Inhaled Corticosteroids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of Action
| Increased transcription |
| • Lipocortin-1 |
| • β2-Adrenergic receptors |
| • Secretory leukocyte inhibitory protein |
| • IκB-α (inhibitor of NF-κB) |
| • Anti-inflammatory or inhibitory cytokines |
| IL-10, IL-12, IL-1 receptor antagonist |
| • Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1, inhibits MAP kinase pathways) |
| Decreased transcription |
| • Inflammatory cytokines |
| IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-11, IL-13, IL-15, TNFα, GM-CSF, SCF |
| • Chemokines |
| IL-8, RANTES, MIP-1α, eotaxin |
| • Inflammatory enzymes |
| Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), inducible cyclo-oxygenase (COX-2) |
| inducible phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) |
| • Inflammatory peptides |
| Endothelin-1 |
| • Mediator Receptors |
| Neurokinin (NK1)-, bradykinin (B2)-receptors |
| • Adhesion molecules |
| ICAM-1,VCAM-1 |
2.1. Cellular Effects
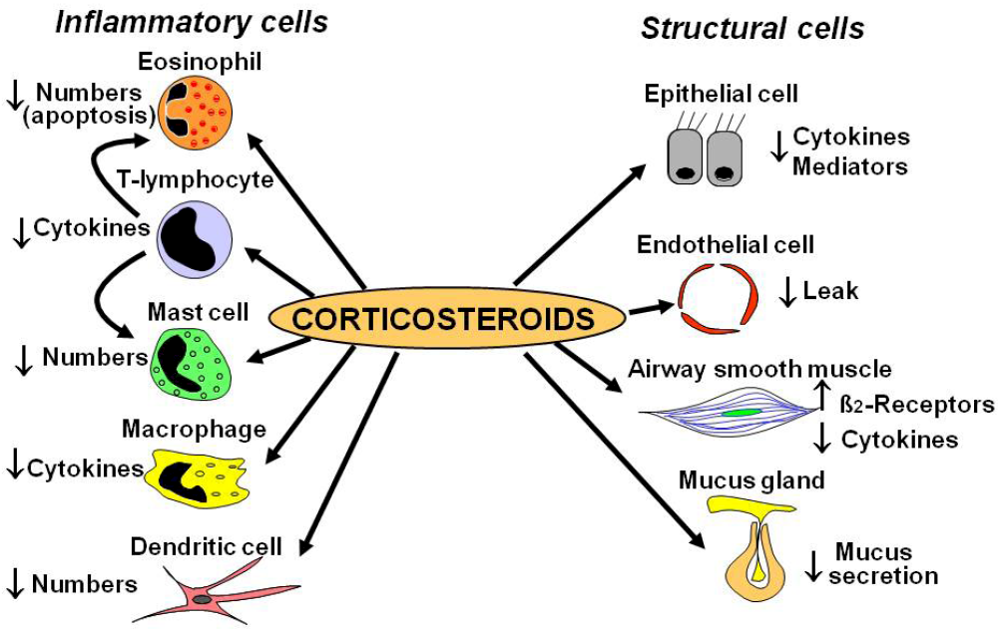
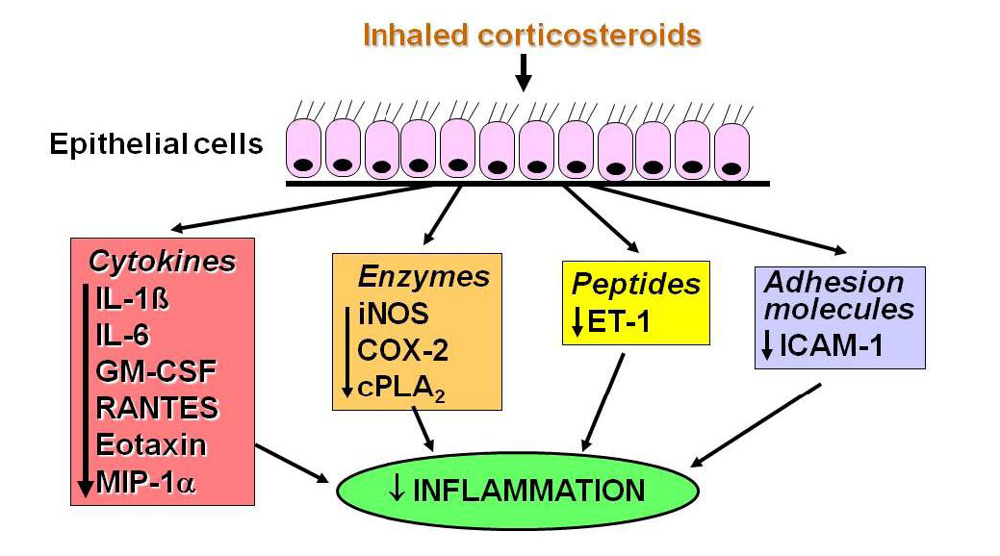
2.2. Glucocorticoid Receptors
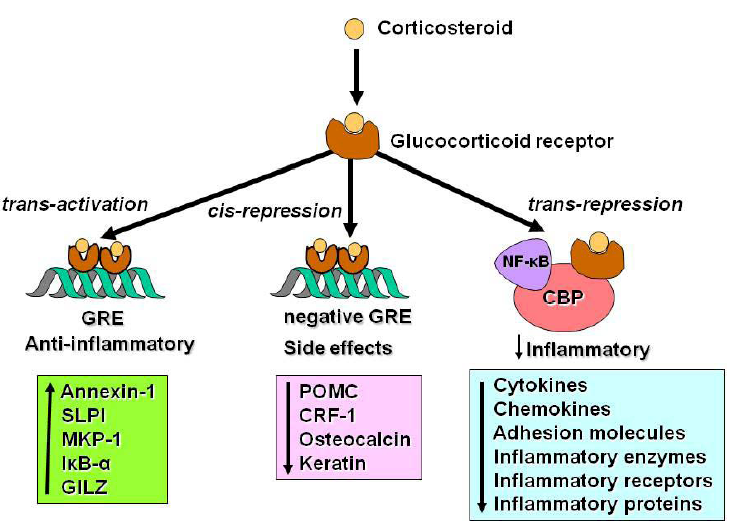
2.3. Switching off Inflammation
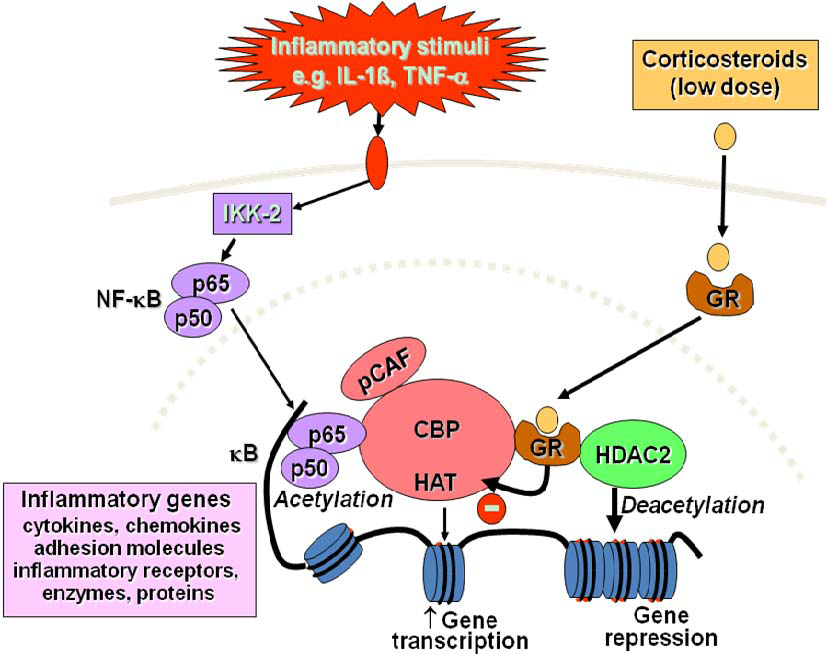
2.4. Corticosteroid Resistance
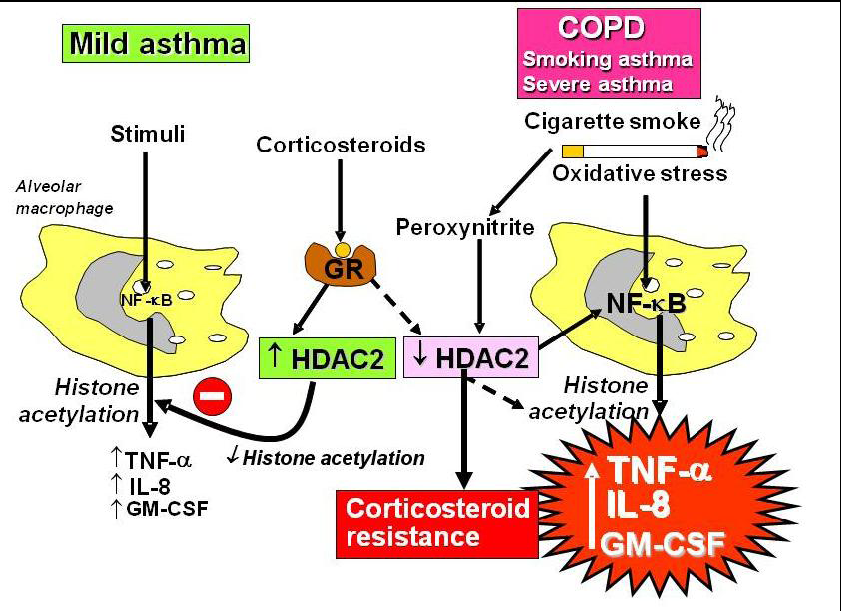
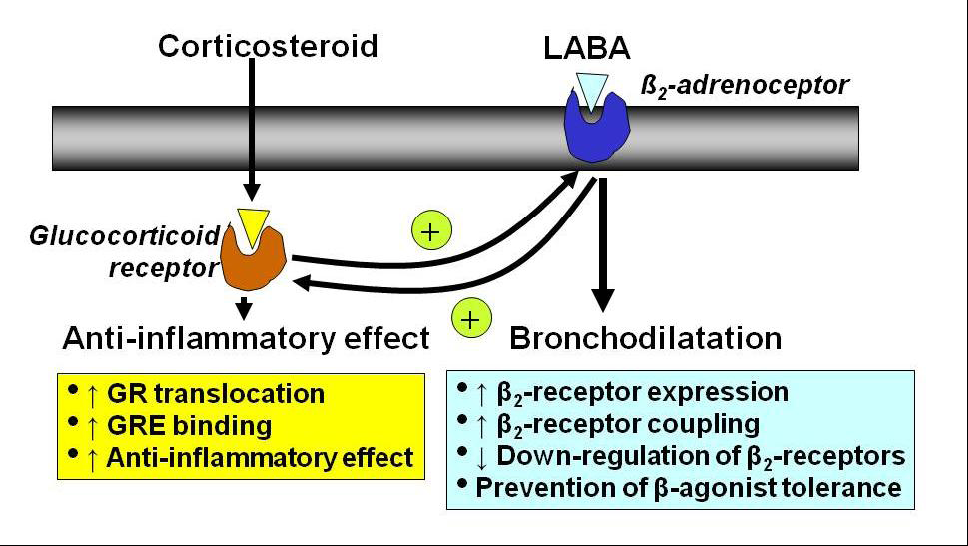
2.5. Interaction with β2-Adrenergic Receptors
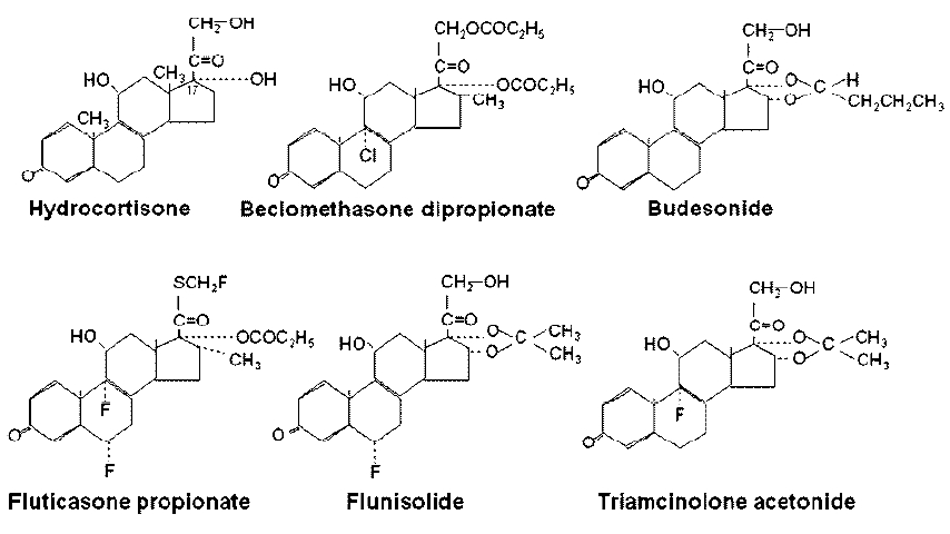
3. Pharmacokinetics

4. Clinical Use
4.1. Use in Asthma
4.2. Dose-Response Studies
4.3. Prevention of Irreversible Airway Changes in Asthma
4.4. Reduction in Mortality
4.5. Comparison between ICS
4.6. Clinical Application in Asthma Patients
4.7. Use in COPD
5. Add-on Therapy
5.1. Long-Acting β2-Agonists
5.2. Theophylline
5.3. Anti-Leukotrienes
6. Side Effects
| Local side effects |
| Dysphonia |
| Oropharyngeal candidiasis |
| Cough |
| Pneumonia (COPD patients) |
| Systemic side effects |
| Adrenal suppression |
| Growth suppression |
| Bruising |
| Osteoporosis |
| Cataracts |
| Glaucoma |
| Metabolic abnormalities (glucose, insulin, triglycerides) |
| Psychiatric disturbances |
6.1. Local Side Effects
6.2. Infections
6.3. Systemic Side Effects
References
- Barnes, P.J. How corticosteroids control inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 148, 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- Rhen, T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids--new mechanisms for old drugs. New Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.M. Glucocorticoid resistance in inflammatory diseases. Lancet 2009, 342, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, P.G.; Saltos, N.; Fakes, K. Acute anti-inflammatory effects of inhaled budesonide in asthma: a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ketchell, R.I.; Jensen, M.W.; Lumley, P.; Wright, A.M.; Allenby, M.I.; O'Connor, B.J. Rapid effect of inhaled fluticasone propionate on airway responsiveness to adenosine 5'-monophosphate in mild asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 603–606. [Google Scholar]
- Erin, E.M.; Zacharasiewicz, A.S.; Nicholson, G.C.; Tan, A.J.; Neighbour, H.; Engelstatter, R.; Hellwig, M.; Minn, K.O.; Barnes, P.J.; Hansel, T.T. Rapid anti-inflammatory effect of inhaled ciclesonide in asthma: a randomised, placebo-controlled study. Chest 2008. [CrossRef]
- Juniper, E.F.; Kline, P.A.; Yan Zieleshem, M.A.; Ramsdale, E.H.; O'Byrne, P.M.; Hargreave, F.E. Long-term effects of budesonide on airway responsiveness and clinical asthma severity in inhaled steroid-dependent asthmatics. Eur. Respir. J. 1990, 3, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis-Tuffin, L.J.; Cidlowski, J.A. The physiology of human glucocorticoid receptor beta (hGRbeta) and glucocorticoid resistance. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2006, 1069:1-9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujols, L.; Mullol, J.; Picado, C. Alpha and beta glucocorticoid receptors: relevance in airway diseases. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2007, 7, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, P.J. Corticosteroid effects on cell signalling. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 413–426. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A.R.; Martins, J.R.; Tchen, C.R. Role of dual specificity phosphatases in biological responses to glucocorticoids. J. Biol.Chem. 2008, 283, 25765–25769. [Google Scholar]
