Differences and Similarities in Protein and Nucleic Acid Structures and Their Biological Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
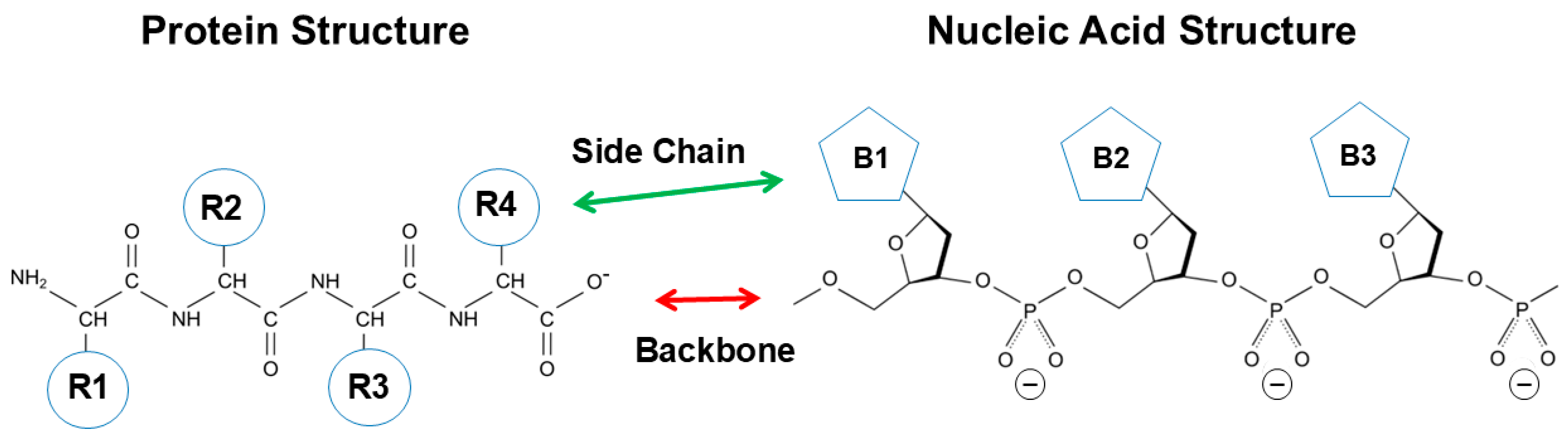
2. Structure
3. Interactions
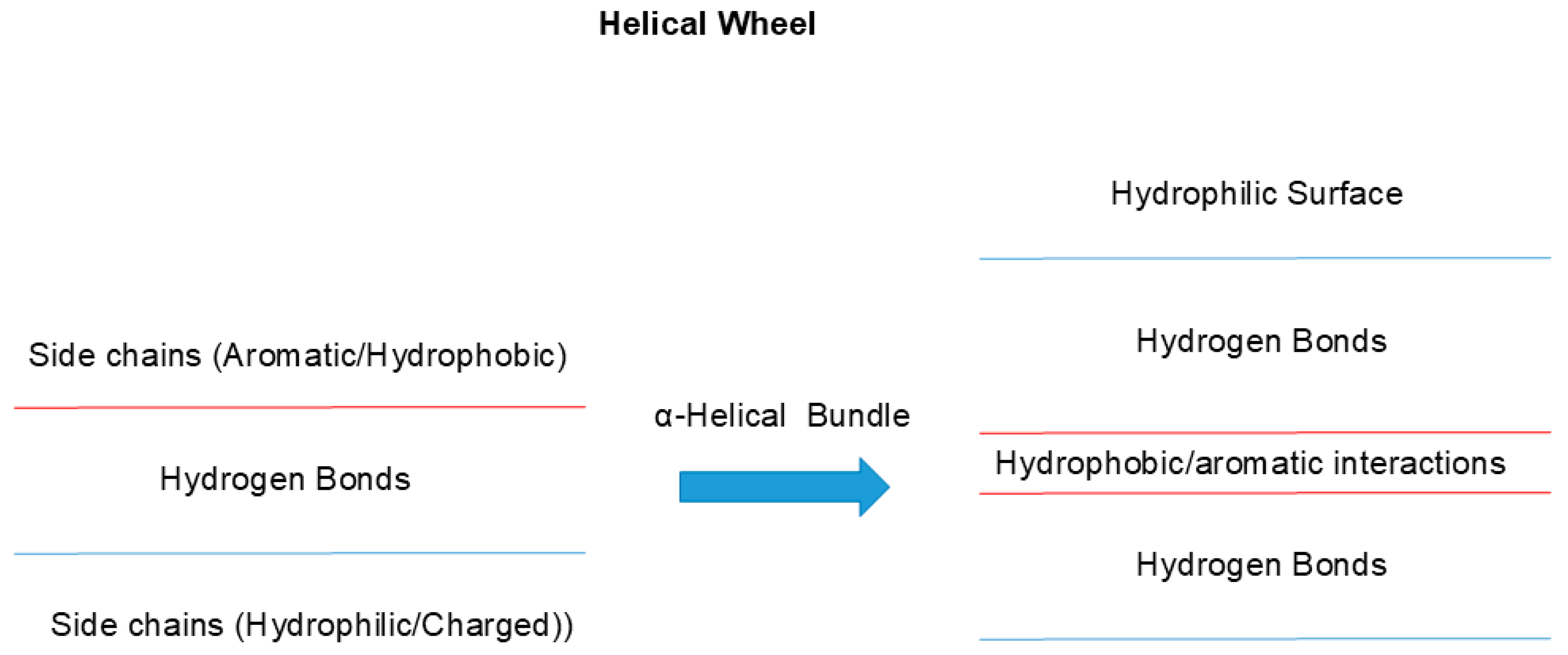
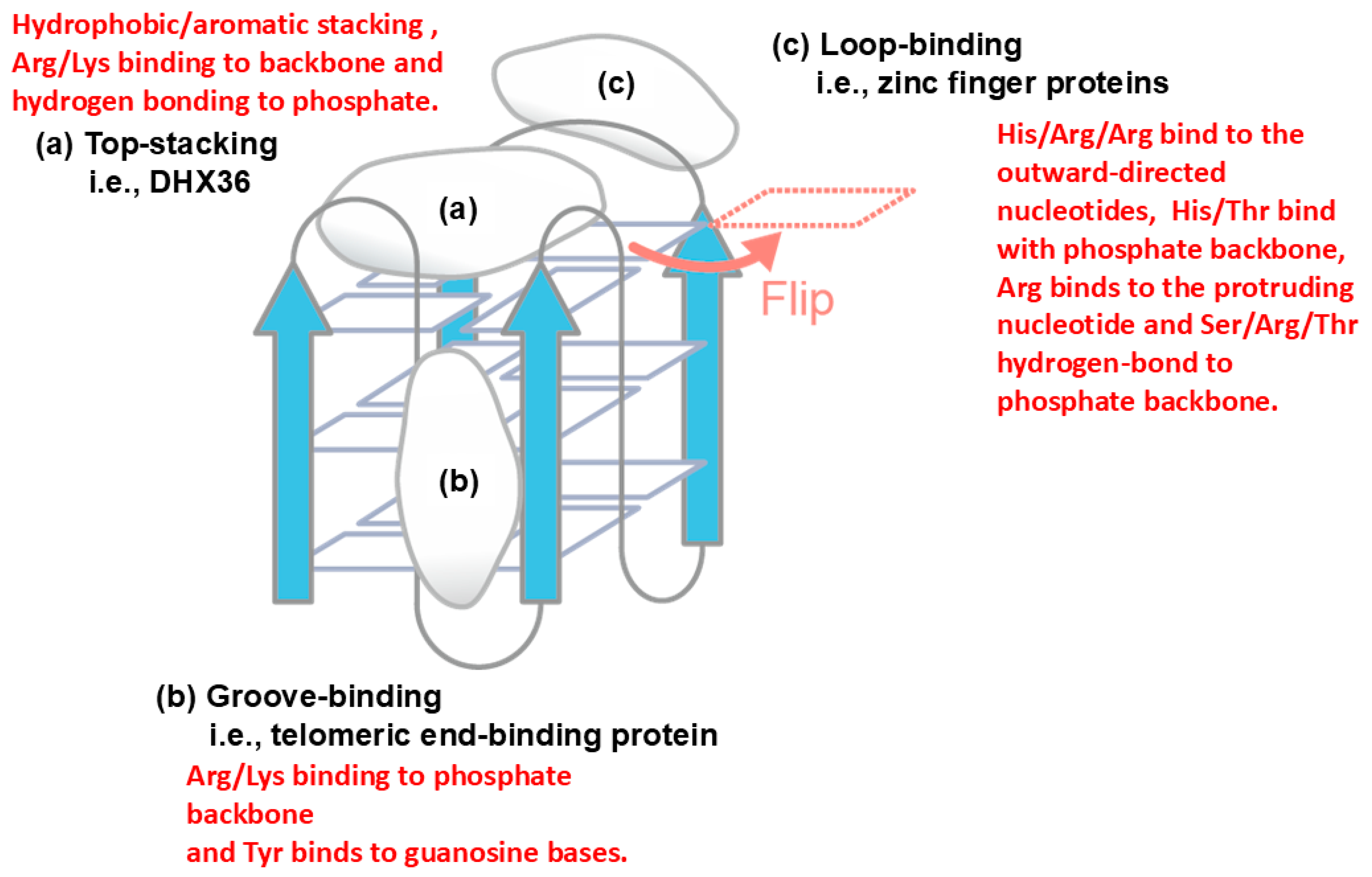
3.1. Macromolecular Interactions
3.2. Specific Role of Arginine in Molecular Interaction
3.3. Biomolecular Condensates
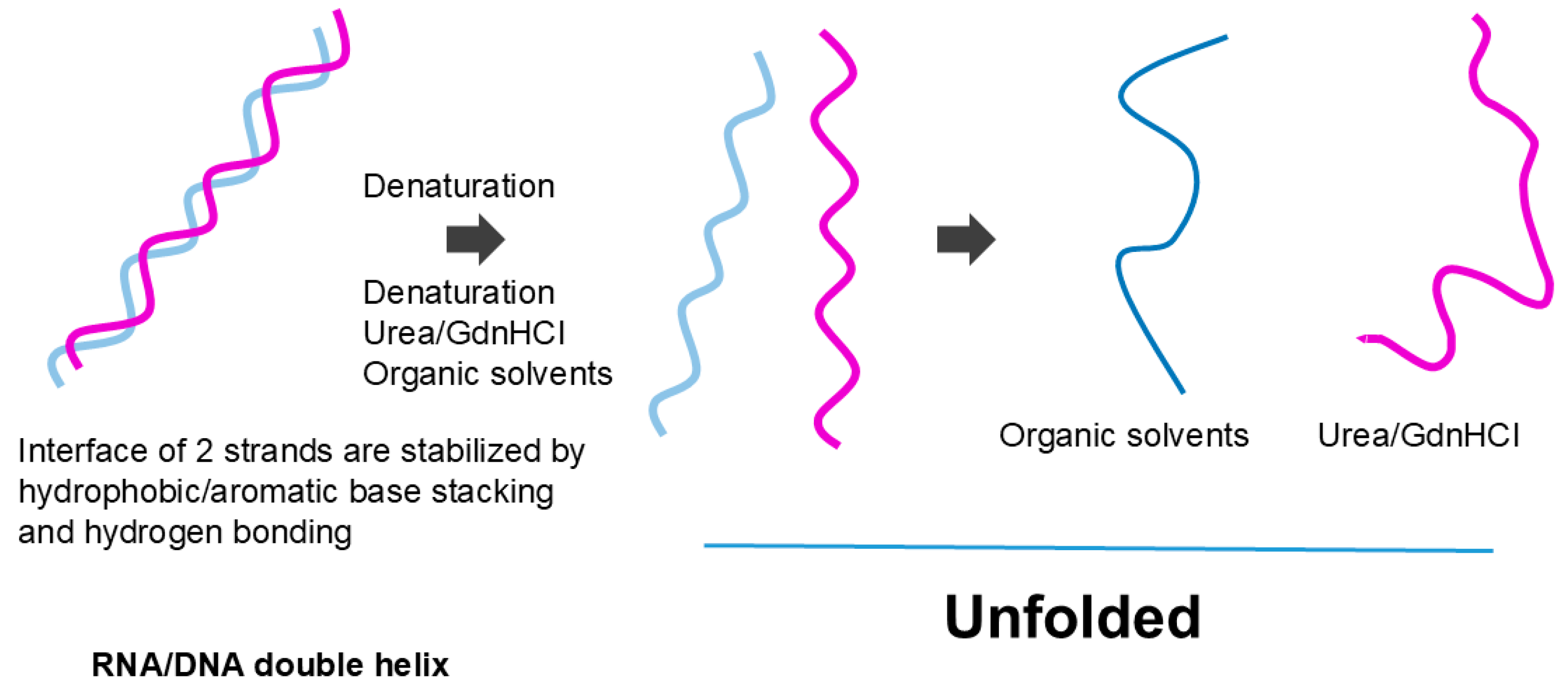
3.4. Co-Solvent Interaction
3.4.1. Organic Solvent
3.4.2. Denaturants
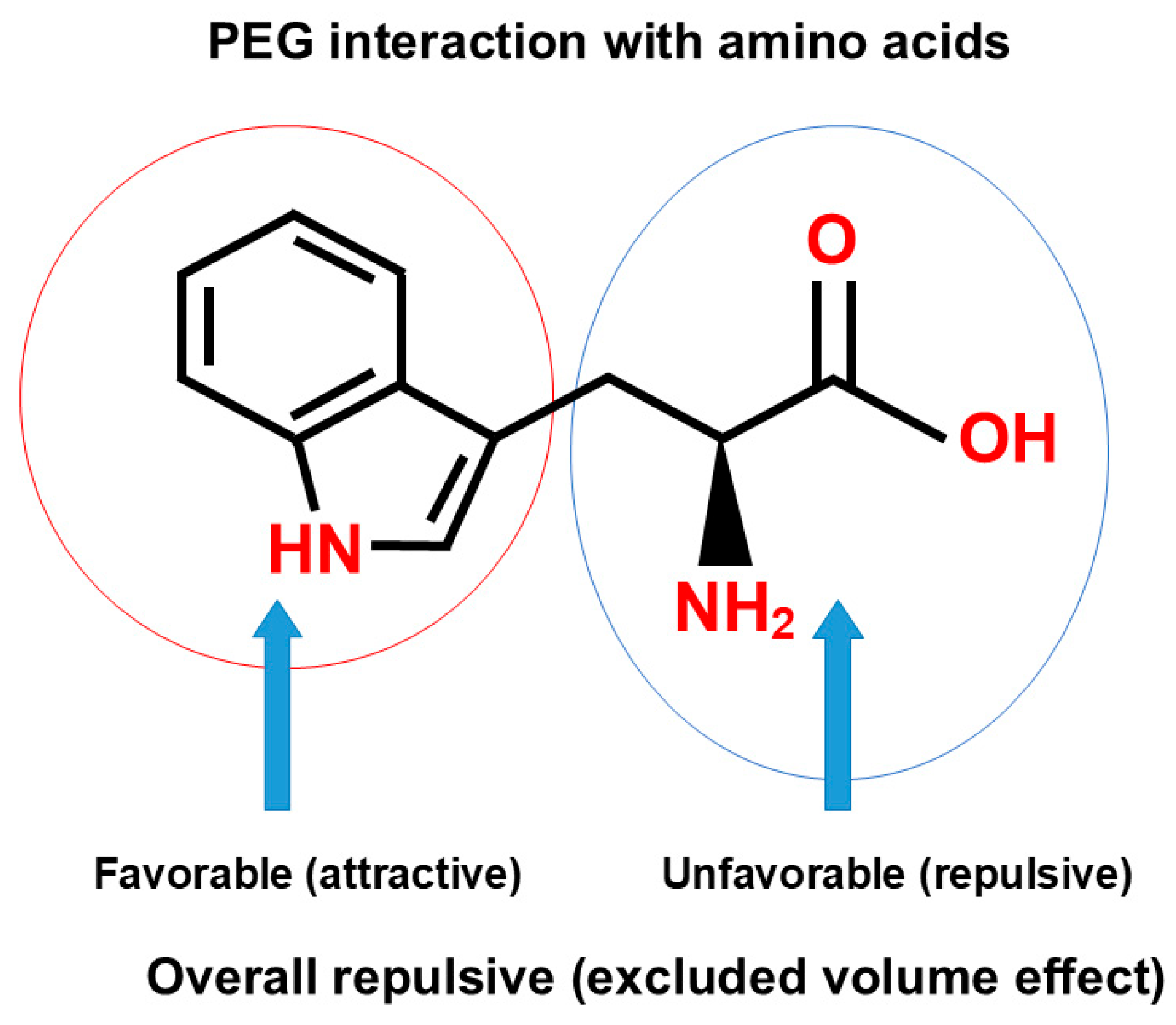
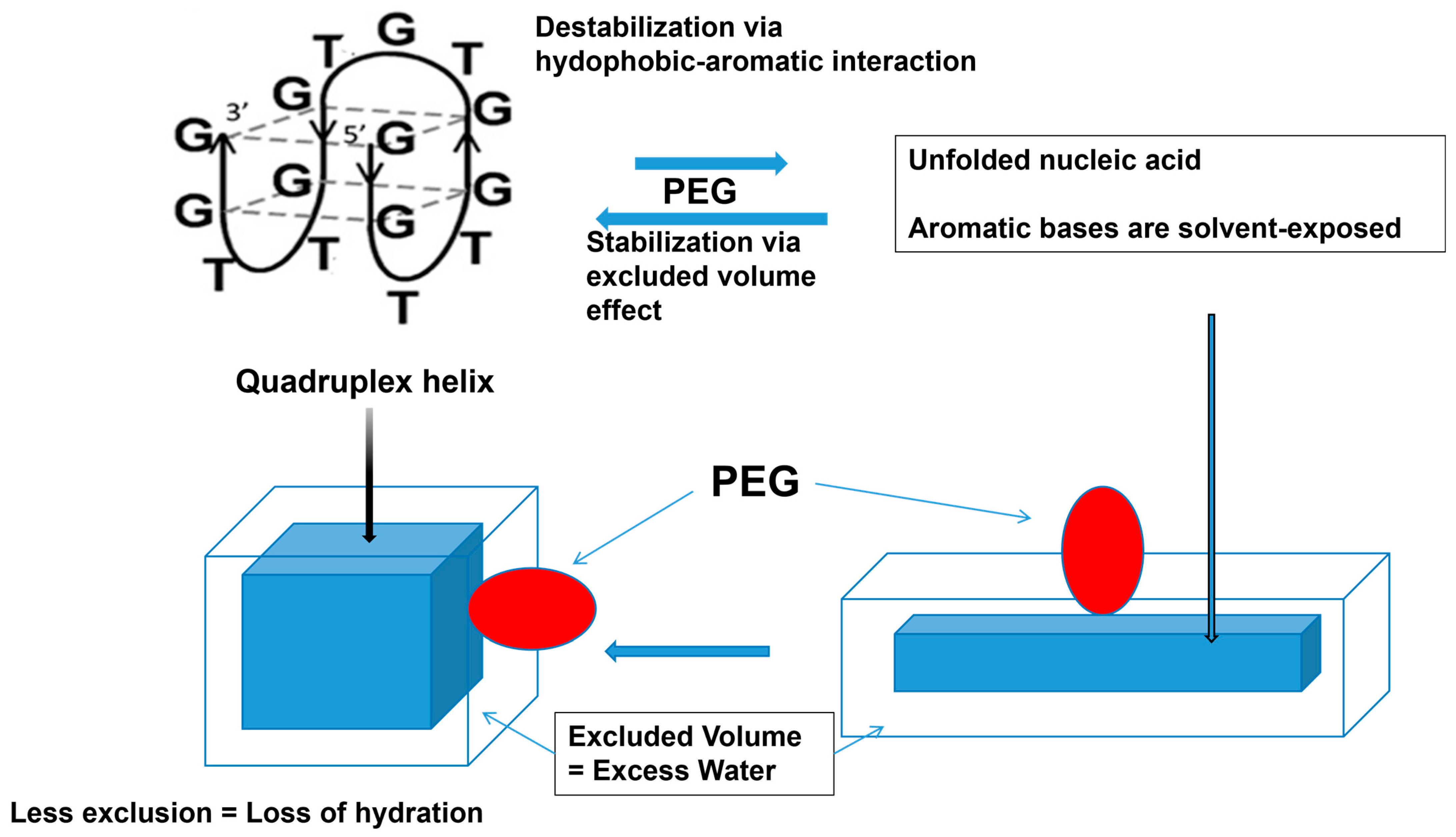
3.4.3. Polymers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD | circular dichroism |
| SF1 | splicing factor 1 |
| GdnHCl | guanidine hydrochloride |
| PEG | polyethylene glycol |
References
- Agyei, D.; Ahmed, I.; Akram, Z.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Danquah, M.K. Protein and peptide biopharmaceuticals: An overview. Protein Pept. Lett. 2017, 24, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesik-Brodacka, M. Progress in biopharmaceutical development. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2018, 65, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulligan, M.J.; Lyke, K.E.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Raabe, V.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K.A.; et al. Phase I/II study of COVID-19 RNA vaccine BNT162b1 in adults. Nature 2021, 590, E26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Chen, X. Aptamer-based targeted therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 134, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooke, S.T.; Liang, X.H.; Baker, B.F.; Crooke, R.M. Antisense technology: A review. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, S.S.; Prazeres, D.M.F.; Azevedo, A.M.; Marques, M.P.C. mRNA vaccines manufacturing: Challenges and bottlenecks. Vaccine 2021, 39, 2190–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kis, Z.; Kontoravdi, C.; Shattock, R.; Shah, N. Resources, production scales and time required for producing RNA vaccines for the global pandemic demand. Vaccines 2021, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, G.; Särnefält, A.; Kumar, A. Considerations for bioanalytical characterization and batch release of COVID-19 vaccines. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, X.; Bauzá, A.; Frontera, A.; Quiñonero, D. A thorough anion-π interaction study in biomolecules: On the importance of cooperativity effects. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, D.A. The cation-π interaction. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, C.C.; Misiura, M.; Hulgan, S.A.H.; Peterson, C.M.; Williams, J.W., 3rd; Kolomeisky, A.B. Cation-π interactions and their role in assembling collagen triple helices. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 4645–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallivan, J.P.; Dougherty, D.A. Cation-π interactions in structural biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9459–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, L.; Stucchi, R.; Konstantoulea, K.; van de Kamp, G.; Kos, R.; Geerts, W.; van der Geer, R.M.J.; Schreurs, M.A.H.; van Dam, B.H.C.; Schutten, L.H.E.; et al. Arginine π-stacking drives binding to fibrils of the Alzheimer protein Tau. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter-Fenk, K.; Liu, M.; Pujal, L.; Loipersberger, M.; Tsanai, M.; Vernon, R.M.; Johnson, E.R.; Sherrill, C.D. The energetic origins of P–π contacts in proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 24836–24851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumpstey, I.; Salomonsson, E.; Sundin, A.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J. Studies of arginine–arene interactions through synthesis and evaluation of a series of galectin-binding aromatic lactose esters. ChemBioChem 2007, 8, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herskovits, T.T.; Bowen, J.J. Solution studies of the nucleic acid bases and related compounds. Solubility in aqueous urea and amide solutions. Biochemistry 1974, 13, 5474–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herskovits, T.T.; Harrington, J.P. Solution studies of the nucleic acid bases and related model compounds. Solubility in aqueous alcohol and glycol solutions. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 4800–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, A.; Tokunaga, H.; Tokunaga, M.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. The solubility of nucleobases in aqueous arginine solutions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 497, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, E.; Haertlé, T. Alcohol-induced changes of β-lactoglobulin–retinol-binding stoichiometry. Protein Eng. 1990, 4, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraki, K.; Nishikawa, K.; Goto, Y. Trifluoroethanol-induced stabilization of the α-helical structure of β-lactoglobulin: Implication for non-hierarchical protein folding. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 245, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreon, A.C.M.; Deniz, A.A. Alpha-synuclein multistate folding thermodynamics: Implications for protein misfolding and aggregation. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 4499–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J. Influence of conventional surfactants on the self-assembly of a bola-type amphiphilic peptide. Langmuir 2017, 33, 5446–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, T.; Tokunaga, M.; Kita, Y.; Niikura, T.; Baker, R.W.; Reimer, J.M.; Vaughn, D.F.; Roberts, C.J.; Joshi, P.K. Structure analysis of proteins and peptides by difference circular dichroism spectroscopy. Protein J. 2021, 40, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahari, D.; Sahil, K.; Kaushal, S.; Sharma, A.; Rangan, L.; Swaminathan, R. Structural transitions of dehydrin in response to temperature, the presence of trifluoroethanol and sodium dodecyl sulfate, and its protective role in heat and cold stress. Biochemistry 2025, 64, 3045–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.F.; Wang, F.; Wang, M.Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Z.S.; Hao, G.F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Q. CIPDB: A biological structure databank for studying cation and π interactions. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.H.; Horng, J.C. Cation–π interaction induced folding of AAB-type collagen heterotrimers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, M.; Edmundson, A.B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys. J. 1967, 7, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, M.A.; Suter, R.; Schestak, I.; Kiss, G.; Wright, E.R.; Plemper, R.K. A stabilized headless measles virus attachment protein stalk efficiently triggers membrane fusion. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 11693–11703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, H.B.T.; Phuong, N.T.; Bui, L.M.; Thi, H.P.; Tran, T.T.P.; Quoc, T.N.; Nguyen, L.T.; Le, P.; Nguyen, D.T. Optimizing amphipathic antimicrobial peptides via helical wheel rotation. ChemMedChem 2025, 20, e202500316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.C.; Sánchez, R.; Blanco, S.; Alonso, J.L. Microsolvation of 2-azetidione: A model for the peptide group–water interactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 2054–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoppola, E.; Sodo, A.; McLain, S.E.; Ricci, M.A.; Bruni, L. Water–peptide site-specific interactions: A structural study on the hydration of glutathione. Biophys. J. 2014, 106, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scognamiglio, P.L.; Platella, C.; Napolitano, E.; Musumeci, D.; Roviello, G.N. From prebiotic chemistry to supramolecular biomedical materials: Exploring the properties of self-assembling nucleobase-containing peptides. Molecules 2021, 26, 3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, M.; Jönsson, B.; Woodward, C.E. Implications of a high dielectric constant in proteins. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 225103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimple, A.J.; Soundararajan, M.; Hutsell, S.Q.; Roos, A.K.; Urban, D.J.; Setola, V.; Sucic, M.B.; Tesmer, K.K. Structural determinants of G-protein alpha subunit selectivity by regulator of G-protein signaling 2 (RGS2). J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19402–19411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.T.; Lee, J.Y.; Lim, H.; Lee, S.H.; Moon, Y.J.; Pyo, H.J.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, D.H. Molecular mechanism of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade via anti-PD-L1 antibodies atezolizumab and durvalumab. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumoto, K.; Ogasahara, K.; Ueda, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Yutani, K.; Kumagai, I. Role of Tyr residues in the contact region of anti-lysozyme monoclonal antibody HyHEL-10 for antigen binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 18551–18557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumoto, K.; Yokota, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Ui, M.; Tsumuraya, T.; Fujii, I.; Kato, M.; Kobayashi, S. Critical contribution of aromatic rings to specific recognition of polyether rings: The case of ciguatoxin CTX3C-ABC and its specific antibody 1C49. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 12259–12266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, H.; Tsumoto, K. Thermodynamics of antibody–antigen interaction revealed by mutation analysis of antibody variable regions. J. Biochem. 2015, 158, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimasu, H.; Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Konermann, S.; Shehata, S.I.; Dohmae, N.; Ishitani, R.; Zhang, F.; Nureki, O. Crystal structure of Cas9 in complex with guide RNA and target DNA. Cell 2014, 156, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, A.D.; Pai, S.; Ellington, A. Aptamers as therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines—A new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Luyten, I.; Bottomley, M.J.; Messias, A.C.; Houngninou-Molango, S.; Sprangers, R.; Lam, R.F.; de Almeida, M.S.; Abrahams, J.P.; Steinmetz, M.O. Structural basis for recognition of the intron branch site RNA by splicing factor 1. Science 2001, 294, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, M.M.; Thomas, J.M.; Zheng, Y.; Tran, K.; Phelps, K.J.; Scott, A.I.; Lam, R.F.; Roberts, C.; Zimmerman, M.I.; Vithani, N.; et al. Structures of human ADAR2 bound to dsRNA reveal base-flipping mechanism and basis for site selectivity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamma, T.; Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R. Structure of protein L7Ae bound to a K-turn derived from an archaeal box H/ACA sRNA at 1.8 Å resolution. Structure 2004, 12, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.; Zhang, Y.; Fenley, M.O.; Li, H. Molecular basis of box C/D RNA–protein interactions: Cocrystal structure of archaeal L7Ae and a box C/D RNA. Structure 2004, 12, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Stephenson, V. G4-quadruplex-binding proteins: Review and insights into selectivity. Biophys. Rev. 2022, 14, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Tippana, R.; Demeshkina, N.A.; Murat, P.; Balasubramanian, S.; Myong, S.; Yu, H.; Gross, J.T.; Zhao, K. Structural basis of G-quadruplex unfolding by the DEAH/RHA helicase DHX36. Nature 2018, 558, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, M.P.; Schultz, S.C. DNA G-quartets in a 1.86 Å resolution structure of an Oxytricha nova telomeric protein–DNA complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 310, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladame, S.; Schouten, J.A.; Roldan, J.; Redman, J.E.; Neidle, S.; Balasubramanian, S. Exploring the recognition of quadruplex DNA by an engineered Cys2–His2 zinc finger protein. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavali, S.S.; Cavender, C.E.; Mathews, D.H.; Wedekind, J.E. Arginine forks are a widespread motif to recognize phosphate backbones and guanine nucleobases in the RNA major groove. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 19835–19839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDougall, G.; Anderton, R.S.; Trimble, A.; Mastaglia, F.L.; Knuckey, N.W.; Meloni, B.P. Poly-arginine-18 (R18) confers neuroprotection through glutamate receptor modulation, intracellular calcium reduction, and preservation of mitochondrial function. Molecules 2020, 25, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Casado, A.; Molina, M.; Carmona, P. Core protein–nucleic acid interactions in hepatitis C virus as revealed by Raman and circular dichroism spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 61, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, S.; Lee, C. Exploring the impact of nucleic acids on protein stability in bacterial cell lysate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2023, 1867, 130445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubuk, J.; Alston, J.J.; Incicco, J.J.; Singh, S.; Struchell-Brereton, M.D.; Ward, M.D.; Zimmerman, M.I.; Vithani, N.; Griffith, D.; Wagoner, J.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is dynamic, disordered, and phase separates with RNA. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, J.D.; Aguilar, P.P.; Köppl, C.; Fischer, A.; Grünwald-Gruber, C.; Dürkop, M.; Becker, S.; Fuchs, R.; Müller, S.; Schneider, T.M. Production of full-length SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein from Escherichia coli optimized by native hydrophobic interaction chromatography hyphenated to multi-angle scattering detection. Talanta 2021, 235, 122691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.R.; Asfaha, J.B.; Ghent, C.M.; Howard, C.J.; Hartooni, N.; Safari, M.; Gerber, R.A.; Gardner, D.A.; Williamson, E.M. Phosphoregulation of phase separation by the SARS-CoV-2 N protein suggests a biophysical basis for its dual functions. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ye, Q.; Singh, D.; Cao, Y.; Diedrich, J.K.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Guttman, S.H.; Smith, R.R. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein forms mutually exclusive condensates with RNA and the membrane-associated M protein. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laue, T.M.; Shire, S.J. The molecular interaction process. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 307, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banani, S.F.; Lee, H.O.; Hyman, A.A.; Rosen, M.K. Biomolecular condensates: Organizers of cellular biochemistry. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garabedian, M.V.; Su, Z.; Dabdoub, J.; Tong, M.; Deiters, A.; Hammer, D.A.; Good, M.C. Protein condensate formation via controlled multimerization of intrinsically disordered sequences. Biochemistry 2022, 61, 2237–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.W.; Holehouse, A.S.; Peran, I.; Farag, M.; Incicco, J.J.; Bremer, A.; Grace, C.R.; Soranno, A.; Pappu, R.V.; Mittag, T. Valence and patterning of aromatic residues determine the phase behavior of prion-like domains. Science 2020, 367, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieregg, J.R.; Lueckheide, M.; Marciel, A.; Leon, D.M.; Tirrell, K.L. Oligonucleotide–peptide complexes: Phase control by hybridization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadsworth, G.; Srinivasan, S.; Lai, L.; Datta, M.; Gopalan, V.; Banerjee, P.R. RNA-driven phase transitions in biomolecular condensates. Mol. Cell 2024, 85, 3670–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; You, R.