Involvement of the Interleukin-23/Interleukin-17 Axis in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Its Treatment Responses
Abstract
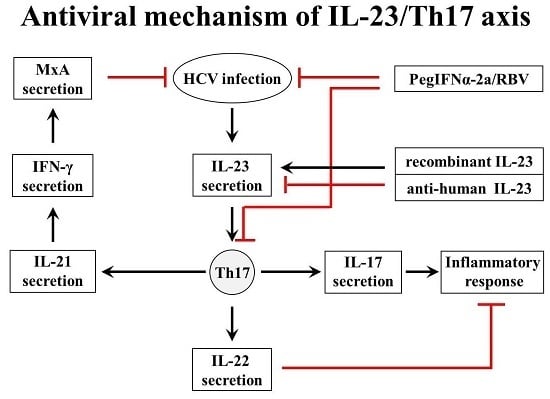
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Treatment Responses of IFN/RBV Therapy
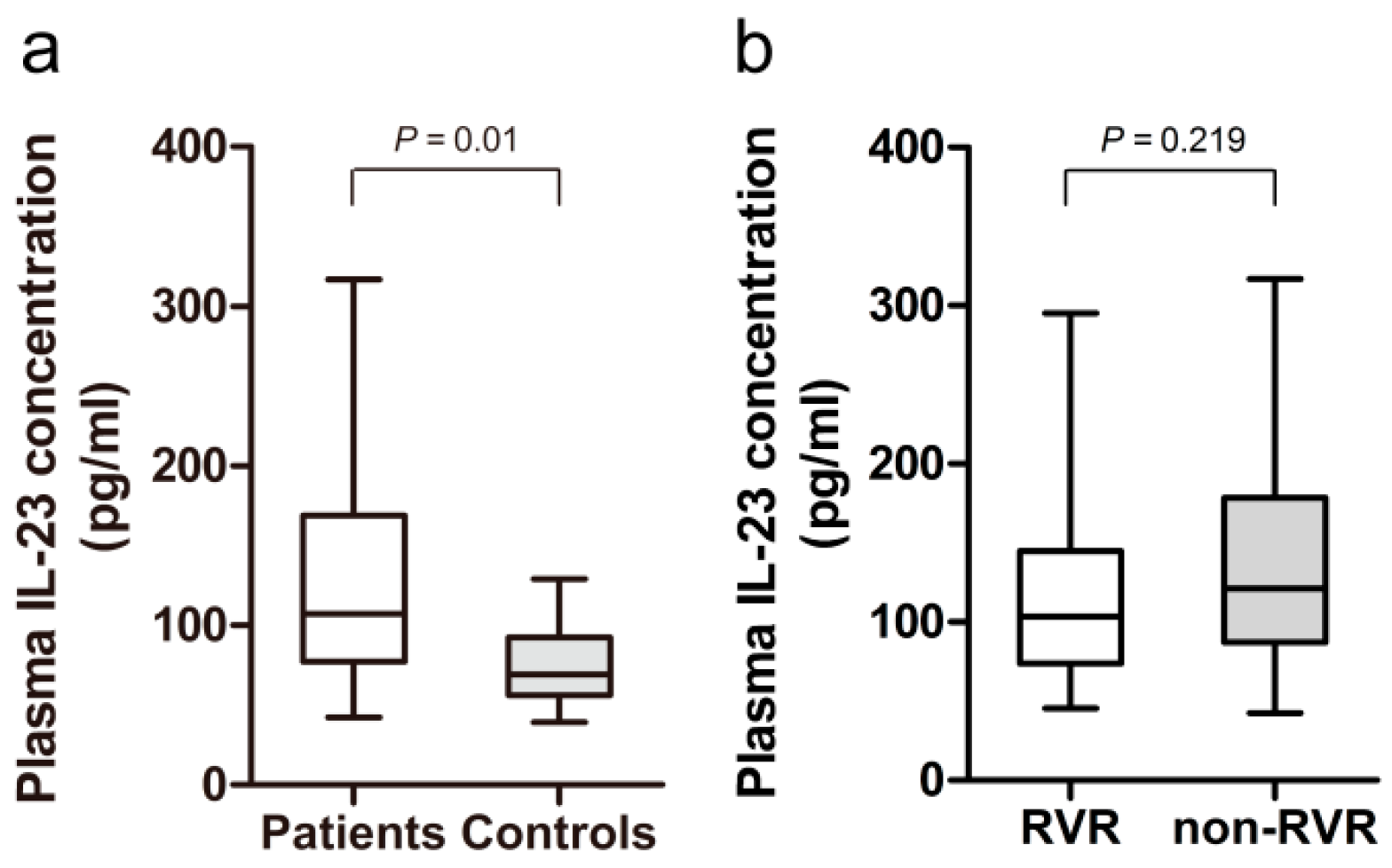
2.2. Increased Plasma Level of IL-23 in HCV-Infected Patients
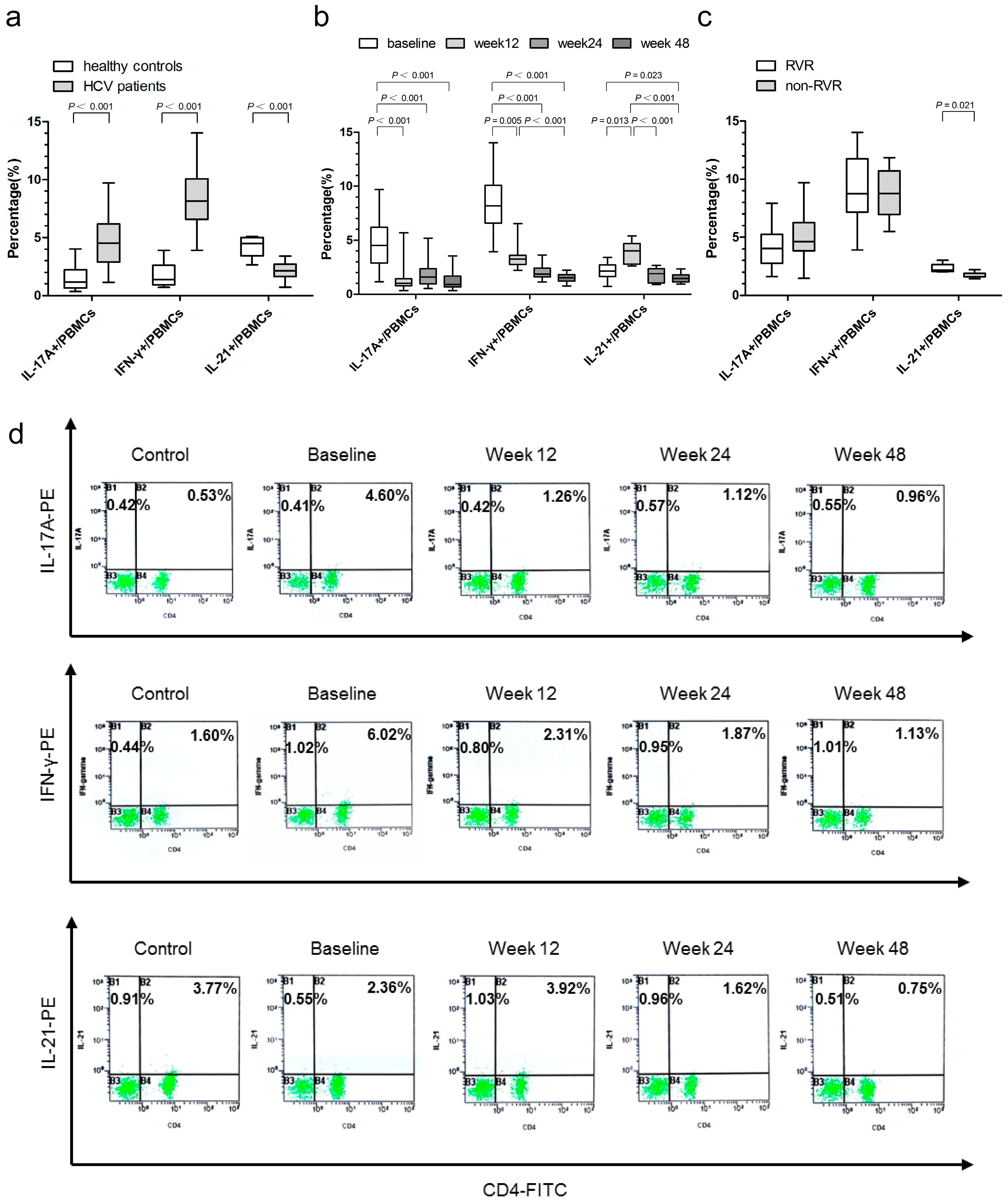
2.3. Associations of IL-17A-, IFN-γ-, and IL-21-Producing Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) with Virological Responses
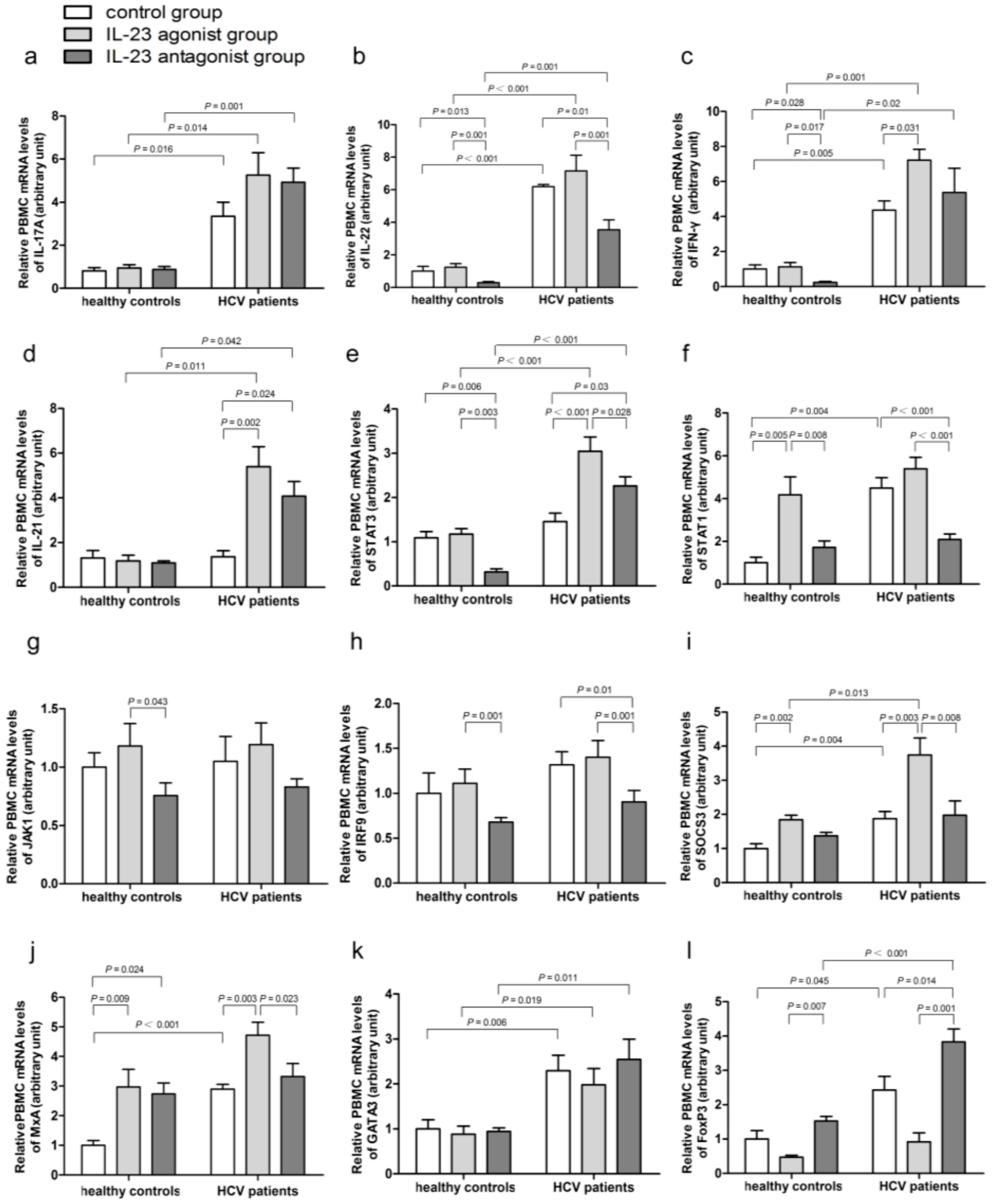
2.4. Impact of IL-23 on the Expression of Th17 Cells Related Immune Molecules
2.5. IL-23 Regulates the mRNA Expressions of SOCS3 and MxA
2.6. IL-23 Alters the mRNA Expressions of the CD4+ T-Cells Transcription Factors
2.7. Low Baseline Serum Viral Load May Be a Useful Predictor for Treatment Response in Patients Undertaking PegIFN-α Plus RBV Therapy
2.8. Relationship between the Proportion of IL-17A-, IFN-γ-, and IL-21-Producing PBMCs and HCV Genotypes, Baseline Viral Load, ALT, and AST
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Detection of HCV Antibody, Viral Load, and Genotypes of HCV
4.3. Biochemical Assays
4.4. Detection of Plasma IL-23
4.5. Antiviral Treatments and Assessments of Virological Responses
4.6. Measurement of IL-17A-, IFN-γ-, and IL-21-Producing PBMCs by Flow Cytometry
4.7. PBMC Isolation and Culture
4.8. Analysis of mRNA Expression in PBMCs by qRT-PCR
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FoxP3 | forkhead box P3 |
| GATA3 | GATA binding protein 3 |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| IL-23 | Interleukin-23 |
| MxA | myxovirus resistance protein A |
| PBMC | peripheral blood mononuclear cell |
| SOCS3 | suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 |
| STAT1 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 |
| T-bet | T-box expressed in T cells |
References
- Mohd Hanafiah, K.; Groeger, J.; Flaxman, A.D.; Wiersma, S.T. Global epidemiology of hepatitis c virus infection: New estimates of age-specific antibody to hcv seroprevalence. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.J.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhao, P.; Qi, Z.T. Entry inhibitors: New advances in hcv treatment. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2016, 5, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolucci, S.; Fiorina, L.; Mariani, B.; Landini, V.; Gulminetti, R.; Novati, S.; Maserati, R.; Barbarini, G.; Bruno, R.; Baldanti, F. Development and persistence of DAA resistance associated mutations in patients failing HCV treatment. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 72, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for Study of Liver. EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C 2015. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 199–236. [Google Scholar]
- AASLD/IDSA HCV Guidance Panel. Hepatitis C guidance: AASLD-IDSA recommendations for testing, managing, and treating adults infected with hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 2015, 62, 932–954. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, Y.M.; Zheng, H.W.; Sun, D.X.; An, C.M.; Li, Y.S.; Kong, L.; Dai, E.H.; Zhang, Y.G.; Zhao, S.X.; Su, S.S.; et al. Study of using an individualized treatment strategy to treat patients with chronic hepatitis C. Chin. J. Hepatol. 2013, 21, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Grakoui, A.; Shoukry, N.H.; Woollard, D.J.; Han, J.H.; Hanson, H.L.; Ghrayeb, J.; Murthy, K.K.; Rice, C.M.; Walker, C.M. HCV persistence and immune evasion in the absence of memory T cell help. Science 2003, 302, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoukry, N.H.; Grakoui, A.; Houghton, M.; Chien, D.Y.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Walker, C.M. Memory CD8+ T cells are required for protection from persistent hepatitis C virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulsenheimer, A.; Gerlach, J.T.; Gruener, N.H.; Jung, M.C.; Schirren, C.A.; Schraut, W.; Zachoval, R.; Pape, G.R.; Diepolder, H.M. Detection of functionally altered hepatitis C virus-specific CD4 T cells in acute and chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.M. Immunopathogenesis of hepatitis C virus infection. Clin. Liver Dis. 2003, 7, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, F.; Zou, Z.S.; Xu, R.N.; Jin, L.; Fu, J.L.; Shi, F.; Shi, M.; Wang, H.F.; et al. Interleukin-17-producing CD4(+) T cells increase with severity of liver damage in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2010, 51, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, N.J.; Boniface, K.; Chan, J.R.; McKenzie, B.S.