Is Anticoagulation Necessary for Severely Disabled Cardioembolic Stroke Survivors?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
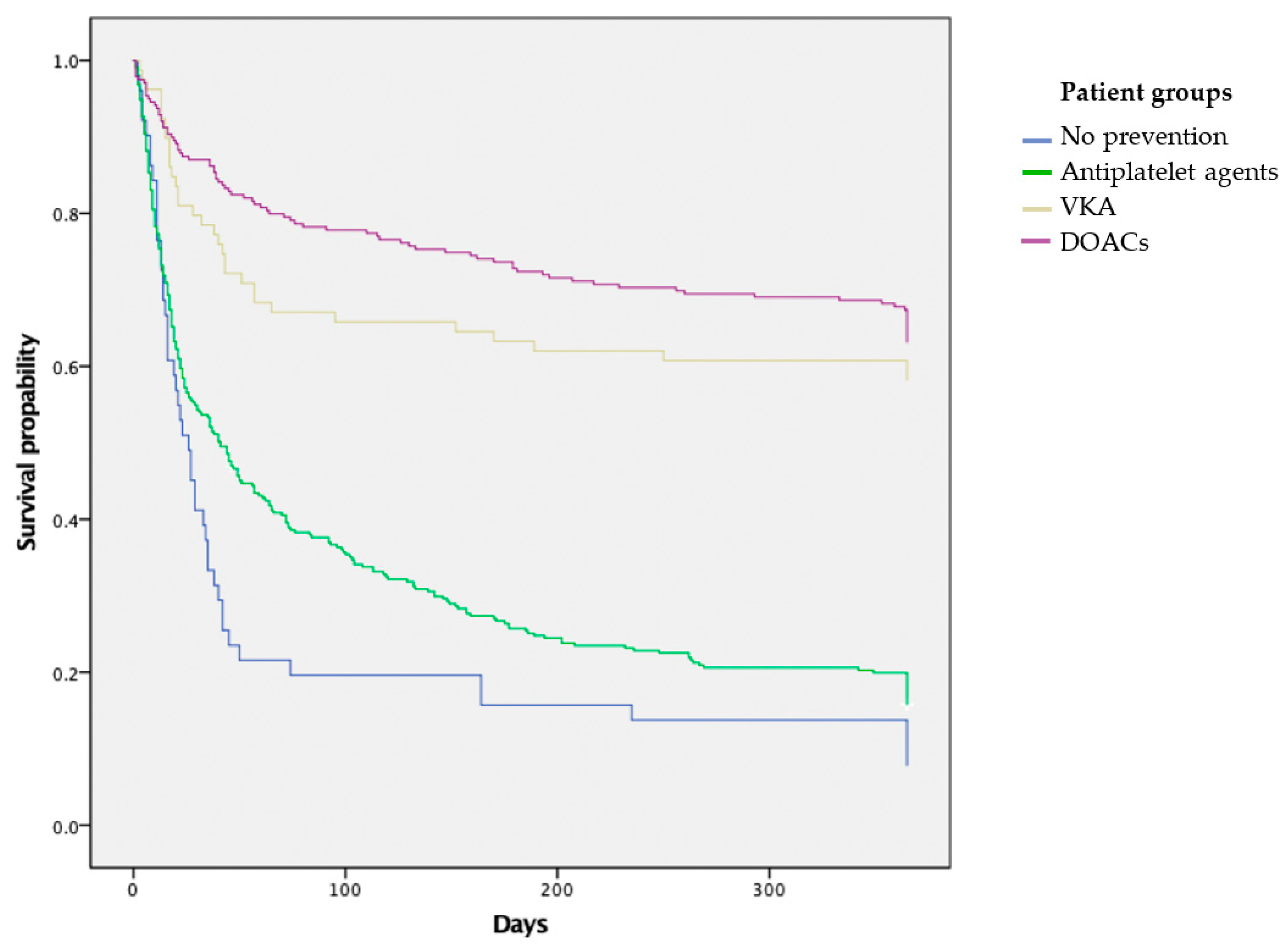
3.2. Survival Analysis
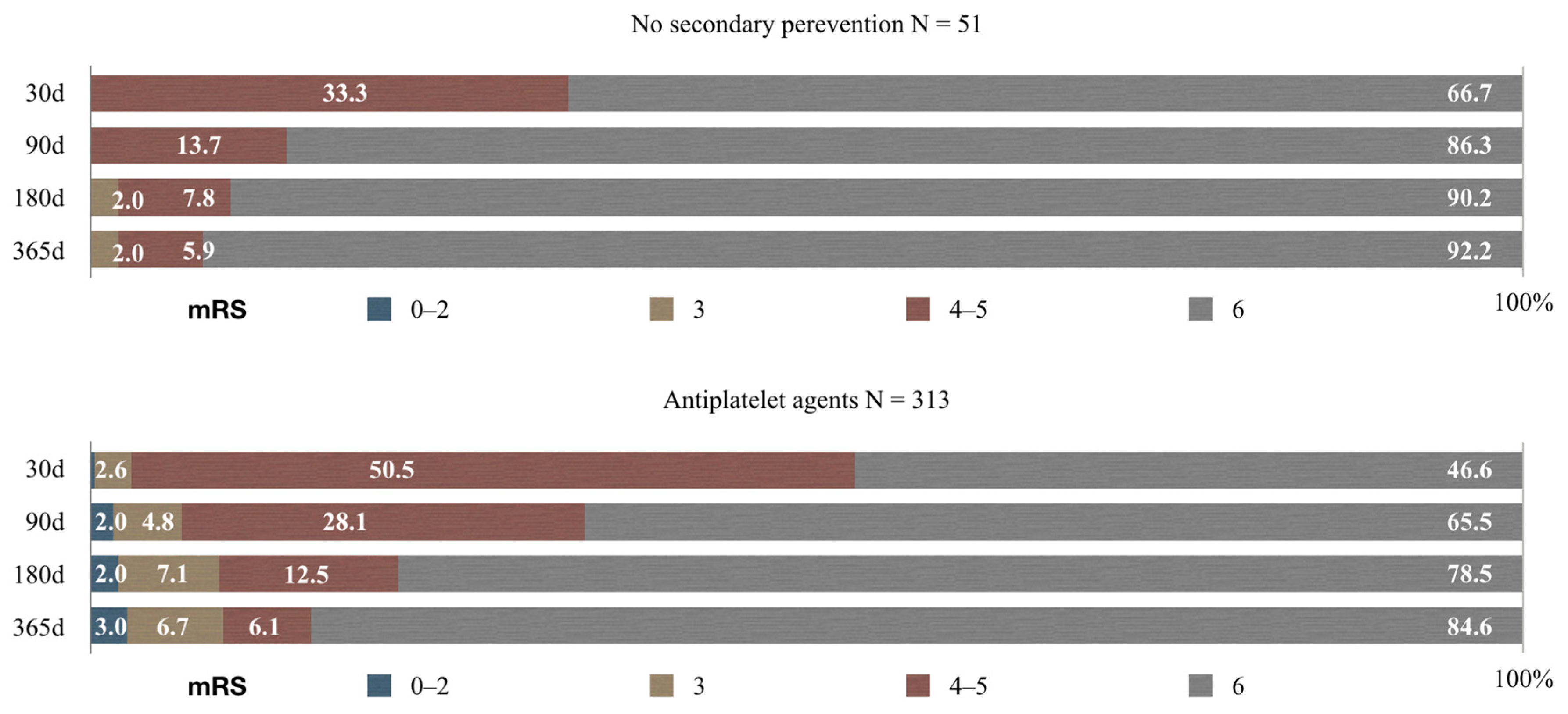
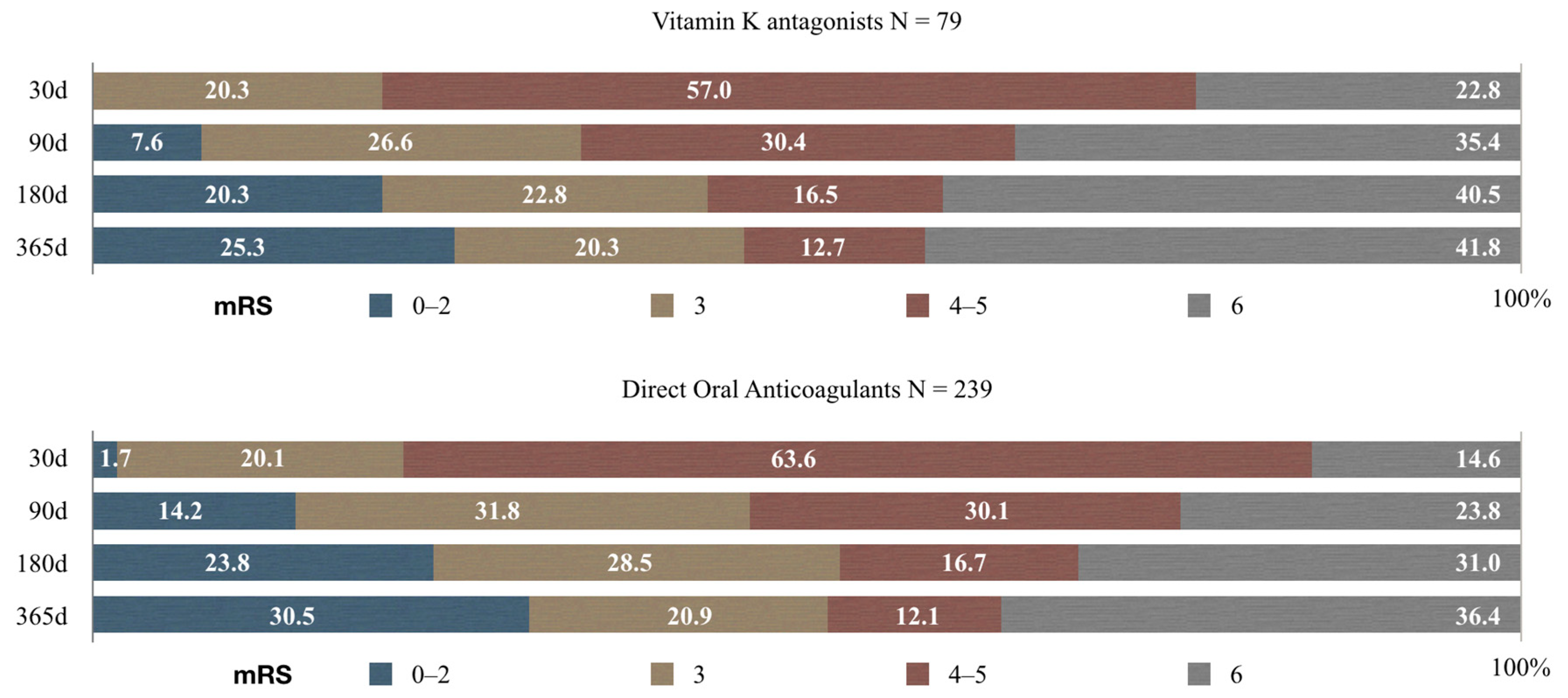
3.3. Functional Outcome Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, H.P.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E., 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogiatzi, C.; Hackam, D.G.; McLeod, A.I.; Spence, J.D. Secular trends in ischemic stroke subtypes and stroke risk factors. Stroke 2014, 45, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; Isasi, C.R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, H.; Healey, J.S. Cardioembolic Stroke. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, A.S.; Hylek, E.M.; Phillips, K.A.; Chang, Y.; Henault, L.E.; Selby, J.V.; Singer, D.E. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: National implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: The AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA 2001, 285, 2370–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katan, M.; Luft, A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Norrving, B.; Mensah, G.A. Global Burden of Stroke. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.I.; Hart, R.; Pearce, L.A. Oral anticoagulants versus antiplatelet therapy for preventing stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and no history of stroke or transient ischemic attacks. Cochrane Database. Syst. Rev. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Grisoglio, E.; Brunetti, E.; Falcone, Y.; Marchionni, N. Oral anticoagulant therapy for older patients with atrial fibrillation: A review of current evidence. Eur. J. Int. Med. 2017, 41, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.; Hoh, B. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018, 49, e46–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, I.; Kashif, T.; Ahmed, M.M.; Sohail, W.; Sarwar, M.; Khokhar, I. Dual or Mono Antiplatelet Therapy for the Prevention of Ischemic Stroke: A Literature Review. Cureus 2018, 10, e2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melon, P.; Lancellotti, P. 2010 European guidelines for antithrombotic therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation and new risk score for the assessment of the risk of bleeding. Rev. Med. Liege 2010, 65, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jurjāns, K.; Noviks, I.; Volčeka, D.; Zandersone, L.; Meilerte, K.; Miglāne, E.; Stepens, A.; Millers, A. The adaption and evaluation of a Latvian version of the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.D.; Starkman, S.; Hamilton, S.; Craig, S.; Grace, A.; Conwit, R.; Saver, J.L. The Rankin Focused Assessment-Ambulation: A Method to Score the Modified Rankin Scale with Emphasis on Walking Ability. J. Stroke Cereb. Dis. 2016, 25, 2172–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulter, G.; Steen, C.; De Keyser, J. Use of the Barthel index and modified Rankin scale in acute stroke trials. Stroke 1999, 30, 1538–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topcuoglu, M.A.; Liu, L.; Kim, D.E.; Gurol, M.E. Updates on Prevention of Cardioembolic Strokes. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, J.D. Cardioembolic stroke: Everything has changed. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2018, 3, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurjans, K. Problems of cardioembolic stroke primary and secondary prevention in Latvian population. Proc. Latvian Acad. Sci. Sect. B Nat. Exact Appl. Sci. 2015, 69, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Elina, P. Cardioembolic Stroke in Latvia: Prevention and Long-Term Outcome. In CBU International Conference on Innovations in Science and Education; Petr Hájek, T.S., Jones, M.-A., Eds.; Central Bohemia University: Prague, Czech Republic, 2016; pp. 615–621. [Google Scholar]
