Dihydroartemisinin Alleviates the Symptoms of a Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Through Regulating Splenic T/B-Cell Heterogeneity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Dihydroartemisinin Treatment
2.3. Tissue Histological Study
2.4. Isolation of Splenic T and B Cells
2.5. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
2.6. scRNA-Seq Data Processing and Quality Control
2.7. Pseudotime Trajectory Analysis
2.8. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.9. Cell–Cell Communication Analysis with CellChat
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
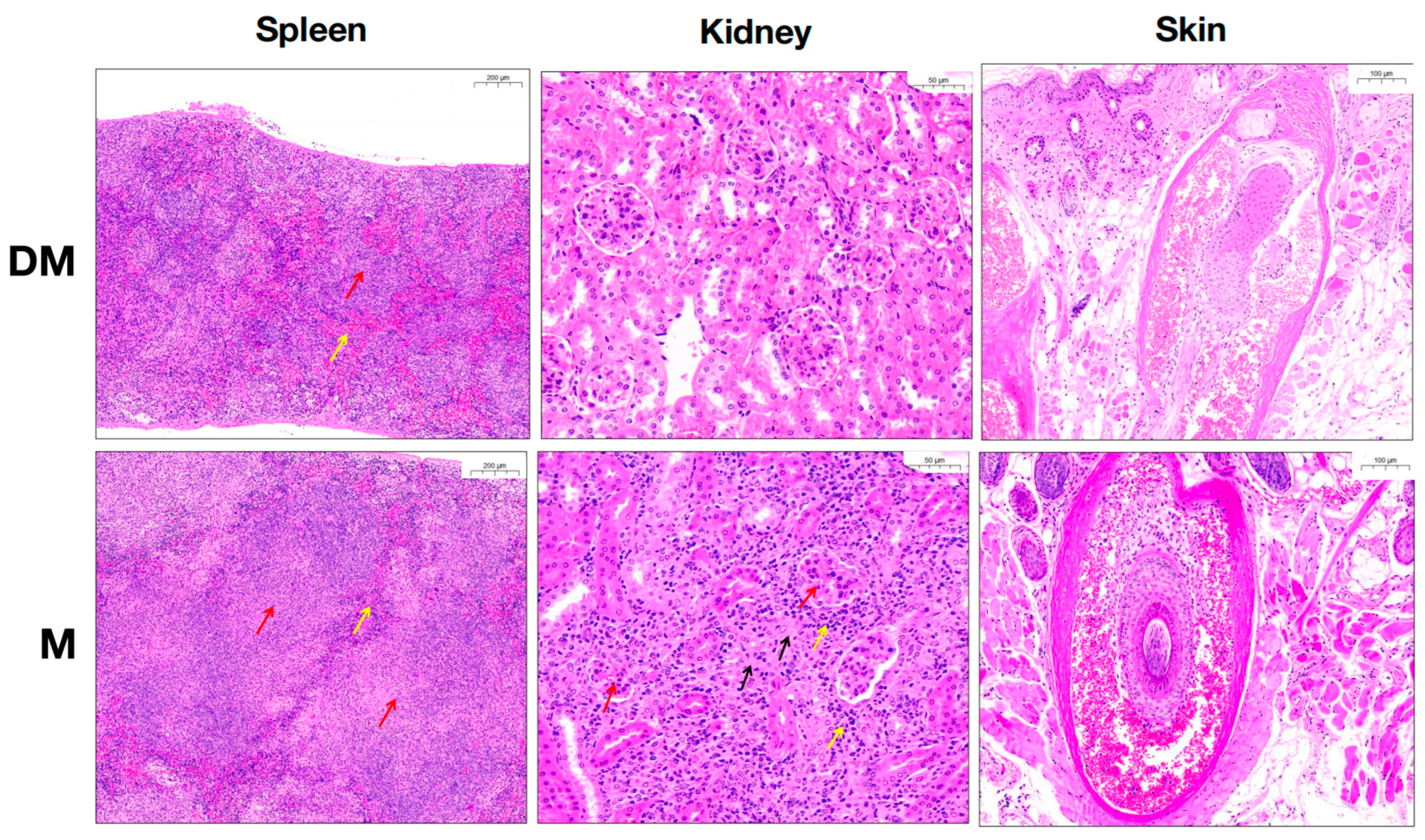
3.1. DHA Significantly Attenuated Clinical Symptoms and Renal Inflammation of MRL/lpr Mice
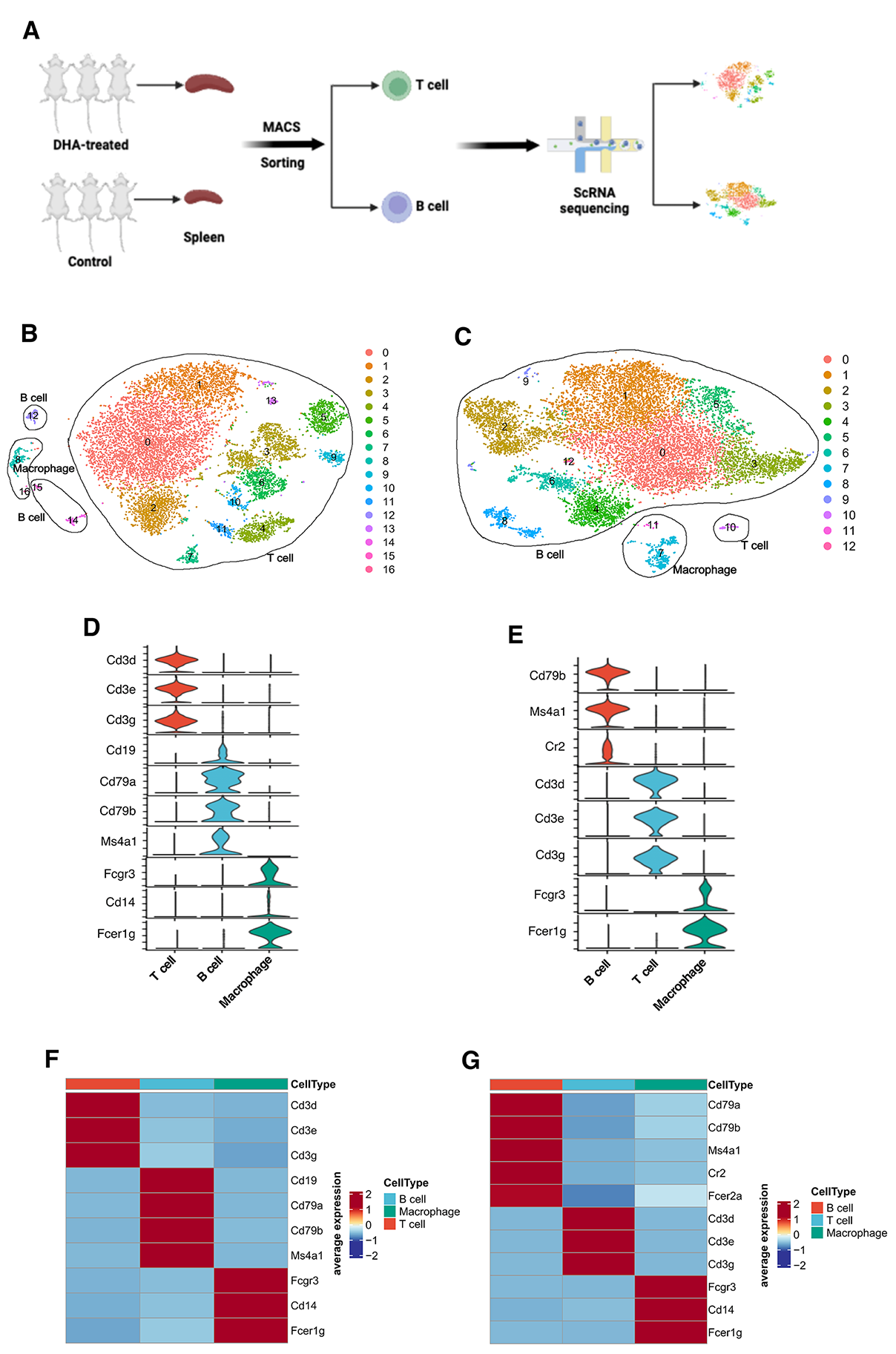
3.2. scRNA-Seq Workflow and Clustering of Sorted T Cells and B Cells from Spleen
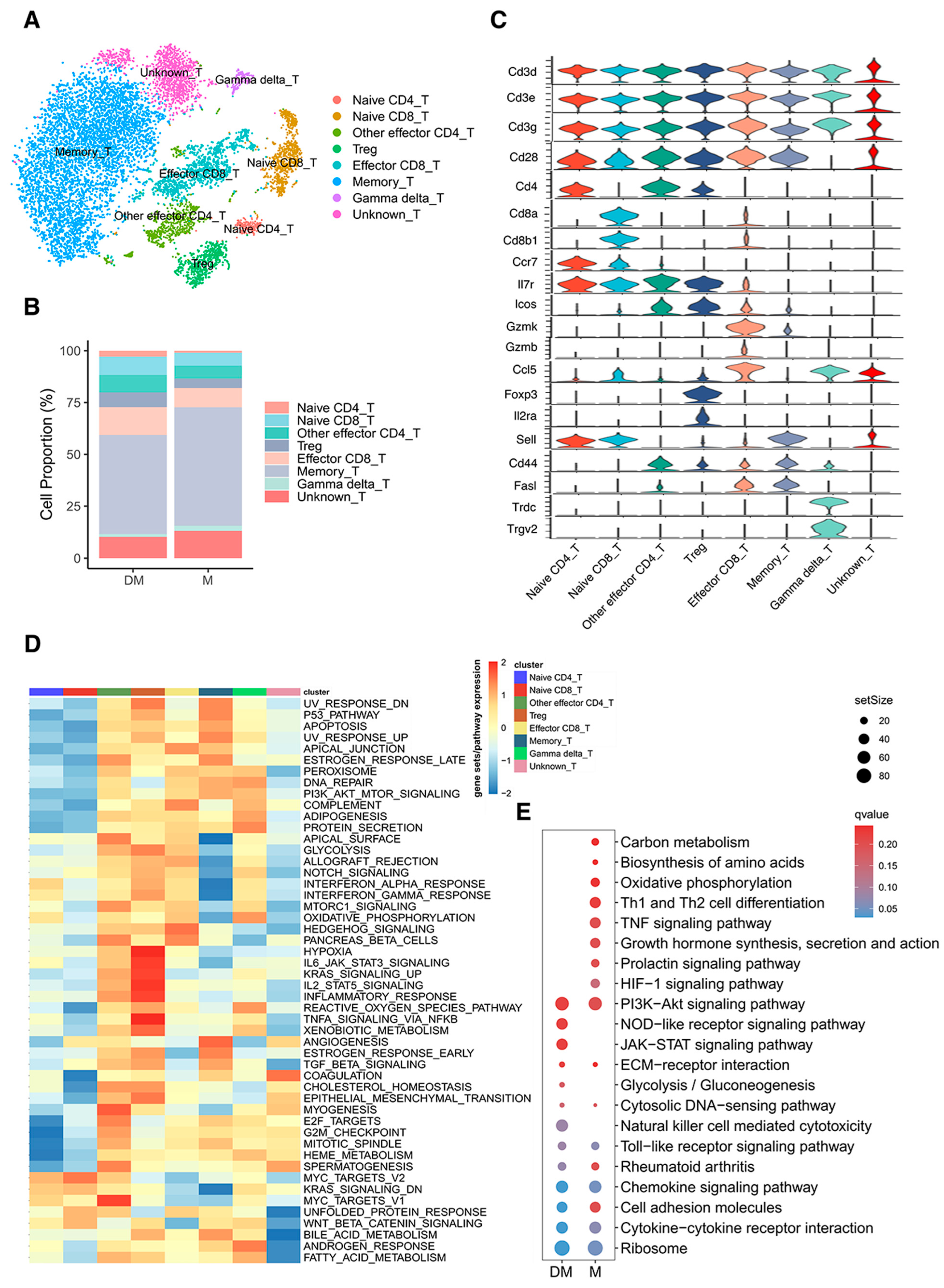
3.3. Re-Clustering of T Cells Illustrated Different Cell Proportions and Signaling Pathways in DHA-Treated and Control Mice
3.4. Re-Clustering of B Cells Revealed Significant Reduction of Plasma Cells in Spleen of DHA-Treated Mice
3.5. Pseudotime Trajectory Analysis Unveiled the Developmental and Molecular Characteristics of T-Cell and B-Cell Subtypes in Spleen
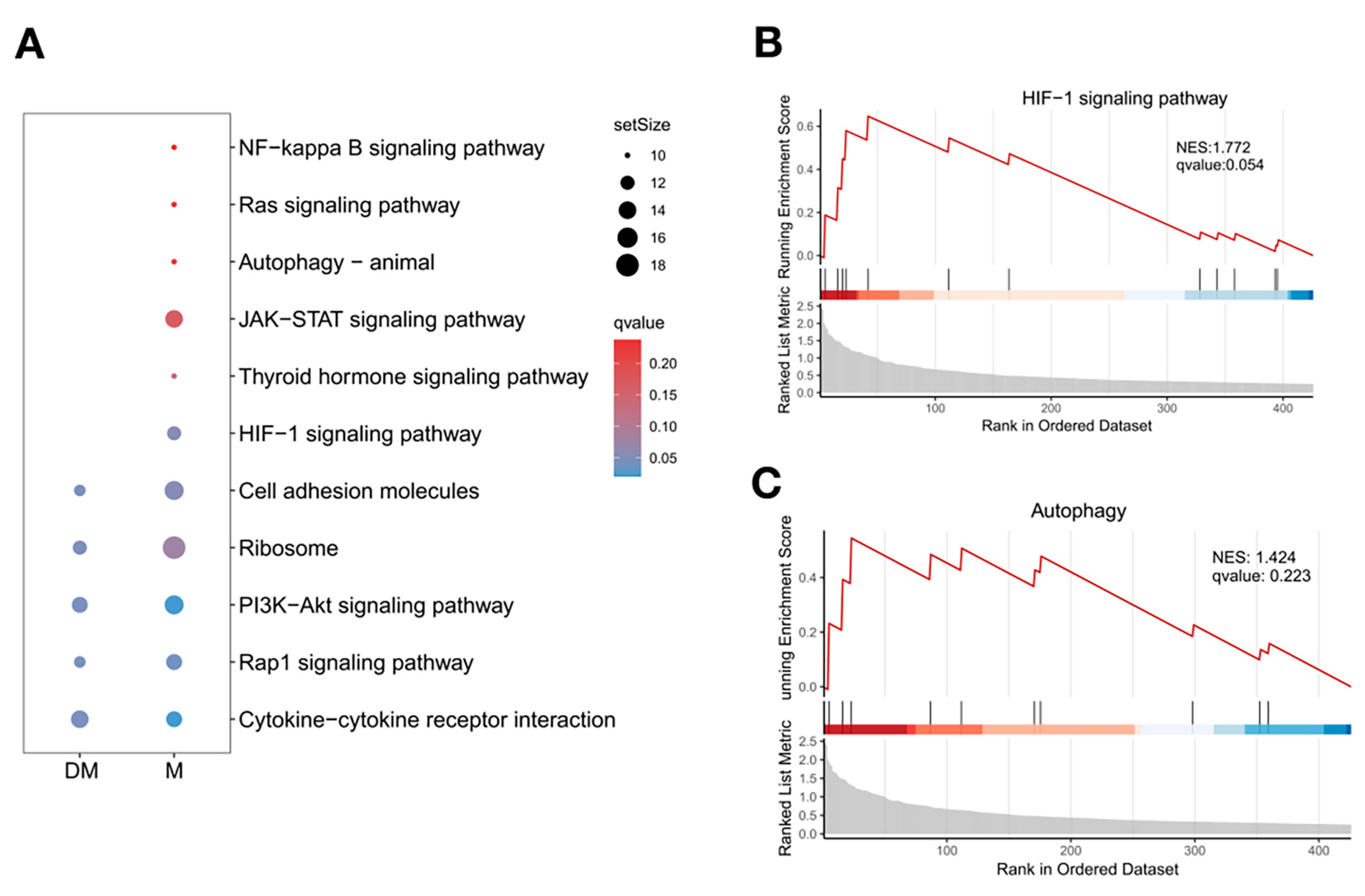
3.6. DHA Might Inhibit B-Cell Differentiation into Plasma Cells by Regulating the Function of Effector CD4+T Cells in Lupus Spleen
3.7. Different Interactions Were Found Between Effector CD4+T Cells and B Cells in DHA-Treated and Control Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsokos, G.C. Autoimmunity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H.; Liao, J.; Cheng, B.; Lu, Q. Therapeutic advances in the treatment of SLE. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 72, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basta, F.; Fasola, F.; Triantafyllias, K.; Schwarting, A. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Therapy: The Old and the New. Rheumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möckel, T.; Basta, F.; Weinmann-Menke, J.; Schwarting, A. B cell activating factor (BAFF): Structure, functions, autoimmunity and clinical implications in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, N.; Manaye, S.; Naushad, H.; Cheran, K.; Murthy, C.; Bornemann, E.A.; Kamma, H.K.; Alabbas, M.; Elashahab, M.; Siddiqui, H.N. The Safety and Efficacy of Rituximab and Belimumab in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e40719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Lin, W.; Deng, X.; Ba, X.; Han, L.; Chen, Z.; Qin, K.; Huang, Y.; Tu, S. Potential Implications of Quercetin in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 689044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, M. Application of herbal traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of lupus nephritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 981063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makenga, G.; Baraka, V.; Francis, F.; Nakato, S.; Gesase, S.; Mtove, G.; Madebe, R.; Kyaruzi, E.; Minja, D.T.R.; Lusingu, J.P.A.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of intermittent preventive treatment with dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine or artesunate-amodiaquine for reducing malaria and related morbidities in schoolchildren in Tanzania: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Glob. Health 2023, 11, e1277–e1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Mo, S.; Lu, J. Dihydroartemisinin: A Potential Natural Anticancer Drug. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Wu, F.; Ying, K.; Xu, Y.; Shan, L.; Lv, Y.; Gao, X.; Xu, D.; Lu, J.; Xie, B. Therapeutic effects of dihydroartemisinin in multiple stages of colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6225–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, Q.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, X.; Pu, W.; Zhong, X.; Guo, X. Dihydroartemisinin as a Sensitizing Agent in Cancer Therapies. Onco Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 2563–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tao, T.; Wang, W.; Yang, B.; Cha, X. Dihydroartemisinin attenuated the symptoms of mice model of systemic lupus erythematosus by restoring the Treg/Th17 balance. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 48, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, J.; Liao, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; He, R.; Men, L.; Lu, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.; et al. Dihydroartemisinin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xie, Z.; Liu, F.; Han, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, D.; Bao, X.; Sun, J.; Wen, C.; Fan, Y. Dihydroartemisinin inhibits activation of the Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway and production of type I interferon in spleen cells from lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Qi, J.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Xia, X.; Dou, H.; Hou, Y. Protective effect of dihydroartemisinin in inhibiting senescence of myeloid-derived suppressor cells from lupus mice via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 143, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Boulougoura, A.; Endo, Y.; Tsokos, G.C. Abnormalities of T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: New insights in pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 132, 102870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, D.; Yang, B.; Yang, M.; Xiong, F.; Zhu, X.; Tan, Y.; Wu, H. Bach2 in CD4(+) T cells from SLE patients modulates B-cell differentiation and IgG production. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, e2250109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Jiang, N.; Su, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Lv, L.; Sang, X.; Chen, R.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Q. Dihydroartemisinin beneficially regulates splenic immune cell heterogeneity through the SOD3-JNK-AP-1 axis. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 1636–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Y.; Wang, D.C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Huang, A.F.; Xu, W.D. Emerging role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in inflammatory autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1073971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.I.; Lee, A.H.; Shin, H.Y.; Song, H.R.; Park, J.H.; Kang, T.B.; Lee, S.R.; Yang, S.H. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-α Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Ren, Y.; Feng, X.; Yao, G.; Chen, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Sun, L. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha promotes mesangial cell proliferation in lupus nephritis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 40, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garchow, B.; Acosta, Y.M.; Kiriakidou, M. HIF-1α and miR-210 differential and lineage-specific expression in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 133, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.D.; Dong, Y.J.; Tu, Y.Y.; Lin, Z.B. Dihydroarteannuin ameliorates lupus symptom of BXSB mice by inhibiting production of TNF-alpha and blocking the signaling pathway NF-kappa B translocation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, L.Y.; Tesselaar, K.; Borghans, J.A.M. Memories that last: Dynamics of memory T cells throughout the body. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 316, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, S.E.; O'Neill, L.A. HIF1α and metabolic reprogramming in inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3699–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, A.R.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, C.R.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, M.L. IL-17 Induces Autophagy Dysfunction to Promote Inflammatory Cell Death and Fibrosis in Keloid Fibroblasts via the STAT3 and HIF-1α Dependent Signaling Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 888719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldhoff, L.M.; Rueda, C.M.; Moreno-Fernandez, M.E.; Sauer, J.; Jackson, C.M.; Chougnet, C.A.; Rupp, J. IL-1β induced HIF-1α inhibits the differentiation of human FOXP3(+) T cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wei, J.; Zhan, F.; Wang, R.; Fu, K.; Wan, X.; Li, Z. Urinary hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha levels are associated with histologic chronicity changes and renal function in patients with lupus nephritis. Yonsei Med. J. 2012, 53, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Wu, C.; Li, L.J.; Fan, Y.G.; Pan, H.F.; Tao, J.H.; Leng, R.X.; Ye, D.Q. RNAi Silencing of HIF-1α Ameliorates Lupus Development in MRL/lpr Mice. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Hou, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, H. Dihydroartemisinin suppresses glycolysis of LNCaP cells by inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway and downregulating HIF-1α expression. Life Sci. 2019, 233, 116730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, H.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Wu, H.; Wu, J. Dihydroartemisinin Alleviates the Symptoms of a Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Through Regulating Splenic T/B-Cell Heterogeneity. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070528
Qin H, Zhu X, Liu X, Wang Y, Liang J, Wu H, Wu J. Dihydroartemisinin Alleviates the Symptoms of a Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Through Regulating Splenic T/B-Cell Heterogeneity. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070528
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Haihong, Xiaohua Zhu, Xiao Liu, Yilun Wang, Jun Liang, Hao Wu, and Jinfeng Wu. 2025. "Dihydroartemisinin Alleviates the Symptoms of a Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Through Regulating Splenic T/B-Cell Heterogeneity" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070528
APA StyleQin, H., Zhu, X., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Liang, J., Wu, H., & Wu, J. (2025). Dihydroartemisinin Alleviates the Symptoms of a Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Through Regulating Splenic T/B-Cell Heterogeneity. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070528







