B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Child with Down Syndrome and High-Risk Genomic Lesions
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Background of ALL
1.2. Molecular Diagnostics in Risk Stratification
1.3. Down Syndrome as a Distinct High-Risk Subgroup
1.4. Molecular Landscape of DS-ALL
1.5. iAMP21 in DS-ALL
1.6. Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) in DS-ALL Management
1.7. Multidisciplinary Supportive Care
1.8. Emerging Therapies in DS-ALL
1.9. Case as a Bridge to the Review
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review Strategy
2.2. Diagnostic, Immunophenotypic, and Genomic Procedures
2.3. Ethical Considerations
2.4. Statistical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Presentation and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Genomic Profile
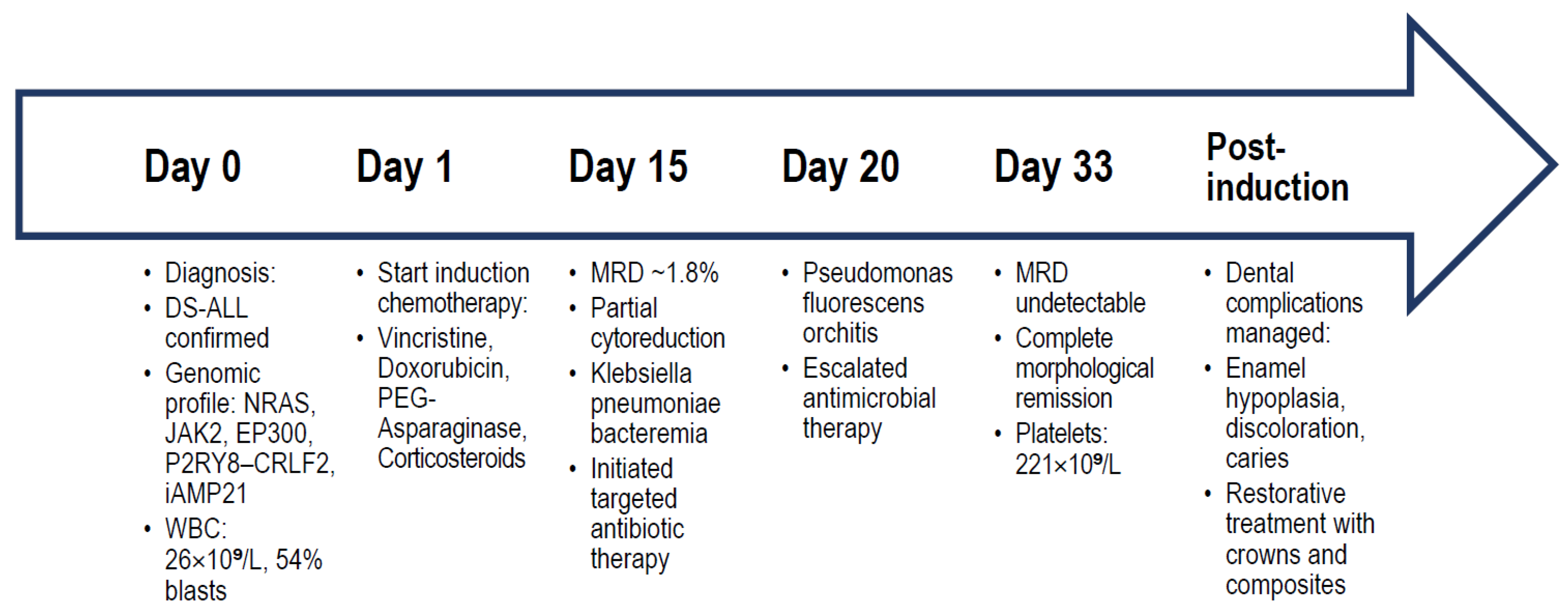
3.3. Induction Therapy and Early Treatment Response
- Day 15: MRD ~1.8%, indicating partial cytoreduction.
- Day 33: Complete morphological remission with undetectable MRD; platelet recovery to 221 × 109/L; hemoglobin stable at 9.7 g/dL.
3.4. Infectious Complications and Supportive Measures
- Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infection, managed with broad-spectrum antibiotics tailored to sensitivity testing.
- Pseudomonas fluorescens orchitis, required escalated targeted therapy.
