Molecular Insights into Tumor Immunogenicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.1.1. Set of T-Cell Epitopes
2.1.2. Set of Non-T-Cell Epitopes
2.1.3. X-Ray Structure of TCR-Peptide-HLA Class I Complex
2.2. Logo Method
2.3. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
3. Results
3.1. Logo Model for T-Cell Epitopes
3.2. Logo Model for Non-T-Cell Epitopes
3.3. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations of HLA–Peptide–TCR Complexes Containing a T-Cell Epitope and a Non-T-Cell Epitope
3.4. The T-Cell Epitope Forms a More Stable Complex with HLA and TCR
3.5. The T-Cell Epitope Is More Flexible in the Complex with HLA and TCR
3.6. Residues from the Middle Part of the T-Cell Epitope Form Long-Lasting Hydrogen Bonds with TCR
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigen |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| nTCE | Non-T-cell epitope |
| pMHC | Peptide–MHC complex |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviations |
| QM | Quantitative matrix |
| RMSF | Root mean square fluctuations |
| TCE | T-cell epitope |
| TCR | T-cell receptor |
References
- Davis, M.M.; Bjorkman, P.J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature 1988, 334, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, M.G.; Stanfield, R.L.; Wilson, I.A. How TCRs bind MHCs, peptides, and coreceptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 419–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.; Sette, A. Generating quantitative models describing the sequence specificity of biological processes with the stabilized matrix method. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Weiskopf, D.; Angelo, M.A.; Sidney, J.; Peters, B.; Sette, A. HLA class I alleles are associated with peptide-binding repertoires of different size, affinity, and immunogenicity. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5831–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappuoli, R.; Bottomley, M.J.; D’Oro, U.; Finco, O.; De Gregorio, E. Reverse vaccinology 2.0: Human immunology instructs vaccine antigen design. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, K.C.; Scott, C.A.; Brunmark, A.; Carbone, F.R.; Peterson, P.A.; Wilson, I.A.; Teyton, L. CD8 enhances formation of stable T-cell receptor/MHC class I molecule complexes. Nature 1996, 384, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossjohn, J.; Gras, S.; Miles, J.J.; Turner, S.J.; Godfrey, D.I.; McCluskey, J. T cell antigen receptor recognition of antigen-presenting molecules. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 169–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, M.; Albertsson, P.; Boeryd, B. T cell responses in cancer. J. Clin. Immunol. 2002, 22, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gatti-Mays, M.E.; Redman, J.M.; Collins, J.M.; Bilusic, M. Cancer vaccines: Enhanced immunogenic modulation through therapeutic combinations. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 2561–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewell, A.K. Why must T cells be cross-reactive? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, M.E.; Mendoza, J.L.; Sethi, D.K.; Dong, S.; Glanville, J.; Dobbins, J.; Ozkan, E.; Davis, M.M.; Wucherpfennig, K.W.; Garcia, K.C. Deconstructing the peptide-MHC specificity of T cell recognition. Cell 2014, 157, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, C.H.; Mulvaney, R.M.; Malla, S.; Walker, A.; Smith, K.J.; Lloyd, A.; Lowe, K.L.; McCully, M.L.; Hague, R.M.; Aleksic, M.; et al. TCRs with distinct specificity profiles use different binding modes to engage an identical peptide–HLA complex. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June, C.H.; Sadelain, M. Chimeric antigen receptor therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.; Labarriere, N.; Leclerc, C. Neoantigen-specific T cell responses in human tumors: Detection, function, and therapeutic implications. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 64, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.R.; Alonso, J.A.; Ayres, C.M.; Singh, N.K.; Hellman, L.M.; Baker, B.M. Structurally silent peptide anchor modifications allosterically modulate T cell recognition in a receptor-dependent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2018125118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laugel, B.; van den Berg, H.A.; Gostick, E.; Cole, D.K.; Wooldridge, L.; Boulter, J.; Milicic, A.; Price, D.A.; Sewell, A.K. Different T-cell receptor affinity thresholds and CD8 coreceptor dependence govern cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activation and