Stability-Indicating Assay of Novel 5-(Hydroxamic acid)methyl Oxazolidinones with 5-Lipooxygenase Inhibitory Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
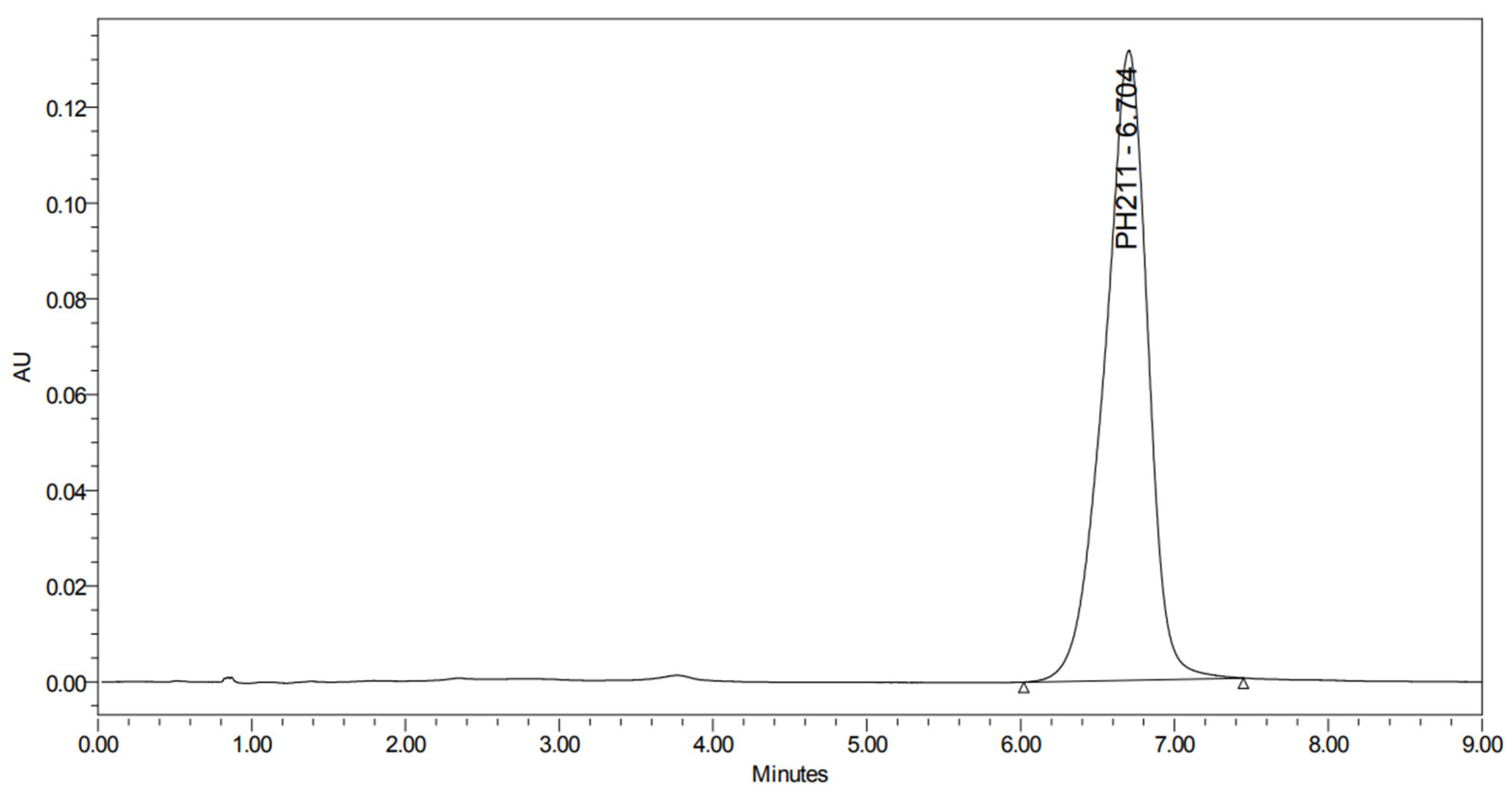
2.2. Method Validation for PH-211
2.2.1. Linearity and Sensitivity
2.2.2. Precision and Accuracy
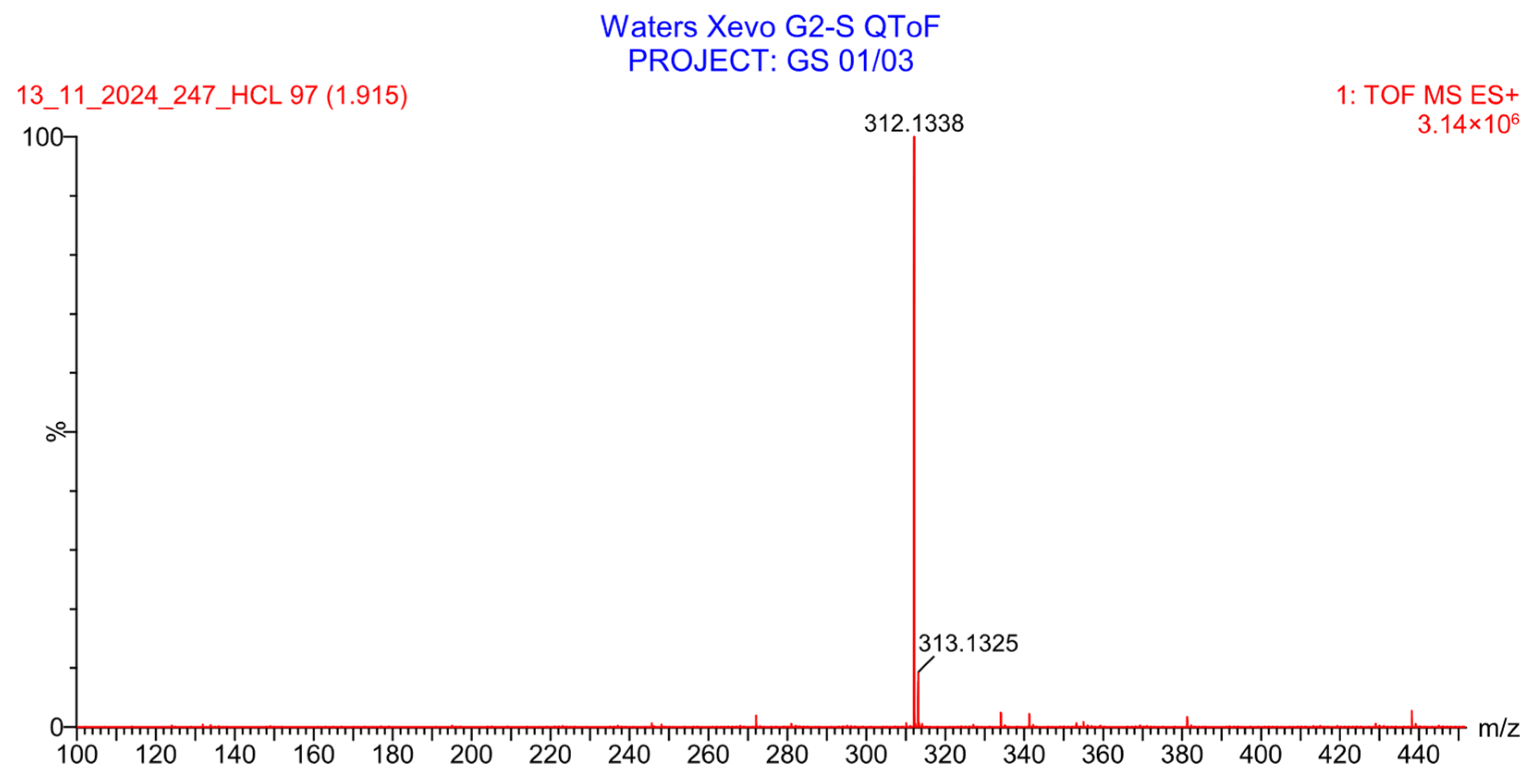
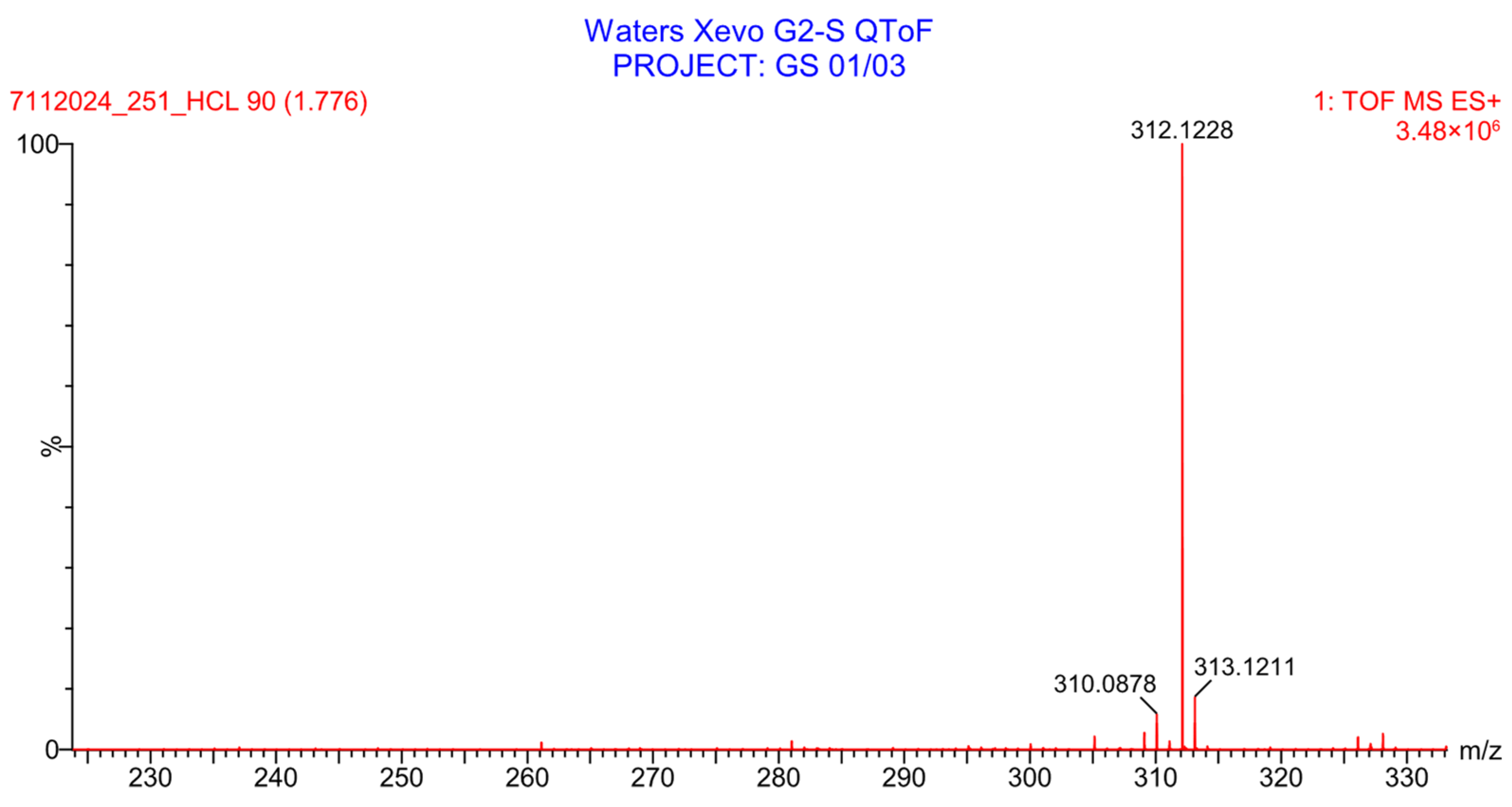
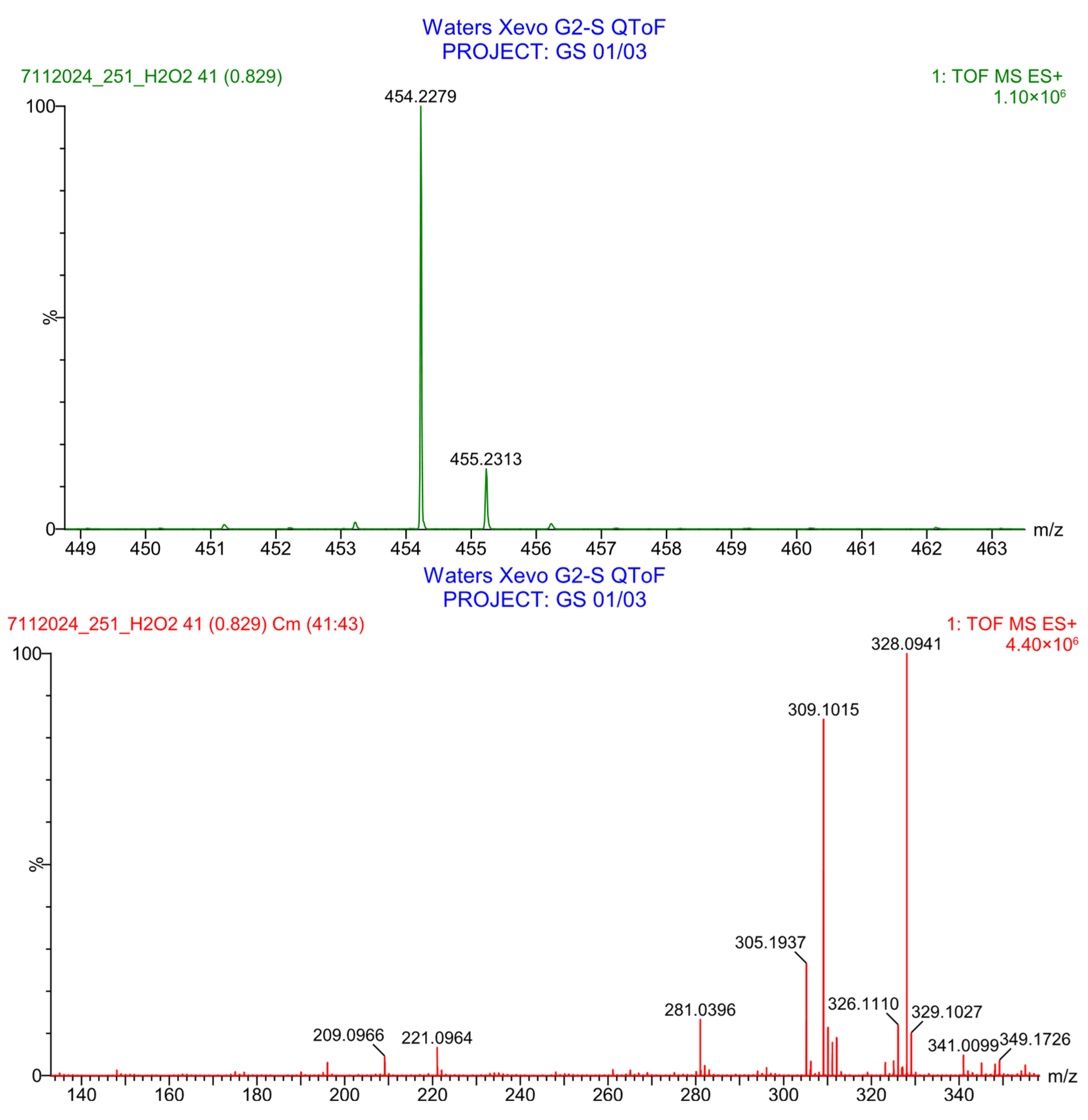
2.2.3. Evaluation of PH-211 Extraction and Stability in Human Plasma
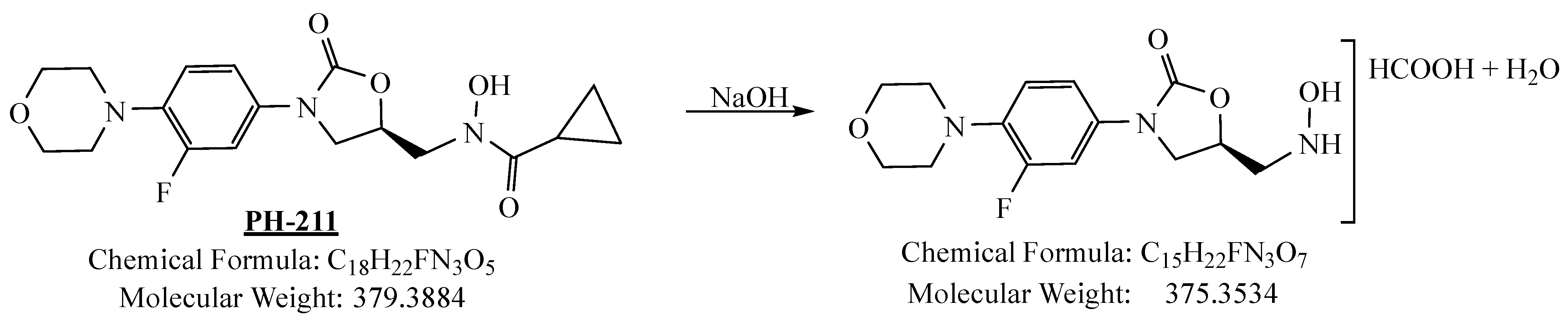
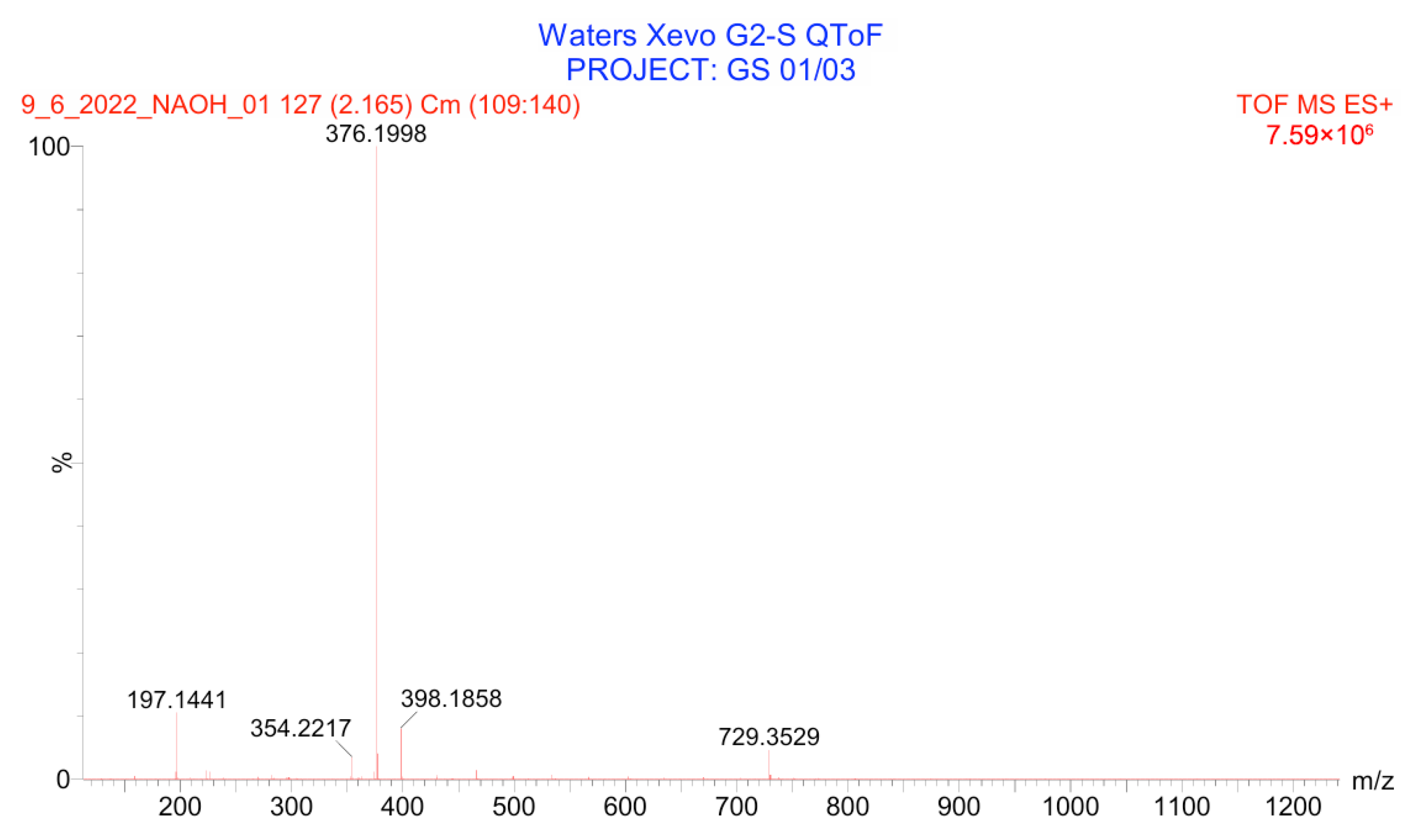
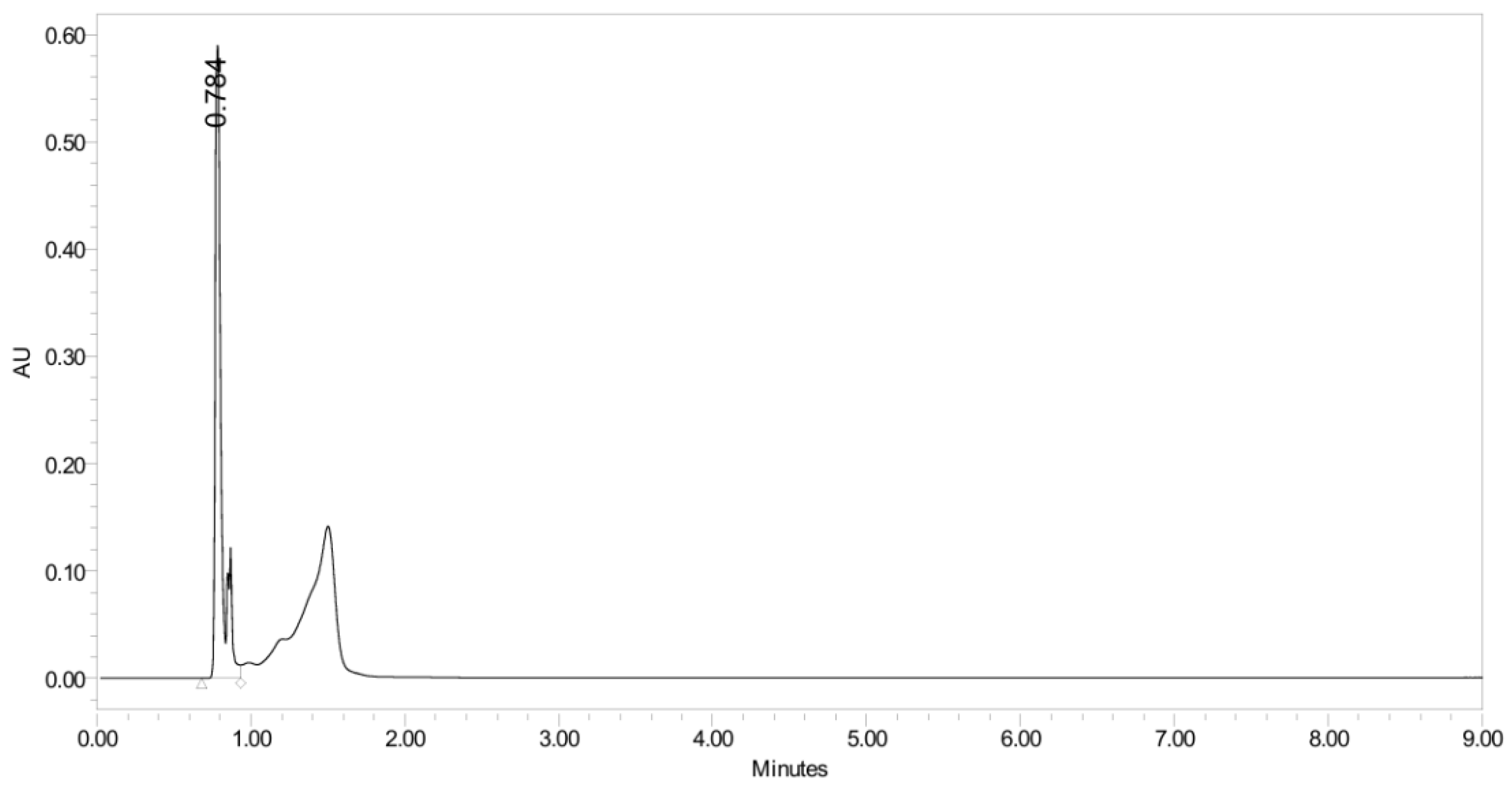
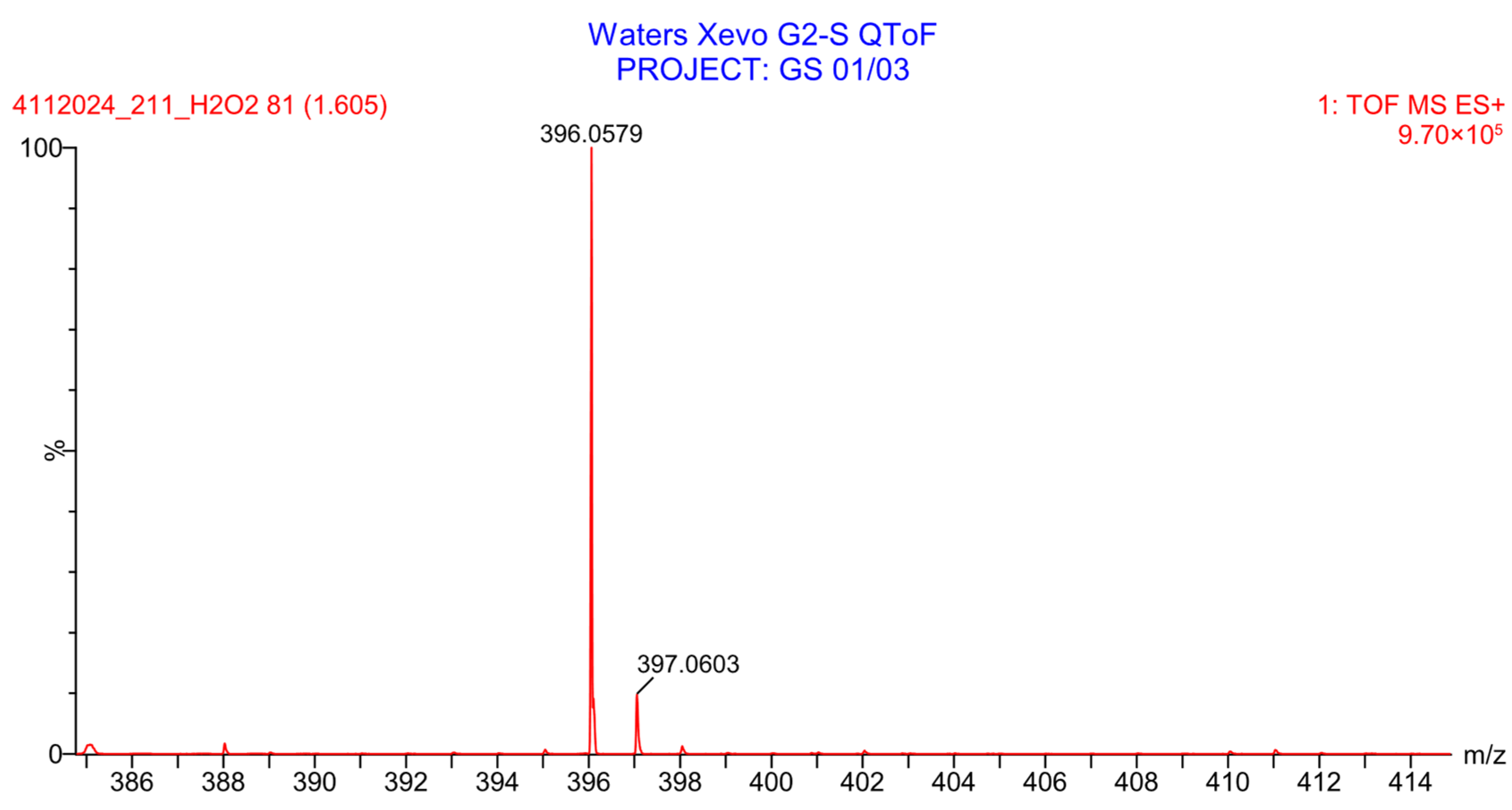
2.2.4. Stability Study
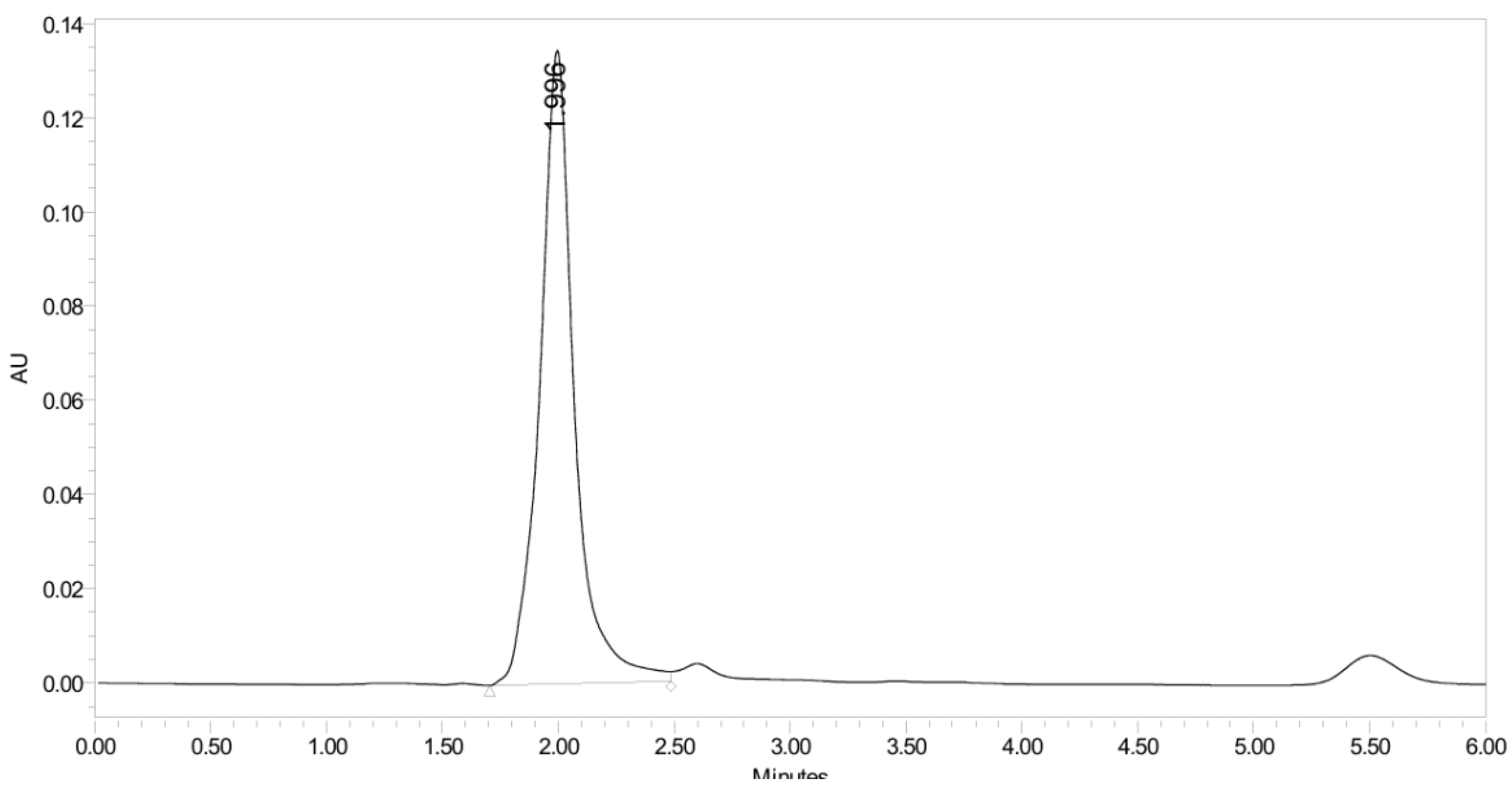
2.3. Method Validation for PH-247
2.3.1. Linearity and Sensitivity
2.3.2. Precision and Accuracy
2.3.3. Estimation of PH-247 Extraction and Stability in Human Plasma
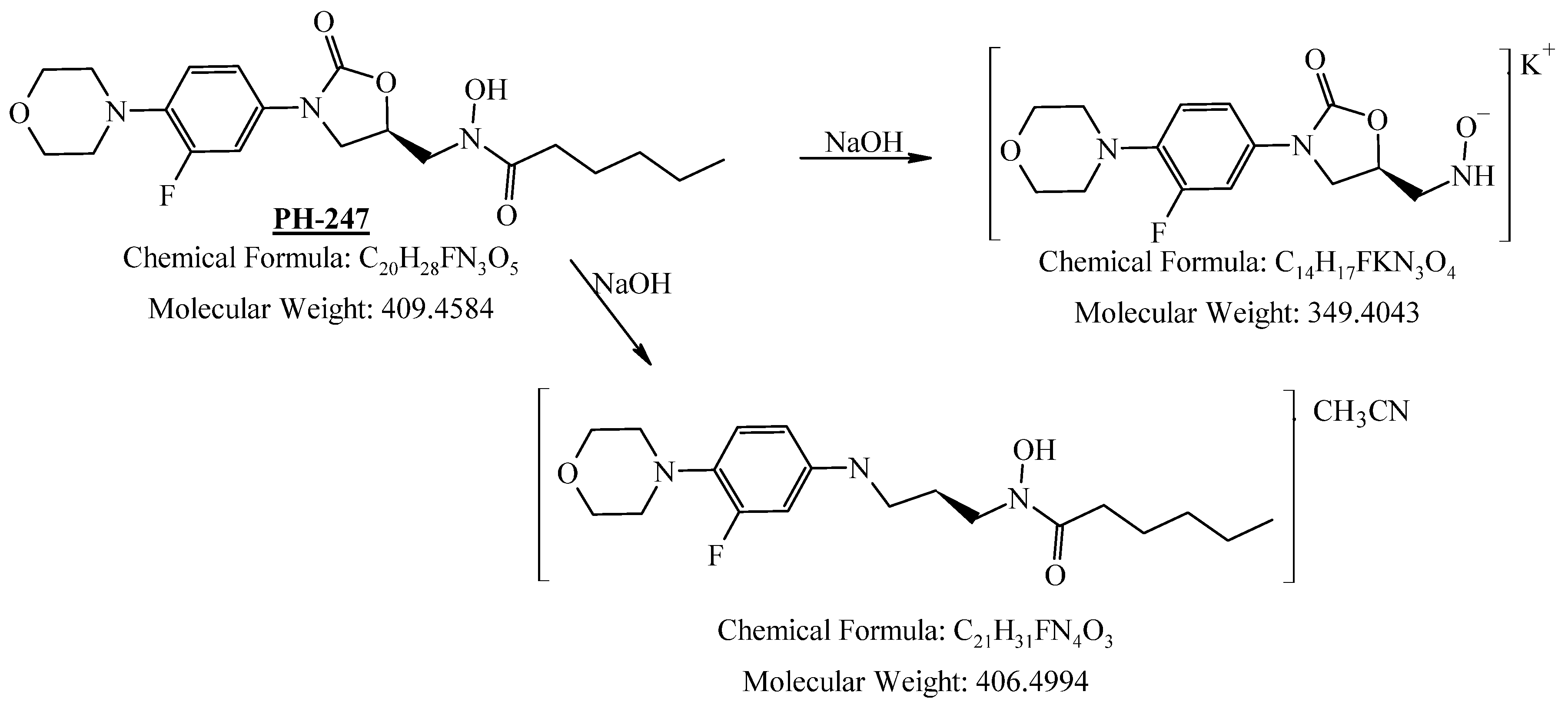
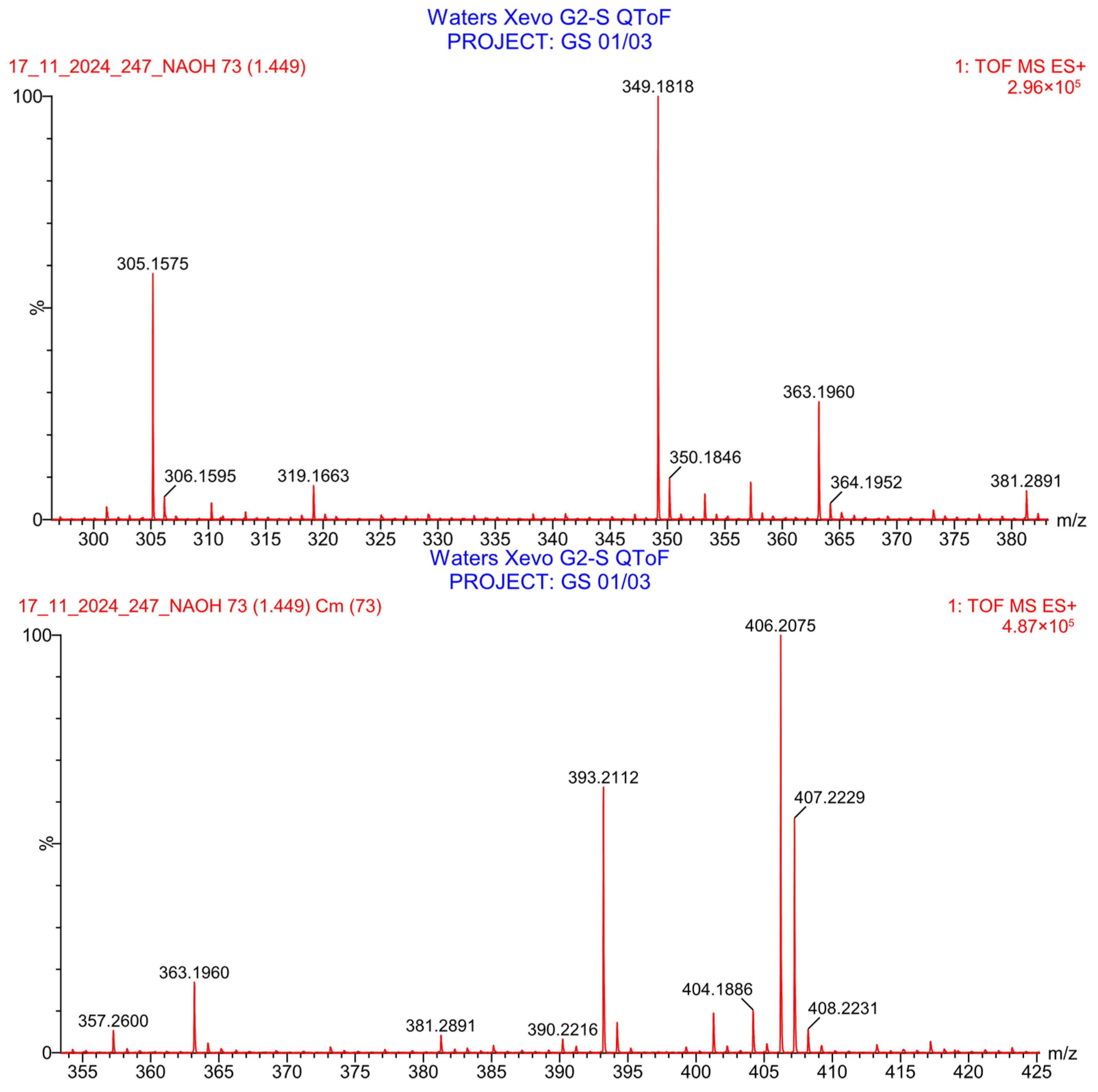
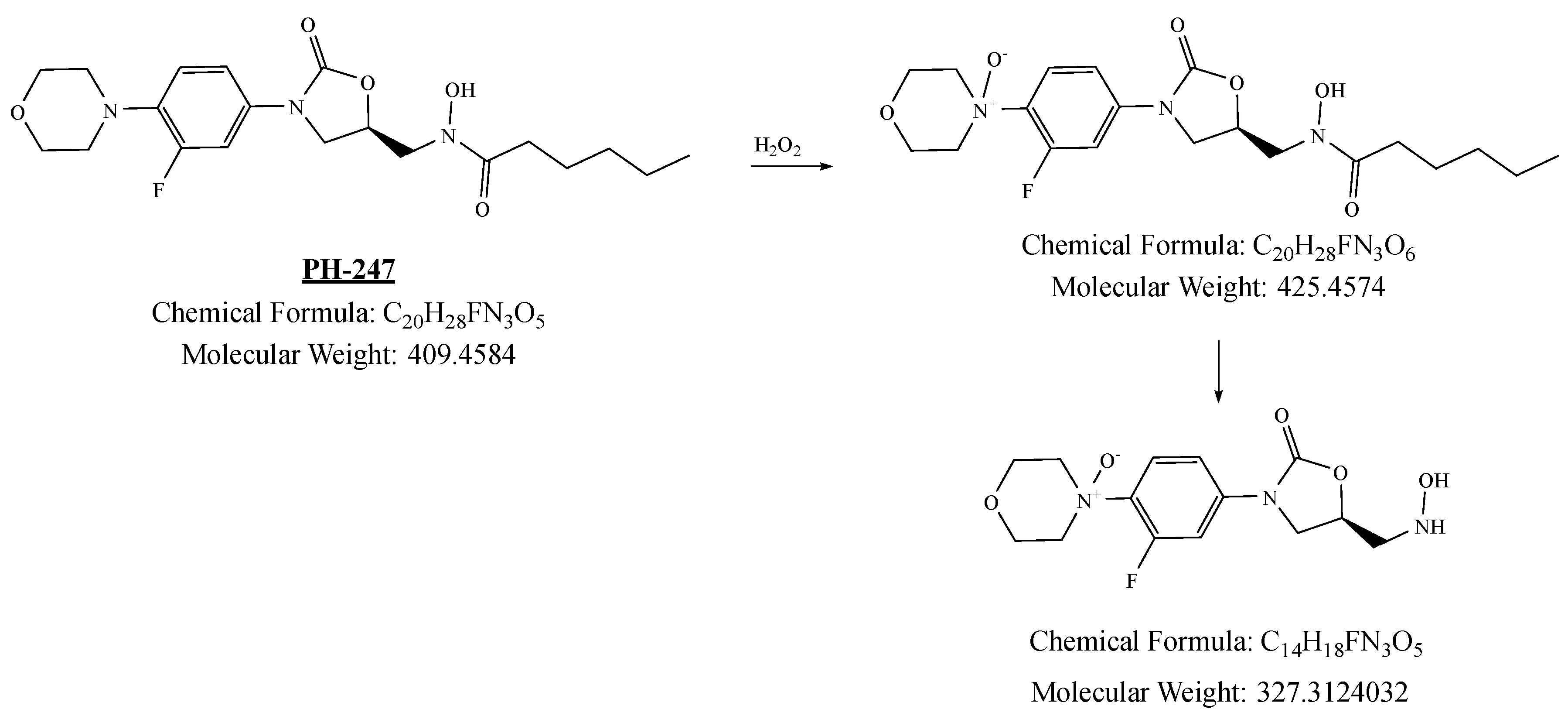
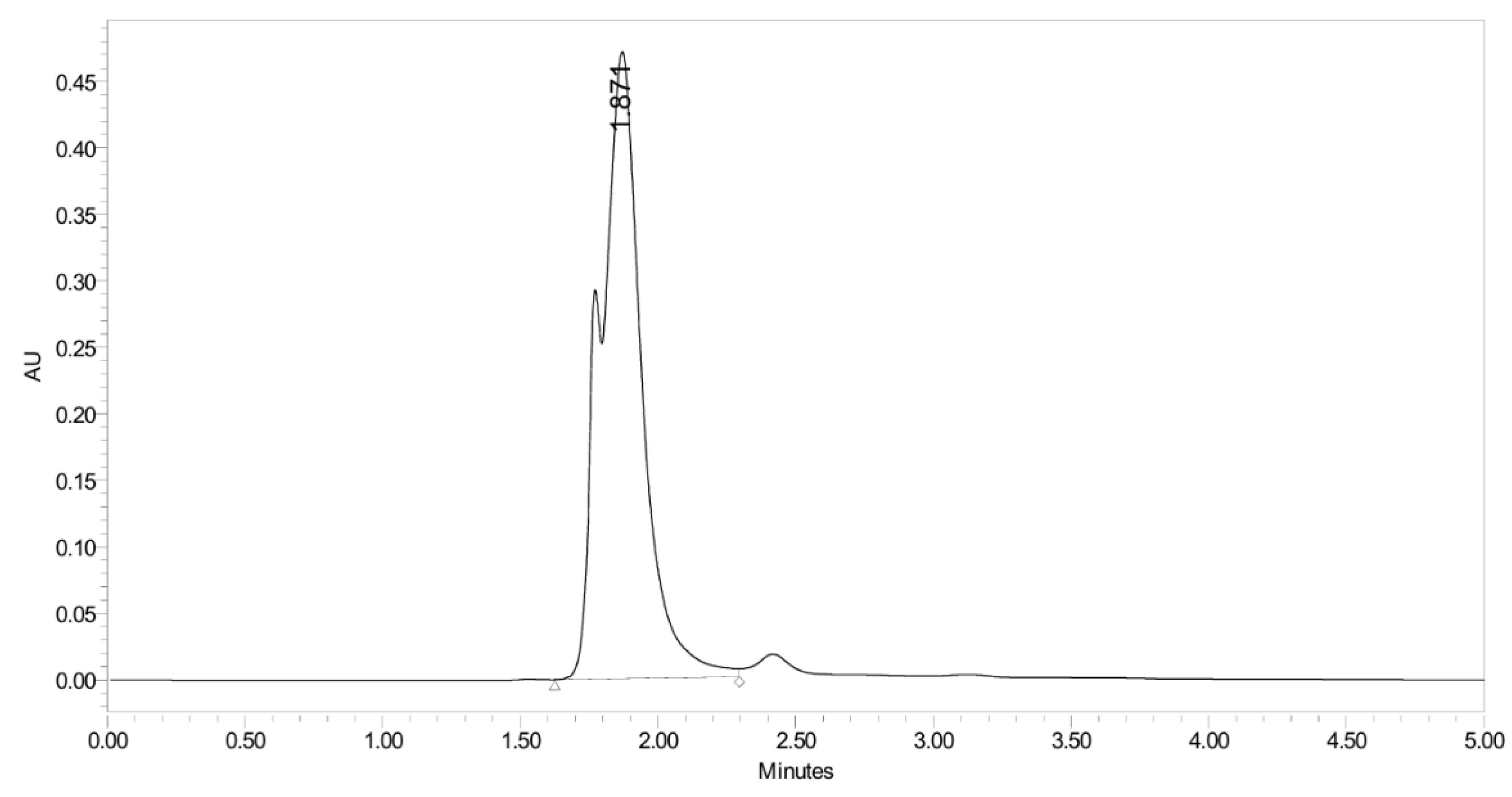
2.3.4. Stability Study
2.4. Method Validation for PH-249
2.4.1. Linearity and Sensitivity
2.4.2. Precision and Accuracy
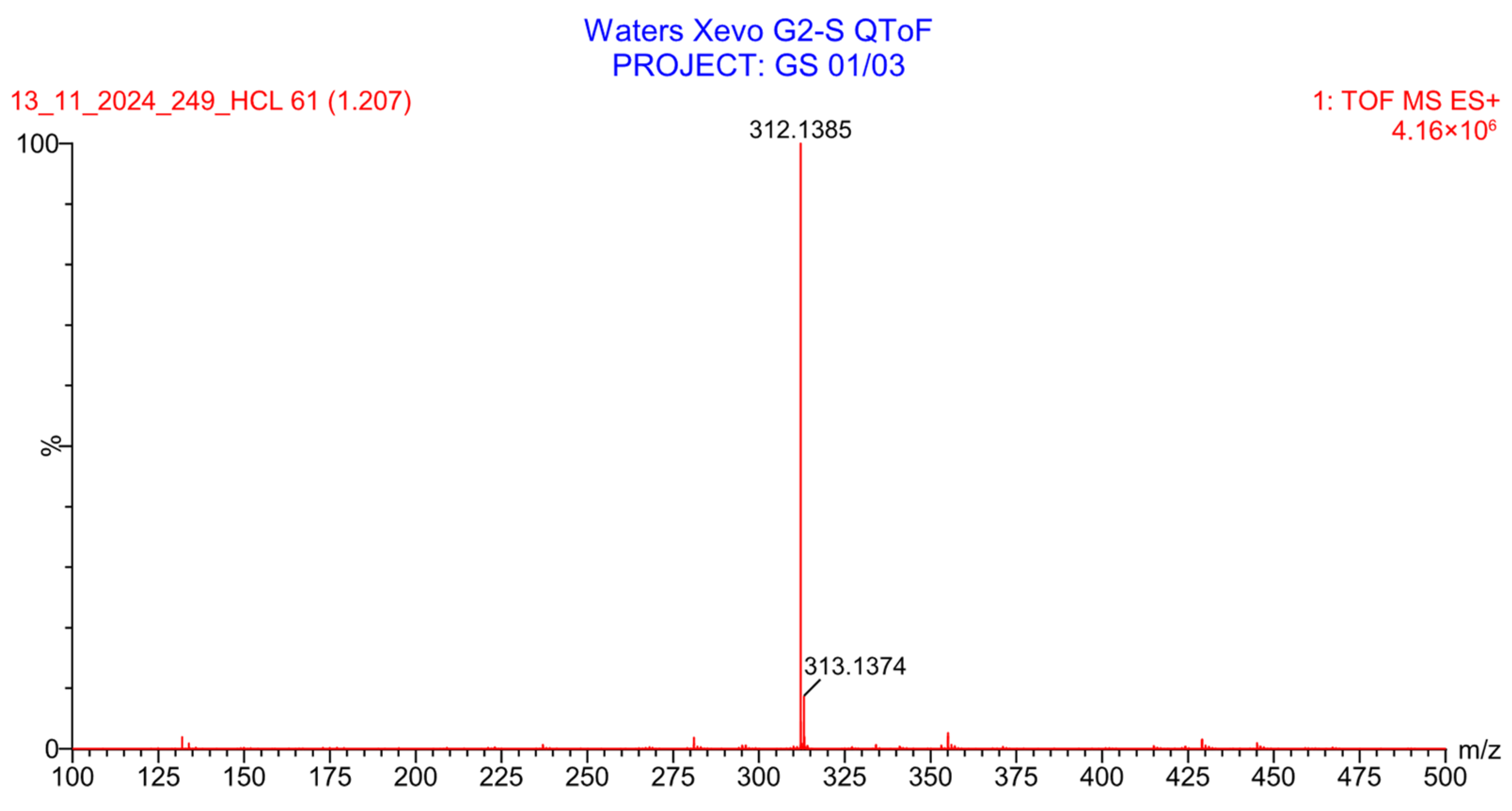
2.4.3. Evaluation of PH-249 Extraction and Stability in Human Plasma
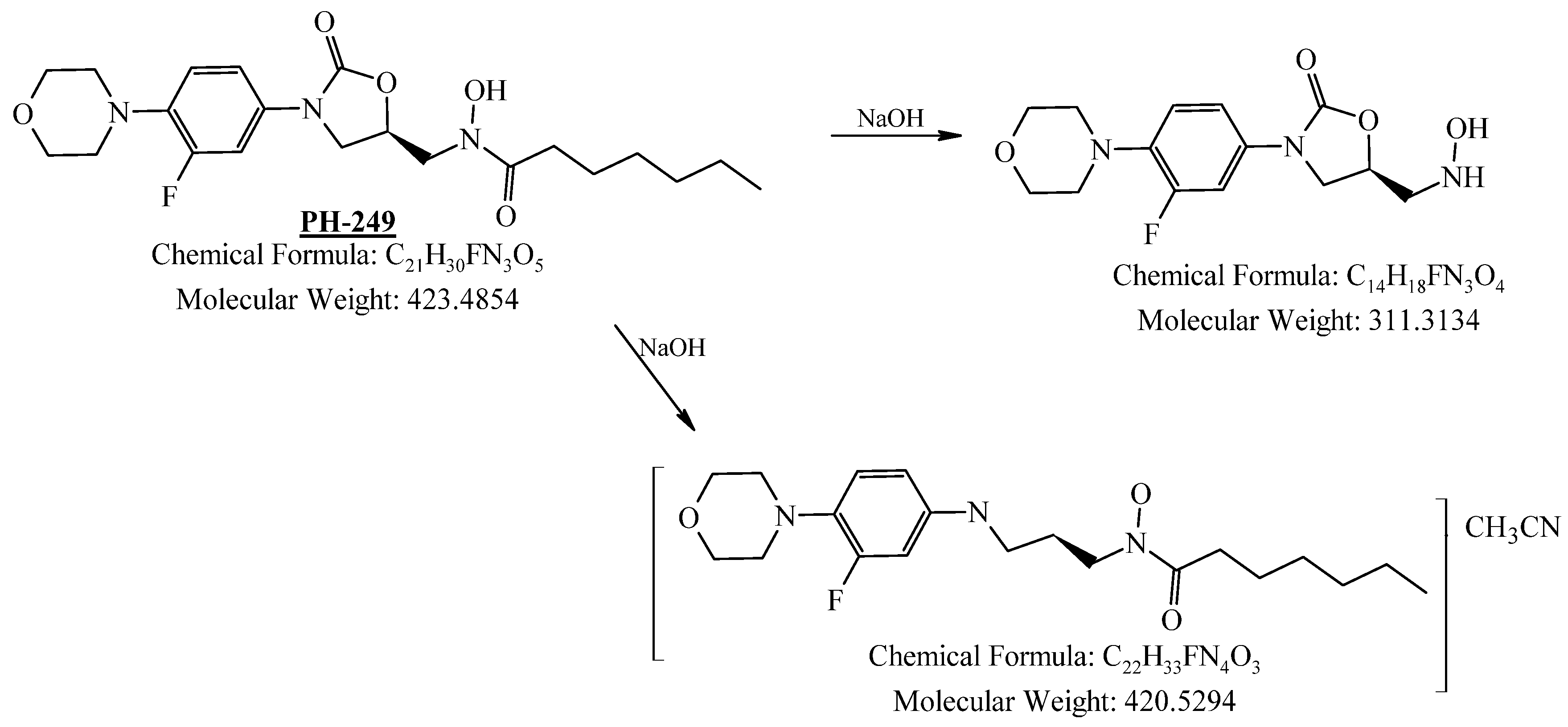
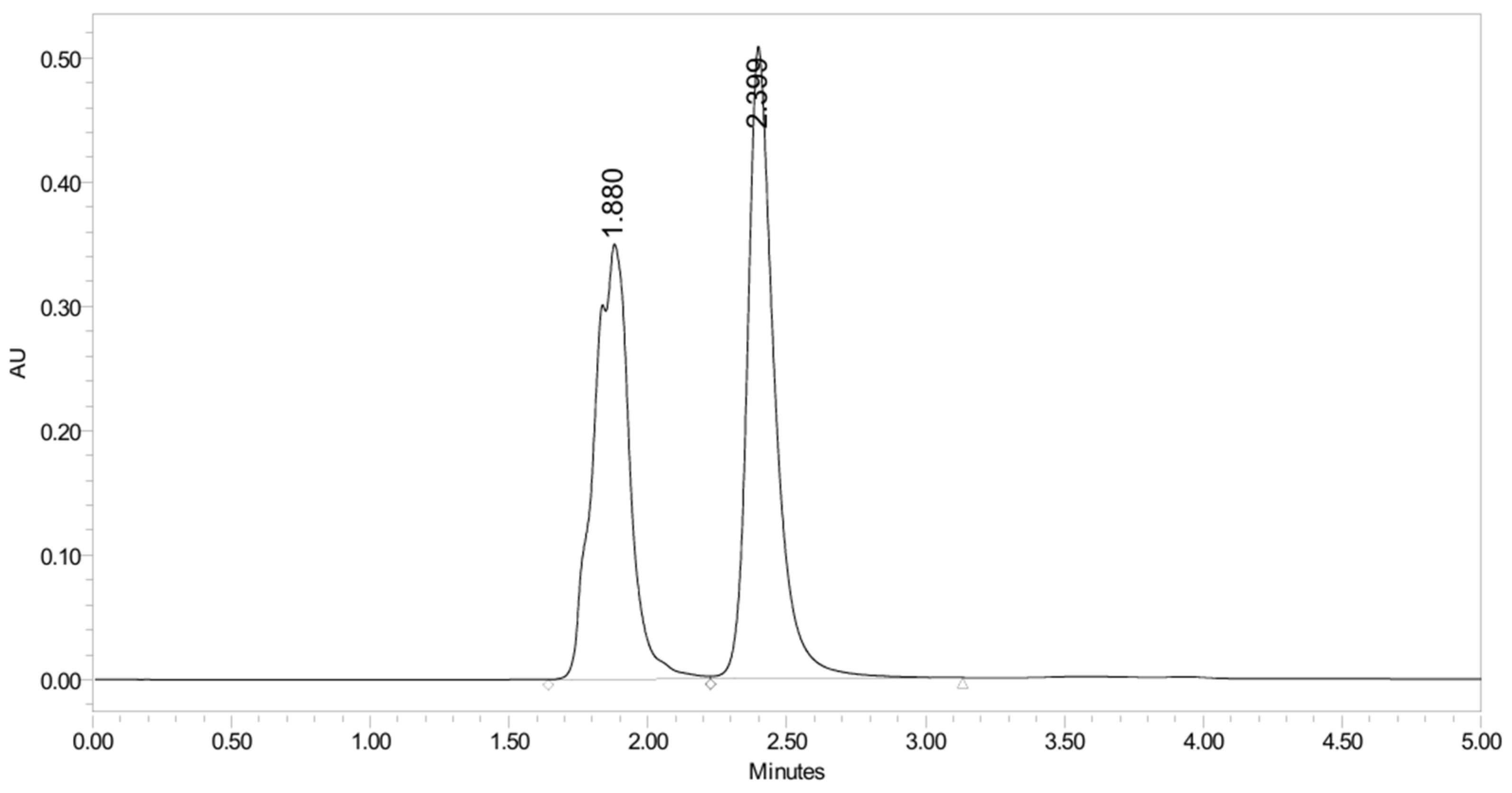
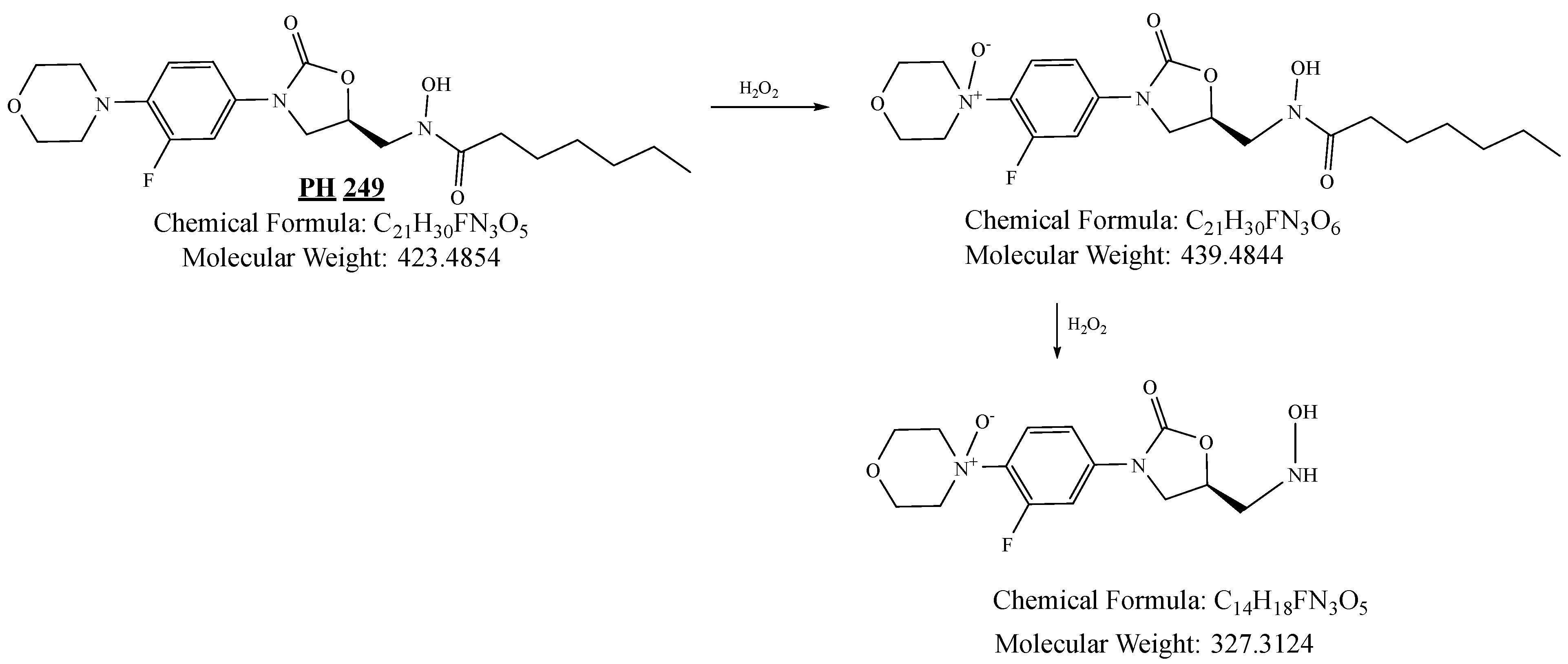
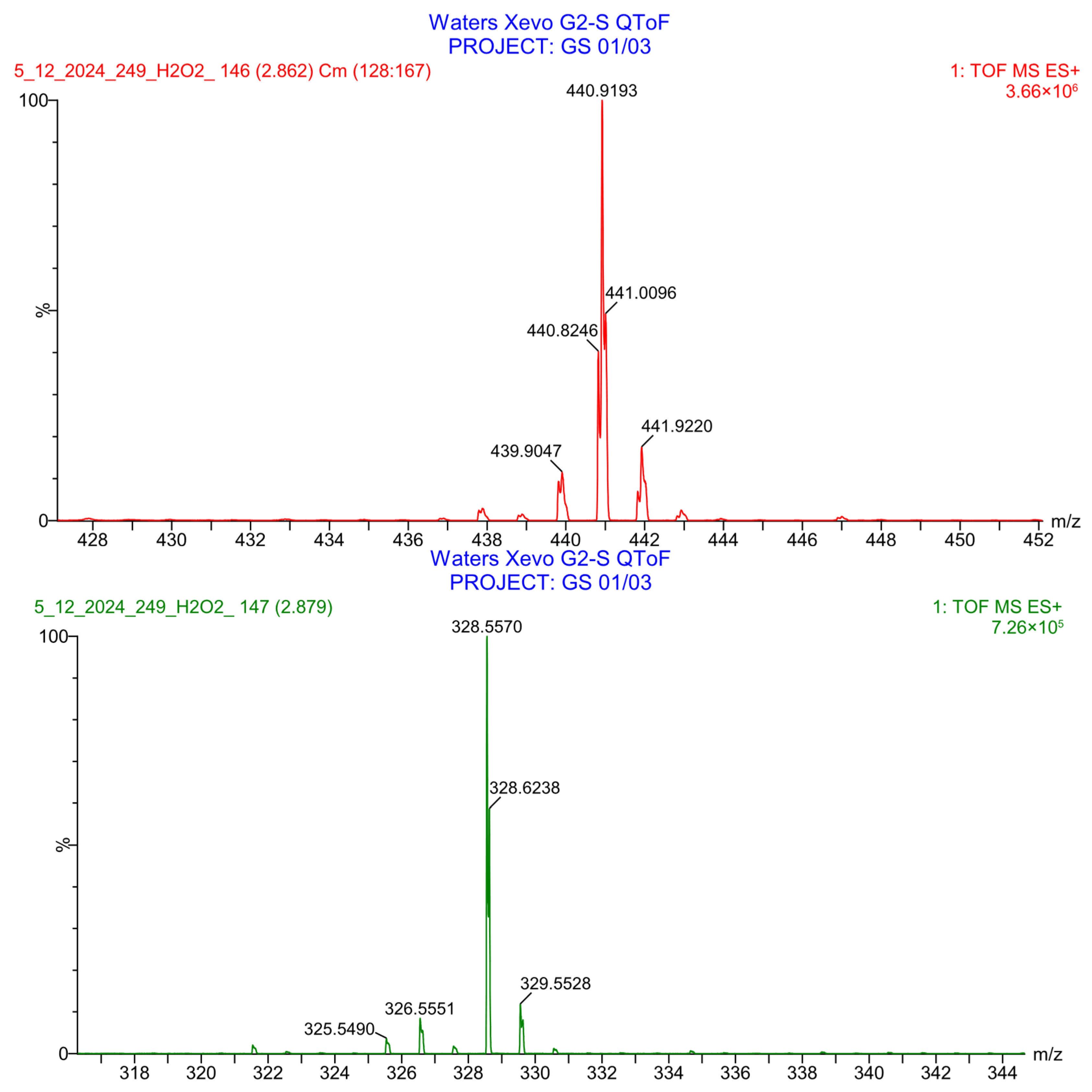
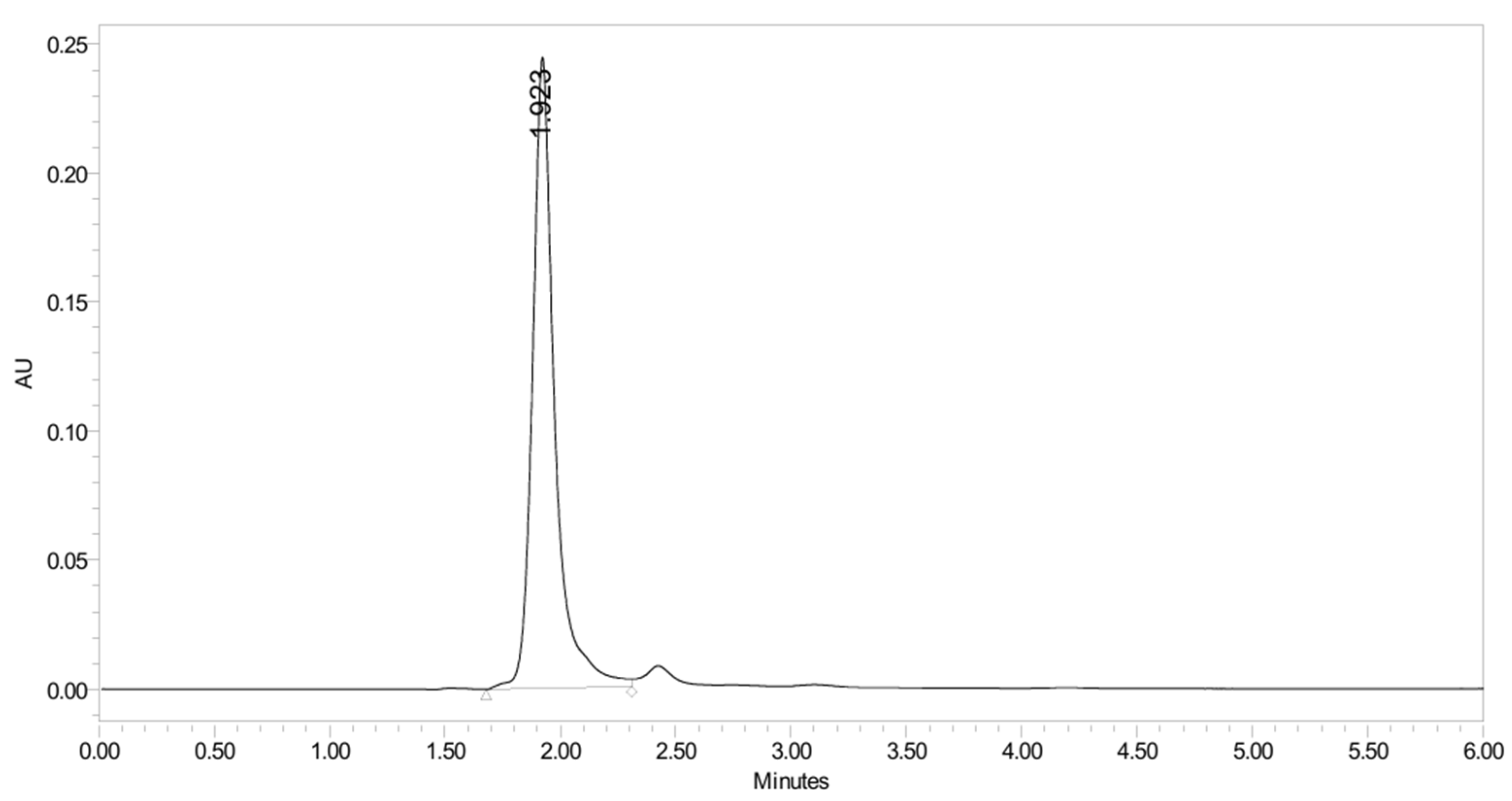
2.4.4. Stability Study
2.5. Method Validation for PH-251
2.5.1. Linearity and Sensitivity
2.5.2. Precision and Accuracy
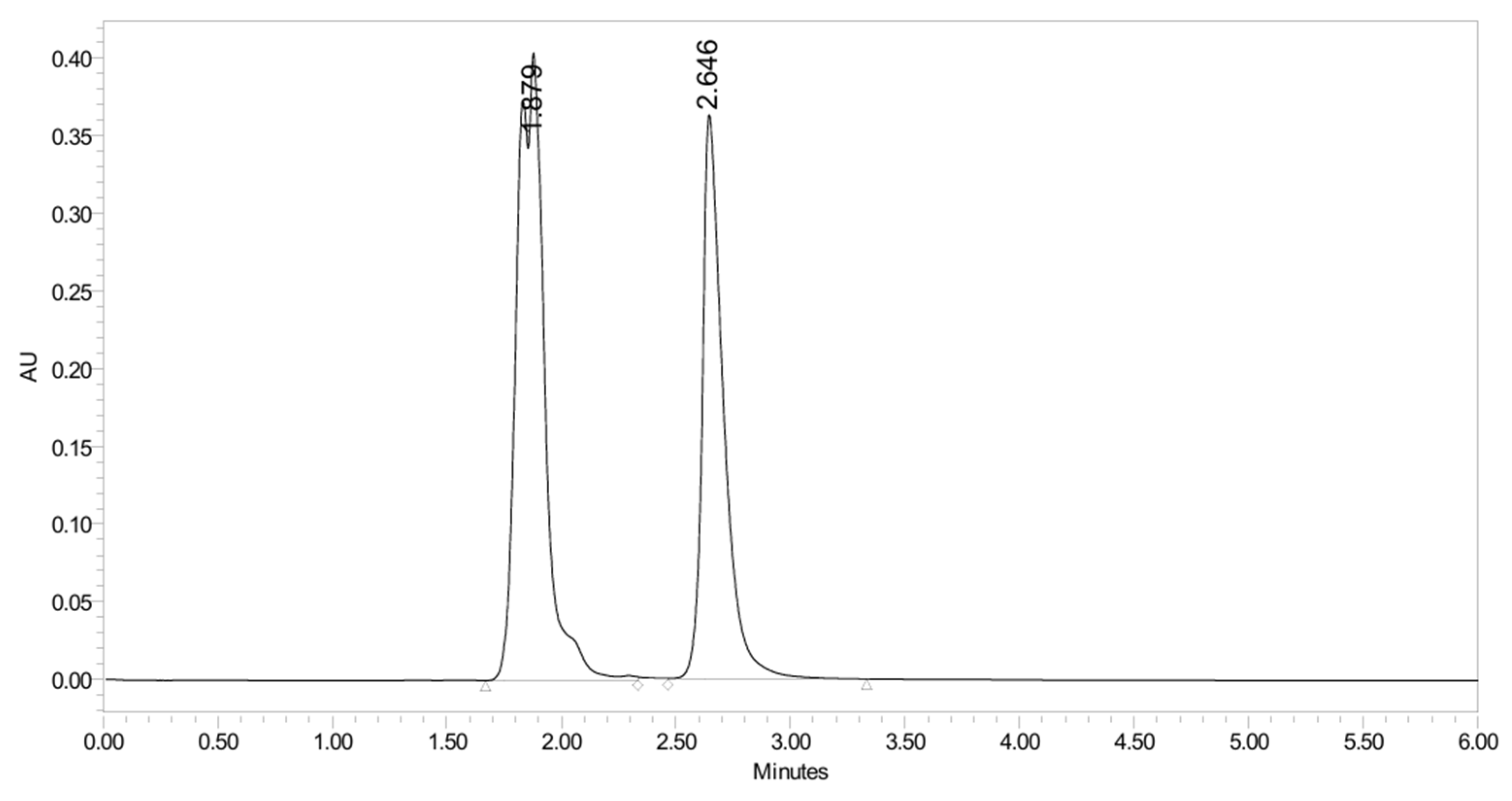
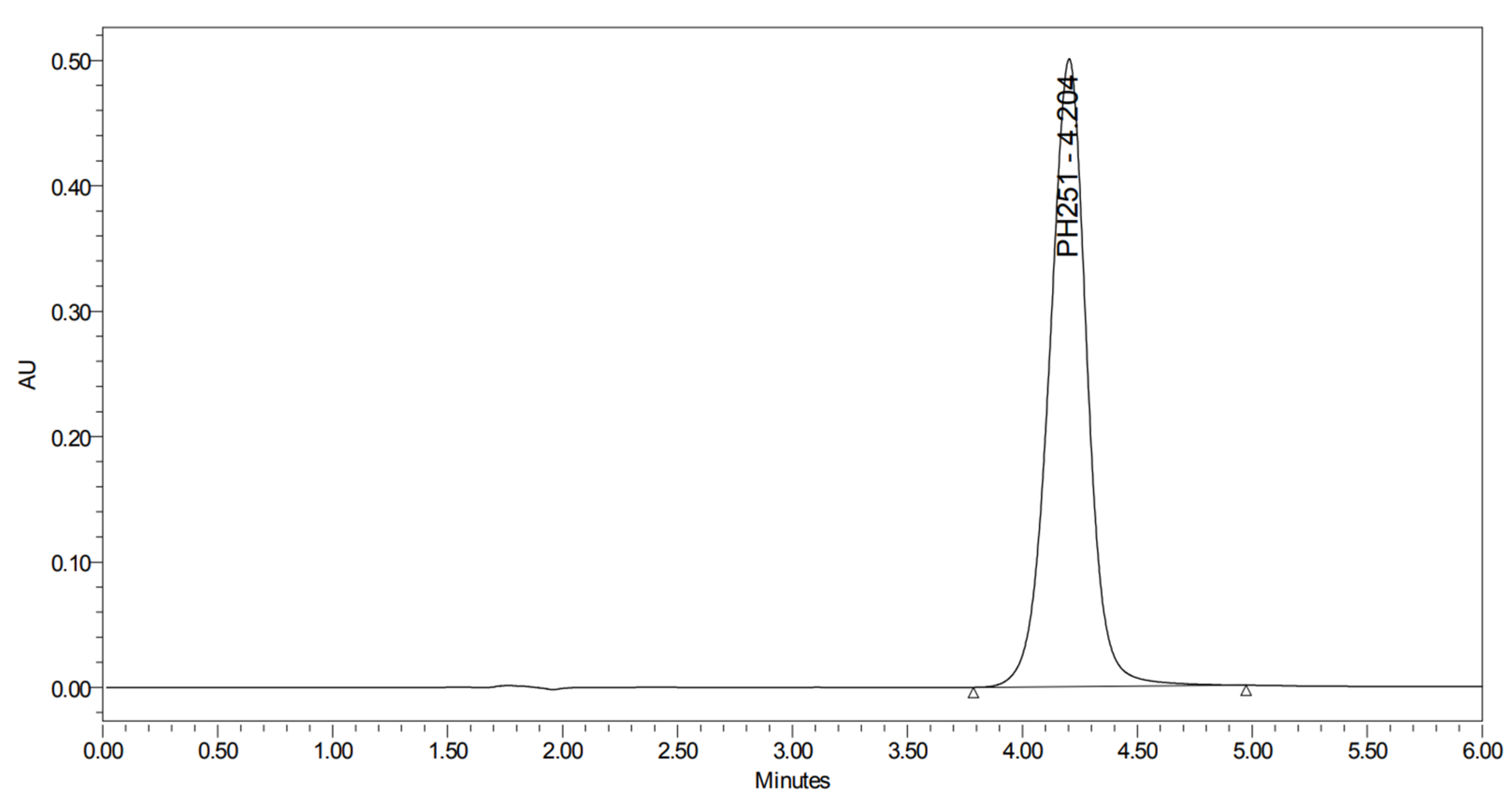
2.5.3. Assessment of PH-251 Extraction and Stability in Human Plasma
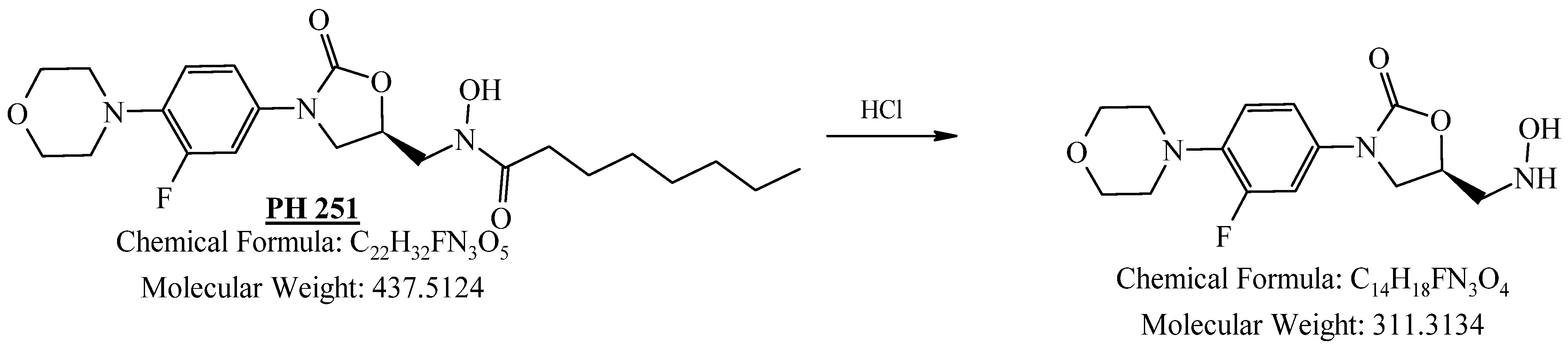
2.5.4. Stability Study
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.1.1. Chemistry
3.1.2. Chemicals
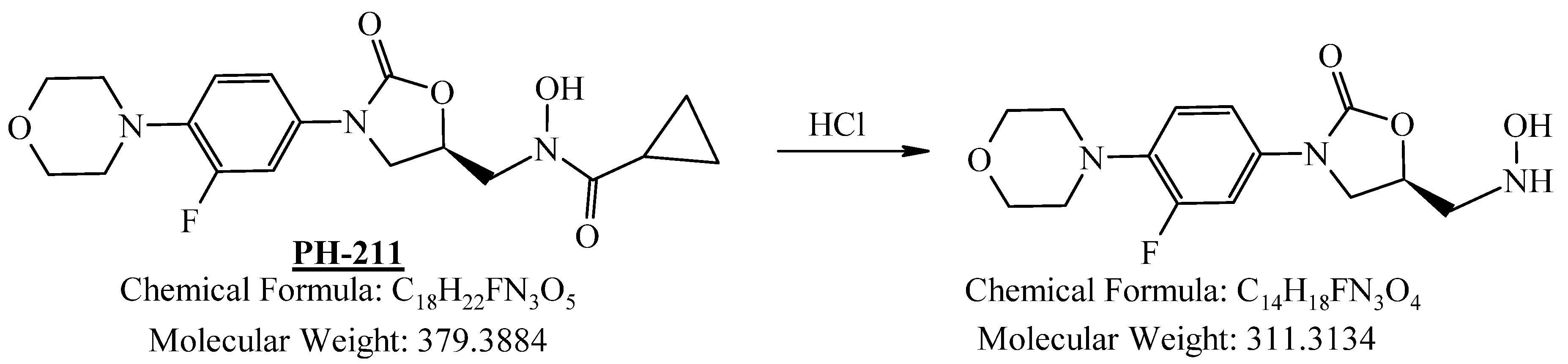
3.1.3. Preparation of (R)-N-((3-(3-Fluoro-4-morpholinylphenyl)-2-oxooxazolidin-5-yl)methyl)-N-hydroxycyclopropanecarboxamide (PH-211)