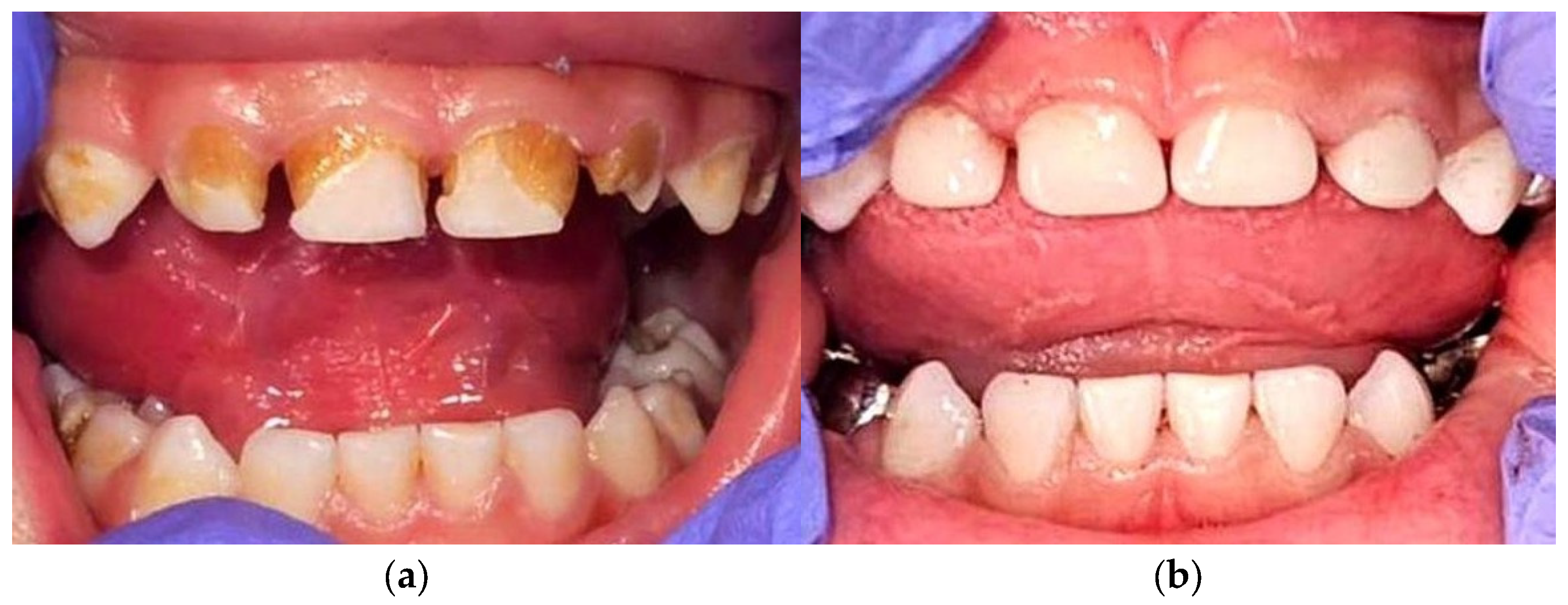
3.5. Dental Complications and Interdisciplinary Care
3.6. Case Report Highlights
- To our knowledge, the first pediatric DS-ALL case documented with five concurrent high-risk genomic lesions (NRAS p.G13D, JAK2 p.R683G, EP300 p.Q1766*, P2RY8–CRLF2 fusion, and iAMP21).
- Early MRD-negative remission was achieved by Day 33 despite an aggressive genomic profile.
- Severe infectious complications (Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia and Pseudomonas fluorescens orchitis) were successfully managed with targeted antimicrobials and protective isolation.
- Chemotherapy-exacerbated dental pathology (enamel hypoplasia, discoloration, and caries) reported and managed with restorative interventions—first DS-ALL case to detail this complication.
- Multidisciplinary care (cardiology-guided chemotherapy, structured dental interventions, and DS-specific infection prophylaxis) ensured treatment continuity and reduced morbidity.
4. Discussion
4.1. Integration of Previous Genomic and Clinical Studies (2007–2025)
4.2. NRAS p.G13D in the Context of DS-ALL and Other Disorders
4.3. Early Intensification and Supportive Care
4.4. Management of Comorbidities
4.5. Molecular Targets and Future Therapies
4.6. Limitations
4.7. Outcomes of Current Protocols in DS-ALL
4.8. Key Findings
5. Suggestions for Future Research
- -
- Advanced molecular profiling to define risk stratification and support earlier integration of targeted therapies;
- -
- Evaluation of integrated care models to assess the impact of multidisciplinary coordination on survival and treatment tolerance;
- -
- Prospective studies on oral health interventions aimed at reducing complications and improving the quality of life in patients with DS-ALL.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALL | acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| DS | Down syndrome |
| JAK2 | Janus kinase 2 |
| NRAS | neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog |
| EP300 | E1A-binding protein p300 |
| CRLF2 | cytokine receptor-like factor 2 |
| iAMP21 | intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21 |
| MRD | minimal residual disease |
| B-ALL | B-cell ALL |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| AML | megakaryoblastic leukemia |
| P2RY8-CRLF2 | receptor P2Y, G protein-coupled, 8–CRLF2 |
| FISH | fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| WBC | white blood cell count |
| Hb | hemoglobin |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| PDA | patent ductus arteriosus |
| PLT | platelet count |
| HDAC | histone deacetylase |
| TSLPR | thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor |
| VDLP | Vincristine, Daunorubicin, L-asparaginase, Prednisone |
| MTX | Methotrexate |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
References
- Mullighan, C.G. Molecular genetics of B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3407–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A.; Farber, I.M.; Kheiri, S. Global incidence and mortality of childhood leukemia and its relationship with the Human Development Index. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Alecsa, M.S.; Popescu, R.; Starcea, M.I.; Mocanu, A.M.; Rusu, C.; Miron, I.C. Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Emerging Therapies—From Pathway to Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aureli, A.; Marziani, B.; Venditti, A.; Sconocchia, T.; Sconocchia, G. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Immunotherapy Treatment: Now, Next, and Beyond. Cancers 2023, 15, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliaro, L.; Chen, S.J.; Herranz, D.; Mecucci, C.; Harrison, C.J.; Mullighan, C.G.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.; Boissel, N.; Winter, S.S.; et al. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment (PDQ®): Health professional version. In PDQ Cancer Information Summaries; National Cancer Institute (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK65763/ (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Brown, P.A.; Shah, B.; Advani, A.; Aoun, P.; Boyer, M.W.; Burke, P.W.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Dinner, S.; Fathi, A.T.; Gauthier, J.; et al. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, version 2.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, N.R.; Cahill, H.; Diamond, Y.; McCleary, K.; Kotecha, R.S.; Marshall, G.M.; Mateos, M.K. Down syndrome-associated leukaemias: Current evidence and challenges. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2024, 15, 20406207241257901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.G.; Mullighan, C.G. Genomic and epigenomic insights into acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Bülbül, H.; Kaya, Ö.Ö.; Karadağ, F.K.; Olgun, A.; Demirci, Z.; Ceylan, C. Prognostic impact of next-generation sequencing on myelodysplastic syndrome: A single-center experience. Medicine 2024, 103, e39909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, S.; Chaudhary, P.; Ahmad, F.; Arora, N. Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Next-Generation Sequencing Panels for Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Review. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 46, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongen, J.J.; van der Velden, V.H.; Brüggemann, M.; Orfao, A. Minimal residual disease diagnostics in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Need for sensitive, fast, and standardized technologies. Blood 2015, 125, 3996–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, U.; Dey, A.; Chandel, A.K.S.; Sanyal, R.; Mishra, A.; Pandey, D.K.; De Falco, V.; Upadhyay, A.; Kandimalla, R.; Chaudhary, A.; et al. Cancer chemotherapy and beyond: Current status, drug candidates, associated risks and progress in targeted therapeutics. Genes Dis. 2022, 10, 1367–1401, Correction in Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 101211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chea, M.; Rigolot, L.; Canali, A.; Vergez, F. Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Old and New Concepts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasaart, K.A.L.; Bertrums, E.J.M.; Manders, F.; Goemans, B.F.; van Boxtel, R. Increased risk of leukaemia in children with Down syndrome: A somatic evolutionary view. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2021, 23, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, G.; Skladzien, E.; Buckley, F.; Skotko, B.G. Estimation of the number of people with Down syndrome in Australia and New Zealand. Genet. Med. 2022, 24, 2568–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruchel, A.; Bourquin, J.P.; Crispino, J.; Cuartero, S.; Hasle, H.; Hitzler, J.; Klusmann, J.H.; Izraeli, S.; Lane, A.A.; Malinge, S.; et al. Down syndrome and leukemia: From basic mechanisms to clinical advances. Haematologica 2023, 108, 2570–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, A.M.; Ahmad, F.; Bhat, A.; Aein, Q.-U.; Ahmad, A.; Reshi, A.A.; Kaul, R.-U.-R. Unraveling Down Syndrome: From Genetic Anomaly to Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Diagnosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, S.E.; Skotko, B.G.; Rafii, M.S.; Strydom, A.; Pape, S.E.; Bianchi, D.W.; Sherman, S.L.; Reeves, R.H. Down syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, F.; Bokhari, S.R.A. Down Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526016/ (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Hasle, H.; Clemmensen, I.H.; Mikkelsen, M. Risks of leukaemia and solid tumors in individuals with Down’s syndrome. Lancet 2000, 355, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasle, H. Pattern of malignant disorders in individuals with Down syndrome. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, e174–e185. [Google Scholar]
- Freedman, M.H.; Cohen, A.; Grunberger, T.; Lange, B.J.; Liu, W.; Sather, H.N.; Heerema, N.A. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children with Down syndrome. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 1993, 10, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, V.; Devidas, M.; Chen, Z.B.; Carroll, A.J.; Heerema, N.A.; Borowitz, M.J.; Wood, B.L.; Carroll, W.L.; Winick, N.J.; Raetz, E.A.; et al. Patients with Down Syndrome and High-Risk B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Demonstrate Improved Outcomes on a Modified Chemotherapy Regimen: A Report from Children’s Oncology Group Study AALL1131. Blood 2023, 142, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabin, K.R.; Devidas, M.; Chen, Z.; Ji, L.; Kairalla, J.; Hitzler, J.K.; Yang, J.J.; Carroll, A.J.; Heerema, N.A.; Borowitz, M.J.; et al. Outcomes in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults with Down Syndrome and ALL: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamil, V.I.; Downing, K.F.; Oster, M.E.; Andrews, J.G.; Galindo, M.K.; Patel, J.; Klewer, S.E.; Nembhard, W.N.; Farr, S.L. Comorbidities and Healthcare Utilization Among Young Adults With Congenital Heart Defects by Down Syndrome Status—Congenital Heart Survey to Recognize Outcomes, Needs, and Wellbeing, 2016–2019. Birth Defects Res. 2025, 11, e2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albu, C.-C.; Cilievici, S.E.; Albu, D.-F.; Albu, Ș.-D.; Pătrașcu, A.; Goganău, A.-M. Impact of maternal serum screening in early prenatal diagnosis and management of congenital anomalies. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 1534–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaan, C.M.; Reinhardt, D.; Hitzler, J.K.; Vyas, P. Acute leukemias in children with Down syndrome. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 24, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpa, Q.L.; Akahara, P.C.; Anderson, A.M.; Adekoya, O.O.; Ajayi, O.O.; Alabi, P.O.; Okobi, O.E.; Jaiyeola, O.; Ekanem, M.S. A review of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) in the pediatric population: Evaluating current trends and changes in guidelines in the past decade. Cureus 2023, 15, e49930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronica, T.S.; Carella, M.; Balistreri, C.R. Different Levels of Therapeutic Strategies to Recover the Microbiome to Prevent/Delay Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) or Arrest Its Progression in Children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.-P.; Colita, A.; Ivanov, A.-V.; Coriu, D.; Miron, I.-C. Outcomes of patients with Down syndrome and acute leukemia: A retrospective observational study. Medicine 2021, 100, e27459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, M.L.; Mullighan, C.G. JAK mutations and pediatric myeloproliferative disorders: Pathogenesis, therapeutic targets, and clinical studies. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 24, 875–888. [Google Scholar]
