Lactoferrin from Milk: Nutraceutical and Pharmacological Properties
Abstract
:1. Introducing Lactoferrin
2. Lactoferrin’s Antimicrobial Activity
3. Nutraceutical and Immunomodulation Protective Effects
- Saraiva et al. [82] fed piglets with 3.6 g/L of bLF and showed higher IgG concentrations in serum and more IL-10, an immunomodulatory cytokine potentially limiting inflammation, was secreted by spleen cells into the culture media;
- Liu et al. [83] administering orally bLf to piglets, and found an increase of the blood NK cell populations and NK Lf receptor expression without affecting NK cell cytotoxicity, suggesting that Lf could help protect the organism of infants from infections;
- Cooper et al. [84] fed young pigs with transgenic cows’ milk containing rhLf. They showed favorable changes in systemic health in rhLf-milk fed pigs that had beneficial changes in circulating leukocyte populations with a decrease in neutrophils and increase in lymphocytes which is an indicator of decreased systemic inflammation. Moreover, favorable changes in intestinal villi architecture were also observed both in the duodenum and in the ileum of rhLf-milk fed pigs;
- Yang et al. [85] showed that the percentage of piglets with symptoms of diarrhea during the first 38 days of life was decreased, if compared with the control group, from 54% to 15% by orally administered Lf at a dose level of 155 and 285 mg/kg/day, respectively. A significant delay in the onset of diarrhea by at least 1 week in the higher Lf dose group and 4 days in the lower Lf dose group, compared with the control group of piglets, was also observed;
- Wu et al. [86] investigated the effect of enteral bLf supplementation on intestinal adaptation and barrier function in a rat model of short bowel syndrome (SBS) and they demonstrated a protective effect of Lf due to small-bowel luminal sIgA and TJ protein expression upregulation together with reduced intestinal permeability, supporting intestinal barrier integrity and providing better protection against bacterial infections;
- Arciniega-Martınez et al. [87] analyzed the effects of bLf orally administered to healthy male BALB/c mice. They found that antibodies, antibody-secreting cells, and B and T responses in both Peyer’s patches and in lamina propria were higher in bLf-treated than bLf-untreated mice, suggesting a potential application of bLf as a nutraceutical to control inflammation in the distal small intestine;
- Kawashima et al. [88] demonstrated the protective effect of Lf towards “Dry Eye Syndrome” caused by age-induced decrease in lacrimal gland secretory function. They attributed this activity to Lf anti-inflammatory properties since oral administration to aged mice of Lf alone or in combination with other antioxidants resulted in decreasing inflammatory cell infiltration in eyes. On the other hand [89] they demonstrated also that Lactoferrin administration decreases MCP-1 and TNF-α expression levels and markers for oxidative damage while increases the volume of tear secretion. Moreover, a combined dietary supplement containing fish oil, lactoferrin, zinc, vitamin C, lutein, vitamin E, γ-aminobutanoic acid, and Enterococcus faecium WB2000 improves the symptoms of dry eye syndrome with no side effects [90].
4. Anticancer Activity of Orally Administered Lactoferrin
5. Other Lactoferrin Activities
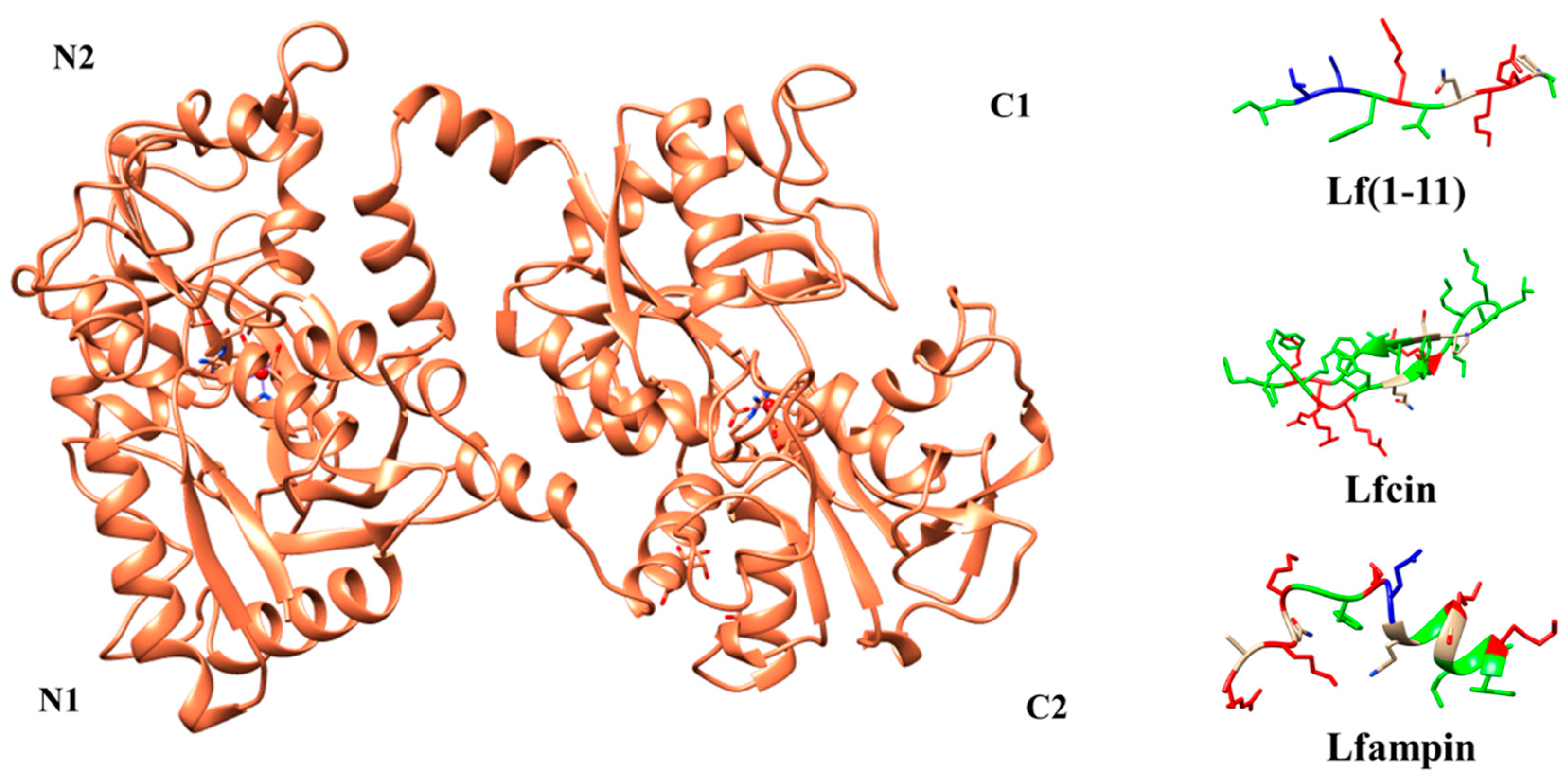
6. Lactoferrin Peptides
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sorensen, M.; Sorensen, S.P.L. The proteins in whey. Comptes-rendus des Trav. du Lab. Carlsberg 1939, 23, 55–99. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, M.L. The isolation of a red protein from milk. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960, 82, 3345–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Chávez, S.A.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. Lactoferrin: Structure, function and applications. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 301.e1–301.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, L.; Calvo, M.; Brock, J.H. Biological role of lactoferrin. Arch. Dis. Child. 1992, 67, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, J. Lactoferrin: A multifunctional immunoregulatory protein? Immunol. Today 1995, 16, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Iyer, S. Lactoferrin: Molecular structure and biological function. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1995, 15, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorland, L.H. Lactoferrin: A multifunctional glycoprotein. APMIS 1999, 107, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, J.H. The physiology of lactoferrin. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 80, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenti, P.; Antonini, G. Lactoferrin: An important host defence against microbial and viral attack. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2576–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, E.N.; Baker, H.M. A structural framework for understanding the multifunctional character of lactoferrin. Biochimie 2009, 91, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leboffe, L.; Giansanti, F.; Antonini, G. Antifungal and antiparasitic activities of lactoferrin. Anti-Infect. Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 8, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lima, C.F.; Rodrigues, L.R. Anticancer effects of lactoferrin: Underlying mechanisms and future trends in cancer therapy. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giansanti, F.; Leboffe, L.; Angelucci, F.; Antonini, G. The nutraceutical properties of ovotransferrin and its potential utilization as a functional food. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9105–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giansanti, F.; Leboffe, L.; Pitari, G.; Ippoliti, R.; Antonini, G. Physiolgical roles of ovotransferrin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connely, O.M. Antiinflammatory activities of lactoferrin. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2001, 20, 389S–395S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, D.A.; Vazquez, L.; Ramos, G. Antimicrobial mechanisms and potential clinical application of lactoferrin. Rev. Latino. Microbiol. 2005, 47, 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Strate, B.W.; Beljaars, L.; Molema, G.; Harmsen, M.C.; Meijer, D.K. Antiviral activities of lactoferrin. Antivir. Res. 2001, 52, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztas, Y.E.R.; Özgünes, N. Lactoferrin: A multifunctional protein. Adv. Mol. Med. 2005, 1, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, R.M.; Kokocinski, T. Lactoferrin content of peripheral blood cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 39, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.F.; Baker, H.M.; Dodson, E.J.; Norris, G.E.; Rumball, S.V.; Waters, J.M.; Baker, E.N. Structure of human lactoferrin at 3.2-Å resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1769–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.F.; Baker, H.M.; Norris, G.E.; Rice, D.W.; Baker, E.N. Structure of human lactoferrin: Crystallographic structure analysis and refinement at 2.8 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1989, 209, 711–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.N. Structure and reactivity of transferrins. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 41, 389–463. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, S.A.; Anderson, B.F.; Groom, C.R.; Haridas, M.; Baker, E.N. Threedimensional structure of diferric bovine lactoferrin at 2.8 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 274, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswar, N.; Webb, B.; Marti-Renom, M.A.; Madhusudhan, M.S.; Eramian, D.; Shen, M.Y.; Pieper, U.; Sali, A. Comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2006, 8, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, N.; Singh, A.; Singh, P.K.; Tyagi, T.K.; Pandey, S.; Shin, K.; Kaur, P.; Sharma, S.; Singh, T.P. Structure of iron saturated C-lobe of bovine lactoferrin at pH 6.8 indicates a weakening of iron coordination. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2016, 84, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisen, P.; Harris, D.C. Physical biochemistry of the transferrins. In Iron Carriers and Iron Proteins; Loehr, T., Ed.; VCH: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 241–351. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, E.N.; Anderson, B.F.; Baker, H.M.; Day, C.L.; Haridas, M.; Norris, G.E.; Rumball, S.V.; Smith, C.A.; Thomas, D.H. Three-dimensional structure of lactoferrin in various functional states. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1994, 357, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, E.N.; Baker, H.M. Molecular structure, binding properties and dynamics of lactoferrin. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, H.M.; Baker, E.N. A structural perspective on lactoferrin function. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rulis, A.M. Agency Response Letter GRAS Notice No. GRN 000077. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/Food/IngredientsPackagingLabeling/GRAS/NoticeInventory/ucm154188.htm (accessed on 21 September 2016).
