Differential Genetic Architecture of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) Based on Obesity Status: Evidence from a Large-Scale GWAS of Koreans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Clinical Measurements, Definition of the HOMA-IR, and Determination of Obese Group
2.3. Genotype
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
3.2. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS)
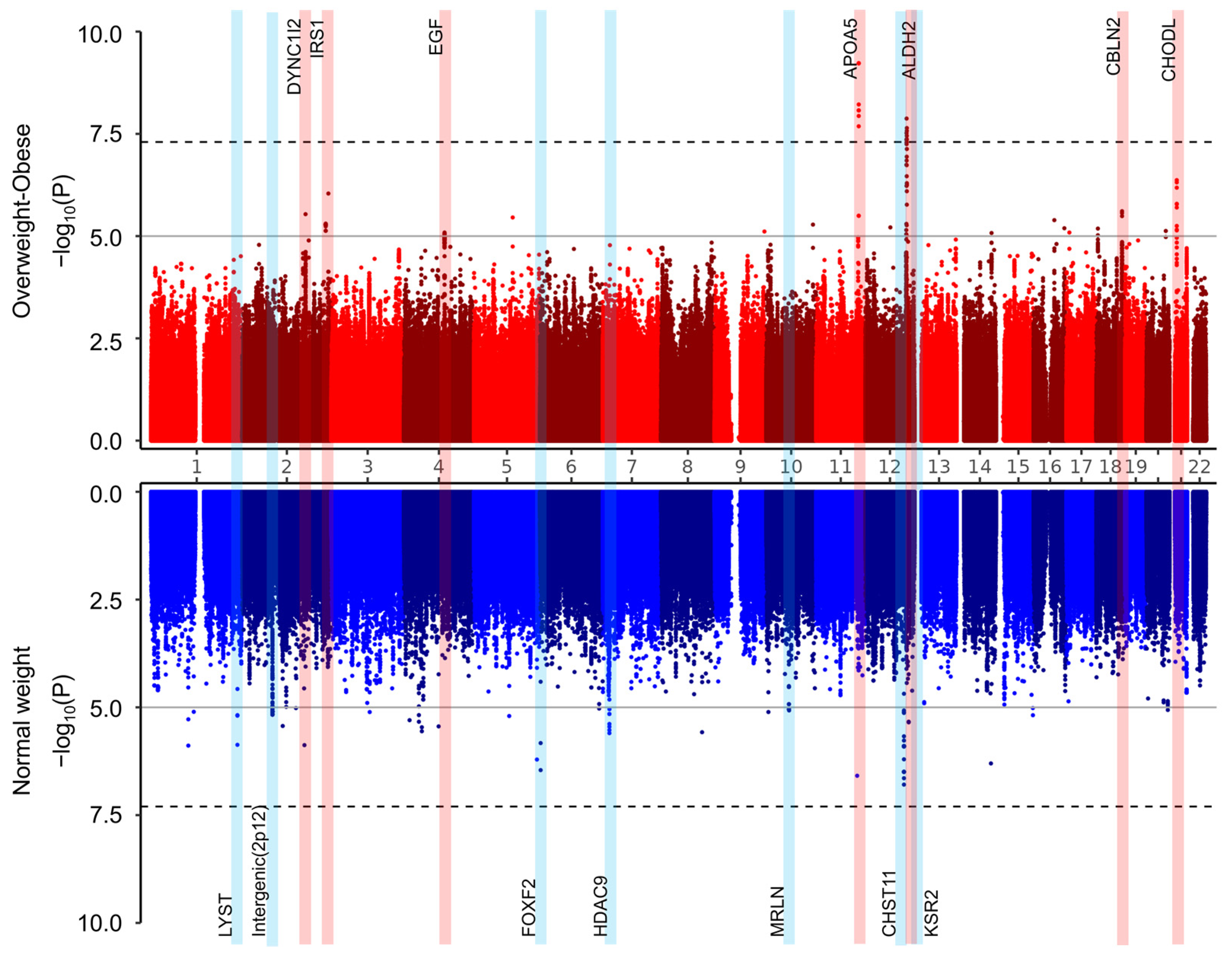
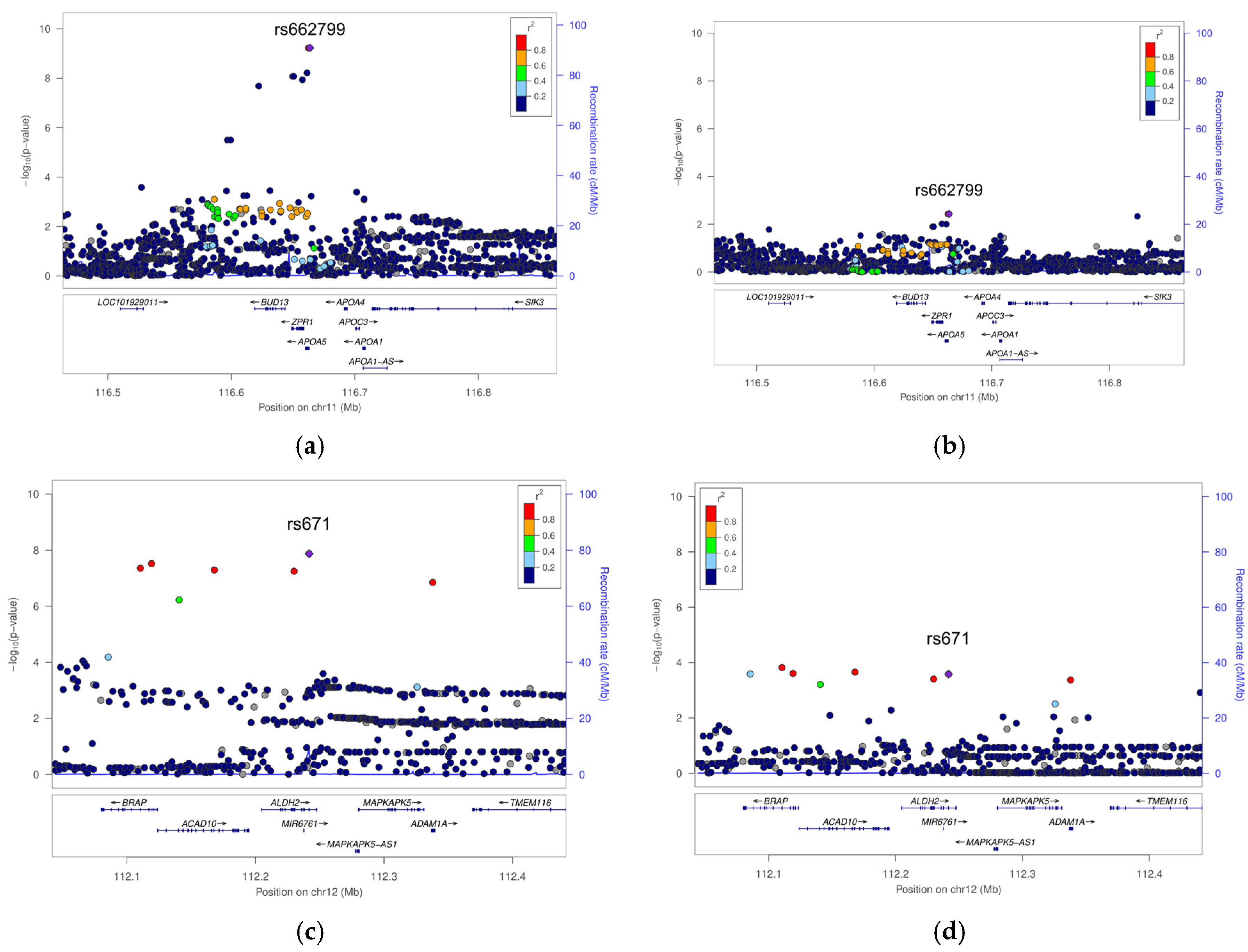
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.-H.; Park, S.-Y.; Choi, C.S. Insulin Resistance: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, G. Insulin and Insulin Resistance. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2005, 26, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Li, M.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhao, X.; Mi, J. Insulin Resistance Determined by Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) and Associations with Metabolic Syndrome among Chinese Children and Teenagers. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2013, 5, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdev, S.S.; Jamil, A.; Gunabalasingam, P.; Safdar, N.A. The Effects of Acitretin on Insulin Resistance, Glucose Metabolism, and Lipid Levels in Patients with Psoriasis. Indian J. Dermatol. 2022, 67, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Timón, I.; Sevillano-Collantes, C.; Segura-Galindo, A.; Del Cañizo-Gómez, F.J. Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease: Have All Risk Factors the Same Strength? World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 444–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruze, R.; Liu, T.; Zou, X.; Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, R.; Yin, X.; Xu, Q. Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Connections in Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Treatments. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1161521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic Adipose Tissue Inflammation Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chi, X.; Wang, Y.; Setrerrahmane, S.; Xie, W.; Xu, H. Trends in Insulin Resistance: Insights into Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Han, B.-G.; KoGES Group. Cohort Profile: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) Consortium. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, S.; Hwang, M.Y.; Shin, D.M.; Park, M.Y.; Lu, Y.; Yoon, K.; Jang, H.-M.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. The Korea Biobank Array: Design and Identification of Coding Variants Associated with Blood Biochemical Traits. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughton, A.P.; Welch, R.P.; Flickinger, M.; VandeHaar, P.; Taliun, D.; Abecasis, G.R.; Boehnke, M. LocusZoom.Js: Interactive and Embeddable Visualization of Genetic Association Study Results. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 3017–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietzner, M.; Wheeler, E.; Carrasco-Zanini, J.; Cortes, A.; Koprulu, M.; Wörheide, M.A.; Oerton, E.; Cook, J.; Stewart, I.D.; Kerrison, N.D.; et al. Mapping the Proteo-Genomic Convergence of Human Diseases. Science 2021, 374, eabj1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spracklen, C.N.; Chen, P.; Kim, Y.J.; Wang, X.; Cai, H.; Li, S.; Long, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Takeuchi, F.; et al. Association Analyses of East Asian Individuals and Trans-Ancestry Analyses with European Individuals Reveal New Loci Associated with Cholesterol and Triglyceride Levels. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 1770–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kang, S. Alcohol, Carbohydrate, and Calcium Intakes and Smoking Interactions with APOA5 Rs662799 and Rs2266788 Were Associated with Elevated Plasma Triglyceride Concentrations in a Cross-Sectional Study of Korean Adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 1318–1329.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, Y.; Hachiya, T.; Hara, M.; Shimanoe, C.; Tanaka, K.; Sutoh, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Hishida, A.; Tsukamoto, M.; Kadomatsu, Y.; et al. The Interaction between ABCA1 Polymorphism and Physical Activity on the HDL-Cholesterol Levels in a Japanese Population. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Huang, J.; Mo, Z.; He, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Tan, A.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Gu, C.C.; et al. Genetic Susceptibility to Lipid Levels and Lipid Change Over Time and Risk of Incident Hyperlipidemia in Chinese Populations. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2016, 9, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennacchio, L.A.; Olivier, M.; Hubacek, J.A.; Cohen, J.C.; Cox, D.R.; Fruchart, J.C.; Krauss, R.M.; Rubin, E.M. An Apolipoprotein Influencing Triglycerides in Humans and Mice Revealed by Comparative Sequencing. Science 2001, 294, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Vliet, H.N.; Sammels, M.G.; Leegwater, A.C.; Levels, J.H.; Reitsma, P.H.; Boers, W.; Chamuleau, R.A. Apolipoprotein A-V: A Novel Apolipoprotein Associated with an Early Phase of Liver Regeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 44512–44520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.-P.; Hu, S.; Li, J.; Hu, M.; Liu, Q.; Wu, L.-J.; Zhang, T. Association of Human Serum Apolipoprotein A5 with Lipid Profiles Affected by Gender. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 376, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, S.-P.; Hu, M.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W. Decreased Apolipoprotein A5 Is Implicated in Insulin Resistance-Related Hypertriglyceridemia in Obesity. Atherosclerosis 2010, 210, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.J.; Cho, Y.; Davey Smith, G. Alcohol Consumption, Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 Gene Polymorphisms, and Cardiovascular Health in Korea. Yonsei Med. J. 2017, 58, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, A.; Huang, I.Y.; Ikawa, M. Molecular Abnormality of an Inactive Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Variant Commonly Found in Orientals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.; Kamatani, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Usami, M.; Hosono, N.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tsunoda, T.; Kamatani, N.; Kubo, M.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Functional Variants in ADH1B and ALDH2 Coupled with Alcohol and Smoking Synergistically Enhance Esophageal Cancer Risk. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Ji, Y.I.; Choi, Y.H.; Kang, M.Y.; Jung, E.; Cho, S.Y.; Cho, H.-Y.; Kang, B.K.; Joung, Y.S.; Kim, D.-H.; et al. Candidate Gene Polymorphisms for Diabetes Mellitus, Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer Are Associated with Longevity in Koreans. Exp. Mol. Med. 2009, 41, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.-G.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, S.I. National Distribution of Rs671 (ALDH2) Genotypes and the Effect of Alcohol on Chronic Disease in Each Genotype. Epidemiol. Surveill. 2021, 14, 2095–2110. [Google Scholar]
