleWallace, Robert Keith. 2020. "Ayurgenomics and Modern Medicine" Medicina 56, no. 12: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120661
APA StyleWallace, R. K. (2020). Ayurgenomics and Modern Medicine. Medicina, 56(12), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120661





