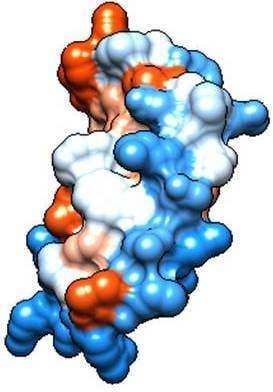
High-Level Expression of Recombinant Bovine Lactoferrin in Pichia pastoris with Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
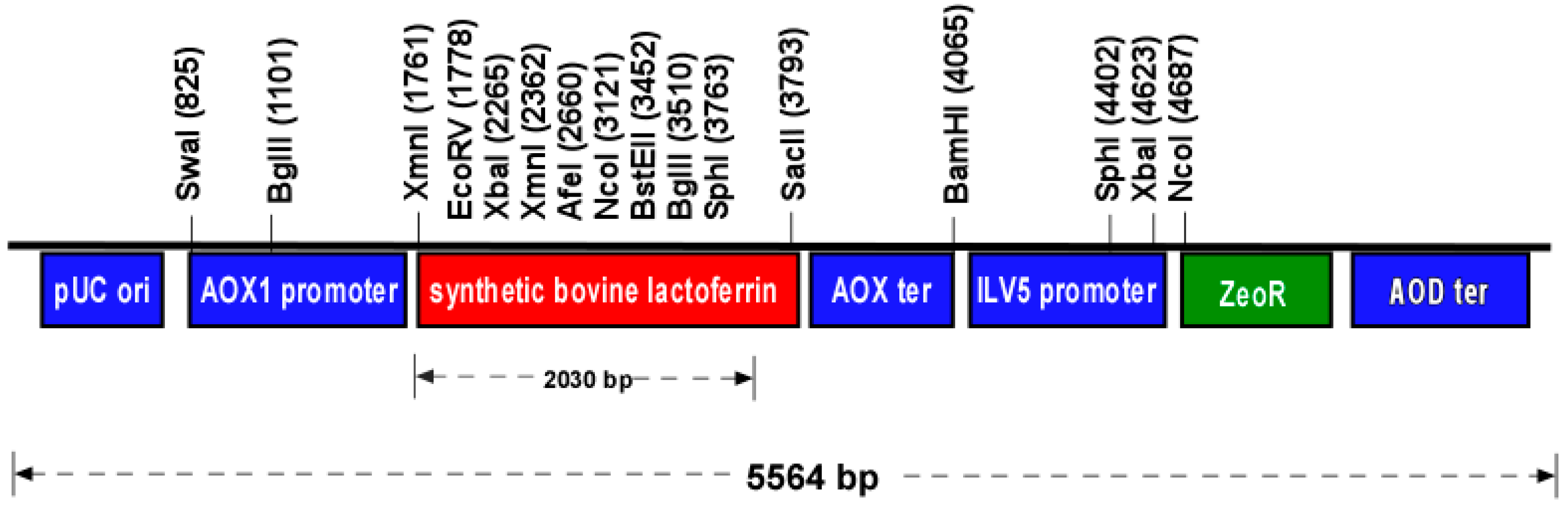
2.1. Expression Vector Design and Synthesis
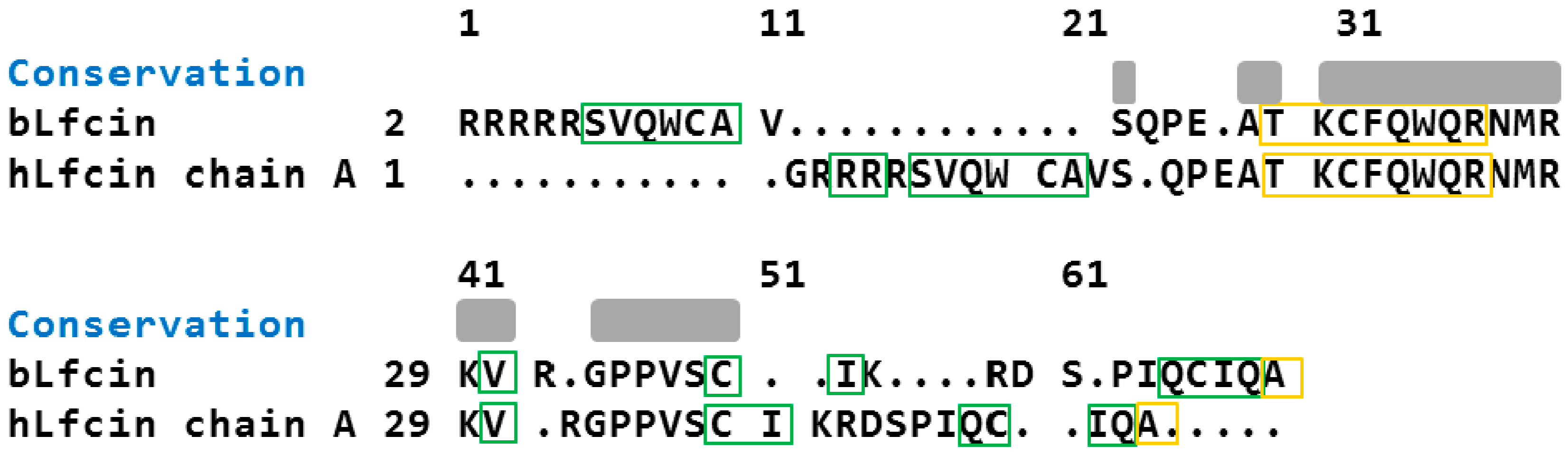
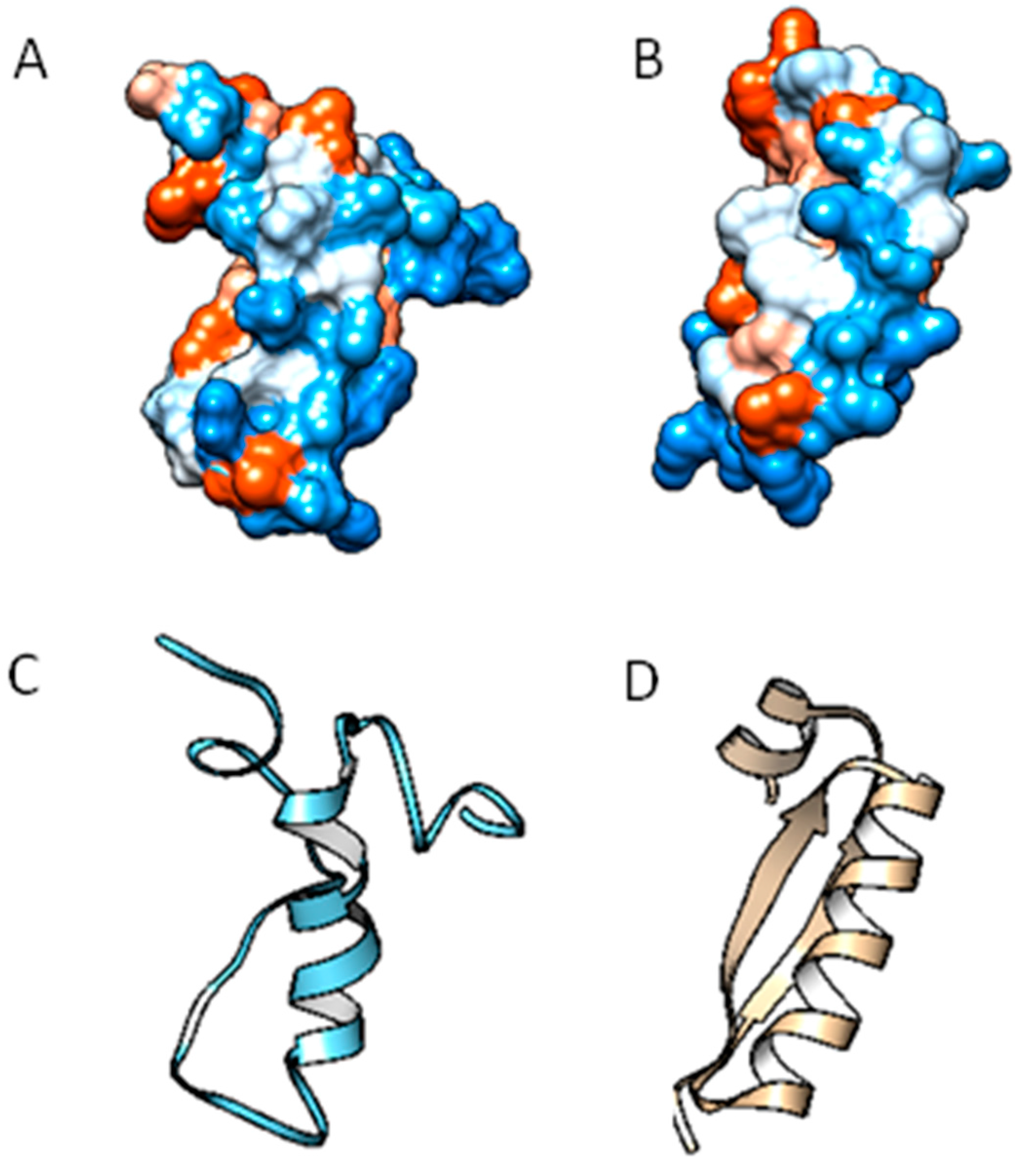
2.2. Molecular Analysis of Peptides Derived from Lactoferrin
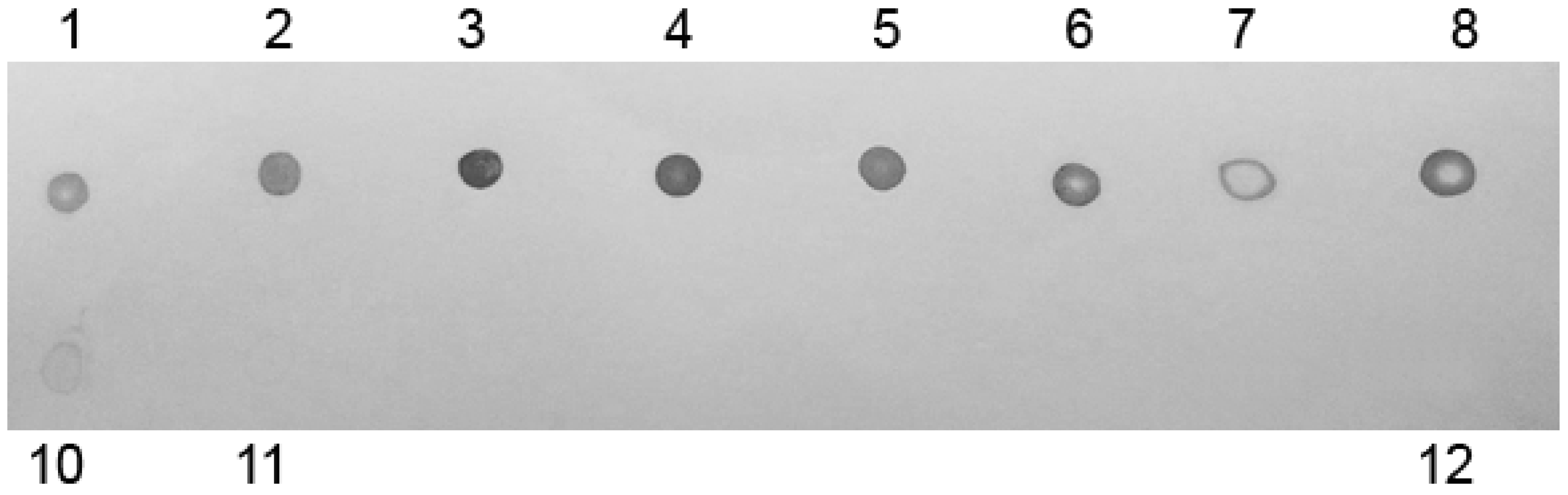
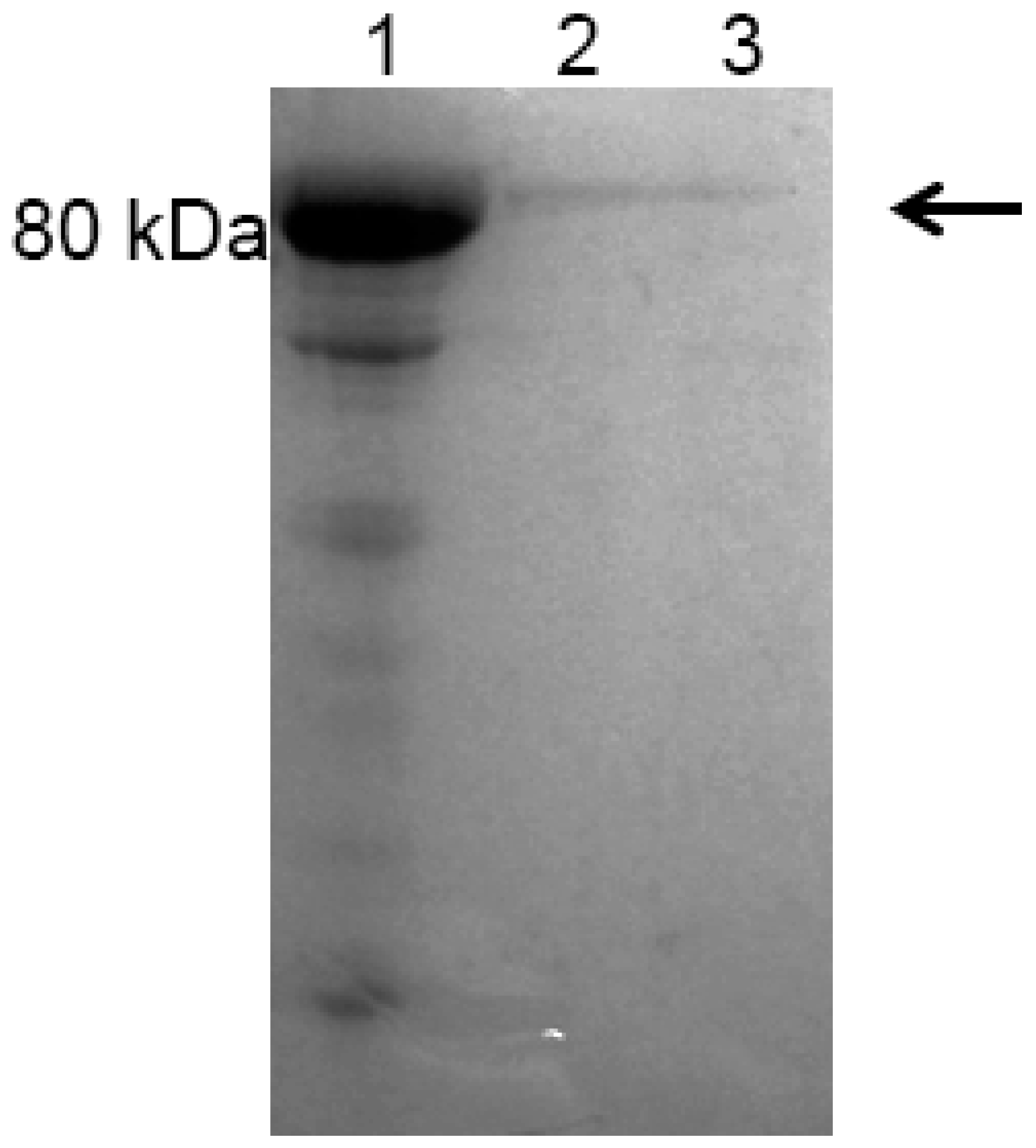
2.3. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Bovine Lactoferrin (rbLf)
2.4. Antibacterial Activity of rbLf
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Strains, Enzymes, and Plasmids
4.2. Media and Growth Condition
4.3. Transformation of Pichia pastoris KM71-H
4.4. Expression of rbLf
4.5. Batch Fermentation
4.6. Purification of rbLf
4.7. Dot-Blot Analysis
4.8. rbLf-Bioactive Peptide Recovery and Antimicrobial Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Lf | Lactoferrin |
| rbLf | recombinant bovine lactoferrin |
| rbLfcin | recombinant bovine lactoferricin |
| cbLf | commercial bovine lactoferrin |
| cbLfcin | commercial bovine lactoferricin |
| Kan | Kanamycin |
References
- Conesa, C.; Calvo, M.; Sánchez, L. Recombinant human lactoferrin: A valuable protein for pharmaceutical products and functional foods. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, P. Milk proteins: General and historical aspects. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry—1 Proteins; Springer: Heidelberger, Germany, 2003; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen, M.; Sorensen, S. The proteins in whey. Compte rendu des Travaux du Laboratoire de Carlsberg Ser. Chim. 1940, 23, 55–99. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, M.L. The isolation of a red protein from Milk2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960, 82, 3345–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Montoya, I.A.; Cendón, T.S.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. Lactoferrin a multiple bioactive protein: An overview. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueiros-Cendón, T.