miRNAs and Alcohol-Related Hepatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
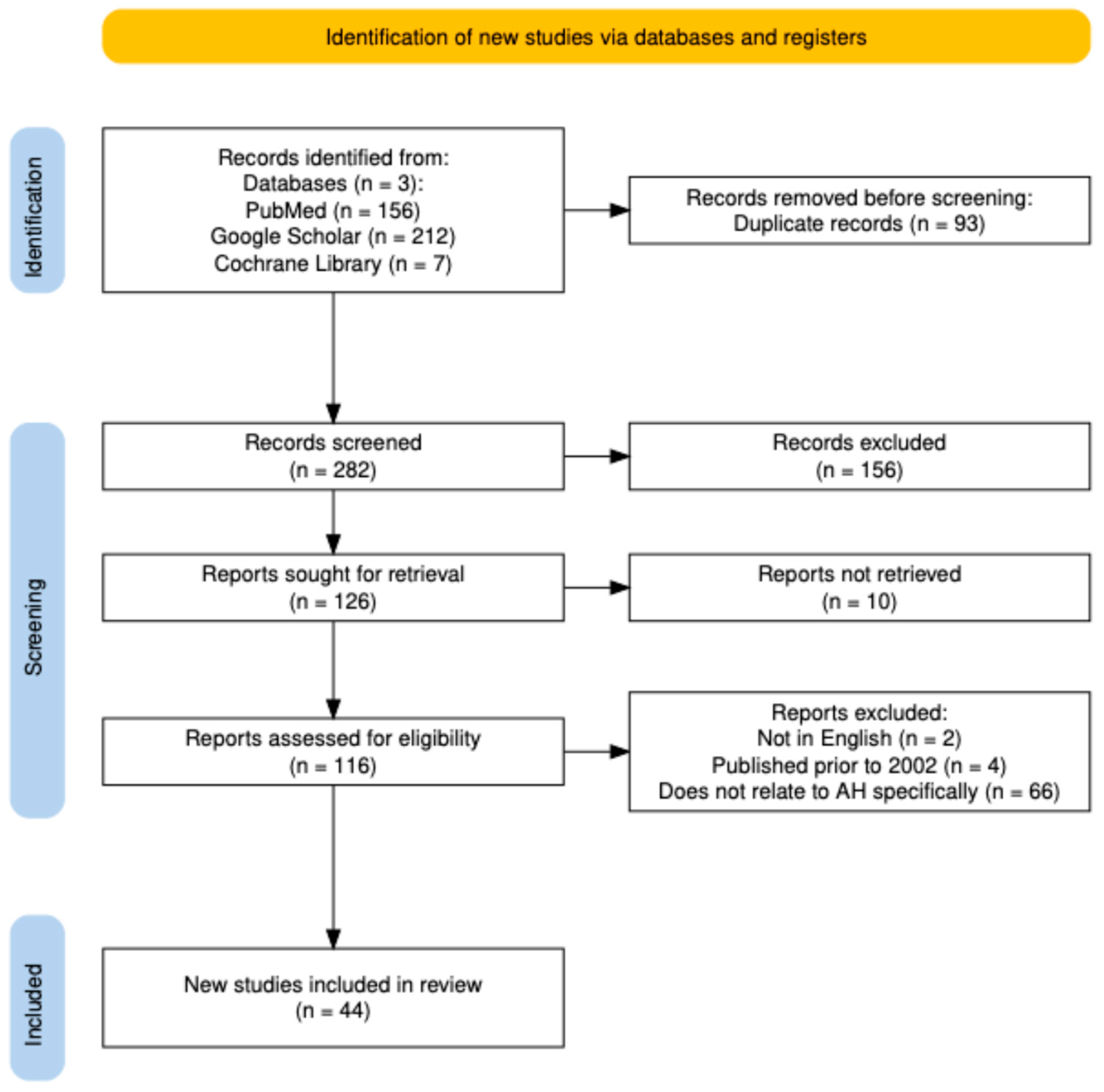
2. Search Methodology
3. TLR, NF-kB Signaling, and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production
3.1. MiRNA-217
3.2. Let-7b
3.3. MiRNA-182
3.4. MiRNA-21
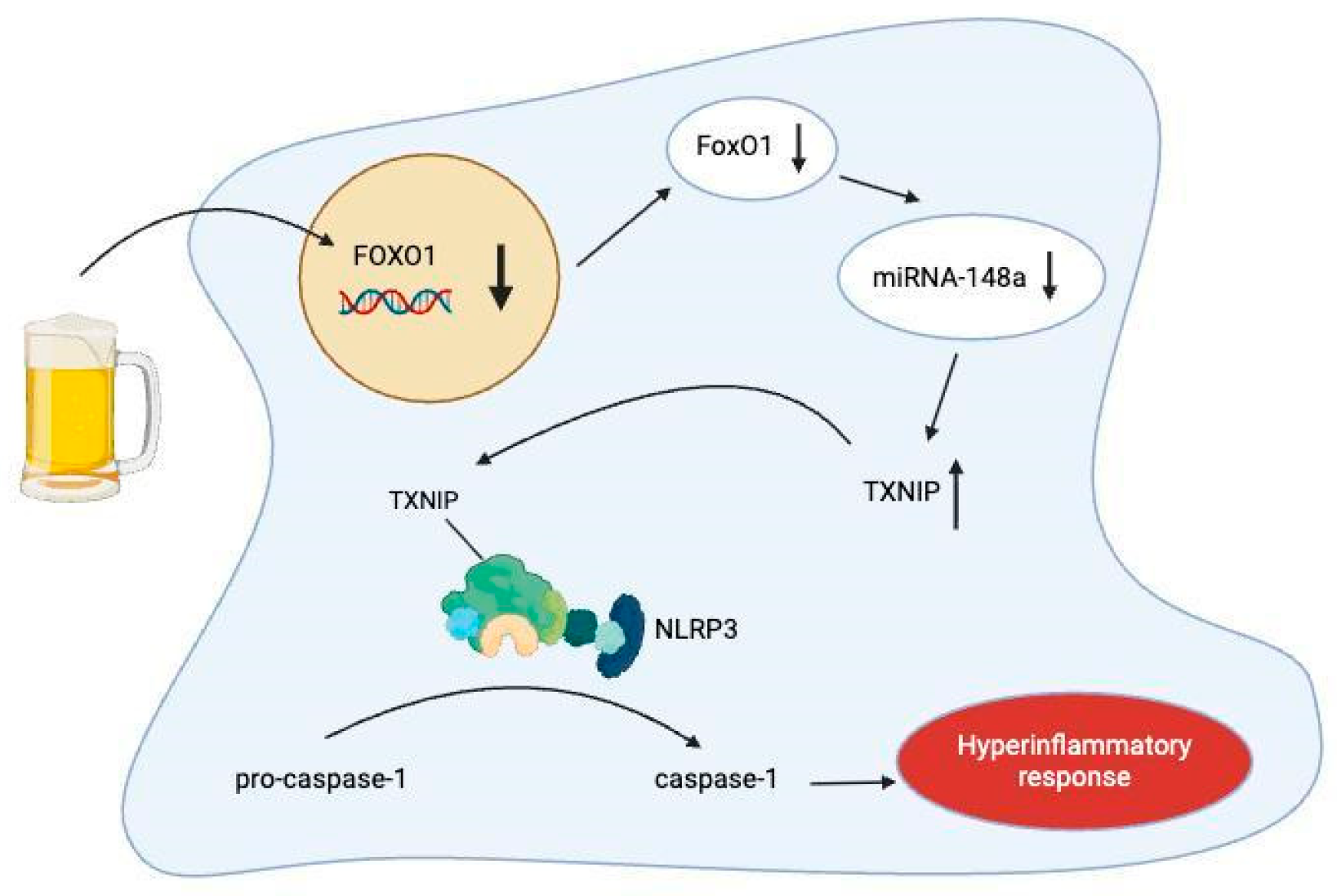
3.5. MiRNA-148a
3.6. MiRNA-30e
4. Circulating miRNAs
4.1. MiRNA-27a
4.2. MiRNA-181
4.3. MiRNA-122, miRNA-30a, and miRNA-192
5. Mechanisms of Alcoholic Hepatitis
5.1. MiRNA-34a and miRNA-483-3p
5.2. Role of Ethanol
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jophlin, L.L.; Singal, A.K.; Bataller, R.; Wong, R.J.; Sauer, B.G.; Terrault, N.A.; Shah, V.H. ACG Clinical Guideline: Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 119, 30–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gao, B.; Ahmad, M.F.; Nagy, L.E.; Tsukamoto, H. Inflammatory pathways in alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yu, C.H.; Xu, C.F.; Ye, H.; Li, L.; Li, Y.M. Early mortality of alcoholic hepatitis: A review of data from placebo-controlled clinical trial. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 2435–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shah, N.J.; Royer, A.; John, S. Alcoholic-Associated Hepatitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470217/ (accessed on 30 October 2025).
