Therapeutic Compliance of Patients with Arterial Hypertension in Primary Care
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
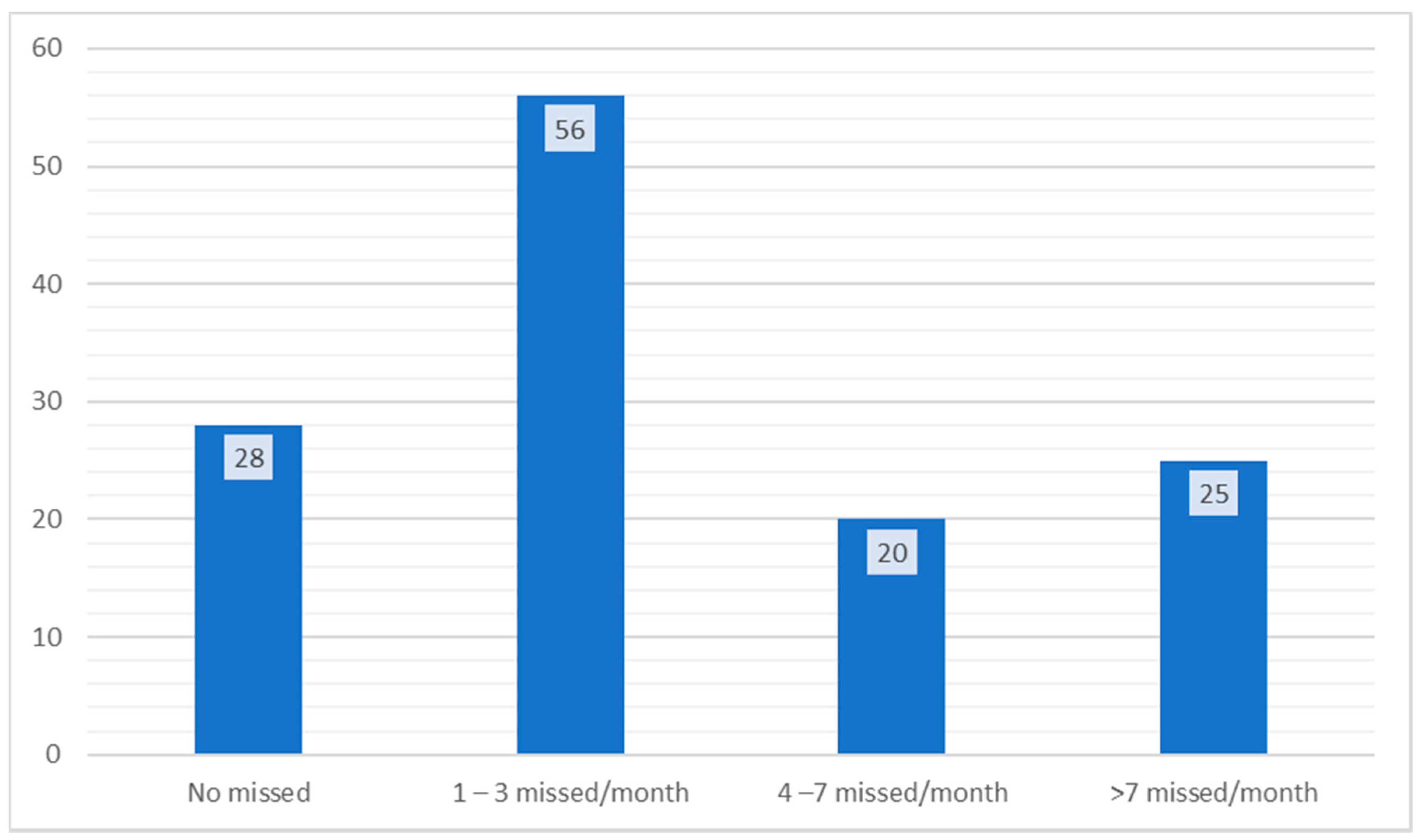
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Patients Survey
| First Name | ||||
| Last Name | ||||
| Age | ||||
| Gender | M | F | ||
| Environment | Rural | Urban | ||
| 1 | Your attending physician has diagnosed you with arterial hypertension. Are you aware of this diagnosis? | Yes | ||
| No | ||||
| 2 | What was the highest value of blood pressure you ever had measured? | |||
| 3 | Have you ever been diagnosed with diabetes? | Yes | What treatment are you following? | Diet |
| Antidiabetic oral drugs | ||||
| Insulin | ||||
| No | ||||
| 4 | Have you ever been diagnosed with dyslipidemia? (increased levels of fat in your blood—cholesterol or triglycerides? | Yes | ||
| No | ||||
| 5 | Are you a smoker? | Yes | How many cigarettes a day? | |
| For how many years? | ||||
| No | ||||
| 6 | Is there a history of early deaths (under 55–65 years) because of heart attack, stroke or sudden death in your family? | Yes | ||
| No | ||||
| 7 | Let’s go back to blood pressure. Are you aware of the consequences of untreated high blood pressure? | Yes | Can you name at least one? | |
| No | ||||
| 8 | What treatment are you following at home? | |||
| 9 | Over the course of a month, how often do you forget to take your medication? | Never | ||
| 1–3 times a month | ||||
| 4–7 times a month | ||||
| Over 7 times a month | ||||
| 10 | Do you strictly follow a low-sodium diet, which is specific for patients suffering from high blood pressure? | Never | ||
| Sometimes | ||||
