Physical Factors Affecting Plasmid DNA Compaction in Stearylamine-Containing Nanoemulsions Intended for Gene Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Plasmid PIRES2-EGFP DNA (pDNA)
2.3. Preparation of Cationic Lipid Nanoemulsions (CLNs)
| Component | CLN1 %(w/w) | CLN2 %(w/w) |
|---|---|---|
| Oily phase | ||
| Captex® 355 (TCM) | 5 | 5 |
| Span® 80 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Stearylamine | - | 0.16 |
| Aqueous phase | ||
| Tween® 80 | 1.20 | 1.20 |
| Stearylamine | 0.16 | - |
| Water qsp. | 100 | 100 |
2.4. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analysis
2.5. Preparation of PDNA/CLN Complexes
2.5.1. Influence of the Stearylamine Loading Process at the Water or Oil Phase on the PDNA Compaction Process
| CLN (μL) | pDNA(ng)/CLN(ng oil phase) ratio |
|---|---|
| 2 | 4.60 |
| 4 | 2.30 |
| 5 | 1.84 |
| 6 | 1.53 |
| 7 | 1.31 |
| 8 | 1.15 |
| 9 | 1.02 |
| 10 | 0.92 |
2.5.2. Influence of the Time of Complexation
2.5.3. Influence of the Temperature on the Lipoplex Formation
2.6. Efficiency of Complexation by Electrophoresis Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size and Zeta-Potential Characteristics
| Formulation | Size (nm) ± SD | PI (± SD) | Zeta Potential (mV) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLN1 | 195.1 ± 2.9 | 0.185 ± 0.015 | 41.9 ± 4.3 |
| CLN1-lipoplex | 200.7 ± 4.2 | 0.177 ± 0.027 | 22.5 ± 3.4 |
| CLN2 | 199.1 ± 4.2 | 0.185 ± 0.004 | 39.6 ± 4.1 |
| CLN2-lipoplex | 204.0 ± 0.2 | 0.213 ± 0.010 | 25.7 ± 0.3 |
3.2. Effects of Stearylamine Loading Phase on the pDNA/CLN Complexation

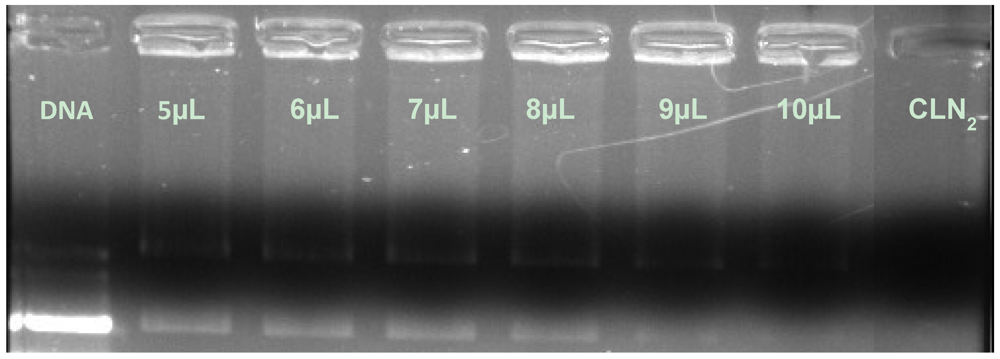
3.3. Time Effect on pDNA/CLN Complexation
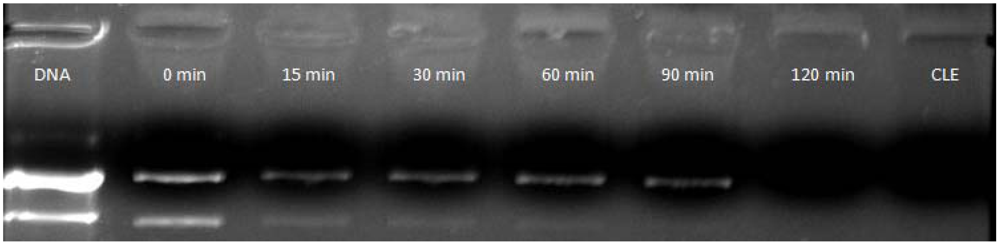
3.4. Effects of the Environmental Temperature on the pDNA/CLN Complexation
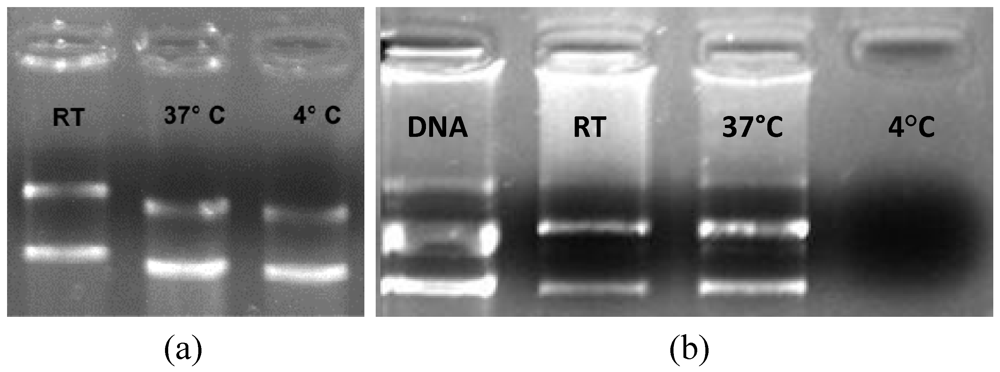
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Rolland, A.; Sullivan, S.M. Pharmaceutical Gene Delivery System; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Gjetting, T.; Mattebjerg, M.A.; Wu, C.; Andresen, T.L. Elucidating the Interplay between DNA-condensing and Free Polycations in Gene Transfection through a Mechanistic Study of Linear and Branched Pei. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8626–8634. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Jin, F.; Deng, R.; Cai, J.; Dai, Z.; Lin, M.C.M.; Kung, H.F.; Mattebjerg, M.A.; Andresen, T.L.; Wu, C. Revisit Complexation between DNA and Polyethylenimine — Effect of Length of Free Polycationic Chains on Gene Transfection. J. Control. Release 2011, 152, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geusens, B.; Strobbe, T.; Bracke, S.; Dynoodt, P.; Sanders, N.; Van Gele, M.; Lambert, J. Lipid-mediated Gene Delivery to the Skin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 43, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Khoshhamdam, M.; Dehshahri, A.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. The Influence of Size, Lipid Composition and Bilayer Fluidity of Cationic Liposomes on the Transfection Efficiency of Nanolipoplexes. Colloid Surface B 2009, 72, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Huang, L. Development of Non-viral Vectors for Systemic Gene Delivery. J. Control. Release 2002, 78, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ilarduya, C.T.; Sun, Y.; Duezguenes, N. Gene Delivery by Lipoplexes and Polyplexes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 40, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verissimo, L.M.; Agnez Lima, L.F.; Monte Egito, L.C.; de Oliveira, A.G.; Tabosa do Egito, E.S. Pharmaceutical Emulsions: A new Approach for Gene Therapy. J. Drug Targeting 2010, 18, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.; Burgess, D.J.; Patil, S.D. Physicochemical Characterization Techniques for Lipid Based Delivery Systems for Sirna. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 427, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Yu, S.-Y. Cationic Nanoemulsions as Non-viral Vectors for Plasmid DNA Delivery. Colloid. Surface. B. 2010, 79, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruxel, F.; Cojean, S.; Bochot, A.; Teixeira, H.; Bories, C.; Loiseau, P.M.; Fattal, E. Cationic Nanoemulsion as a Delivery System for Oligonucleotides Targeting Malarial Topoisomerase ii. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 416, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, C.R.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Gissel, H.; Gothelf, A.; Jakobsen, M.; Hansen, B.H.; Frystyk, J.; Oliveira, N.A.J.; Higuti, E.; Bartolini, P.; Peroni, C.N.; Jensen, T.G. Non-viral Gene Transfer to Skin, Muscle and Liver for Expression of Growth Hormone. Hum. Gene Ther. 2011, 22, A86–A86. [Google Scholar]
- Castilho, L.R.; Moraes, Â.M.; Augusto, E.F.P.; Butler, M. Animal Cell Technology: From Biopharmaceuticals to Gene Therapy; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.S.; Lee, S.K.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, Y.B.; Shin, S.C.; Lee, K.C.; Oh, I.J. Physicochemical Characterization of Poly(l-lactic acid) and Poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) Nanoparticles with Polyethylenimine as Gene Delivery Carrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 298, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Gao, J.; Liu, W.; Li, B.; Guo, Y.; Chen, J. Dc-chol/Dope Cationic Liposomes: A Comparative Study of the Influence Factors on Plasmid Pdna and Sirna Gene Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 390, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, H.; Rosilio, V.; Laigle, A.; Lepault, J.; Erk, I.; Scherman, D.; Benita, S.; Couvreur, P.; Dubernet, C. Characterization of Oligonucleotide/Lipid Interactions in Submicron Cationic Emulsions: Influence of the Cationic Lipid Structure and the Presence of Peg-lipids. Biophys. Chem. 2001, 92, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, E.; Fattal, E.; de Oliveira, M.C.; Teixeira, H. Effect of Cationic Lipid Composition on Properties of Oligonucleotide/Emulsion Complexes: Physico-chemical and Release Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 352, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.L.; Ramachandran, C.; Bielinska, A.U.; Kingzett, K.; Sun, R.; Weiner, N.D.; Roessler, B.J. Topical Transfection using Plasmid DNA in a Water-in-oil Nanoemulsion. Int. J.Pharm. 2001, 221, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, S.; Messai, I.; Delair, T.; Verrier, B.; Ataman-Onal, Y. Cationic pla nanoparticles for DNA Delivery: Comparison of Three Surface Polycations for DNA Binding, Protection and Transfection Properties. Colloid. Surface. B. 2005, 43, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Ji, W.; Wang, C. Synthesis and Characterization of New Poly(ortho ester amidine) Copolymers for Non-viral Gene Delivery. Polymer 2011, 52, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.A.; Jin, F.; Deng, R.; Cai, J.G.; Chen, Y.C.; Lin, M.C.M.; Kung, H.F.; Wu, C. Revisit Complexation between DNA and Polyethylenimine - effect of Uncomplexed Chains Free in the Solution Mixture on Gene Transfection. J. Control. Release 2011, 155, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Jeong, S.Y. Lipid-based Emulsion System as Non-Viral Gene Carriers. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.M.; Nam, H.Y.; Nam, T.; Park, K.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, J.; Kang, D.; Park, J.H.; Jeong, S.Y. In Vivo Time-dependent Gene Expression of Cationic Lipid-based Emulsion as a Stable and Biocompatible Non-viral Gene Carrier (vol 128, pg 89, 2008). J. Control. Release 2009, 140, 74–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, R.; N'Soukpoe-Kossi, C.N.; Charbonneau, D.; Weinert, C.M.; Kreplak, L.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.-A. Structural Analysis of DNA Complexation with Cationic Lipids. Nucl. Acid. Res. 2009, 37, 849–857. [Google Scholar]
