Natural History of Influenza B Virus—Current Knowledge on Treatment, Resistance and Therapeutic Options
Abstract
1. Introduction
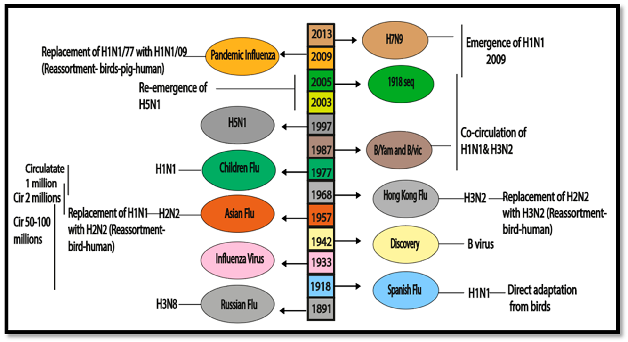
2. Epidemiological Histories
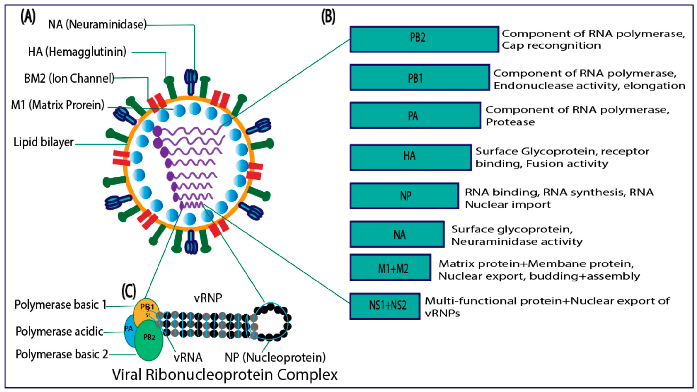
3. Organization of Genome
3.1. The Hemagglutinin
3.2. The Neuraminidase
3.3. The NB Protein
3.4. The Matrix Protein (BM1)
3.5. The BM2 Ion Channel
3.6. The Nucleocapsid Protein
3.7. The NS1 Protein
3.8. The NEP or NS2 Protein
3.9. Noncoding Sequences
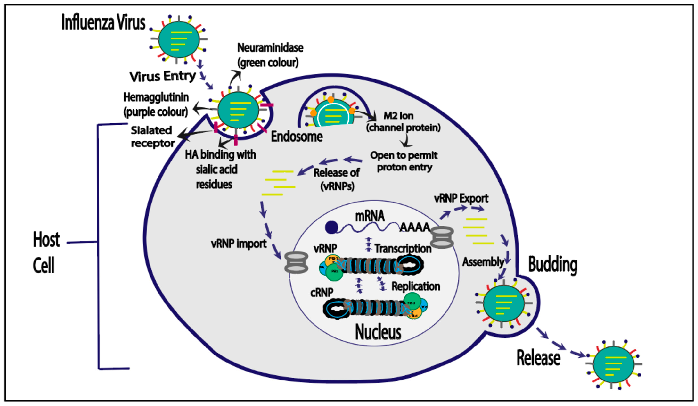
4. Life Cycle of Influenza Virus
4.1. Influenza Virus Entry
4.2. Viral Ribonucleoproteins’ (vRNPs) Entry into the Cell Nucleus
4.3. Replication and Transcription
4.4. vRNPs Export
4.5. Budding Host Cell Plasma Membrane
5. Treatment: Anti-IBV Drugs and Resistance
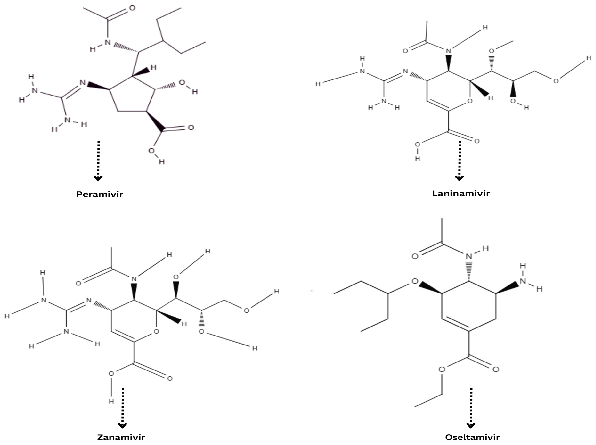
5.1. Neuraminidase Inhibitors (NIs)
5.2. Zanamivir (Relenza®)
Contraindications/Adverse Events
5.3. Oseltamivir
Contraindications/Adverse Events
5.4. Peramivir
Contraindications/Adverse Events
5.5. Laninamivir
Contraindications/Adverse Events
5.6. Viral Polymerase Inhibitors (PIs)
5.6.1. Contraindications/Adverse Events
5.6.2. Baloxavir Marboxil
5.6.3. Favipiravir (T-705)
| Resistance-Conferring Mutation of Influenza B Virus to Neuraminidase and Polymerase Inhibitor | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Site Inhibitor | Generic Name | Routes of Administration | DrugBank Accession Number | Period of Time | Mutations Conferring Resistance | Worlds Region | Techniques Used | Ref |
| Neuraminidase Inhibitors | Zanamivir | Respiratory (inhalation) | DB00558 | 2004–2005 | R371K | Hong Kong | Chemiluminescent NAI assay, IC50 analysis, reverse transcription-PCR, and sequence analysis | [60] |
| 2014–2015 | D197N, I221T | Australia, USA, China, Ukraine, Japan, Russia | None (Report from global update) | [61] | ||||
| 2018–2020 | T146K | Philippines | NA activity assay, fluorometric NAI assay | [62] | ||||
| T146P, N169S, G247D, I361V, G108E, H101L, A200T, H439P | Malaysia | NA activity assay, fluorometric NAI assay | [62] | |||||
| Oseltamivir | Oral | DB00198 | 2004–2005 | R371K | Hong Kong | Chemiluminescent NAI assay, IC50 analysis, reverse transcription-PCR, and sequence analysis | [60] | |
| 2011 | H273Y | Canada | Chemiluminescent NAI assay, IC50 analysis, sequence analysis | [63] | ||||
| 2014–2015 | I221T(NA), K152M(NA), D197N(NA) | Honduras, Bangladesh, Australia USA, China Ukraine, Japan, Russia | None (Report from global update) | [61] | ||||
| 2016–2019 | T146K, T146P, T146P, N169S, G108E, A200T | Asia | NA activity assay, fluorometric NAI assay | [62] | ||||
| Peramivir | Intravenous | DB06614 | 2014–2015 | T106P, G104R/G, G145E, I221T, D197N, I221T | Japan, Honduras, Australia, USA, China Ukraine, Russia | None (Report from global update) | [61] | |
| 2009–2012 | I221T, A245T, K360E, A395E, D432G, G145R + Y142H | Asia, Africa, Oceania | Chemiluminescent NAI assay, IC50 analysis, reverse transcription-PCR, and sequence analysis | [65] | ||||
| 2011 | H273Y | Canada | Chemiluminescent NAI assay, IC50 analysis, reverse transcription-PCR, and sequence analysis | [62] | ||||
| 2016–2020 | T146K, T146P, N169S, G247D, I361V, G108E, H101L, A200T, D432G, H439P | Asia | NA activity assay, fluorometric NAI assay | [62] | ||||
| Laninamivir | Respiratory (inhalation) | DB12791 | 2019 | T146P, N169S, T146K | Malaysia | NA activity assay, fluorometric NAI assay | [62] | |
| 2018 | T146K | Philippines | NA activity assay, fluorometric NAI assay | [62] | ||||
| 2019 | A200T | Malaysia | NA activity assay, fluorometric NAI assay | [62] | ||||
| Polymerase Inhibitor | Baloxavir Marboxil | Oral | DB13997 | 2020 | PA-I38T, PA-I38M | Reported only in vitro | Minigenome assay for polymerase activity, replication kinetics experiments, In vitro genetic stability | [73] |
6. Targeted Therapies
6.1. Antibody-Based Therapies
6.2. Host Cell Targeting Compound—DAS-181
6.3. Host-Cell-Targeting Compound—Nitazoxanide
6.4. Nucleoprotein Inhibitor—FA-6005
6.5. Viral Polymerase Inhibitor—S-033188
6.6. Antiviral Peptides
7. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IBV | Influenza B virus |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| NA | Neuraminidase |
| HA | Hemagglutinin |
| PA | Acidic Polymerase |
| vRNP | Viral ribonucleoprotein |
