Research on Sinomenine Inhibiting the cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway to Alleviate Renal Inflammatory Injury in db/db Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. SIN Effectively Prevents the Progression of Renal Dysfunction in db/db Mice
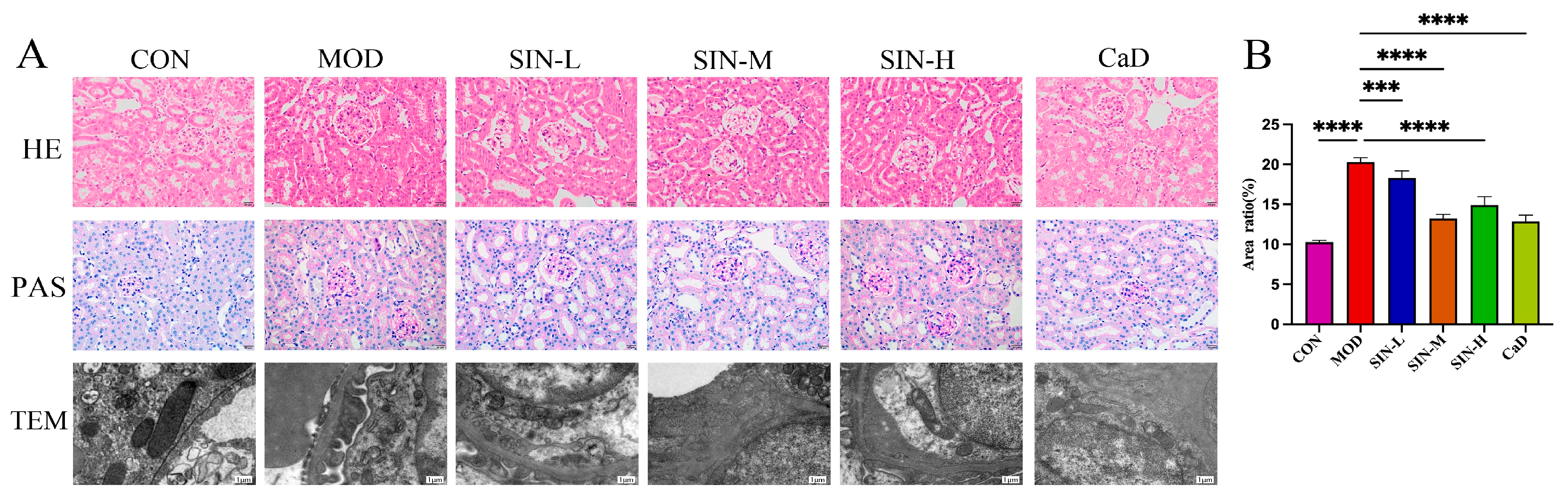
2.2. SIN Improves Renal Pathological Damage in db/db Mice
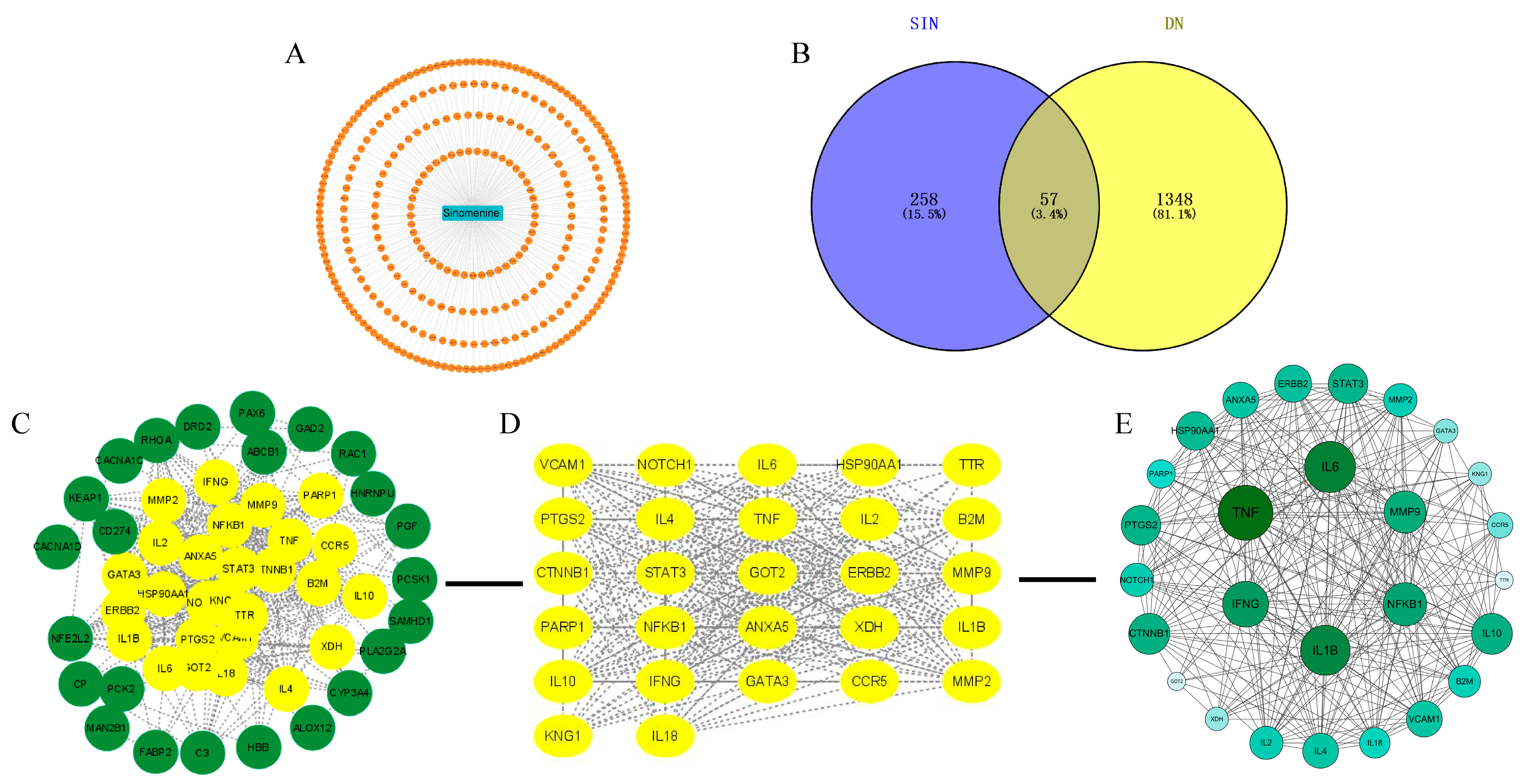
2.3. Network Pharmacology Analysis of SIN and DN
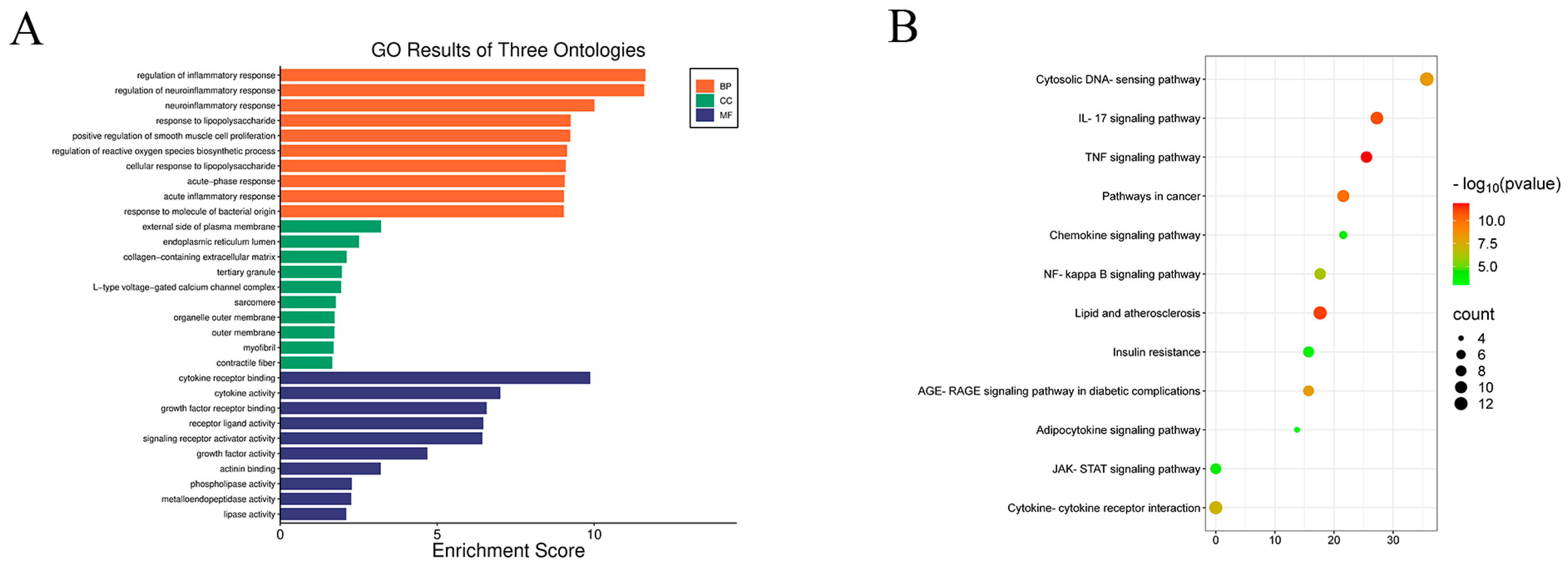
2.4. KEGG and GO Analysis
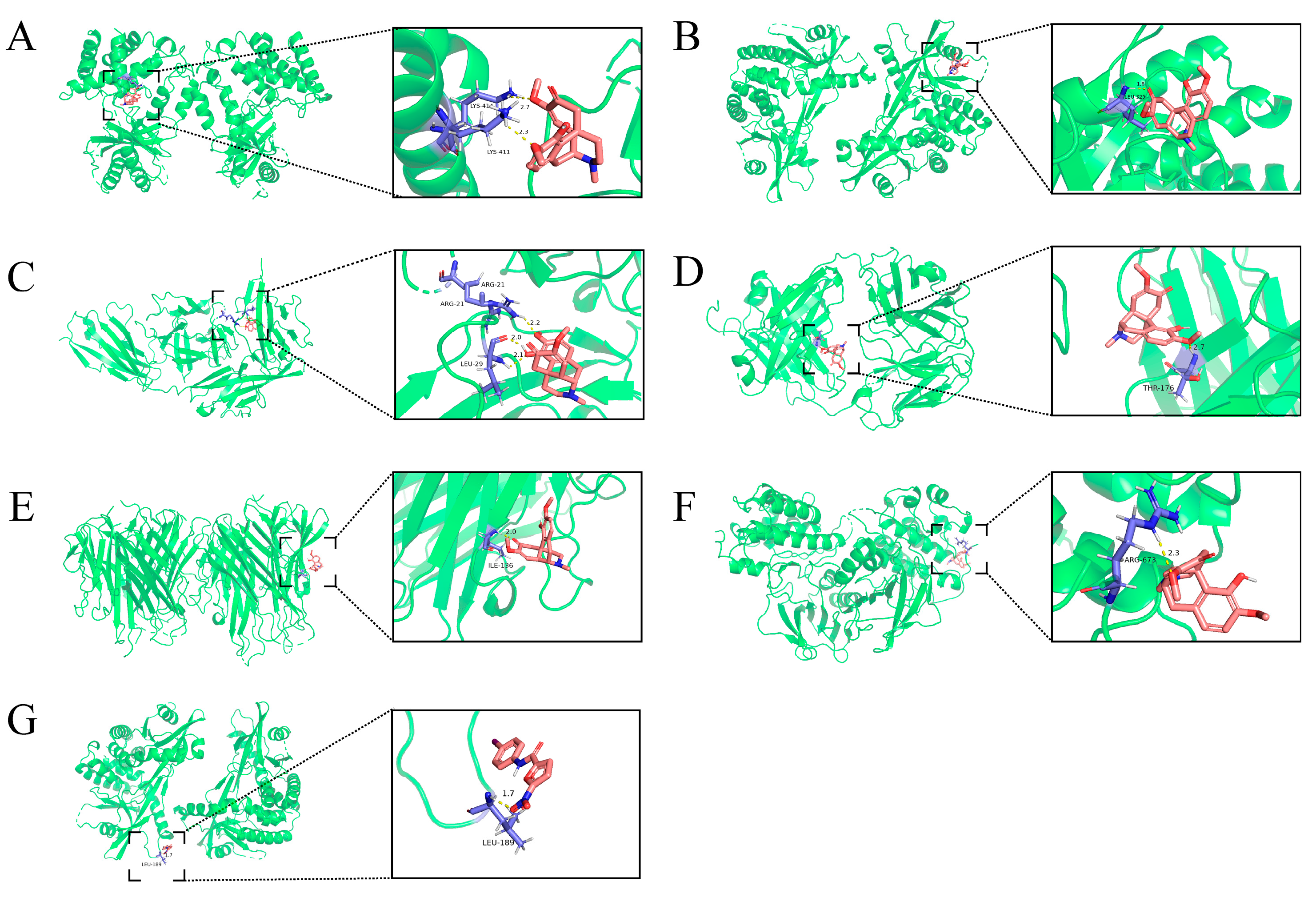
2.5. Molecular Docking of SIN with Core Targets
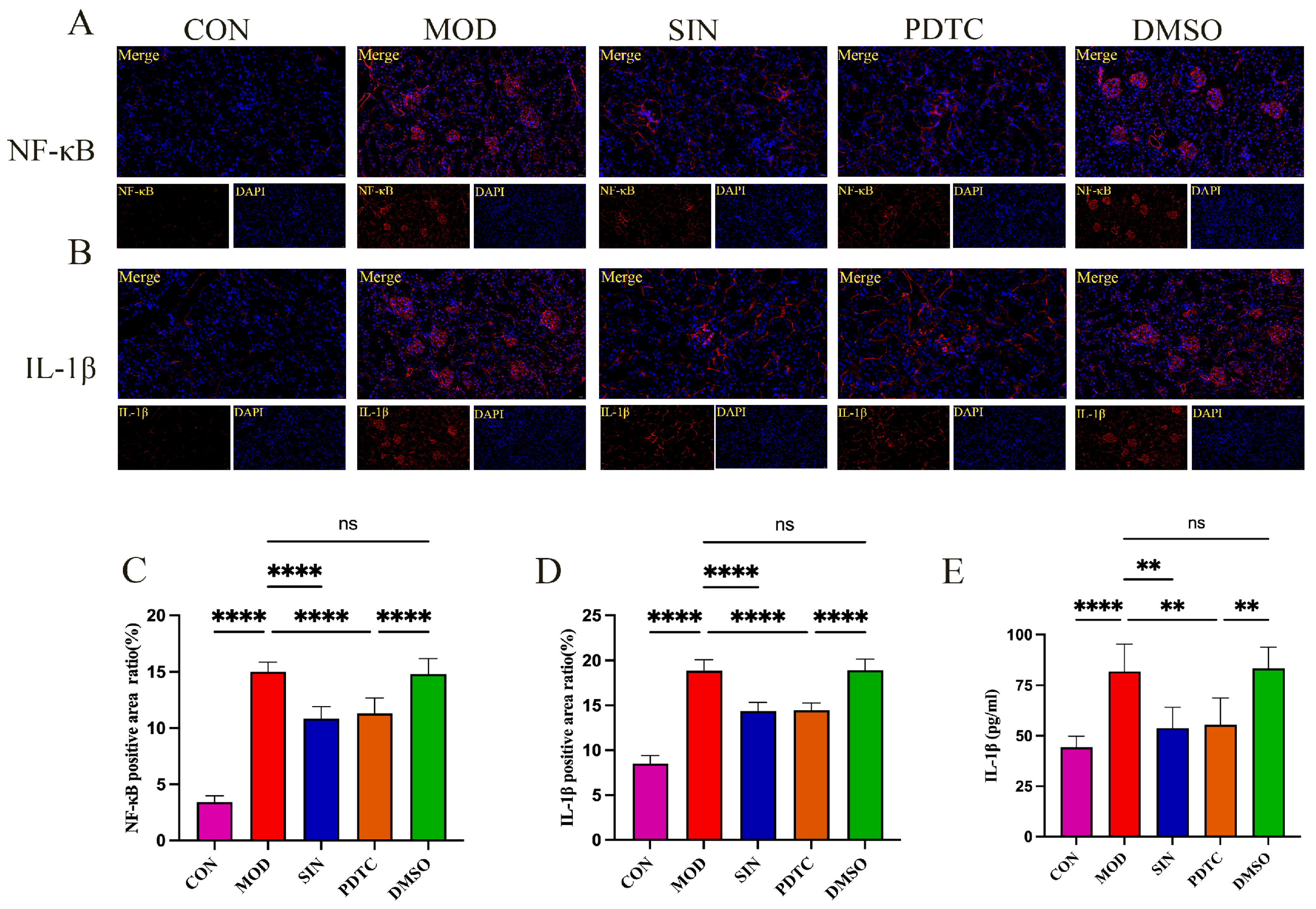
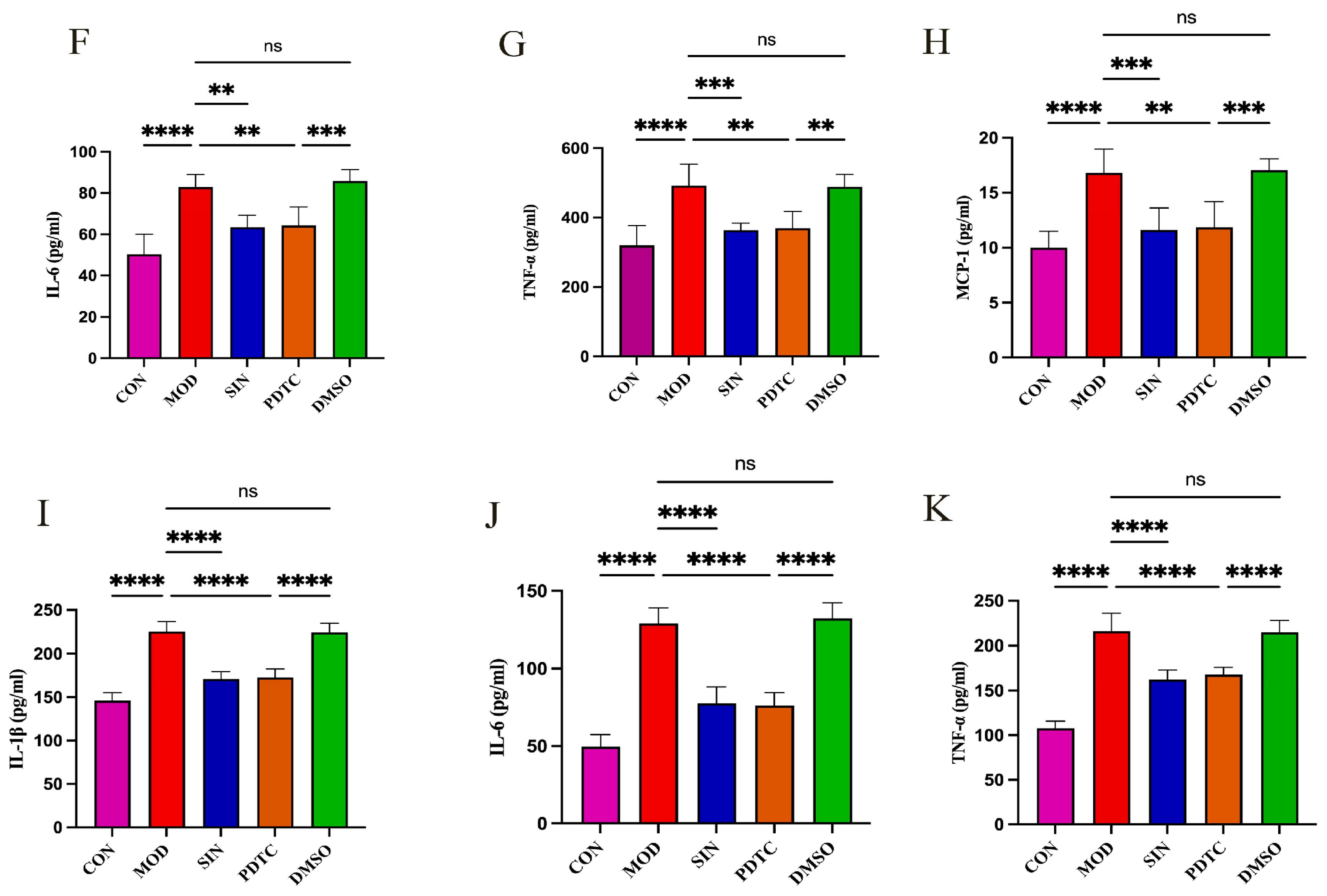
2.6. SIN Inhibits Inflammatory Injury in db/db Mice
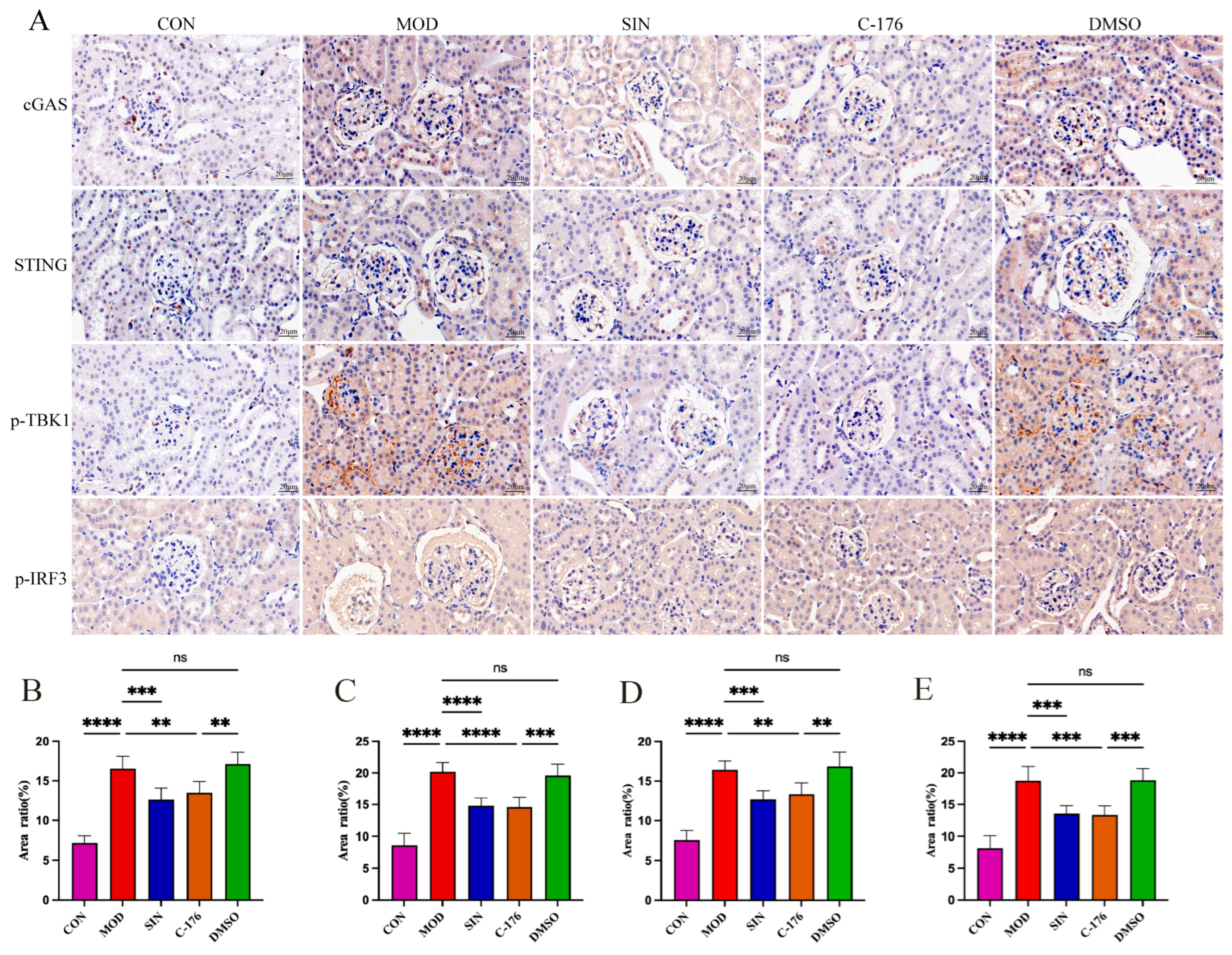
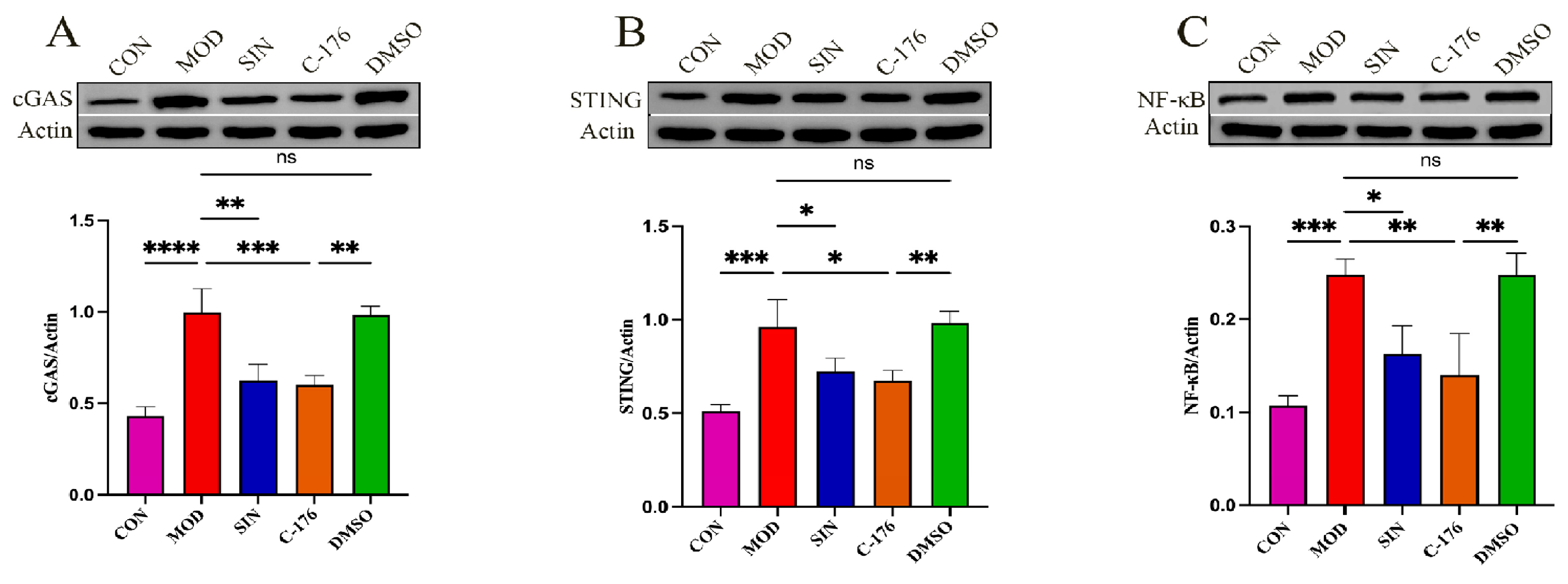
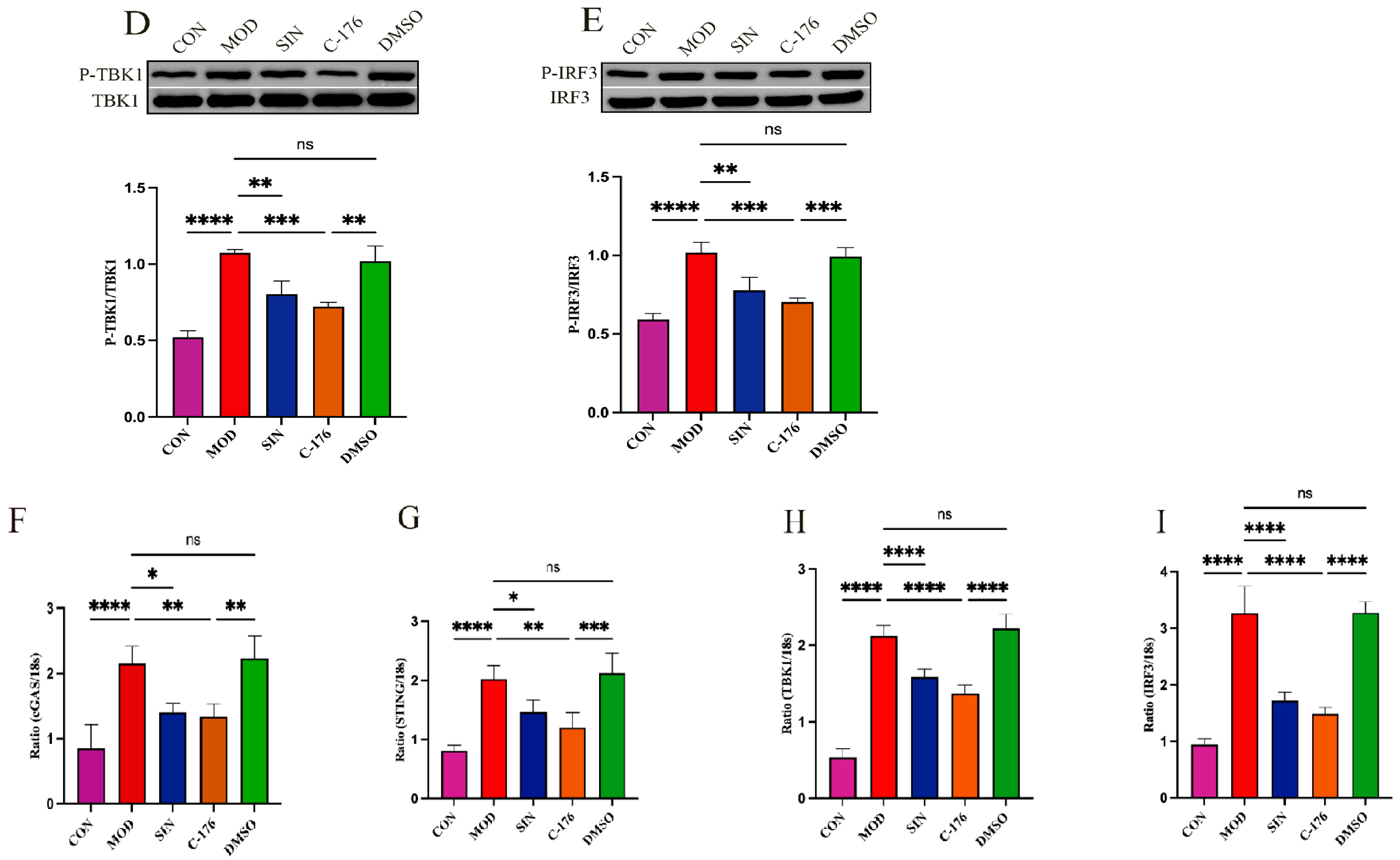
2.7. SIN Alleviates Renal Inflammatory Injury in db/db Mice by the cGAS/STING Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animals and Experimental Design
4.2.1. Experiment 1
4.2.2. Experiment 2
4.2.3. Experiment 3
4.3. Biochemical Assays
4.4. ELISA
4.5. H&E and PAS
4.6. TEM
4.7. Network Pharmacology Analysis
4.8. Immunofluorescence
4.9. Immunohistochemistry
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BP | Biological processes |