- Dostert, A.; Heinzel, T. Negative glucocorticoid receptor response elements and their role in glucocorticoid action. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 2807–2816. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.M.; Ito, K. Histone acetylation and deacetylation: importance in inflammatory lung diseases. Eur. Respi. J. 2005, 25, 552–563. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, L.; Lim, S.; Adcock, I.; Barnes, P.J.; Chung, K.F. Effects of inhaled corticosteroid therapy on expression and DNA-binding activity of nuclear factor-kB in asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 224–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, K.; Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.M. Glucocorticoid receptor recruitment of histone deacetylase 2 inhibits IL-1b-induced histone H4 acetylation on lysines 8 and 12. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 6891–6903. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, M.W.; Staples, K.J.; Smith, S.J.; Barnes, P.J.; Newton, R. Glucocorticoid inhibition of GM-CSF from T cells is independent of control by NF-kB and CLE0. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2004, 30, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brook, M.; Tchen, C.R.; Santalucia, T.; McIlrath, J.; Arthur, J.S.; Saklatvala, J.; Clark, A.R. Posttranslational regulation of tristetraprolin subcellular localization and protein stability by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 2408–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, N.C.; Spears, M. The influence of smoking on the treatment response in patients with asthma. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 5, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Adcock, I.M.; Barnes, P.J. Molecular mechanisms of corticosteroid resistance. Chest 2008, 134, 394–401. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, K.; Ito, M.; Elliott, W.M.; Cosio, B.; Caramori, G.; Kon, O.M.; Barczyk, A.; Hayashi, M.; Adcock, I.M.; Hogg, J.C.; Barnes, P.J. Decreased histone deacetylase activity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. New Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar]
- Hew, M.; Bhavsar, P.; Torrego, A.; Meah, S.; Khorasani, N.; Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.; Chung, K.F. Relative corticosteroid insensitivity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in severe asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, P.J. Role of HDAC2 in the pathophysiology of COPD. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 2009, 71, 451–464. [Google Scholar]
- Irusen, E.; Matthews, J.G.; Takahashi, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Chung, K.F.; Adcock, I.M. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase-induced glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation reduces its activity: Role in steroid-insensitive asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 649–657. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, J.G.; Ito, K.; Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.M. Defective glucocorticoid receptor nuclear translocation and altered histone acetylation patterns in glucocorticoid-resistant patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, P.J. Scientific rationale for combination inhalers with a long-acting b2-agonists and corticosteroids. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 19, 182–191. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, J.C.W.; Nishikawa, M.; Barnes, P.J. Glucocorticosteroids increase b2-adrenergic receptor transcription in human lung. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 12, L41–L46. [Google Scholar]