| Often | ||||
| Always | ||||
| 11 | Presently, when you monitor your blood pressure values at home, what are the values? | |||
| 12 | Is your family supportive in maintaining the diet and following the treatment for your condition? | Yes | ||
| No | ||||
| It is not necessary | ||||
| 13 | For how long do you think you will have to follow the treatment for high blood pressure? | |||
| 14 | Apart from your general practitioner, is there any other doctor who periodically assesses your high blood pressure? | Yes | What is their medical specialty? | |
| No | ||||
| 15 | How many times a year do you visit a specialist physician? | Once a year | ||
| Twice a year | ||||
| ≥Three times a year | ||||
| 16 | What investigations have been done by the specialist physicians who is assessing your blood pressure? | Electrocardiogram | ||
| Cardiac ultrasound | ||||
| Doppler ultrasound of carotid and cerebral arteries | ||||
| Abdominal ultrasound | ||||
| Blood and urine tests | ||||
| Fundoscopy Exam | ||||
| Others | ||||
| 17 | Do you suffer from other diseases, other than the conditions mentioned above (high blood pressure, dyslipidemia, diabetes)? | |||
| 18 | If you were to rate your general state today from 1 to 10, how would you rate it? | |||
References
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Rosei, E.A.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.F.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, P.M.; Whelton, M.; Reynolds, K.; Muntner, P.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005, 365, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf-Maier, K.; Cooper, R.S.; Banegas, J.R.; Giampaoli, S.; Hense, H.