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Mattson, J.D.; Basham, B.; Smith, K.; Chen, T.; Morel, F.; et al. Development, cytokine profile and function of human interleukin 17-producing helper T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; van Velkinburgh, J.C.; Ni, B.; Wu, Y. Pivotal roles of the interleukin-23/T helper 17 cell axis in hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Tian, Z.; Tang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Jia, Z.; Tang, Y.; et al. Hepatitis B virus induces IL-23 production in antigen presenting cells and causes liver damage via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.H.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, T. Changes to the migratory inhibitory factor, IL-17, and IL-10 levels in serum from chronic hepatitis B patients and clinical significance following baraclude® treatment. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 3362–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.J.; Yu, X.P.; Guo, R.Y.; Ming, D.S.; Huang, L.Y.; Su, M.L.; Deng, Y.; Lin, Z.Z. Changes in the balance between treg and Th17 cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 76, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafi Hafez, A.; Ahmadi Vasmehjani, A.; Baharlou, R.; Mousavi Nasab, S.D.; Davami, M.H.; Najafi, A.; Joharinia, N.; Rezanezhad, H.; Ahmadi, N.A.; Imanzad, M. Analytical assessment of interleukin-23 and -27 cytokines in healthy people and patients with hepatitis C virus infection (genotypes 1 and 3a). Hepat. Mon. 2014, 14, e21000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.M.; Shi, L.; Ma, C.J.; Ji, X.J.; Ying, R.S.; Wu, X.Y.; Wang, K.S.; Li, G.; Moorman, J.P.; Yao, Z.Q. Differential regulation of interleukin-12 (IL-12)/IL-23 by tim-3 drives T(h)17 cell development during hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4372–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Tang, Y.; You, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liang, S.; Han, X.; Qiu, D.; Wei, J.; Liu, Y.; Shen, L.; et al. Interleukin-17 contributes to the pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis through inducing hepatic interleukin-6 expression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happel, K.I.; Dubin, P.J.; Zheng, M.; Ghilardi, N.; Lockhart, C.; Quinton, L.J.; Odden, A.R.; Shellito, J.E.; Bagby, G.J.; Nelson, S.; et al. Divergent roles of IL-23 and IL-12 in host defense against klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante-Duarte, C.; Horton, H.F.; Byrne, M.C.; Kamradt, T. Microbial lipopeptides induce the production of IL-17 in Th cells. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 6107–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Na, L.; Fidel, P.L.; Schwarzenberger, P. Requirement of interleukin-17A for systemic anti-candida albicans host defense in mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaraa, R.; Mareckova, H.; Urbanek, P.; Fucikova, T. T helper, cytotoxic T lymphocyte, NK cell and NK-T cell subpopulations in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Folia Microbiol. 2002, 47, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, Y.; Nabeshima, S.; Furusyo, N.; Sawayama, Y.; Hayashi, J.; Kashiwagi, S. Increased frequency of interferon-gamma-producing peripheral blood CD4+ T cells in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Nagai, H.; Sumino, Y.; Miki, K. Relationship of peripheral blood CD4-positive T cells to carcinogenesis in patients with HCV-related chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2008, 62, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Sousa, M.A.; Almansa, R.; de la Fuente, C.; Caro-Paton, A.; Ruiz, L.; Sanchez-Antolin, G.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Aller, R.; Alcaide, N.; Largo, P.; et al. Increased Th1, Th17 and pro-fibrotic responses in hepatitis C-infected patients are down-regulated after 12 weeks of treatment with pegylated interferon plus ribavirin. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2010, 21, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fathy, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Metwally, L.; Hassan, A. T helper type 1/T helper type 17-related cytokines in chronic hepatitis C patients before and after interferon and ribavirin therapy. Med. Princ. Pract. 2011, 20, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish-Novak, J.; Dillon, S.R.; Nelson, A.; Hammond, A.; Sprecher, C.; Gross, J.A.; Johnston, J.; Madden, K.; Xu, W.; West, J.; et al. Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature 2000, 408, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zeng, Q.L.; Jin, L.; Fu, J.; Yang, B.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, T.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; et al. HCV-specific interleukin-21+CD4+ T cells responses associated with viral control through the modulation of HCV-specific CD8+ T cells function in chronic hepatitis C patients. Mol. Cells 2013, 36, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, J.J.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Mechanism of action of interferon and ribavirin in treatment of hepatitis C. Nature 2005, 436, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.W.