3.1.4. Preparation of (R)-N-((3-(3-Fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)-2-oxooxazolidin-5-yl)methyl)-N-hydroxyoctanamide (PH-251)
3.1.5. Solutions
3.1.6. Human Plasma Extraction Technique
3.2. Instrumentation
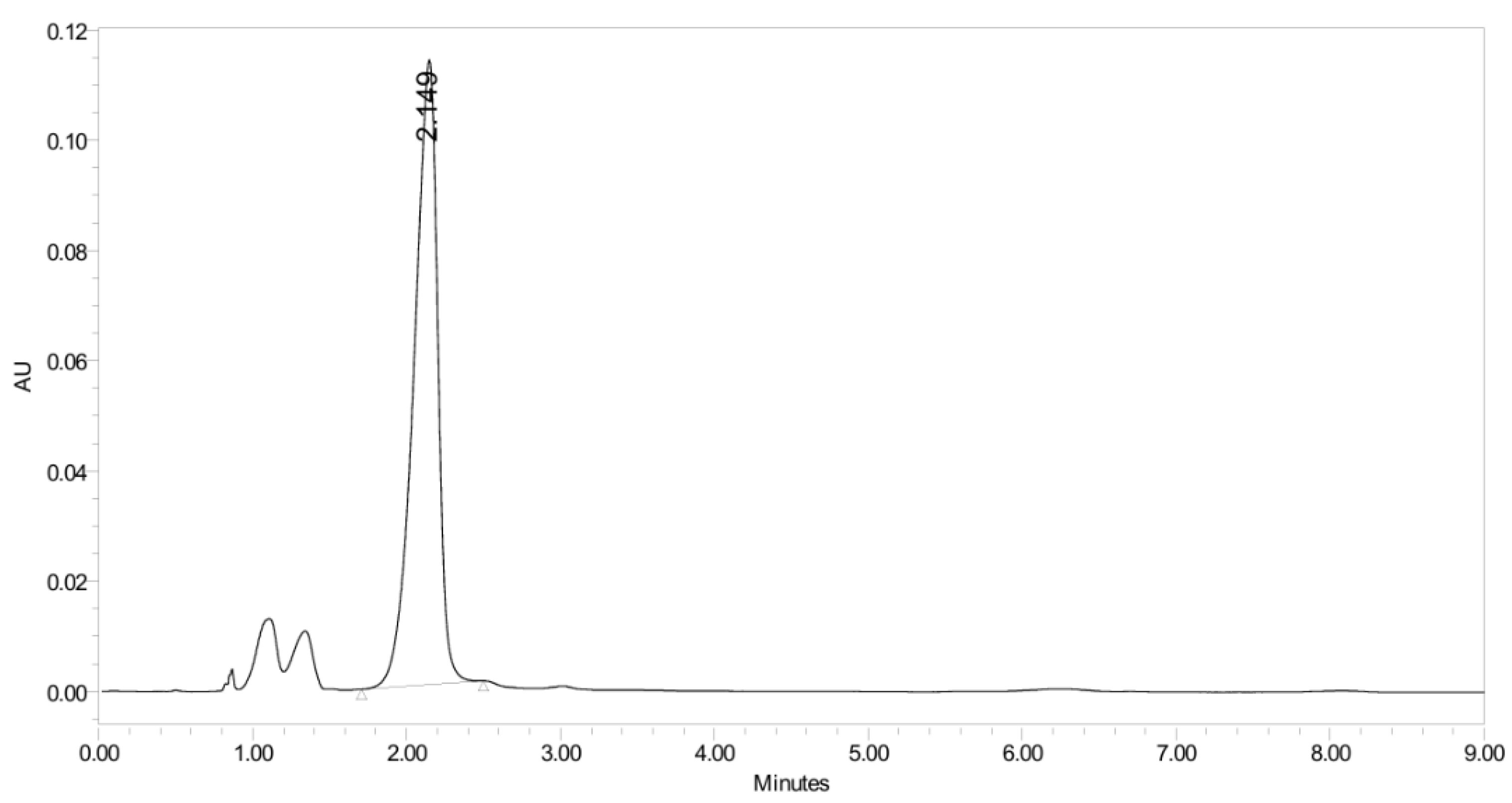
3.2.1. Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Ultraviolet (UHPLC-UV)
3.2.2. Chromatographic Conditions
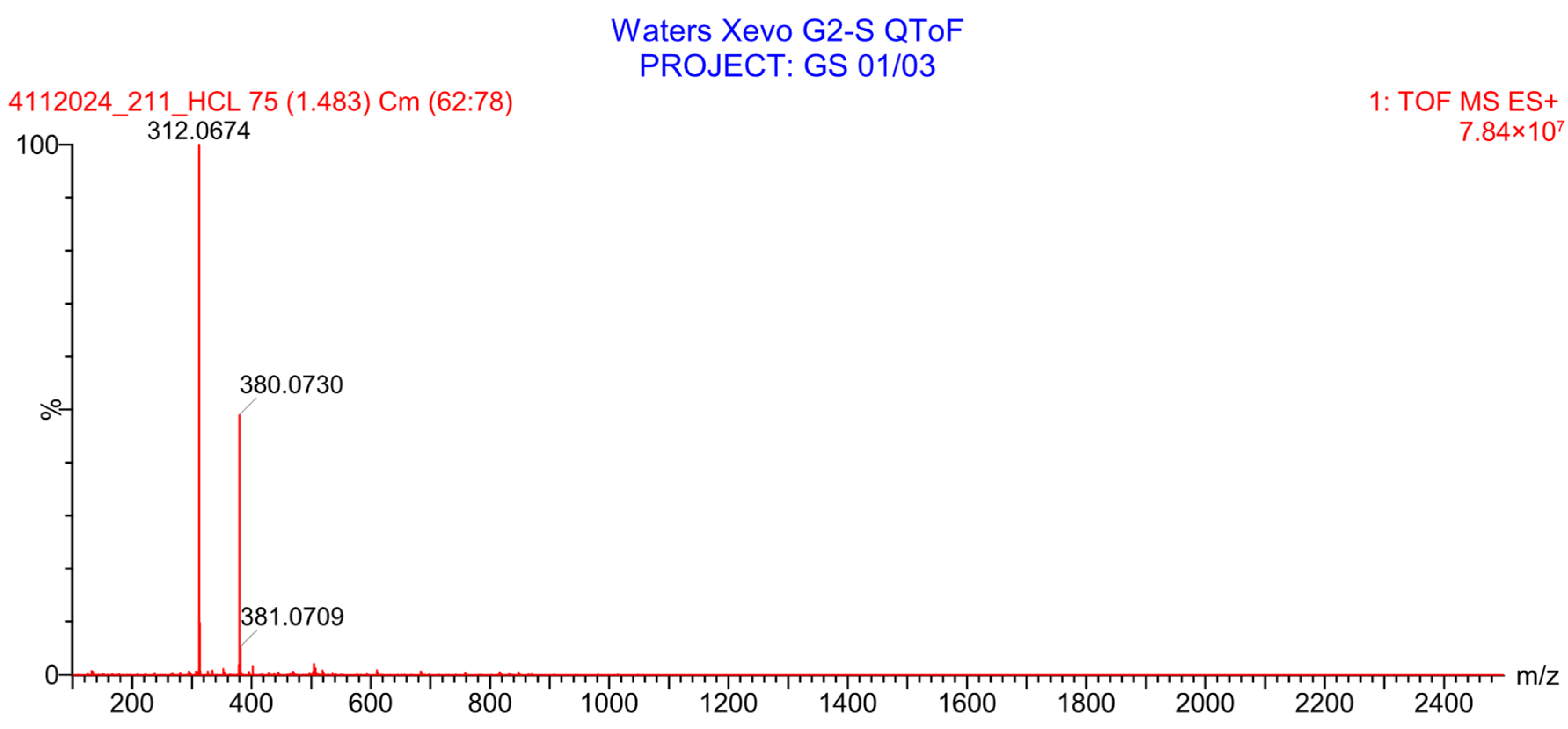
3.2.3. Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-MS)
3.3. Method Validation
3.3.1. Calibration Curve
3.3.2. Accuracy and Precision
3.3.3. Extraction Recovery and Matrix Effect
3.3.4. Evaluation of PH-211, PH-247, PH-249, and PH-251 Extraction and Stability in Human Plasma
3.3.5. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
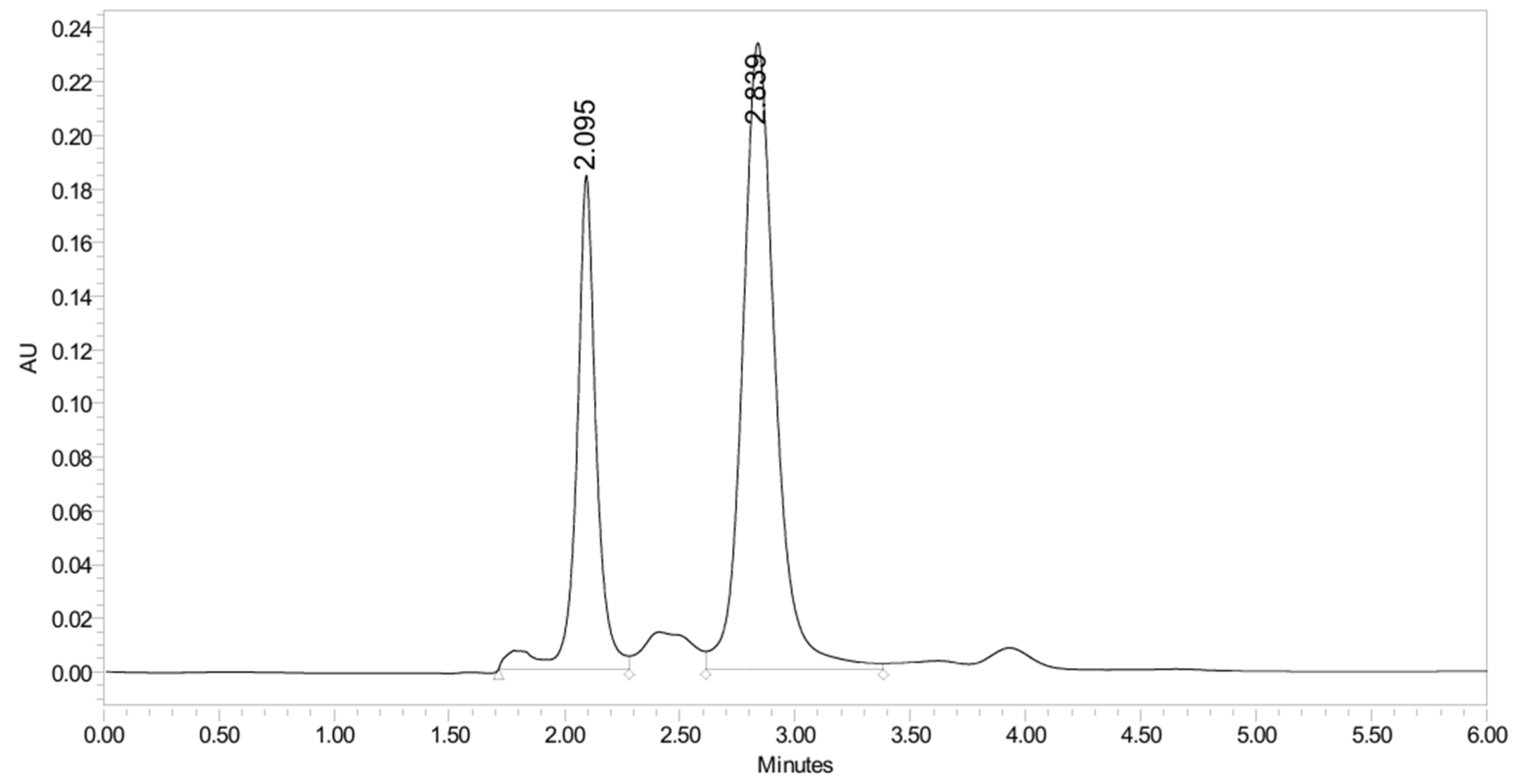
3.4. Forced Degradation Studies
3.4.1. Acidic Degradation
3.4.2. Basic Degradation
3.4.3. Oxidation Degradation
3.4.4. Thermal Degradation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phillips, O.A.; Sharaf, L.H. Oxazolidinone antimicrobials: A patent review (2012–2015). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, O.A.; Udo, E.E.; Ali, A.A.M.; Al-Hassawi, N. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of 5-substituted oxazolidinones. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, F.; Zhou, F.; Girardot, M.; Kern, G.; Eyermann, C.J.; Hales, N.J.; Ramsay, R.R.; Gravestock, M.B. Identification of 4-substituted 1,2,3-triazoles as novel oxazolidinone antibacterial agents with reduced activity against monoamine oxidase A. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedaya, O.M.; Mathew, P.M.; Mohamed, F.H.; Phillips, O.A.; Luqmani, Y.A. Antiproliferative activity of a series of 5-(1H-1,2,3-triazolyl) methyl- and 5-acetamidomethyl-oxazolidinone derivatives. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3311–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hasawi, N.A.; Phillips, O.A.; Al-Awadhi, F.; Sharaf, L.H.; Amine, S.A.; Novotny, L. Anti-progressive Effects of a Series of Glycinyl and Alaninyl Triazolyl-oxazolidinones on Kelly Neuroblastoma Cell Line. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 5125–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, N.; Singla, R.K.; Shrivastava, B. Current updates on oxazolidinone and its significance. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 2012, 159285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombian, S.B.; Phillips, O.A. In vitro electrophysiological investigations of the acute effects of linezolid and novel oxazolidinones on central nervous system neurons. Neuroscience 2011, 180, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombian, S.B.; Phillips, O.A. Novel actions of oxazolidinones: In vitro screening of a triazolyloxazolidinone for anticonvulsant activity. Med. Princ. Pract. 2013, 22, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaddoumi, M.G.; Phillips, O.A.; Kombian, S.B. A novel oxazolidinone derivative PH192 demonstrates anticonvulsant activity in vivo in rats and mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 130, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brijesh Kumar, S.; Rina, S.; Jayendra, Z.P.; Mukul, R.J.; Pankaj, R.P. Oxazolidinone Antibacterials and Our Experience. Anti-Infect. Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 7, 258–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Shen, D.D.; Bai, Y.R.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, T.; Sun, C.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.Q.; Liu, H.M. Oxazolidinone: A promising scaffold for the development of antibacterial drugs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 250, 115239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdogan, B.; Appelbaum, P.C. Oxazolidinones: Activity, mode of action, and mechanism of resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 23, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekema, D.J.; Jones, R.N. Oxazolidinone antibiotics. Lancet 2001, 358, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.C.; Swaney, S.M.; Shinabarger, D.L.; Stockman, B.J. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance study of oxazolidinone binding to bacterial ribosomes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Sun, L.; Qiu, J.J.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; So, C.W.; Dong, S. A novel application of furazolidone: Anti-leukemic activity in acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, O.A.; D’Silva, R.; Bahta, T.O.; Sharaf, L.H.; Udo, E.E.; Benov, L.; Eric Walters, D. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 5-(hydroxamic acid)methyl oxazolidinone derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 106, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, O.A.; Bosso, M.A.; Ezeamuzie, C.I. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel 5-(hydroxamic acid)methyl oxazolidinone derivatives as 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, S.; Honn, K.V. Inflammation and disease progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchette, D.; Patel, P.; Preuss, C.V. Zileuton; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhilber, D.; Hofmann, B. Recent advances in the search for novel 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 114, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foti, C.; Piperno, A.; Scala, A.; Giuffrè, O. Oxazolidinone Antibiotics: Chemical, Biological and Analytical Aspects. Molecules 2021, 26, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tannak, N.F.; Phillips, O.A. Antimycobacterial Activities of N-Substituted-Glycinyl 1H-1,2,3-Triazolyl Oxazolidinones and Analytical Method Development and Validation for a Representative Compound. Sci. Pharm. 2017, 85, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.K.; Kim, E.J.; Kwon, J.W.; Kim, W.B.; Lee, M.G. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of DA-7867, a new oxazolidinone, in human plasma and urine and in rat tissue homogenates. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 794, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazos-Rocha, N.; Carmona-Alvarado, I.; Vera-Cabrera, L.; Waksman-de-Torres, N.; Salazar-Cavazos, M.D.L.L. HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Analysis of Fluoroquinolones and Oxazolidinones in Plasma. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2014, 52, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, O.A.; Abdel-Hamid, M.E. Determination of novel antibacterial triazolylmethyl oxazolidinones concentrations in human plasma by APCI-LC-MS: Application to stability study. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 11, 22s–31s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, O.A.; Sharaf, L.H.; Abdel-Hamid, M.E.; Varghese, R. Assessment of the stability of novel antibacterial triazolyl oxazolidinones using a stability-indicating high-performance liquid chromatography method. Med. Princ. Pract. 2011, 20, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.F.D.S.; Salgado, H.R.N.; Santos, J.L.d. A critical review of HPLC-based analytical methods for quantification of Linezolid. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 50, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.P.; Jin, B.; Li, T.; Zhang, T.T.; Ma, C. Studies on the degradation impurity of linezolid tablets by UFLC-MS/MS. Yaoxue Xuebao 2017, 52, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tannak, N.F.; Phillips, O.A.; Kamal, H.J.; Hemdan, A. Development and Validation of Stability-Indicating Assay Method for a Novel Oxazolidinone (PH-192) with Anticonvulsant Activity by Using UHPLC-QToF-MS. Molecules 2022, 27, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brickner, S.J.; Hutchinson, D.K.; Barbachyn, M.R.; Manninen, P.R.; Ulanowicz, D.A.; Garmon, S.A.; Grega, K.C.; Hendges, S.K.; Toops, D.S.; Ford, C.W.; et al. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of U-100592 and U-100766, Two Oxazolidinone Antibacterial Agents for the Potential Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana Raju, T.; Vishweshwari Kutty, O.; Ganesh, V.; Yadagiri Swamy, P. A validated stability-indicating LC method for the separation of enantiomer and potential impurities of Linezolid using polar organic mode. J. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 2, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Jin, B.; Ma, C. Characterization of degradation products and process-related impurity of sutezolid by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 169, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Jin, B.; Ma, C.; Zhang, T.; Li, T. Identification of forced degradation products of tedizolid phosphate by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 139, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline. Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2 (R1); Somatek Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 1, p. 5. [Google Scholar]

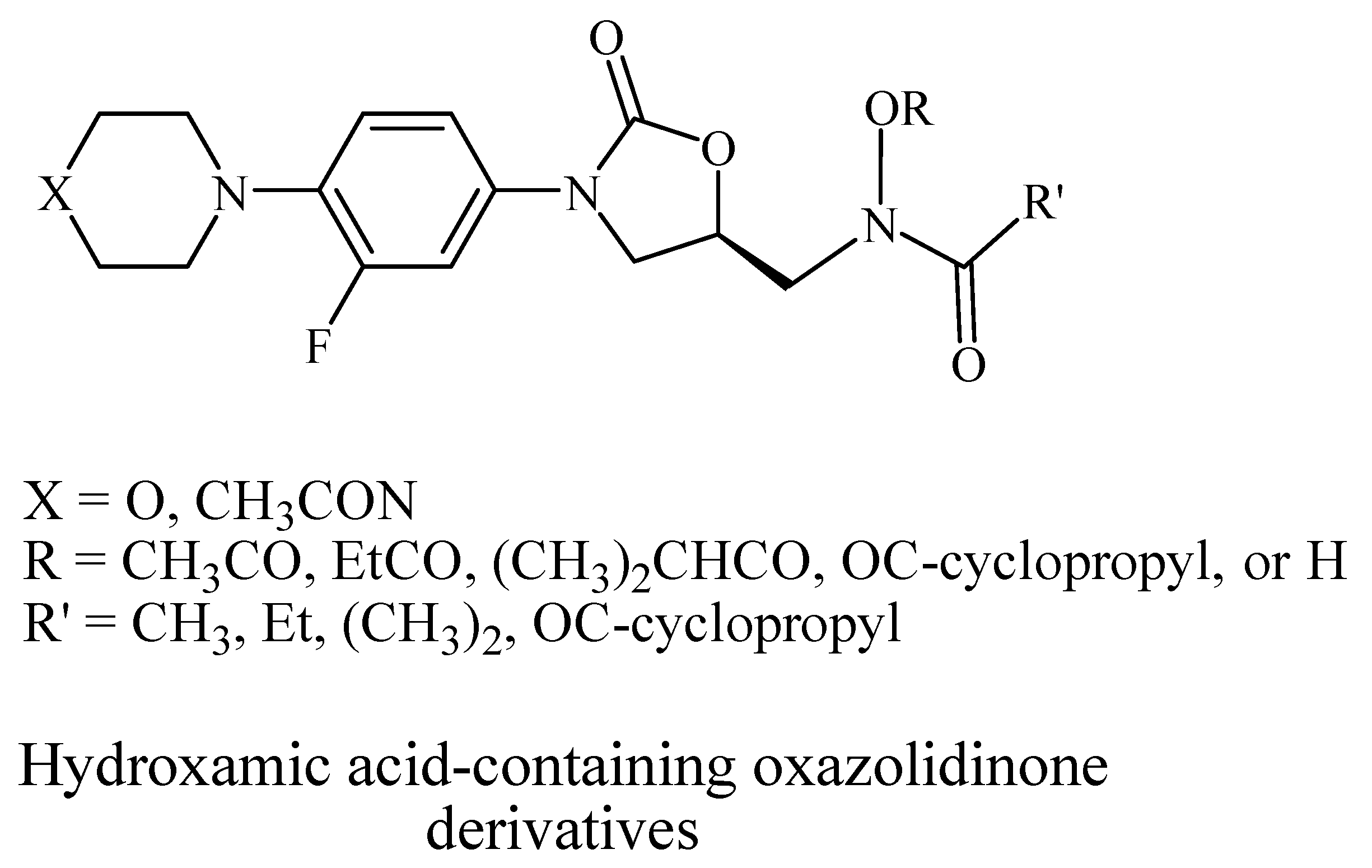







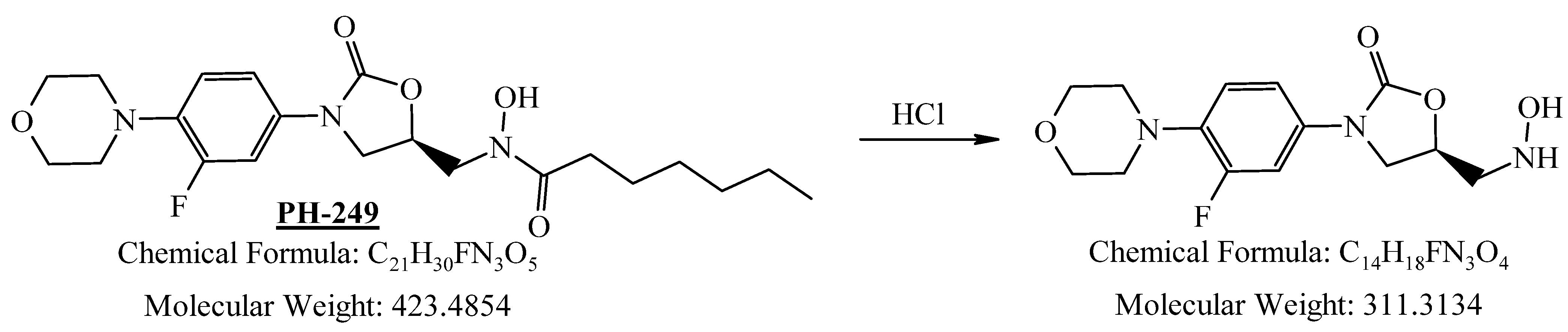







| Compound ID | Structure | Mol. Wt. | Mol. Form. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zileuton |  | 236.29 | C11H12FN2O2S |
| PH-211 | 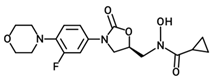 | 379.38 | C18H22FN3O5 |
| PH-247 |  | 409.46 | C20H28FN3O5 |
| PH-249 | 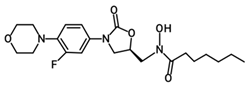 | 423.49 | C21H30FN3O5 |
| PH-251 | 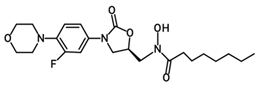 | 437.51 | C22H32FN3O5 |
| Parameters | PH-211 |
|---|---|
| Range (mg/mL) | 0.01–0.1 |
| Regression equation | y = 0.0167x − 0.0006 |
| Correlation coefficient (r) | 0.999 |
| LOQ (mg/mL) | 0.01 |
| LOD (mg/mL) | 0.003 |
| Intra-assay precision a | 0.22 |
| Inter-assay precision a | 0.16 |
| Accuracy b | 100.19 |
| PH-211 Concentration mg/mL | Relative Peak Area | Mean ± SD (n = 3) Observed/mg/mL | Precision a (%) | Accuracy b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.556634 | 0.557696 ± 0.00125436 | 0.22 | 100.19 |
| 0.04 | 2.527021 | 2.53283 ± 0.005082246 | 0.20 | 100.23 |
| 0.1 | 6.010906 | 6.021317 ± 0.009537771 | 0.16 | 100.17 |
| PH-211 Concentration mg/mL | Relative Peak Area | Mean ± SD (n = 3) Observed/mg/mL | Precision a (%) | Accuracy b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.541716 | 0.542095 ± 0.000859498 | 0.16 | 100.07 |
| 0.04 | 2.500928 | 2.502639 ± 0.001872342 | 0.07 | 100.07 |
