Real Time Imaging of Biomarkers in the Parkinson's Brain Using Mini-Implantable Biosensors. II. Pharmaceutical Therapy with Bromocriptine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. NMI and the BRODERICK PROBE®
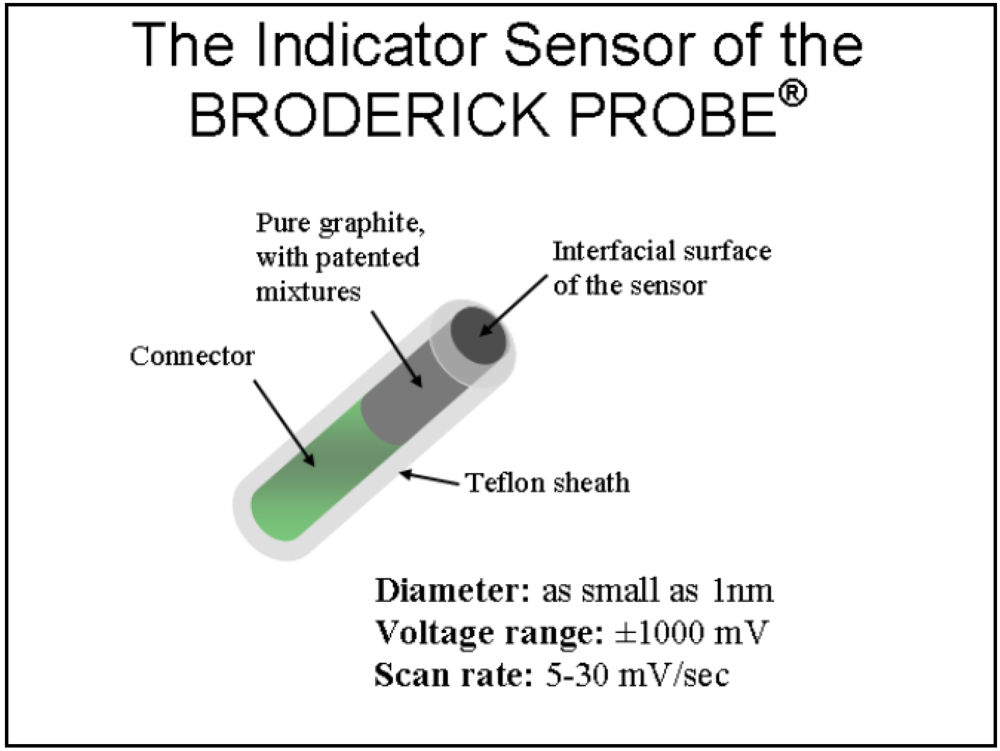
- i = current at time, t
- n = number of electron transfers, eq/mol
- F = Faraday’s constant, 96486 C/eq
- A = electrode area, cm 2
- C = concentration of O, mol/cm3
- D = Diffusion coefficient of O, cm3/s
1.3. The PD paradigm
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. In vivo comparison of endogenous neurochemicals in PD versus non-PD striatal brain
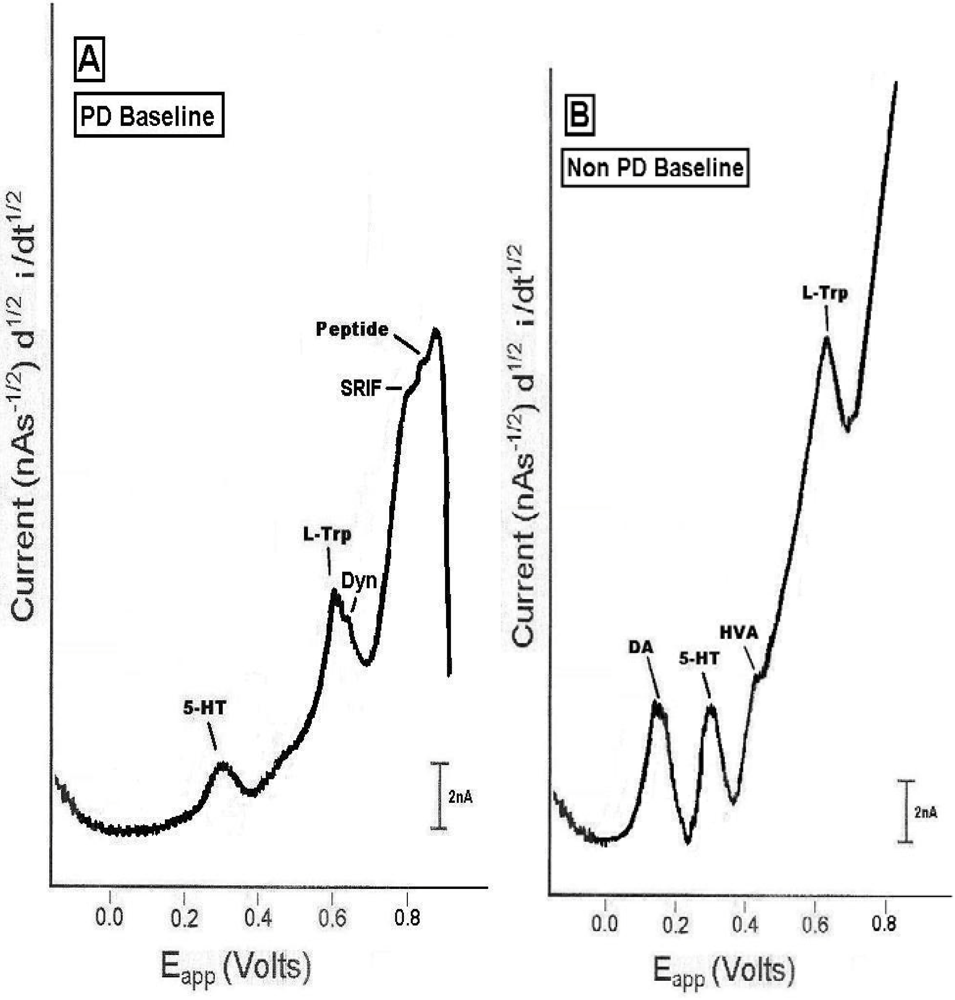
2.2. In vivo Bromocriptine Studies in dorsal striatal brain of PD versus non-PD animals
- ▪
- Is bromocriptine useful for PD if it may reduce DA in motor neurons?
- ▪
- What is the mechanism of action for bromocriptine in PD patients?
- ▪
- Can the effects of bromocriptine be biphasically dose dependent?
- ▪
- Does bromocriptine act through other neurochemicals, neurotransmitters in PD?
- ▪