- Łączak, M.; Kuczyńska, M.; Grygier, J.; Andrzejewska, D.; Grochowska, W.; Gulaczyk, H.; Lewandowski, K. JAK and STAT gene mutations and JAK-STAT pathway activation in lympho- and myeloproliferative neoplasms. Hematol. Clin. Pract. 2021, 12, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasian, S.K.; Teachey, D.T.; Rheingold, S.R. Targeting JAK/STAT pathway alterations in high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 384, 325–359. [Google Scholar]
- Marcuzzi, A.; Rimondi, E.; Melloni, E.; Gonelli, A.; Grasso, A.G.; Barbi, E.; Maximova, N. New Applications of JAK/STAT Inhibitors in Pediatrics: Current Use of Ruxolitinib. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.G.; Li, Y.; Payne-Turner, D.; Harvey, R.C.; Yang, Y.-L.; Pei, D.; McCastlain, K.; Ding, L.; Lu, C.; Song, G.; et al. Targetable kinase-activating lesions in Ph-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, E.C.; Heatley, S.L.; Rehn, J.; Thomas, P.Q.; Yeung, D.T.; White, D.L. Gain of chromosome 21 increases the propensity for P2RY8:CRLF2 acute lymphoblastic leukemia via increased HMGN1 expression. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1177871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.G.; Mullighan, C.G. Genomics in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Insights and treatment implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Habeebu, S.S.M.; Li, W. Prognostic and Predictive Biomarkers in Precursor B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. In Leukemia; Li, W., Ed.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2022; Chapter 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniyal, P.; Kashyap, V.K.; Behl, T.; Parashar, D.; Rawat, R. KRAS Mutations in Cancer: Understanding Signaling Pathways to Immune Regulation and the Potential of Immunotherapy. Cancers 2025, 17, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, J.A.; Harrison, C.J.; Bloodworth, L. Ras pathway mutations: An emerging prognostic marker in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia? Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2016, 23, 339–345. [Google Scholar]
- Hof, J.; Krentz, S.; van den Ham, E.; Zimmermann, M.; van den Berge, I.; Beverloo, H.B.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; Pieters, R.; den Boer, M.L. Mutations and outcome in relapsed pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2011, 118, 643–650. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadoss, G.S.; Mishra, P.; Eppert, K.; Sinha, A.U.; Mungall, A.J.; Marra, M.A.; Wilson, R.K.; Scherer, S.W.; Mak, T.W.; Tsao, M.S.; et al. EP300 mutations and epigenetic dysregulation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. S1), 2543. [Google Scholar]
- Tzoneva, G.; Ferrando, A.A. Epigenetic therapy in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A new frontier. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2012, 5, 793–796. [Google Scholar]
- Heerema, N.A.; Sather, H.N.; Sensel, M.G.; Liu Mares, W.; Lange, B.J.; Bostrom, B.C. Clinical significance of deletions of chromosome 21 in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2000, 14, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, D.R.; Arancibia, A.M.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Land, M.G.; Silva, M.L. Intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21 (iAMP21) detected by ETV6/RUNX1 FISH screening in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A case report. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 2013, 35, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Ryan, S.L.; Iacobucci, I.; Ghate, P.S.; Cranston, R.E.; Schwab, C.; Elsayed, A.H.; Shi, L.; Pounds, S.; Lei, S.; et al. The genomic landscape of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21. Blood 2023, 142, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.J.; Moorman, A.V.; Schwab, C.; Carroll, A.J.; Raetz, E.A.; Devidas, M.; Strehl, S.; Nebral, K.; Harbott, J.; Teigler-Schlegel, A.; et al. An international study of intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21 (iAMP21): Cytogenetic characterization and outcome. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.V.; Avetisyan, G.; de las Heras, S.; Miralles, A.; del Cañizo, M.; Rico, Á.; Valerio, M.E.; Díaz, V.; Piñero, P.; Orellana, C.; et al. Atypical B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with iAMP21 in the Context of Constitutional Ring Chromosome 21: A Case Report and Review of the Genetic Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.V.; Enshaei, A.; Schwab, C.; Wade, R.; Chilton, L.; Elliott, A.; Richardson, S.; Hancock, J.; Kinsey, S.E.; Mitchell, C.D.; et al. A novel integrated cytogenetic and genomic classification refines risk stratification in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2014, 124, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.M.; Matos, R.R.C.; Figueiredo, A.F.; Melgaço, A.H.; Lima, L.B.; Marques-Salles, T.J.; Liehr, T.; Abdelhay, E.; Ferreira, G.; Silva, M. Flexibility of fish probes in monitoring iAMP21 acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Study of four Brazilian children. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2022, 44, S343–S344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdoni, A.M.; Zilla, M.L.; Bullock, G.; Guinipero, T.L.; Meade, J.; Yatsenko, S.A. B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with iAMP21 in a patient with Down syndrome due to a constitutional isodicentric chromosome 21. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 188, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. Measurable residual disease testing in acute leukemia: Technology and clinical significance. In Leukemia; Li, W., Ed.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2022; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuser, M.; Freeman, S.D.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Buccisano, F.; Hourigan, C.S.; Ngai, L.L.; Tettero, J.M.; Bachas, C.; Baer, C.; Béné, M.C.; et al. 2021 Update on MRD in acute myeloid leukemia: A consensus document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood 2021, 138, 2753–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Velden, V.H.J.; van Dongen, J.J.M. Development of sensitive flow cytometry approaches for minimal residual disease detection in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2012, 25, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Pui, C.H.; Pei, D.; Sandlund, J.T.; Ribeiro, R.C.; E Rubnitz, J.; Raimondi, S.C.; Onciu, M.; Campana, D.; E Kun, L.; Jeha, S.; et al. Long-term results of St Jude Total Therapy studies 11, 12, 13A, 13B, and 14 for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2010, 24, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Pui, C.-H. Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delany, D.R.; Gaydos, S.S.; Romeo, D.A.; Henderson, H.T.; Fogg, K.L.; McKeta, A.S.; Kavarana, M.N.; Costello, J.M. Down syndrome and congenital heart disease: Perioperative planning and management. J. Congenit. Cardiol. 2021, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandonnet, J.; Poggi, V.; Saitta, S.C.; Bertozzi, I.; Barazzoni, E.; Cimaz, R.; Crovella, S.; Dagna, L.; Dufour, C.; Faldella, G.; et al. Infectious complications in children with Down syndrome and acute leukemia: A prospective study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27529. [Google Scholar]
- Stanhope, C.; White, G.; Carter, M.J.; Das, A.; Giffin, N.J.; Gould, N.J.; Hildick-Smith, D.; Khair, K.; McKendrick, K.; Morgan, E.; et al. Cardiac monitoring and management in children with Down syndrome undergoing chemotherapy for leukemia. Cardiol. Young 2021, 31, 569–576. [Google Scholar]
- Maloney, K.W.; McKenzie, S.E.; Neglia, J.P. Down syndrome and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 2010, 116, 2335–2343. [Google Scholar]
- Fazio, G.; Trama, A.; Salvatore, E.; Cilloni, D.; Palumbo, G.A.; Gaidano, G.; Pinto, A.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Basso, G.; Biondi, A.; et al. JAK inhibitors in pediatric acute leukemias: From biology to clinical advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6408. [Google Scholar]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Teachey, D.T.; Maier, S.L.; Curran, K.J.; Shpall, E.J.; George, T.I.; Reinhardt, D.; Pui, C.-H.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, M.H.; Zwaan, C.M. Down syndrome-specific pathways in acute leukemia: Novel therapeutic directions. Semin. Hematol. 2020, 57, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Zwaan, C.M.; Meshinchi, S.; Radich, J.P.; Pui, C.-H.; Hunger, S.P.; Carroll, W.L.; Cowan, M.J.; De Angelo, D.J.; Druker, B.J.; Evans, W.E.; et al. Multidisciplinary approaches for Down syndrome acute leukemias. Leukemia 2017, 31, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Malinge, S.; Ben-Abdelali, R.; Settegrana, C.; Radford-Weiss, I.; Debre, M.; Beldjord, K.; Macintyre, E.A.; Villeval, J.L.; Vainchenker, W.; Berger, R.; et al. Novel activating JAK2 mutation in a patient with Down syndrome and B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2007, 109, 2202–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, L.; Gonzalez De Castro, D.; Yeung, J.; Procter, J.; Horsley, S.W.; Eguchi-Ishimae, M.; Bateman, C.M.; Anderson, K.; Chaplin, T.; Young, B.D.; et al. Specific JAK2 mutation (JAK2R683) and multiple gene deletions in Down syndrome acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2009, 113, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzberg, L.; Vendramini, E.; Ganmore, I.; Cazzaniga, G.; Schmitz, M.; Chalker, J.; Shiloh, R.; Iacobucci, I.; Shochat, C.; Zeligson, S.; et al. Down syndrome acute lymphoblastic leukemia, a highly heterogeneous disease in which aberrant expression of CRLF2 is associated with mutated JAK2: A report from the International BFM Study Group. Blood 2010, 115, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, E.C.; Heatley, S.L.; Eadie, L.N.; McClure, B.J.; de Bock, C.E.; Omari, S.; Yeung, D.T.; Hughes, T.P.; Thomas, P.Q.; White, D.L. HMGN1 plays a significant role in CRLF2 driven Down syndrome leukemia and provides a potential therapeutic target in this high-risk cohort. Oncogene 2022, 41, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestra, T.; Niswander, L.M.; Bagashev, A.; Loftus, J.P.; Ross, S.L.; Chen, R.K.; McClellan, S.M.; Junco, J.J.; Bárcenas López, D.A.; Rabin, K.R.; et al. Co-targeting of the thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor to decrease immunotherapeutic resistance in CRLF2-rearranged Ph-like and Down syndrome acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2025, 39, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blink, M.; Buitenkamp, T.D.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; Danen-van Oorschot, A.A.; de Haas, V.; Reinhardt, D.; Klusmann, J.H.; Zimmermann, M.; Devidas, M.; Carroll, A.J.; et al. Frequency and prognostic implications of JAK1–3 aberrations in Down syndrome acute lymphoblastic and myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, R.; Guirales, F.; Glaser, J.; Tirado, C.A. JAK2 in Ph-like B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Assoc. Genet. Technol. 2023, 49, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Koschut, D.; Ray, D.; Li, Z.; Giarin, E.; Groet, J.; Alić, I.; Kham, S.K.; Chng, W.J.; Ariffin, H.; Weinstock, D.M.; et al. RAS-protein activation but not mutation status is an outcome predictor and unifying therapeutic target for high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncogene 2021, 40, 746–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peroni, E.; Gottardi, M.; D’Antona, L.; Randi, M.L.; Rosato, A.; Coltro, G. Hematologic Neoplasms Associated with Down Syndrome: Cellular and Molecular Heterogeneity of the Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, I. Leukemogenesis in infants and young children with trisomy 21. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2022, 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, H.; Yakushijin, K.; Adachi, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Yamashita, T.; Higashime, A.; Kawaguchi, K.; Kurata, K.; et al. A Pathogenic NRAS c.38G>A (p.G13D) Mutation in RARA Translocation-Negative Acute Promyelocytic-Like Leukemia with Concomitant Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Intern. Med. 2023, 62, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jing, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Gao, X.; Yu, J.; Liang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, H.; et al. Ras-MAPK pathway in patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus Sci. Med. 2025, 12, e001345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekciu, I.; Zucha, D.M.; Christmann, J.; Wisser, S.; Heuer, V.; Sargin, B.; Hollerbach, S.; Lamberti, C.; Müller, L.; Lugnier, C.; et al. Exploring the molecular profile of localized colon cancer: Insights from the AIO Colopredict Plus registry. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1434791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Duque, M.S.; Martín Soler, P.; González Vela, M.C.; Gómez Román, J.J. Histiocitosis combinada de tipo Langerhans (Histiocitosis de células de Langerhans y enfermedad de Erdheim-Chester) en varón de 64 años con mutaciones en BRAF y NRAS: A propósito de un caso. Rev. Esp. Patol. 2023, 56, 186–190, Erratum in Rev. Esp. Patol. 2023, 57, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagan, N.; Huggard, D.; Mc Grane, F.; Leahy, T.R.; Franklin, O.; Roche, E.; Webb, D.; O’ Marcaigh, A.; Cox, D.; El-Khuffash, A.; et al. Multiorgan involvement and management in children with Down syndrome. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 1096–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotta, F.; Piscopiello, D.; Rizzo, D.; Iosa, G.; Garzya, G.; Calò, P.; Gemma, D. Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia in a Patient with Down Syndrome. Medicina 2024, 60, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgel, E.; Bhojwani, D. Medical supportive care for treatment-related toxicity in childhood ALL. In Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia; Vora, A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, C.-C.; Albu, D.-F.; Albu, Ș.-D.; Pătrașcu, A.; Mușat, A.-R.; Goganău, A.-M. Early prenatal diagnosis of an extremely rare association of Down syndrome and transposition of the great vessels. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 2574–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.C.; Roux, L.J.D.; Castro, A.R.; Silva, C.C.; Rodrigues, R.; Macho, V.M.P.; Silva, F.; Costa, C. Oral Manifestations: A Warning-Sign in Children with Hematological Disease Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia. Hematol. Rep. 2023, 15, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, B.; Zhailaubaeva, A.; Tashenova, G.; Tulebayeva, A.; Bulabaeva, G. Extramedullary symptoms at the initial presentation of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. Interdiscip. Approaches Med. 2023, 4, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Luo, S.; Ye, P. Extramedullary Relapse of Acute B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia Leading to Paraplegia in a Child with Down Syndrome. Clin. Lab. 2025, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busenhart, D.M.; Erb, J.; Rigakos, G.; Eliades, T.; Papageorgiou, S.N. Adverse effects of chemotherapy on the teeth and surrounding tissues of children with cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2018, 83, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, X.; Que, J.; Du, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, J. Oral Health, Caries Risk Profiles, and Oral Microbiome of Pediatric Patients with Leukemia Submitted to Chemotherapy. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6637503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albu, C.-C.; Bencze, M.-A.; Dragomirescu, A.-O.; Suciu, I.; Tănase, M.; Albu, Ş.-D.; Russu, E.-A.; Ionescu, E. Folic Acid and Its Role in Oral Health: A Narrative Review. Processes 2023, 11, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.; Khalifa, A.R.; Rezallah, N.N.; Lozanoff, S.; Abdelkarim, A.Z. Craniofacial and Airway Morphology in Down Syndrome: A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Case Series Evaluation. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergier, V.; Collignon, A.M.; Gosset, M.; Bonnet, A.L. Periodontal diseases in Down syndrome during childhood: A scoping review. BMC Oral Health 2025, 25, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, D.-F.; Onofriescu, M.; Nada, E.-S.; Ion, G.; Milicescu, S.; Albu, Ș.-D.; Albu, C.-C. The importance of customized biometric correlations in the prevention of growth and development disorders—A determining factor in the social integration of children and adolescents with mental disabilities. Rev. Cercet. Interv. Soc. 2021, 72, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousserouit, M.; Benjelloune, L.; Chbicheb, S. Late dental effects in children submitted to chemotherapy: A case report. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 84, 104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodłowska, A.; Postek-Stefańska, L. Tooth Abnormalities and Their Age-Dependent Occurrence in Leukemia Survivors. Cancers 2023, 15, 5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan-Andreescu, C.F.; Defta, C.L.; Albu, Ș.D.; Manea, A.; Botoacă, O.; Russu, E.-A.; Albu, C.-C. Application of artificial intelligence in dental caries prediction related to diet and oral hygiene. Rom. J. Oral Rehabil. 2024, 16, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botoacă, O.; Albu, C.-C.; Bogdan-Andreescu, C.F.; Albu, Ș.D.; Grama, A.; Defta, C.L. Comparison of antimicrobial activity of two commercial toothpastes. Rom. J. Oral Rehabil. 2023, 15, 356–371. [Google Scholar]
- Dumitriu, A.S.; Păunică, S.; Nicolae, X.A.; Bodnar, D.C.; Albu, Ș.D.; Suciu, I.; Ciongaru, D.N.; Giurgiu, M.C. The effectiveness of the association of chlorhexidine with mechanical treatment of peri-implant mucositis. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michels, N.; Boer, J.M.; Enshaei, A.; Sutton, R.; Heyman, M.; Ebert, S.; Fiocco, M.; A de Groot-Kruseman, H.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Barbany, G.; et al. Minimal residual disease, long-term outcome, and IKZF1 deletions in children and adolescents with Down syndrome and acute lymphocytic leukaemia: A matched cohort study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e700–e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoshima, M.; Yagasaki, H.; Shimozawa, K.; Kanezawa, K.; Ueno, M.; Morioka, I. Six Years of Disease-free Survival After a Second Cord Blood Transplantation for Recurrent Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia in a Child With Down Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 46, e100–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohso, A.; Toyoda, H.; Hanaki, R.; Niwa, K.; Okumura, Y.; Morimoto, M.; Ito, T.; Hirayama, M. Inotuzumab ozogamicin for relapse prevention in a boy with Down syndrome and relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2025, 121, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, E.; Tragiannidis, A.; Ampatzidou, M.; Katzilakis, N.; Nikita, M.; Totikidis, G.; Athanasiadou, K.I.; Antari, V.; Kelaidi, C.; Pelagiadis, I.; et al. Acute Leukemia in Children with Down Syndrome: A Report from the Hellenic HESPHO Group. Hemato 2025, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Liu, Y. Treatment outcomes in children with Acute lymphoblastic leukemia with versus without coexisting Down’s syndrome A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e21015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sora, F.; Annunziata, M.; Laurenti, L.; Giammarco, S.; Chiusolo, P.; Innocenti, I.; Autore, F.; Metafuni, E.; Galli, E.; Bacigalupo, A.; et al. Blinatumomab as a successful and safe therapy in Down syndrome patients with relapsed/refractory b-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Case reports and literature review. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e29044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value | Normal Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (×109/L) | 26.08 | 5.0–15.0 | Leukocytosis |