- Baraniuk, J.N.; Ali, M.; Brody, D.; Maniscalco, J.; Gaumond, E.; Fitzgerald, T.; Wonk, G.; Mak, J.C.W.; Bascom, R.; Barnes, P.J.; Troost, T. Glucocorticoids induce b2-adrenergic receptor function in human nasal mucosa. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 704–710. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, J.C.W.; Nishikawa, M.; Shirasaki, H.; Miyayasu, K.; Barnes, P.J. Protective effects of a glucocorticoid on down-regulation of pulmonary b2-adrenergic receptors in vivo. J. Clin. Invest. 1995, 96, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, J.C.; Chuang, T.T.; Harris, C.A.; Barnes, P.J. Increased expression of G protein-coupled receptor kinases in cystic fibrosis lung. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 436, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, M.; Johnson, P.R.; Rudiger, J.J.; King, G.G.; Ge, Q.; Burgess, J.K.; Anderson, G.; Tamm, M.; Black, J.L. Interaction between glucocorticoids and b2 agonists on bronchial airway smooth muscle cells through synchronised cellular signalling. Lancet 2002, 360, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Usmani, O.S.; Ito, K.; Maneechotesuwan, K.; Ito, M.; Johnson, M.; Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.M. Glucocorticoid receptor nuclear translocation in airway cells following inhaled combination therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit Care Med. 2005, 172, 704–712. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, P.J.; Pedersen, S.; Busse, W.W. Efficacy and safety of inhaled corticosteroids: an update. Am. J. Respir. Crit Care Med. 1998, 157, S1–S53. [Google Scholar]
- Lipworth, B.J. Systemic adverse effects of inhaled corticosteroid therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis [see comments]. Arch.Intern.Med. 1999, 159, 941–955. [Google Scholar]
- Derendorf, H.; Hochhaus, G.; Meibohm, B.; Mollmann, H.; Barth, J. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of inhaled corticosteroids. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 101, S440–S446. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, P.H.; Greening, A.P.; Crompton, G.K. Large volume spacer devices and the influence of high dose beclomethasone diproprionate on hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis function. Thorax 1993, 48, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Derendorf, H. Corticosteroid pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters and their relationship to safety and efficacy. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2005, 26, 327–335. [Google Scholar]
- Derendorf, H. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of inhaled ciclesonide. J. Clin.Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 782–789. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, E.D.; Hurd, S.S.; Barnes, P.J.; Bousquet, J.; Drazen, J.M.; Fitzgerald, M.; Gibson, P.; Ohta, K.; O'Byrne, P.; Pedersen, S.E.; Pizzichini, E.; Sullivan, S.D.; Wenzel, S.E.; Zar, H.J. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 143–178. [Google Scholar]
- Suissa, S.; Barnes, P.J. Inhaled corticosteroids in COPD: the case against. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Haahtela, T.; Jarvinen, M.; Kava, T.; Kiviranta, K.; Koskinen, S.; Lehtonen, K.; Nivander, K.; Persson, T.; Reinikainen, R.; Selroos, O.; Sovijarvi, A.; Stenius-Aarniala, B.; Svahn, T.; Tammivaara, R.; Laitinen, L.A. Comparison of a b2-agonist terbutaline with an inhaled steroid in newly detected asthma. New Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 388–392. [Google Scholar]