tetramer binding properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23799–23810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitmer, K.J.; Romball, C.G.; Weigle, W.O. Induction of tolerance to human gamma-globulin in FcR gamma- and Fc gammaRII-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasagi, M.; Shukla, S.A.; Fritsch, E.F.; Keskin, D.B.; DeLuca, D.; Carmona, E.; Zhang, W.; Sougnez, C.; Cibulskis, K.; Sidney, J.; et al. Systematic identification of personal tumor-specific neoantigens in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2014, 124, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Scheper, W.; Kvistborg, P. Cancer neoantigens. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 173–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Mallik, L.; Hwang, D.; Sun, Y.; Kaku, C.; Hoces, D.; Sun, S.M.; Ghinnagow, R.; Carro, S.D.; Phan, H.A.T.; et al. Targeting peptide antigens using a multiallelic MHC I-binding system. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024. Published online December 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, B.M.; Gagnon, S.J.; Wiley, D.C.; Birnbaum, M.E. T cell receptor interaction with peptide–MHC influences thymic selection. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Alspach, E.; Lussier, D.M.; Schreiber, R.D. Interferon γ and Its Important Roles in Promoting and Inhibiting Spontaneous and Therapeutic Cancer Immunity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a028480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neefjes, J.; Jongsma, M.L.M.; Paul, P.; Bakke, O. Towards a systems understanding of MHC class I and MHC class II antigen presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, E.W.; Sigal, N.; Nair, N.; Kidd, B.A.; Gretenberg, H.B.; Dalvis, M.M. Combinatorial tetramer staining and mass cytometry analysis facilitate T-cell epitope mapping and characterization. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, E.F.; Rajasagi, M.; Ott, P.A.; Brusic, V.; Hacohen, N.; Wu, C.J. HLA-binding properties of tumor neoantigens in humans. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGranahan, N.; Furness, A.J.S.; Rosenthal, R.; Ramskov, S.; Lyngaa, R.; Saini, S.K.