Molecular Model of Plasma PAF Acetylhydrolase-Lipoprotein Association: Insights from the Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
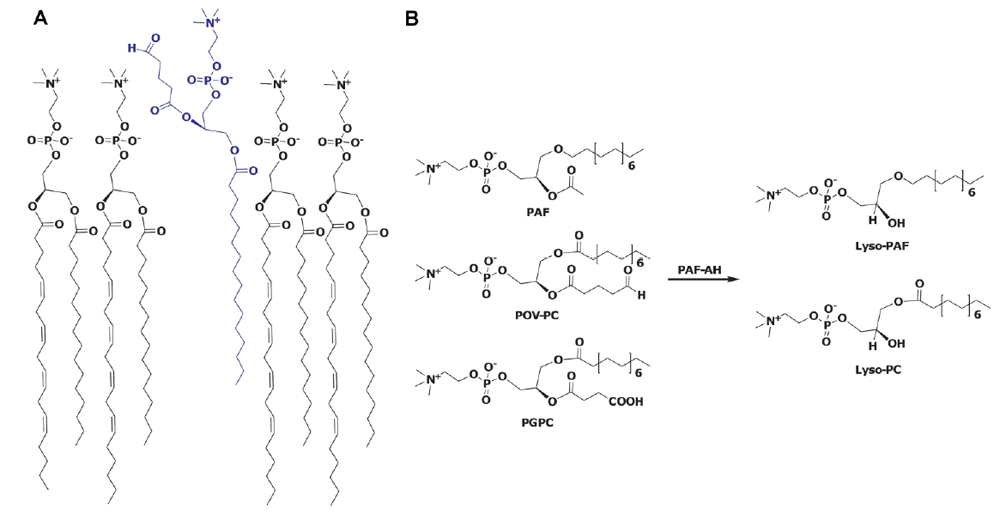
2. Physiological Role of Plasma PAF-AH
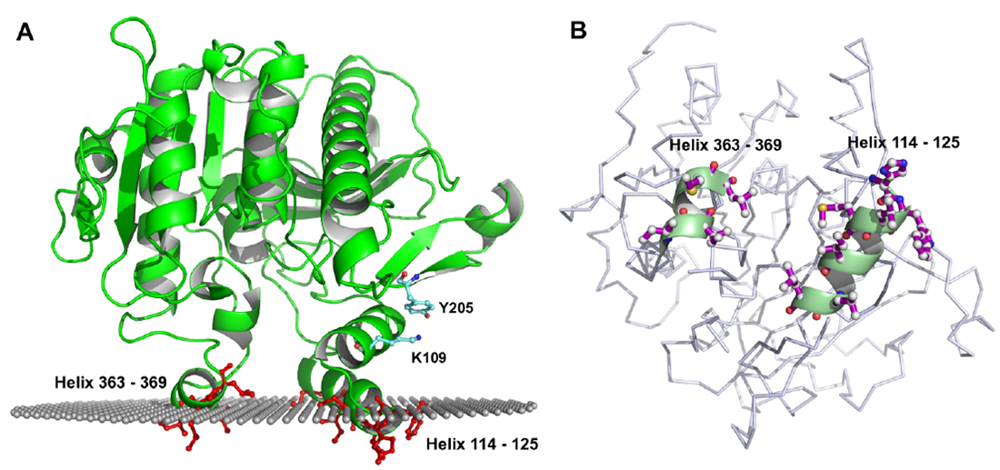
| i-face amino acids | Charged amino acids | |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Patch | Acidic Patch | |
| Helix 114–125: H114*, W115*, L116*, M117*, I120, L123, L124 Helix 363–369: I364, I365, M368*, L369* | K55, R58, K363, K101, R122 H367*, K370* | D374, D376, D382, D401, D403, D406, D412, D413, E414 |
3. Plasma PAF-AH Association with Lipoproteins
3.1. Plasma PAF-AH binding to LDL
3.2. Plasma PAF-AH binding to HDL
4. Current Knowledge of the Determinants of PAF-AH Binding to Lipoproteins
5. Molecular Model of Lipoprotein-PAF-AH Association: Hints from the Structure
5.1. Role of Hydrophobic and Aromatic Residues

5.2. Role of Y205
5.3. Role of Glycosylation in the Interaction of Plasma PAF-AH with Lipoproteins
5.4. Role of Charged Amino Acids in the Interaction with Lipoproteins
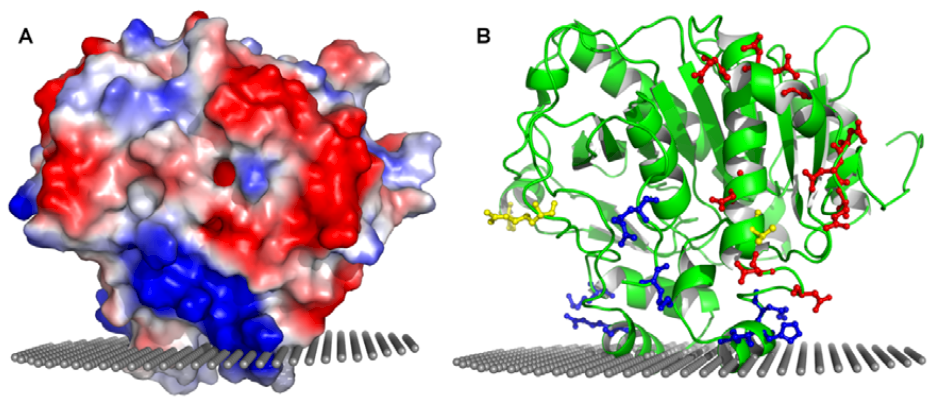
5.5. Number of Plasma PAF-AH Molecule Per Lipoprotein Molecule
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Farr, R.S.; Cox, C.P.; Wardlow, M.L.; Jorgensen, R. Preliminary studies of an acid-labile factor (ALF) in human sera that inactivates platelet-activating factor (PAF). Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1980, 15, 318–330. [Google Scholar]
- Blank, M.L.; Lee, T.; Fitzgerald, V.; Snyder, F. A specific acetylhydrolase for 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (a hypotensive and platelet-activating lipid). J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, G.A.; McIntyre, T.M.; Prescott, S.M.; Stafforini, D.M. The platelet-activating factor signaling system and its regulators in syndromes of inflammation and thrombosis. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, S294–S301. [Google Scholar]
- Six, D.A.; Dennis, E.A. The expanding superfamily of phospholipase A(2) enzymes: Classification and characterization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1488, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hattori, K.; Hattori, M.; Adachi, H.; Tsujimoto, M.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Purification and characterization of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase II from bovine liver cytosol. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 22308–22313. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, M.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Purification and characterization of bovine brain platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 18748–18753. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, U.; Bahnson, B.J. Crystal structure of human plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase: Structural implication to lipoprotein binding and catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31617–31624. [Google Scholar]
- Min, J.H.; Wilder, C.; Aoki, J.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K.; Paul, L.; Gelb, M.H. Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolases: Broad substrate specificity and lipoprotein binding does not modulate the catalytic properties of the plasma enzyme. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 4539–4549. [Google Scholar]