| vRNA | Viral RNA |
| RBS | Receptor-binding site |
| LAIV | live attenuated influenza vaccine |
| NLS | Nuclear localization signal |
| TGN | Trans-Golgi network |
| RdRp | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| CTD | C-terminal repeat domain |
| CRM | Chromosome Region Maintenance |
| GTP | Guanosine triphosphate |
| NAI | Neuraminidase Inhibitors |
| PIs | Viral polymerase inhibitors |
| bnAbs | Broadly neutralizing antibodies |
| RBS | Receptor binding site |
| HI | Hemagglutination inhibition |
| DADs | Direct-acting drugs |
| NTZ | Nitazoxanide |
| TIZ | Tizoxanide |
References
- Peasah, S.K.; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Breese, J.; Meltzer, M.I.; Widdowson, M.-A. Influenza cost and cost-effectiveness studies globally—A review. Vaccine 2013, 31, 5339–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, W.A., II; Gong, M.; Bhagwanjee, S.; Sevransky, J. Global Burden of Influenza as a Cause of Cardiopulmonary Morbidity and Mortality. Glob. Heart 2014, 9, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javanian, M.; Barary, M.; Ghebrehewet, S.; Koppolu, V.; Vasigala, V.R.; Ebrahimpour, S. A brief review of influenza virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 4638–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederman, M.S.; Krilov, L.R. Acute lower respiratory infection in developing countries. Lancet 2013, 381, 1341–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Y.T.; Graitcer, S.B.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tran, D.N.; Pham, T.D.; Le, M.T.; Tran, H.N.; Bui, C.T.; Dang, D.T.; Nguyen, L.T.; et al. National surveillance for influenza and influenza-like illness in Vietnam, 2006–2010. Vaccine 2013, 31, 4368–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eisenstein, M. Towards a universal flu vaccine. Nature 2019, 573, S50–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohskopf, L.A. Prevention and control of seasonal influenza with vaccines: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, 2019–2020 influenza season. MMWR. Recomm. Rep. 2019, 68, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nypaver, C.; Dehlinger, C.; Carter, C. Influenza and influenza vaccine: A review. J. Midwifery Women’s Health 2021, 66, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, M.E.; King, M.L.; Kelvin, A.A. Back to the future for influenza preimmunity—Looking back at influenza virus history to infer the outcome of future infections. Viruses 2019, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumpey, T.M.; Basler, C.F.; Aguilar, P.V.; Zeng, H.; Solórzano, A.; Swayne, D.E.; Cox, N.J.; Katz, J.M.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Palese, P.; et al. Characterization of the reconstructed 1918 Spanish influenza pandemic virus. Science 2005, 310, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, S.M.; Burke, D.S. Historical perspective—Emergence of influenza A (H1N1) viruses. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.I.; Viboud, C.; Simonsen, L.; Bennett, R.T.; Griesemer, S.B.; St George, K.; Taylor, J.; Spiro, D.J.; Sengamalay, N.A.; Ghedin, E.; et al. Multiple reassortment events in the evolutionary history of H1N1 influenza A virus since 1918. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jester, B.J.; Uyeki, T.M.; Jernigan, D.B. Fifty years of influenza A (H3N2) following the pandemic of 1968. Am. J. Public Health 2020, 110, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadbent, A.J.; Subbarao, K. Influenza virus vaccines: Lessons from the 2009 H1N1 pandemic. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannoun, C. The evolving history of influenza viruses and influenza vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2013, 12, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsakos, M.; Nguyen, T.H.; Barclay, W.S.; Kedzierska, K. Knowns and unknowns of influenza B viruses. Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, X.; Chen, X.; Ma, J. Structural basis for receptor specificity of influenza B virus hemagglutinin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16874–16879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Shen, X.; Yan, H.; Lu, W.Y.; Zhong, G.J.; Dong, K.G.; Yang, J.; Yu, H.J. Estimating the disease burden of seasonal influenza in China, 2006–2019. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021, 101, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorratoltaj, N.; Marathe, A.; Lewis, B.L.; Swarup, S.; Eubank, S.G.; Abbas, K.M. Epidemiological and economic impact of pandemic influenza in Chicago: Priorities for vaccine interventions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, F.; Mbawuike, I.N.; Kondrashkina, E.; Wang, Q. The roles of hemagglutinin Phe-95 in receptor binding and pathogenicity of influenza B virus. Virology 2014, 450, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmeister, W.; Ruigrok, R.; Cusack, S. The 2.2 A resolution crystal structure of influenza B neuraminidase and its complex with sialic acid. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnham, A.J.; Baranovich, T.; Govorkova, E.A. Neuraminidase inhibitors for influenza B virus infection: Efficacy and resistance. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demers, A.; Ran, Z.; Deng, Q.; Wang, D.; Edman, B.; Lu, W.; Li, F. Palmitoylation is required for intracellular trafficking of influenza B virus NB protein and efficient influenza B virus growth in vitro. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95 Pt 6, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, W.B.; Pitkeathly, M.; Wallace, B.A.; Forrest, L.R.; Smith, G.R.; Sansom, M.S.P. Transmembrane peptide NB of influenza B: A simulation, structure, and conductance study. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 12708–12716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tosteson, M.T.; Auld, D.S.; Tosteson, D.C. Voltage-gated channels formed in lipid bilayers by a positively charged segment of the Na-channel polypeptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, M.; Kawaoka, Y. The NB protein of influenza B virus is not necessary for virus replication in vitro. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6050–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McCullers, J.A.; Hoffmann, E.; Huber, V.C.; Nickerson, A.D. A single amino acid change in the C-terminal domain of the matrix protein M1 of influenza B virus confers mouse adaptation and virulence. Virology 2005, 336, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Yan, J.; Gao, G.F.; Liu, W. Characterization of the nucleocytoplasmic shuttle of the matrix protein of influenza B virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7464–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pielak, R.M.; McClintock, M.A.; Chou, J.J. Solution structure and functional analysis of the influenza B proton channel. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 1267–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mould, J.A.; Paterson, R.G.; Takeda, M.; Ohigashi, Y.; Venkataraman, P.; Lamb, R.A.; Pinto, L.H. Influenza B virus BM2 protein has ion channel activity that conducts protons across membranes. Dev. Cell 2003, 5, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Ahmad, W.; Duan, M.; Guan, Z. The BM2 protein of influenza B virus interacts with p53 and inhibits its transcriptional and apoptotic activities. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 403, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, C.M.; Williams, M.A.; Lamb, R.A. Eukaryotic coupled translation of tandem cistrons: Identification of the influenza B virus BM2 polypeptide. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 2639–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, M.; Kohlmeier, C.K.; Hatta, Y.; Ozawa, M.; Kawaoka, Y. Region required for protein expression from the stop-start pentanucleotide in the M gene of influenza B virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5939–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, M.L.; Napthine, S.; Jackson, R.J.; Brierley, I.; Brown, T.D.K. Characterization of the termination–reinitiation strategy employed in the expression of influenza B virus BM2 protein. RNA 2008, 14, 2394–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, A.K.-L.; Lam, M.K.-H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Au, S.W.-N.; Chan, P.K.-S.; Wang, J.; Shaw, P.-C. Structural basis for RNA binding and homo-oligomer formation by influenza B virus nucleoprotein. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6758–6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chu, S.