- GBD 2016 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 439–458. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiar de Sousa, D.; von Martial, R.; Abilleira, S.; Gattringer, T.; Kobayashi, A.; Gallofré, M.; Fazekas, F.; Szikora, I.; Feigin, V.; Caso, V.; et al. Access to and delivery of acute ischaemic stroke treatments: A survey of national scientific societies and stroke experts in 44 European countries. Eur. Stroke J. 2019, 4, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, E.R.; Kapral, M.K.; Fang, J.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Conghaile, A.; Conghaile, A.; Canavan, M.; O’Donnell, M.J. Antithrombotic therapy after acute ischemic stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Stroke 2014, 45, 3637–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamassa, M.; Di Carlo, A.; Pracucci, G.; Basile, A.M.; Trefoloni, G.; Vanni, P.; Spolveri, S.; Baruffi, M.C.; Landini, G.; Ghetti, A.; et al. Characteristics, outcome, and care of stroke associated with atrial fibrillation in Europe: Data from a multicenter multinational hospital-based registry (The European Community Stroke Project). Stroke 2001, 32, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, R.D.; Shah, B.R.; Olson, D.M.; Zhao, X.; Pan, W.; Bushnell, C.D.; Peterson, E.D. Antithrombotic therapy use at discharge and 1 year in patients with atrial fibrillation and acute stroke: Results from the AVAIL Registry. Stroke 2011, 42, 3477–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fang, M.C.; Go, A.S.; Chang, Y.; Borowsky, L.H.; Pomernacki, N.K.; Udaltsova, N.; Singer, D.E. Thirty-day mortality after ischemic stroke and intracranial hemorrhage in patients with atrial fibrillation on and off anticoagulants. Stroke 2012, 43, 1795–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arauz, A.; Ruiz-Navarro, F.; Barboza, M.A.; Ruiz, A.; Colin, J.; Reyes, M.; Silos, H.; Cantu-Brito, C.; Murillo-Bonilla, L.; Barinagarrementeria, F. Outcome, Recurrence and Mortality after Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation Stroke: Long-Term Follow-Up Study. J. Vasc. Int. Neurol. 