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.Y.; Tang, L.B.; Sun, X.F.; Jiang, X.T.; Zhang, Y.X.; Sun, J.; Liu, Z.H.; Abbott, W.G.; et al. High serum IL-21 levels after 12 weeks of antiviral therapy predict HBeAg seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.S.; Hsu, S.J.; Liu, W.L.; Chen, C.L.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S.; Kao, J.H. IL-21R gene polymorphisms and serum IL-21 levels predict virological response to interferon-based therapy in asian chronic hepatitis C patients. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, E.; Witte, K.; Warszawska, K.; Sabat, R.; Wolk, K. Interleukin-22: A cytokine produced by T, NK and NKT cell subsets, with importance in the innate immune defense and tissue protection. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Laurence, A.; Elias, K.M.; O’Shea, J.J. IL-21 is produced by Th17 cells and drives IL-17 production in a STAT3-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34605–34610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strengell, M.; Sareneva, T.; Foster, D.; Julkunen, I.; Matikainen, S. IL-21 up-regulates the expression of genes associated with innate immunity and Th1 response. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 3600–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.; Jyothi Prasanna, S.; Chandrasekar, B.; Nandi, D. Gene modulation and immunoregulatory roles of interferon gamma. Cytokine 2010, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, K.; Hertzog, P.J.; Ravasi, T.; Hume, D.A. Interferon-γ: An overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Laurence, A.; Kanno, Y.; Pacher-Zavisin, M.; Zhu, B.M.; Tato, C.; Yoshimura, A.; Hennighausen, L.; O’Shea, J.J. Selective regulatory function of SOCS3 in the formation of IL-17-secreting T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8137–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, A.S.; Ahmed, S.; Napoletano, S.; Schroeder, M.; Johnston, J.A.; Hegarty, J.E.; O’Farrelly, C.; Stevenson, N.J. Hepatitis C virus (HCV)-induced suppressor of cytokine signaling (Socs) 3 regulates proinflammatory TNF-alpha responses. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2014, 96, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatto, L.; Berlato, C.; Poli, V.; Tininini, S.; Kinjyo, I.; Yoshimura, A.; Cassatella, M.A.; Bazzoni, F. Analysis of Socs-3 promoter responses to interferon gamma. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 13746–13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staeheli, P.; Pitossi, F.; Pavlovic, J. Mx proteins: Gtpases with antiviral activity. Trends Cell Biol. 1993, 3, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, O.; Ahmed, A.; Doss, W.; Abdel-Hamid, M. MxA expression as marker for assessing the therapeutic response in HCV genotype 4 Egyptian patients. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, V.; Mihm, S.; Ramadori, G. MxA gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients infected chronically with hepatitis C virus treated with interferon-alpha. J. Med. Virol. 2000, 62, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestreich, K.J.; Weinmann, A.S. Encoding stability versus flexibility: Lessons learned from examining epigenetics in T helper cell differentiation. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 356, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Zhou, Y.; He, Y.; Fan, C.; Sun, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, L.; Peng, M.; Wang, P.; Lian, J.; et al. Imbalance of regulatory T cells and T helper type 17 cells in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Immunology 2014, 143, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapero-Marugan, M.; Garcia-Buey, L.; Munoz, C.; Quintana, N.E.; Moreno-Monteagudo, J.A.; Borque, M.J.; Fernandez, M.J.; Salvanes, F.R.; Medina, J.; Moreno-Otero, R. Sustained virological response to peginterferon plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 patients is associated with a persistent Th1 immune response. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteleone, G.; Pallone, F.; MacDonald, T.T. Interleukin-21: A critical regulator of the balance between effector and regulatory T-cell responses. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Q.; Wang, Y.K.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, C.Z.; Hu, Y.Z.; Wu, B.Y. Th17 cells are increased with severity of liver inflammation in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Saadany, S.; Ziada, D.H.; El Bassat, H.; Farrag, W.; El-Serogy, H.; Eid, M.; Abdallah, M.; Ghazy, M.; Salem, H.A. The role of hepatic expression of stat1, SOCS3 and Pias1 in the response of chronic hepatitis C patients to therapy. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, e13–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihm, S.; Frese, M.; Meier, V.; Wietzke-Braun, P.; Scharf, J.G.; Bartenschlager, R.; Ramadori, G. Interferon type I gene expression in chronic hepatitis C. Lab. Investig. 2004, 84, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, C.; Li, H.; Li, W.; Jin, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, P.; Wei, L.; et al. Up-regulation of interleukin-22 mediates liver fibrosis via activating hepatic stellate cells in patients with hepatitis C. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 158, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoras Eda, S.; Gomes, S.T.; Freitas, F.B.; Santana, B.B.; Ishak, G.; Ferreira de Araujo, M.T.; Demachki, S.; Conde, S.R.; Ishak Mde, O.; Ishak, R.; et al. Intrahepatic mRNA expression of FAS, FASL, and FOXP3 genes is associated with the pathophysiology of chronic HCV infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for Study of Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatitis C virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 392–420. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Hou, J.L. The guideline of prevention and treatment for hepatitis C: A 2015 Update. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2015, 23, 906–923. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.H.; Yang, H.L.; Wei, M.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, C.R.; Shi, Y.L.; Ma, W.L. Preparation and application of oligo microarrays for hepatitis virus detection and genotyping. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2007, 15, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Parameter | HCV Patients (n = 66) | Healthy Controls (n = 20) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (M/F) | 28/38 | 8/12 | 0.774 |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 49.2 ± 10.8 | 45.9 ± 9.37 | 0.367 |
| BMI (mean ± SD, kg/m2) | 25.1 ± 3.1 | 23.8 ± 2.1 | 0.105 |
| ALT (IU/L), median (range) | 48 (15–239) | 19 (9–35) | 0.000 |
| AST (IU/L), median (range) | 39 (15–188) | 21 (14–41) | 0.000 |
| HCV RNA (median/range, log10 IU/mL) | 6.26/2.29–7.84 | n.d. | |
| Possible Route of Contamination | |||
| Transfusion, n (%) | 39 (59.09) | -- | |
| Previous surgery, n (%) | 21 (31.82) | -- | |
| Others or unknown, n (%) | 6 (9.09) | -- | |
| HCV genotypes (1b/2a) | 39/15 | -- | |
| Gene | Product Length | Primer Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| IL-17A | 154 bp | F 5′-AACCGATCCACCTCACCTTG-3′ |