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Wilson, G.A.; Birkbak, N.J.; Hiley, C.T.; et al. Clonal neoantigens elicit T cell immunoreactivity and sensitivity to immune checkpoint blockade. Science 2016, 351, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, P.A.; Hu, Z.; Keskin, D.B.; Shukla, S.A.; Sun, J.; Bozym, D.J.; Zhang, W.; Luoma, A.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Peter, L.; et al. An immunogenic personal neoantigen vaccine for patients with melanoma. Nature 2017, 547, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.T.; Kranz, D.M. Adoptive T cell therapies: A comparison of T cell receptors and chimeric antigen receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardetzky, T.S.; Lane, W.S.; Robinson, R.A.; Madden, D.R.; Wiley, D.C. Identification of self peptides bound to purified HLA-B27. Nature 2018, 555, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Irvine, D.J.; Krummel, M.F. Engineering the T cell immunological synapse. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 267–289. [Google Scholar]
- Restifo, N.P.; Dudley, M.E.; Rosenberg, S.A. Adoptive immunotherapy for cancer: Harnessing the T cell response. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Schreiber, R.D. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science 2015, 348, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wilbur, W.J. PubMed related articles: A probabilistic topic-based model for content similarity. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, R.; Blazeska, N.; Marrama, D.; IEDB Curation Team Members; Duesing, S.; Bennett, J.; Greenbaum, J.; De Almeida Mendes, M.; Mahita, J.; Wheeler, D.K.; et al. The Immune Epitope Database (IEDB): 2024 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D436–D443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doytchinova, I.; Atanasova, M.; Fernandez, A.; Moreno, F.J.; Koning, F.; Dimitrov, I. Modeling peptide-protein interactions by a logo-based method: Application in peptide-HLA binding predictions. Molecules 2024, 29, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doytchinova, I.; Atanasova, M.; Sotirov, S.; Dimitrov, I. In silico identification of peanut peptides suitable for allergy immunotherapy in HLA-DRB1*03:01-restricted patients. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.D.; Stephens, R.M. Sequence Logos: A New Way to Display Consensus Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6097–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelman, S.A.; Doll, J.D. Generalized Langevin equation approach for atom/solid-surface scattering: Collinear atom/harmonic chain model. J. Chem. Phys. 1974, 61, 4242–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N·log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 40, 2998–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccotti, G.; Ryckaert, J.P. Molecular dynamics simulation of rigid molecules. Comput. Phys. Rep. 1986, 4, 346–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Ben-Shalom, I.Y.; Brozell, S.R.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Cruzeiro, V.W.D.; Darden, T.A.; Duke, R.E.; Ghoreishi, D.; Gilson, M.K.; et al. AMBER 18; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, T.E., III. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: Software for processing and analysis of molecular dynamics trajectory data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chen, L.; Crichlow, G.V.; Christie, C.H.; Dalenberg, K.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D437–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Merwe, P.A.; Dushek, O. Mechanisms for T cell receptor triggering. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiepiela, P.; Leslie, A.J.; Honeyborne, I.; Ramduth, D.; Thobakgale, C.; Chetty, S.; Rathnavalu, P.; Moore, C.; Pfafferott, K.J.; Hilton, L.; et al. Dominant influence of HLA-B in mediating the potential co-evolution of HIV and HLA. Nature 2004, 432, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, D.A.; Wilke, C.O. The evolutionary consequences of erroneous protein synthesis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patronov, A.; Doytchinova, I. T-cell epitope vaccine design by immunoinformatics. Open Biol. 2013, 3, 120139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardis, E.R. Neoantigens and genome instability: Impact on immunogenomic phenotypes and immunotherapy response. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laumont, C.M.; Daouda, T.; Laverdure, J.-P.; Bonneil, É.; Caron-Lizotte, O.; Hardy, M.-P.; Granados, D.P.; Durette, C.; Lemieux, S.; Thibault, P.; et al. Global proteogenomic analysis of human MHC class I–associated peptides derived from noncanonical reading frames. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Lu, M.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Bai, J.-J.; Gu, J.-Y.; Xie, L.; Wu, W.-Z. Neoantigen-targeted TCR-engineered T cell immunotherapy: Current advances and challenges. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Wen, F.; Tuerhong, N.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy: Focusing on alternative splicing. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1437774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorkman, P.J.; Parham, P. Structure, function, and diversity of class I major histocompatibility complex molecules. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1990, 59, 253–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harndahl, M.; Rasmussen, M.; Roder, G.; Pedersen, I.D.; Sørensen, M.; Nielsen, M.; Buus, S. Peptide–MHC class I stability is a better predictor than peptide of CTL immunogenicity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. Modeling the peptide–T cell receptor interaction by the Comparative Molecular Similarity Indices Analysis–Soft Independent Modeling of Class Analogy technique. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
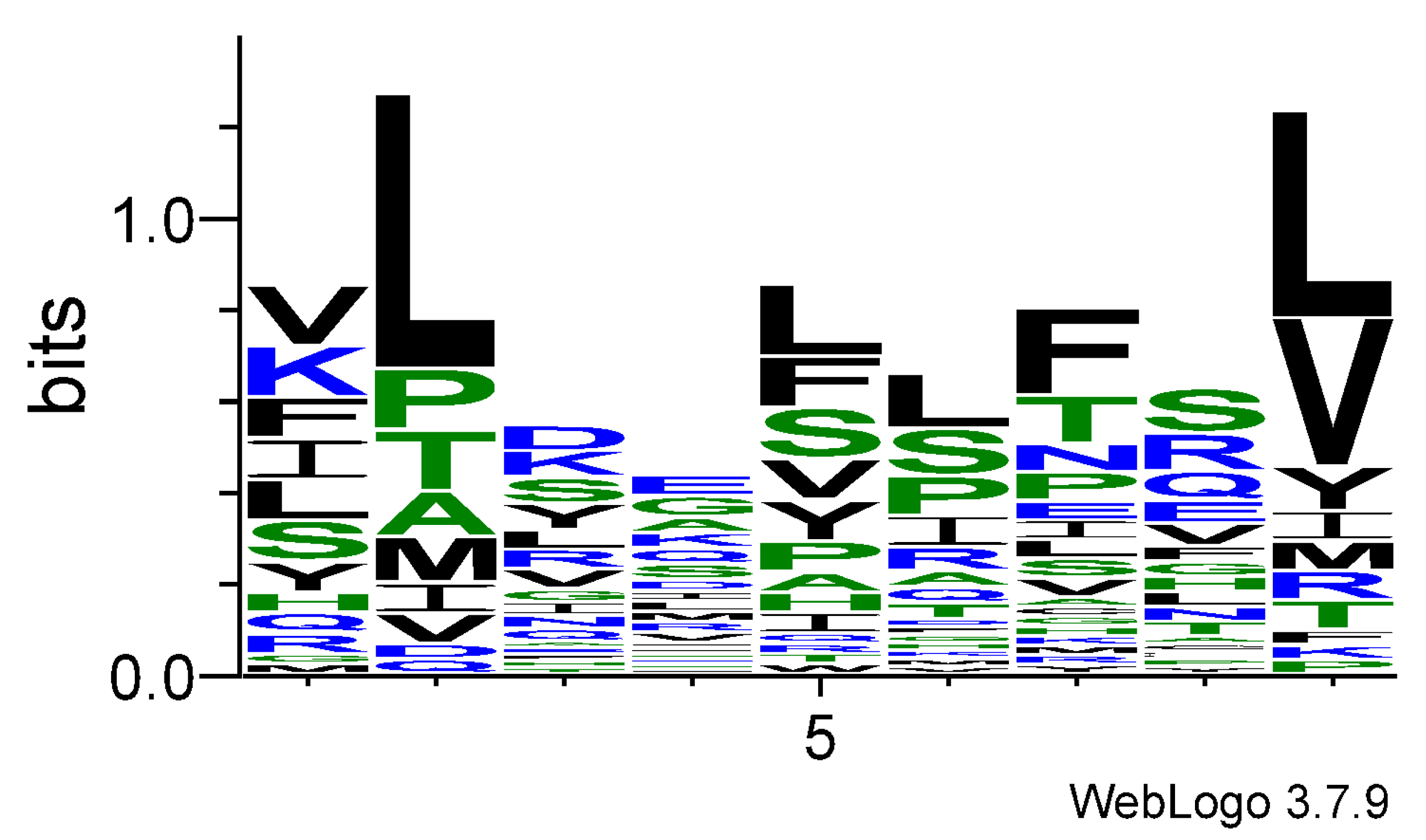
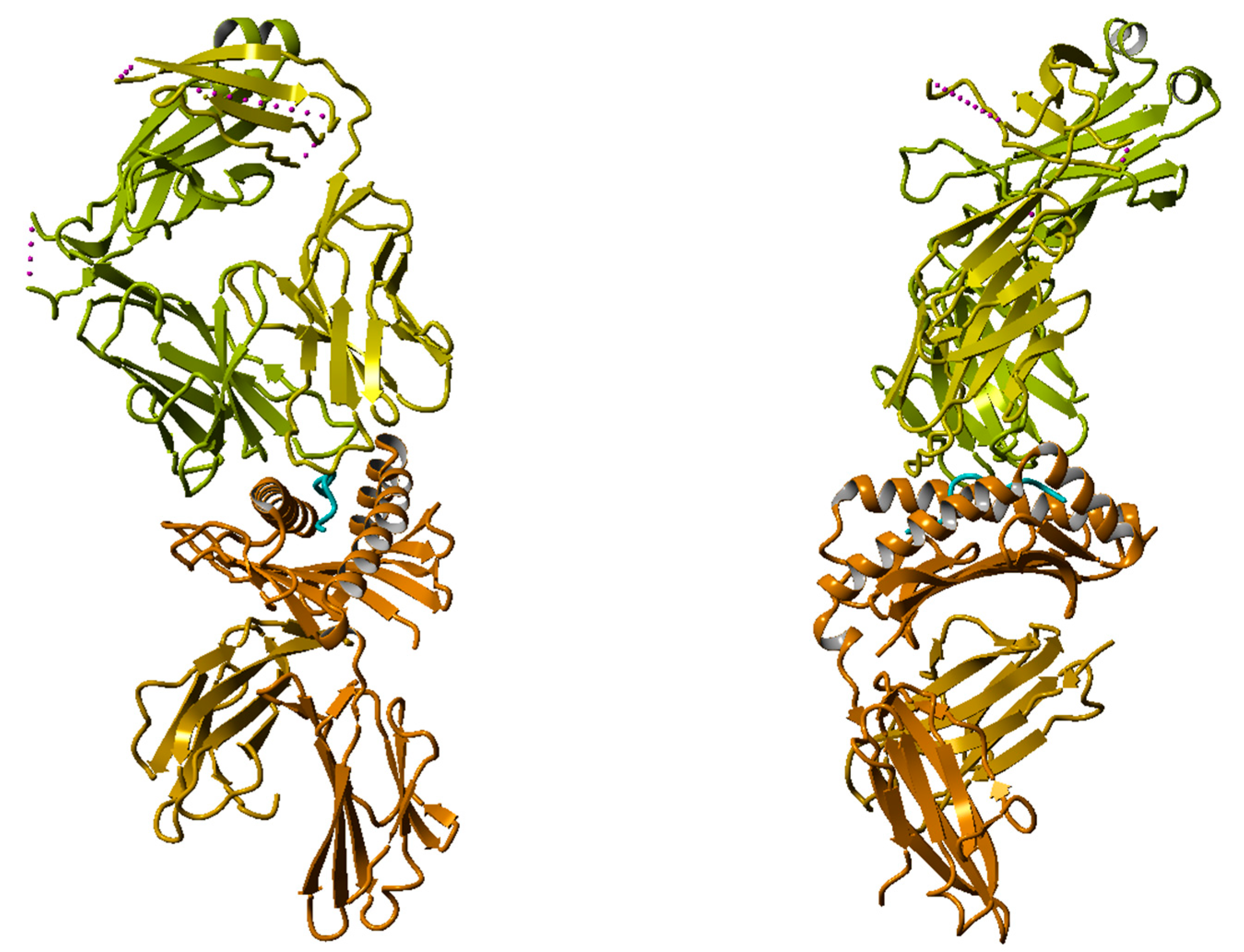


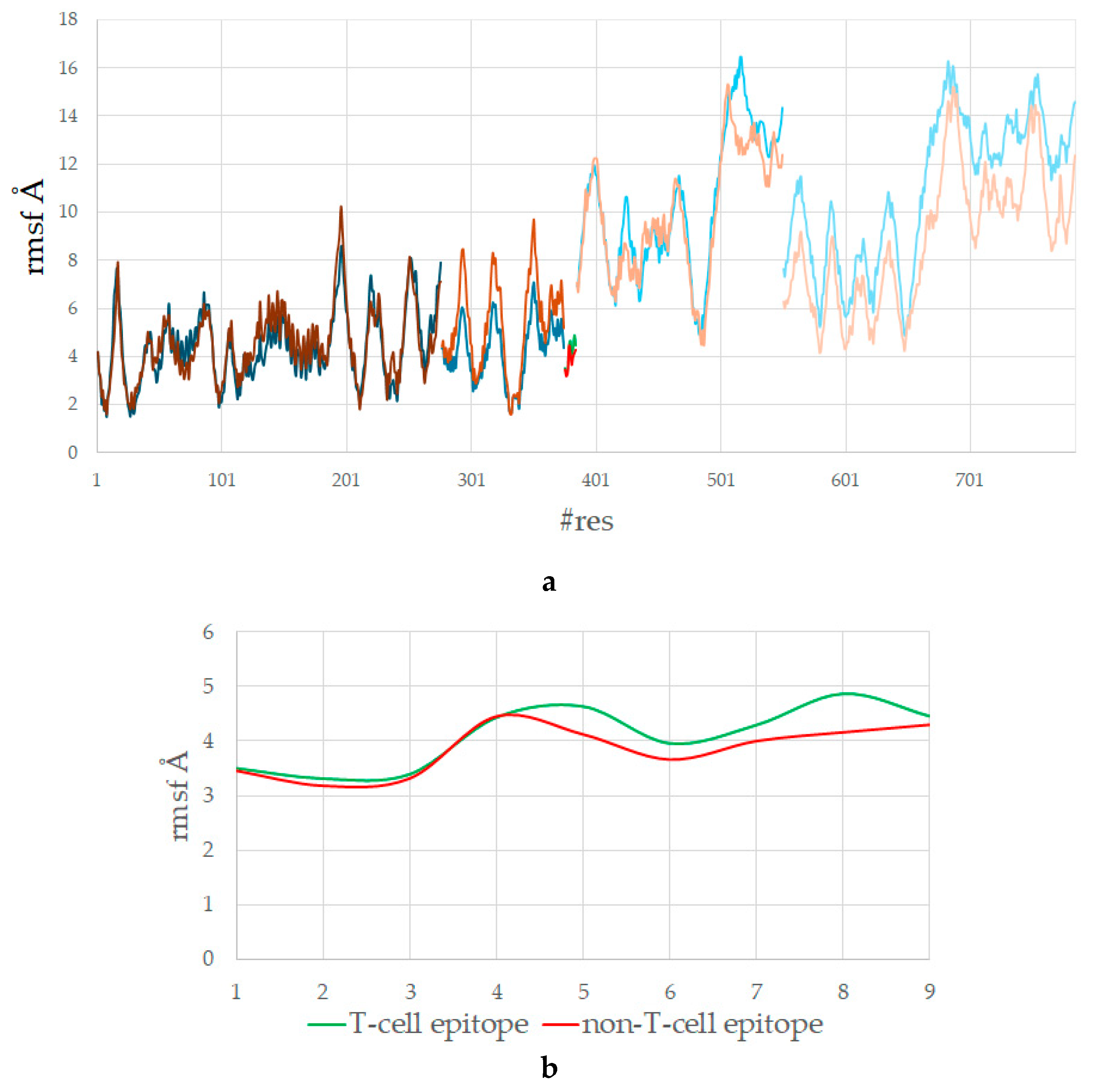
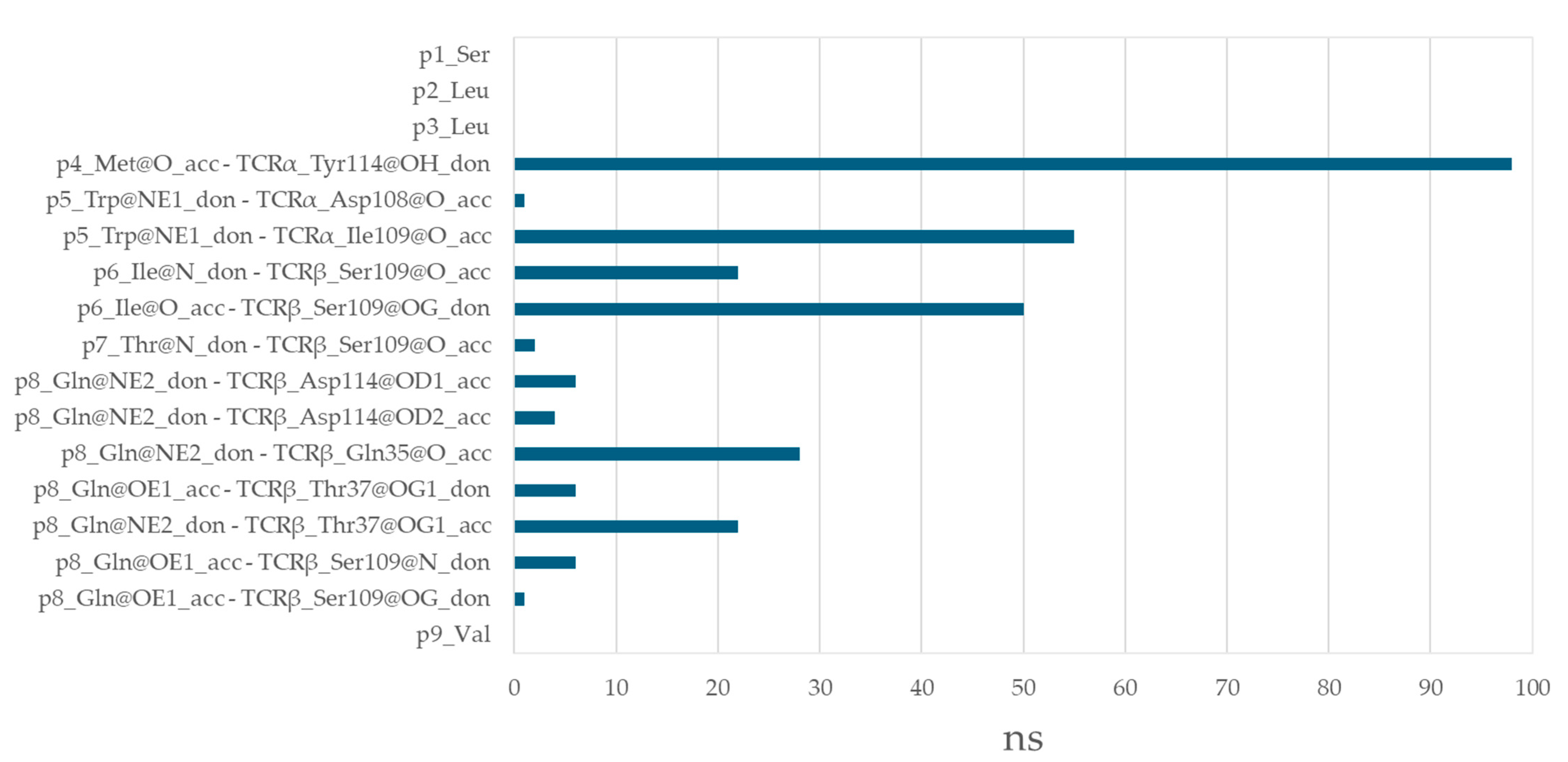
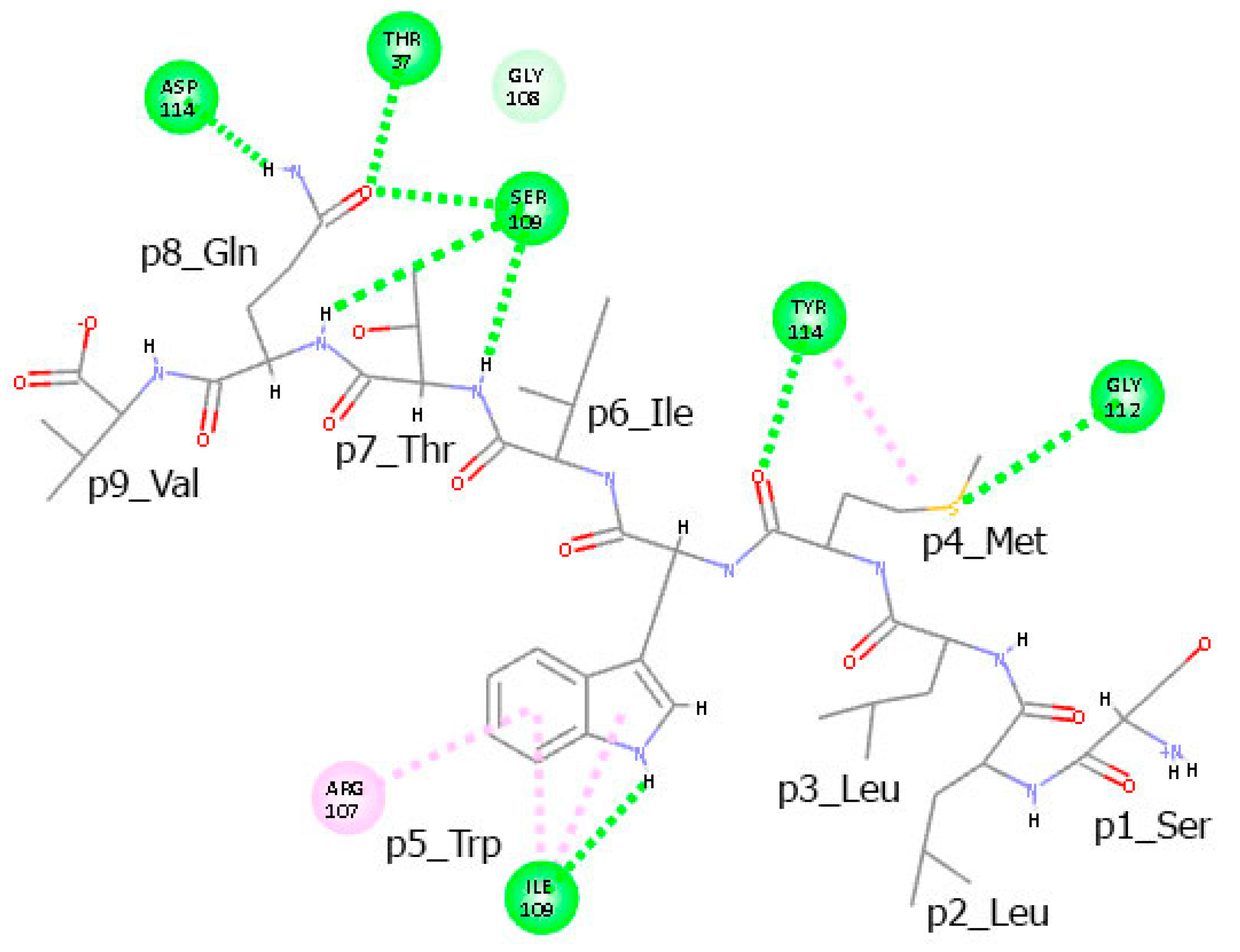
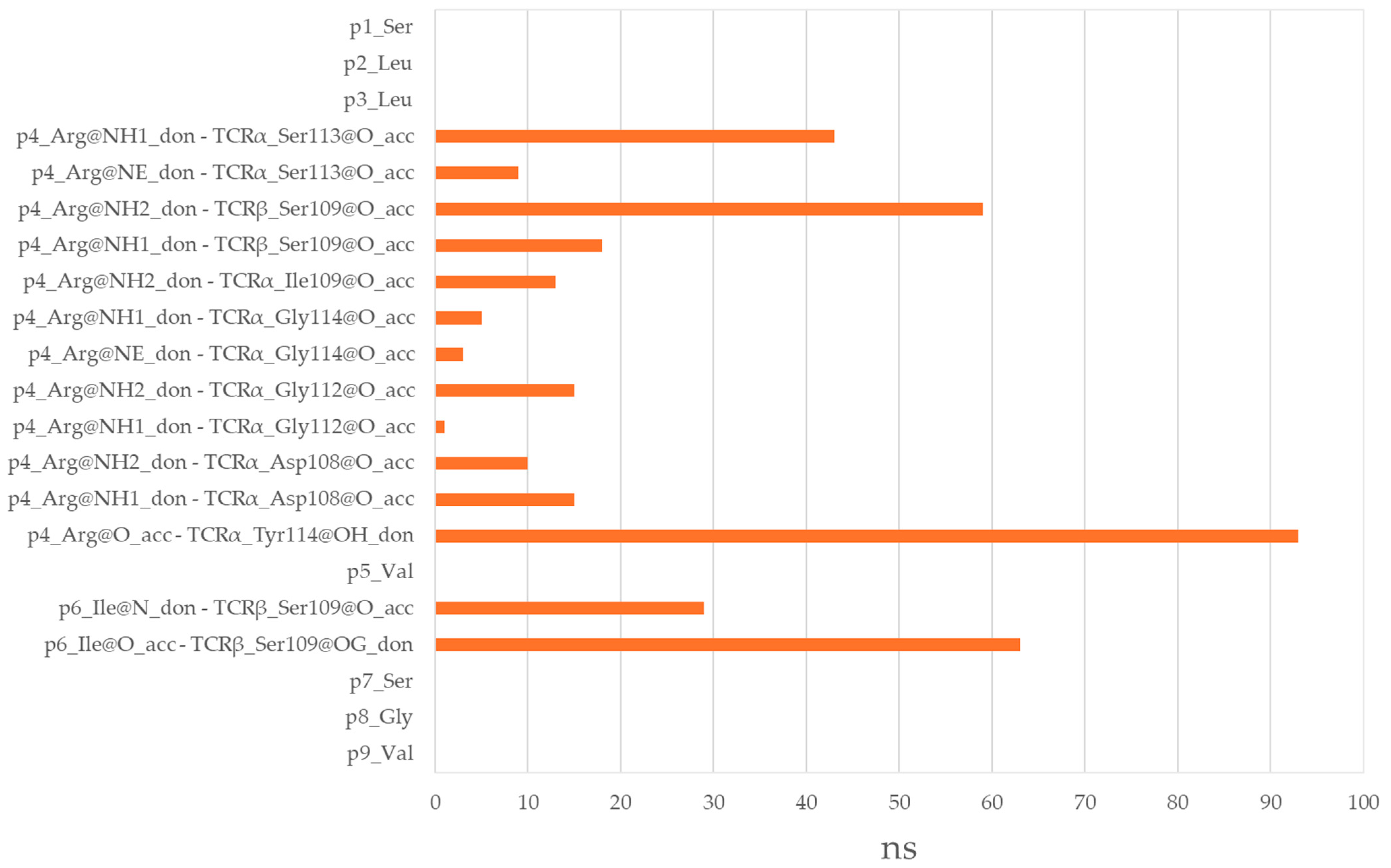
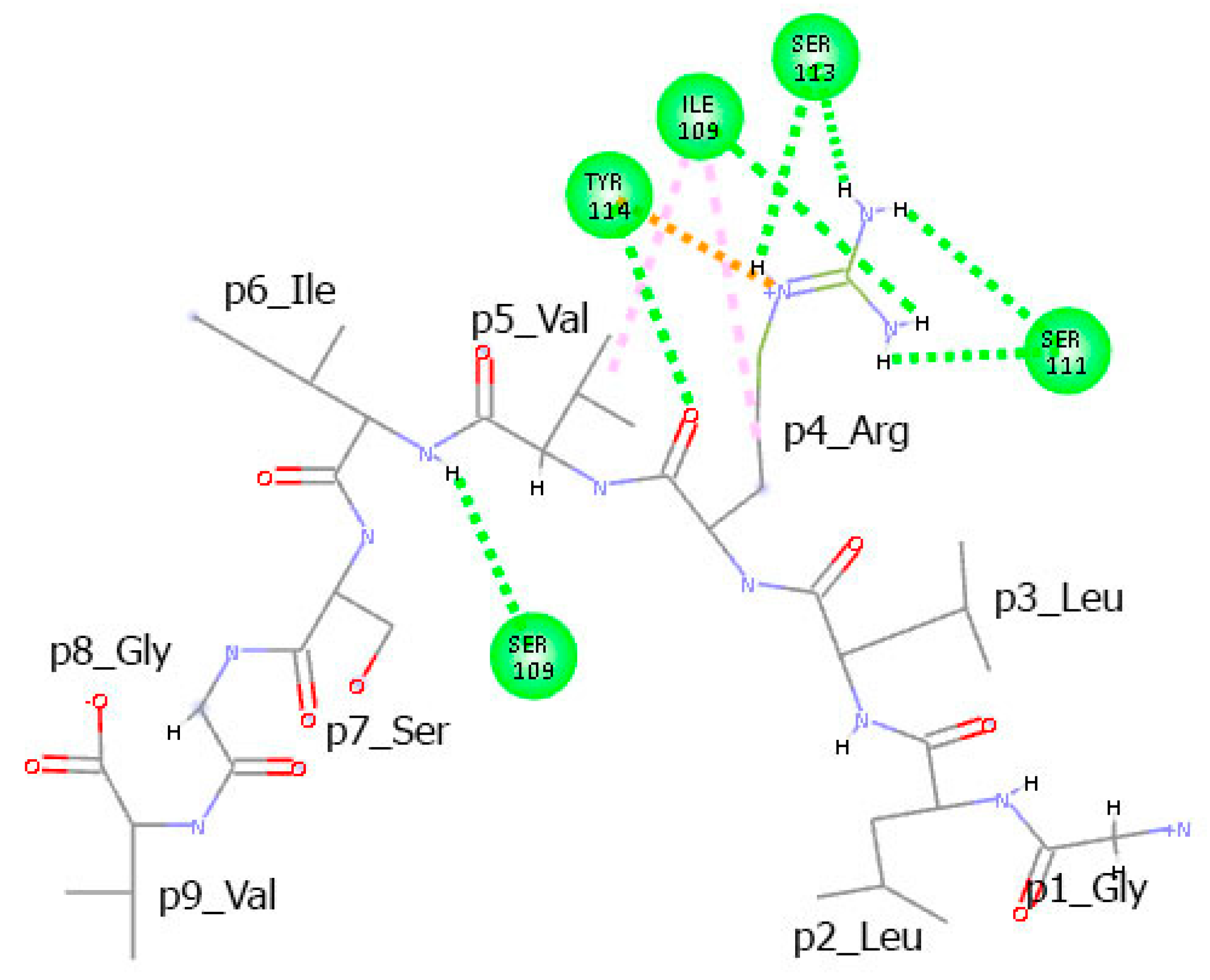
| aas | p1 | p2 | p3 | p4 | p5 | p6 | p7 | p8 | p9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (Ala) | −0.106 | 0.061 | −0.050 | 0.061 | 0.006 | 0.006 | −0.050 | −0.050 | −0.106 |
| C (Cys) | −0.106 | −0.106 | −0.106 | −0.050 | −0.106 | −0.106 | −0.050 | −0.050 | −0.106 |
| D (Asp) | −0.106 | −0.050 | 0.117 | 0.006 | −0.106 | −0.050 | −0.106 | −0.106 | −0.106 |
| E (Glu) | −0.106 | −0.106 | −0.050 | 0.117 | −0.106 | −0.106 | 0.006 | 0.061 | −0.106 |
| F (Phe) | 0.117 | −0.106 | −0.050 | −0.050 | 0.172 | −0.050 | 0.394 | 0.006 | −0.050 |
| G (Gly) | −0.050 | −0.106 | 0.006 | 0.117 | −0.106 | −0.050 | −0.050 | 0.006 | −0.106 |
| H (His) | 0.006 | −0.106 | −0.050 | −0.050 | 0.006 | −0.050 | −0.050 | 0.006 | −0.106 |
| I (Ile) | 0.117 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.117 | 0.006 | −0.050 | 0.006 |