- Jouve, M.; Carpentier, R.; Kraiem, S.; Legrand, N.; Sobolewski, C. miRNAs in Alcohol-Related Liver Diseases and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Step Toward New Therapeutic Approaches? Cancers 2023, 15, 5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Orang, A.V.; Safaralizadeh, R.; Kazemzadeh-Bavili, M. Mechanisms of miRNA-Mediated Gene Regulation from Common Downregulation to mRNA-Specific Upregulation. Int. J. Genom. 2014, 2014, 970607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippold, R.P.; Vadigepalli, R.; Gonye, G.E.; Patra, B.; Hoek, J.B. Chronic ethanol feeding alters miRNA expression dynamics during liver regeneration. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, E59–E69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Im, G.Y. Emerging Biomarkers in Alcohol-associated Hepatitis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2023, 13, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaratani, H.; Tsujimoto, T.; Douhara, A.; Takaya, H.; Moriya, K.; Namisaki, T.; Noguchi, R.; Yoshiji, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Fukui, H. The effect of inflammatory cytokines in alcoholic liver disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 495156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Slevin, E.; Baiocchi, L.; Wu, N.; Ekser, B.; Sato, K.; Lin, E.; Ceci, L.; Chen, L.; Lorenzo, S.R.; Xu, W.; et al. Kupffer Cells: Inflammation Pathways and Cell-Cell Interactions in Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 2185–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Szabo, G. Gut-liver axis in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yin, H.; Liang, X.; Jogasuria, A.; Davidson, N.O.; You, M. miR-217 regulates ethanol-induced hepatic inflammation by disrupting sirtuin 1-lipin-1 signaling. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Massey, V.L.; Qin, L.; Cabezas, J.; Caballeria, J.; Sancho-Bru, P.; Bataller, R.; Crews, F.T. TLR7-let-7 Signaling Contributes to Ethanol-Induced Hepatic Inflammatory Response in Mice and in Alcoholic Hepatitis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 2107–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gustot, T.; Lemmers, A.; Moreno, C.; Nagy, N.; Quertinmont, E.; Nicaise, C.; Franchimont, D.; Louis, H.; Devière, J.; Le Moine, O. Differential liver sensitization to toll-like receptor pathways in mice with alcoholic fatty liver. Hepatology 2006, 43, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stärkel, P.; De Saeger, C.; Strain, A.J.; Leclercq, I.; Horsmans, Y. NFkappaB, cytokines, TLR 3 and 7 expression in human end-stage HCV and alcoholic liver disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 40, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaya, D.; Coll, M.; Rodrigo-Torres, D.; Vila-Casadesús, M.; Altamirano, J.; Llopis, M.; Graupera, I.; Perea, L.; Aguilar-Bravo, B.; Díaz, A.; et al. Integrative microRNA profiling in alcoholic hepatitis reveals a role for microRNA-182 in liver injury and inflammation. Gut 2016, 65, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho-Bru, P.; Altamirano, J.; Rodrigo-Torres, D.; Coll, M.; Millán, C.; Lozano, J.J.; Miquel, R.; Arroyo, V.; Caballería, J.; Ginès, P.; et al. Liver progenitor cell markers correlate with liver damage and predict short-term mortality in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, H.; McDaniel, K.; Han, Y.; Liu, X.; Kennedy, L.; Yang, F.; McCarra, J.; Zhou, T.; Glaser, S.; Venter, J.; et al. Regulation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway by microRNA-21 in alcoholic liver injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27526–27539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wake, K. Hepatic stellate cells: Three-dimensional structure, localization, heterogeneity and development. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2006, 82, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, N.; McDaniel, K.; Zhou, T.; Ramos-Lorenzo, S.; Wu, C.; Huang, L.; Chen, D.; Annable, T.; Francis, H.; Glaser, S.; et al. Knockout of microRNA-21 attenuates alcoholic hepatitis through the VHL/NF-κB signaling pathway in hepatic stellate cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G385–G398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, S.L.; Liu, L. microRNA-148a inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion by targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Heo, M.J.; Kim, T.H.; You, J.S.; Blaya, D.; Sancho-Bru, P.; Kim, S.G. Alcohol dysregulates miR-148a in hepatocytes through FoxO1, facilitating pyroptosis via TXNIP overexpression. Gut 2019, 68, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nakae, J.; Kitamura, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Biggs, W.H., 3rd; Arden, K.C.; Accili, D. The forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 regulates adipocyte differentiation. Dev. Cell 2003, 4, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.H.; Park, S.J. TXNIP: A key protein in the cellular stress response pathway and a potential therapeutic target. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Tardivel, A.; Thorens, B.; Choi, I.; Tschopp, J. Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Yu, M.S.; Huang, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Chen, Y.P. MiR-30e-UCP2 pathway regulates alcoholic hepatitis progress by influencing ATP and hydrogen peroxide expression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 64294–64302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, J.; Shao, T.; Ding, N.; Li, Y.; Li, X. miRNA-miRNA crosstalk: From genomics to phenomics. Briefings Bioinform. 2017, 18, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, S.; Petrasek, J.; Mundkur, S.; Catalano, D.; Levin, I.; Ward, J.; Alao, H.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. Circulating microRNAs in exosomes indicate hepatocyte injury and inflammation in alcoholic, drug-induced, and inflammatory liver diseases. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ratajczak, J.; Wysoczynski, M.; Hayek, F.; Janowska Wieczorek, A.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Membrane-derived microvesicles: Important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia 2006, 20, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.; Momen-Heravi, F.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. MicroRNA Cargo of Extracellular Vesicles from Alcohol-exposed Monocytes Signals Naive Monocytes to Differentiate into M2 Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Brenner, D.A.; Kisseleva, T. Reversibility of Liver Fibrosis and Inactivation of Fibrogenic Myofibroblasts. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2013, 1, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Eguchi, A.; Yan, R.; Pan, S.Q.; Wu, R.; Kim, J.; Chen, Y.; Ansong, C.; Smith, R.D.; Tempaku, M.; Ohno-Machado, L.; et al. Comprehensive characterization of hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles identifies direct miRNA-based regulation of hepatic stellate cells and DAMP-based hepatic macrophage IL-1β and IL-17 upregulation in alcoholic hepatitis mice. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, W.R.; Flamm, S.L.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Bodenheimer, H.C.; Public Policy Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease. Serum activity of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) as an indicator of health and disease. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momen-Heravi, F.; Saha, B.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Satishchandran, A.; Szabo, G. Increased number of circulating exosomes and their microRNA cargos are potential novel biomarkers in alcoholic hepatitis. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hou, J.; Lin, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Dong, Q.; Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Identification of miRNomes in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Rick, J.; Lehmann, J.; Schierwagen, R.; Schierwagen, I.G.; Verbeke, L.; Hittatiya, K.; Uschner, F.E.; Manekeller, S.; Strassburg, C.P.; et al. Janus-kinase-2 relates directly to portal hypertension and to complications in rodent and human cirrhosis. Gut 2017, 66, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piano, M.R. Alcoholic cardiomyopathy: Incidence, clinical characteristics, and pathophysiology. Chest 2002, 121, 1638–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtovic, E.; Zubair, M. Mallory Bodies. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545300/ (accessed on 30 October 2025).