- Is this study of bromocriptine relevant to the clinical treatment of PD?
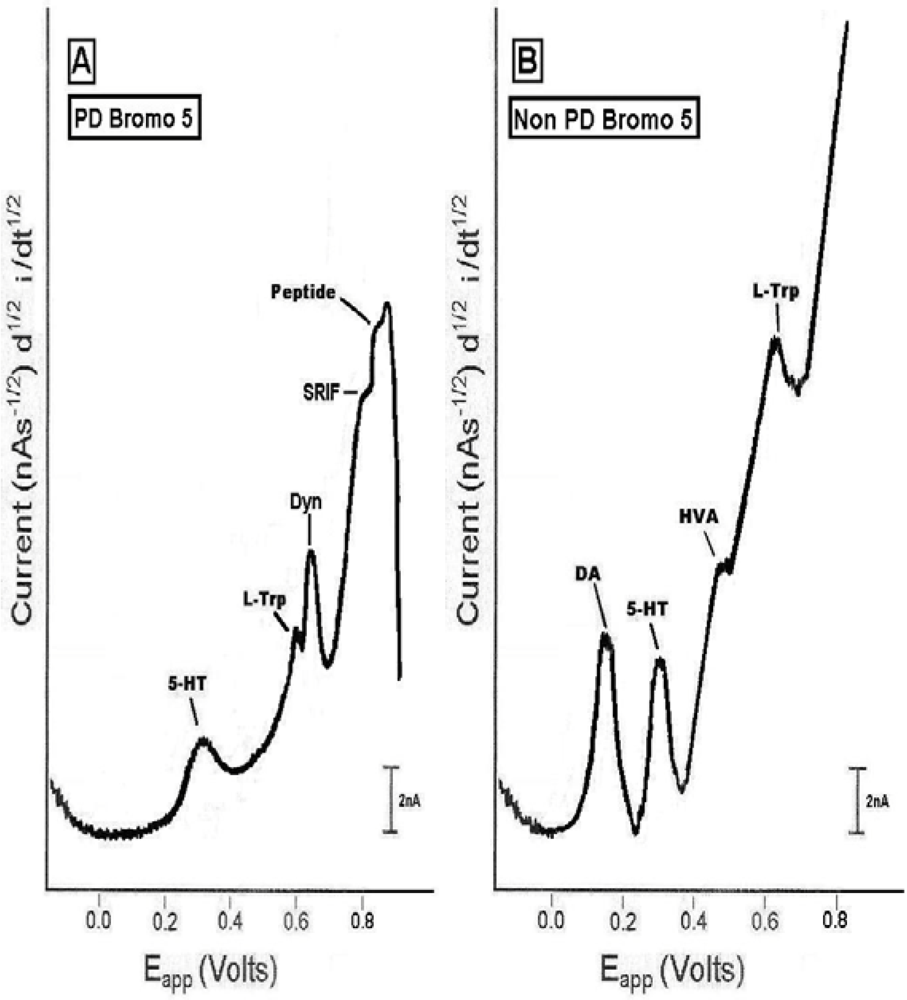
2.3. In vivo studies of low dose bromocriptine effects on dorsal striatum in PD versus non-PD animals
2.4. In vivo studies of high dose bromocriptine effects on dorsal striatum in PD versus non-PD animals
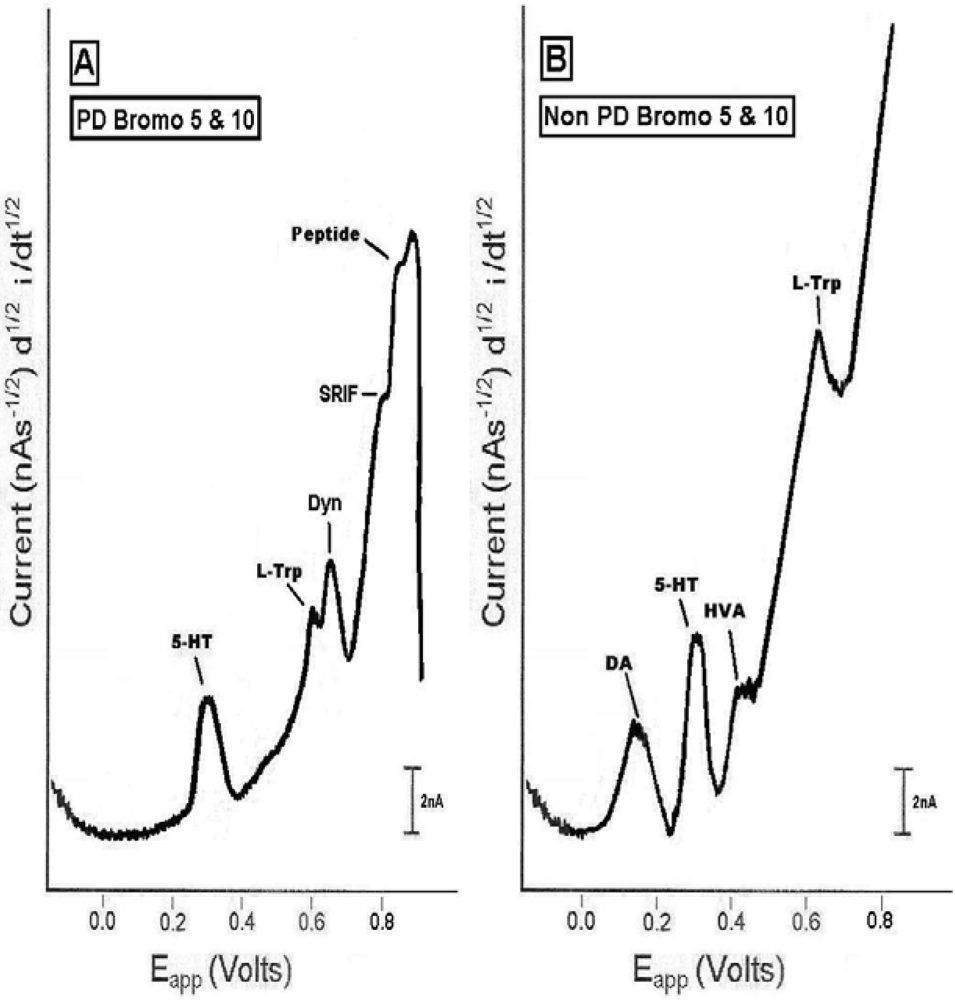
2.5. Line graphs showing the time course of endogenous effects in PD versus non-PD animals
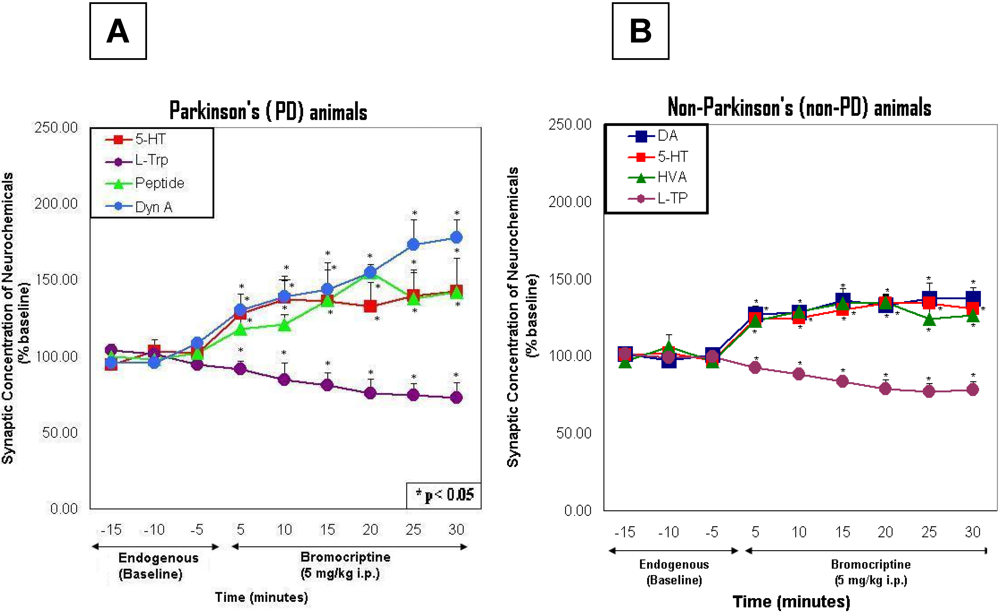
2.6. Line graphs showing the time course of bromocriptine effects in PD versus non-PD animals
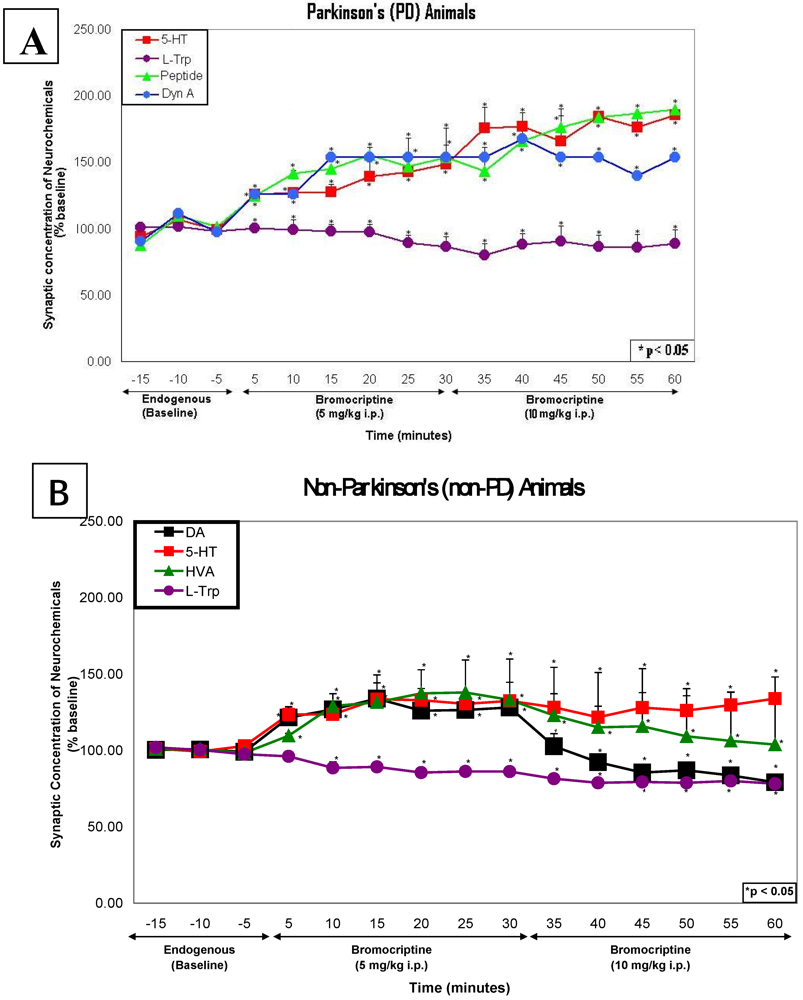
3. Methods
3.1. Study design
3.2. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Matthias, C.J. L-dihydroxyphenylserine (Droxidopa) in the treatment of orthostatic hypotension: the European experience. Clin. Auton. Res. 2008, 18 (Suppl. 1), 25–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matuja, W.B.; Aris, E.A. Motor and non-motor features of Parkinson’s disease. E. Afr. Med. J. 2008, 85, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, P.A. Distinguishing