| K (Lys) | 0.172 | −0.106 | 0.117 | 0.061 | −0.106 | −0.050 | −0.050 | −0.106 | −0.050 |
| L (Leu) | 0.117 | 0.894 | 0.061 | 0.006 | 0.283 | 0.283 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.672 |
| M (Met) | −0.050 | 0.061 | −0.106 | 0.006 | −0.106 | −0.050 | −0.050 | −0.106 | 0.006 |
| N (Asn) | −0.106 | −0.106 | 0.006 | −0.050 | −0.106 | −0.106 | 0.061 | 0.006 | −0.106 |
| P (Pro) | −0.106 | 0.117 | −0.106 | −0.050 | 0.061 | 0.172 | 0.061 | −0.050 | −0.050 |
| Q (Gln) | 0.006 | −0.050 | 0.006 | 0.061 | −0.050 | 0.006 | −0.106 | 0.117 | −0.106 |
| R (Arg) | 0.006 | −0.106 | 0.061 | 0.006 | −0.050 | 0.061 | −0.050 | 0.172 | 0.006 |
| S (Ser) | 0.117 | −0.106 | 0.117 | 0.061 | 0.172 | 0.228 | 0.006 | 0.228 | −0.106 |
| T (Thr) | −0.106 | 0.117 | −0.050 | −0.106 | −0.050 | 0.006 | 0.172 | 0.006 | 0.006 |
| V (Val) | 0.228 | 0.006 | 0.061 | 0.006 | 0.117 | −0.050 | 0.006 | 0.061 | 0.450 |
| W (Trp) | −0.106 | −0.106 | −0.106 | −0.106 | −0.050 | −0.106 | −0.106 | −0.106 | −0.106 |
| Y (Tyr) | 0.061 | −0.106 | 0.117 | −0.050 | 0.117 | −0.106 | −0.050 | −0.050 | 0.061 |
| aas | p1 | p2 | p3 | p4 | p5 | p6 | p7 | p8 | p9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (Ala) | 0.170 | 0.003 | 0.093 | 0.106 | 0.106 | 0.003 | 0.029 | 0.119 | 0.003 |
| C (Cys) | −0.151 | −0.163 | −0.163 | −0.138 | −0.112 | −0.138 | −0.151 | −0.151 | −0.138 |
| D (Asp) | −0.087 | −0.074 | 0.272 | 0.170 | −0.048 | −0.074 | −0.061 | −0.087 | −0.138 |
| E (Glu) | −0.061 | −0.048 | 0.054 | 0.183 | 0.003 | −0.087 | 0.029 | 0.080 | −0.112 |
| F (Phe) | 0.080 | −0.099 | −0.048 | −0.087 | −0.022 | −0.048 | −0.035 | −0.010 | 0.067 |
| G (Gly) | 0.042 | −0.061 | 0.016 | 0.131 | 0.080 | 0.080 | 0.003 | 0.042 | −0.087 |
| H (His) | −0.074 | −0.112 | −0.022 | −0.074 | −0.035 | −0.087 | −0.035 | −0.035 | −0.138 |
| I (Ile) | −0.048 | 0.029 | −0.022 | −0.125 | −0.035 | 0.080 | 0.003 | −0.074 | 0.016 |
| K (Lys) | −0.048 | −0.151 | −0.074 | 0.003 | −0.022 | −0.01 | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.003 |
| L (Leu) | 0.375 | 0.696 | 0.247 | 0.042 | 0.067 | 0.234 | 0.311 | 0.183 | 0.837 |
| M (Met) | −0.074 | −0.074 | −0.087 | −0.125 | −0.112 | −0.112 | −0.087 | −0.099 | −0.112 |
| N (Asn) | −0.061 | −0.151 | −0.061 | −0.099 | −0.022 | −0.061 | −0.087 | −0.074 | −0.125 |
