The Liver as a Target Organ for Gene Therapy: State of the Art, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Hepatocyte-Directed Gene Transfer
2. Parenchymal Liver Cells as a Gene Transfer Target: The Role of Sinusoidal Cells
3. Parenchymal Liver cells as a Gene Transfer Target: the Role of Sinusoidal Fenestrae
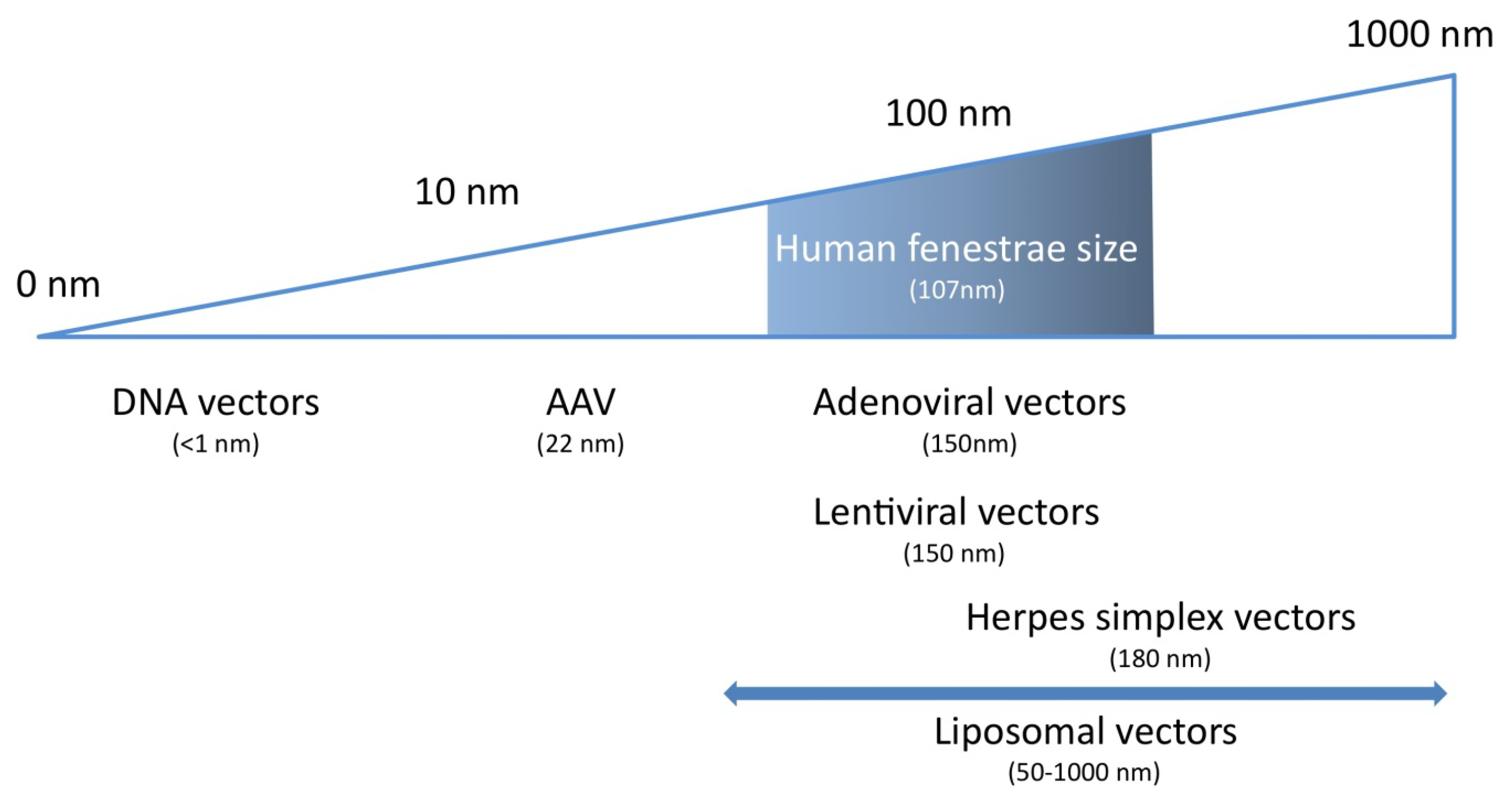
4. Characteristics of the Ideal Vector for Hepatocyte-Directed Gene Transfer
| Properties | Vector |
|---|---|
| Facilitated passage through fenestrae | AAV, some non-viral gene transfer vectors |
| Efficient transduction or transfection | AAV, adenoviral vectors |
| Target specific | No vector system, apply transcriptional targeting |
| Repeated use possible | Minicircles, non-viral gene transfer vectors, apply serotype switch |
| No or minor vector-induced innate immune responses | AAV, minicircles? |
| No or minor vector-induced adaptive immune responses | Minicircles, non-viral gene transfer vectors |
| No non-immune toxicity | AAV, some non-viral gene transfer vectors |
| High insertion capacity | Adenoviral vectors, minicircles, non-viral gene transfer systems |
5. AAV-Mediated Hepatocyte-Directed Gene Transfer: Introduction
6. AAV2-Mediated Hepatocyte-Directed Gene Transfer
7. Hepatocyte-Directed Gene Transfer Using Alternative AAV Serotypes
8. Challenges for AAV-Mediated Hepatocyte-Directed Gene Transfer
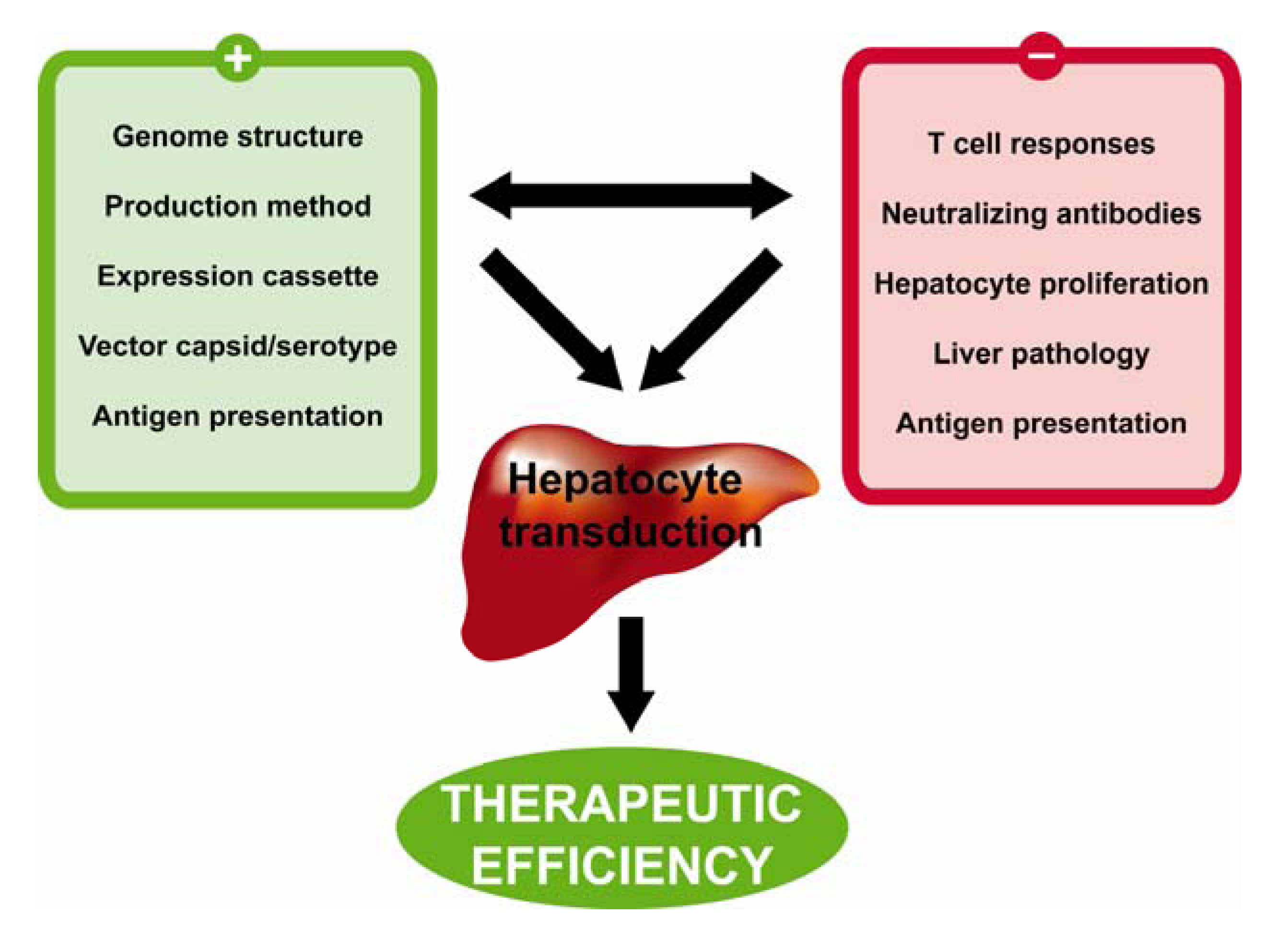
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Nguyen, T.H.; Ferry, N. Liver gene therapy: Advances and hurdles. Gene Ther. 2004, 11 (Suppl. 1), S76–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Alcoceba, R.; Sangro, B.; Prieto, J. Gene therapy of liver cancer. Ann. Hepatol. 2007, 6, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, D.; Kay, M.A. Therapeutic short hairpin RNA expression in the liver: viral targets and vectors. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisse, E. An electron microscopic study of the fenestrated endothelial lining of rat liver sinusoids. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1970, 31, 125–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.; Healey, J.F.; Waller, E.K.; Lollar, P. Expression of factor VIII by murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19587–19592. [Google Scholar]
- Sasse, D.; Spornitz, U.M.; Maly, I.P. Liver architecture. Enzyme 1992, 46, 8–32. [Google Scholar]
- Blouin, A.; Bolender, R.P.; Weibel, E.R. Distribution of organelles and membranes between hepatocytes and nonhepatocytes in the rat liver parenchyma. A stereological study. J. Cell Biol. 1977, 72, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knook, D.L.; Sleyster, E.C. Isolated parenchymal, Kupffer and endothelial rat liver cells characterized by their lysosomal enzyme content. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1980, 96, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arii, S.; Imamura, M. Physiological role of sinusoidal endothelial cells and Kupffer cells and their implication in the pathogenesis of liver injury. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2000, 7, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shiratori, Y.; Tananka, M.; Kawase, T.; Shiina, S.; Komatsu, Y.; Omata, M. Quantification of sinusoidal cell function in vivo. Semin. Liver Dis. 1993, 13, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemany, R.; Suzuki, K.; Curiel, D.T. Blood clearance rates of adenovirus type 5 in mice. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2605–2609. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, N.; Gao, G.P.; Parr, M.; Johnston, J.; Baradet, T.; Wilson, J.M.; Barsoum, J.; Fawell, S.E. Sequestration of adenoviral vector by Kupffer cells leads to a nonlinear dose response of transduction in liver. Mol. Ther. 2001, 3, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, G.; Worgall, S.; van Rooijen, N.; Song, W.R.; Harvey, B.G.; Crystal, R.G. Enhancement ofin vivo adenovirus-mediated gene transfer and expression by prior depletion of tissue macrophages in the target organ. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 624–629. [Google Scholar]
