Multi-Omics Elucidation of Edulinine’s Intervention Mechanism in Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method and Materials
2.1. Animal
2.2. Materials and Instruments
2.3. Animal Models and Drug Administration
2.4. Histopathological Staining Protocols
2.5. Serum Metabolomics Analysis
2.6. Proteomics Analysis
2.7. Molecular Docking
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
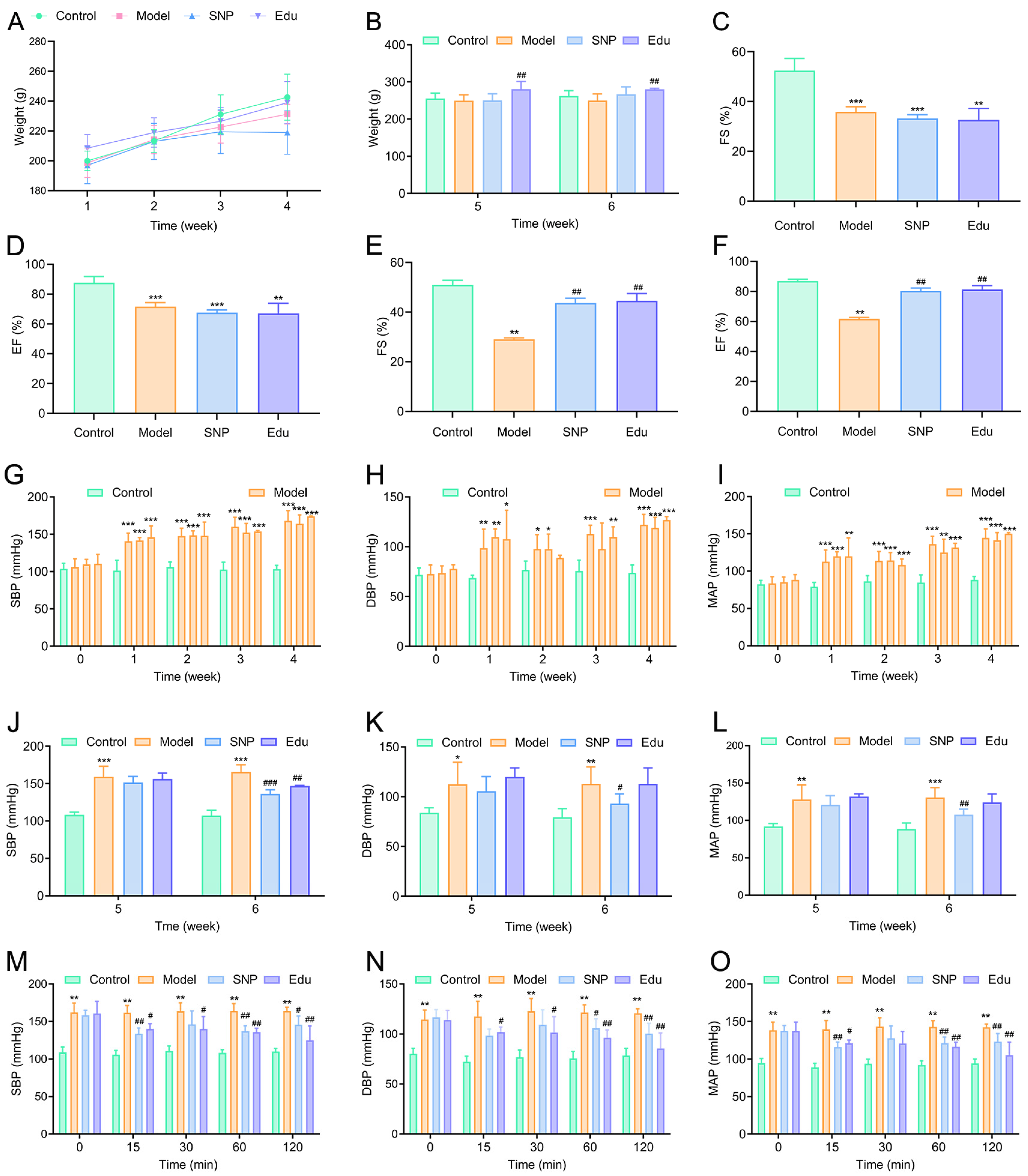
3.1. Antihypertensive Effect of Edu on L-NNA-Induced Hypertensive Rats
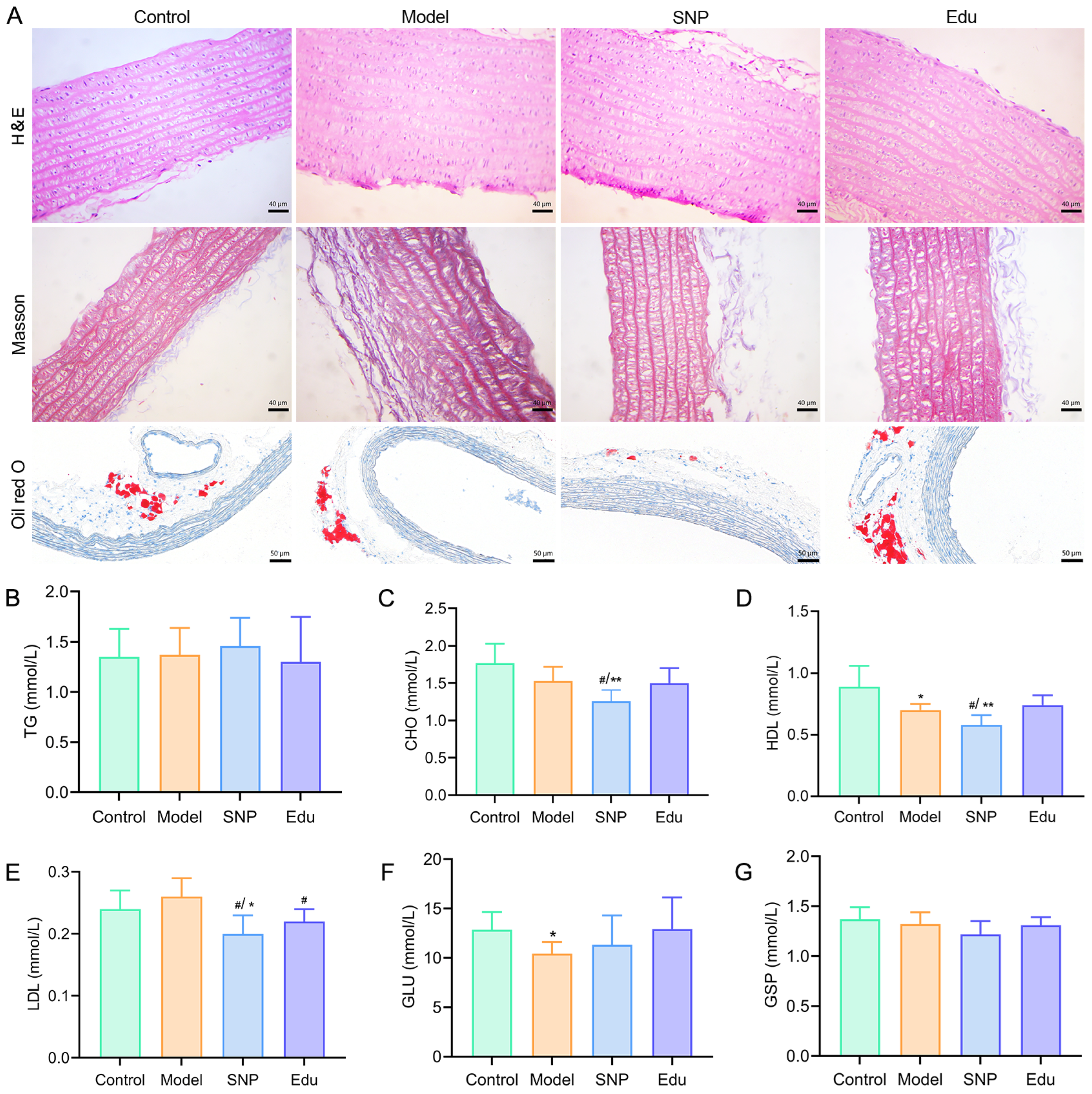
3.2. Ameliorative Effects of Edu on Abnormal Biochemical Indicators and Histopathological Injury
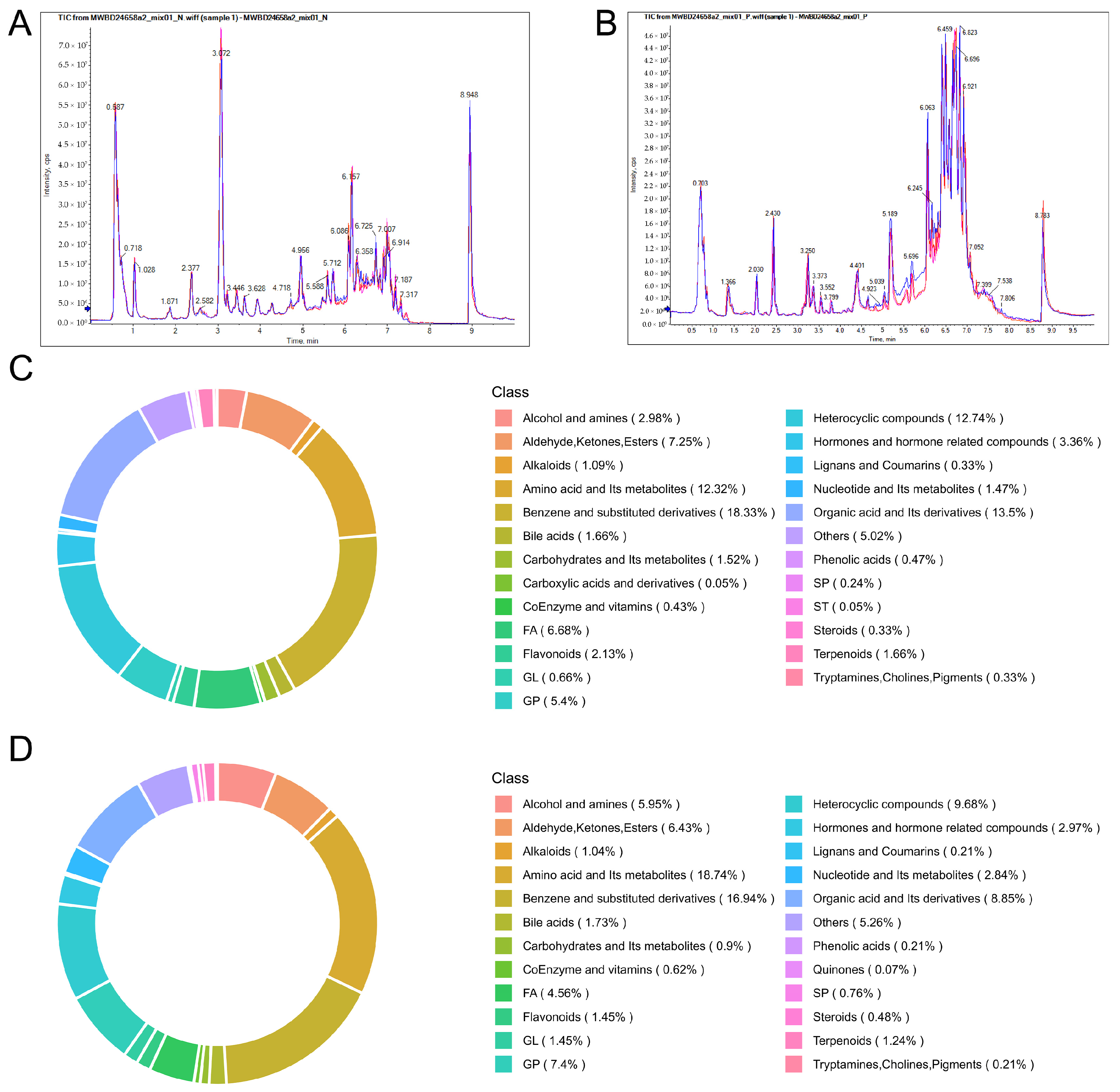
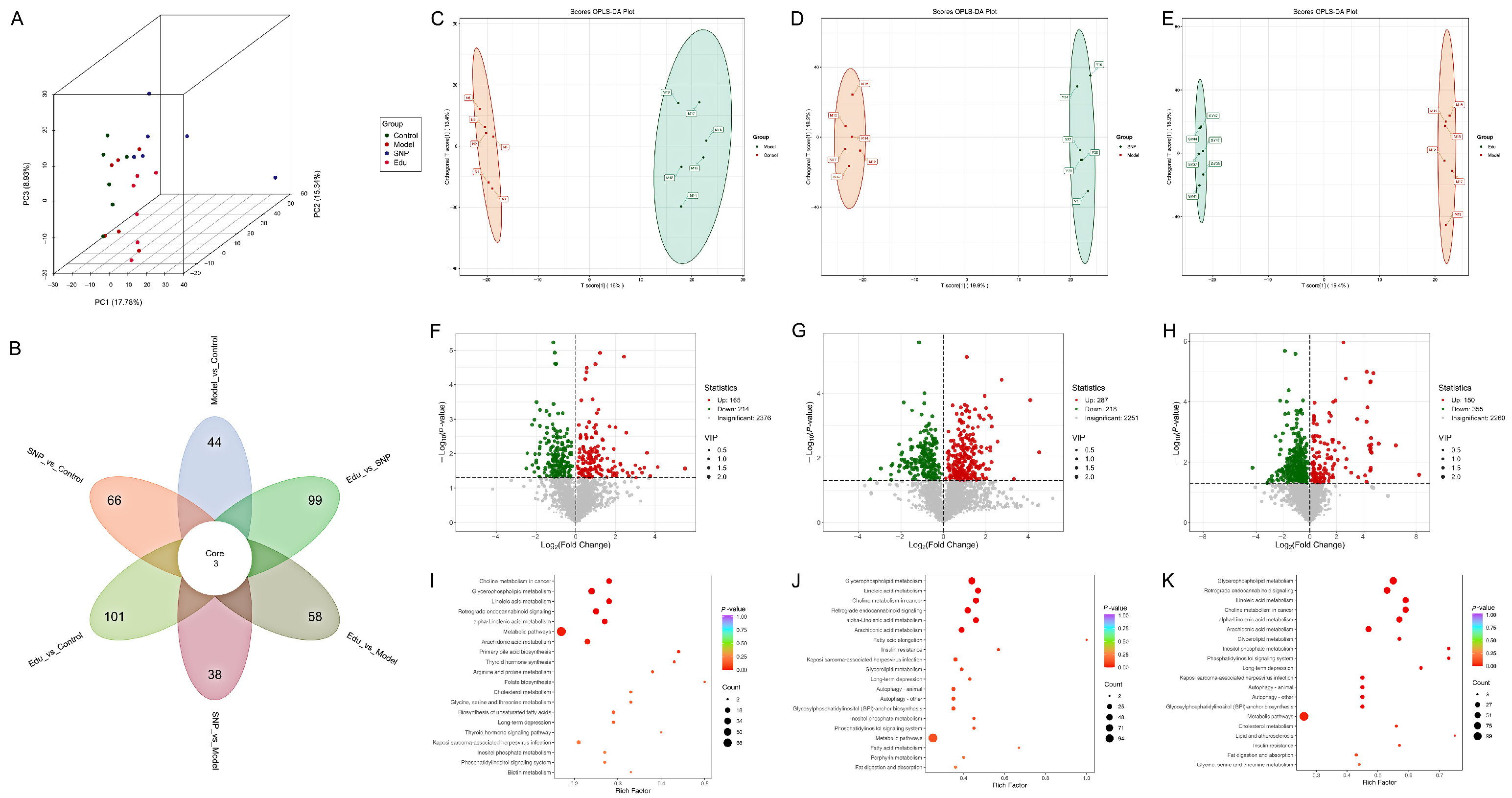
3.3. Serum Metabolomics Investigation of the Regulatory Mechanism of Edu in Improving Metabolic Disorders in Hypertensive Rats
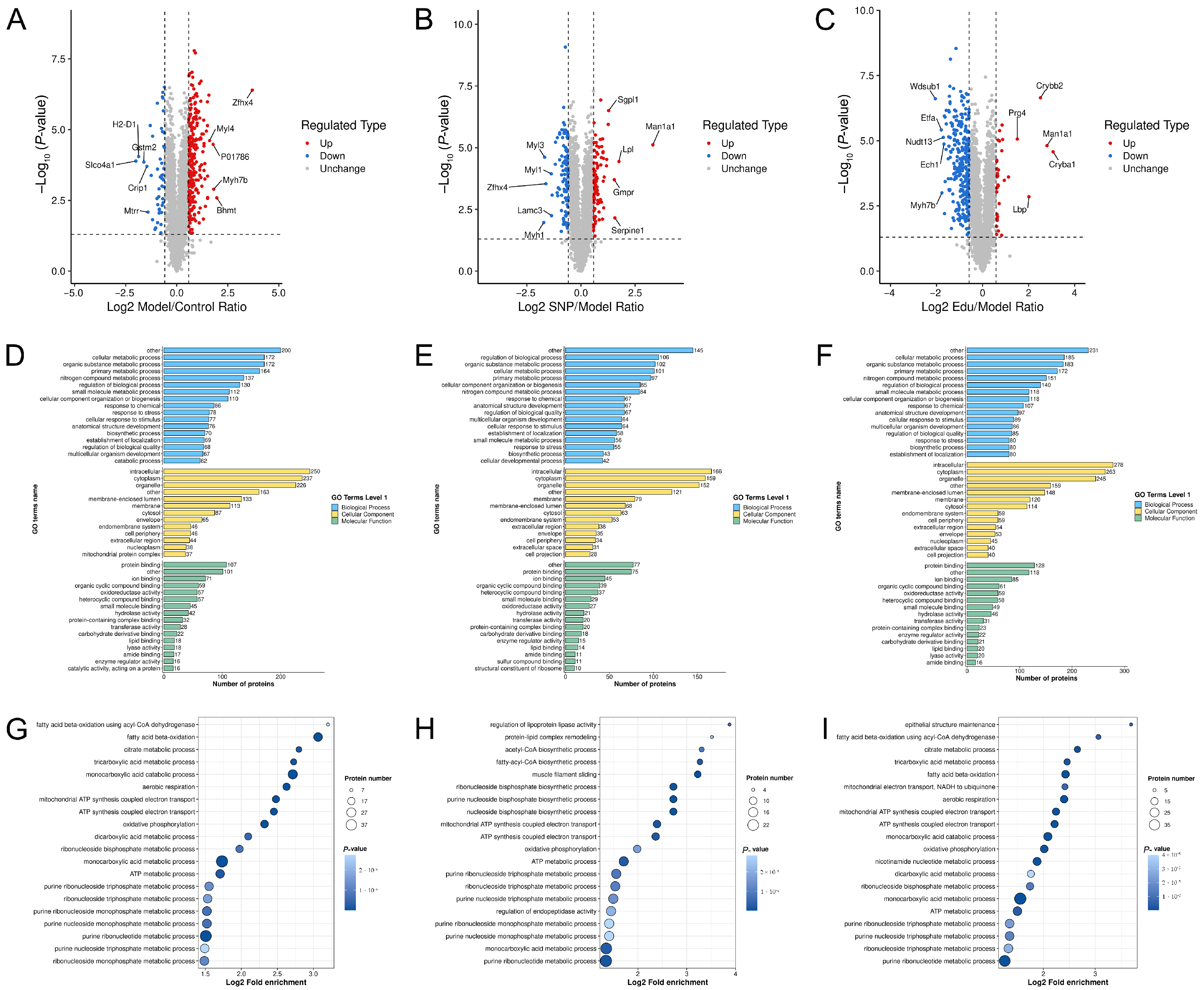
3.4. Proteomics Analysis
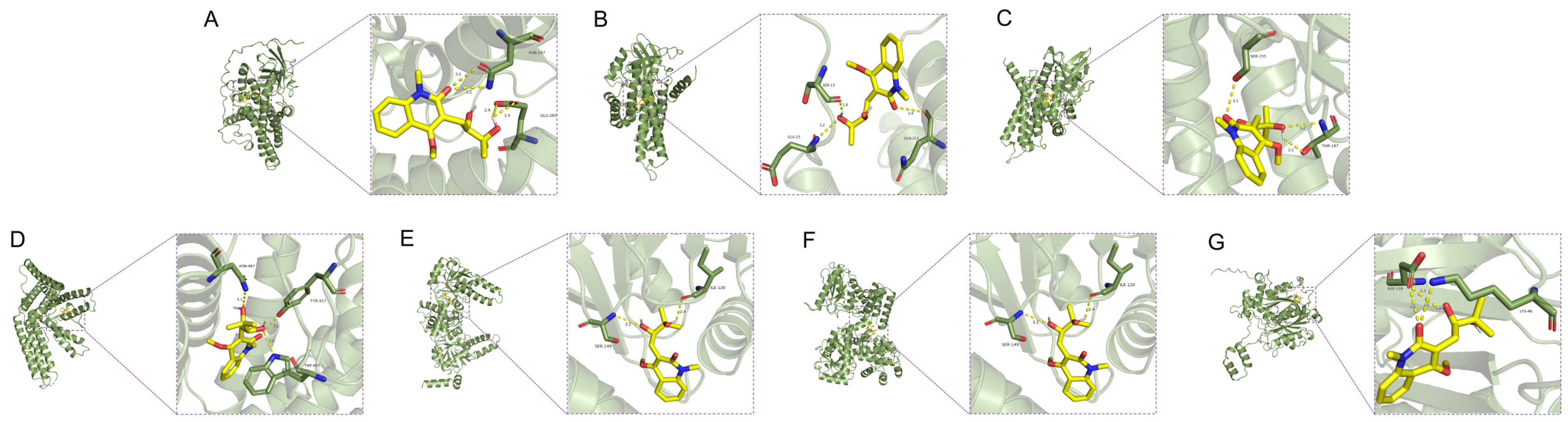
3.5. Molecular Docking Results
3.6. Integrated Analysis of Metabolomics and Proteomics
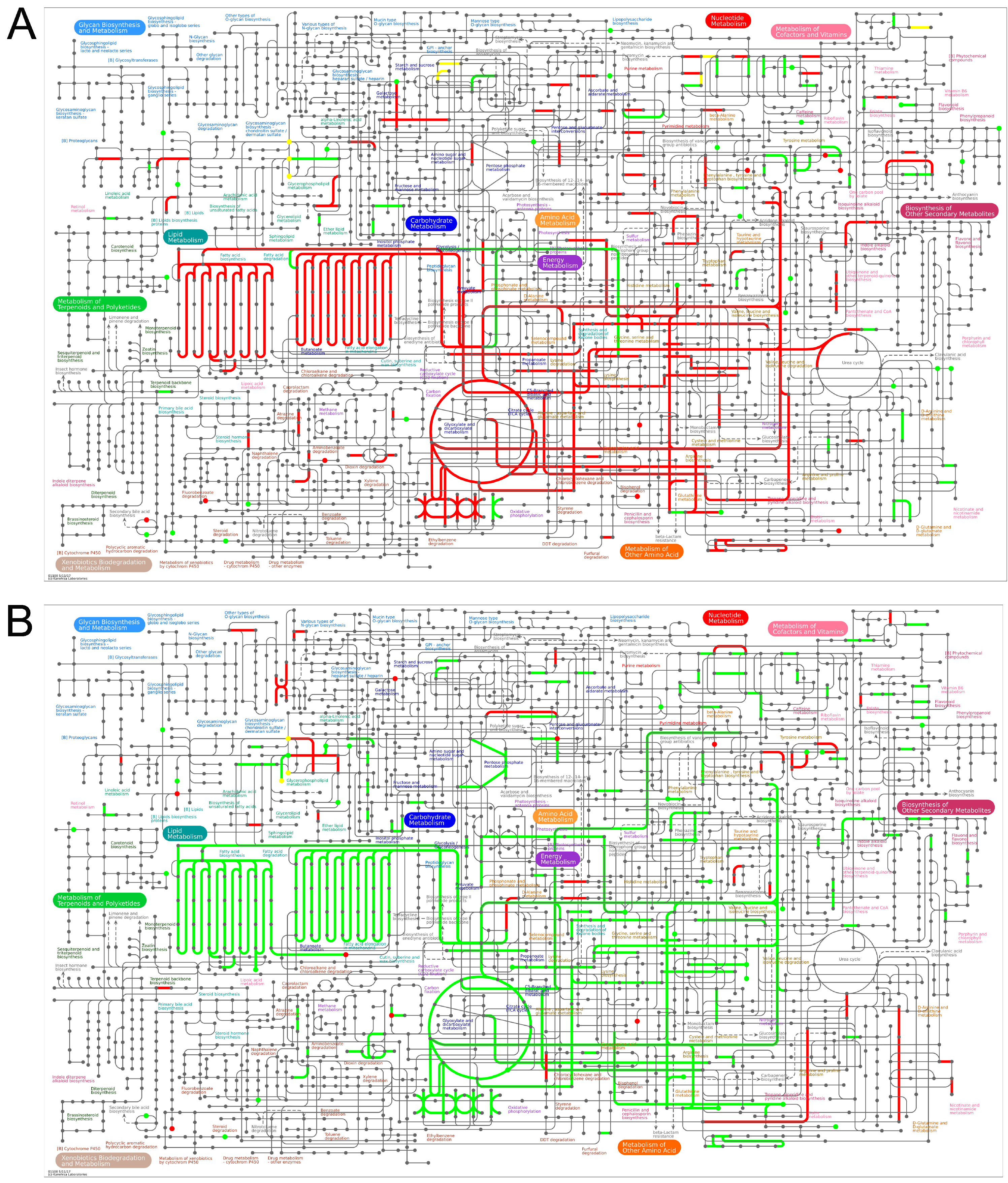
3.6.1. Ipathway Analysis
3.6.2. Kegg Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chong, B.; Jayabaskaran, J.; Jauhari, S.M. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases: Projections from 2025 to 2050. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2025, 32, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.S. Report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China 2023: An updated summary. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 399–430. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.E.; Hayden, S.L.; Meyer, H.R. The Evolving Role of Calcium Channel Blockers in Hypertension Management: Pharmacological and Clinical Considerations. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 6315–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrijens, B.; Vincze, G.; Kristanto, P. Adherence to prescribed antihypertensive drug treatments: Longitudinal study of electronically compiled dosing histories. BMJ 2008, 336, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, L.J.; Wright, J.T., Jr.; Greene, T. Long-term effects of renin-angiotensin system-blocking therapy and a low blood pressure goal on progression of hypertensive chronic kidney disease in African Americans. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 16, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DRossi, G.P.; Seccia, T.M.; Maniero, C. Drug-related hypertension and resistance to antihypertensive treatment: A call for action. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 2295–2309. [Google Scholar]
- Szabó, T.; Volk, B.; Milen, M. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of β-Carboline Alkaloid. Molecules 2021, 26, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totoń-Żurańska, J.; Mikolajczyk, T.P.; Saju, B. Vascular remodelling in cardiovascular diseases: Hypertension, oxidation, and inflammation. Clin. Sci. 2024, 138, 817–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ying, M.; Gu, S. Matrine alleviates hypoxia-induced inflammation and pulmonary vascular remodelling via RPS5/NF-κB signalling pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2024, 38, e23583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, G.; Mark, A.; Esler, M. The sympathetic nervous system alterations in human hypertension. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Chen, J.; Pang, L. The Acid Sphingomyelinase Inhibitor Amitriptyline Ameliorates TNF-α-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2024, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, S.; Stenoien, D.L. High-throughput proteomics. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 7, 427–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrell, N.; Sadeghirad, H.; Blick, T. Metabolomics at the tumor microenvironment interface: Decoding cellular conversations. Med. Res. Rev. 2024, 44, 1121–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, R. Histopathology images-based deep learning prediction of prognosis and therapeutic response in small cell lung cancer. NPJ Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yan, W.; Wang, H. APOE polymorphism is associated with blood lipid and serum uric acid metabolism in hypertension or coronary heart disease in a Chinese population. Pharmacogenomics 2019, 20, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linz, W.; Wiemer, G.; Gohlke, P. Contribution of kinins to the cardiovascular actions of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1995, 47, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.Y.; Fan, Y.M.; Liu, Q. Quinoline Alkaloids from the Roots of Orixa japonica with the Anti-Pathogenic Fungi Activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202201097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonow, R.O.; Lakatos, E.; Maron, B.J. Serial long-term assessment of the natural history of asymptomatic patients with chronic aortic regurgitation and normal left ventricular systolic function. Free Radic. Circ. 1991, 84, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticone, S.; D’Ascenzo, M.; Moretti, C. Cardiovascular events and target organ damage in primary aldosteronism compared with essential hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, L. Associations of Blood Pressure Variability, Heart Rate, and Target Organ Damage in Resistant Hypertension Patients. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2025, 27, e70081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Kumazaki, S.; Kusunoki, K. A High-Fat and High-Cholesterol Diet Induces Cardiac Fibrosis, Vascular Endothelial, and Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in SHRSP5/Dmcr Rats. Free Radic. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipp, M.L.; Ge, Z.D.; DeBerge, M. Myeloid Fatty Acid Metabolism Activates Neighboring Hematopoietic Stem Cells to Promote Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circulation 2025, 151, 1451–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagautdinov, B.; Ukita, Y.; Miyano, M. Structure of 3-oxoacyl-(acyl-carrier protein) synthase II from Thermus thermophilus HB8. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2008, 64, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalhat, M.H.; Mohammed, M.R.S.; Ahmad, A. Remodelin, a N-acetyltransferase 10 (NAT10) inhibitor, alters mitochondrial lipid metabolism in cancer cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2021, 122, 1936–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, D.; Huang, J.; Smith, A. Blood pressure, plasma proteins, and cardiovascular diseases: A network Mendelian randomization and observational study. Eur. Heart J. 2025, ehaf725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, M.I.; Bartolomaeus, H.; Anandakumar, H. Metformin modulates microbiota and improves blood pressure and cardiac remodeling in a rat model of hypertension. Acta Physiol. 2024, 240, e14226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, D. Piezo2 channel in nodose ganglia neurons is essential in controlling hypertension in a pathway regulated directly by Nedd4-2. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 164, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourraindeloup, M.; Adamy, C.; Candiani, G. N-acetylcysteine treatment normalizes serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha level and hinders the progression of cardiac injury in hypertensive rats. Circulation 2004, 110, 2003–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvanova, A.; Reseghetti, E.; Abbate, M. Mechanisms and treatment of obesity-related hypertension-Part 1: Mechanisms. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 17, sfad282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y. Metabolomic characterization of hypertension and dyslipidemia. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, D.I.; Kang, D.H.; Nakagawa, T. Uric acid and hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2006, 8, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E. Metabolic abnormalities of hypertension. A lesson in complexity. Hypertension 1991, 18, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kućmierz, J.; Frąk, W.; Młynarska, E. Molecular Interactions of Arterial Hypertension in Its Target Organs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Masaki, T.; Sawamura, T. LOX-1, the receptor for oxidized low-density lipoprotein identified from endothelial cells: Implications in endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 95, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirillo, A.; Norata, G.D.; Catapano, A.L. LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 152786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Yan, M.; Frohlich, E.D. Novel concepts in the genesis of hypertension: Role of LOX-1. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2011, 25, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, X.; Liu, B. LOX-1 Deletion Attenuates Myocardial Fibrosis in the Aged Mice, Particularly Those with Hypertension. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 736215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, Q.N.