Approved and Off-Label Uses of Obesity Medications, and Potential New Pharmacologic Treatment Options
Abstract
:Introduction
Established Therapies
Orlistat
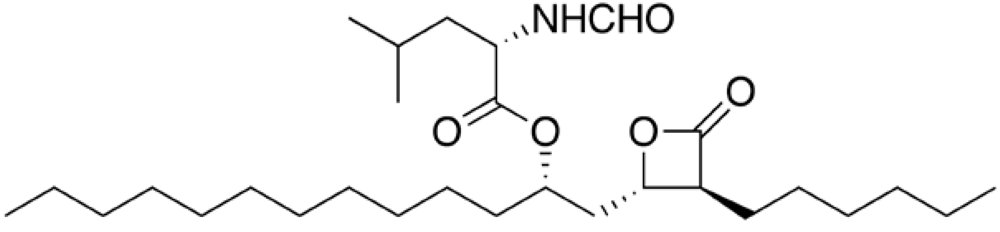
Sibutramine
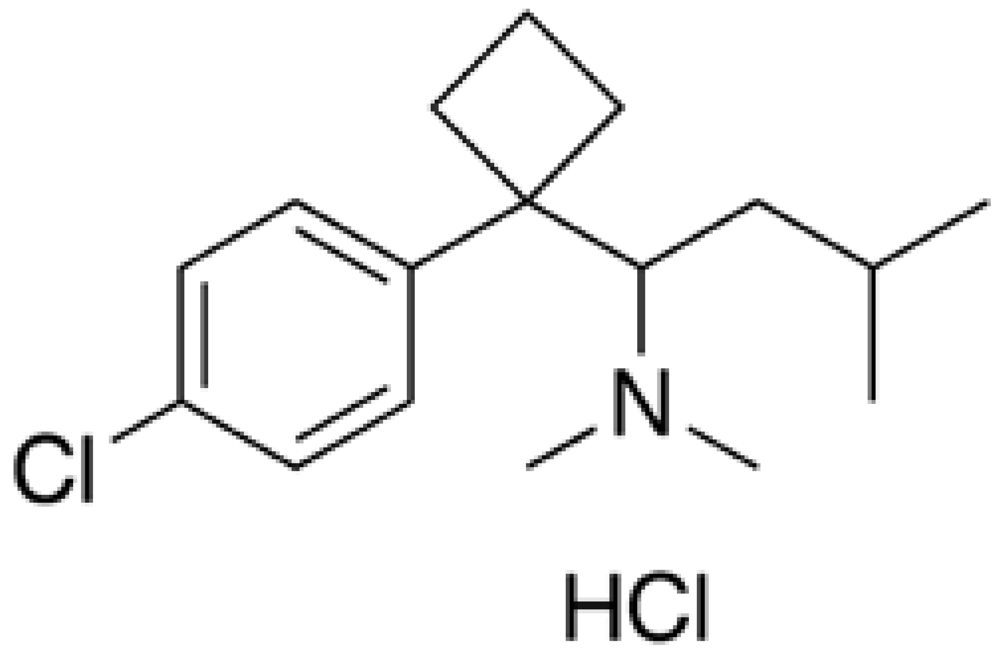
Rimonabant

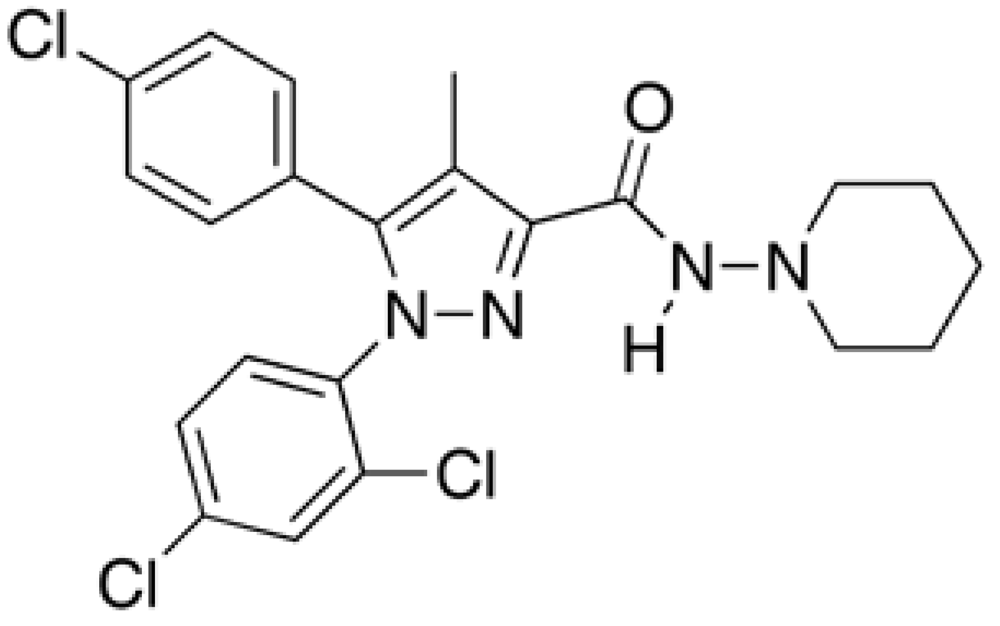
Phentermine
Emerging Therapies
| Drugs that stimulate anorexigenic signals: |
|---|
| Leptin receptor superagonists |
| Peptides downstream of leptin: agonists of melanocortin receptor-4 |
| Ciliary neurotrophic factor analogues |
| Agonists of 5-HT |
| Drugs that inhibit orexigenic signals: |
| Neuropeptide Y receptor anatagonists |
| Melanin-concentrating hormone-1 receptor antagonists |
| Somatostatin analogues |
| Gastrointestinal peptides as drug targets: |
| GLP-1 receptor agonists |
| Peptide YY 3-36 analogues |
| Ghrelin receptor antagonists or inverse agonists |
| Oxyntomodulin analogues |
| Drugs that increase energy expenditure: |
| Beta-adrenergic agonists |
| Growth-hormone receptor agonists |
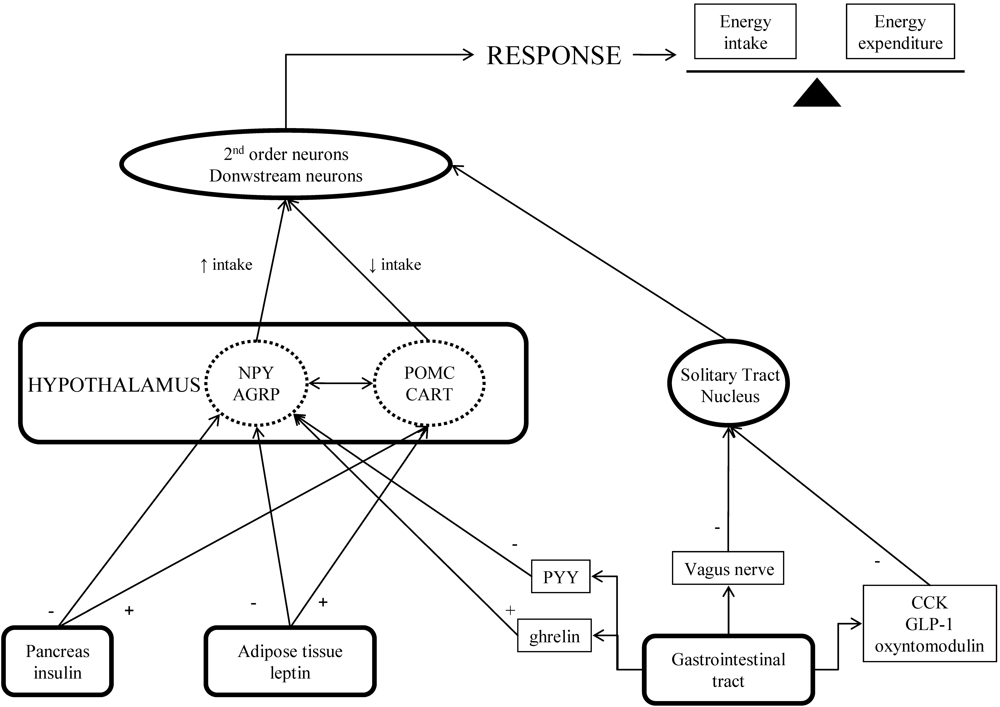
Stimulation of Anorexigenic Signals
Leptin
Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor
Subtype-Selective Serotonin-Receptor Agonists
Inhibition of Orexigenic Signals
Neuropeptide Y Receptor Antagonists
Melanin-Concentrating Hormone Antagonists
Somatostatin Analogues
Gastrointestinal Peptides That Regulate Food Intake, As Drug Targets
Glucagon Like Peptide (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists
Peptide YY Analogues
Ghrelin Receptor Antagonists and Inverse Agonists
Oxyntomodulin Analogues
Drugs That Increase Energy Expenditure
β3-Adrenergic Agonists
Growth Hormone
Other Thermogenic And Metabolic Drugs
Anti-Obesity Drugs And Safety Concerns
Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Enç, F.Y.; Ones, T.; Akin, H.L.; Dede, F.; Turoğlu, H.T.; Ulfer, G.; Bekiroğlu, N.; Haklar, G.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Holst, J.J.; Ulusoy, N.; Imeryüz, N. Orlistat accelerates gastric emptying and attenuates GIP release in healthy subjects. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Maglione, M.; Tu, W.; Mojica, W.; Arterburn, D.; Shugarman, L.R.; Hilton, L.; Suttorp, M.; Solomon, V.; Shekelle, P.G.; Morton, S.C. Meta-analysis: pharmacologic treatment of obesity. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rucker, D.; Padwal, R; Li, S.K.; Curioni, C.; Lau, D.C. Long term pharmacotherapy for obesity and overweight: updated meta-analysis . BMJ 2007, 335, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, R.; Kristensen, P.K.; Bartels, E.M.; Bliddal, H.; Astrup, A. Efficacy and safety of the weight-loss drug rimonabant: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2007, 370, 1706–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgerson, J.S.; Hauptman, J.; Boldrin, M.N.; Sjöström, L. XENical in the prevention of diabetes in obese subjects (XENDOS) study: a randomized study of orlistat as an adjunct to lifestyle changes for the prevention of type 2 diabetes in obese patients. Diab. Care 2004, 27, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérubé-Parent, S.; Prud´homme, D.; St-Pierre, S.; Doucet, E; Tremblay, A. Obesity treatment with a progressive clinical tri-therapy combining sibutramine and a supervised diet--exercise intervention . Int. J. Obes, 2001, 25, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellocchio, L.; Cervino, C.; Pasquali, R.; Pagotto, R. The endocannabinoid system and energy metabolism. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbas, F.; Gasteyger, C.; Sjödin, A.; Astrup, A.; Larsen, T.M. A critical review of the cannabinoid receptor as a drug target for obesity management . Obes. Rev. 2008, 10, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addy, C.; Li, S.; Agrawal, N.; Stone, J.; Majumdar, A.; Zhong, L.; Li, H.; Yuan, J.; Maes, A.; Rothenberg, P.; Cote, J.; Rosko, K.; Cummings, C.; Warrington, S.; Boyce, M.; Gottesdiener, K.; Stoch, A.; Wagner, J. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamic properties of taranabant, a novel selective cannabinoid-1 receptor inverse agonist, for the treatment of obesity: results from a double-blind, placebo-controlled, single oral dose study in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 48, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addy, C.; Wright, H.; Van Laere, K.; Gantz, I.; Erondu, N.; Musser, B.J.; Lu, K.; Yuan, J.; Sanabria-Bohórquez, S.M.; Stoch, A.; Stevens, C.; Fong, T.M.; De Lepeleire, I.; Cilissen, C.; Cote, J.; Rosko, K.; Gendrano 3rd, I.N.; Nguyen, A.M.; Gumbiner, B.; Rothenberg, P.; de Hoon, J.; Bormans, G.; Depré, M.; Eng, W.S.; Ravussin, E.; Klein, S.; Blundell, J.; Herman, G.A.; Burns, H.D.; Hargreaves, R.J.; Wagner, J.; Gottesdiener, K.; Amatruda, J.M.; Heymsfield, S.B. The acyclic CB1R inverse agonist taranabant mediates weight loss by increasing energy expenditure and decreasing caloric intake . Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamota, L.; Bermudez-Silva, F.J.; Marco, E.M.; Llorente, R.; Gallego, A.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; Viveros, M.P. Effects of adolescent nicotine and SR 147778 (Surinabant) administration on food intake, somatic growth and metabolic parameters in rats. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.S.; Kim, M.J.; Seo, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, M.E.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, J.; Lee, J. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of novel diarylpyrazole imide analogues as CB1 cannabinoid receptor ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3080–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster-Schubert, K.E.; Cummings, D.E. Emerging therapeutic strategies for obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cawthorne, M.A. Opportunities and challenges for the development of pharmacological therapies for obesity treatment . Obes. Rev. 2007, 8 (Suppl. 1), 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Kim, K.S.; Chung, Y.S.; Shong, M.; Park, S.B. Anti-obesity agents: a focused review on the structural classification of therapeutic entities. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, M.D.; Jakobsdottir, S.; Drent, M.L. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: A review. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Considine, R.V.; Sinha, M.K.; Heiman, M.L.; Kriauciunas, A.; Stephens, T.W.; Nyce, M.R.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Marco, C.C.; McKee, L.J.; Bauer, T.L.; Caro, J.F. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.W.; Seeley, R.J.; Campfield, L.A.; Burn, P.; Baskin, D.G. Identification of targets of leptin action in rat hypothalamus. J. Clin. Invest. 1996, 98, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otvos Jr., L.; Terrasi, M.; Cascio, S.; Cassone, M.; Abbadessa, G.; De Pascali, F.; Scolaro, L.; Knappe, D.; Stawikowski, M.; Cudic, P.; Wade, J.D.; Hoffmann, R.; Surmacz, E. Development of a pharmacologically improved peptide agonist of the leptin receptor . Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A. Leptin transport across the blood-brain barrier: implications for the cause and treatment of obesity. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2001, 7, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Haschimi, K.; Pierroz, D.D.; Hileman, S.M.; Bjorbaek, C.; Flier, J.S. Two defects contribute to hypothalamic leptin resistance in mice with diet-induced obesity. J. Clin. Invest. 2000, 105, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huszar, D.; Lynch, C.A.; Fairchild-Huntress, V.; Dunmore, J.H.; Fang, Q.; Berkemeier, L.R.; Gu, W.; Kesterson, R.A.; Boston, B.A.; Cone, R.D.; Smith, F.J.; Campfield, L.A.; Burn, P.; Lee, F. Targeted disruption of the melanocortin-4 receptor results in obesity in mice. Cell 1997, 88, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.S.; Marsh, D.J.; Trumbauer, M.E.; Frazier, E.G.; Guan, X.M.; Yu, H.; Rosenblum, C.I.; Vongs, A.; Feng, Y.; Cao, L.; Metzger, J.M.; Strack, A.M.; Camacho, R.E.; Mellin, T.N.; Nunes, C.N.; Min, W.; Fisher, J.; Gopal-Truter, S.; MacIntyre, D.E.; Chen, H.Y.; Van der Ploeg, L.H. Inactivation of the mouse melanocortin-3 receptor results in increased fat mass and reduced lean body mass. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, S.C.; Schwartz, M.W.; Lachey, J.L.; Hagan, M.M.; Rushing, P.A.; Blake, K.A.; Yagaloff, K.A.; Kurylko, G.; Franco, L.; Danhoo, W.; Seeley, R.J. A novel selective melanocortin-4 receptor agonist reduces food intake in rats and mice without producing aversive consequences. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3442–3448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mancini, M.C.; Halpern, A. Investigational therapies in the treatment of obesity. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2006, 15, 897–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, A.P. Effects of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) on food intake and body weight: mechanisms and therapeutic potential? Clin. Sci. 2007, 113, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ALS CNTF Treatment Study Group. A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial of subcutaneous recombinant human ciliary neurotrophic factor (rHCNTF) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis . Neurology 1996, 46, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, M.P.; Littlejohn, T.W.; Schwartz, S.L.; Weiss, S.R.; McIlwain, H.H.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Bray, G.A.; Roberts, W.G.; Heyman, E.R.; Stambler, N.; Heshka, S.; Vicary, C.; Guler, H.P. Recombinant variant of ciliary neurotrophic factor for weight loss in obese adults: A randomized, dose-ranging study. JAMA 2003, 289, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Febbraio, M.A. gp130 receptor ligands as potential therapeutic targets for obesity. J. Clin. Invest. 2007, 117, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, V.B.; Febbraio, M.A. CNTF: A target therapeutic for obesity-related metabolic disease? J. Mol. Med. 2008, 86, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tecott, L.H.; Sun, L.M.; Akana, S.F.; Strack, A.M.; Lowenstein, D.H.; Dallman, M.F.; Julius, D. Eating disorder and epilepsy in mice lacking 5-HT2c serotonin receptors. Nature 1995, 374, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonogaki, K.; Strack, A.M.; Dallman, M.F.; Tecott, L.H. Leptin-independent hyperphagia and type 2 diabetes in mice with a mutated serotonin 5-HT2C receptor gene. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, L.K.; Jobst, E.E.; Sutton, G.M.; Zhou, L.; Borok, E.; Thornton-Jones, Z.; Liu, H.Y.; Zigman, J.M.; Balthasar, N.; Kishi, T.; Lee, C.E.; Aschkenasi, C.