The Potential Therapeutic Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in Children with Food Allergies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Rationale for the Use of Infant Formulas Containing Probiotics in Cow’s Milk Allergy
| Effects within intestinal lumen | Effects at mucosal level | Effects beyond the intestinal mucosa |
|---|---|---|
| modulation of intestinal microflora | modulation of intestinal permeability | modulation of innate/adaptive immune system |
| hydrolysis of antigenic peptides | stimulation of cell growth and differentiation | induction of oral tolerance |
| impact on the enteric nervous system |
3. Oral Tolerance and Intestinal Microflora
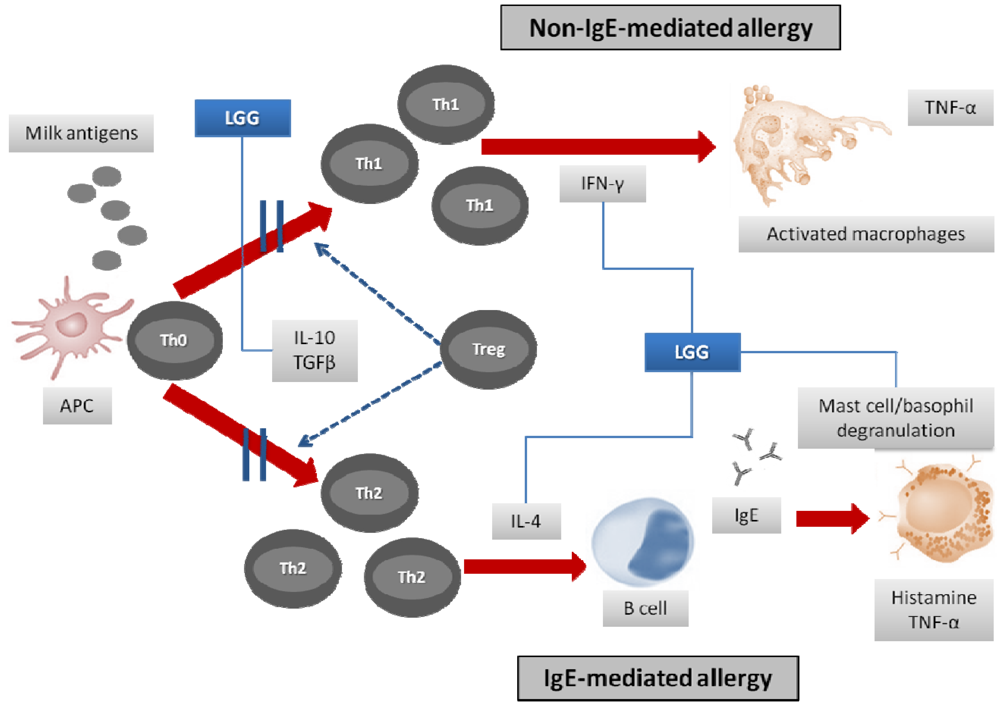
3.1. Symptoms’ Resolution
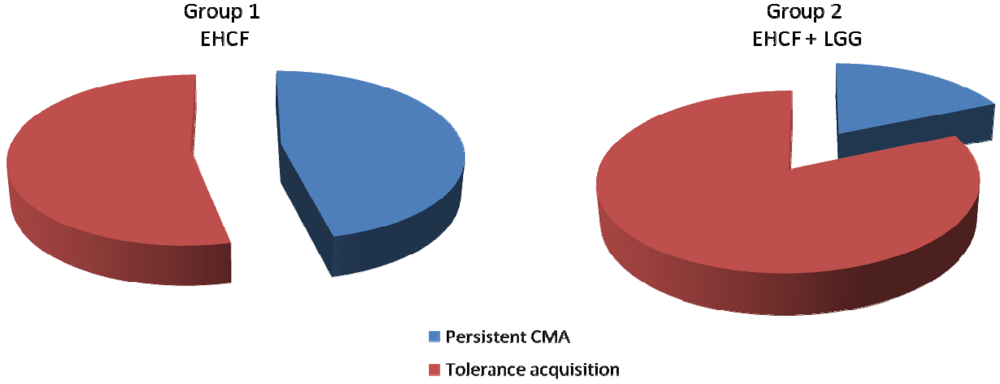
3.2. Tolerance Acquisition
3.3. Prevention of Atopic March and Intestinal Functional Disorders
4. Safety of LGG Added to Infant Formula
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Allen, K.J.; Koplin, J.J. The epidemiology of IgE-mediated food allergy and anaphylaxis Immun. Allergy Clin. North Am. 2012, 32, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apps, J.R.; Beattie, R.M. Cow's milk allergy in children. Cont. Med. Educ. 2009, 339, b2275. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Høst, A.; Halken, S.; Jacobsen, HP.; Christensen, A.E.; Herskind, A.M.; Plesner, K. Clinical course of cow's milk protein allergy/intolerance and atopic diseases in childhood. Pediatr. Allergy Immun. 2002, 13, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skripak, J.M.; Matsui, E.C.; Mudd, K.; Wood, R.A. The natural history of IgE-mediated cow’s milk allergy. JAllergyClin. Immun. 2007, 120, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, Y.; Segal, N.; Garty, B.; Danon, Y.L. Lessons from the clinical course of IgE-mediated cow milk allergy in Israel. Pediatr. Allergy Immun. 2007, 18, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneepkens, C.M.; Meijer, Y. Clinical practice. Diagnosis and treatment of cow's milk allergy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 168, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Ö. Various effects of different probiotic strains in allergic disorders: An update from laboratory and clinical data. Clin. Exp. Immun. 2010, 160, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Ö. Gut flora development in infancy and its effect on immune system (in Turkish). ÇocukEnf. Derg. (J. Pediatr. Inf.) 2009, 3, 202–203. [Google Scholar]
- Agheyisi, R. The Probiotics Market: Ingredients,Supplements,Foods. BCC Research. Report: FOD013D. Available online: http://www.bccresearch.com/report/nutraceuticals-markets-processing-technologies-fod013d.html (accessed on 18 June 2012).
- Yan, F.; Polk, D.B. Probiotics: progress toward novel therapies for intestinal diseases. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 26, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkstén, B.; Sepp, E.; Julge, K.; Voor, T.; Mikelsaar, M. Allergy developmentand the intestinal microflora during the first year of life. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2001, 108, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, H.J.; Wildeboer-Veloo, A.C.; Raangs, G.C.; Wagendorp, A.A.; Klijn, N.; Bindels, J.G.; Welling, G.W. Analysis of intestinal flora development in breast-fed and formula-fed infants by using molecular identification and detection methods. J. Pediatr. Gastr. Nutr. 2000, 30, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalliomaki, M.; Kirjavainen, P.; Eerola, E.; Kero, P.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Distinct patterns of neonatal gut microflora in infants in whom atopy was and was not developing. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2001, 107, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, P.M.; Ossa, J.C.; Johnson-Henry, K. Unraveling Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2009, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sütas, Y.; Soppi, E.; Korhonen, H.; Syväoja, E.L.; Saxelin, M.; Rokka, T.; Isolauri, E. Suppression of lymphocyte proliferation in vitro by bovine caseins hydrolyzed with Lactobacillus casei GG-derived enzymes. J. Allergy Clin. Immu. 1996, 98, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Cao, H.; Cover, T.L.; Washington, M.K.; Polk, D.B. Soluble proteins produced by probiotic bacteria regulate intestinal epithelial cell survival and growth. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourbeyre, P.; Denery, S.; Bodinier, M. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics: Impact on the gut immune system and allergic reactions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni Canani, R.; Di Costanzo, M.; Leone, L.; Bedogni, G.; Brambilla, P.K; Cianfarani, S.; Nobili, V.M; Pietrobelli, A.; Agostoni, C. Epigenetic mechanisms elicited by nutrition in early life. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2011, 24, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni Canani, R.; Di Costanzo, M.; Leone, L. The epigenetic effects of butyrate: Potential therapeutic implications for clinical practice. Clin. Epigenetics 2012, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowat, A.M. Anatomical basis of tolerance and immunity to intestinal antigens. Nat. Rev. Immun. 2003, 3, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vighi, G.; Marcucci, F.; Sensi, L.; Di Cara, G.; Frati, F. Allergy and the gastrointestinal system. Clin. Exp. Immun. 2008, 153, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, S. Regulation of the development of type 2 T-helper cells in allergy. Curr. Opin. Immun. 1994, 6, 838–846. [Google Scholar]
- Sudo, N.; Sawamura, S.A.; Tanaka, K.; Aiba, Y.; Kubo, C.; Koga, Y. The requirement of intestinal bacterial flora for the development of an IgE production system fully susceptible to oral tolerance induction. J. Immun. 1997, 159, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, B.; Prioult, G.; Hacini-Rachinel, F.; Moine, D.; Bruttin, A.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Labellie, C.; Nicolis, I.; Berger, B.; Mercenier, A. Infant gut microbiota is protective against cow's milk allergy in mice despite immature ileal T-cell response. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 79, 192–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kalliomaki, M.; Antoine, J.M.; Herz, U.; Rijkers, G.T.; Wells, J.M.; Mercenier, A. Guidance for substantiating the evidence for beneficial effects of probiotics: Prevention and management of allergic diseases by probiotics. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni Canani, R.; Ruotolo, S.; Discepolo, V.; Troncone, R. The diagnosis of food allergy in children. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2008, 20, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majamaa, H.; Isolauri, E. Probiotics: A novel approach in the management of food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 1997, 99, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isolauri, E.; Arvola, T.; Sutas, Y.; Moilanen, E.; Salminen, S. Probiotics in the management of atopic eczema. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 1604–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri, E. Studies on Lactobacillus GG in food hypersensitivity disorders. Nutr. Today Suppl. 1996, 31, 285–315. [Google Scholar]
- Nermes, M.; Kantele, J.M.; Atosuo, T.J.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Interaction of orally administered Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG with skin and gut microbiota and humoral immunity in infants with atopic dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 41, 370–377. [Google Scholar]