| 0.1 | 5.999658 | 6.007606 ± 0.011840756 | 0.20 | 100.13 |
| Parameters | PH-247 |
|---|---|
| Range (mg/mL) | 0.005–0.08 |
| Regression equation | y = 0.0452x + 0.0014 |
| Correlation coefficient (r) | 0.999 |
| LOQ (mg/mL) | 0.005 |
| LOD (mg/mL) | 0.0015 |
| Intra-assay precision a | 1.35 |
| Inter-assay precision a | 1.08 |
| Accuracy b | 100.90 |
| PH-247 Concentration mg/mL | Relative Peak Area | Mean ± SD (n = 3) Observed/mg/mL | Precision a (%) | Accuracy b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.005 | 0.088609 | 0.089403 ± 0.001205543 | 1.35 | 100.90 |
| 0.02 | 0.405741 | 0.402656 ± 0.002881902 | 0.72 | 99.24 |
| 0.08 | 1.744349 | 1.724051 ± 0.018591924 | 1.08 | 98.84 |
| PH-247 Concentration mg/mL | Relative Peak Area | Mean ± SD (n = 3) Observed/mg/mL | Precision a (%) | Accuracy b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.005 | 0.101431 | 0.100522 ± 0.001089 | 1.08 | 99.10 |
| 0.02 | 0.400455 | 0.402642 ± 0.001895 | 0.47 | 100.55 |
| 0.08 | 1.65512 | 1.663723 ± 0.007615 | 0.46 | 100.52 |
| Parameters | PH-249 |
|---|---|
| Range (mg/mL) | 0.01–0.1 |
| Regression equation | y = 0.0439x − 0.0001 |
| Correlation coefficient (r) | 0.999 |
| LOQ (mg/mL) | 0.01 |
| LOD (mg/mL) | 0.003 |
| Intra-assay precision a | 0.13 |
| Inter-assay precision a | 0.19 |
| Accuracy b | 100.15 |
| PH-249 Concentration mg/mL | Relative Peak Area | Mean ± SD (n = 3) Observed/mg/mL | Precision a (%) | Accuracy b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.205913 | 0.206218 ± 0.000266067 | 0.13 | 100.15 |
| 0.04 | 0.904915 | 0.906149 ± 0.001072511 | 0.12 | 100.14 |
| 0.1 | 2.26952 | 2.271416 ± 0.002031025 | 0.09 | 100.08 |
| PH-249 Concentration mg/mL | Relative Peak Area | Mean ± SD (n = 3) Observed/mg/mL | Precision a (%) | Accuracy b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.208052 | 0.208422082 ± 0.00039268 | 0.19 | 100.18 |
| 0.04 | 0.895176 | 0.892203737 ± 0.00645177 | 0.72 | 99.67 |
| 0.1 | 2.248628 | 2.247660945 ± 0.00329549 | 0.15 | 99.96 |
| Parameters | PH-251 |
|---|---|
| Range (mg/mL) | 0.01–0.1 |