-Y.; Lin, M.-I.; Hsu, H.-T.; Wu, P.-Y.; Wu, C.-J.; Liu, H.-W.; Lin, F.-Y.; Lin, G.; et al. E339-R416 salt bridge of nucleoprotein as a feasible target for influenza virus inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16515–16520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanitchang, A.; Narkpuk, J.; Jongkaewwattana, A. Nuclear import of influenza B virus nucleoprotein: Involvement of an N-terminal nuclear localization signal and a cleavage-protection motif. Virology 2013, 443, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sherry, L.; Smith, M.; Davidson, S.; Jackson, D. The N terminus of the influenza B virus nucleoprotein is essential for virus viability, nuclear localization, and optimal transcription and replication of the viral genome. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12326–12338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, S.; Guilligay, D.; Pflug, A.; Malet, H.; Berger, I.; Crépin, T.; Hart, D.; Lunardi, T.; Nanao, M.; Ruigrok, R.W.H.; et al. Structural insight into cap-snatching and RNA synthesis by influenza polymerase. Nature 2014, 516, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakai, C.; Iwama, M.; Mizumoto, K.; Nagata, K. Recognition of cap structure by influenza B virus RNA polymerase is less dependent on the methyl residue than recognition by influenza A virus polymerase. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 7504–7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauber, B.; Heins, G.; Wolff, T. The influenza B virus nonstructural NS1 protein is essential for efficient viral growth and antagonizes beta interferon induction. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, R.; Ma, L.-C.; Leonard, P.G.; Amer, B.R.; Sridharan, H.; Zhao, C.; Krug, R.M.; Montelione, G.T. Structural basis for the sequence-specific recognition of human ISG15 by the NS1 protein of influenza B virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13468–13473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noah, D.L.; Twu, K.Y.; Krug, R.M. Cellular antiviral responses against influenza A virus are countered at the posttranscriptional level by the viral NS1A protein via its binding to a cellular protein required for the 3′ end processing of cellular pre-mRNAS. Virology 2003, 307, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donelan, N.R.; Dauber, B.; Wang, X.; Basler, C.F.; Wolff, T.; García-Sastre, A. The N-and C-terminal domains of the NS1 protein of influenza B virus can independently inhibit IRF-3 and beta interferon promoter activation. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 11574–11582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, A.; Pillai, P.S. Innate immunity to influenza virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paragas, J.; Talon, J.; O’Neill, R.E.; Anderson, D.K.; García-Sastre, A.; Palese, P. Influenza B and C virus NEP (NS2) proteins possess nuclear export activities. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7375–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulo, S.; Akarsu, H.; Ruigrok, R.W.; Baudin, F. Nuclear traffic of influenza virus proteins and ribonucleoprotein complexes. Virus Res. 2007, 124, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crow, M.; Deng, T.; Addley, M.; Brownlee, G.G. Mutational analysis of the influenza virus cRNA promoter and identification of nucleotides critical for replication. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6263–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Plotch, S.J.; Tomasz, J.; Krug, R.M. Absence of detectable capping and methylating enzymes in influenza virions. J. Virol. 1978, 28, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, R.; Chanock, R.M.; Lai, C.J. Nonviral oligonucleotides at the 5′ terminus of cytoplasmic influenza viral mRNA deduced from cloned complete genomic sequences. Cell 1980, 21, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.L.; Rao, P.; Krug, R.M. The active sites of the influenza cap-dependent endonuclease are on different polymerase subunits. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, O.G.; Smith, M.; Fodor, E. Association of the influenza A virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase with cellular RNA polymerase II. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5812–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, D.P.; Balogun, R.A.; Yamada, H.; Zhou, Z.H.; Barman, S. Influenza virus morphogenesis and budding. Virus Res. 2009, 143, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samji, T. Influenza A: Understanding the viral life cycle. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2009, 82, 153. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, M.; Watanabe, S.; Odagiri, T. Influenza B virus NS2, a nuclear export protein, directly associates with the viral ribonucleoprotein complex. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, E.; Mahmood, K.; Yang, C.-F.; Webster, R.G.; Greenberg, H.B.; Kemble, G. Rescue of influenza B virus from eight plasmids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11411–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyk, J.M.; Szydłowska, N.; Szulc, W.; Majewska, A. Evolution of Influenza Viruses—Drug Resistance, Treatment Options, and Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świerczyńska, M.; Mirowska-Guzel, D.M.; Pindelska, E. Antiviral drugs in influenza. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappenden, P.; Jackson, R.; Cooper, K.; Rees, A.; Simpson, E.; Read, R.; Nicholson, K.G. Amantadine, oseltamivir, and zanamivir for the prophylaxis of influenza (including a review of existing guidance no. 67): A systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 2009, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, T.G.; Deyde, V.M.; Okomo-Adhiambo, M.; Garten, R.J.; Xu, X.; Bright, R.A.; Butler, E.N.; Wallis, T.R.; Klimov, A.I.; Gubareva, L.V. Surveillance for neuraminidase inhibitor resistance among human influenza A and B viruses circulating worldwide from 2004 to 2008. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3284–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.C.; Besselaar, T.G.; Daniels, R.S.; Ermetal, B.; Fry, A.; Gubareva, L.; Huang, W.; Lackenby, A.; Lee, R.T.; Lo, J.; et al. Global update on the susceptibility of human influenza viruses to neuraminidase inhibitors, 2014–2015. Antivir. Res. 2016, 132, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.K.; Tseng, Y.-Y.; Aziz, A.; Baz, M.; Barr, I.G. Characterization of influenza B viruses with reduced susceptibility to influenza neuraminidase inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2022, 200, 105280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, R.R.; Beniprashad, M.; Chong-King, E.; Li, Y.; Bastien, N.; Low, D.E.; Gubbay, J.B. Recovery of influenza B virus with the H273Y point mutation in the neuraminidase active site from a human patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2500–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kohno, S.; Kida, H.; Mizuguchi, M.; Hirotsu, N.; Ishida, T.; Kadota, J.; Shimada, J.; S-021812 Clinical Study Group. Intravenous peramivir for treatment of influenza A and B virus infection in high-risk patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, A.C. The epidemiology and spread of drug resistant human influenza viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 8, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.K.; Peek, L.A. Peramivir for the treatment of influenza. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2012, 10, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, A.; Shetty, A.K. Peramivir injection in the treatment of acute influenza: A review of the literature. Infect. Drug Resist. 2016, 9, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie, J.J.; Fang, J.M. Development of effective anti-influenza drugs: Congeners and conjugates—A review. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Chang, S.C.; Kim, M.J.; Chu, D.W.; Ohashi, Y.; MARVEL Study Group. Long-acting neuraminidase inhibitor laninamivir octanoate versus oseltamivir for treatment of influenza: A double-blind, randomized, noninferiority clinical trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Oh, J.M.; Kim, I.W. Assessment of adverse events related to anti-influenza neuraminidase inhibitors using the FDA adverse event reporting system and online patient reviews. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashita, E. Influenza polymerase inhibitors: Mechanisms of action and resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mifsud, E.J.; Hayden, F.G.; Hurt, A.C. Antivirals targeting the polymerase complex of influenza viruses. Antivir. Res. 2019, 169, 104545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, Y.; Fage, C.; Checkmahomed, L.; Venable, M.-C.; Boivin, G. Characterization of contemporary influenza B recombinant viruses harboring mutations of reduced susceptibility to baloxavir marboxil, in vitro and in mice. Antivir. Res. 2020, 179, 104807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampejo, T. Influenza and antiviral resistance: An overview. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Wei, F.; Chen, J.; et al. An IgM antibody targeting the receptor binding site of influenza B blocks viral infection with great breadth and potency. Theranostics 2019, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Wang, G.; Stegalkina, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Cao, J.; Bi, X.; et al. A multimechanistic antibody targeting the receptor binding site potently cross-protects against influenza B viruses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaam5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekhuysen, J.; Stockis, A.; Lins, R.; De Graeve, J.; Rossignol, J. Nitazoxanide: Pharmacokinetics and metabolism in man. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 38, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.C., Jr. Nitazoxanide: A new broad spectrum antiparasitic agent. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2004, 2, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, J.F. Nitazoxanide: A first-in-class broad-spectrum antiviral agent. Antivir. Res. 2014, 110, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszalka, P.; Tilmanis, D.; Hurt, A.C. Influenza antivirals currently in late-phase clinical trial. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2017, 11, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Pang, B.; Lai, K.K.; Cheung, N.N.; Dai, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Chan, K.-H.; Chen, H.; Sze, K.-H.; et al. Discovery of a novel specific inhibitor targeting influenza A virus nucleoprotein with pleiotropic inhibitory effects on various steps of the viral life cycle. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01432-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, T.; Shishido, T.; Ishibashi, T. S-033188, a small molecule inhibitor of Cap-dependent endonuclease of influenza A and B virus, leads to rapid and profound viral load reduction. Options IX Control. Influenza 2016, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalickova, S.; Heger, Z.; Krejcova, L.; Pekarik, V.; Bastl, K.; Janda, J.; Kostolansky, F.; Vareckova, E.; Zitka, O.; Adam, V.; et al. Perspective of use of antiviral peptides against influenza virus. Viruses 2015, 7, 5428–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.K.; Bansal, S.; Banik, A. Noninvasive routes of proteins and peptides drug delivery. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 73, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlieghe, P.; Lisowski, V.; Martinez, J.; Khrestchatisky, M. Synthetic therapeutic peptides: Science and market. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Din, G.U.; Hasham, K.; Amjad, M.N.; Hu, Y. Natural History of Influenza B Virus—Current Knowledge on Treatment, Resistance and Therapeutic Options. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 183-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46010014
Din GU, Hasham K, Amjad MN, Hu Y. Natural History of Influenza B Virus—Current Knowledge on Treatment, Resistance and Therapeutic Options. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(1):183-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleDin, Ghayyas Ud, Kinza Hasham, Muhammad Nabeel Amjad, and Yihong Hu. 2024. "Natural History of Influenza B Virus—Current Knowledge on Treatment, Resistance and Therapeutic Options" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 1: 183-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46010014
APA StyleDin, G. U., Hasham, K., Amjad, M. N., & Hu, Y. (2024). Natural History of Influenza B Virus—Current Knowledge on Treatment, Resistance and Therapeutic Options. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(1), 183-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46010014