- Stremler, K.E.; Stafforini, D.M.; Prescott, S.M.; McIntyre, T.M. Human plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Oxidatively fragmented phospholipids as substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 11095–11103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stafforini, D.M.; McIntyre, T.M.; Carter, M.E.; Prescott, S.M. Human plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Association with lipoprotein particles and role in the degradation of platelet-activating factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 4215–4222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sudhir, K. Clinical review: Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, a novel inflammatory biomarker and independent risk predictor for cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 3100–3105. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.L. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2: An independent predictor of coronary artery disease events in primary and secondary prevention. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 23F–33F. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig, W.; Khuseyinova, N. Lipoprotein-associated and secretory phospholipase A2 in cardiovascular disease: The epidemiological evidence. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2009, 23, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Carlquist, J.F.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Anderson, J.L. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2: A new biomarker for cardiovascular risk assessment and potential therapeutic target. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2007, 7, 511–517. [Google Scholar]
- Corson, M.A.; Jones, P.H.; Davidson, M.H. Review of the evidence for the clinical utility of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 as a cardiovascular risk marker. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, F41–F50. [Google Scholar]
- Boden, G.; She, P.; Mozzoli, M.; Cheung, P.; Gumireddy, K.; Reddy, P.; Xiang, X.; Luo, Z.; Ruderman, N. Free fatty acids produce insulin resistance and activate the proinflammatory nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in rat liver. Diabetes 2005, 54, 3458–3465. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, S.S.; Steinberg, H.O. FFAs: Do they play a role in vascular disease in the insulin resistance syndrome? Curr. Diab. Rep. 2005, 5, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata-Kaneko, S.; Wakatsuki, Y.; Usui, T.; Matsunaga, Y.; Itoh, T.; Nishi, E.; Kume, N.; Kita, T. Lysophosphatidylcholine upregulates CD40 ligand expression in newly activated human CD4+ T cells. FEBS Lett. 1998, 433, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kume, N.; Gimbrone, M.A. Lysophosphatidylcholine transcriptionally induces growth factor gene expression in cultured human endothelial cells. J. Clin. Invest. 1994, 93, 907–911. [Google Scholar]
- Karabina, S.A.; Ninio, E. Plasma PAF-acetylhydrolase: An unfulfilled promise? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1761, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilensky, R.L.; Macphee, C.H. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) and atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2009, 20, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Lomize, A.L.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Lomize, M.A.; Mosberg, H.I. Positioning of proteins in membranes: A computational approach. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 1318–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Lomize, M.A.; Lomize, A.L.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Mosberg, H.I. OPM: Orientations of proteins in membranes database. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 623–625. [Google Scholar]
- McCall, M.R.; La Belle, M.; Forte, T.M.; Krauss, R.M.; Takanami, Y.; Tribble, D.L. Dissociable and nondissociable forms of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase in human plasma LDL: Implications for LDL oxidative susceptibility. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1437, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tselepis, A.D.; Karabina, S.A.; Stengel, D.; Piedagnel, R.; Chapman, M.J.; Ninio, E. N-linked glycosylation of macrophage-derived PAF-AH is a major determinant of enzyme association with plasma HDL. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Karabina, S.A.; Liapikos, T.A.; Grekas, G.; Goudevenos, J.; Tselepis, A.D. Distribution of PAF-acetylhydrolase activity in human plasma low-density lipoprotein subfractions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1213, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tselepis, A.D.; Dentan, C.; Karabina, S.A.; Chapman, M.J.; Ninio, E. PAF-degrading acetylhydrolase is preferentially associated with dense LDL and VHDL-1 in human plasma. Catalytic characteristics and relation to the monocyte-derived enzyme. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez, S.; Sanchez-Quesada, J.L.; Ribas, V.; Jorba, O.; Blanco-Vaca, F.; Gonzalez-Sastre, F.; Ordonez-Llanos, J. Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase is mainly associated with electronegative low-density lipoprotein subfraction. Circulation 2003, 108, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Quesada, J.L.; Benitez, S.; Ordonez-Llanos, J. Electronegative low-density lipoprotein. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2004, 15, 329–335. [Google Scholar]
- Blencowe, C.; Hermetter, A.; Kostner, G.M.; Deigner, H.P. Enhanced association of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase with lipoprotein (a) in comparison with low density lipoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 31151–31157. [Google Scholar]
- Erqou, S.; Kaptoge, S.; Perry, P.L.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Thompson, A.; White, I.R.; Marcovina, S.M.; Collins, R.; Thompson, S.G.; Danesh, J. Lipoprotein(a) concentration and the risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and nonvascular mortality. JAMA 2009, 302, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsimikas, S.; Witztum, J.L. The role of oxidized phospholipids in mediating lipoprotein(a) atherogenicity. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2008, 19, 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Stafforini, D.M.; Tjoelker, L.W.; McCormick, S.P.; Vaitkus, D.; McIntyre, T.M.; Gray, P.W.; Young, S.G.; Prescott, S.M. Molecular basis of the interaction between plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase and low density lipoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7018–7024. [Google Scholar]
- Gaubatz, J.W.; Gillard, B.K.; Massey, J.B.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Huang, M.; Lloyd, E.E.; Raya, J.L.; Yang, C.Y.; Pownall, H.J. Dynamics of dense electronegative low density lipoproteins and their preferential association with lipoprotein phospholipase A(2). J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 348–357. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, A.D.; Navab, M.; Hama, S.Y.; Sevanian, A.; Prescott, S.M.; Stafforini, D.M.; McIntyre, T.M.; Du, B.N.; Fogelman, A.M.; Berliner, J.A. Effect of platelet activating factor-acetylhydrolase on the formation and action of minimally oxidized low density lipoprotein. J. Clin. Invest. 1995, 95, 774–782. [Google Scholar]
- Tellis, C.C.; Tselepis, A.D. Tauhe role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) in atherosclerosis may depend on its lipoprotein carrier in plasma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1791, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marathe, G.K.; Zimmerman, G.A.; McIntyre, T.M. Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase, and not paraoxonase-1, is the oxidized phospholipid hydrolase of high density lipoprotein particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Theilmeier, G.; De Geest, B.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Stengel, D.; Michiels, C.; Lox, M.; Landeloos, M.; Chapman, M.J.; Ninio, E.; Collen, D.; Himpens, B.; Holvoet, P. HDL-associated PAF-AH reduces endothelial adhesiveness in apoE-/- mice. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar]