- Juniper, E.F.; Kline, P.A.; Vanzieleghem, M.A.; Ramsdale, E.H.; O'Byrne, P.M.; Hargreave, F.E. Effect of long-term treatment with an inhaled corticosteroid (budesonide) on airway hyperresponsiveness and clinical asthma in nonsteroid-dependent asthmatics. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1990, 142, 832–836. [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels, R.A.; Pedersen, S.; Busse, W.W.; Tan, W.C.; Chen, Y.Z.; Ohlsson, S.V.; Ullman, A.; Lamm, C.J.; O'Byrne, P.M. Early intervention with budesonide in mild persistent asthma: a randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Mash, B.; Bheekie, A.; Jones, P.W. Inhaled vs. oral steroids for adults with chronic asthma. Cochrane Database. Syst. Rev. 2000, 2, CD002160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jatakanon, A.; Lim, S.; Barnes, P.J. Changes in sputum eosinophils predict loss of asthma control. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Leuppi, J.D.; Salome, C.M.; Jenkins, C.R.; Anderson, S.D.; Xuan, W.; Marks, G.B.; Koskela, H.; Brannan, J.D.; Freed, R.; Andersson, M.; Chan, H.K.; Woolcock, A.J. Predictive markers of asthma exacerbation during stepwise dose reduction of inhaled corticosteroids. Am. J. Respir. Crit Care Med. 2001, 163, 406–412. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, W.E. Budesonide inhalation suspension for the treatment of asthma in infants and children. Drugs 2005, 65, 1973–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Busse, W.W.; Chervinsky, P.; Condemi, J.; Lumry, W.R.; Petty, T.L.; Rennard, S.; Townley, R.G. Budesonide delivered by Turbuhaler is effective in a dose- dependent fashion when used in the treatment of adult patients with chronic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 101, 457–463. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, N.P.; Jones, P.W. The dose-response characteristics of inhaled corticosteroids when used to treat asthma: an overview of Cochrane systematic reviews. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels, R.A.; Lofdahl, C.-G.; Postma, D.S.; Tattersfield, A.E.; O'Byrne, P.M.; Barnes, P.J.; Ullman, A. Effect of inhaled formoterol and budesonide on exacerbations of asthma. New Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.; Jatakanon, A.; John, M.; Gilbey, T.; O'Connor, B.J.; Chung, K.F.; Barnes, P.J. Effect of inhaled budesonide on lung function and airway inflammation. Assessment by various inflammatory markers in mild asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jatakanon, A.; Lim, S.; Chung, K.F.; Barnes, P.J. An inhaled steroid improves markers of inflammation in asymptomatic steroid-naive asthmatic patients. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 12, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Jatakanon, A.; Kharitonov, S.; Lim, S.; Barnes, P.J. Effect of differing doses of inhaled budesonide on markers of airway inflammation in patients with mild asthma. Thorax 1999, 54, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kharitonov, S.A.; Donnelly, L.E.; Montuschi, P.; Corradi, M.; Collins, J.V.; Barnes, P.J. Dose-dependent onset and cessation of action of inhaled budesonide on exhaled nitric oxide and symptoms in mild asthma. Thorax 2002, 57, 889–896. [Google Scholar]
- Sont, J.K.; Willems, L.N.; Bel, E.H.; van Krieken, J.H.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Sterk, P.J. Clinical control and histopathologic outcome of asthma when using airway hyperresponsiveness as an additional guide to long- term treatment. The AMPUL Study Group. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Green, R.H.; Brightling, C.E.; McKenna, S.; Hargadon, B.; Parker, D.; Bradding, P.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Pavord, I.D. Asthma exacerbations and sputum eosinophil counts: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 360, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaram, L.; Pizzichini, M.M.; Cook, R.J.; Boulet, L.P.; Lemiere, C.; Pizzichini, E.; Cartier, A.; Hussack, P.; Goldsmith, C.H.; Laviolette, M.; Parameswaran, K.; Hargreave, F.E. Determining asthma treatment by monitoring sputum cell counts: effect on exacerbations. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 483–494. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.D.; Cowan, J.O.; Brassett, K.P.; Herbison, G.P.; Taylor, D.R. Use of exhaled nitric oxide measurements to guide treatment in chronic asthma. New Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Dompeling, E.; Van Schayck, C.P.; Molema, J.; Folgering, H.; van Grusven, P.M.; van Weel, C. Inhaled beclomethasone improves the course of asthma and COPD. Eur. Resp. J. 1992, 5, 945–952. [Google Scholar]
- O'Byrne, P.M.; Pedersen, S.; Busse, W.W.; Tan, W.C.; Chen, Y.Z.; Ohlsson, S.V.; Ullman, A.; Lamm, C.J.; Pauwels, R.A. Effects of early intervention with inhaled budesonide on lung function in newly diagnosed asthma. Chest 2006, 129, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, P.; Scharling, H.; Ulrik, C.S.; Vestbo, J. Inhaled corticosteroids and decline of lung function in community residents with asthma. Thorax 2006, 61, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Haahtela, T.; Järvinsen, M.; Kava, T.; Kiviranta, K.; Koskinen, S.; Lemtonen, K.; Nikander, K.; Person, T.; Selroos, O.; Sovijäri, A.; Stenius-Aarniala, B.; Svahn, T.; Tammivaara, R.; Laitinen, L.A. Effects of reducing or discontinuing inhaled budesonide in patients with mild asthma. New Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 700–705. [Google Scholar]
- Agertoft, L.; Pedersen, S. Effects of long-term treatment with an inhaled corticosteroid on growth and pulmonary function in asthmatic children. Resp. Med. 1994, 5, 369–372. [Google Scholar]
- Selroos, O.; Pietinalcho, A.; Lofroos, A.-B.; Riska, A. Effect of early and late intervention with inhaled corticosteroids in asthma. Chest 1995, 108, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Suissa, S.; Ernst, P.; Benayoun, S.; Baltzan, M.; Cai, B. Low-dose inhaled corticosteroids and the prevention of death from asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 332–336. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, P.; Habbick, B.; Suissa, S.; Hemmelgarn, B.; Cockcroft, D.; Buist, A.S.; Horwitz, R.I.; McNutt, M.; Spitzer, W.O. Is the association between inhaled beta-agonist use and life-threatening asthma because of confounding by severity? Am. Rev.Respir. Dis. 1993, 148, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nelson, H.S.; Weiss, S.T.; Bleecker, E.R.; Yancey, S.W.; Dorinsky, P.M. The Salmeterol Multicenter Asthma Research Trial: a comparison of usual pharmacotherapy for asthma or usual pharmacotherapy plus salmeterol. Chest 2006, 129, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall, M.; Wijesinghe, M.; Perrin, K.; Harwood, M.; Beasley, R. Meta-analysis of the risk of mortality with salmeterol and the effect of concomitant inhaled corticosteroid therapy. Thorax 2010, 65, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, H.W. Comparison of inhaled corticosteroids: an update. Ann. Pharmacother. 2009, 43, 519–527. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, R.A.; Nayak, A.S.; Graft, D.F.; Lawrence, M.; Picone, F.J.; Ahmed, T.; Wolfe, J.; Vanderwalker, M.L.; Nolop, K.B.; Harrison, J.E. Mometasone furoate: efficacy and safety in moderate asthma compared with beclomethasone dipropionate. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001, 86, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, N.A.; Scott, L.J. Ciclesonide. Drugs 2004, 64, 511–519. [Google Scholar]
- Malo, J.-L.; Cartier, A.; Merland, N.; Ghezzo, H.; Burke, A.; Morris, J.; Jennings, B.H. Four-times-a-day dosing frequency is better than twice-a-day regimen in subjects requiring a high-dose inhaled steroid, budesonide, to control moderate to severe asthma. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 140, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Otulana, B.A.; Varma, N.; Bullock, A.; Higenbottam, T. High dose nebulized steroid in the treatment of chronic steroid-dependent asthma. Resp. Med. 1992, 86, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, G.; McMahon, A.D.; Twaddle, S.; Wood, S.F.; Ford, I.; Thomson, N.C. Stepping down inhaled corticosteroids in asthma: randomised controlled trial. Br. Med. J. 2003, 326, 1115. [Google Scholar]
