Elucidating the Role of CNOT2 in Regulating Cancer Cell Growth via the Modulation of p53 and c-Myc Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Oncogenic Functions of CNOT2 in Cancer Cells
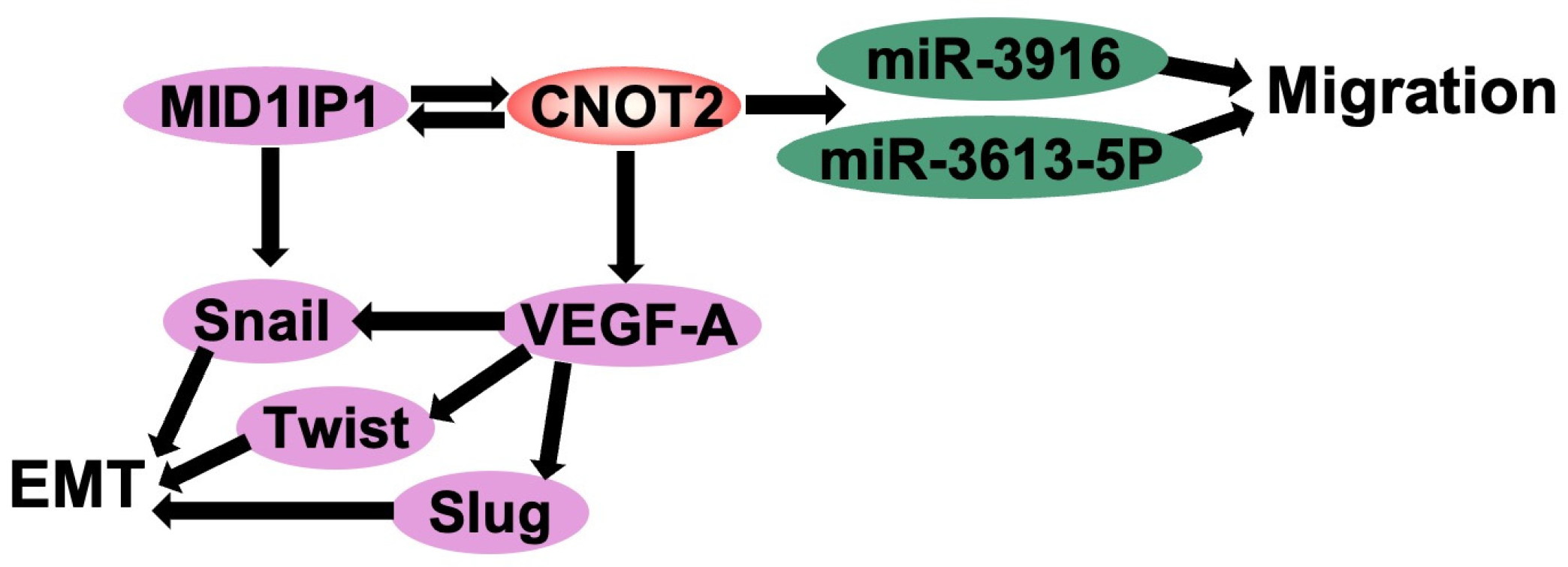
3. CNOT2 Promotes Cancer Cell Proliferation, Angiogenesis, and EMT
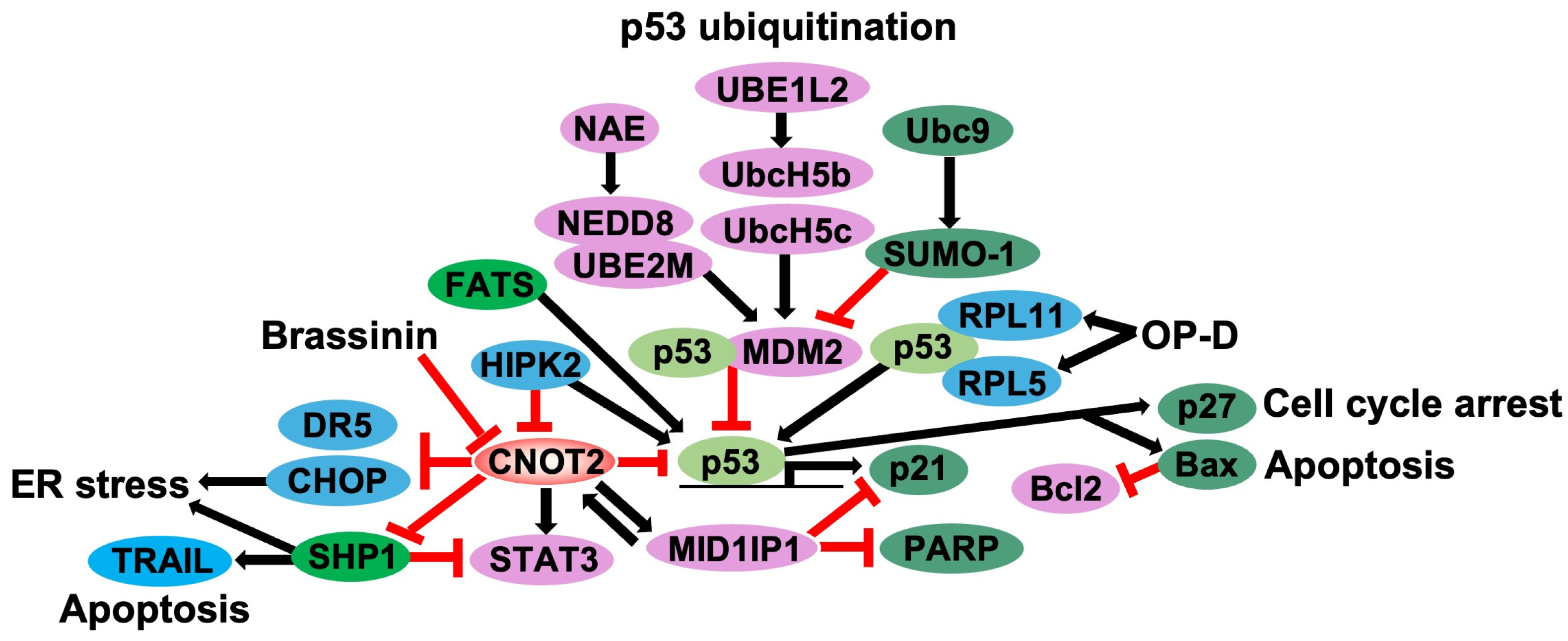
4. Knockdown of CNOT2 Induces p53 Activation
4.1. Regulation of p53-MDM2 Loop by Ribosomal Proteins
4.2. Regulation of p53-MDM2 Loop: Ubiquitylation and Neddylation
4.3. CNOT2 Knockdown Induces p53 in Cancer Cells
4.4. Modulation of p53 Activity Through CNOT2 Inhibition as Potential Anticancer Strategy
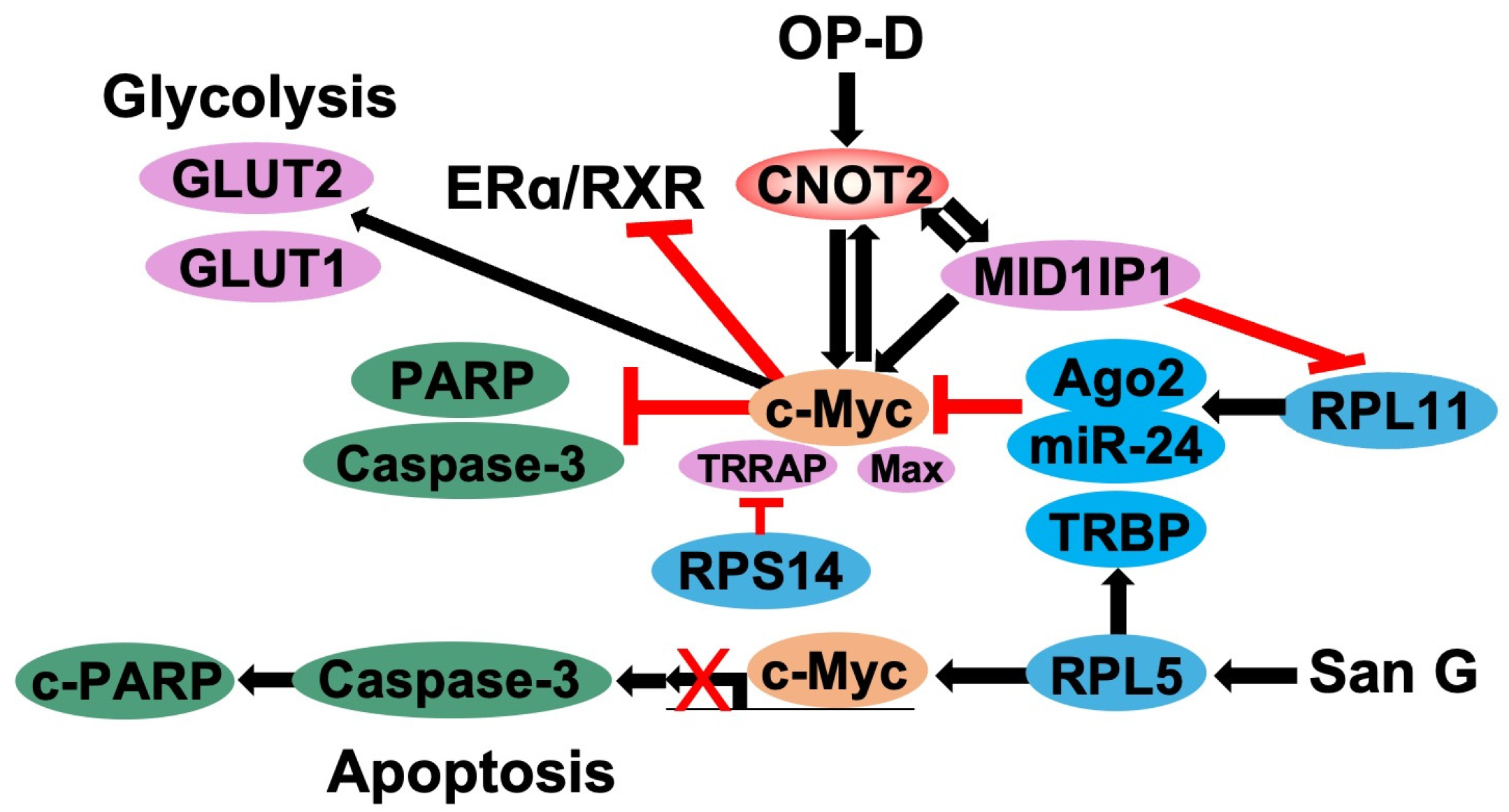
5. CNOT2 Regulates c-Myc Expression via Ribosomal Proteins
5.1. Function of c-Myc in Cancer Cells
5.2. Regulation of c-Myc by Ribosomal Proteins
5.3. Knockdown of CNOT2 Effects c-Myc Expression
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, D.; Liao, W.; Zeng, S.X.; Lu, H. Reviving the guardian of the genome: Small molecule activators of p53. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 178, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilfou, J.T.; Lowe, S.W. Tumor suppressive functions of p53. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.W.; Byun, S.; Kwon, E.; Hwang, S.Y.; Chu, K.; Hiraki, M.; Jo, S.H.; Weins, A.; Hakroush, S.; Cebulla, A.; et al. Control of signaling-mediated clearance of apoptotic cells by the tumor suppressor p53. Science 2015, 349, 1261669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Kroemer, G. Ferroptosis in p53-dependent oncosuppression and organismal homeostasis. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1237–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanapradeepan, K.; Basu, S.; Barnoud, T.; Budina-Kolomets, A.; Kung, C.P.; Murphy, M.E. The p53 Tumor Suppressor in the Control of Metabolism and Ferroptosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, E.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Piwnica-Worms, H. Contribution of p53 to metastasis. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J. The Cell-Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor Initiation and Progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhang Ghahremani, M.; Goossens, S.; Nittner, D.; Bisteau, X.; Bartunkova, S.; Zwolinska, A.; Hulpiau, P.; Haigh, K.; Haenebalcke, L.; Drogat, B.; et al. p53 promotes VEGF expression and angiogenesis in the absence of an intact p21-Rb pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.A.; Vousden, K.H.; Norman, J.C. p53 and its mutants in tumor cell migration and invasion. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collart, M.A. The CCR4-NOT complex is a key regulator of eukaryotic gene expression. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2016, 7, 438–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, S.; Zwartjes, C.G.; van Schaik, F.M.; Timmers, H.T. Involvement of the SMRT/NCoR-HDAC3 complex in transcriptional repression by the CNOT2 subunit of the human CCR4-NOT complex. Biochem. J. 2006, 398, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, D.; Ko, H.M.; Jang, H.J. Inhibition of CNOT2 Induces Apoptosis via MID1IP1 in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Activating p53. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwartjes, C.G.; Jayne, S.; van den Berg, D.L.; Timmers, H.T. Repression of promoter activity by CNOT2, a subunit of the transcription regulatory CCR4-NOT complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 10848–10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Inoue, T.; Yokoyama, K.; Morita, M.; Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, T. CNOT2 depletion disrupts and inhibits the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex and induces apoptotic cell death. Genes Cells Devoted Mol. Cell. Mech. 2011, 16, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, E.J.; Jung, D.B.; Lee, H.; Han, I.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.H. CNOT2 promotes proliferation and angiogenesis via VEGF signaling in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 412, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jung, J.H.; Hwang, J.; Park, J.E.; Kim, J.H.; Park, W.Y.; Suh, J.Y.; Kim, S.H. CNOT2 Is Critically Involved in Atorvastatin Induced Apoptotic and Autophagic Cell Death in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. Cancers 2019, 11, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Sim, D.Y.; Im, E.; Kim, S.; Chang, S.; Kim, S.H. Colocalization of MID1IP1 and c-Myc is Critically Involved in Liver Cancer Growth via Regulation of Ribosomal Protein L5 and L11 and CNOT2. Cells 2020, 9, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.Y.; Park, J.E.; Jung, J.H. Apoptotic Effect of Brassinin via Inhibition of CNOT2 and Activation of p53 and Its Combination Effect with Doxorubicin. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, B.M. Characterization of CNOT1 and CNOT2, Candidate Colorectal Cancer Genes Identified in a Transposon-Based Genetic Screen in Mice. Master’s Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Faraji, F.; Hu, Y.; Wu, G.; Goldberger, N.E.; Walker, R.C.; Zhang, J.; Hunter, K.W. An integrated systems genetics screen reveals the transcriptional structure of inherited predisposition to metastatic disease. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastushenko, I.; Blanpain, C. EMT Transition States during Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.O.; Kang, S.E.; Choi, M.; Rhee, K.J.; Yun, M. CCR4-NOT transcription complex subunit 2 regulates TRAIL sensitivity in nonsmallcell lung cancer cells via the STAT3 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.M.; Jee, W.; Lee, D.; Jang, H.J.; Jung, J.H. Ophiopogonin D increases apoptosis by activating p53 via ribosomal protein L5 and L11 and inhibiting the expression of c-Myc via CNOT2. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 974468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, E.J. MiRNA 3613-5P and MiRNA 3916 rescued the inhibition of cell migration in CNOT2 depleted MDA-MD-231 cells. Transl Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 4542–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J.; Oren, M. The first 30 years of p53: Growing ever more complex. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigal, A.; Rotter, V. Oncogenic mutations of the p53 tumor suppressor: The demons of the guardian of the genome. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6788–6793. [Google Scholar]
- Kastan, M.B.; Canman, C.E.; Leonard, C.J. P53, cell cycle control and apoptosis: Implications for cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995, 14, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.R.; Fisher, B.E.; Batchelor, E. p53 Pulses Diversify Target Gene Expression Dynamics in an mRNA Half-Life-Dependent Manner and Delineate Co-regulated Target Gene Subnetworks. Cell Syst. 2016, 2, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.L.; Levine, A.J. The p53 pathway: Positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2899–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyurovsky, M.V.; Katz, C.; Laptenko, O.; Beckerman, R.; Lokshin, M.; Ahn, J.; Byeon, I.J.; Gabizon, R.; Mattia, M.; Zupnick, A.; et al. The C terminus of p53 binds the N-terminal domain of MDM2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liao, W.J.; Liao, J.M.; Liao, P.; Lu, H. Ribosomal proteins: Functions beyond the ribosome. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 7, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.S.; Lu, H. Inhibition of MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination and degradation by ribosomal protein L5. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44475–44482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Rayburn, E.R.; Hill, D.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. Ribosomal protein S7 as a novel modulator of p53-MDM2 interaction: Binding to MDM2, stabilization of p53 protein, and activation of p53 function. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5029–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Hao, Q.; Liao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, H. Ribosomal protein S14 unties the MDM2-p53 loop upon ribosomal stress. Oncogene 2013, 32, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, R. Identification of ribosomal protein S25 (RPS25)-MDM2-p53 regulatory feedback loop. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2782–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungstrom, V.; Cortese, D.; Young, E.; Pandzic, T.; Mansouri, L.; Plevova, K.; Ntoufa, S.; Baliakas, P.; Clifford, R.; Sutton, L.A.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing in relapsing chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Clinical impact of recurrent RPS15 mutations. Blood 2016, 127, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chi, H.; Shan, P. Silencing Ribosomal Protein L22 Promotes Proliferation and Migration, and Inhibits Apoptosis of Gastric Cancer Cells by Regulating the Murine Double Minute 2-Protein 53 (MDM2-p53) Signaling Pathway. Med Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e928375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Park, J.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.E.; Song, E.J. Ribosomal protein S2 interplays with MDM2 to induce p53. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 523, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ren, C.; Jiang, D.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y. RPL34-AS1-induced RPL34 inhibits cervical cancer cell tumorigenesis via the MDM2-P53 pathway. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, F.; Wei, D.; Thomas, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, P.; Sun, Y. Ribosomal protein S27-like is a physiological regulator of p53 that suppresses genomic instability and tumorigenesis. Elife 2014, 3, e02236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanos, S.; Serrano, M. Depletion of ribosomal protein L37 occurs in response to DNA damage and activates p53 through the L11/MDM2 pathway. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 4005–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Ikeda, K.; Okumura, T.; Sato, W.; Horie-Inoue, K.; Okamoto, K.; Takeda, S.; Inoue, S. Short hairpin RNA library-based functional screening identified ribosomal protein L31 that modulates prostate cancer cell growth via p53 pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, Y.; Dai, M.S.; Sun, X.X. Ribosomal protein L4 is a novel regulator of the MDM2-p53 loop. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16217–16226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Hou, Z.; Zuo, S.; Zhou, X.; Feng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, X. LUCAT1 promotes colorectal cancer tumorigenesis by targeting the ribosomal protein L40-MDM2-p53 pathway through binding with UBA52. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1194–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, S.Y.; Adler, V.; Buschmann, T.; Wu, X.; Ronai, Z. Mdm2 association with p53 targets its ubiquitination. Oncogene 1998, 17, 2543–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulmeester, E.; Frenk, R.; Stad, R.; de Graaf, P.; Marine, J.C.; Vousden, K.H.; Jochemsen, A.G. Critical role for a central part of Mdm2 in the ubiquitylation of p53. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 4929–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Honda, R.; Yasuda, H. Association of p19(ARF) with Mdm2 inhibits ubiquitin ligase activity of Mdm2 for tumor suppressor p53. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saville, M.K.; Sparks, A.; Xirodimas, D.P.; Wardrop, J.; Stevenson, L.F.; Bourdon, J.C.; Woods, Y.L.; Lane, D.P. Regulation of p53 by the ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes UbcH5B/C in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 42169–42181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelzer, C.; Kassner, I.; Matentzoglu, K.; Singh, R.K.; Wollscheid, H.P.; Scheffner, M.; Schmidtke, G.; Groettrup, M. UBE1L2, a novel E1 enzyme specific for ubiquitin. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23010–23014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Qiu, L.; Ma, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Hao, X.; Li, Z. FATS is an E2-independent ubiquitin ligase that stabilizes p53 and promotes its activation in response to DNA damage. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5424–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, T.; Lerner, D.; Lee, C.G.; Ronai, Z. The Mdm-2 amino terminus is required for Mdm2 binding and SUMO-1 conjugation by the E2 SUMO-1 conjugating enzyme Ubc9. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 40389–40395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Sim, D.Y.; Im, E.; Park, J.; Park, W.Y.; Ahn, C.H.; Shim, B.S.; Kim, B.; et al. UBE2M Drives Hepatocellular Cancer Progression as a p53 Negative Regulator by Binding to MDM2 and Ribosomal Protein L11. Cancers 2021, 13, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puca, R.; Nardinocchi, L.; Sacchi, A.; Rechavi, G.; Givol, D.; D’Orazi, G. HIPK2 modulates p53 activity towards pro-apoptotic transcription. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravizza, R.; Gariboldi, M.B.; Passarelli, L.; Monti, E. Role of the p53/p21 system in the response of human colon carcinoma cells to Doxorubicin. BMC Cancer 2004, 4, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondy, S.; David, V.; Verdier, M.; Mathonnet, M.; Perraud, A.; Christou, N. 5-Fluorouracil resistance mechanisms in colorectal cancer: From classical pathways to promising processes. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3142–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Ro, E.J.; Yoon, J.S.; Mizutani, T.; Kang, D.W.; Park, J.C.; Il Kim, T.; Clevers, H.; Choi, K.Y. 5-FU promotes stemness of colorectal cancer via p53-mediated WNT/beta-catenin pathway activation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Kang, Y.; Thapa, D.