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Iglesias-Figueroa, B.F.; García-Montoya, I.A.; Salazar-Martínez, J.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. Immunomodulatory effects of lactoferrin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, D.; Puddu, P.; Valenti, P.; Gessani, S. Reciprocal interactions between lactoferrin and bacterial endotoxins and their role in the regulation of the immune response. Toxins 2010, 2, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenssen, H.; Hancock, R.E. Antimicrobial properties of lactoferrin. Biochimie 2009, 91, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, D.; Pierce, A.; Elass, E.; Carpentier, M.; Mariller, C.; Mazurier, J. Lactoferrin structure and functions. In Bioactive Components of Milk; Springer: Heidelberger, Germany, 2008; pp. 163–194. [Google Scholar]
- Drago-Serrano, M.E.; de la Garza-Amaya, M.; Luna, J.S.; Campos-Rodríguez, R. Lactoferrin-lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding as key to antibacterial and antiendotoxic effects. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Chávez, S.A.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. Lactoferrin: Structure, function and applications. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 301. e1–301. e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, H.J. Lactoferrin, a bird’s eye view. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisha, S.; Bhasker, S.; Mohankumar, C. Recombinant lactoferrin (Lf) of Vechur cow, the critical breed of Bos indicus and the Lf gene variants. Gene 2012, 495, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yemets, A.I.; Tanasienko, I.V.; Krasylenko, Y.A.; Blume, Y.B. Plant-based biopharming of recombinant human lactoferrin. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 38, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Montoya, I.; Salazar-Martínez, J.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Sinagawa-García, S.