- Quarck, R.; De Geest, B.; Stengel, D.; Mertens, A.; Lox, M.; Theilmeier, G.; Michiels, C.; Raes, M.; Bult, H.; Collen, D.; Van Veldhoven, P.; Ninio, E.; Holvoet, P. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of human platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase prevents injury-induced neointima formation and reduces spontaneous atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation 2001, 103, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar]
- Tsaoussis, V.; Vakirtzi-Lemonias, C. The mouse plasma PAF acetylhydrolase: II. It consists of two enzymes both associated with the HDL. J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal 1994, 9, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gardner, A.A.; Reichert, E.C.; Topham, M.K.; Stafforini, D.M. Identification of a domain that mediates association of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase with high density lipoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 17099–17106. [Google Scholar]
- Noto, H.; Hara, M.; Karasawa, K.; Iso, O.N.; Satoh, H.; Togo, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Kosaka, T.; Kawamura, M.; Kimura, S.; Tsukamoto, K. Human plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase binds to all the murine lipoproteins, conferring protection against oxidative stress. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 829–835. [Google Scholar]
- Okamura, K.; Miura, S.; Zhang, B.; Uehara, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Kumagai, K.; Saku, K. Ratio of LDL- to HDL-associated platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase may be a marker of inflammation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circ. J. 2007, 71, 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Karabina, S.A.; Elisaf, M.; Bairaktari, E.; Tzallas, C.; Siamopoulos, K.C.; Tselepis, A.D. Increased activity of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase in low-density lipoprotein subfractions induces enhanced lysophosphatidylcholine production during oxidation in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 1997, 27, 595–602. [Google Scholar]
- Tsimihodimos, V.; Karabina, S.A.; Tambaki, A.P.; Bairaktari, E.; Miltiadous, G.; Goudevenos, J.A.; Cariolou, M.A.; Chapman, M.J.; Tselepis, A.D.; Elisaf, M. Altered distribution of platelet-activating factor- acetylhydrolase activity between LDL and HDL as a function of the severity of hypercholesterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 256–263. [Google Scholar]
- Kujiraoka, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Ishihara, M.; Ito, M.; Nagano, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Takahashi, S.; Ishi, J.; Tsuji, M.; Egashira, T.; Stepanova, I.P.; Miller, N.E.; Hattori, H. Altered distribution of plasma PAF-AH between HDLs and other lipoproteins in hyperlipidemia and diabetes mellitus. J. Lipid Res. 2003, 44, 2006–2014. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, W.S.; Thompson, T.B. The structure of apolipoprotein A-I in high density lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 22249–22253. [Google Scholar]
- Camejo, G.; Olofsson, S.O.; Lopez, F.; Carlsson, P.; Bondjers, G. Identification of Apo B-100 segments mediating the interaction of low density lipoproteins with arterial proteoglycans. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1988, 8, 368–377. [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber, K.H.; Rall, S.C. Human apolipoprotein B-100 heparin-binding sites. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 11097–11103. [Google Scholar]
- Hirose, N.; Blankenship, D.T.; Krivanek, M.A.; Jackson, R.L.; Cardin, A.D. Isolation and characterization of four heparin-binding cyanogen bromide peptides of human plasma apolipoprotein B. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 5505–5512. [Google Scholar]
