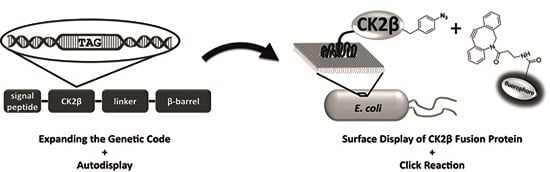
Site-Specific Labeling of Protein Kinase CK2: Combining Surface Display and Click Chemistry for Drug Discovery Applications †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
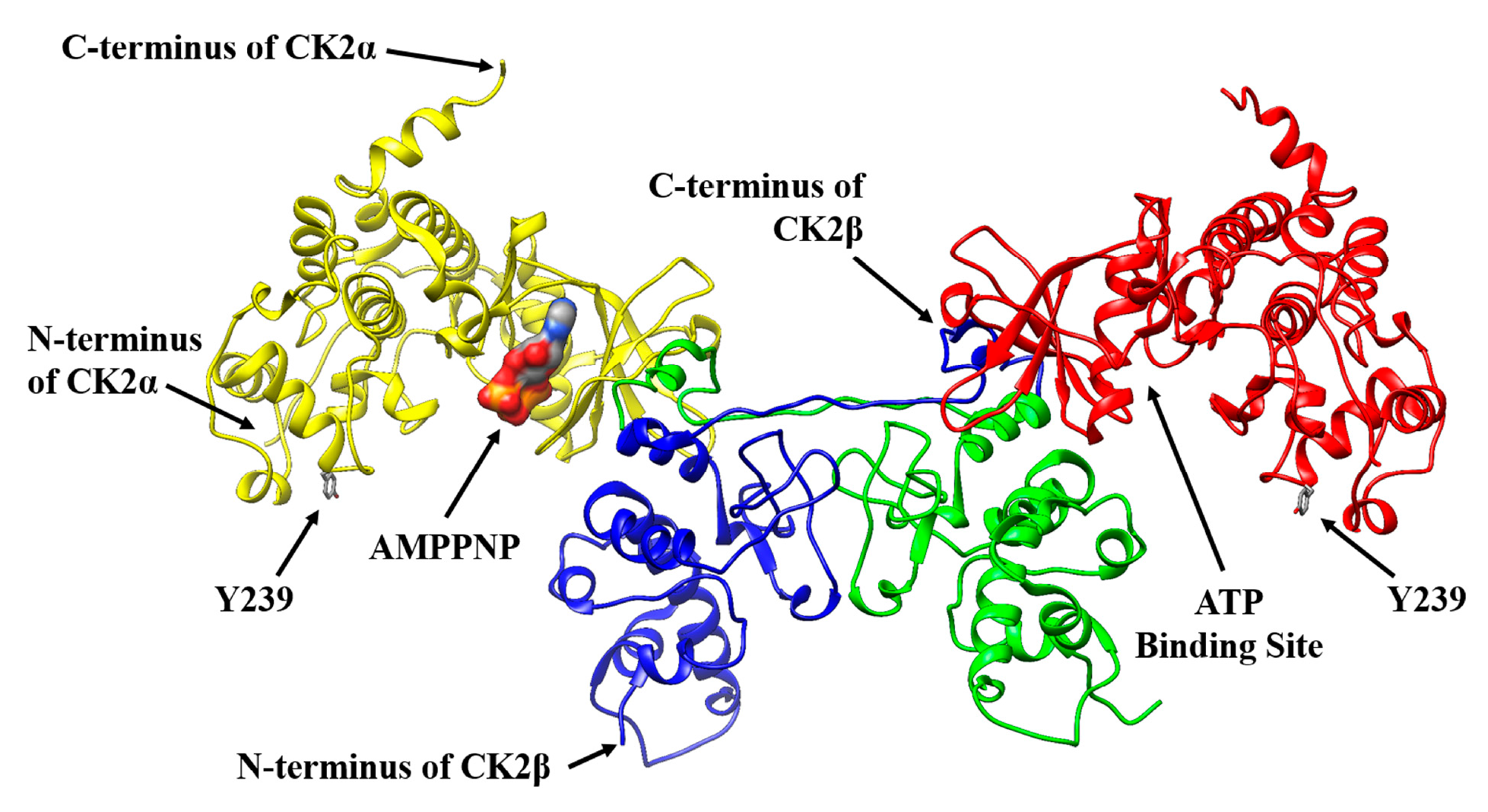
2.1. Selecting a Suitable Position in CK2α for a Specific Fluorophore Labeling
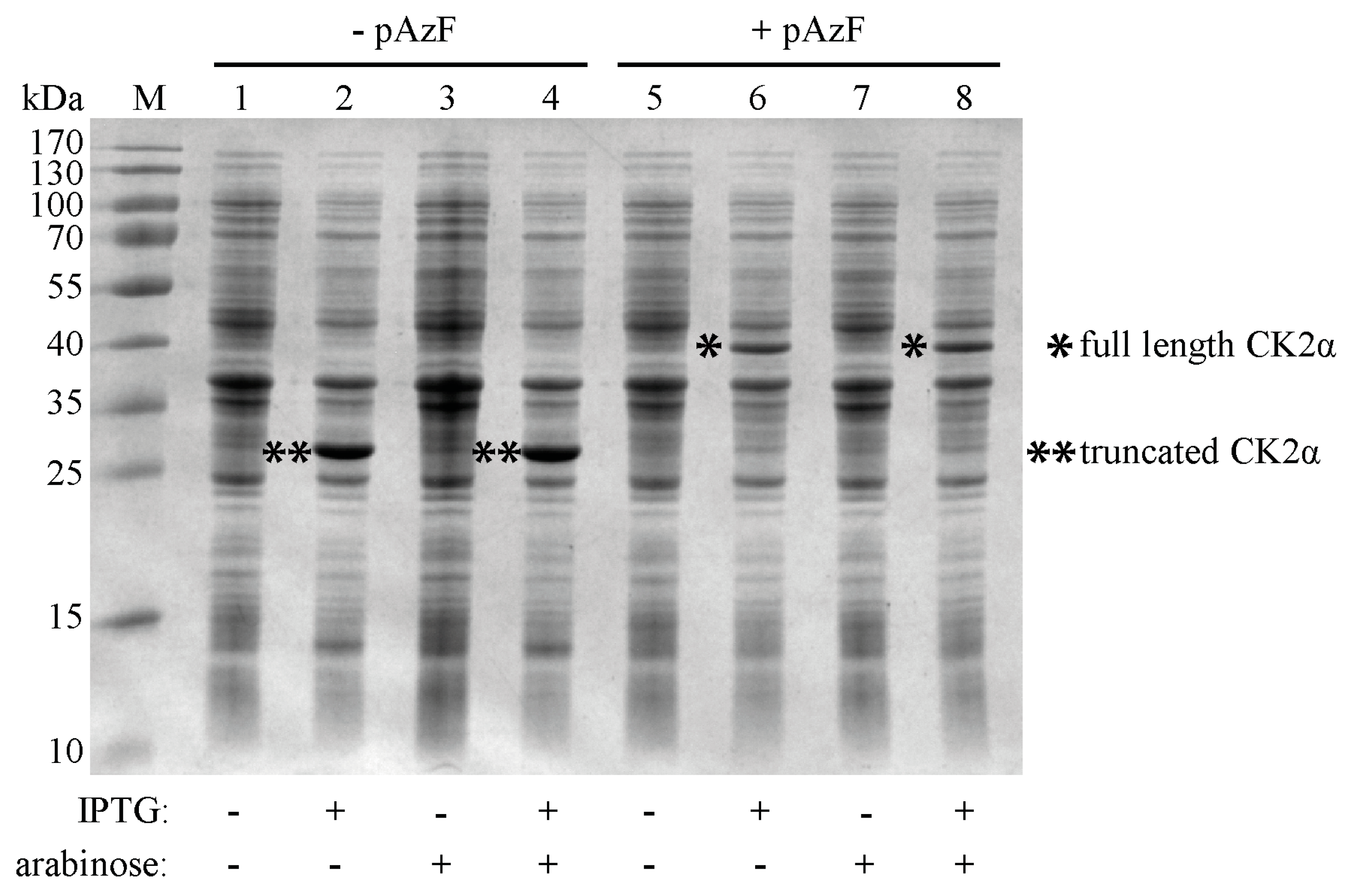
2.2. Incorporation of pAzF into CK2α
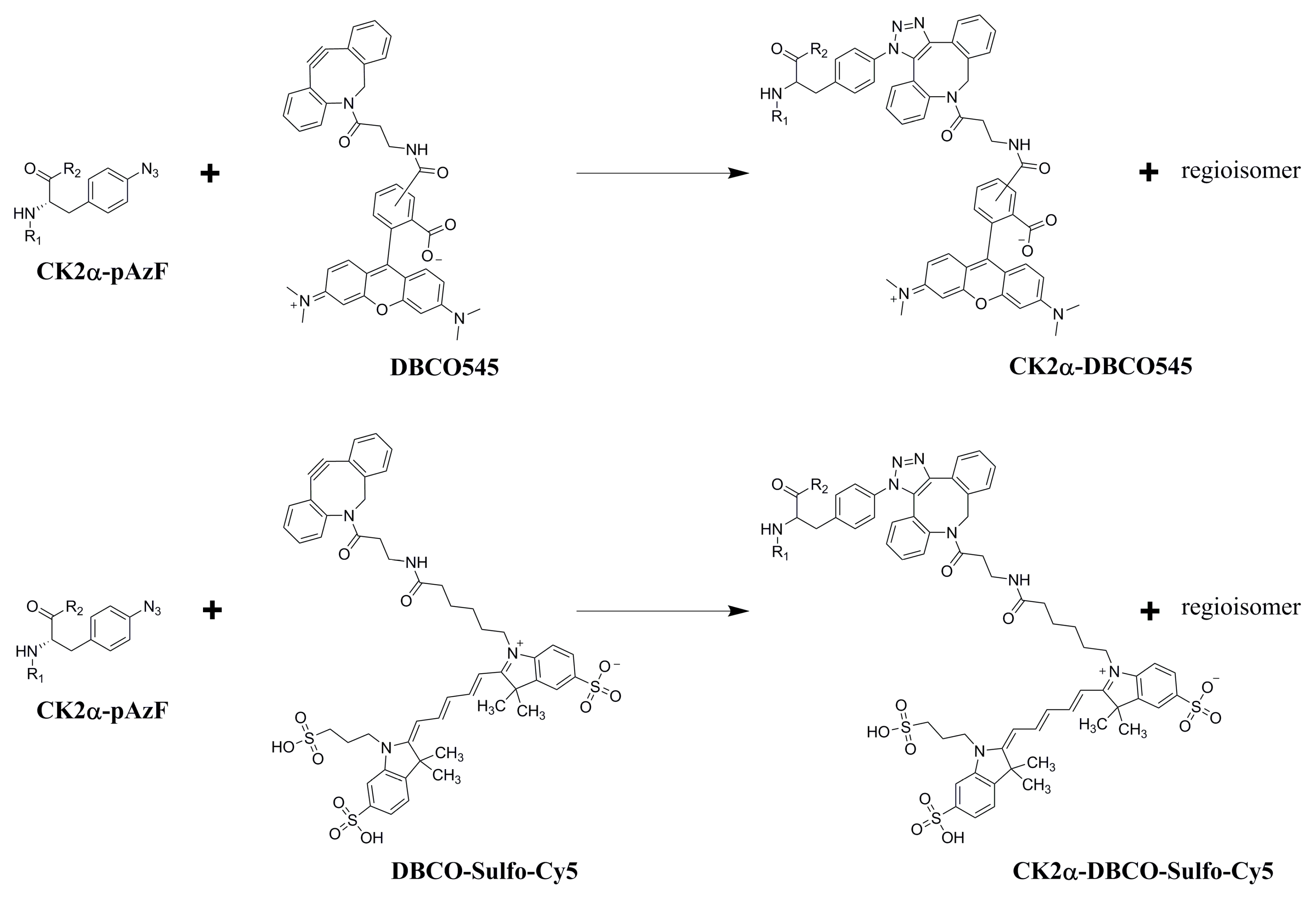
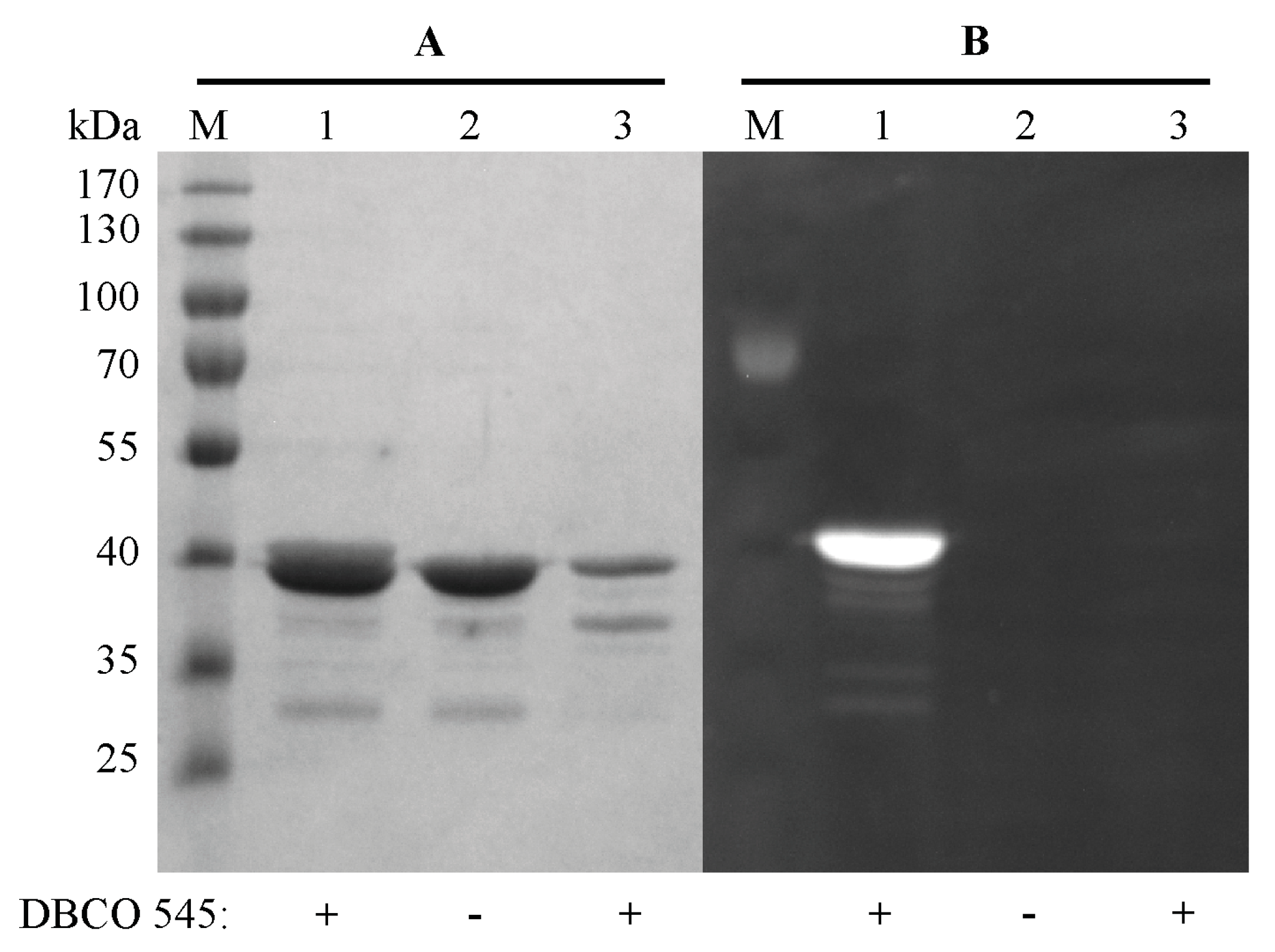
2.3. Purification and Click Chemistry of CK2α-pAzF
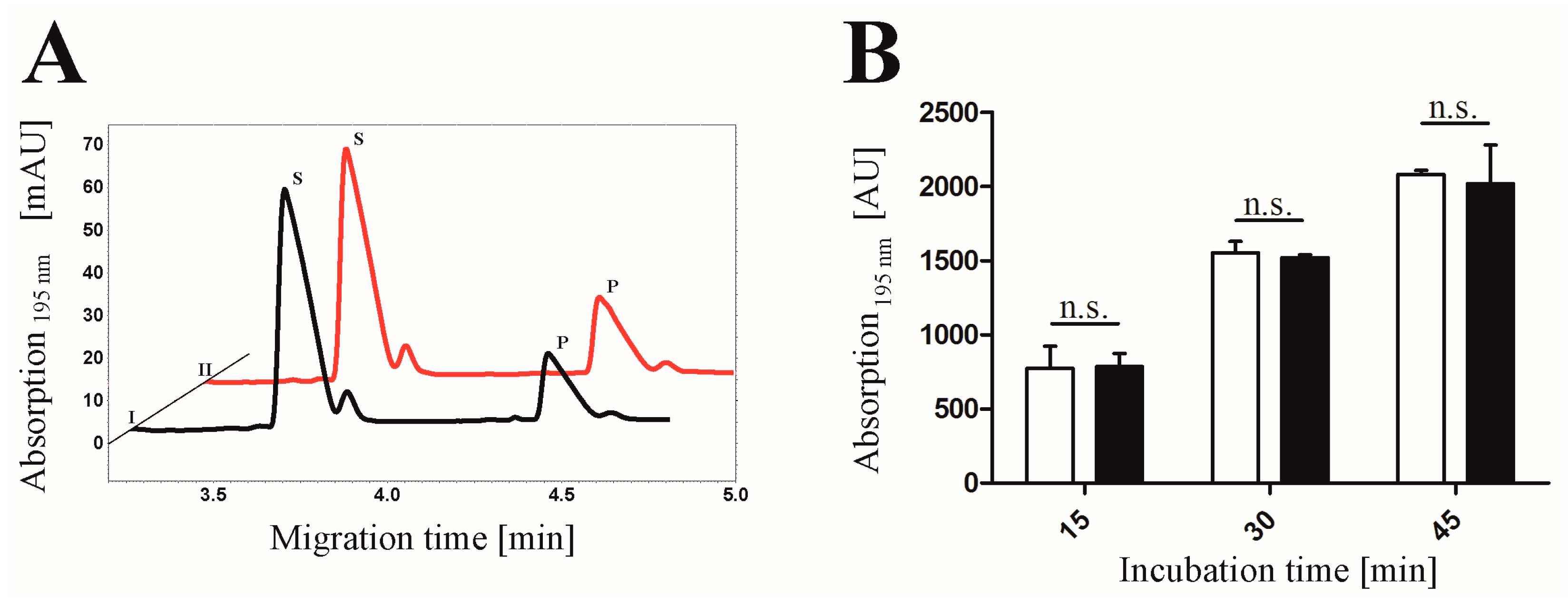
2.4. Proof of Phosphorylation Activity of CK2α-pAzF/CK2α-DBCO545
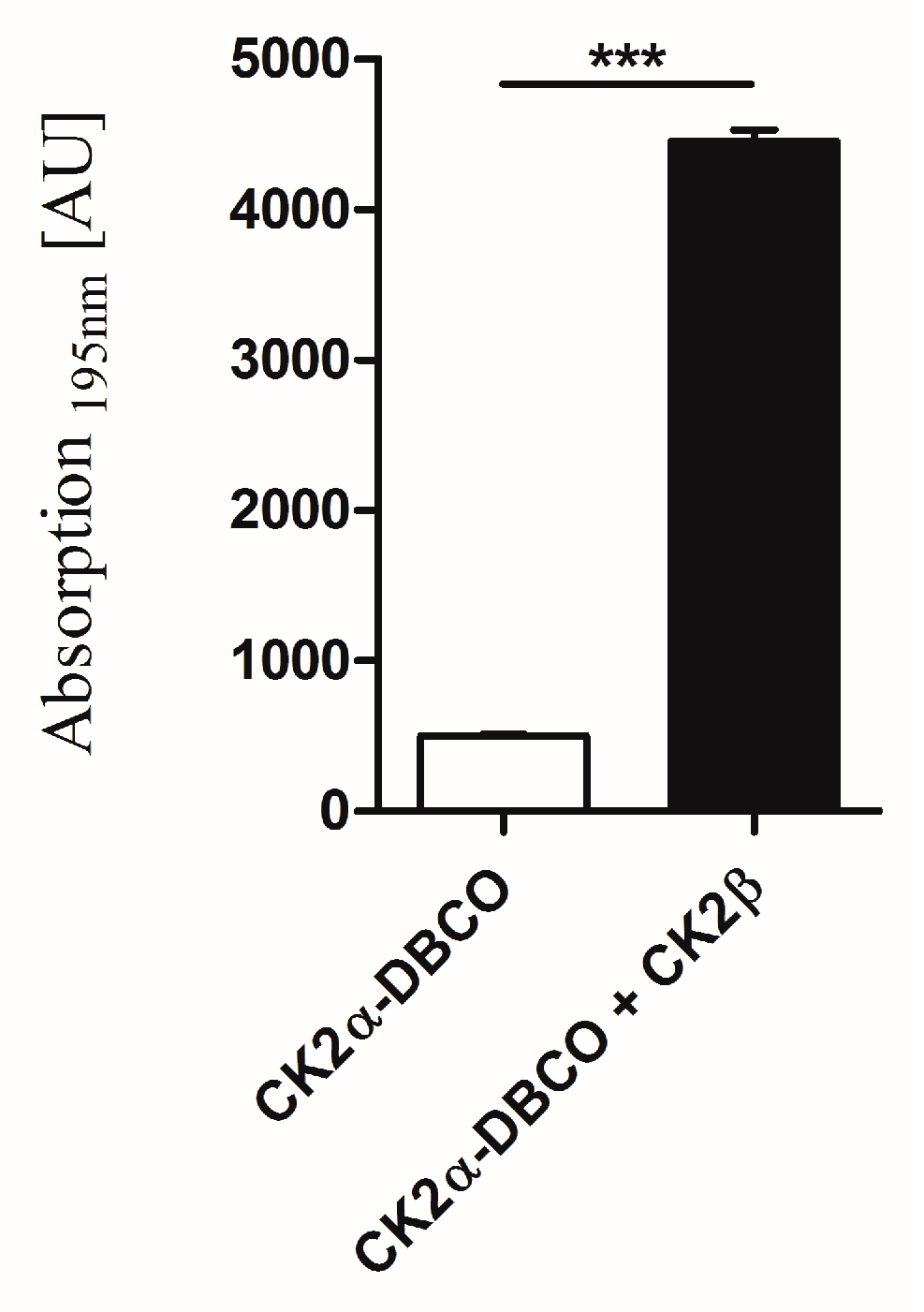
2.5. Interaction of Surface-Displayed CK2β and CK2α-DBCO545
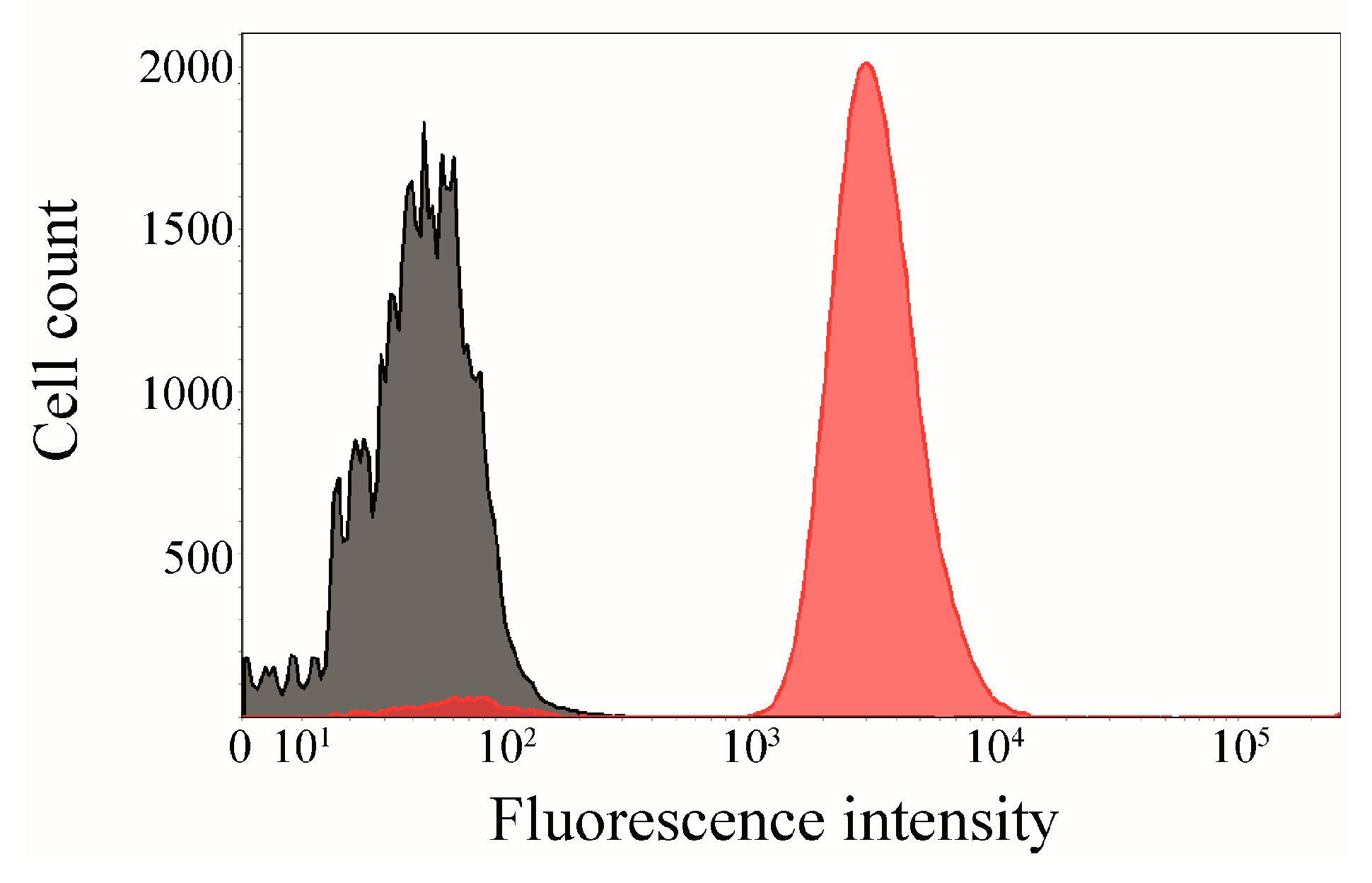
2.6. Click Chemistry of CK2β-AT on the Surface of E. coli
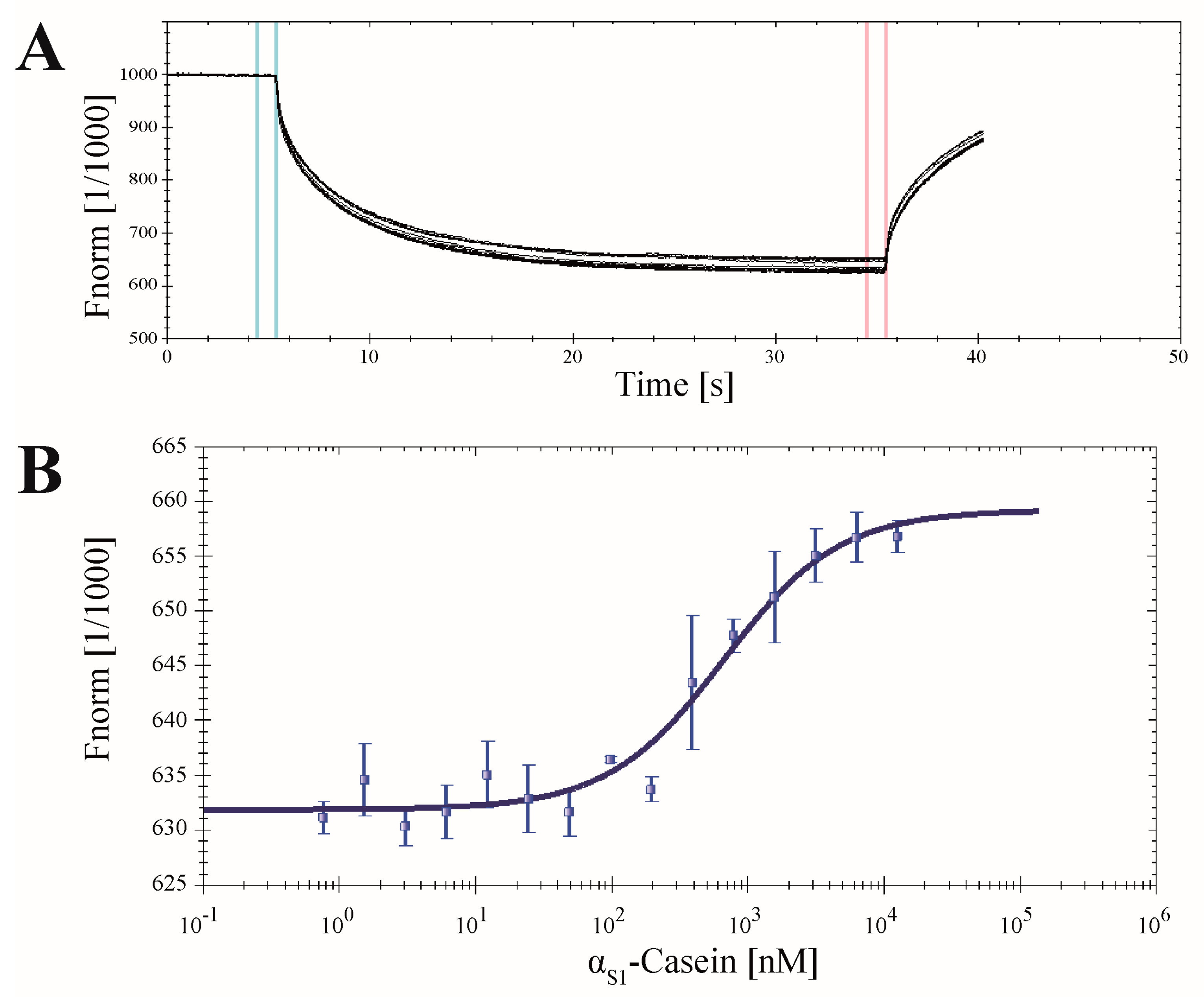
2.7. Application of CK2α-pAzF for MST Measurements
3. Materials and Method
3.1. Bacterial Strain and Culture Conditions
3.2. Design of pCK2αY239Stop and pCK2β-ATY108Stop Plasmids
3.3. Biosynthesis and Purification of CK2α-pAzF
3.4. Surface Display of CK2β-AT-pAzF
3.5. SDS-PAGE
3.6. SPAAC Reaction of CK2α-pAzF
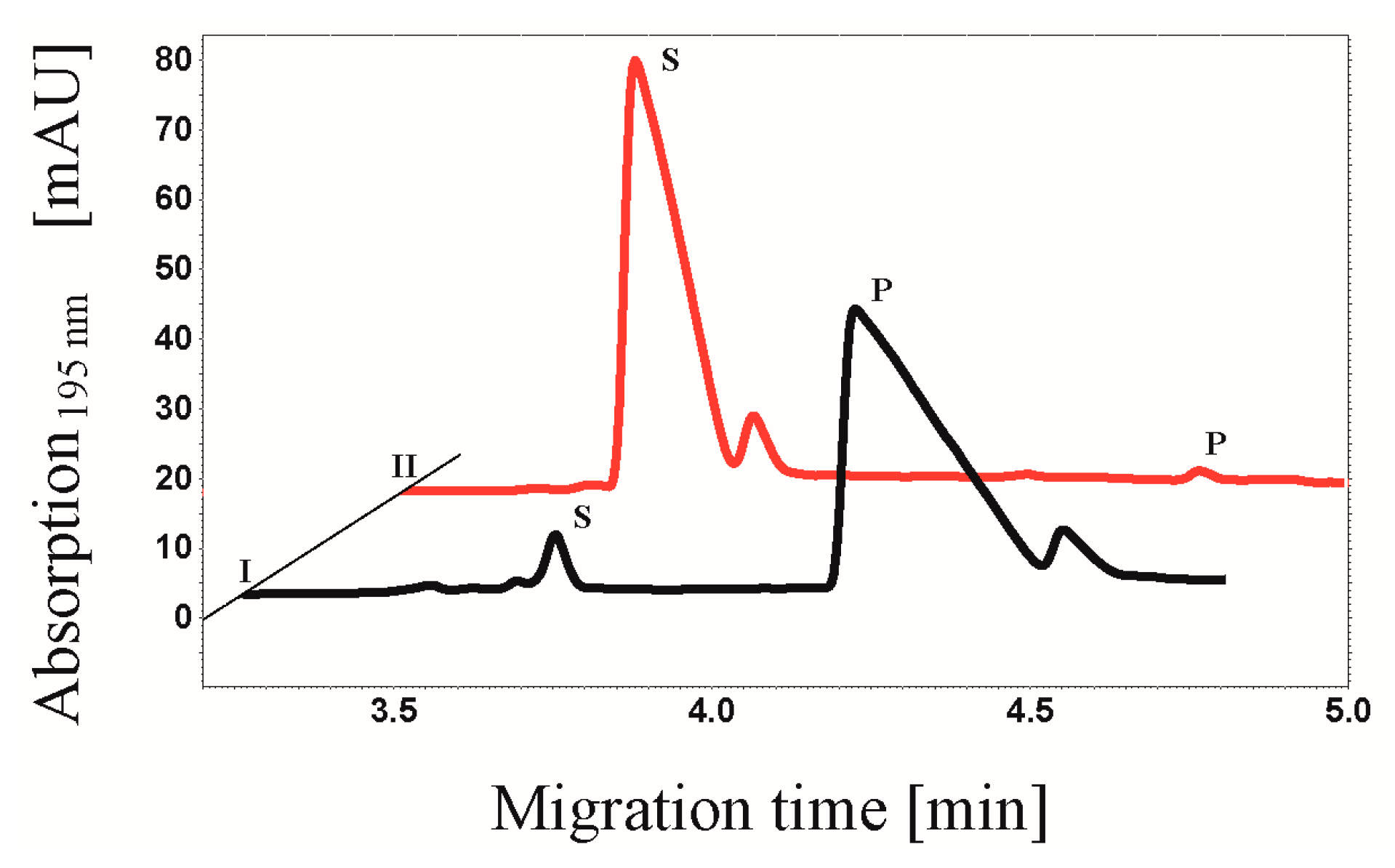
3.7. CE-based Activity Measurements of CK2
3.8. Flow Cytometry