- Snoeys, J.; Mertens, G.; Lievens, J.; van Berkel, T.; Collen, D.; Biessen, E.A.; De Geest, B. Lipid emulsions potently increase transgene expression in hepatocytes after adenoviral transfer. Mol. Ther. 2006, 13, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Waddington, S.N.; Parker, A.L.; Havenga, M.; Nicklin, S.A.; Buckley, S.M.; McVey, J.H.; Baker, A.H. Targeting of adenovirus serotype 5 (Ad5) and 5/47 pseudotyped vectors in vivo: fundamental involvement of coagulation factors and redundancy of CAR binding by Ad5. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9568–9571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.; Liu, Y.; Shayakhmetov, D.; Li, Z.Y.; Ni, S.; Lieber, A. Adenovirus-platelet interaction in blood causes virus sequestration to the reticuloendothelial system of the liver. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4866–4871. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Tian, J.; Smith, J.S.; Byrnes, A.P. Clearance of adenovirus by Kupffer cells is mediated by scavenger receptors, natural antibodies, and complement. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11705–11713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, N.C.; van Rooijen, N.; Shayakhmetov, D.M. Redundant and synergistic mechanisms control the sequestration of blood-born adenovirus in the liver. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.; Ni, S.; Li, Z.Y.; Gaggar, A.; DiPaolo, N.; Feng, Q.; Sandig, V.; Lieber, A. Development and assessment of human adenovirus type 11 as a gene transfer vector. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5090–5104. [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai, F.; Mizuguchi, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hayakawa, T. Characterization of in vitro and in vivo gene transfer properties of adenovirus serotype 35 vector. Mol. Ther. 2003, 8, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Tuve, S.; Strauss, R.; Lieber, A. Comparison of adenoviruses from species B, C, E, and F after intravenous delivery. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 2146–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, A.I.; Finegold, M.J.; Eisensmith, R.C. Macrophage depletion increases the safety, efficacy and persistence of adenovirus-mediated gene transfer in vivo. Gene Ther. 1997, 4, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Schiedner, G.; Hertel, S.; Johnston, M.; Dries, V.; van Rooijen, N.; Kochanek, S. Selective depletion or blockade of Kupffer cells leads to enhanced and prolonged hepatic transgene expression using high-capacity adenoviral vectors. Mol. Ther. 2003, 7, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwano, M.; Arii, S.; Monden, K.; Ishiguro, S.; Nakamura, T.; Mizumoto, M.; Takeda, Y.; Fujioka, M.; Imamura, M. Amelioration of sinusoidal endothelial cell damage by Kupffer cell blockade during cold preservation of rat liver. J. Surg. Res. 1997, 72, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaciuc, I.V.; Bagby, G.J.; Niesman, M.R.; Skrepnik, N.; Spitzer, J.J. Modulation of hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cell function by Kupffer cells: an example of intercellular communication in the liver. Hepatology 1994, 19, 464–470. [Google Scholar]
- Haisma, H.J.; Kamps, J.A.; Kamps, G.K.; Plantinga, J.A.; Rots, M.G.; Bellu, A.R. Polyinosinic acid enhances delivery of adenovirus vectors in vivo by preventing sequestration in liver macrophages. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braet, F.; Wisse, E. Structural and functional aspects of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrae: a review. Comp. Hepatol 2002, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisse, E.; De Zanger, R.B.; Charels, K.; Van Der Smissen, P.; McCuskey, R.S. The liver sieve: considerations concerning the structure and function of endothelial fenestrae, the sinusoidal wall and the space of Disse. Hepatology 1985, 5, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, F.; Wisse, E.; De Geest, B. The role of liver sinusoidal cells in hepatocyte-directed gene transfer. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, F.; Feng, Y.; Van Craeyveld, E.; Lievens, J.; Snoeys, J.; De Geest, B. Species differences in hepatocyte-directed gene transfer: implications for clinical translation. Curr. Gene Ther. 2009, 9, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisse, E.; Braet, F.; Duimel, H.; Vreuls, C.; Koek, G.; Olde Damink, S.W.; van den Broek, M.A.; De Geest, B.; Dejong, C.H.; Tateno, C.; et al. Fixation methods for electron microscopy of human and other liver. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 2851–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, J.; Snoeys, J.; Vekemans, K.; Van Linthout, S.; de Zanger, R.; Collen, D.; Wisse, E.; De Geest, B. The size of sinusoidal fenestrae is a critical determinant of hepatocyte transduction after adenoviral gene transfer. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Snoeys, J.; Lievens, J.; Wisse, E.; Jacobs, F.; Duimel, H.; Collen, D.; Frederik, P.; De Geest, B. Species differences in transgene DNA uptake in hepatocytes after adenoviral transfer correlate with the size of endothelial fenestrae. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisse, E.; Jacobs, F.; Topal, B.; Frederik, P.; De Geest, B. The size of endothelial fenestrae in human liver sinusoids: implications for hepatocyte-directed gene transfer. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H. Comparative observation of the recombinant adeno-associated virus 2 using transmission electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. Microsc. Microanal. 2007, 13, 384–389. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Bu, W.; Bhatia, S.; Hare, J.; Somasundaram, T.; Azzi, A.; Chapman, M.S. The atomic structure of adeno-associated virus (AAV-2), a vector for human gene therapy. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10405–10410. [Google Scholar]
- Govindasamy, L.; Padron, E.; McKenna, R.; Muzyczka, N.; Kaludov, N.; Chiorini, J.A.; Agbandje-McKenna, M. Structurally mapping the diverse phenotype of adeno-associated virus serotype 4. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11556–11570. [Google Scholar]
- DiMattia, M.A.; Nam, H.J.; Van Vliet, K.; Mitchell, M.; Bennett, A.; Gurda, B.L.; McKenna, R.; Olson, N.H.; Sinkovits, R.S.; Potter, M.; et al. Structural insight into the unique properties of adeno-associated virus serotype 9. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6947–6958. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.J.; Lane, M.D.; Padron, E.; Gurda, B.; McKenna, R.; Kohlbrenner, E.; Aslanidi, G.; Byrne, B.; Muzyczka, N.; Zolotukhin, S.; et al. Structure of adeno-associated virus serotype 8, a gene therapy vector. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12260–12271. [Google Scholar]
- Szilagyi, J.F.; Berriman, J. Herpes simplex virus L particles contain spherical membrane-enclosed inclusion vesicles. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 1749–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Rizzo, M.A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Huang, L. Characterization of cationic lipid-protamine-DNA (LPD) complexes for intravenous gene delivery. Gene Ther. 1998, 5, 930–937. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, R. Liposomes: applications in medicine. J. Biomater. Appl. 2001, 16, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raper, S.E.; Yudkoff, M.; Chirmule, N.; Gao, G.P.; Nunes, F.; Haskal, Z.J.; Furth, E.E.; Propert, K.J.; Robinson, M.B.; Magosin, S.; et al. A pilot study of in vivo liver-directed gene transfer with an adenoviral vector in partial ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Budker, V.; Wolff, J.A. High levels of foreign gene expression in hepatocytes after tail vein injections of naked plasmid DNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 1735–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herweijer, H.; Wolff, J.A. Gene therapy progress and prospects: hydrodynamic gene delivery. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Suda, T.; Gao, X.; Stolz, D.B.; Liu, D. Structural impact of hydrodynamic injection on mouse liver. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wisse, E.; De Zanger, R.B.; Jacobs, R.; McCuskey, R.S. Scanning electron microscope observations on the structure of portal veins, sinusoids and central veins in rat liver. Scan Electron. Microsc. 1983, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.Y.; He, C.Y.; Ehrhardt, A.; Kay, M.A. Minicircle DNA vectors devoid of bacterial DNA result in persistent and high-level transgene expression in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2003, 8, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; He, C.Y.; Meuse, L.; Kay, M.A. Silencing of episomal transgene expression by plasmid bacterial DNA elements in vivo. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, F.; Snoeys, J.; Feng, Y.; Van Craeyveld, E.; Lievens, J.; Armentano, D.; Cheng, S.H.; De Geest, B. Direct comparison of hepatocyte-specific expression cassettes following adenoviral and nonviral hydrodynamic gene transfer. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 594–603. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Sawyer, G.J.; Collins, L.; Fabre, J.W. Regional hydrodynamic gene delivery to the rat liver with physiological volumes of DNA solution. J. Gene Med. 2004, 6, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, S.J.; Baskin, K.M.; Hodges, B.L.; Chu, Q.; Gates, A.; Dreusicke, R.; Anderson, S.; Scheule, R.K. Development of catheter-based procedures for transducing the isolated rabbit liver with plasmid DNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino, H.; Hashizume, K.; Kobayashi, E. Naked plasmid DNA transfer to the porcine liver using rapid injection with large volume. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Alino, S.F.; Herrero, M.J.; Noguera, I.; Dasi, F.; Sanchez, M. Pig liver gene therapy by noninvasive interventionist catheterism. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, J.W.; Grehan, A.; Whitehorne, M.; Sawyer, G.J.; Dong, X.; Salehi, S.; Eckley, L.; Zhang, X.; Seddon, M.; Shah, A.M.; et al. Hydrodynamic gene delivery to the pig liver via an isolated segment of the inferior vena cava. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T.; Suda, K.; Liu, D. Computer-assisted hydrodynamic gene delivery. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geest, B.R.; Van Linthout, S.A.; Collen, D. Humoral immune response in mice against a circulating antigen induced by adenoviral transfer is strictly dependent on expression in antigen-presenting cells. Blood 2003, 101, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar]
- Follenzi, A.; Battaglia, M.; Lombardo, A.; Annoni, A.; Roncarolo, M.G.; Naldini, L. Targeting lentiviral vector expression to hepatocytes limits transgene-specific immune response and establishes long-term expression of human antihemophilic factor IX in mice. Blood 2004, 103, 3700–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, L.; Morral, N.; Zhou, H.; Garcia, R.; Parks, R.J.; Kochanek, S.; Graham, F.L.; Lee, B.; Beaudet, A.L. Use of a liver-specific promoter reduces immune response to the transgene in adenoviral vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Jacobs, F.; Van Craeyveld, E.; Lievens, J.; Snoeys, J.; Van Linthout, S.; De Geest, B. The impact of antigen expression in antigen-presenting cells on humoral immune responses against the transgene product. Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- De Geest, B.; Van Linthout, S.; Lox, M.; Collen, D.; Holvoet, P. Sustained expression of human apolipoprotein A-I after adenoviral gene transfer in C57BL/6 mice: role of apolipoprotein A-I promoter, apolipoprotein A-I introns, and human apolipoprotein E enhancer. Hum. Gene Ther. 2000, 11, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Linthout, S.; Lusky, M.; Collen, D.; De Geest, B. Persistent hepatic expression of human apo A-I after transfer with a helper-virus independent adenoviral vector. Gene therapy 2002, 9, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar]
- De Geest, B.; Van Linthout, S.; Collen, D. Sustained expression of human apo A-I following adenoviral gene transfer in mice. Gene therapy 2001, 8, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingozzi, F.; Liu, Y.L.; Dobrzynski, E.; Kaufhold, A.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Arruda, V.R.; High, K.A.; Herzog, R.W. Induction of immune tolerance to coagulation factor IX antigen by in vivo hepatic gene transfer. J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 111, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Calne, R.Y.; Sells, R.A.; Pena, J.R.; Davis, D.R.; Millard, P.R.; Herbertson, B.M.; Binns, R.M.; Davies, D.A. Induction of immunological tolerance by porcine liver allografts. Nature 1969, 223, 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, A.W.; Knolle, P.A. Antigen-presenting cell function in the tolerogenic liver environment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamboat, Z.M.; Stableford, J.A.; Plitas, G.; Burt, B.M.; Nguyen, H.M.; Welles, A.P.; Gonen, M.; Young, J.W.; DeMatteo, R.P. Human liver dendritic cells promote T cell hyporesponsiveness. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, A.W.; Lu, L. Are dendritic cells the key to liver transplant tolerance? Immunol. Today 1999, 20, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordts, S.C.; Van Craeyveld, E.; Jacobs, F.; De Geest, B. Gene transfer for inherited metabolic disorders of the liver: immunological challenges. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 2542–2549. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Bell, P.; McMenamin, D.; Wilson, J.M. Hepatic gene transfer in neonatal mice by adeno-associated virus serotype 8 vector. Hum. Gene Ther. 2012, 23, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morral, N.; O'Neal, W.; Rice, K.; Leland, M.; Kaplan, J.; Piedra, P.A.; Zhou, H.; Parks, R.J.; Velji, R.; Aguilar-Cordova, E.; et al. Administration of helper-dependent adenoviral vectors and sequential delivery of different vector serotype for long-term liver-directed gene transfer in baboons. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12816–12821. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, F.A.; Furth, E.E.; Wilson, J.M.; Raper, S.E. Gene transfer into the liver of nonhuman primates with E1-deleted recombinant adenoviral vectors: safety of readministration. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Schnell, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Tazelaar, J.; Gao, G.P.; Yu, Q.C.; Qian, R.; Chen, S.J.; Varnavski, A.N.; LeClair, C.; Raper, S.E.; et al. Activation of innate immunity in nonhuman primates following intraportal administration of adenoviral vectors. Mol. Ther. 2001, 3, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geest, B.; Snoeys, J.; Van Linthout, S.; Lievens, J.; Collen, D. Elimination of innate immune responses and liver inflammation by PEGylation of adenoviral vectors and methylprednisolone. Hum. Gene Ther. 2005, 16, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaiss, A.K.; Liu, Q.; Bowen, G.P.; Wong, N.C.; Bartlett, J.S.; Muruve, D.A. Differential activation of innate immune responses by adenovirus and adeno-associated virus vectors. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 4580–4590. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Lu, Y.; Calcedo, R.; Grant, R.L.; Bell, P.; Wang, L.; Figueredo, J.; Lock, M.; Wilson, J.M. Biology of AAV serotype vectors in liver-directed gene transfer to nonhuman primates. Mol. Ther. 2006, 13, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai, H.; Sakurai, F.; Kawabata, K.; Sasaki, T.; Koizumi, N.; Huang, H.; Tashiro, K.; Kurachi, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Mizuguchi, H. Comparison of gene expression efficiency and innate immune response induced by Ad vector and lipoplex. J. Control Release 2007, 117, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Hemmi, H.; Akira, S.; Cheng, S.H.; Scheule, R.K.; Yew, N.S. Contribution of Toll-like receptor 9 signaling to the acute inflammatory response to nonviral vectors. Mol. Ther. 2004, 9, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Krieg, A.M. Direct immunologic activities of CpG DNA and implications for gene therapy. J. Gene Med. 1999, 1, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Alvira, M.R.; Lu, Y.; Calcedo, R.; Zhou, X.; Wilson, J.M. Clades of Adeno-associated viruses are widely disseminated in human tissues. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6381–6388. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.P.; Alvira, M.R.; Wang, L.; Calcedo, R.; Johnston, J.; Wilson, J.M. Novel adeno-associated viruses from rhesus monkeys as vectors for human gene therapy. Proc. Nat. Academy Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11854–11859. [Google Scholar]
- Chiorini, J.A.; Kim, F.; Yang, L.; Kotin, R.M. Cloning and characterization of adeno-associated virus type 5. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu, S.; Mizukami, H.; Young, N.S.; Brown, K.E. Nucleotide sequencing and generation of an infectious clone of adeno-associated virus 3. Virology 1996, 221, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Wilson, J.M. New recombinant serotypes of AAV vectors. Curr. Gene Ther. 2005, 5, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilwell, J.L.; Samulski, R.J. Adeno-associated virus vectors for therapeutic gene transfer. Biotechniques 2003, 34, 148–159. [Google Scholar]