-W.; Joffres, M.; Kastarinen, M.; Poulter, N.; Primatesta, P.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; et al. Hypertension Prevalence and Blood Pressure Levels in 6 European Countries, Canada, and the United States. JAMA 2003, 289, 2363–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusufali, A.; Hawken, S.; Ôunpuu, S.; Dans, T.; Avezum, A.; Lanas, F.; McQueen, M.B.; Budaj, A.; Pais, P.; Varigos, J.; et al. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): Case-control study. Lancet 2004, 364, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorobantu, M.; Tautu, O.-F.; Dimulescu, D.; Sinescu, C.; Gusbeth-Tatomir, P.; Arsenescu-Georgescu, C.; Mitu, F.; Lighezan, D.; Pop, C.; Babes, K.; et al. Perspectives on hypertension’s prevalence, treatment and control in a high cardiovascular risk East European country. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roșu, M.-M.; Moța, M. The Prevalence of Arterial Hypertension in Romanian Adult Population: Results from the Predatorr Study. Rom. J. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. Dis. 2018, 25, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Masi, S.; Wolf, J.; Schmieder, R.E. Facing the Challenge of Lowering Blood Pressure and Cholesterol in the Same Patient: Report of a Symposium at the European Society of Hypertension. Cardiol. Ther. 2020, 9, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omezzine, R.G.; Akkara, A.; Koubaa, A.A.; Sriha, A.B.; Rdissi, A.; Amamou, K. Predictors of Poor Adherence to Hypertension Treatment. Tunis. Med. 2019, 97, 564–571. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilova, A.; Bandere, D.; Rutkovska, I.; Smits, D.; Maurina, B.; Poplavska, E.; Urtāne, I. Knowledge about Disease, Medication Therapy, and Related Medication Adherence Levels among Patients with Hypertension. Medicina 2019, 55, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlou, D.I.; Paschou, S.A.; Anagnostis, P.; Spartalis, M.; Spartalis, E.; Vryonidou, A.; Tentolouris, N.; Siasos, G. Hypertension in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Targets and management. Maturitas 2018, 112, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkrishnan, R. The Importance of Medication Adherence in Improving Chronic-Disease Related Outcomes. Med. Care 2005, 43, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, H.R. Triple fixed-dose combination therapy: Back to the past. Hypertension 2009, 54, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmsmann, T.; Himmel, W. Comparison of therapy persistence for fixed versus free combination antihypertensives: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnier, M.; Egan, B.M. Adherence in Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1124–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.L.; Lennie, T.A.; Mudd-Martin, G.; Moser, D.K. Adherence to a Low-Sodium Diet in Patients With Heart Failure Is Best When Family Members Also Follow the Diet. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2015, 30, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diemer, F.S.; Snijder, M.B.; Agyemang, C.; Haan, Y.C.; Karamat, F.A.; Van Montfrans, G.A.; Oehlers, G.P.; Peters, R.J.G.; Brewster, L.M.; Stronks, K. Hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control in Surinamese living in Suriname and The Netherlands: The HELISUR and HELIUS studies. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2020, 15, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán-Tordecilla, D.N.; García, A.B.; Rodríguez, I. Interventions to increase the pharmacological adherence on arterial hypertension in Latin America: A systematic review. Int. J. Public Health 2020, 65, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.S.; Santos, P. Medication Adherence in Patients with Arterial Hypertension: The Relationship With Healthcare Systems’ Organizational Factors. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2019, 13, 1761–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, N.E.; Heredia, L.P.D. Validity and Reliability of the Treatment Adherence Questionnaire for Patients with Hypertension. Invest. Educ. Enferm. 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkareva, E.V.; Butina, E.K.; Kim, I.V.; Kontsevaya, A.V.; Drapkina, O.M.; Leon, D.; McKee, M. Adherence to antihypertensive medication in Russia: A scoping review of studies on levels, determinants and intervention strategies published between 2000 and 2017. Arch. Public Health 2019, 77, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzau, V.J.; Balatbat, C.A. Future of Hypertension. Hypertension 2019, 74, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorobantu, M.; Onciul, S.; Darabont, R.; Tautu, O.; Ghiorghe, S.; Vasilescu, M.; Manitiu, I.; Pop, C.; Lighezan, D.; Apetrei, E. Arterial hypertension epidemiology: Romania among the balkan countries–data from SEPHAR Surveys. Mod. Med. 2014, 21, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Diaconu, C.C.; Dediu, G.N.; Iancu, M.A. Drug-induced arterial hypertension–a frequently ignored cause of secondary hypertension: A review. Acta Cardiol. 