- Rabe, K.F.; Hurd, S.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Buist, S.A.; Calverley, P.; Fukuchi, Y.; Jenkins, C.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R.; van Weel, C.; Zielinski, J. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of COPD - 2006 Update. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 532–555. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, I.A.; Fong, K.M.; Sim, E.H.; Black, P.N.; Lasserson, T.J. Inhaled corticosteroids for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, CD002991. [Google Scholar]
- Calverley, P.M.; Anderson, J.A.; Celli, B.; Ferguson, G.T.; Jenkins, C.; Jones, P.W.; Yates, J.C.; Vestbo, J. Salmeterol and fluticasone propionate and survival in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 775–789. [Google Scholar]
- Kankaanranta, H.; Lahdensuo, A.; Moilanen, E.; Barnes, P.J. Add-on therapy options in asthma not adequately controlled by inhaled corticosteroids: a comprehensive review. Respir. Res. 2004, 5, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Greening, A.P.; Ind, P.W.; Northfield, M.; Shaw, G. Added salmeterol versus higher-dose corticosteroid in asthma patients with symptoms on existing inhaled corticosteroid. Lancet 1994, 344, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Shrewsbury, S.; Pyke, S.; Britton, M. Meta-analysis of increased dose of inhaled steroid or addition of salmeterol in symptomatic asthma (MIASMA). BMJ 2000, 320, 1368–1373. [Google Scholar]
- O'Byrne, P.M.; Barnes, P.J.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R.; Runnerstrom, E.; Sandstrom, T.; Svensson, K.; Tattersfield, A. Low dose inhaled budesonide and formoterol in mild persistent asthma: the OPTIMA randomized trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit Care Med. 2001, 164, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, P.G.; Powell, H.; Ducharme, F.M. Differential effects of maintenance long-acting beta-agonist and inhaled corticosteroid on asthma control and asthma exacerbations. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 344–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, C.M.; Greenstone, I.R.; Ducharme, F.M. Addition of inhaled long-acting beta2-agonists to inhaled steroids as first line therapy for persistent asthma in steroid-naive adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, CD005307. [Google Scholar]
- O'Byrne, P.M.; Bisgaard, H.; Godard, P.P.; Pistolesi, M.; Palmqvist, M.; Zhu, Y.; Ekstrom, T.; Bateman, E.D. Budesonide/formoterol combination therapy as both maintenance and reliever medication in asthma. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Rabe, K.F.; Pizzichini, E.; Stallberg, B.; Romero, S.; Balanzat, A.M.; Atienza, T.; Lier, P.A.; Jorup, C. Budesonide/formoterol in a single inhaler for maintenance and relief in mild-to-moderate asthma: a randomized, double-blind trial. Chest 2006, 129, 246–256. [Google Scholar]
- Rabe, K.F.; Atienza, T.; Magyar, P.; Larsson, P.; Jorup, C.; Lalloo, U.G. Effect of budesonide in combination with formoterol for reliever therapy in asthma exacerbations: a randomised controlled, double-blind study. Lancet 2006, 368, 744–753. [Google Scholar]