2017, 9, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Casciano, J.P.; Singer, D.E.; Kwong, W.J.; Fox, E.S.; Martin, B.C. Anticoagulation therapy for patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: Comparison of decision analytic model recommendations and real-world warfarin prescription use. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2012, 12, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.C.; Go, A.S.; Chang, Y.; Borowsky, L.H.; Pomernacki, N.K.; Udaltsova, N.; Singer, D.E. Long-term survival after ischemic stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Neurology 2014, 82, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marijon, E.; Le Heuzey, J.Y.; Connolly, S.; Yang, S.; Pogue, J.; Brueckmann, M.; Eikelboom, J.; Themeles, E.; Ezekowitz, M.; Wallentin, L.; et al. Response to letter regarding article, “Causes of death and influencing factors in patients with atrial fibrillation: A competing-risk analysis from the randomized evaluation of long-term anticoagulant therapy study”. Circulation 2014, 130, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijon, E.; Le Heuzey, J.Y.; Connolly, S.; Yang, S.; Pogue, J.; Brueckmann, M.; Eikelboom, J.; Themeles, E.; Ezekowitz, M.; Wallentin, L.; et al. Causes of death and influencing factors in patients with atrial fibrillation: A competing-risk analysis from the randomized evaluation of long-term anticoagulant therapy study. Circulation 2013, 128, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, N.L.; Nagel, V.; Conforto, A.B.; Magalhaes, P.S.; Venancio, V.G.; Safanelli, J.; Ibiapina, F.; Mazin, S.; França, P.; Liberato, R.M.; et al. High five-year mortality rates of ischemic stroke subtypes: A prospective cohort study in Brazil. Int. J. Stroke 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, G.; Marott, J.L.; Grønbaek, M.; Hassanpour, H.; Truelsen, T. Long-term survival after stroke: 30 years of follow-up in a cohort, the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Neuroepidemiology 2009, 33, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelros, P.; Nydevik, I.; Viitanen, M. Poor outcome after first-ever stroke: Predictors for death, dependency, and recurrent stroke within the first year. Stroke 2003, 34, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sennfält, S.; Norrving, B.; Petersson, J.; Ullberg, T. Long-Term Survival and Function After Stroke. Stroke 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullberg, T.; Zia, E.; Petersson, J.; Norrving, B. Changes in functional outcome over the first year after stroke: An observational study from the Swedish stroke register. Stroke 2015, 46, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Barker-Collo, S.; Parag, V.; Senior, H.; Lawes, C.M.; Ratnasabapathy, Y.; Glen, E.; ASTRO Study Group. Auckland Stroke Outcomes Study. Part 1: Gender, stroke types, ethnicity, and functional outcomes 5 years poststroke. Neurology 2010, 75, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halkes, P.H.; van Gijn, J.; Kappelle, L.J.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Algra, A. Classification of cause of death after stroke in clinical research. Stroke 2006, 37, 1521–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No Prophylaxis N = 51 (7.5%) | Antiplatelet Agents N = 313 (45.9%) | VKA N = 79 (11.6%) | DOACs N = 234 (35%) | Total N = 682 (%) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average age (IQR 1) | 83 (IQR = 74–86) | 83 (IQR = 77–87) | 78 (IQR = 72–84) | 78 (IQR = 72–84) | 80 (IQR = 75–85) | <0.005 |
| ≥70 years old | 45 (88.2%) | 295 (94.2%) | 64 (81%) | 198 (84.6%) | 602 (88.3%) | <0.005 |
| Hypertension | 44 (86.3%) | 287 (91.7%) | 66 (83.5%) | 209 (89.3%) | 606 (88.9%) | 0.131 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 4 (7.8%) | 42 (13.1%) | 12 (15.2%) | 36 (15.4%) | 94 (13.8%) | 0.570 |
| Dyslipidemia | 38 (74.5%) | 237 (75.7%) | 61 (77.2%) | 188 (80.3%) | 524 (76.8%) | 0.843 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 10 (19.6%) | 52 (16.6%) | 15 (19%) | 47 (20.1%) | 124 (18.2%) | 0.807 |