- Matulis, D.; Rouzina, I.; Bloomfield, V.A. Thermodynamics of Cationic Lipid Binding to DNA and DNA Condensation: Roles of Electrostatics and Hydrophobicity. J Am Chem Soc. 2002, 124, 7331–7342. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, 2001; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.W.; Chung, H.; Kwon, I.C.; Sung, H.C.; Jeong, S.Y. Optimization of Lipid Composition in Cationic Emulsion as in Vitro and in Vivo Transfection Agents. Pharmaceut. Res. 2001, 18, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonarbourg, A.; Passirani, C.; Desigaux, L.; Allard, E.; Saulnier, P.; Lambert, O.; Benoit, J.-P.; Pitard, B. The Encapsulation of DNA Pharmaceuticals within Biomimetic Lipid Nanocapsules. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3197–3204. [Google Scholar]
- Badea, I.; Wettig, S.; Verrall, R.; Foldvari, M. Topical Non-invasive Gene Delivery Using Gemini Nanoparticles in Interferon-gamma-deficient Mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch-Lerner, D.; Zhang, M.; Eliyahu, H.; Ferrari, M.E.; Wheeler, C.J.; Barenholz, Y. Effect of “Helper Lipid” on Lipoplex Electrostatics. BBA-Biomembranes 2005, 1714, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuidam, N.J.; Barenholz, Y. Electrostatic and Structural Properties of Complexes Involving Plasmid DNA and Cationic Lipids Commonly Used for Gene Delivery. BBA-Biomembranes 1998, 1368, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TseDinh, Y.C.; Qi, H.Y.; Menzel, R. DNA Supercoiling and Bacterial Adaptation: Thermotolerance and Thermoresistance. Trends Microbiol. 1997, 5, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleef, M. Plasmids for Therapy and Vaccinatio; Wiley-VCH: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Witz, G.; Stasiak, A. DNA Supercoiling and Its Role in DNA Decatenation and Unknotting. Nucl. Acid. Res. 38, 2119–2133. [CrossRef]
- Walther, W.; Stein, U.; Voss, C.; Schmidt, T.; Schleef, M.; Schlag, P.M. Stability Analysis for Long-term Storage of Naked DNA: Impact on Nonviral In Vivo Gene Transfer. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 318, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, A.L.; Alexandrino, F., Júnior; Verissimo, L.M.; Agnez-Lima, L.F.; Egito, L.C.M.; De Oliveira, A.G.; Do Egito, E.S.T. Physical Factors Affecting Plasmid DNA Compaction in Stearylamine-Containing Nanoemulsions Intended for Gene Delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 643-654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5060643
Silva AL, Alexandrino F Júnior, Verissimo LM, Agnez-Lima LF, Egito LCM, De Oliveira AG, Do Egito EST. Physical Factors Affecting Plasmid DNA Compaction in Stearylamine-Containing Nanoemulsions Intended for Gene Delivery. Pharmaceuticals. 2012; 5(6):643-654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5060643
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, André Leandro, Francisco Alexandrino, Júnior, Lourena Mafra Verissimo, Lucymara Fassarella Agnez-Lima, Lucila Carmem Monte Egito, Anselmo Gomes De Oliveira, and Eryvaldo Socrates Tabosa Do Egito. 2012. "Physical Factors Affecting Plasmid DNA Compaction in Stearylamine-Containing Nanoemulsions Intended for Gene Delivery" Pharmaceuticals 5, no. 6: 643-654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5060643
APA StyleSilva, A. L., Alexandrino, F., Júnior, Verissimo, L. M., Agnez-Lima, L. F., Egito, L. C. M., De Oliveira, A. G., & Do Egito, E. S. T. (2012). Physical Factors Affecting Plasmid DNA Compaction in Stearylamine-Containing Nanoemulsions Intended for Gene Delivery. Pharmaceuticals, 5(6), 643-654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5060643