- Stafforini, D.M.; Satoh, K.; Atkinson, D.L.; Tjoelker, L.W.; Eberhardt, C.; Yoshida, H.; Imaizumi, T.; Takamatsu, S.; Zimmerman, G.A.; McIntyre, T.M.; Gray, P.W.; Prescott, S.M. Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase deficiency. A missense mutation near the active site of an anti-inflammatory phospholipase. J. Clin. Invest. 1996, 97, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Yokota, M. Loss of activity of plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase due to a novel Gln281-->Arg mutation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 772–775. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, Y.; Ichihara, S.; Fujimura, T.; Yokota, M. Identification of the G994--> T missense in exon 9 of the plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase gene as an independent risk factor for coronary artery disease in Japanese men. Metabolism 1998, 47, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Stafforini, D.M.; Numao, T.; Tsodikov, A.; Vaitkus, D.; Fukuda, T.; Watanabe, N.; Fueki, N.; McIntyre, T.M.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Makino, S.; Prescott, S.M. Deficiency of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase is a severity factor for asthma. J. Clin. Invest. 1999, 103, 989–997. [Google Scholar]
- Unno, N.; Nakamura, T.; Kaneko, H.; Uchiyama, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Sugatani, J.; Miwa, M.; Nakamura, S. Plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase deficiency is associated with atherosclerotic occlusive disease in japan. J. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 32, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Stafforini, D.M. Functional consequences of mutations and polymorphisms in the coding region of the PAF acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) gene. Pharmaceuticals 2009, 2, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Wu, H.L.; Chao, T.H.; Tsai, L.M.; Lin, L.J.; Shi, G.Y.; Chen, J.H. Platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase A379V (exon 11) gene polymorphism is an independent and functional risk factor for premature myocardial infarction. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Ninio, E.; Tregouet, D.; Carrier, J.L.; Stengel, D.; Bickel, C.; Perret, C.; Rupprecht, H.J.; Cambien, F.; Blankenberg, S.; Tiret, L. Platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase and PAF-receptor gene haplotypes in relation to future cardiovascular event in patients with coronary artery disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, M.M.; Winkler, K.; Renner, W.; Winkelmann, B.R.; Seelhorst, U.; Wellnitz, B.; Boehm, B.O.; Marz, W. Genetic variants and haplotypes of lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2 and their influence on cardiovascular disease (The Ludwigshafen Risk and Cardiovascular Health Study). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mulgrew-Nesbitt, A.; Diraviyam, K.; Wang, J.; Singh, S.; Murray, P.; Li, Z.; Rogers, L.; Mirkovic, N.; Murray, D. The role of electrostatics in protein-membrane interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1761, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Srinivasan, P.; Bahnson, B.J. Molecular Model of Plasma PAF Acetylhydrolase-Lipoprotein Association: Insights from the Structure. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 541-557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030541
Srinivasan P, Bahnson BJ. Molecular Model of Plasma PAF Acetylhydrolase-Lipoprotein Association: Insights from the Structure. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(3):541-557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030541
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrinivasan, Prabhavathi, and Brian J. Bahnson. 2010. "Molecular Model of Plasma PAF Acetylhydrolase-Lipoprotein Association: Insights from the Structure" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 3: 541-557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030541
APA StyleSrinivasan, P., & Bahnson, B. J. (2010). Molecular Model of Plasma PAF Acetylhydrolase-Lipoprotein Association: Insights from the Structure. Pharmaceuticals, 3(3), 541-557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030541