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. Expression and characterization of recombinant bovine lactoferrin in E. coli. BioMetals 2013, 26, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Rosano, G.L.; Ceccarelli, E.A. Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Recomb. Protein Expr. Microb. Syst. 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahardooli, M.; Niazi, A.; Aram, F.; Sohrabi, S.M. Expression of recombinant Arabian camel lactoferricin-related peptide in Pichia pastoris and its antimicrobial identification. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 96, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehl, M.A.; Stadheim, T.A. Biopharmaceutical discovery and production in yeast. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.-S.; Tang, Z.-R.; Wang, S.-P.; Feng, Z.-M.; Zhou, D.; Li, T.-J.; Yin, Y.-L. Expression, purification, and antibacterial activity of bovine lactoferrampin–lactoferricin in Pichia pastoris. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, M.; Wakabayashi, H.; Shin, K.; Yamauchi, K.; Yaeshima, T.; Iwatsuki, K. Twenty-five years of research on bovine lactoferrin applications. Biochimie 2009, 91, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, M.; Anju, C.; Biswas, L.; Kumar, V.A.; Mohan, C.G.; Biswas, R. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and alternative therapeutic options. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Chai, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, H.-M.; Shang, J.; Tian, W.; Yang, P.; Jiang, A.C. Effect of bovine lactoferrin from iron-fortified formulas on morbidity of diarrhea and respiratory tract infections of weaned infants in a randomized controlled trial. Nutrition 2016, 32, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoni, P.; Meyer, M.; Stolfi, I.; Rinaldi, M.; Cattani, S.; Pugni, L.; Romeo, M.G.; Messner, H.; Decembrino, L.; Laforgia, N. Bovine lactoferrin supplementation for prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in very-low-birth-weight neonates: A randomized clinical trial. Early Hum. Dev. 2014, 90, S60–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puxbaum, V.; Mattanovich, D.; Gasser, B. Quo