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G. Roles of inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction in hypertension. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 406960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Effect of inflammation on HDL structure and function. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2016, 27, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navab, M.; Reddy, S.T.; Van Lenten, B.J.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Fogelman, A.M. The role of dysfunctional HDL in atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S145–S149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.B.J.; Lajczak, N.K.; Kelly, O.B. Ursodeoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid exert anti-inflammatory actions in the colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G550–G558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hao, C.; Jiao, T. Osteoarthritis treatment via the GLP-1-mediated gut-joint axis targets intestinal FXR signaling. Science 2025, 388, eadt0548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.F. The continuing importance of bile acids in liver and intestinal disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 2647–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, T.; Katagiri, K.; Hoshino, M. Microtubule-independent choleresis and anti-cholestatic action of tauroursodeoxycholate in colchicine-treated rat liver. Biochem. J. 1992, 288, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Han, W. Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 20194–20210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Feng, H. Rifampicin-induced injury in HepG2 cells is alleviated by TUDCA via increasing bile acid transporters expression and enhancing the Nrf2-mediated adaptive response. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 112, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, C.; Aldeguer, X.; Vivas, D. The gut microbiota and its role in the development of cardiovascular disease. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2025, 23, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, L.D.; Alotaibi, M.; Tai, Y.Y. Lysosomal dysfunction and inflammatory sterol metabolism in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Science 2025, 387, eadn7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.K. A Review of Current Evidence on the Relationship between Phosphate Metabolism and Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.K.; Lim, M.; Byeon, S.H.; Lee, Y.H. Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress improves coronary artery function in the spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.N.; Cao, X.; Guruju, M.R. ER stress in the brain subfornical organ mediates angiotensin-dependent hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3960–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, I.N.; da Silva, J.A., Jr.; de Oliveira, K.M. Insights by which TUDCA is a potential therapy against adiposity. Front Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1090039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athenstaedt, K.; Daum, G. Phosphatidic acid, a key intermediate in lipid metabolism. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 266, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tei, R. The dynamic regulatory network of phosphatidic acid metabolism: A spotlight on substrate cycling between phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2024, 52, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, F.; Tysseling, K.A.; Rice, J. Free fatty acid impairment of nitric oxide production in endothelial cells is mediated by IKKbeta. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbecki, J.; Bajdak-Rusinek, K. The effect of palmitic acid on inflammatory response in macrophages: An overview of molecular mechanisms. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmedov, A.T.; Rybin, V.; Marín-García, J. Mitochondrial oxidative metabolism and uncoupling proteins in the failing heart. Heart. Fail. Rev. 2015, 20, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes. Nutrients 2010, 2, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, L.; Jian, J.; Chen, T.; Wu, X.; Jiang, F.; Ming, H.; Han, D.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; et al. Multi-Omics Elucidation of Edulinine’s Intervention Mechanism in Hypertensive Rats. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47120987
Tao L, Jian J, Chen T, Wu X, Jiang F, Ming H, Han D, Zhang G, Li L, Liu S, et al. Multi-Omics Elucidation of Edulinine’s Intervention Mechanism in Hypertensive Rats. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(12):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47120987
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Ling, Junyou Jian, Tingting Chen, Xingjie Wu, Fei Jiang, Huaiju Ming, Dayao Han, Guangqiong Zhang, Lingyan Li, Shaobo Liu, and et al. 2025. "Multi-Omics Elucidation of Edulinine’s Intervention Mechanism in Hypertensive Rats" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 12: 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47120987
APA StyleTao, L., Jian, J., Chen, T., Wu, X., Jiang, F., Ming, H., Han, D., Zhang, G., Li, L., Liu, S., Yuan, C., Shen, X., & Hao, X. (2025). Multi-Omics Elucidation of Edulinine’s Intervention Mechanism in Hypertensive Rats. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(12), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47120987