in vitro electrochemical signatures for norepinephrine and dopamine. Neurosci. Lett. 1988, 95, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, P.A. Cathodic Electrochemical Current Arrangement with Telemetric Application. U.S. Patent 4,883,057, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, P.A. Characterizing stearate probes in vitro for the electrochemical detection of dopamine and serotonin. Brain Res. 1989, 495, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Broderick, P.A. Microelectrodes and their use in cathodic electrochemical current arrangement with telemetric application. U.S. Pat. 5,433,710, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, P.A. Microelectrodes and their use in an electrochemical arrangement with telemetric application. U.S. Pat. 5, 938, 903, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, P.A.; Pacia, S.V.; Doyle, W.K.; Devinsky, O. Monoamine neurotransmitters in resected hippocampal subparcellations from neocortical and mesial temporal lobe epilepsy patients: in situ microvoltammetric studies. Brain Res. 2000, 878, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, P.A.; Pacia, S.V. Imaging white matter signals in epilepsy patients: A unique sensor technology. In Bioimaging in Neurodegeneration; Broderick, P.A., Rahni, D.N., Kolodny, E.H., Eds.; Humana Press Inc., Springer: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, P.A.; Pacia, S.V. Identification, diagnosis, and treatment of neuropathologies, neurotoxicities, tumors and brain and spinal cord injuries using microelectrodes with microvoltammetry. U.S. Pat. 7,112,319, 2006. Continuation in Part, 2009, Pending. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, P.A. Studies of oxidative stress mechanism using a morphine/ascorbate animal model and novel N-stearoyl cerebroside and laurate sensors. J. Neural Transm. 2008, 115, 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, P.A.; Ho, H.; Wat, K.; Murthy, V. Laurate biosensors image brain neurotransmitters in vivo: Can an antihypertensive medication alter psychostimulant behavior? Sensors 2008, 8, 4033–4061. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, P.A. In vivo voltammetric studies on release mechanisms for cocaine with gamma-butyrolactone. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 40, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, P.A.; Ho, H.; Li, Y.-S.; Kolodny, E.H. Lovenox® affects striatal neurotransmitters on line with laser Doppler flowmetry Neuromolecular imaging (NMI) in an animal model of acute ischemic stroke. Oral Presentation in Society for Neuroscence, Chicago, IL, USA, 18 October, 2009.
- Haile, M.M.; Broderick, P.A.; Li, Y.-S.; Quartermain, D.; Blanck, T.J.J.; Bekker, A.Y. Nimodipine reverses the hypoxia-induced elevation of dopamine and serotonin in striatum of adult rats. Poster Presentation at American Society of Anesthesiologists, Orlando, FL, USA, 17 October 2008.
- Haile, M.M.; Broderick, P.A.; Li, Y.-S.; Quartermain, D.; Blanck, J.J.; Bekker, A.Y. Nimodipine reverses the hypoxic elevation of tryptophan and serotonin in the striatum of adult rats. Poster Presentation at the International Anesthesia Research Society, San Diego, CA, USA, March 13–17, 2009.