- Tattersfield, A.E.; Postma, D.S.; Barnes, P.J.; Svensson, K.; Bauer, C.A.; O'Byrne, P.M.; Lofdahl, C.G.; Pauwels, R.A.; Ullman, A. Exacerbations of asthma. A descriptive study of 425 severe exacerbations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. New therapies for asthma. Trends Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Calverley, P.; Pauwels, R.; Vestbo, J.; Jones, P.; Pride, N.; Gulsvik, A.; Anderson, J. Combined salmeterol and fluticasone in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomoised controlled trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Szafranski, W.; Cukier, A.; Ramirez, A.; Menga, G.; Sansores, R.; Nahabedian, S.; Peterson, S.; Olsson, H. Efficacy and safety of budesonide/formoterol in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 21, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Nannini, L.; Cates, C.; Lasserson, T.; Poole, P. Combined corticosteroid and long-acting beta-agonist in one inhaler versus long-acting beta-agonists for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, CD006829. [Google Scholar]
- Wedzicha, J.A.; Calverley, P.M.; Seemungal, T.A.; Hagan, G.; Ansari, Z.; Stockley, R.A. The prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations by salmeterol/fluticasone propionate or tiotropium bromide. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D.J.; Taylor, D.A.; Zetterstrom, O.; Chung, K.F.; O'Connor, B.J.; Barnes, P.J. A comparison of low-dose inhaled budesonide plus theophylline and high-dose inhaled budesonide for moderate asthma. New Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Ukena, D.; Harnest, U.; Sakalauskas, R.; Magyar, P.; Vetter, N.; Steffen, H.; Leichtl, S.; Rathgeb, F.; Keller, A.; Steinijans, V.W. Comparison of addition of theophylline to inhaled steroid with doubling of the dose of inhaled steroid in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 1997, 10, 2754–2760. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.; Jatakanon, A.; Gordon, D.; Macdonald, C.; Chung, K.F.; Barnes, P.J. Comparison of high dose inhaled steroids, low dose inhaled steroids plus low dose theophylline, and low dose inhaled steroids alone in chronic asthma in general practice. Thorax 2000, 55, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.J.; Gibson, P.G.; Coughlan, J. Long acting beta-agonists versus theophylline for maintenance treatment of asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2000, CD001281. [Google Scholar]
- Laviolette, M.; Malmstrom, K.; Lu, S.; Chervinsky, P.; Pujet, J.C.; Peszek, I.; Zhang, J.; Reiss, T.F. Montelukast added to inhaled beclomethasone in treatment of asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar]
- Price, D.B.; Hernandez, D.; Magyar, P.; Fiterman, J.; Beeh, K.M.; James, I.G.; Konstantopoulos, S.; Rojas, R.; van Noord, J.A.; Pons, M.; Gilles, L.; Leff, J.A. Randomised controlled trial of montelukast plus inhaled budesonide versus double dose inhaled budesonide in adult patients with asthma. Thorax 2003, 58, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, H.S.; Busse, W.W.; Kerwin, E.; Church, N.; Emmett, A.; Rickard, K.; Knobil, K. Fluticasone propionate/salmeterol combination provides more effective asthma control than low-dose inhaled corticosteroid plus montelukast. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Ducharme, F.; Schwartz, Z.; Hicks, G.; Kakuma, R. Addition of anti-leukotriene agents to inhaled corticosteroids for chronic asthma. Cochrane Databas. Syst. Rev. 2004, CD003133. [Google Scholar]
- Ducharme, F.M.; Lasserson, T.J.; Cates, C.J. Long-acting beta2-agonists versus anti-leukotrienes as add-on therapy to inhaled corticosteroids for chronic asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, CD003137. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, I.J.; Matusiewicz, S.P.; Brown, P.H.; Greening, A.P.; Crompton, G.K. Frequency of voice problems and cough in patients using pressurised aersosol inhaled steroid preparations. Eur. Resp. J. 1995, 8, 590–592. [Google Scholar]