- Surosky, R.T.; Urabe, M.; Godwin, S.G.; McQuiston, S.A.; Kurtzman, G.J.; Ozawa, K.; Natsoulis, G. Adeno-associated virus Rep proteins target DNA sequences to a unique locus in the human genome. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 7951–7959. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, R.O.; Miao, C.H.; Patijn, G.A.; Spratt, S.K.; Danos, O.; Nagy, D.; Gown, A.M.; Winther, B.; Meuse, L.; Cohen, L.K.; Thompson, A.R.; et al. Persistent and therapeutic concentrations of human factor IX in mice after hepatic gene transfer of recombinant AAV vectors. Nat. Genet. 1997, 16, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Niemeyer, G.P.; Herzog, R.W.; Mount, J.; Arruda, V.R.; Tillson, D.M.; Hathcock, J.; van Ginkel, F.W.; High, K.A.; Lothrop, C.D., Jr. Long-term correction of inhibitor-prone hemophilia B dogs treated with liver-directed AAV2-mediated factor IX gene therapy. Blood 2009, 113, 797–806. [Google Scholar]
- Nathwani, A.C.; Davidoff, A.M.; Hanawa, H.; Hu, Y.; Hoffer, F.A.; Nikanorov, A.; Slaughter, C.; Ng, C.Y.; Zhou, J.; Lozier, J.N.; et al. Sustained high-level expression of human factor IX (hFIX) after liver-targeted delivery of recombinant adeno-associated virus encoding the hFIX gene in rhesus macaques. Blood 2002, 100, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, H.; Storm, T.A.; Kay, M.A. Recruitment of single-stranded recombinant adeno-associated virus vector genomes and intermolecular recombination are responsible for stable transduction of liver in vivo. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 9451–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, H.; Yant, S.R.; Storm, T.A.; Fuess, S.; Meuse, L.; Kay, M.A. Extrachromosomal recombinant adeno-associated virus vector genomes are primarily responsible for stable liver transduction in vivo. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 6969–6976. [Google Scholar]
- Manno, C.S.; Arruda, V.R.; Pierce, G.F.; Glader, B.; Ragni, M.; Rasko, J.; Ozelo, M.C.; Hoots, K.; Blatt, P.; Konkle, B.; et al. Successful transduction of liver in hemophilia by AAV-Factor IX and limitations imposed by the host immune response. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- Mingozzi, F.; Maus, M.V.; Hui, D.J.; Sabatino, D.E.; Murphy, S.L.; Rasko, J.E.; Ragni, M.V.; Manno, C.S.; Sommer, J.; Jiang, H.; et al. CD8(+) T-cell responses to adeno-associated virus capsid in humans. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 419–422. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, H.; Thomas, C.E.; Storm, T.A.; Fuess, S.; Powell, S.; Wright, J.F.; Kay, M.A. A limited number of transducible hepatocytes restricts a wide-range linear vector dose response in recombinant adeno-associated virus-mediated liver transduction. J. Virol 2002, 76, 11343–11349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcedo, R.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Gao, G.; Lin, J.; Wilson, J.M. Worldwide epidemiology of neutralizing antibodies to adeno-associated viruses. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 381–390. [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff, A.M.; Gray, J.T.; Ng, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Spence, Y.; Bakar, Y.; Nathwani, A.C. Comparison of the ability of adeno-associated viral vectors pseudotyped with serotype 2, 5, and 8 capsid proteins to mediate efficient transduction of the liver in murine and nonhuman primate models. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Figueredo, J.; Calcedo, R.; Lin, J.; Wilson, J.M. Cross-presentation of adeno-associated virus serotype 2 capsids activates cytotoxic T cells but does not render hepatocytes effective cytolytic targets. Hum. Gene Ther. 2007, 18, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Bell, P.; McCarter, R.J.; He, J.; Calcedo, R.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Morizono, H.; Batshaw, M.L.; Wilson, J.M. Systematic evaluation of AAV vectors for liver directed gene transfer in murine models. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zincarelli, C.; Soltys, S.; Rengo, G.; Rabinowitz, J.E. Analysis of AAV serotypes 1–9 mediated gene expression and tropism in mice after systemic injection. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Couto, L.B.; Patarroyo-White, S.; Liu, T.; Nagy, D.; Vargas, J.A.; Zhou, S.; Scallan, C.D.; Sommer, J.; Vijay, S.; et al. Effects of transient immunosuppression on adenoassociated, virus-mediated, liver-directed gene transfer in rhesus macaques and implications for human gene therapy. Blood 2006, 108, 3321–3328. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Calcedo, R.; Nichols, T.C.; Bellinger, D.A.; Dillow, A.; Verma, I.M.; Wilson, J.M. Sustained correction of disease in naive and AAV2-pretreated hemophilia B dogs: AAV2/8 mediated, liver-directed gene therapy. Blood 2005.
- Thomas, C.E.; Storm, T.A.; Huang, Z.; Kay, M.A. Rapid uncoating of vector genomes is the key to efficient liver transduction with pseudotyped adeno-associated virus vectors. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3110–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Lu, H.; Chen, L.; Hauck, B.; Samulski, R.J.; Xiao, W. Existence of transient functional double-stranded DNA intermediates during recombinant AAV transduction. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13104–13109. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, S.C.; Dane, A.P.; Spinoulas, A.; Logan, G.J.; Alexander, I.E. Gene delivery to the juvenile mouse liver using AAV2/8 vectors. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, L.H.; Wang, L.; Somanathan, S.; Zhi, Y.; Figueredo, J.; Calcedo, R.; Sanmiguel, J.; Desai, R.A.; Chen, C.S.; Johnston, J.; et al. Heparin binding directs activation of T cells against adeno-associated virus serotype 2 capsid. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 967–971. [Google Scholar]
- Nathwani, A.C.; Tuddenham, E.G.; Rangarajan, S.; Rosales, C.; McIntosh, J.; Linch, D.C.; Chowdary, P.; Riddell, A.; Pie, A.J.; Harrington, C.; et al. Adenovirus-associated virus vector-mediated gene transfer in hemophilia B. New Eng. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar]
- McCarty, D.M.; Monahan, P.E.; Samulski, R.J. Self-complementary recombinant adeno-associated virus (scAAV) vectors promote efficient transduction independently of DNA synthesis. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Nathwani, A.C.; Gray, J.T.; Ng, C.Y.; Zhou, J.; Spence, Y.; Waddington, S.N.; Tuddenham, E.G.; Kemball-Cook, G.; McIntosh, J.; Boon-Spijker, M.; et al. Self-complementary adeno-associated virus vectors containing a novel liver-specific human factor IX expression cassette enable highly efficient transduction of murine and nonhuman primate liver. Blood 2006, 107, 2653–2661. [Google Scholar]
- Van Craeyveld, E.; Jacobs, F.; Gordts, S.C.; De Geest, B. Gene therapy for familial hypercholesterolemia. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 2575–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, F.; Wang, L. Adeno-associated viral vectors for correction of inborn errors of metabolism: progressing towards clinical application. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 2500–2515. [Google Scholar]
- Mingozzi, F.; Meulenberg, J.J.; Hui, D.J.; Basner-Tschakarjan, E.; Hasbrouck, N.C.; Edmonson, S.A.; Hutnick, N.A.; Betts, M.R.; Kastelein, J.J.; Stroes, E.S.; et al. AAV-1-mediated gene transfer to skeletal muscle in humans results in dose-dependent activation of capsid-specific T cells. Blood 2009, 114, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.L.; Li, H.; Mingozzi, F.; Sabatino, D.E.; Hui, D.J.; Edmonson, S.A.; High, K.A. Diverse IgG subclass responses to adeno-associated virus infection and vector administration. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirmule, N.; Propert, K.; Magosin, S.; Qian, Y.; Qian, R.; Wilson, J. Immune responses to adenovirus and adeno-associated virus in humans. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Boutin, S.; Monteilhet, V.; Veron, P.; Leborgne, C.; Benveniste, O.; Montus, M.F.; Masurier, C. Prevalence of serum IgG and neutralizing factors against adeno-associated virus (AAV) types 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, and 9 in the healthy population: implications for gene therapy using AAV vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallan, C.D.; Jiang, H.; Liu, T.; Patarroyo-White, S.; Sommer, J.M.; Zhou, S.; Couto, L.B.; Pierce, G.F. Human immunoglobulin inhibits liver transduction by AAV vectors at low AAV2 neutralizing titers in SCID mice. Blood 2006, 107, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar]