- EFSA. Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on bovine lactoferrin. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, H. Lactoferrin delivery systems: Approaches for its more effective use. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, Y.; Oshima, K.; Kuhara, T.; Shin, K.; Abe, F.; Iwatsuki, K.; Nadano, D.; Matsuda, T. A lactoferrin-receptor, intelectin 1, affects uptake, sub-cellular localization and release of immunochemically detectable lactoferrin by intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. J. Biochem. 2013, 154, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullen, J.J. The significance of iron in infection. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1981, 3, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, V.; Braun, M. Active transport of iron and siderophore antibiotics. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, J.J. Iron-binding proteins in milk and resistance to Escherichia coli infection in infants. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1972, 65, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, E.D. Human lactoferrin: A novel therapeutic with broad spectrumpotential. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, M.; Wakabayashi, H.; Yamauchi, K.; Teraguchi, S.; Hayasawa, H. Bovine lactoferrin and lactoferricin derived from milk: Production and applications. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 80, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teraguchi, S.; Wakabayashi, H.; Kuwata, H.; Yamauchi, K.; Tamura, Y. Protection against infections by oral lactoferrin: Evaluation in animal models. Biometals 2004, 17, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Mario, F.; Aragona, G.; Dal Bò, N.; Cavestro, G.M.; Cavallaro, L.; Iori, V.; Comparato, G.; Leandro, G.; Pilotto, A.; Franzè, A. Use of bovine lactoferrin for helicobacter pylori eradication. Dig. Liver Dis. 2003, 35, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yekta, M.A.; Cox, E.; Goddeeris, B.M.; Vanrompay, D. Reduction of Escherichia coli O157: H7 excretion in sheep by oral lactoferrin administration. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 150, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, K.J.; Hwang, S.A.; Boyd, S.; Kruzel, M.L.; Hunter, R.L.; Actor, J.K. Influence of oral lactoferrin on Mycobacterium tuberculosis induced immunopathology. Tuberculosis 2011, 91, S105–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velliyagounder, K.; Alsaedi, W.; Alabdulmohsen, W.; Markowitz, K.; Fine, D.H. Oral lactoferrin protects against experimental candidiasis in mice. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 118, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, M.P.; Bennett, S.H.; Hwang, F.F.; Yu, C. Neonatal small bowel epithelia: Enhancing anti-bacterial defense with lactoferrin and Lactobacillus GG. Biometals 2004, 17, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Li, N. Transgenic milk containing recombinant human lactoferrin modulates the intestinal flora in piglets. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, A.; Rawat, S.; Nagpal, J. Efficacy of fermented milk and whey proteins in Helicobacter pylori eradication: A review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vongbhavit, K.; Underwood, M.A. Prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis through manipulation of the intestinal microbiota of the premature Infant. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 716–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pammi, M.; Abrams, S.A. Oral lactoferrin for the treatment of sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 10, CD007138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsen, M.C.; Swart, P.J.; de Béthune, M.P.; Pawels, R.; De Clercq, E.; The, T.H.; Meijer, D.K.F. Antiviral effects of plasma and milk proteins: Lactoferrin shows a potent activity against both human immunodeficiency virus and human cytomegalovirus replication in vitro. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 280–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.H.; Osbakk, S.A.; Vorland, L.H.; Traavik, T.; Gutteberg, T.J. Lactoferrin and cyclic lactoferricin inhibit the entry of human cytomegalovirus into human fibroblasts. Antivir. Res. 2001, 51, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.; Longhi, C.; Conte, M.P.; Pisani, S.; Valenti, P.; Seganti, L. Lactoferrin inhibits herpes simplex virus type 1 adsorption to Vero cells. Ativir. Res. 1996, 29, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.; Pisani, S.; Antonini, G.; Valenti, P.; Seganti, L.; Orsi, N. Metal complexes of bovine lactoferrin inhibit in vitro replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2. Biometals 1998, 11, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, R.; Rega, B.; Marchetti, M.; Seganti, L.; Antonini, G.; Valenti, P. Bovine lactoferrin peptidic fragments involved in inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 264, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swart, P.J.; Kuipers, M.E.; Smith, C.; Pawels, R.; de Béthune, M.P.; De Clerck, E.; Meijer, D.K.F.; Huisman, J.G. Antiviral effects of milk proteins: Acylation results in polyanionic compounds with potent activity against human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 in vitro. AIDS Res. Human Retrov. 1996, 12, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puddu, P.; Borghi, P.; Gessani, S.; Valenti, P.; Belardelli, F.; Seganti, L. Antiviral effects of bovine lactoferrin saturated with metal ions on early steps of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 30, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, B.; Floris, R.; Recio, I.; Visser, S. The antiviral activity of the milk protein lactoferrin against the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Biometals 2004, 17, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Sugiyama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, K.; Sekihara, H.; Shimotohno, K.; Kato, N. Lactoferrin markedly inhibits hepatitis C virus infection in cultured human hepatocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 245, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, K.; Ikeda, M.; Saito, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Numata, K.; Kato, N. Lactoferrin inhibits hepatitis B virus infection in cultured human hepatocytes. Hepatol. Res. 2002, 24, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Ikeda, M.; Nozaki, A.; Kato, N.; Tsuda, H.; Saito, S.; Sekihara, H. Lactoferrin inhibits hepatitis C virus viremia in patients with chronic hepatitis C: A pilot study. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1999, 90, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, H.; Sato, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Tanaka, K.; Ohkawa, S.; Takagi, H.; Yokosuka, O.; Furuse, J.; Saito, H.; Sawaki, A.; et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of bovine lactoferrin in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrantoni, A.; Dofrelli, E.; Tinari, A.; Ammendolia, M.G.; Puzelli, S.; Fabiani, C.; Donatelli, I.; Superti, F. Bovine lactoferrin inhibits influenza A virus induced programmed cell death in vitro. Biometals 2010, 23, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, H.; Oda, H.; Yamauchi, K.; Abe, F. Lactoferrin for prevention of common viral infections. J. Infect. Chemother. 2014, 20, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, G.A. Iron chelators as therapeutic agents against Pneumocystis carinii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirioni, O.; Giacometti, A.; Barchiesi, F.; Scalise, G. Inhibition of growth of Pneumocystis carinii by lactoferrins alone and in combination with pyrimethamine, clarithromycin and minocycline. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachezy, J.; Kulda, J.; Bahnikova, I.; Suchan, P.; Razga, J.; Schrevel, J. Tritrichomonas foetus: Iron acquisition from lactoferrin and transferrin. Exp. Parasitol. 1996, 83, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakibaei, M.; Frevert, U. Dual interaction of the malaria circumsporozoite protein with the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) and heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giansanti, F.; Leboffe, L.; D’Elia, I.; Antonini, G. An update on the antifungal activities of Lactoferrin: New promising applications in diagnostic, therapeutics and biotechnology. Anti-Infect. Agents 2013, 11, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddu, P.; Valenti, P.; Gessani, S. Immunomodulatory effects of lactoferrin on antigen presenting cells. Biochimie 2009, 91, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embleton, N.D.; Berrington, J.E.; McGuire, W.; Stewart, C.J.; Cummings, S.P. Lactoferrin: Antimicrobial activity and therapeutic potential. Semin. Fetal Neonat. Med. 2013, 18, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, D.; Mazurier, J. A critical review of the roles of host lactoferrin in immunity. Biometals 2010, 23, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Actor, J.K.; Hwang, S.A.; Kruzel, M.L. Lactoferrin as a natural immune modulator. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 1956–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turin, C.G.; Zea-Vera, A.; Pezo, A.; Cruz, K.; Zegarra, J.; Bellomo, S.; Cam, L.; Llanos, R.; Castañeda, A.; Tucto, L.; et al. Lactoferrin for prevention of neonatal sepsis. Biometals 2014, 27, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruzel, M.L.; Actor, J.K.; Boldogh, I.; Zimecki, M. Lactoferrin in health and disease. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2007, 61, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Sato, K.; Shinmoto, H.; Dosako, S. Role of basic residues of human lactoferrin in the interaction with B lymphocytes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhennin-Duthille, I.; Masson, M.; Damiens, E.; Fillebeen, C.; Spik, G.; Mazurier, J. Lactoferrin upregulates the expression of CD4 antigen through the stimulation of the mitogen- activated protein kinase in the human lymphoblastic T Jurkat cell line. J. Cell. Biochem. 2000, 79, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueiros-Cendón, T.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Iglesias-Figueroa, BF.; García-Montoya, IA.; Salazar-Martínez, J.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. Immunomodulatory effects of lactoferrin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, D.; Elass, E.; Carpentier, M.; Mazurier, J. Lactoferrin: A modulator of immune and inflammatory responses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2549–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.A.; Kruzel, M.L.; Actor, J.K. Lactoferrin augments BCG vaccine efficacy to generate T helper response and subsequent protection against challenge with virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2005, 5, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, A.M.; Connellan, P.A.; Oliver, C.J.; Morris, C.A.; Stevenson, L.M. Bovine lactoferrin supplementation supports immune and antioxidant status in healthy human males. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayeur, S.; Spahis, S.; Pouliot, Y.; Levy, E. Lactoferrin, a Pleiotropic Protein inHealth and Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 813–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, M.; O’Garra, A. The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.Y.; Comstock, S.S.; Shunk, J.M.; Monaco, M.H.; Donovan, S.M. Natural killer cell populations and cytotoxic activity in pigs fed mother’s milk, formula, or formula supplemented with bovine lactoferrin. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 74, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.A.; Nelson, K.M.; Maga, E.A.; Murray, J.D. Consumption of transgenic cows’ milk containing human lactoferrin results in beneficial changes in the gastrointestinal tract and systemic health of young pigs. Transgenic. Res. 2013, 22, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, X.; Liu, N.; Chen, Y.; Gan, H.; Troy, F.A.; Wang, B. Lactoferrin up-regulates intestinal gene expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factors BDNF, UCHL1 and alkaline phosphatase activity to alleviate early weaning diarrhea in postnatal piglets. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, W.; Shi, J.; Zhong, Y.; van Tol, E.A.F.; Tang, Q.; Cai, W. Enteral supplementation of bovine lactoferrin improves gut barrier function in rats after massive bowel resection. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciniega-Martínez, I.M.; Campos-Rodríguez, R.; Drago-Serrano, M.E.; Sánchez-Torres, L.E.; Cruz-Hernández, T.R.; Reséndiz-Albor, A.A. Modulatory Effects of Oral Bovine Lactoferrin on the IgA Response at Inductor and Effector Sites of Distal Small Intestine from BALB/c Mice. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz). 2016, 64, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, M.; Kawakita, T.; Inaba, T.; Okada, N.; Ito, M.; Shimmura, S.; Watanabe, M.; Shinmura, K.; Tsubota, K. Dietary Lactoferrin Alleviates Age-Related Lacrimal Gland Dysfunction in Mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, M.; Nakamura, S.; Izuta, Y.; Inoue, S.; Tsubota, K. Dietary Supplementation with a Combination of Lactoferrin, Fish Oil, and Enterococcus faecium WB2000 for Treating Dry Eye: A Rat Model and Human Clinical Study. Ocul. Surf. 2016, 14, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.A.; Maga, E.A.; Murray, J.D. Production of human lactoferrin and lysozyme in the milk of transgenic dairy animals: Past, present, and future. Transgenic Res. 2015, 24, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mejia, E.G.; Dia, V.P. The role of nutraceutical proteins and peptides in apoptosis, angiogenesis, and metastasis of cancer cells. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, C.; Gladwell, W.; Raphiou, I.; Liu, E. Methylation and expression of the lactoferrin gene in human tissues and cancer cells. Biometals 2004, 17, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheduzzaman, S.; Vishwanath, A.; Furusato, B.; Cullen, J.; Chen, Y.; Bañez, L.; Nau, M.; Ravindranath, L.; Kim, K.H.; Mohammed, A.; et al. Silencing of Lactotransferrin expression by methylation in prostate cancer progression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, K.; Ou, Y.; Han, Z.; Gao, D.; Li, J. Effects of adenovirus vectors mediated human lactoferrin cDNA on mice bearing EMT6 breast carcinoma. Die Pharm. 2011, 66, 704–709. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.Y.; Li, Q.W.; Han, Z.S.; Jiang, Z.L.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.B. Growth suppression effects of recombinant adenovirus expressing human lactoferrin on cervical cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2011, 26, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiburgahus, C.; Janicke, B.; Lindmark-Mansson, H.; Oredsson, S.M.; Paulsson, M.A. Lactoferricin treatment decreases the rate of cell proliferation of a human colon cancer cell line. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 2477–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Jiang, R.; Du, X. Bovine lactoferrin can be taken up by the human intestinal lactoferrin receptor and exert bioactivities. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 53, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhara, T.; Iigo, M.; Itoh, T.; Ushida, Y.; Sekine, K.; Terada, N.; Okamura, H.; Tsuda, H. Orally administered lactoferrin exerts an antimetastatic effect and enhances production of IL-18 in the intestinal epithelium. Nutr. Cancer 2000, 38, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iigo, M.; Shimamura, M.; Matsuda, E.; Fujita, K.; Nomoto, H.; Satoh, J.; Kojima, S.; Alexander, D.B.; Moore, M.A.; Tsuda, H. Orally Orally administered bovine lactoferrin induces caspase-1 and interleukin-18 in the mouse intestinal mucosa: A possible explanation for inhibition of carcinogenesis and metastasis. Cytokine 2004, 25, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.R.; Chen, P.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Hsu, H.C.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, W.J. Bovine lactoferricin B induces apoptosis of human gastric cancer cell line AGS by inhibition of autophagy at a late stage. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 7511–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Zhang, W.; Tang, H.; Ye, Q.; Liao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, M.; Xiong, W.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, X.; et al. Lactotransferrin acts as a tumor suppressor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by repressing AKT through multiple mechanisms. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4273–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letchoumy, P.V.; Mohan, K.V.; Stegeman, J.J.; Gelboin, H.V.; Hara, Y.; Nagini, S. In vitro antioxidative potential of lactoferrin and black tea polyphenols and protective effects in vivo on carcinogen activation, DNA damage, proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis during experimental oral carcinogenesis. Oncol. Res. 2008, 17, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J. S.; Li, G.; Varadhachary, A.; Petark, K.; Schneyer, M.; Li, D.; Ongkasuwan, J.; Zhang, X.; Taylor, R.J.; Strome, S.E.; et al. Oral lactoferrin results in T cell-dependent tumor inhibition of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Monitto, C.L.; Minhas, K.M.; Sidransky, D. Lactoferrin down-regulates G1 cyclin-dependent kinases during growth arrest of head and neck cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8683–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T.; Banno, Y.; Kato, Y.; Nozawa, Y.; Kawaguchi, M. Pepsin-digested lactoferrin induces apoptotic cell death with JNK/SAPK activation in oral cancer cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 98, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardosn, A.; de Antueno, R.; Duncan, R.; Hoskin, D.W. Intracellular delivery of bovine lactoferricin’s antimicrobial core (RRWQWR) kills T-leukemia cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, J.S.; Salsman, J.; Conrad, D.M.; Hoskin, D.W. Bovine lactoferricin selectively induces apoptosis in human leukemia and carcinoma cell lines. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, T.F.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, H.W.; Chen, Q.; Wei, B.Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, T.X.; Chinn, Y.E.; Kang, J.; et al. PFR peptide, one of the antimicrobial peptides identified from the derivatives of lactoferrin, induces necrosis inleukemia cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Hwang, H.M.; Pyo, C.W.; Hahm, D.H.; Choi, S.Y. E2F1-directed activation of Bcl-2 is correlated with lactoferrin-induced apoptosis in Jurkat leukemia T lymphocytes. Biometals 2010, 23, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, Y.; Saoo, K.; Hosokawa, K.; Yamakawa, K.; Yokohira, M.; Zeng, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Imaida, K. Post-initiation chemopreventive effects of dietary bovine lactoferrin on 4-(methynitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone-induced lung tumorigenesis in female A/J mice. Cancer Lett. 2007, 246, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, S.Y. Human lactoferrin controls the level of retinoblastoma protein and its activity. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 84, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Tu, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Huang, L.; Tao, L.; Zhao, L. The effect of Lfcin-B on non-small cell lung cancer H460 cells is mediated by inhibiting VEGF expression and inducing apoptosis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2015, 38, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliassen, L.T.; Berge, G.; Leknessund, A.; Wikman, M.; Lindin, I.; Løkke, C.; Ponthan, F.; Johnsen, J.I.; Sveinbjørnsson, B.; Kogner, P.; et al. The antimicrobial peptide, lactoferricin B, is cytotoxic to neuroblastoma cells in vitro and inhibits xenograft growth in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcella, A.; Oliva, M.A.; Staffieri, S.; Aalberti, S.; Grillea, G.; Madonna, M.; Bartolo, M.; Pavone, L.; Giangaspero, F.; Cantore, G.; et al. In vitro and in vivo effect of human lactoferrin on glioblastoma growth. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoedt, E.; Hardivillé, S.; Mariller, C.; Elass, E.; Perraudin, J.P.; Pierce, A. Discrimination and evaluation of lactoferrin and delta-lactoferrin gene expression levels in cancer cells and under inflammatory stimuli using TaqMan real-time PCR. Biometals 2010, 23, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benaïssa, M.; Peyrat, J.P.; Hornez, L.; Mariller, C.; Mazurier, J.; Pierce, A. Expression and prognostic value of lactoferrin mRNA isoforms in human breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwar, J.R.; Palmano, K.P.; Sun, X.; Kanwar, R.K.; Gupta, R.; Haggarty, N.; Rowan, A.; Ram, S.; Krissansen, G.W. ‘Iron-saturated’ lactoferrin is a potent natural adjuvant for augmenting cancer chemotherapy. Immunol. Cell Boil. 2008, 86, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwar, J.R.; Mahidhara, G.; Kanwar, R.K. Novel alginate-enclosed chitosan-calcium phosphate-loaded iron-saturated bovine lactoferrin nanocar-riers for oral delivery in colon cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 1521–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, H.; Kozu, T.; Iinuma, G.; Ohashi, Y.; Saito, Y.; Saito, D.; Akasu, T.; Alexander, D.B.; Futakuchi, M.; Fukamachi, K.; et al. Cancer prevention by bovine lactoferrin: From animal studies to human trial. Biometals 2010, 23, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlong, S.J.; Mader, J.S.; Hoskin, D.W. Lactoferricin-induced apoptosis in estrogen- nonresponsive MDA-MB-435 breast cancer cells is enhanced by C6 ceramide or tamoxifen. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 15, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massodi, I.; Thomas, E.; Raucher, D. Application of thermally responsive elastin-like polypeptide fused to a lactoferrin-derived peptide for treatment of pancreatic cancer. Molecules 2009, 14, 1999–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roseanu, A.; Florian, P.E.; Moisei, M.; Sima, L.E.; Evans, R.W.; Trif, M. Liposomalization of lactoferrin enhanced its anti-tumoral effects on melanoma cells. Biometals 2010, 23, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artym, J.; Zimecki, M.; Kruzel, M.L. Effect of lactoferrin on the methotrexate- induced suppression of the cellular and humoral immune response in mice. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 3831–3836. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Artym, J.; Zimecki, M.; Kuryszko, J.; Kruzel, M.L. Lactoferrin accelerates reconstitution of the humoral and cellular immune response during chemotherapy-induced immunosuppression and bone marrow transplant in mice. Stem. Cells Dev. 2005, 14, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Jiang, R.; Przepiorski, A.; Reddy, S.; Palmano, K.P.; Krissansen, G.W. “Iron-saturated” bovine lactoferrin improves the chemotherapeutic effects of tamoxifen in the treatment of basal-like breast cancer in mice. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.Y.; Jiang, L.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Ren, F.Z. Orally administered lactoferrin preserves bone mass and microarchitecture in ovariectomized rats. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharadwaj, S.; Naidu, A.G.; Betageri, G.V.; Prasadarao, N.V.; Naidu, A.S. Milk ribonuclease-enriched lactoferrin induces positive effects on bone turnover markers in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos. Int. 2009, 20, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, J.; Naot, D. Lactoferrin as an effector molecule in the skeleton. Biometals 2010, 23, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgieff, M.K. The role of iron in neurodevelopment: Fetal iron deficiency and the developing hippocampus. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somm, E.; Larvaron, P.; van de Looij, Y.; Toulotte, A.; Chatagner, A.; Faure, M.; Métairon, S.; Mansourian, R.; Raymond, F.; Gruetter, R.; et al. Protective effects of maternal nutritional supplementation with lactoferrin on growth and brain metabolism. Pediatr. Res. 2014, 75, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szwajkowska, M.; Wolanciuk, A.; Barłowska, J.; Król, J.; Litwińczuk, Z. Bovine milk proteins as the source of bioactive peptides influencing the consumers’ immune system. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 2011, 29, 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer, C.P.; Welling, M.M. Various routes of administration of (99m) Tc-labeled synthetic lactoferrin antimicrobial peptide hLF 1–11 enables monitoring and effective killing of multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in mice. Peptides 2008, 29, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gifford, J.L.; Hunter, H.N.; Vogel, H.J. Lactoferricin: A lactoferrin-derived peptide with antimicrobial, antiviral, antitumor and immunological properties. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2588–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Villaseñor, H.; Canizalez-Román, A.; Reyes-Lopez, M.; Nazmi, K.; de la Garza, M.; Zazueta-Beltrán, J.; León-Sicairos, N.; Bolscher, J.G. Bactericidal effect of bovine lactoferrin, LFcin, LFampin and LFchimera on antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Biometals 2010, 23, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, H.; Bellamy, W.; Takase, M.; Tomita, M. Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes by lactoferricin, a potent antimicrobial peptide derived from cow’s milk. J. Food Prot. 1992, 55, 238–240. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Brouwer, C.P.; Bogaards, S.J.; Nemec, A.; van den Broek, P.J.; Nibbering, P.H. The synthetic N-terminal peptide of human lactoferrin, hLF(1–11), is highly effective against experimental infection caused by multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4919–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, B.; Pinto, L.; Quintieri, L.; Carito, A.; Calabrese, N.; Caputo, L. Efficacy of lactoferricin B in controlling ready-to-eat vegetable spoilage caused by Pseudomonas spp. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 215, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Gómez, S.; Ferrer-Espada, R.; Stewart, P.S.; Pitts, B.; Lohner, K.; Martínez de Tejada, G. Antimicrobial activity of synthetic cationic peptides and lipopeptides derived from human lactoferricin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa planktonic cultures and biofilms. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Calvijo, M.A.; Leal-Castro, A.L.; Almanzar-Reina, G.A.; Rosas-Pérez, J.E.; García-Castañeda, J.E.; Rivera-Monroy, Z.J. Antibacterial activity of synthetic peptides derived from lactoferricin against Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 453826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Stewart, A.F.; Geng, M.; Tang, X.; Tu, Q.; Yin, Y. High-level expression, purification and antibacterial activity of bovine lactoferricin and lactoferrampin in Photorhabdus luminescens. Protein Expr. Purif. 2010, 73, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, J.; Ortiz, C.; Guzmán, F.; Cárdenas, C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Torres, R. Design and activity of novel lactoferrampin analogues against O157:H7 enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kraan, M.I.; Nazmi, K.; van ’t Hof, W.; Amerongen, A.V.; Veerman, E.C.; Bolscher, J.G. Distinct bactericidal activities of bovine lactoferrin peptides LFampin 268–284 and LFampin 265–284: Asp-Leu-Ile makes a difference. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2006, 84, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.Y.; Wong, J.H.; Ip, D.T.; Wan, D.C.; Cheung, R.C.; Ng, T.B. Bovine Lactoferrampin, Human Lactoferricin, and Lactoferrin 1–11 Inhibit Nuclear Translocation of HIV Integrase. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 179, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.B.; Cheung, R.C.; Wong, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Ip, D.T.; Wan, D.C.; Xia, J. Antiviral activities of whey proteins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6997–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, Y.A.; Huang, H.J.; Lin, W.W.; Chen, C.Y. Investigation of anti-infection mechanism of lactoferricin and splunc-1. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 2014, 907028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenssen, H.; Sandvik, K.; Andersen, J.H.; Hancock, R.E.; Gutteberg, T.J. Inhibition of HSV cell-to-cell spread by lactoferrin and lactoferricin. Antivir. Res. 2008, 79, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, N.; Drobni, P.; Näslund, J.; Sunkari, V.G.; Jenssen, H.; Evander, M. The anti-papillomavirus activity of human and bovine lactoferricin. Antivir. Res. 2007, 75, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupetti, A.; Brouwer, C.P.; Bogaards, S.J.; Welling, M.M.; de Heer, E.; Campa, M.; van Dissel, J.T.; Friesen, R.H.; Nibbering, P.H. Human lactoferrin-derived peptide’s antifungal activities against disseminated Candida albicans infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, J.; Saha, S.; Khetan, A.; Sarkar, S.K.; Mandal, S.M. Effects of lactoferricin Bagainst keratitis-associated fungal biofilms. J. Infect. Chemother. 2012, 18, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vylkova, S.; Sun, J.N.; Edgerton, M. The role of released ATP in killing Candida albicans and other extracellular microbial pathogens by cationic peptides. Purinergic Signal. 2007, 3, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.S.; Shao, H.; Li, T.J.; Tang, Z.R.; Huang, R.L.; Wang, S.P.; Kong, X.F.; Wu, X.; Yin, Y.L. Dietary supplementation with bovine lactoferrampin-lactoferricin produced by Pichia pastoris fed-batch fermentation affects intestinal microflora in weaned piglets. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haney, E.F.; Nazmi, K.; Lau, F.; Bolscher, J.G.; Vogel, H.J. Novel lactoferrampin antimicrobial peptides derived from human lactoferrin. Biochimie 2009, 91, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitch, G.J.; Ceballos, C. A role for antimicrobial peptides in intestinal microsporidiosis. Parasitology 2009, 136, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Soto, F.; León-Sicairos, N.; Nazmi, K.; Bolscher, J.G.; de la Garza, M. Microbicidal effect of the lactoferrin peptides lactoferricin17–30, lactoferrampin265–284, and lactoferrin chimera on the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Biometals 2010, 23, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliassen, L.T.; Berge, G.; Sveinbjørnsson, B.; Svendsen, J.S.; Vorland, L.H.; Rekdal, Ø. Evidence for a direct antitumor mechanism of action of bovine lactoferricin. Anticancer Res. 2002, 22, 2703–2710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Mollstedt, O.; Tsai, M.H.; Kreider, R.B. Potential clinical applications of multi-functional milk proteins and peptides in cancer management. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 2424–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.M.; Wong, J.H.; Xia, J.; Ng, T.B. Studies on anticancer activities of lactoferrin and lactoferricin. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2013, 14, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, P.; Guo, X.; Ma, J.; Li, G. New function of lactoferrin: Protection against cancer development and metastasis. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2012, 37, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Cancer Type | Mechanism of Anticancer Action | References |
|---|---|---|
| Breast | hLf causes arrest in the G0/G1 phase, induction of cell apoptosis and regulation of the expression of Bcl-2, Bax and activation of caspase 3. | [94] |
| Cervix | hLf inhibits cervical cancer due to elevated expression of Fas and decreased the ratio of anti- to pro-apoptotic molecule Bcl-2/Bax. | [95] |
| Colon | Lfcin causes arrest in the at S phase through downregulation of cyclin E1 in CaCO2 cells. | [96] |
| hLF increases expression of TGF-β1, and holo-forms of LFs stimulate IL-18 secretion in CaCO2 cells. | [97] | |
| Lf induces caspase-1 and IL-18. | [98] | |
| bLf increases production of CD4+, CD8+, and IL-18 | [99] | |
| Gastric | BLfcin induces apoptosis human gastric cancer cell line AGS. | [100] |
| Head, neck, and oral | Lf induces suppression of AKT signaling via inhibition of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 expression and/or blocking of the K18-14-3-3 complex. | [101] |
| bLf and [Polyphenon-B (P-B)] P-B was more effective in inhibiting hamster buccal pouch (HBP) carcinogenesis by inhibiting oxidative DNA damage, carcinogen activation, cell proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis. | [102] | |
| Lf inhibits tumor through direct cellular inhibition and immunomodulation. | [103] | |
| Lf causes cell cycle arrest through downregulation of cyclin-dependent kinases and upregulation of p27 protein expression in head and neck cancer cell lines. | [104] | |
| Lf derivated peptides induce apoptosis via JNK/SAPK activation in squamous cell carcinoma cell line SAS. | [105] | |
| Leukemia | LfcinB6 (RRWQWR) induces citoxicity via caspase-mediated and cathepsin B-mediated mechanism in T-leukemia cells. | [106] |
| Lfcin kills T-leukemia cells by triggering the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis and through the generation of reactive oxygen species. | [107] | |
| LF11-322 (PFWRIRIRR-NH2), peptide fragment derived from human lactoferricin, induces necrosis in leukemia cells (MEL and HL-60 leukemia cells). | [108] | |
| Lf increases CDK6 and hyper-phosphorylated retinoblastoma protein, resulting in the induction of E2F1-dependent apoptosis in Jurkat human leukemia T lymphocytes. | [109] | |
| Lung | bLf inhibits NNK-induced mouse lung tumorigenesis, through the modification of cell proliferation and/or apoptosis. | [110] |
| hLf inhibits the growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via direct cellular inhibition as well as systemically via immunomodulation. | [103] | |
| Lf shows antiproliferative effects via hypophosphorylation of Rb on H1299 cells. | [111] | |
| Lfcin inhibits VEGF expression and induces apoptosis on non-small cell lung cancer H460. | [112] | |
| NCS | Lfcin inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis through activation of caspases in neuroblastoma cells and in vivo). | [113] |
| Lf causes growth inhibition in the NMD and FN primary cell lines and in the U87MG continuous cell line (downregulation of cyclin D1 and D4). Administration of hLf with TMZ enhanced the effect of chemotherapy both in vitro and in vivo. | [114] |
| Activity | Peptide | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial | Gram positive | Lf(1–11) | [132] |
| Lfcin | [133,134,135] | ||
| Lfampin | [134] | ||
| Gram negative | Lf(1–11) | [136] | |
| Lfcin | [137,138,139] | ||
| Lfampin | [140,141,142] | ||
| Antiviral | Lf(1–11) | [143] | |
| Lfcin | [54,144,145,146,147] | ||
| Lfampin | [143] | ||
| Antifungal | Lf(1–11) | [148] | |
| Lfcin | [149,150] | ||
| Lfampin | [151,152] | ||
| Antiparasitic | Lfcin | [153] | |
| Lfampin | [154] | ||
| Anticancer | Lfcin | [155,156,157,158] | |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giansanti, F.; Panella, G.; Leboffe, L.; Antonini, G. Lactoferrin from Milk: Nutraceutical and Pharmacological Properties. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9040061
Giansanti F, Panella G, Leboffe L, Antonini G. Lactoferrin from Milk: Nutraceutical and Pharmacological Properties. Pharmaceuticals. 2016; 9(4):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9040061
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiansanti, Francesco, Gloria Panella, Loris Leboffe, and Giovanni Antonini. 2016. "Lactoferrin from Milk: Nutraceutical and Pharmacological Properties" Pharmaceuticals 9, no. 4: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9040061
APA StyleGiansanti, F., Panella, G., Leboffe, L., & Antonini, G. (2016). Lactoferrin from Milk: Nutraceutical and Pharmacological Properties. Pharmaceuticals, 9(4), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9040061