| Blasts in smear (%) | ~54% | 0% | Marker of acute leukemia |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.9 | 11.5–13.5 | Mild anemia |
| PLT (×109/L) | 81 | 150–450 | Thrombocytopenia |
| CRP (mg/L) | 49 | <5 | Inflammatory response |
| LDH (U/L) | ~458 (elevated) | <250 | Accelerated cellular turnover |
| Clinical Features | Lymphadenopathy, petechiae, DS facies, PDA | - | Systemic infiltrative disease |
| Gene/Abnormality | Alteration Type | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| NRAS p.G13D | Point mutation | RAS–MAPK activation; relapse risk, chemoresistance |
| JAK2 p.R683G | Point mutation | JAK–STAT hyperactivation; frequent in DS-ALL |
| EP300 p.Q1766* | Truncating mutation | Epigenetic disruption; potential HDAC inhibitor target |
| P2RY8-CRLF2 | Gene fusion | CRLF2 overexpression; variable prognosis |
| iAMP21 | Amplification | High-risk cytogenetic lesion, potential negative prognostic marker |
| Parameter | Day 15 | Day 33 | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRD (%) | ~1.8 | Undetectable | Deep remission |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 8.5 | 9.7 | Moderate fluctuations; RBC transfusion during aplasia |
| WBC (/mm3) | 1.500 | 3.970 | Pronounced neutropenia during aplasia |
| PLT (×109/L) | 20 | 221 | Significant increase after critical aplasia phase |
| Nosocomial Infections | Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas fluorescens | None | Managed with broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy |
| Hemorrhagic Manifestations | Mild | Absent | Prophylaxis with tranexamic acid |
| Clinical Status | Stable | Clinical remission | No meningeal signs, good general status at discharge |
| Study Type and Year | Therapy | Patients | Results | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retrospective observational study 2021 [31] | Not specified. | 14 DS-ALL patients vs. ALL controls | Survival in DS-ALL: 35.7%; in non-DS ALL: 75.8%. Relapse rate higher in DS-ALL. | Chemotherapy-related infections and toxicities |
| Match cohort study 2021 [98] | Not specified. | 251 subjects | MRD at end of induction similar between DS and non-DS groups. Higher relapse risk in DS-ALL. | Not specified. |
| Case report 2023 [99] | Standard chemotherapy | 2-year-old boy | Complete remission; later relapses in bone marrow and CNS. | Recurrence (twice) |
| Case report 2025 [100] | Sequential therapies: reduced-dose MTX and prednisolone → ALL-REZ BFM-2002 → Inotuzumab-based salvage regimens | Male, diagnosed at age 3 | Initial remission; relapse at 15 months; second remission after 20 months of inotuzumab-based therapy. | Persistent fever, joint pain, prolonged thrombocytopenia |
| Case report 2025 [86] | VDLP regimen + CNS prophylaxis (intrathecal chemo via lumbar puncture) | 11-year-old male | MRD-negative status achieved. | Acute paraplegia, progressive lower back pain |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albu, C.-C.; Bica, F.; Nan, L.; Bubulac, L.; Bogdan-Andreescu, C.F.; Şerbanică, I.V.; Poalelungi, C.-V.; Cadar, E.; Bănățeanu, A.-M.; Burcea, A. B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Child with Down Syndrome and High-Risk Genomic Lesions. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090704
Albu C-C, Bica F, Nan L, Bubulac L, Bogdan-Andreescu CF, Şerbanică IV, Poalelungi C-V, Cadar E, Bănățeanu A-M, Burcea A. B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Child with Down Syndrome and High-Risk Genomic Lesions. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(9):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090704
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbu, Cristina-Crenguţa, Florin Bica, Laura Nan, Lucia Bubulac, Claudia Florina Bogdan-Andreescu, Ionuţ Vlad Şerbanică, Cristian-Viorel Poalelungi, Emin Cadar, Andreea-Mariana Bănățeanu, and Alexandru Burcea. 2025. "B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Child with Down Syndrome and High-Risk Genomic Lesions" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 9: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090704
APA StyleAlbu, C.-C., Bica, F., Nan, L., Bubulac, L., Bogdan-Andreescu, C. F., Şerbanică, I. V., Poalelungi, C.-V., Cadar, E., Bănățeanu, A.-M., & Burcea, A. (2025). B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Child with Down Syndrome and High-Risk Genomic Lesions. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(9), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090704