| Regression Equation | y = 0.0226x + 0.0011 |
| Correlation Coefficient (r) | 0.999 |
| LOQ (mg/mL) | 0.01 |
| LOD (mg/mL) | 0.003 |
| Intra-assay precision a | 0.17 |
| Inter-assay precision a | 0.10 |
| Accuracy b | 99.81 |
| PH-251 Concentration mg/mL | Relative Peak Area | Mean ± SD (n = 3) Observed/mg/mL | Precision a (%) | Accuracy b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.392615 | 0.391862 ± 0.00066 | 0.17 | 99.81 |
| 0.04 | 1.692602 | 1.695633 ± 0.003542 | 0.21 | 100.18 |
| 0.1 | 4.370119 | 4.369349 ± 0.001657 | 0.04 | 99.98 |
| PH-251 Concentration mg/mL | Relative Peak Area | Mean ± SD (n = 3) Observed/mg/mL | Precision a (%) | Accuracy b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.383002 | 0.382554 ± 0.000389 | 0.10 | 99.88 |
| 0.04 | 1.672021 | 1.684208 ± 0.012462 | 0.74 | 100.73 |
| 0.1 | 4.330851 | 4.337159 ± 0.007248 | 0.17 | 100.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Al-Mutairi, H.M.; Phillips, O.A.; Al-Tannak, N.F. Stability-Indicating Assay of Novel 5-(Hydroxamic acid)methyl Oxazolidinones with 5-Lipooxygenase Inhibitory Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2026, 19, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19010069
Al-Mutairi HM, Phillips OA, Al-Tannak NF. Stability-Indicating Assay of Novel 5-(Hydroxamic acid)methyl Oxazolidinones with 5-Lipooxygenase Inhibitory Activity. Pharmaceuticals. 2026; 19(1):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19010069
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Mutairi, Hessa M., Oludotun A. Phillips, and Naser F. Al-Tannak. 2026. "Stability-Indicating Assay of Novel 5-(Hydroxamic acid)methyl Oxazolidinones with 5-Lipooxygenase Inhibitory Activity" Pharmaceuticals 19, no. 1: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19010069
APA StyleAl-Mutairi, H. M., Phillips, O. A., & Al-Tannak, N. F. (2026). Stability-Indicating Assay of Novel 5-(Hydroxamic acid)methyl Oxazolidinones with 5-Lipooxygenase Inhibitory Activity. Pharmaceuticals, 19(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19010069