| Congenital heart disease | 31 (60.8%) | 205 (65.5%) | 46 (58.2%) | 140 (59.8%) | 422 (61.9%) | 0.346 |
| History of stroke or TIA | 21 (41.2%) | 118 (37.7%) | 30 (38%) | 86 (36.8%) | 255 (36.4%) | 0.910 |
| CHA2DS2-VASc score | ||||||
| 0–3 (low and moderate risk) | 2 (3.9%) | 5 (1.6%) | 6 (7.6%) | 9 (3.8%) | 22 (3.2%) | 0.51 |
| >3 (severe risk) | 49 (96.1%) | 308 (98.4%) | 73 (92.4%) | 230 (96.2%) | 660 (96.8%) | 0.51 |
| HAS-BLED score | ||||||
| 0–3 (low bleeding risk) | 35 (68.6%) | 202 (64.5%) | 57 (72.2%) | 173 (73.9%) | 467 (68.5%) | 0.218 |
| >3 (high bleeding risk) | 16 (31.4%) | 111 (35.5%) | 22 (27.8%) | 66 (26.1%) | 215 (31.5%) | 0.218 |
| LV-NIHSS on admission | 15 (IQR = 11–20) | 15 (IQR = 9–19) | 10 (IQR = 6–15) | 13 (IQR = 7–17) | 14 (IQR = 8–18) | <0.005 |
| LV-NIHSS on discharge | 13 (IQR = 7–16) | 12 (IQR = 6–17) | 6 (IQR = 6–10) | 8 (IQR = 4–14) | 10 (IQR = 5–16) | <0.005 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jurjans, K.; Vikmane, B.; Vetra, J.; Miglane, E.; Kalejs, O.; Priede, Z.; Millers, A. Is Anticoagulation Necessary for Severely Disabled Cardioembolic Stroke Survivors? Medicina 2019, 55, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55090586
Jurjans K, Vikmane B, Vetra J, Miglane E, Kalejs O, Priede Z, Millers A. Is Anticoagulation Necessary for Severely Disabled Cardioembolic Stroke Survivors? Medicina. 2019; 55(9):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55090586
Chicago/Turabian StyleJurjans, Kristaps, Baiba Vikmane, Janis Vetra, Evija Miglane, Oskars Kalejs, Zanda Priede, and Andrejs Millers. 2019. "Is Anticoagulation Necessary for Severely Disabled Cardioembolic Stroke Survivors?" Medicina 55, no. 9: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55090586
APA StyleJurjans, K., Vikmane, B., Vetra, J., Miglane, E., Kalejs, O., Priede, Z., & Millers, A. (2019). Is Anticoagulation Necessary for Severely Disabled Cardioembolic Stroke Survivors? Medicina, 55(9), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55090586