- Zatloukal, K.; Spurej, G.; Rainer, I.; Lackinger, E.; Denk, H. Fate of Mallory body-containing hepatocytes: Disappearance of Mallory bodies and restoration of the hepatocytic intermediate filament cytoskeleton after drug withdrawal in the griseofulvin-treated mouse. Hepatology 1990, 11, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; French, B.A.; Li, J.; Tillman, B.; French, S.W. Altered regulation of miR-34a and miR-483-3p in alcoholic hepatitis and DDC fed mice. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- He, L.; He, X.; Lim, L.P.; de Stanchina, E.; Xuan, Z.; Liang, Y.; Xue, W.; Zender, L.; Magnus, J.; Ridzon, D.; et al. A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature 2007, 447, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bertero, T.; Gastaldi, C.; Bourget-Ponzio, I.; Mari, B.; Meneguzzi, G.; Barbry, P.; Ponzio, G.; Rezzonico, R. CDC25A targeting by miR-3p decreases CCND-CDK4/6 assembly and contributes to cell cycle arrest. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gao, B.; Bataller, R. Alcoholic liver disease: Pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Szabo, G.; Bala, S. Alcoholic liver disease and the gut-liver axis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]



| MiRNA | Principal Function | Key Target(s)/Pathway(s) | Model Type | Expression in AH | Strength of Evidence | Translational Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA-217 | Pro-inflammatory signaling | SIRT1 → NF-κB | Animal + in vitro mechanistic | Up | Moderate | Mechanistically strong; limited human validation |
| Let-7b | Innate immune activation | TLR7 → MyD88/NF-κB | Mouse, human RNA-seq | Up | Low | Links ethanol exposure to TLR-driven inflammation |
| miRNA-182 | Inflammation, ductular reaction | Mcp-1, Ccl20, Cxcl5, Cxcl1, Bcl2 | Human liver, animal | Up | Moderate | Correlates with MELD and bilirubin; limited replication in large human cohorts |
| miRNA-21 | Stellate cell activation, inflammation | VHL → NF-κB | Animal, HSC mechanistic | Up | Low | Good mechanistic data; weak clinical correlation |
| miRNA-27a | M2 macrophage polarization | CD206, CD163 | In vitro, animal EV | Up | Low | Early mechanistic stage; no human data |
| miRNA-181 | Hepatic stellate cell activation | HSC genes | In vitro, animal EV | Up | Low | Early mechanistic stage; no human data |
| miRNA-192 | Exosomal signaling, fibrosis | TGF-β/Smad, Jak2/Arhgef1 signaling pathways | Human plasma, animal | Up | Moderate | Promising diagnostic marker; high translational directness |
| miRNA-122 | Hepatocyte injury, lipid metabolism | CD320, AldoA, BCKDK | Human, animal ALD | Up | Moderate | Sensitive liver injury marker; not AH-specific |
| miRNA-30a | Autophagy inhibition | Beclin-1 | Human, animal | Up | Moderate | Consistent directionality; small cohorts |
| miRNA-34a | Mallory–Denk Body formation | NAMPT, SIRT1 | Human, animal | Up | Low | Not AH-specific; elevated in multiple liver diseases |
| miRNA-148a | Pyroptosis suppression | TXNIP → NLRP3 | Human, mouse | Down | Moderate | Mechanistic and translationally coherent; small human sample |
| miRNA-30e | Regulation of ROS | ATP, H2O2 | Human, animal | Down | Moderate | Small cohorts; consistent directionality |
| miRNA-483-3p | Tumor suppressor | CDC25A phosphatase | Human, mouse | Down | Low | Very limited studies; possible link to fibrosis and neoplasia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bandara, D.; Romany, C.A.B.S.; Kumar, V.; Sohal, A.; Al-Qaisi, M.; Najafian, N. miRNAs and Alcohol-Related Hepatitis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121048
Bandara D, Romany CABS, Kumar V, Sohal A, Al-Qaisi M, Najafian N. miRNAs and Alcohol-Related Hepatitis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(12):1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121048
Chicago/Turabian StyleBandara, Dinuka, Clara Ashraf Boshra Shaker Romany, Vikash Kumar, Aalam Sohal, Mohanad Al-Qaisi, and Nilofar Najafian. 2025. "miRNAs and Alcohol-Related Hepatitis" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 12: 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121048
APA StyleBandara, D., Romany, C. A. B. S., Kumar, V., Sohal, A., Al-Qaisi, M., & Najafian, N. (2025). miRNAs and Alcohol-Related Hepatitis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(12), 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121048