- Tasdelen, I.; Berger, R.; Kalkhoven, E. PPARγ Regulates Expression of Carbohydrate Sulfotransferase 11 (CHST11/C4ST1), a Regulator of LPL Cell Surface Binding. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, L.R.; Atanassova, N.; Banton, M.C.; Bottomley, B.; van der Klaauw, A.A.; Revelli, J.-P.; Hendricks, A.; Keogh, J.M.; Henning, E.; Doree, D.; et al. KSR2 Mutations Are Associated with Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Impaired Cellular Fuel Oxidation. Cell 2013, 155, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, P.; Hanson, R.L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Yang, X.; Kobes, S.; Permana, P.A.; Bogardus, C.; Baier, L.J. The Role of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 Gene (IRS1) in Type 2 Diabetes in Pima Indians. Diabetes 2003, 52, 3005–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | SNP | CHR | BP | EA | EA Freq. | Nearby Gene | Subgroups | Association with HOMA-IR Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stratified Associations | SNP × Obesity Interaction Term p-Value | ||||||||||
| beta | se | p | |||||||||
| 1 | rs184772418 | 1 | 235941421 | T | 0.08 | LYST | Overweight/Obese | −0.672 | 0.756 | 3.74 × 10−1 | 4.22 × 10−3 |
| Normal Weight | 3.618 | 0.746 | 1.35 × 10−6 | ||||||||
| 2 | rs1367437 | 2 | 82379605 | G | 0.2 | Intergenic (2p12) | Overweight/Obese | 0.559 | 0.555 | 3.13 × 10−1 | 2.98 × 10−1 |
| Normal Weight | −2.33 | 0.516 | 6.77 × 10−6 | ||||||||
| 3 | rs115567901 | 2 | 172612621 | T | 0.07 | DYNC1I2 | Overweight/Obese | 3.18 | 0.679 | 2.91 × 10−6 | 5.81 × 10−2 |
| Normal Weight | −0.431 | 0.666 | 5.18 × 10−1 | ||||||||
| 4 | rs77723860 | 2 | 227651047 | A | 0.03 | IRS1 | Overweight/Obese | 4.877 | 1.067 | 4.95 × 10−6 | 3.91 × 10−1 |
| Normal Weight | −0.295 | 1.097 | 7.88 × 10−1 | ||||||||
| 5 | rs2255355 | 4 | 110891543 | A | 0.38 | EGF | Overweight/Obese | −1.94 | 0.434 | 8.17 × 10−6 | 5.30 × 10−1 |
| Normal Weight | −0.554 | 0.405 | 1.71 × 10−1 | ||||||||
| 6 | rs723137 | 6 | 1471646 | G | 0.17 | FOXF2 | Overweight/Obese | −0.254 | 0.595 | 6.70 × 10−1 | 7.10 × 10−2 |
| Normal Weight | 2.83 | 0.553 | 3.50 × 10−7 | ||||||||
| 7 | rs13247375 | 7 | 18183650 | T | 0.19 | HDAC9 | Overweight/Obese | −0.738 | 0.511 | 1.48 × 10−1 | 2.75 × 10−2 |
| Normal Weight | 2.261 | 0.479 | 2.52 × 10−6 | ||||||||
| 8 | rs1046608284 | 10 | 61524156 | T | 0.1 | MRLN | Overweight/Obese | 0.809 | 0.753 | 2.83 × 10−1 | 2.52 × 10−1 |