- Pohjavuori, E.; Viljanen, M.; Korpela, R.; Kuitunen, M.; Tiittanen, M.; Vaarala, O.; Savilahti, E. Lactobacillus GG effect in increasing IFN-γ production in infants with cow’s milk allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2004, 114, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, M.E.; Laforgia, N.; Fanelli, M.; Laneve, A.; Grosso, R.; Lifschitz, C. Lactobacillus GG improves recovery in infants with blood in the stools and presumptive allergic colitis compared with extensively hydrolyzed formula alone. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hol, J.; van Leer, E.H.; Elink Schuurman, B.E.; de Ruiter, L.F.; Samsom, J.N.; Hop, W.; Neijens, H.J.; de Jongste, J.C.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E. Cow's Milk Allergy Modified by Elimination and Lactobacilli study group. The acquisition of tolerance toward cow's milk through probiotic supplementation: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2008, 121, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canani, R.B.; Nocerino, R.; Terrin, G.; Coruzzo, A.; Cosenza, L.; Leone, L.; Troncone, R. Effect of extensively hydrolyzed casein formula supplemented with Lactobacillus GG on tolerance acquisition in infants with cow’s milk allergy: A randomized trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2012, 129, 580–582. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, B.R. The allergic march: Can we prevent allergies and asthma? Otolaryngol Clin. North Am. 2011, 44, 765–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saps, M.; Lu, P.; Bonilla, S. Cow’s-milk allergy is a risk factor for the development of FGIDs in children. J. Ped. Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011, 52, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseaux, C.; Thuru, X.; Gelot, A.; Barnich, N.; Neut, C.; Dubuquoy, L.; Dubuquoy, C.; Merour, E.; Geboes, K.; Chamaillard, M.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus modulates intestinal pain and induces opioid and cannabinoid receptors. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawrońska, A.; Dziechciarz, P.; Horvath, A.; Szajewska, H. A randomized double blind placebo controlled trial of Lactobacillus GG for abdominal pain disorders in children. Aliment Pharm. Ther. 2007, 25, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Muraro, A.; Hoekstra, M.O.; Meijer, Y.; Lifschitz, C.; Wampler, J.L.; Harris, C.; Scalabrin, D.M. Extensively hydrolysed casein formula supplemented with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG maintains hypoallergenic status: Randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. BMJ Open 2012, 5, 2. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Berni Canani, R.; Di Costanzo, M.; Pezzella, V.; Cosenza, L.; Granata, V.; Terrin, G.; Nocerino, R. The Potential Therapeutic Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in Children with Food Allergies. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 655-664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5060655
Berni Canani R, Di Costanzo M, Pezzella V, Cosenza L, Granata V, Terrin G, Nocerino R. The Potential Therapeutic Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in Children with Food Allergies. Pharmaceuticals. 2012; 5(6):655-664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5060655
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerni Canani, Roberto, Margherita Di Costanzo, Vincenza Pezzella, Linda Cosenza, Viviana Granata, Gianluca Terrin, and Rita Nocerino. 2012. "The Potential Therapeutic Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in Children with Food Allergies" Pharmaceuticals 5, no. 6: 655-664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5060655
APA StyleBerni Canani, R., Di Costanzo, M., Pezzella, V., Cosenza, L., Granata, V., Terrin, G., & Nocerino, R. (2012). The Potential Therapeutic Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in Children with Food Allergies. Pharmaceuticals, 5(6), 655-664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph5060655