| P (Pro) | −0.112 | 0.029 | −0.061 | 0.119 | 0.054 | 0.183 | 0.029 | −0.022 | −0.138 |
| Q (Gln) | −0.035 | −0.035 | 0.003 | 0.016 | −0.022 | −0.061 | 0.042 | 0.093 | −0.112 |
| R (Arg) | 0.093 | 0.144 | −0.010 | 0.042 | 0.131 | −0.010 | −0.035 | −0.022 | −0.048 |
| S (Ser) | 0.144 | 0.106 | 0.106 | 0.119 | 0.054 | 0.093 | 0.029 | 0.131 | −0.074 |
| T (Thr) | −0.035 | 0.042 | −0.087 | −0.061 | −0.010 | 0.119 | 0.003 | 0.106 | −0.010 |
| V (Val) | 0.080 | 0.067 | −0.061 | 0.016 | 0.170 | 0.106 | 0.170 | 0.016 | 0.260 |
| W (Trp) | −0.138 | −0.138 | −0.099 | −0.138 | −0.112 | −0.112 | −0.112 | −0.138 | −0.151 |
| Y (Tyr) | −0.061 | −0.010 | 0.003 | −0.099 | −0.112 | −0.099 | −0.048 | −0.074 | 0.196 |
| T-Cell Epitopes | Non-T-Cell Epitopes | Identical Residues | X-Ray Structures PDB Id |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLLMWITQV | GLLRVISGV | 4 | 6RPA, 6RPB, 6RP9 [12] |
| VTIGPRLLL | LPVSPRLQL | 4 | - |
| RATVAPRSL | SAYGEPRKL | 4 | - |
| RMSF (Avg) | T-Cell Epitope SLLMWITQV | Non-T-Cell Epitope GLLRVISGV |
|---|---|---|
| HLA | 4.378 | 4.506 |
| peptide (overall) | 4.055 | 3.798 |
| p1 | 3.505 | 3.463 |
| p2 | 3.314 | 3.189 |
| p3 | 3.394 | 3.323 |
| p4 | 4.441 | 4.452 |
| p5 | 4.644 | 4.125 |
| p6 | 3.963 | 3.666 |
| p7 | 4.303 | 4.004 |
| p8 | 4.879 | 4.163 |
| p9 | 4.464 | 4.302 |
| TCRα | 10.340 | 9.883 |
| TCRβ | 10.890 | 8.847 |
| Total | 7.568 | 7.039 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doytchinova, I.; Sotirov, S.; Dimitrov, I. Molecular Insights into Tumor Immunogenicity. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080641
Doytchinova I, Sotirov S, Dimitrov I. Molecular Insights into Tumor Immunogenicity. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(8):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080641
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoytchinova, Irini, Stanislav Sotirov, and Ivan Dimitrov. 2025. "Molecular Insights into Tumor Immunogenicity" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 8: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080641
APA StyleDoytchinova, I., Sotirov, S., & Dimitrov, I. (2025). Molecular Insights into Tumor Immunogenicity. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(8), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080641