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, J.A. Role of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 in docetaxel-induced cell death of human colorectal cancer cells with different p53 status. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2011, 34, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamble, D.B.; Jacks, T.; Lippard, S.J. p53-Dependent and -independent responses to cisplatin in mouse testicular teratocarcinoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6163–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorolla, A.; Wang, E.; Golden, E.; Duffy, C.; Henriques, S.T.; Redfern, A.D.; Blancafort, P. Precision medicine by designer interference peptides: Applications in oncology and molecular therapeutics. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hann, S.R.; Eisenman, R.N. Proteins encoded by the human c-myc oncogene: Differential expression in neoplastic cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1984, 4, 2486–2497. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.M.; Thomas, S.D.; Islam, A.; Muench, D.; Sedoris, K. c-Myc and cancer metabolism. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5546–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.S.; Lu, H. Crosstalk between c-Myc and ribosome in ribosomal biogenesis and cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 105, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, M.; Henriksson, M. The Myc oncoprotein as a therapeutic target for human cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2006, 16, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.M.; Zhou, X.; Gatignol, A.; Lu, H. Ribosomal proteins L5 and L11 co-operatively inactivate c-Myc via RNA-induced silencing complex. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4916–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fancello, L.; Kampen, K.R.; Hofman, I.J.; Verbeeck, J.; De Keersmaecker, K. The ribosomal protein gene RPL5 is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor in multiple cancer types. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 14462–14478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challagundla, K.B.; Sun, X.X.; Zhang, X.; DeVine, T.; Zhang, Q.; Sears, R.C.; Dai, M.S. Ribosomal protein L11 recruits miR-24/miRISC to repress c-Myc expression in response to ribosomal stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 4007–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, W.; Ko, H.M.; Park, D.I.; Park, Y.R.; Park, S.M.; Kim, H.; Na, Y.C.; Jung, J.H.; Jang, H.J. Momordicae Semen inhibits migration and induces apoptotic cell death by regulating c-Myc and CNOT2 in human pancreatic cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Sim, D.Y.; Im, E.; Park, W.Y.; Shim, B.S.; Ko, S.G.; Kim, S.H. Ribosomal protein L5 mediated inhibition of c-Myc is critically involved in sanggenon G induced apoptosis in non-small lung cancer cells. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Hao, Q.; Liao, J.M.; Liao, P.; Lu, H. Ribosomal protein S14 negatively regulates c-Myc activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21793–21801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Hoshina, M.; Nishijima, S.; Hoshina, N.; Kikuguchi, C.; Tomohiro, T.; Fukao, A.; Fujiwara, T.; Yamamoto, T. Regulation of CCR4-NOT complex deadenylase activity and cellular responses by MK2-dependent phosphorylation of CNOT2. RNA Biol. 2022, 19, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collart, M.A.; Panasenko, O.O. The Ccr4–Not complex: Architecture and structural insights. In Macromolecular Protein Complexes: Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 83, pp. 349–379. [Google Scholar]
- Collart, M.A.; Panasenko, O.O. The Ccr4–Not complex. Gene 2012, 492, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| RPs (p53↓) | RPs (p53↑) |
|---|---|
| S27L | RPL5 |
| RPL37 | RPL11 |
| L31 | RPL23 |
| RPL4 | S7 |
| RPL40 | S14 |
| RPS25 | |
| RPS15 | |
| RPL22 | |
| RPS25 | |
| RPL34 |
| Downregulated Genes by CNOT2 | Upregulated Genes by CNOT2 | Genes Downregulating CNOT2 | Genes Upregulating CNOT2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| p53 | MID1IP1 | RPL5 | c-Myc |
| p21 | c-Myc | RPL11 | MID1IP1 |
| ER/RXR | VEGF | RPS14 | |
| Snail | |||
| Slug | |||
| Twist | |||
| has-miR-3613-5p | |||
| has-miR-3916 | |||
| S27L | |||
| RPL37 | |||
| L31 | |||
| RPL4 | |||
| RPL40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, Y.J.; Oh, J.J.; Han, Y.J.; Jung, J.H. Elucidating the Role of CNOT2 in Regulating Cancer Cell Growth via the Modulation of p53 and c-Myc Expression. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080615
Lee J, Kim J-H, Lee YJ, Oh JJ, Han YJ, Jung JH. Elucidating the Role of CNOT2 in Regulating Cancer Cell Growth via the Modulation of p53 and c-Myc Expression. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(8):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080615
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jihyun, Ju-Ha Kim, Yu Jin Lee, Je Joung Oh, Yeo Jeong Han, and Ji Hoon Jung. 2025. "Elucidating the Role of CNOT2 in Regulating Cancer Cell Growth via the Modulation of p53 and c-Myc Expression" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 8: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080615
APA StyleLee, J., Kim, J.-H., Lee, Y. J., Oh, J. J., Han, Y. J., & Jung, J. H. (2025). Elucidating the Role of CNOT2 in Regulating Cancer Cell Growth via the Modulation of p53 and c-Myc Expression. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(8), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080615