2018, 73, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-C. Factors affecting therapeutic compliance: A review from the patient’s perspective. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almourani, R.; Chinnakotla, B.; Patel, R.; Kurukulasuriya, L.R.; Sowers, J. Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, D.I.; Guevara, S.L.R.; Sánchez, L.Z.R. Influential Factors in Adherence to the Therapeutic Regime in Hypertension and Diabetes. Invest. Educ. Enferm. 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korzh, O.; Krasnokutskiy, S.; Pankova, O. Improving the drug compliance of hypertensive patients in primary care: Importance of health education and self-management. Arch. Balk. Med. Union 2019, 54, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalva, C.M.; Alvarez-Muiño, X.L.L.; Mondelo, T.G.; Fachado, A.A.; Fernández, J.C. Adherence to Treatment in Hypertension. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 956, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.L.-T.; Abellán, G.B.; Hidalgo, M.R.L.-T.; García, R.M.M.; Martínez, C.L. Evaluation of satisfaction with pharmacological treatment in people with hypertension. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2019, 93, e201910080. [Google Scholar]
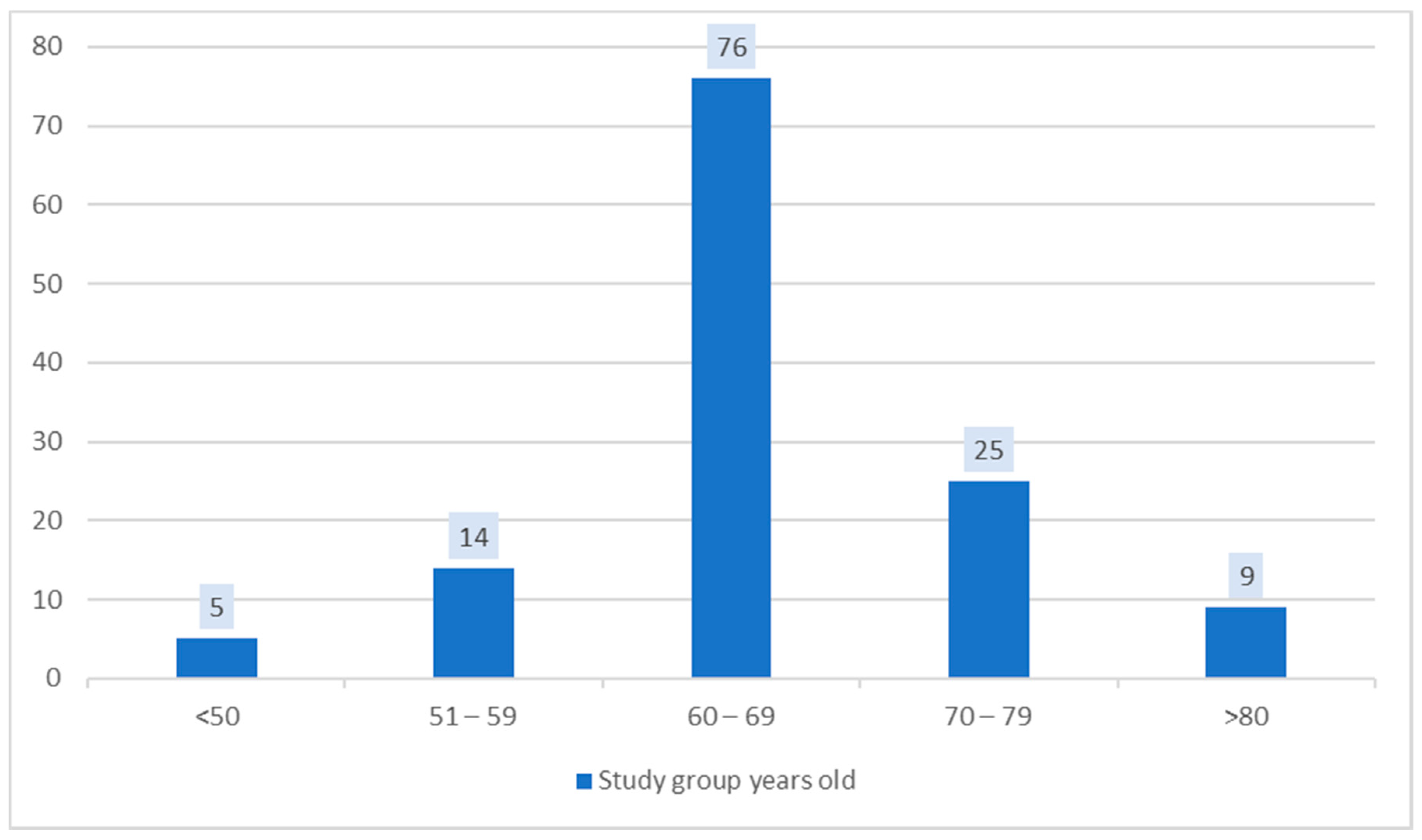
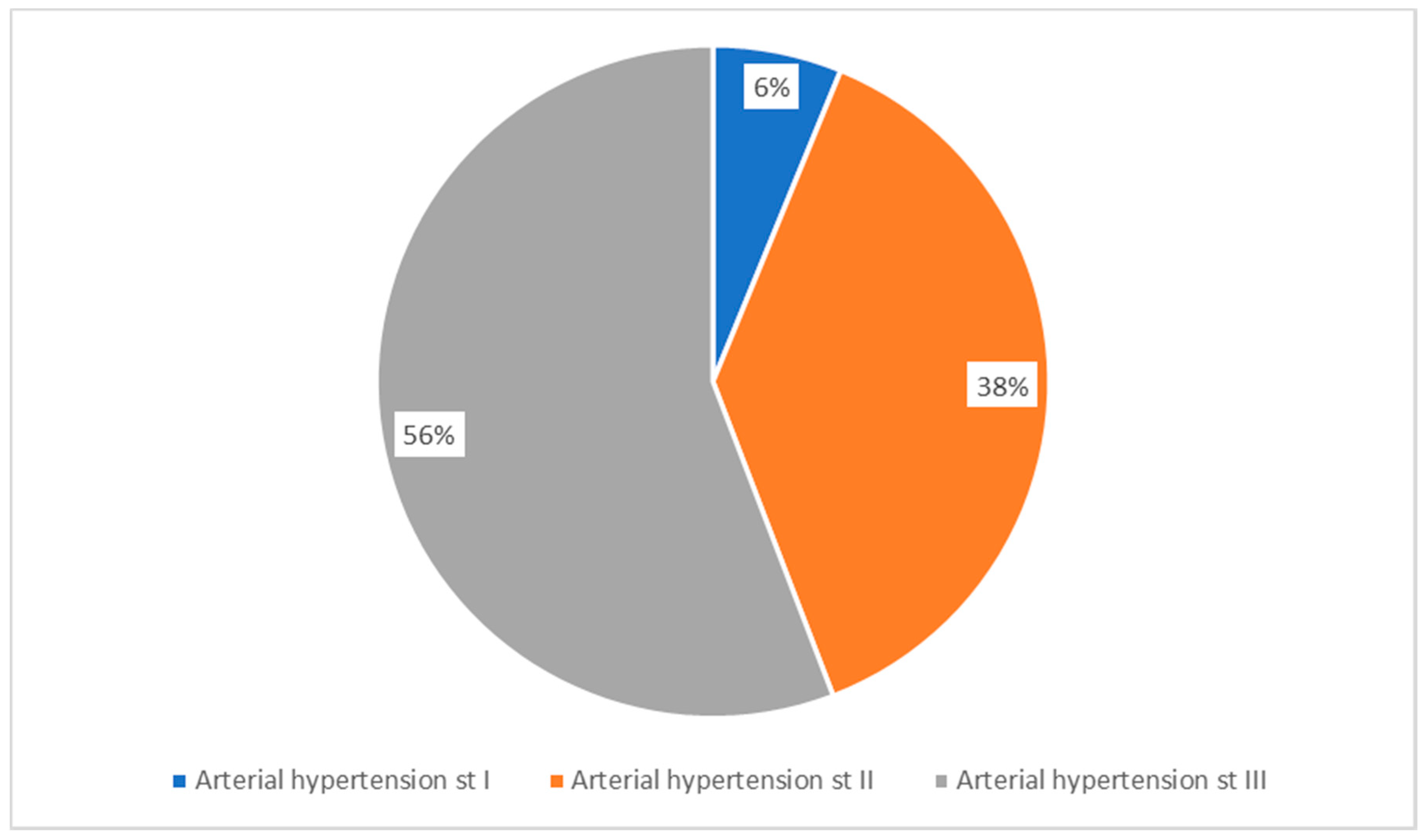
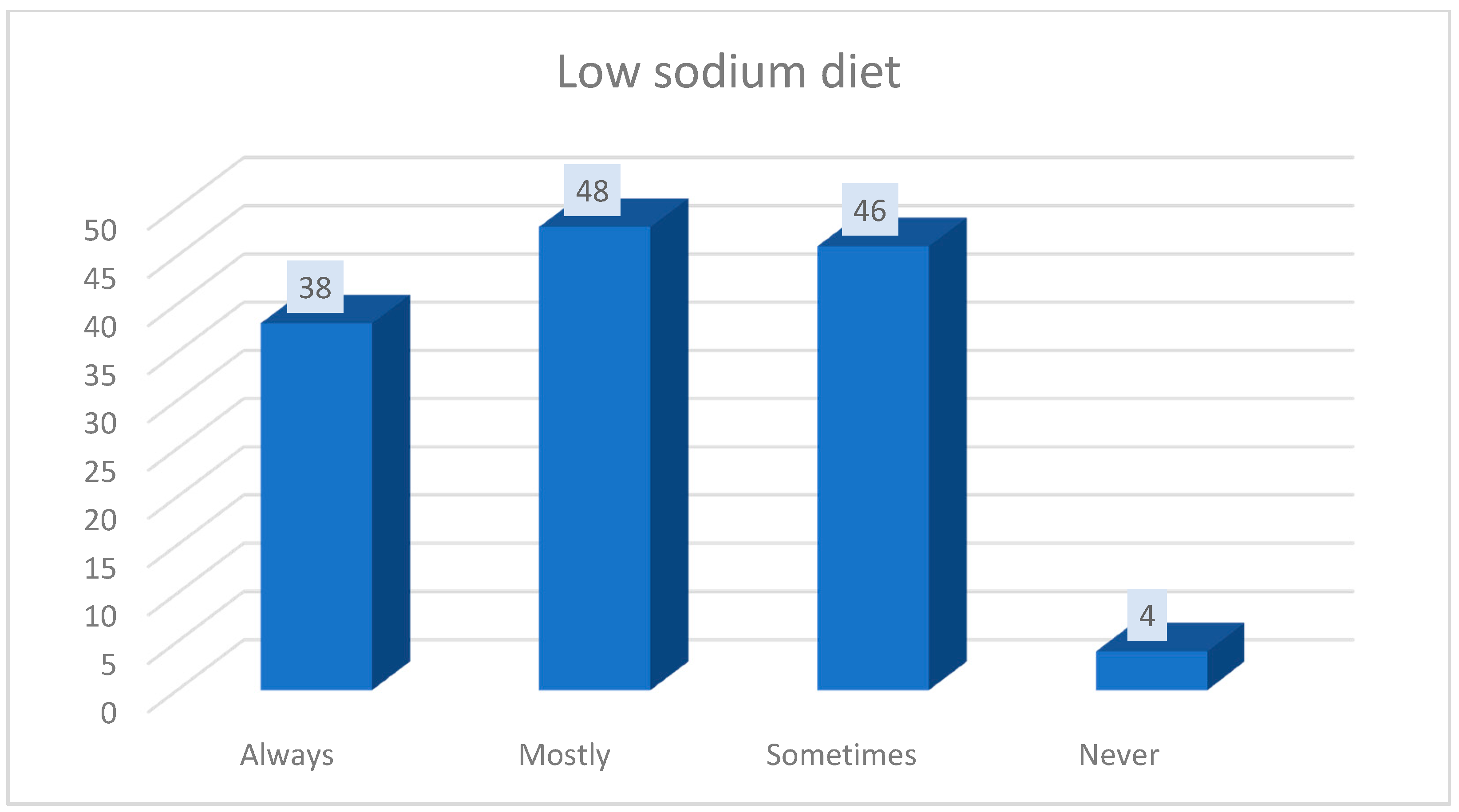
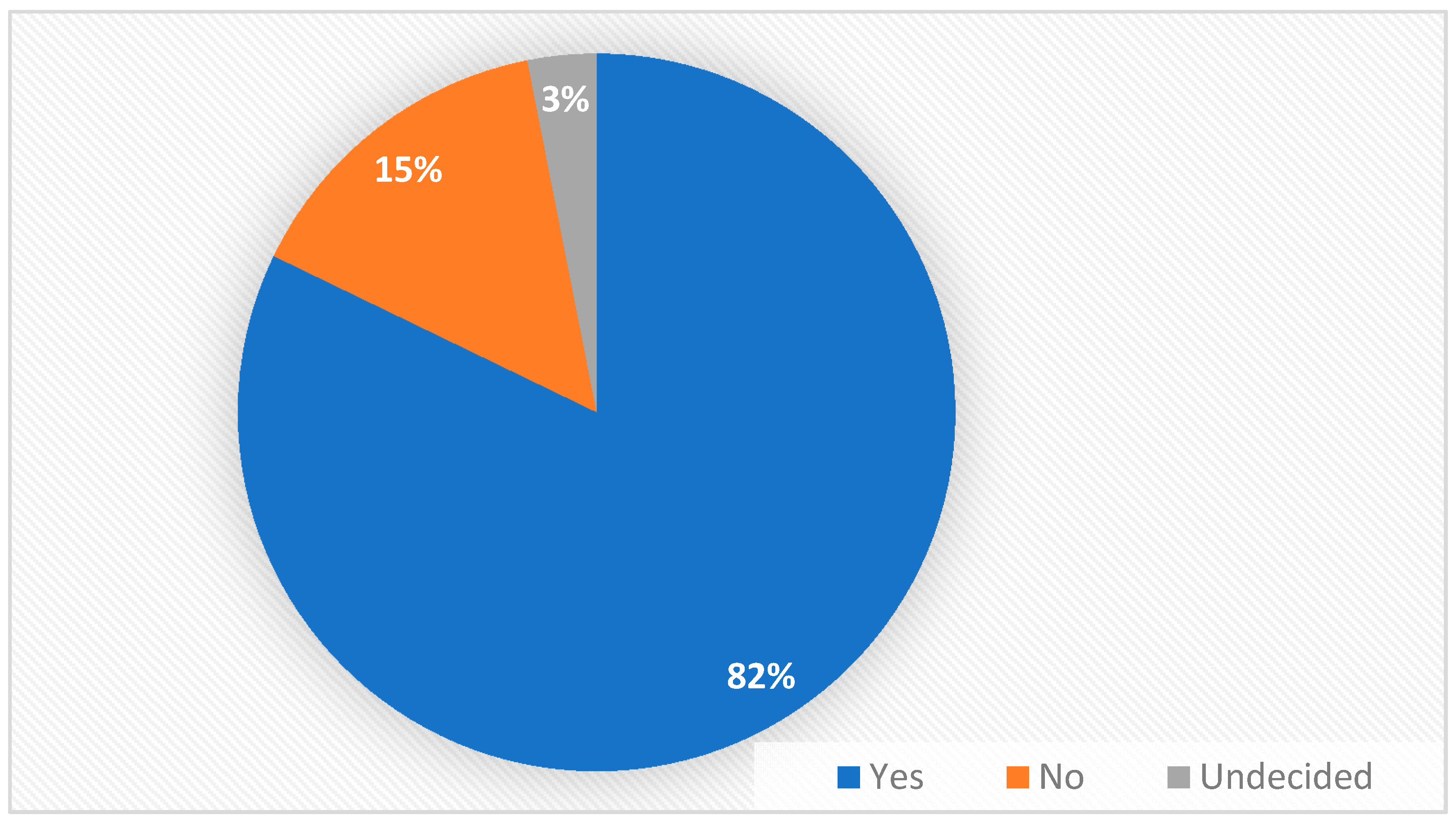
| Group Characteristics (n = 129) | |
|---|---|
| Gender | Female—65.89% (104) |
| Male—34.10% (44) | |
| Living environment | Urban—80.62% (104) |