vadis? The challenges of recombinant protein folding and secretion in Pichia pastoris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2925–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz-Boutigue, M.H.; Jollés, J.; Mazurier, J.; Schoentgen, F.; Legrand, D.; Spik, G.; Montreuil, J.; Jollès, P. Human lactotransferrin: Amino acid sequence and structural comparisons with other transferrins. Eur. J. Biochem. 1984, 145, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kraan, M.I.; Nazmi, K.; van’t Hof, W.; Amerongen, A.V.N.; Veerman, E.C.; Bolscher, J.G. Distinct bactericidal activities of bovine lactoferrin peptides LFampin 268–284 and LFampin 265–284: Asp-Leu-Ile makes a difference. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 84, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gifford, J.; Hunter, H.; Vogel, H. Lactoferricin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2588–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, T.; Glieder, A. Regulation of Pichia pastoris promoters and its consequences for protein production. New Biotechnol. 2013, 30, 385–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Chen, L.; Jia, S.; Chen, L.; Ma, Y. High-level expression and production of human lactoferrin in Pichia pastoris. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2008, 88, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, W.; Luo, M.; Ren, H.; Tang, L.; Liao, H.; Wang, Y. Molecular cloning, expression and purification of lactoferrin from Tibetan sheep mammary gland using a yeast expression system. Protein Expr. Purif. 2015, 109, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-H.; Yang, T.-S.; Lin, S.-M.; Tsai, M.-S.; Wu, S.-C.; Mao, S.J. Expression, characterization, and purification of recombinant porcine lactoferrin in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 25, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramasivam, M.; Saravanan, K.; Uma, K.; Sharma, S.; Singh, T.; Srinivasan, A. Expression, purification, and characterization of equine lactoferrin in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 26, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Molecular cloning and expression of yak (Bos grunniens) lactoferrin cDNA in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.H.; Yin, L.J.; Chiang, I.H.; Jiang, S.T. Expression and purification of goat lactoferrin from Pichia pastoris expression system. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, M67–M71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cregg, J.M.; Cereghino, J.L.; Shi, J.; Higgins, D.R. Recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Mol. Biotechnol. 2000, 16, 23–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenblum, H.; Gasser, B.; Maurer, M.; Borth, N.; Mattanovich, D. Effects of gene dosage, promoters, and substrates on unfolded protein stress of recombinant Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 85, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifton, L.A.; Holt, S.A.; Hughes, A.V.; Daulton, E.L.; Arunmanee, W.; Heinrich, F.; Khalid, S.; Jefferies, D.; Charlton, T.R.; Webster, J.R. An accurate in vitro model of the E. coli envelope. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11952–11955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, M.; McDonald, L.J.; Haney, E.F.; Nazmi, K.; Bolscher, J.G.; Vogel, H.J. Bovine and human lactoferricin peptides: Chimeras and new cyclic analogs. Biometals 2014, 27, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, T.-F.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, H.-W.; Chen, Q.; Wei, B.-Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, T.-X.; Chinn, Y.E.; Kang, J. PFR peptide, one of the antimicrobial peptides identified from the derivatives of lactoferrin, induces necrosis in leukemia cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweytick, D.; Deutsch, G.; Andrä, J.; Blondelle, S.E.; Vollmer, E.; Jerala, R.; Lohner, K. Studies on lactoferricin-derived Escherichia coli membrane-active peptides reveal differences in the mechanism of N-acylated versus nonacylated peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21266–21276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreier, J.; Ruggerone, P. Interaction