| R 5′-TCTCTTGCTGGATGGGGACA-3′ | ||
| IL-21 | 101 bp | F 5′-CAAATCAAGCTCCCAAGGTC-3′ |
| R 5′-CAGGGACCAAGTCATTCACA-3′ | ||
| IL-22 | 114 bp | F 5′-TATATCACCAACCGCACCTTC-3′ |
| R 5′-GCGCTCACTCATACTGACTCC-3′ | ||
| IFN-γ | 101 bp | F 5′-TTGGGTTCTCTTGGCTGT-3′ |
| R 5′-CCATTATCCGCTACATCTGAA-3′ | ||
| JAK1 | 101 bp | F 5′-GGATTGCTCCTGAGTGTGTTG-3′ |
| R 5′-CTCGCCATTGTAGCAGATTTC-3′ | ||
| STAT1 | 151 bp | F 5′-CACCCAAAGTATCAGGACGAG-3′ |
| R 5′-CGTTCCTACGTCAAGCAGTTC-3′ | ||
| STAT3 | 109 bp | F 5′-TTTATCAGTAAGGAGCGGGA-3′ |
| R 5′-CCCAAGTGAAAGTGACGC-3′ | ||
| IRF9 | 105 bp | F 5′-CACACGATTGACCTGTCCTCT-3′ |
| R 5′-TTAGCCTTGAGTTCTCCACCA-3′ | ||
| MxA | 102 bp | F 5′-GCATCCCACCCTCTATTACTG-3′ |
| R 5′-CACCTTCTCCTCATACTGGCT-3′ | ||
| T-bet | 104 bp | F 5′-TCGTTGGCATGTGTGTTAATC-3′ |
| R 5′-TGTCCAAAGTCAGGTGAGTCC-3′ | ||
| GATA3 | 100 bp | F 5′-AAGCCTAAACGCGATGGATA-3′ |
| R 5′-AGTGGTTGGAACACAGACACC-3′ | ||
| FoxP3 | 122 bp | F 5′-TCCCAGAGTTCCTCCACAAC-3′ |
| R 5′-ATTGAGTGTCCGCTGCTTCT-3′ | ||
| SOCS3 | 114 bp | F 5′-AGGAGACGGGACATCTTTCAC-3′ |
| R 5′-ATGGGACAGGGAGCATTTAAG-3′ |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, P.; Zhao, S.; Niu, X.; Fu, N.; Su, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Nan, Y. Involvement of the Interleukin-23/Interleukin-17 Axis in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Its Treatment Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071070
Meng P, Zhao S, Niu X, Fu N, Su S, Wang R, Zhang Y, Qiao L, Nan Y. Involvement of the Interleukin-23/Interleukin-17 Axis in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Its Treatment Responses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(7):1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071070
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Ping, Suxian Zhao, Xuemin Niu, Na Fu, Shanshan Su, Rongqi Wang, Yuguo Zhang, Liang Qiao, and Yuemin Nan. 2016. "Involvement of the Interleukin-23/Interleukin-17 Axis in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Its Treatment Responses" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 7: 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071070
APA StyleMeng, P., Zhao, S., Niu, X., Fu, N., Su, S., Wang, R., Zhang, Y., Qiao, L., & Nan, Y. (2016). Involvement of the Interleukin-23/Interleukin-17 Axis in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Its Treatment Responses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(7), 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071070