| Rural—19.37 (25) | |
| Age (Mean age) = 66 ± 8 years | 43–81 years old |
| Weight Mean BMI = 28 ± 2.4 Kg/m2 | Normal weight—33.33% (43) |
| Overweight—55.81% (72) | |
| Obesity grade 1—10.85% (14) | |
| Smoking | Non-smokers—62.79% (81) |
| Smokers—23.25% (30) | |
| Ex-smokers—13.95% (18) | |
| Type II Diabetes | Yes—26.35% (34) |
| No—73.64% (95) | |
| Dyslipidemia | Mixed dyslipidemia—77.52% (100) |
| Hypercholesterolemia—15.50% (20) | |
| Hypertriglyceridemia—6.97% (9) | |
| Arterial Hypertension | Grade I—6.2% (8) |
| Grade II—37.98% (49) | |
| Grade III—55.81% (72) |
| Diabetes Mellitus | Dyslipidemia | Onset of Hypertension | Grade of Hypertension | Cardiologist Appointment | Comorbidities | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes mellitus | Pearson Correlation | 1 | 0.159 | 0.016 | −0.083 | 0.194 * | 0.044 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.072 | 0.857 | 0.353 | 0.028 | 0.620 | ||
| N | 129 | 129 | 129 | 129 | 128 | 129 | |
| Dyslipidemia | Pearson Correlation | 0.159 | 1 | 0.137 | 0.172 | 0.309 ** | 0.073 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.072 | 0.123 | 0.051 | 0.000 | 0.413 | ||
| N | 129 | 129 | 129 | 129 | 128 | 129 | |
| Onset of Hypertension | Pearson Correlation | 0.016 | 0.137 | 1 | 0.580 ** | 0.291 ** | 0.048 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.857 | 0.123 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.593 | ||
| N | 129 | 129 | 129 | 129 | 128 | 129 | |
| Grade of Hypertension | Pearson Correlation | –0.083 | 0.172 | 0.580 ** | 1 | 0.306 ** | 0.006 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.353 | 0.051 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.950 | ||