of antibacterial compounds with RND efflux pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, S.M. Role of efflux pumps in the antibiotic resistance of bacteria embedded in a biofilm. Virulence 2013, 4, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.L.; Hwang, I.Y.; Loh, K.; Chang, M.W. Matrix-immobilized yeast for large-scale production of recombinant human lactoferrin. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, W.; Takase, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Wakabayashi, H.; Kawase, K.; Tomita, M. Identification of the bactericidal domain of lactoferrin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1121, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iglesias-Figueroa, B.; Valdiviezo-Godina, N.; Siqueiros-Cendón, T.; Sinagawa-García, S.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. High-Level Expression of Recombinant Bovine Lactoferrin in Pichia pastoris with Antimicrobial Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060902
Iglesias-Figueroa B, Valdiviezo-Godina N, Siqueiros-Cendón T, Sinagawa-García S, Arévalo-Gallegos S, Rascón-Cruz Q. High-Level Expression of Recombinant Bovine Lactoferrin in Pichia pastoris with Antimicrobial Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(6):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060902
Chicago/Turabian StyleIglesias-Figueroa, Blanca, Norberto Valdiviezo-Godina, Tania Siqueiros-Cendón, Sugey Sinagawa-García, Sigifredo Arévalo-Gallegos, and Quintín Rascón-Cruz. 2016. "High-Level Expression of Recombinant Bovine Lactoferrin in Pichia pastoris with Antimicrobial Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 6: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060902
APA StyleIglesias-Figueroa, B., Valdiviezo-Godina, N., Siqueiros-Cendón, T., Sinagawa-García, S., Arévalo-Gallegos, S., & Rascón-Cruz, Q. (2016). High-Level Expression of Recombinant Bovine Lactoferrin in Pichia pastoris with Antimicrobial Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(6), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060902