| Normal Weight | 3.261 | 0.732 | 9.01 × 10−6 | ||||||||
| 9 | rs662799 | 11 | 116663707 | G | 0.29 | APOA5 | Overweight/Obese | 2.801 | 0.451 | 5.89 × 10−10 | 9.41 × 10−1 |
| Normal Weight | 1.252 | 0.431 | 3.71 × 10−3 | ||||||||
| 10 | rs703672 | 12 | 105068918 | G | 0.06 | CHST11 | Overweight/Obese | −2.162 | 1.163 | 6.30 × 10−2 | 5.56 × 10−1 |
| Normal Weight | 5.849 | 1.112 | 1.61 × 10−7 | ||||||||
| 11 | rs671 | 12 | 112241766 | A | 0.22 | ALDH2 | Overweight/Obese | −3.495 | 0.614 | 1.34 × 10−8 | 9.32 × 10−1 |
| Normal Weight | −2.055 | 0.562 | 2.62 × 10−4 | ||||||||
| 12 | rs816189 | 12 | 117991734 | T | 0.34 | KSR2 | Overweight/Obese | 0.115 | 0.449 | 7.98 × 10−1 | 8.82 × 10−2 |
| Normal Weight | 1.978 | 0.43 | 4.49 × 10−6 | ||||||||
| 13 | rs1432073 | 18 | 70188606 | T | 0.32 | CBLN2 | Overweight/Obese | 2.092 | 0.444 | 2.46 × 10−6 | 2.29 × 10−1 |
| Normal Weight | −0.118 | 0.422 | 7.80 × 10−1 | ||||||||
| 14 | rs1491780 | 21 | 19484212 | C | 0.23 | CHODL | Overweight/Obese | −2.428 | 0.48 | 4.28 × 10−7 | 4.03 × 10−1 |
| Normal Weight | −0.697 | 0.466 | 1.35 × 10−1 | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.-E.; Kwon, Y.-J.; Hong, K.-W. Differential Genetic Architecture of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) Based on Obesity Status: Evidence from a Large-Scale GWAS of Koreans. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060461
Choi J-E, Kwon Y-J, Hong K-W. Differential Genetic Architecture of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) Based on Obesity Status: Evidence from a Large-Scale GWAS of Koreans. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(6):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060461
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Ja-Eun, Yu-Jin Kwon, and Kyung-Won Hong. 2025. "Differential Genetic Architecture of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) Based on Obesity Status: Evidence from a Large-Scale GWAS of Koreans" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 6: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060461
APA StyleChoi, J.-E., Kwon, Y.-J., & Hong, K.-W. (2025). Differential Genetic Architecture of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) Based on Obesity Status: Evidence from a Large-Scale GWAS of Koreans. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(6), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47060461