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. G-quadruplex structures trigger RNA phase separation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 11746–11754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauber, D.; Tauber, G.; Parker, R. Mechanisms and regulation of RNA condensation in RNP granule formation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 45, 764–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, H.; Nguyen, H.; Hori, N.; Thirumalai, D. Odd–even disparity in the population of slipped hairpins in RNA repeat sequences with implications for phase separation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2301409120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shil, S.; Tsuruta, M.; Kawauchi, K.; Miyoshi, D. Factors Affecting Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation of RGG Peptides with DNA G-Quadruplex. ChemMedChem 2025, 20, e202400460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, M.; Shil, S.; Taniguchi, S.; Kawauchi, K.; Miyoshi, D. The role of cytosine methylation in regulating the topology and liquid-liquid phase separation of DNA G-quadruplexes. Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 4213–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, J.; Madanayake, T.W.; Iaccarino, N.; Novellino, E.; Randazzo, A.; Hurley, L.H.; Pagano, B. HMGB1 binds to the KRAS promoter G-quadruplex: A new player in oncogene transcriptional regulation? Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 9442–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dickerhoff, J.; Zheng, K.W.; Erramilli, S.; Feng, H.; Wu, G.; Onel, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, K.B.; Carver, M.; et al. Structural basis for nucleolin recognition of MYC promoter G-quadruplex. Science 2025, 388, eadr1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, B.R.; Deng, X.; Wong, E.L.; Clark, N.; Yang, H.J.; Kovalenko, A.; Subramanian, V.; Guzman, B.B.; Harris, S.E.; Dehury, B.; et al. Visualization of liquid-liquid phase transitions using a tiny G-quadruplex binding protein. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, W.; Song, Y.W.; Bansal, V.; Kim, K.K. G-quadruplex-dependent transcriptional regulation by molecular condensation in the Bcl3 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, gkaf827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozaki, Y.; Tanford, C. The solubility of amino acids and two glycine peptides in aqueous ethanol and dioxane solutions. Establishment of a hydrophobicity scale. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikulenko, A.V. Thermodynamic and Stereochemical Parameters to Evaluate Stability of Hydrophobic Cores of Globular Proteins. Biochemistry 1998, 63, 1290–1293. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9864468/ (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Bryzgunova, O.; Bondar, A.; Morozkin, E.; Mileyko, V.; Vlassov, V.; Laktionov, P. A reliable method to concentrate circulating DNA. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 408, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurien, B.T. Extraction of proteins from gels: A brief review. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 869, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilcher, G.; Schlagenhauf, A.; Schneditz, D.; Scharnagal, H.; Ribitsch, W.; Krause, R.; Rosenkranz, A.R.; Stojakovic, T.; Horina, J.H. Ethanol causes protein precipitation—New safety issues for catheter locking techniques. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Precipitation of DNA with ethanol. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2016, 12, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, Y.; Arakawa, T.; Lin, T.Y.; Timasheff, S.N. Contribution of the surface free energy perturbation to protein–solvent interactions. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 15178–15189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y.; Tanford, C. The solubility of amino acids and related compounds in aqueous ethylene glycol solutions. J. Biol. Chem. 1965, 240, 3568–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, T.; Kita, Y.; Timasheff, S.N. Protein precipitation and denaturation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Biophys. Chem. 2007, 131, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, A.; Wada, M.; Sato, T.K.; Kameda, T. The solubility of N-acetyl amino acid amides in organic acid and alcohol solutions: Mechanistic insight into structural protein solubilization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 178, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermaas, J.V.; Pogorelov, T.V.; Tajkhorshid, E. Extension of the highly mobile membrane mimetic to transmembrane systems through customized in silico solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2017, 121, 3764–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, E.P.; Timasheff, S.N. Interaction of ribonuclease A with aqueous 2-methyl-2,4-pentanediol at pH 5.8. Biochemistry 1978, 17, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Yin, C. Force field benchmark of amino acids. 2. Partition coefficients between water and organic solvents. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2018, 58, 1669–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zheng, M.; Farajtabar, A.; Zhao, H. Solubility modelling and preferential solvation of adenine in solvent mixtures of N,N-dimethylformamide, N-methyl pyrrolidone, propylene glycol and dimethyl sulfoxide plus water. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 125, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Han, D.; Tao, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Gong, J.; Li, L.; Sun, H. Solubility measurement, thermodynamic correlation and molecular simulations of uracil in alcohol + water binary solvents at 233.15–318.15 K. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinanoglu, O.; Abdulnur, S. Effect of Water and Other Solvents on the Structure of Biopolymers. Fed. Proc. 1965, 24, S12–S23. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14314560/ (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Alonso, D.O.; Dill, K.A. Solvent denaturation and stabilization of globular proteins. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 5947–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.M.; Malik, A.; Sharma, P.; Fatima, S. Anionic surfactants cause dual conformational changes in insulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Baldwin, R.L. Mechanism of helix induction by trifluoroethanol: A framework for extrapolating the helix-forming properties of peptides from trifluoroethanol/water mixtures back to water. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 8413–8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.K.P.; Jagannadham, M.V. Deciphering the molecular structure of cryptolepain in organic solvents. Biochimie 2011, 94, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srisailam, S.; Kumar, T.K.; Simathi, T.; Yu, C. Influence of backbone conformation on protein aggregation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1884–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiduschek, E.P.; Herskovits, T.T. Nonaqueous solutions of DNA. Reversible and irreversible denaturation in methanol. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1961, 95, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herskovits, T.T.; Singer, S.J.; Geiduschek, E.P. Nonaqueous solutions of DNA. Denaturation in methanol and ethanol. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1961, 94, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, S.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Dependence of ethanol effects on protein charges. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 68, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, H.; Hirano, A.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Mechanistic insights into protein precipitation by alcohol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, H.; Hirano, A.