- Magami, Y.; Azuma, T.; Inokuchi, H.; Kokuno, S.; Moriyasu, F.; Kawai, K.; Hattori, T. Cell proliferation and renewal of normal hepatocytes and bile duct cells in adult mouse liver. Liver 2002, 22, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, T.; Qiao, C.; Zhou, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Xiao, X. Adeno-associated virus serotype 8 efficiently delivers genes to muscle and heart. Nat. Biotechnol 2005, 23, 321–328. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, S.C.; Spinoulas, A.; Carpenter, K.H.; Wilcken, B.; Kuchel, P.W.; Alexander, I.E. AAV2/8-mediated correction of OTC deficiency is robust in adult but not neonatal Spf(ash) mice. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, J.T.; Dehner, L.P. Pediatric Pathology; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nathwani, A.C.; Gray, J.T.; McIntosh, J.; Ng, C.Y.; Zhou, J.; Spence, Y.; Cochrane, M.; Gray, E.; Tuddenham, E.G.; Davidoff, A.M. Safe and efficient transduction of the liver after peripheral vein infusion of self-complementary AAV vector results in stable therapeutic expression of human FIX in nonhuman primates. Blood 2007, 109, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, D.A.; Correia, C.E.; Conlon, T.; Specht, A.; Verstegen, J.; Onclin-Verstegen, K.; Campbell-Thompson, M.; Dhaliwal, G.; Mirian, L.; Cossette, H.; et al. Adeno-associated virus-mediated correction of a canine model of glycogen storage disease type Ia. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Xie, Q.; Wilson, J.M.; Gao, G. Adenovirus-adeno-associated virus hybrid for large-scale recombinant adeno-associated virus production. Hum. Gene Ther. 2009, 20, 922–929. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, N.; Knop, D.R.; Byrne, B.J. Large-scale adeno-associated viral vector production using a herpesvirus-based system enables manufacturing for clinical studies. Hum. Gene Ther. 2009, 20, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virag, T.; Cecchini, S.; Kotin, R.M. Producing recombinant adeno-associated virus in foster cells: overcoming production limitations using a baculovirus-insect cell expression strategy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2009, 20, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, L.H.; Xiao, R.; Lock, M.; Lin, J.; Korn, M.; Wilson, J.M. Efficient serotype-dependent release of functional vector into the culture medium during adeno-associated virus manufacturing. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Lock, M.; Alvira, M.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Samanta, A.; Toelen, J.; Debyser, Z.; Wilson, J.M. Rapid, simple, and versatile manufacturing of recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors at scale. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuso, E.; Mingozzi, F.; Montane, J.; Leon, X.; Anguela, X.M.; Haurigot, V.; Edmonson, S.A.; Africa, L.; Zhou, S.; High, K.A.; et al. High AAV vector purity results in serotype- and tissue-independent enhancement of transduction efficiency. Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jacobs, F.; Gordts, S.C.; Muthuramu, I.; De Geest, B. The Liver as a Target Organ for Gene Therapy: State of the Art, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 1372-1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5121372
Jacobs F, Gordts SC, Muthuramu I, De Geest B. The Liver as a Target Organ for Gene Therapy: State of the Art, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceuticals. 2012; 5(12):1372-1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5121372
Chicago/Turabian StyleJacobs, Frank, Stephanie C. Gordts, Ilayaraja Muthuramu, and Bart De Geest. 2012. "The Liver as a Target Organ for Gene Therapy: State of the Art, Challenges, and Future Perspectives" Pharmaceuticals 5, no. 12: 1372-1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5121372
APA StyleJacobs, F., Gordts, S. C., Muthuramu, I., & De Geest, B. (2012). The Liver as a Target Organ for Gene Therapy: State of the Art, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceuticals, 5(12), 1372-1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5121372