3.9. Microscale Thermophoresis (MST)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burnett, G.; Kennedy, E.P. The enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1954, 211, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venerando, A.; Ruzzene, M.; Pinna, L.A. Casein kinase: The triple meaning of a misnomer. Biochem. J. 2014, 460, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niefind, K.; Guerra, B.; Ermakowa, I.; Issinger, O.G. Crystal structure of human protein kinase CK2: Insights into basic properties of the CK2 holoenzyme. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5320–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, N.; Olsen, B.; Raaf, J.; Bretner, M.; Issinger, O.G.; Niefind, K. Structure of the human protein kinase CK2 catalytic subunit CK2α′ and interaction thermodynamics with the regulatory subunit CK2β. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 407, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meggio, F.; Pinna, L.A. One-thousand-and-one substrates of protein kinase CK2? FASEB J. 2003, 17, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchfield, D.W. Protein kinase CK2: Structure, regulation and role in cellular decisions of life and death. Biochem. J. 2003, 369, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trembley, J.H.; Chen, Z.; Unger, G.; Slaton, J.; Kren, B.T.; van Waes, C.; Ahmed, K. Emergence of protein kinase CK2 as a key target in cancer therapy. Biofactors 2010, 36, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, C.E.; Seidner, Y.; Dominguez, I. Mining CK2 in cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götz, C.; Gratz, A.; Kucklaender, U.; Jose, J. TF—A novel cell-permeable and selective inhibitor of human protein kinase CK2 induces apoptosis in the prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alchab, F.; Ettouati, L.; Bouaziz, Z.; Bollacke, A.; Delcros, J.G.; Gertzen, C.G.W.; Gohlke, H.; Pinaud, N.; Marchivie, M.; Guillon, J.; et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling of substituted indeno[1,2-b]indoles as inhibitors of human protein kinase CK2. Pharmaceuticals 2015, 8, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre, F.; Chua, P.C.; Obrien, S.E.; Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Bourbon, P.; Haddach, M.; Michaux, J.; Nagasawa, J.; Schwaebe, M.K.; Stefan, E.; et al. Discovery and SAR of 5-(3-Chlorophenylamino)benzo[c][2,6]naphthyridine-8-carboxylic Acid (CX-4945), the first clinical stage inhibitor of protein kinase CK2 for the Treatment of Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raaf, J.; Guerra, B.; Neundorf, I.; Bopp, B.; Issinger, O.G.; Jose, J.; Pietsch, M.; Niefind, K. First structure of protein kinase CK2 catalytic subunit with an effective CK2β-competitive ligand. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerabek-Willemsen, M.; Wienken, C.J.; Braun, D.; Baaske, P.; Duhr, S. Molecular interaction studies using microscale thermophoresis. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2011, 9, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratz, A.; Gtz, C.; Jose, J. A FRET-based microplate assay for human protein kinase CK2, a target in neoplastic disease. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2010, 25, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, C.; Wodtke, R.; Löser, R.; Pietsch, M. A fluorescence anisotropy-based assay for determining the activity of tissue transglutaminase. Amino Acids 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axup, J.Y.; Bajjuri, K.M.; Ritland, M.; Hutchins, B.M.; Kim, C.H.; Kazane, S.A.; Halder, R.; Forsyth, J.S.; Santidrian, A.F.; Stafin, K.; et al. Synthesis of site-specific antibody-drug conjugates using unnatural amino acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16101–16106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palei, S.; Mootz, H.D. Cyclic Peptides Made by Linking Synthetic and Genetically Encoded Fragments. ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, A.L.; Matern, J.C.J.; Schütz, V.; Mootz, H.D. Chemical-tag labeling of proteins using fully recombinant split inteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1266, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jose, J.; Betscheider, D.; Zangen, D. Bacterial surface display library screening by target enzyme labeling: Identification of new human cathepsin G inhibitors. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 346, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bopp, B.; Ciglia, E.; Ouald-Chaib, A.; Groth, G.; Gohlke, H.; Jose, J. Design and biological testing of peptidic dimerization inhibitors of human Hsp90 that target the C-terminal domain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratz, A.; Bollacke, A.; Stephan, S.; Nienberg, C.; Le Borgne, M.; Götz, C.; Jose, J. Functional display of heterotetrameric human protein kinase CK2 on Escherichia coli: A novel tool for drug discovery. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollacke, A.; Nienberg, C.; Borgne, M.L.; Jose, J. Toward selective CK2alpha and CK2alpha inhibitors: Development of a novel whole-cell kinase assay by Autodisplay of catalytic CK2alpha. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 121, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratz, A.; Götz, C.; Jose, J. A CE-based assay for human protein kinase CK2 activity measurement and inhibitor screening. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistutta, R. Structural bases of protein kinase CK2 inhibition. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1868–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, J.W.; Santoro, S.W.; Martin, A.B.; King, D.S.; Wang, L.; Schultz, P.G. Addition of p-azido-l-phenylalanine to the genetic code of Escherichia coli. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9026–9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Schultz, P.G. Expanding the genetic code. Chem. Commun. 2002, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.S.; Ahmad, I.; Yin, J.A.; Schultz, P.G. An Enhanced System for Unnatural Amino Acid Mutagenesis in E. coli. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 395, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.; Rydén-Aulin, M. Glutamine is incorporated at the nonsense codons UAG and UAA in a suppressor-free Escherichia coli strain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1627, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grankowski, N.; Boldyreff, B.; Issinger, O.G. Isolation and characterization of recombinant human casein kinase II subunits α and β from bacteria. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 198, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbua, N.E.; Guo, J.; Wolfert, M.A.; Steet, R.; Boons, G.J. Strain-Promoted Alkyne-Azide Cycloadditions (SPAAC) Reveal New Features of Glycoconjugate Biosynthesis. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrowolska, G.; Lozeman, F.J.; Li, D.; Krebs, E.G. CK2, a protein kinase of the next millennium. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1999, 191, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, J.; Von Schwichow, S. Autodisplay of active sorbitol dehydrogenase (SDH) yields a whole cell biocatalyst for the synthesis of rare sugars. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, J.; Meyer, T.F. The autodisplay story, from discovery to biotechnical and biomedical applications. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 600–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vordenbäumen, S.; Saenger, T.; Braukmann, A.; Tahan, T.; Bleck, E.; Jose, J.; Schneider, M. Human casein alpha s1 induces proinflammatory cytokine expression in monocytic cells by TLR4-signaling. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez, M.J.; Cochet, C.; Jiménez, J.S. A surface plasmon resonance study of the interactions between the component subunits of protein kinase CK2 and two protein substrates, casein and calmodulin. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 227, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, S.M.; Herbert, P.J.; Slattery, C.W. Structural studies on casein micelles of human milk: Dissociation of β-casein of different phosphorylation levels induced by cooling and ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nienberg, C.; Retterath, A.; Becher, K.-S.; Saenger, T.; Mootz, H.D.; Jose, J. Site-Specific Labeling of Protein Kinase CK2: Combining Surface Display and Click Chemistry for Drug Discovery Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030036
Nienberg C, Retterath A, Becher K-S, Saenger T, Mootz HD, Jose J. Site-Specific Labeling of Protein Kinase CK2: Combining Surface Display and Click Chemistry for Drug Discovery Applications. Pharmaceuticals. 2016; 9(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleNienberg, Christian, Anika Retterath, Kira-Sophie Becher, Thorsten Saenger, Henning D. Mootz, and Joachim Jose. 2016. "Site-Specific Labeling of Protein Kinase CK2: Combining Surface Display and Click Chemistry for Drug Discovery Applications" Pharmaceuticals 9, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030036
APA StyleNienberg, C., Retterath, A., Becher, K.-S., Saenger, T., Mootz, H. D., & Jose, J. (2016). Site-Specific Labeling of Protein Kinase CK2: Combining Surface Display and Click Chemistry for Drug Discovery Applications. Pharmaceuticals, 9(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030036