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Effects of alcohol on the solubility and structure of native and disulfide-modified bovine serum albumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oss, C.J. On the mechanism of the cold ethanol precipitation method of plasma protein fractionation. J. Protein Chem. 1989, 8, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, W.R. Dehydration: A new alcohol theory. Alcohol 1990, 7, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Dai, H.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, M. Effect of different dehydration methods on the properties of gelatin films. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herskovits, T.T. Nonaqueous solutions of DNA; denaturation by urea and its methyl derivatives. Biochemistry 1963, 2, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghunathan, S. Solvent accessible surface area-assessed molecular basis of osmolyte-induced protein stability. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 25031–25041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, S.; Kumagai, I. Refolding of therapeutic proteins produced in Escherichia coli as inclusion bodies. Biopolymers 1999, 51, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.M.; Panda, A.K. Solubilization and refolding of bacterial inclusion body proteins. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 99, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyyay, V.; Singh, A.; Panda, A.K. Purification of recombinant ovalbumin from inclusion bodies of Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 117, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y.; Tanford, C. The solubility of amino acids and related compounds in aqueous urea solutions. J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238, 4074–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y.; Tanford, C. The solubility of amino acids, diglycine, and triglycine in aqueous guanidine hydrochloride solutions. J. Biol. Chem. 1970, 245, 1648–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Shaikh, A.R. Interaction of arginine, lysine, and guanidine with surface residues of lysozyme: Implication to protein stability. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinami, S.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Classification of protein solubilizing solutes by fluorescence assay. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 203, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Kasavajhala, K.; Priyakumar, U.D. Role of urea-aromatic stacking interactions in stabilizing the aromatic residues of the protein in urea-induced denatured state. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14931–14946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghunathan, S.; Jaganade, T.; Priyakumar, U.D. Urea-aromatic interactions in biology. Biophys. Rev. 2020, 12, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.K.; Rösgen, J.; Englander, S.W. Urea, but not guanidinium, destabilizes proteins by forming hydrogen bonds to the peptide group. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2595–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Timasheff, S.N. Partial specific volumes and interactions with solvent components of proteins in guanidine hydrochloride. Biochemistry 1974, 13, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alodia, N.; Jaganade, T.; Priyakumar, U.D. Quantum mechanical investigation of the nature of nucleobase-urea stacking interaction, a crucial driving force in RNA unfolding in aqueous urea. J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 130, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Singh, P.C. Sequence specific hydrogen bond with DNA with denaturants affects its stability: Spectroscopic and simulation studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2021, 1865, 129735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkel, I.A.; Knowles, B.; Record, M.T., Jr. Separating chemical and excluded volume interactions of polyethylene glycols with native proteins: Comparison with PEG effects on DNA helix formation. Biopolymers 2015, 103, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Timasheff, S.N. Mechanism of poly(ethylene glycol) interaction with proteins. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 6756–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.L.; Lee, J.C. Thermal stability of proteins in the presence of poly(ethylene glycols). Biochemistry 1987, 26, 7813–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Lee, L.L. Preferential solvent interactions between proteins and polyethylene glycols. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellman, J.A. Protein stability in mixed solvents: A balance of contact interaction and excluded volume. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.; de Haro, M.L.; Fiumara, G.; Saija, F. The effective colloid interaction in the Asakura-Oosawa model. Assessment of non-pairwise terms from virial expansion. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 142, 224903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minton, A.P. Macromolecular crowding. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, R269–R271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, G.; Minton, A.P. Macromolecular crowding in vitro, in vivo and in between. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, L.; Baier, D.; Rajput, S.; König, B.; Tiemann, M.; Ebbinghaus, S.; Nayar, D.; Huber, K. Disaggregation at high volume exclusion: An “overcrowding” effect. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2025, 129, 10213–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Simplified equilibrium model for exploring the combined influences of concentration, aggregate shape, excluded volume, and surface adsorption upon aggregation propensity and distribution of globular macromolecules. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2023, 127, 9303–9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, A.; Shiraki, K.; Arakawa, T. Polyethylene glycol behaves like weak organic solvent. Biopolymers 2012, 97, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, D.; Nakao, A.; Sugimoto, N. Molecular crowding regulates the structural switch of the DNA G-quadruplex. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 15017–15024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, S.; Karimata, H.; Ohmichi, T.; Kawakami, J.; Sugiyama, N. The effect of molecular crowding with nucleotide length and cosolute structure on DNA duplex stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 14330–14331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, D.; Karimata, H.; Sugimoto, N. Hydration regulates thermodynamics of G-quadruplex formation under molecular crowding conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7957–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, R.L.; Rose, G.D. How the hydrophobic factor drives protein folding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12462–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arakawa, T.; Oyama, T.; Ura, T.; Nishinami, S.; Shiraki, K.; Akuta, T. Differences and Similarities in Protein and Nucleic Acid Structures and Their Biological Interactions. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121019
Arakawa T, Oyama T, Ura T, Nishinami S, Shiraki K, Akuta T. Differences and Similarities in Protein and Nucleic Acid Structures and Their Biological Interactions. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(12):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121019
Chicago/Turabian StyleArakawa, Tsutomu, Taiji Oyama, Tomoto Ura, Suguru Nishinami, Kentaro Shiraki, and Teruo Akuta. 2025. "Differences and Similarities in Protein and Nucleic Acid Structures and Their Biological Interactions" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 12: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121019
APA StyleArakawa, T., Oyama, T., Ura, T., Nishinami, S., Shiraki, K., & Akuta, T. (2025). Differences and Similarities in Protein and Nucleic Acid Structures and Their Biological Interactions. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(12), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121019