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Yu, J.; Boss, O.; Mountjoy, K.G.; Clifton, P.G.; Lowell, B.B.; Friedman, J.M.; Horvath, T.; Butler, A.A.; Elmquist, J.K.; Cowley, M.A. Serotonin reciprocally regulates melanocortin neurons to modulate food intake. Neuron 2006, 51, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halford, J.C.; Harrold, J.A.; Boyland, E.J.; Lawton, C.L.; Blundell, J.E. Serotonergic drugs : effects on appetite expression and use for the treatment of obesity. Drugs 2007, 67, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacker, D.A.; Miller, K.J. Agonists of the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor: preclinical and clinical progression in multiple diseases. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 2008, 11, 438–435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holenz, J.; Mercè, R.; Díaz, J.L.; Guitart, X.; Codony, X.; Dordal, A.; Romero, G.; Torrens, A.; Mas, J.; Andaluz, B.; Hernández, S.; Monroy, X.; Sánchez, E.; Hernández, E.; Pérez, R.; Cubí, R.; Sanfeliu, O.; Buschmann, H. Medicinal chemistry driven approaches toward novel and selective serotonin 5-HT6 receptor ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1781–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holenz, J.; Pauwels, P.J.; Díaz, J.L.; Mercè, R.; Codony, X.; Buschmann, H. Medicinal chemistry strategies to 5-HT(6) receptor ligands as potential cognitive enhancers and anti-obesity agents. Drug Discov. Today 2006, 11, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heal, D.J.; Smith, S.L.; Fisas, A.; Codony, X.; Buschmann, H. Selective 5-HT6 receptor ligands: progress in the development of a novel pharmacological approach to the treatment of obesity and related metabolic disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 117, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiji, M.M.; Inui, A. Neuropeptide y receptor selective ligands in the treatment of obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 664–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luthin, D.R. Anti-obesity effects of small molecule melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 (MCHR1) antagonists. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kym, P.R. Lead optimization strategies and tactics applied to the discovery of melanin concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonists. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 1471–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, G.; Bocanegra-García, V.; Galiano, S.; Cirauqui, N.; Ceras, J.; Pérez, S.; Aldana, I.; Monge, A. Melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonists: A new perspective for the pharmacologic treatment of obesity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, R.H.; Greenway, F.; Velasquez-Mieyer, P.; Heimburger, D.; Schumacher, D.; Smith, D.; Smith, W.; Soler, N.; Warsi, G.; Berg, W.; Maloney, J.; Benedetto, J.; Zhu, W.; Hohneker, J. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-finding trial of a long-acting formulation of octreotide in promoting weight loss in obese adults with insulin hypersecretion. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2006, 30, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez-Mieyer, P.A.; Cowan, P.A.; Arheart, K.L.; Buffington, C.K.; Spencer, K.A.; Connelly, B.E.; Cowan, G.W.; Lustig, R.H. Suppression of insulin secretion is associated with weight loss and altered macronutrient intake and preference in a subset of obese adults. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2003, 27, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huda, M.S.; Wilding, J.P.; Pinkney, J.H. Gut peptides and the regulation of appetite. Obes. Rev. 2006, 7, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, K.G.; Dhillo, W.S.; Bloom, S.R. Gut peptides in the regulation of food intake and energy homeostasis. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, D.E.; Overduin, J. Gastrointestinal regulation of food intake. J. Clin. Invest. 2007, 117, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, B.C.; Wren, A.M.; Cooke, D.; Bloom, S.R. Gut hormones as potential new targets for appetite regulation and the treatment of obesity. Drugs 2008, 68, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.J.; Nauck, M.A. Glucagon-like peptide 1(GLP-1) in biology and pathology. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2005, 21, 91–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; Navarro, M.; Álvarez, E.; Roncero, I.; Chowen, J.A.; Maestre, O.; Gómez, R.; Muñoz, R.M.; Eng, J.; Blázquez, E. Peripheral versus central effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on satiety and body weight loss in Zucker obese rats . Metabolism 2000, 49, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, A.; Raben, A.; Astrup, A.; Holst, J.J. Glucagon-like peptide 1 promotes satiety and suppresses energy intake in humans. J. Clin. Invest. 1998, 101, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutzwiller, J.P.; Göke, B.; Drewe, J.; Hildebrand, P.; Ketterer, S.; Handschin, D.; Winterhalder, R.; Conen, D.; Beglinger, C. Glucagon-like peptide-1: a potent regulator of food intake in humans. Gut 1999, 44, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.J.; Gallwitz, B.; Schmidt, W.E.; Nauck, M.A. Glucagon-like peptide 1 as a regulator of food intake and body weight: therapeutic perspectives. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 440, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batterham, R.L.; Cowley, M.A.; Small, C.J.; Herzog, H.; Cohen, M.A.; Wren, A.M.; Brynes, A.E.; Low, M.; Ghatei, M.A.; Cone, R.D.; Bloom, S.R. Gut hormone PYY(3-36) physiologically inhibits food intake . Nature 2002, 418, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuña-Goycolea, C.; van den Pol, A.N. Peptide YY(3-36) inhibits both anorexigenic proopiomelanocortin and orexigenic neuropeptide Y neurons: implications for hypothalamic regulation of energy homeostasis. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10510–10519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, K.; Bloom, S.R. The role of oxyntomodulin and peptide tyrosine-tyrosine (PYY) in appetite control. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 2, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, R.P.; le Roux, C.W. The satiety hormone peptide YY as a regulator of appetite. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 61, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Fontán, M.; Cordido, F.; Rodríguez-Carmona, A.; Penín, M.; Díaz-Cambre, H.; López-Muñiz, A.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; García-Buela, J. Short-term regulation of peptide YY secretion by a mixed meal or peritoneal glucose-based dialysate in patients with chronic renal failure. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 3696–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Fontán, M.; Cordido, F.; Rodríguez-Carmona, A.; Peteiro, J.; García-Naveiro, R.; García-Buela, J. Plasma ghrelin levels in patients undergoing haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Nephrol. Dail. Transplant. 2004, 19, 2095–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fontán, M.; Cordido, F.; Rodríguez-Carmona, A.; García-Naveiro, R.; Isidro, M.L.; Villaverde, P.; García-Buela, J. Acute plasma ghrelin and leptin responses to oral feeding or intraperitoneal hypertonic glucose-based dialysate in patients with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 2877–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druce, M.R.; Wren, A.M.; Park, A.J.; Milton, J.E.; Patterson, M.; Frost, G.; Ghatei, M.A.; Small, C.; Bloom, S.R. Ghrelin increases food intake in obese as well as lean subjects. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2005, 29, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- English, P.J.; Ghatei, M.A.; Malik, I.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Wilding, J.P. Food fails to suppress ghrelin levels in obese humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 2984–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Xin, Z.; Liu, G.; Schaefer, V.G.; Falls, H.D.; Kaszubska, W.; Collins, C.A.; Sham, H.L. Discovery of tetralin carboxamide growth hormone secretagogue receptor antagonists via scaffold manipulation. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 6655–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, J.; Esler, W.P.; O'connor, S.; Coish, P.D.; Wickens, P.L.; Brands, M.; Bierer, D.E.; Bloomquist, B.T.; Bondar, G.; Chen, L.; Chuang, C.Y.; Claus, T.H.; Fathi, Z.; Fu, W.; Khire, U.R.; Kristie, J.A.; Liu, X.G.; Lowe, D.B.; McClure, A.C.; Michels, M.; Ortiz, A.A.; Ramsden, P.D.; Schoenleber, R.W.; Shelekhin, T.E.; Vakalopoulos, A.; Tang, W.; Wang, L.; Yi, L.; Gardell, S.J.; Livingston, J.N.; Sweet, L.J.; Bullock, W.H. Quinazolinone derivatives as orally available ghrelin receptor antagonists for the treatment of diabetes and obesity. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5202–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esler, W.P.; Rudolph, J.; Claus, T.H.; Tang, W.; Barucci, N.; Brown, S.E.; Bullock, W.; Daly, M.; Decarr, L.; Li, Y.; Milardo, L.; Molstad, D.; Zhu, J.; Gardell, S.J.; Livingston, J.N.; Sweet, L.J. Small-molecule ghrelin receptor antagonists improve glucose tolerance, suppress appetite, and promote weight loss. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5175–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulin, A.; Demange, L.; Ryan, J.; Mousseaux, D.; Sanchez, P.; Bergé, G.; Gagne, D.; Perrissoud, D.; Locatelli, V.; Torsello, A.; Galleyrand, J.C.; Fehrentz, J.A.; Martinez, J. New trisubstituted 1,2,4-triazole derivatives as potent ghrelin receptor antagonists. 3. Synthesis and pharmacological in vitro and in vivo evaluations. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beck, B.; Richy, S.; Stricker-Krongrad, A. Feeding response to ghrelin agonist and antagonist in lean and obese Zucker rats. Life Sci. 2004, 76, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halem, H.A.; Taylor, J.E.; Dong, J.Z.; Shen, Y.; Datta, R.; Abizaid, A.; Diano, S.; Horvath, T.; Zizzari, P.; Bluet-Pajot, M.T.; Epelbaum, J.; Culler, M.D. Novel analogues of ghrelin: physiological and clinical implications . Eur. J. Endocrinol 2004, 151(Suppl.1), S71–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, B.; Cygankiewicz, A.; Jensen, T.H.; Ankersen, M.; Schwartz, T.W. High constitutive signaling of the ghrelin receptor-identification of a potent inverse agonist. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 2201–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmling, A.; Maasch, C.; Eulberg, D.; Buchner, K.; Schöder, W.; Lange, C.; Vonhoff, S.; Wlotzka, B.; Tschöp, M.H.; Rosewicz, S.; Klussmann, S. Inhibition of ghrelin action in vitro and in vivo by an RNA-Spiegelmer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13174–13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla, E.P.; Iwasaki, S.; Moss, J.A.; Chang, J.; Otsuji, J.; Inoue, K.; Meijler, M.M; Janda, K.D. Vaccination against weight gain . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13226–31321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobelt, P.; Helmling, S.; Stengel, A.; Wlotzka, B.; Andresen, V.; Klapp, B.F.; Wiedenmann, B.; Klussmann, S.; Mönnikes, H. Anti-ghrelin Spiegelmer NOX-B11 inhibits neurostimulatory and orexigenic effects of peripheral ghrelin in rats. Gut 2006, 55, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearman, L.P.; Wang, S.P.; Helmling, S.; Stribling, D.S.; Mazur, P.; Ge, L.; Wang, L.; Klussmann, S.; Macintyre, D.E.; Howard, A.D.; Strack, A.M. Ghrelin neutralization by a ribonucleic acid-SPM ameliorates obesity in diet-induced obese mice. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataille, D.; Gespach, C.; Tatemoto, K.; Marie, J.C.; Coudray, A.M.; Rosselin, G.; Mutt, V. Bioactive enteroglucagon (oxyntomodulin): present knowledge on its chemical structure and its biological activities . Peptides 1981, 2 (Suppl. 2), S41–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakin, C.L.; Gunn, I.; Small, C.J.; Edwards, C.M.; Hay, D.L.; Smith, D.M.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Oxyntomodulin inhibits food intake in the rat. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 4244–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakin, C.L.; Small, C.J.; Batterham, R.L.; Neary, N.M.; Cohen, M.A.; Patterson, M.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Peripheral oxyntomodulin reduces food intake and body weight gain in rats. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2687–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.A.; Ellis, S.M.; Le Roux, C.W.; Batterham, R.L.; Park, A.; Patterson, M.; Frost, G.S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Oxyntomodulin suppresses appetite and reduces food intake in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4696–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, K.; Park, A.J.; Small, C.J.; Meeran, K.; Ghatei, M.A.; Frost, G.S.; Bloom, S.R. Oxyntomodulin increases energy expenditure in addition to decreasing energy intake in overweight and obese humans: A randomised controlled trial. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2006, 30, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, K.; Bloom, S.R. The role of oxyntomodulin and peptide tyrosine-tyrosine (PYY) in appetite control. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrirnol. Metab. 2006, 2, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, J.C.; Arch, J.R. Thermogenic and metabolic anti-obesity drugs: Rationale and opportunities. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2007, 9, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buemann, B.; Toubro, S.; Astrup, A. Effects of the two beta3-agonists, ZD7114 and ZD2079 on 24 hour energy expenditure and respiratory quotient in obese subjects. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arch, J.R. beta(3)-Adrenoceptor agonists: potential, pitfalls and progress. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 440, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, T.M.; Toubro, S.; van Baak, M.A.; Gottesdiener, K.M.; Larson, P.; Saris, W.H.; Astrup, A. Effect of a 28-d treatment with L-796568, a novel beta(3)-adrenergic receptor agonist, on energy expenditure and body composition in obese men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redman, L.M.; de Jonge, L.; Fang, X.; Gamlin, B.; Recker, D.; Greenway, F.L.; Smith, S.; Ravussin, E. Lack of an effect of a novel beta3-adrenoceptor agonist, TAK-677, on energy metabolism in obese individuals: a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized study . J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Castro, P.; Isidro, M.L.; García-Buela, J.; Leal-Cerro, A.; Broglio, F.; Tassone, F.; Ghigo, E.; Diéguez, C.; Casanueva, F.F.; Cordido, F. Marked GH secretion after ghrelin alone or combined with GH-releasing hormone (GHRH) in obese patients . Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2004, 61, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordido, F.; Álvarez-Castro, P.; Isidro, M.L.; Casanueva, F.F.; Diéguez, C. Comparison between insulin tolerance test, growth hormone (GH)-releasing hormone (GHRH), GHRH plus acipimox and GHRH plus GH-releasing peptide-6 for the diagnosis of adult GH deficiency in normal subjects, obese and hypopituitary patients . Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 149, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekala, K.C.; Tritos, N.A. Effects of recombinant human growth hormone therapy in obesity in adults: a meta analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 1, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, F.M.; Sun, J.; Sharma, L.; Libinaka, R.; Jiang, W.J.; Gianello, R. Metabolic studies of a synthetic lipolytic domain (AOD9604) of human growth hormone. Horm. Res. 2000, 53, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan, M.; Summers, R.J.; Thorburn, A.; Ogru, E.; Gianello, R.; Jiang, W.J.; Ng, F.M. The effects of human GH and its lipolytic fragment (AOD9604) on lipid metabolism following chronic treatment in obese mice and beta(3)-AR knock-out mice. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 5182–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costford, S.; Gowing, A.; Harper, M.E. Mitochondrial uncoupling as a target in the treatment of obesity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2007, 10, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannides-Demos, L.L.; Proietto, J.; Tonkin, A.M.; McNeil, J.J. Safety of drug therapies used for weight loss and treatment of obesity. Drug. Saf. 2006, 29, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elangbam, C.S. Review paper: Current strategies in the development of anti-obesity drugs and their safety concerns . Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Early Communication about an Ongoing Safety Review of Meridia (sibutramine hydrochloride). Available online: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/PostmarketDrugSafetyInformationforPatientsandProviders/DrugSafetyInformationforHeathcareProfessionals/ucm191650.htm accessed on January 11, 2010.
- Astrup, A.; Madsbad, S.; Breum, L.; Jensen, T.J.; Kroustrup, J.P.; Larsen, T.M. Effect of tesofensine on bodyweight loss, body composition, and quality of life in obese patients: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2008, 372, 1906–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Isidro, M.L.; Cordido, F. Approved and Off-Label Uses of Obesity Medications, and Potential New Pharmacologic Treatment Options. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 125-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3010125
Isidro ML, Cordido F. Approved and Off-Label Uses of Obesity Medications, and Potential New Pharmacologic Treatment Options. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(1):125-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsidro, Mª Luisa, and Fernando Cordido. 2010. "Approved and Off-Label Uses of Obesity Medications, and Potential New Pharmacologic Treatment Options" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 1: 125-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3010125
APA StyleIsidro, M. L., & Cordido, F. (2010). Approved and Off-Label Uses of Obesity Medications, and Potential New Pharmacologic Treatment Options. Pharmaceuticals, 3(1), 125-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3010125