- Hoffman, R.M.; Yang, M. Whole-body imaging with fluorescent proteins. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.M. The multiple uses of fluorescent proteins to visualize cancer in vivo. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 5, 796–866. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, S.; Yang, M.; Chishima, T.; Miyagi, Y.; Shimada, H.; Moossa, A.R.; Hoffman, R.M. In vivo tumor delivery of the green fluorescent protein gene to report future occurrence of metastasis. Cancer Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castano, A.P.; Liu, Q.; Hamblin, M.R. A green fluorescent protein-expressing murine tumour but not its wild-type counterpart is cured by photodynamic therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Wack, S.; Hajri, A.; Heisel, F.; Sowinska, M.; Berger, C.; Whelan, M.; Marescaux, J.; Aprahamian, M. Feasibility, Sensitivity, and Reliability of Laser-Induced Fluorescence Imaging of Green Fluorescent Protein-expressing Tumors in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2003, 7, 765–773. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, P.A.; Doyle, W.K.; Pacia, S.V.; Kuzniecky, R.I.; Devinsky, O.; Kolodny, E.H. A clinical trial of an advanced diagnostic biomedical device for epilepsy patients. J. Long-Term Eff. Med. Implants. 2009, 18, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, P.A.; Doyle, W.K.; Pacia, S.V.; Kuzniecky, R.I.; Devinsky, O.; Kolodny, E.H. Intra-operative Neuromolecular (NMI) in neocortex of epilepsy patients: Comparison with resected neocortical epileptogenic tissue. Poster Presentation at The American Epilepsy Society, Boston, MA, USA, December 4–8, 2009.
- Pellegrino, L.J.; Pellegrino, A.S.; Cushman, A.J. A Stereotaxic Atlas of the Rat Brain; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, B.; Brotchie, J.M. Potential of opioid antagonists in the treatment of levo-dopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s Disease. Drugs Aging 1996, 9, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Hely, M.A.; Morris, J.G.; Reid, W.G.; O'Sullivan, D.J.; Williamson, P.M.; Rail, D.; Broe, G.A.; Margrie, S. The Sydney Multicentre Study of Parkinson’s disease: a randomized, prospective five year study comparing low dose bromocriptine with low dose levodsopa-carbidopa. J. Neuro. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 903–910. [Google Scholar]
- Montastruc, J.L.; Rascol, O.; Senard, J.M.; Rascol, A. A randomised controlled study comparing bromocriptine to which levodopa was later added, with levodopa alone in previously untreated patients with Parkinson’s disease: a five year follow up. J. Neuro. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Brannan, T.; Martinez-Tica, J.; DiRocco, A.; Yahr, M.D. Low and high dose bromocriptine have different effects on striatal dopamine release: An in vivo study. J. Neural Transm. 1993, 6, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.M.; Mohell, N.; Georgiev, J.; Bengtsson, A.; Larsson, L.G.; Magnusson, O.; Ross, S.B. Time course of bromocriptine induced excitation in the rat: Behavioral and biochemical studies. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1995, 351, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.H.; Ji, Y.; Shan, W.; Zeng, B.; Raksadawan, N.; Pastores, G.M.; Wisnewski, T.; Kolodny, E.H. Therapeutic effects of astrocytes expressing both tyrosine hydroxylase and brain-derived neurotrophic factor on a rat mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2002, 113, 629–640. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.Q.; Stoessel, A.J. Somatostatin modulates the behavioral effects of dopamine receptor activation in parkinsonian rats. Neuroscience 2002, 112, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Broderick, P.A.; Kolodny, E.H. Real Time Imaging of Biomarkers in the Parkinson's Brain Using Mini-Implantable Biosensors. II. Pharmaceutical Therapy with Bromocriptine. Pharmaceuticals 2009, 2, 236-249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph2030236
Broderick PA, Kolodny EH. Real Time Imaging of Biomarkers in the Parkinson's Brain Using Mini-Implantable Biosensors. II. Pharmaceutical Therapy with Bromocriptine. Pharmaceuticals. 2009; 2(3):236-249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph2030236
Chicago/Turabian StyleBroderick, Patricia A., and Edwin H. Kolodny. 2009. "Real Time Imaging of Biomarkers in the Parkinson's Brain Using Mini-Implantable Biosensors. II. Pharmaceutical Therapy with Bromocriptine" Pharmaceuticals 2, no. 3: 236-249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph2030236
APA StyleBroderick, P. A., & Kolodny, E. H. (2009). Real Time Imaging of Biomarkers in the Parkinson's Brain Using Mini-Implantable Biosensors. II. Pharmaceutical Therapy with Bromocriptine. Pharmaceuticals, 2(3), 236-249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph2030236