- Toogood, J.A.; Jennings, B.; Greenway, R.W.; Chung, L. Candidiasis and dysphonia complicating beclomethasone treatment of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1980, 65, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, P.; Gonzalez, A.V.; Brassard, P.; Suissa, S. Inhaled corticosteroid use in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and the risk of hospitalization for pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Sin, D.D.; Tashkin, D.; Zhang, X.; Radner, F.; Sjobring, U.; Thoren, A.; Calverley, P.M.; Rennard, S.I. Budesonide and the risk of pneumonia: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet 2009, 374, 712–719. [Google Scholar]
- Kamada, A.K.; Szefler, S.J.; Martin, R.J.; Boushey, H.A.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Drazen, J.M.; Fish, J.E.; Israel, E.; Lazarus, S.C.; Lemanske, R.F. Issues in the use of inhaled steroids. Am. J. Respir. Crit Care Med. 1996, 153, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar]
- Brutsche, M.H.; Brutsche, I.C.; Munawar, M.; Langley, S.J.; Masterson, C.M.; Daley-Yates, P.T.; Brown, R.; Custovic, A.; Woodcock, A. Comparison of pharmacokinetics and systemic effects of inhaled fluticasone propionate in patients with asthma and healthy volunteers: a randomised crossover study. Lancet 2000, 356, 556–561. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, T.W.; Wisniewski, A.; Honour, J.; Tattersfield, A.E. Comparison of the systemic effects of fluticasone propionate and budesonide given by dry powder inhaler in healthy and asthmatic subjects. Thorax 2001, 56, 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Efthimou, J.; Barnes, P.J. Effect of inhaled corticosteroids on bone and growth. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 11, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.; Leblanc, C.; Paquette, L.; Ghezzo, H.; Cote, J.; Cartier, A.; Malo, J.-L. Skin bruising in asthmatic subjects treated with high does of inhaled steroids: frequency and association with adrenal function. Eur. Respir. J. 1996, 9, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, F.E.R.; Persaud, M.P.; Gillespie, C.A.; Cheang, M.; Shuckett, E.P. Absence of posterior subcapsular cataracts in young patients treated with inhaled glucocorticoids. Lancet 1993, 342, 736–738. [Google Scholar]
- Garbe, E.; LeLorier, J.; Boivin, J.-F.; Suissa, S. Inhaled and nasal glucocorticoids and the risks of ocular hypertension or open-angel glaucoma. JAMA 1997, 227, 722–727. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S. Do inhaled corticosteroids inhibit growth in children? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.B.; Mullen, M.; Mullen, B. A meta-analysis of the effects of oral and inhaled corticosteroids on growth. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 93, 967–976. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, M.D.; Yunginger, J.W.; Reed, C.E.; Petterson, T.; Zimmerman, D.; Li, J.T.; O'Fallon, W.M. Attained adult height after childhood asthma: effect of glucocorticoid therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 99, 466–474. [Google Scholar]
- Agertoft, L.; Pedersen, S. Effect of long-term treatment with inhaled budesonide on adult height in children with asthma. New Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Schatz, M. Asthma and pregnancy. Lancet 1999, 353, 1202–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, P.; Baltzan, M.; Deschenes, J.; Suissa, S. Low-dose inhaled and nasal corticosteroid use and the risk of cataracts. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Barnes, P.J. Inhaled Corticosteroids. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 514-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030514
Barnes PJ. Inhaled Corticosteroids. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(3):514-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030514
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarnes, Peter J. 2010. "Inhaled Corticosteroids" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 3: 514-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030514
APA StyleBarnes, P. J. (2010). Inhaled Corticosteroids. Pharmaceuticals, 3(3), 514-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030514