| N | 129 | 129 | 129 | 129 | 128 | 129 | |
| Cardiologist Appointment | Pearson Correlation | 0.194 * | 0.309 ** | 0.291 ** | 0.306 ** | 1 | 0.212 * |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.028 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.016 | ||
| N | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | |
| Comorbidities | Pearson Correlation | 0.044 | 0.073 | 0.048 | 0.006 | 0.212 * | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.620 | 0.413 | 0.593 | 0.950 | 0.016 | ||
| N | 129 | 129 | 129 | 129 | 128 | 129 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iancu, M.A.; Mateiciuc, I.-I.; Stanescu, A.-M.A.; Matei, D.; Diaconu, C.C. Therapeutic Compliance of Patients with Arterial Hypertension in Primary Care. Medicina 2020, 56, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56110631
Iancu MA, Mateiciuc I-I, Stanescu A-MA, Matei D, Diaconu CC. Therapeutic Compliance of Patients with Arterial Hypertension in Primary Care. Medicina. 2020; 56(11):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56110631
Chicago/Turabian StyleIancu, Mihaela Adela, Irina-Ioana Mateiciuc, Ana-Maria Alexandra Stanescu, Dumitru Matei, and Camelia Cristina Diaconu. 2020. "Therapeutic Compliance of Patients with Arterial Hypertension in Primary Care" Medicina 56, no. 11: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56110631
APA StyleIancu, M. A., Mateiciuc, I.-I., Stanescu, A.-M. A., Matei, D., & Diaconu, C. C. (2020). Therapeutic Compliance of Patients with Arterial Hypertension in Primary Care. Medicina, 56(11), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56110631