| C-176 | STING inhibitor |
| CC | Cellular components |
| cGAS | Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DN | Diabetic nephropathy |
| ESRD | End-stage renal disease |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IRF3 | Interferon regulatory factor 3 |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-B |
| OMIM | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |
| PDTC | Pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate ammonium |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| SIN | Sinomenine hydrochloride |
| STING | Stimulator of interferon genes |
| TBK1 | TANK binding kinase 1 |
| TCMSP | Traditional Chinese Medicine systems pharmacology database and analysis platform |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
References
- Yang, R.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, B.; Liu, S.; Wu, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Modulating HIF-1α/HIF-2α homeostasis with Shen-Qi-Huo-Xue formula alleviates tubular ferroptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic kidney disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 343, 119478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.-X.; Cao, L.-H.; Ni, H.-X.; Zang, Z.-Y.; Chang, H. Chinese herbal medicine for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy: From clinical evidence to potential mechanisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 330, 118179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternlicht, H.; Bakris, G.L. Management of Hypertension in Diabetic Nephropathy: How Low Should We Go? Blood Purif. 2016, 41, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, X.; Luo, N.; Lv, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Y. Prognostic evaluation model of diabetic nephropathy patients. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 6867–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagoo, M.K.; Gnudi, L. Diabetic nephropathy: Is there a role for oxidative stress? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 116, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umanath, K.; Lewis, J.B. Update on Diabetic Nephropathy: Core Curriculum 2018. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Fang, Y.-L.; Tian, T.-T.; Wang, G.-X. Pathological mechanism of immune disorders in diabetic kidney disease and intervention strategies. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Su, J.; Liu, Z.; Ding, S.; Li, Y.; Hou, B.; Hu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Tang, J.; Liu, H.; et al. Identification of immune-associated biomarkers of diabetes nephropathy tubulointerstitial injury based on machine learning: A bioinformatics multi-chip integrated analysis. BioData Min. 2024, 17, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayego-Mateos, S.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.R.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Mora-Fernández, C.; Marchant, V.; Donate-Correa, J.; Navarro-González, J.F.; Ortiz, A.; Ruiz-Ortega, M. Targeting inflammation to treat diabetic kidney disease: The road to 2030. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Geng, K.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wan, S.-R.; Ma, X.-M.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Z.-Z. Hyperglycemia-induced STING signaling activation leads to aortic endothelial injury in diabetes. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.-W.; Tian, J.-L.; Chen, T.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.-R.; Zhao, Z.-J.; Zhang, S.-H.; Chen, Y. Role of cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-stimulator of interferon genes pathway in diabetes and its complications. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 2041–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myakala, K.; Jones, B.A.; Wang, X.X.; Levi, M. Sacubitril/valsartan treatment has differential effects in modulating diabetic kidney disease in db/db mice and KKAy mice compared with valsartan treatment. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2021, 320, F1133–F1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, N.; Cui, C.; Guo, X.; Song, J.; Hu, H.; Yang, M.; Xu, M.; Wang, L.; Hou, X.; He, Q.; et al. cGAS-STING activation contributes to podocyte injury in diabetic kidney disease. iScience 2022, 25, 105145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, R.; Zhao, L.; Lian, C.; Chen, S.; Ma, Y. Metabolic profiling and transcriptome analysis of Sinomenium acutum provide insights into the biosynthesis of structurally diverse benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, X.-K. Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory activities of sinomenine. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Z.; Liang, Z.T.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, Z.H.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wong, Y.F.; Xu, H.X.; Liu, L. Quantification of Sinomenine in Caulis Sinomenii Collected from Different Growing Regions and Wholesale Herbal Markets by a Modified HPLC Method. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potočnjak, I.; Šimić, L.; Batičić, L.; Križan, H.; Domitrović, R. Sinomenine mitigates cisplatin-induced kidney injury by targeting multiple signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 171, 113538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Du, R.; Huang, F.; Yin, S.; Yang, J.; Qin, S.; Cao, W. Sinomenine activation of Nrf2 signaling prevents hyperactive inflammation and kidney injury in a mouse model of obstructive nephropathy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 92, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhu, H. Sinomenine improve diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting fibrosis and regulating the JAK2/STAT3/SOCS1 pathway in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2021, 265, 118855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Xia, Y.; Wang, G. Sinomenine alleviates high glucose-induced renal glomerular endothelial hyperpermeability by inhibiting the activation of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Li, J.; Ni, Y. Sinomenine improves renal fibrosis by regulating mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes and affecting autophagy levels. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 2524–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Qian, C.; Xu, F.; Cheng, P.; Yang, C.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, A. Fuxin Granules ameliorate diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice through TGF-β1/Smad and VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Seabra Rodrigues Dias, I.R.; Lo, H.H.; Zhang, K.; Law, B.Y.K.; Nasim, A.A.; Chung, S.K.; Wong, V.K.W.; Liu, L. Potential therapeutic compounds from traditional Chinese medicine targeting endoplasmic reticulum stress to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Yao, Y.-D.; Luo, J.-F.; Liu, J.-X.; Lu, L.-L.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Dong, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, H. Pharmacological mechanisms of sinomenine in anti-inflammatory immunity and osteoprotection in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Phytomedicine 2023, 121, 155114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Yin, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Huang, F.; Cao, W. Sinomenine attenuates renal fibrosis through Nrf2-mediated inhibition of oxidative stress and TGFβ signaling. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 304, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, S.; Tang, X.-Y.; Sun, H.-F.; Liu, J.-X. Sinomenine Hydrochloride Protects IgA Nephropathy Through Regulating Cell Growth and Apoptosis of T and B Lymphocytes. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 1247–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hou, W.; Wang, D.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, F. Immunoregulatory effects of sinomenine on the T-bet/GATA-3 ratio and Th1/Th2 cytokine balance in the treatment of mesangial proliferative nephritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S.A.; O’Brien, P.D.; Kretzler, K.H.; Jang, D.; Mendelson, F.E.; Hayes, J.M.; Carter, A.; Zhang, H.; Pennathur, S.; Brosius, F.C.; et al. Dietary Interventions Improve Diabetic Kidney Disease, but not Peripheral Neuropathy, in a db/db Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; McCue, P.; Dunn, S.R. Diabetic kidney disease in the db/db mouse. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2003, 284, F1138–F1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.-D.; Yuan, L.; Xu, D.-J.; Che, M.-Y.; Hou, S.-Z.; Lu, D.-D.; Liu, W.-J.; Nan, Y. Exploring the targets and molecular mechanism of glycyrrhetinic acid against diabetic nephropathy based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 1672–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Geng, C.; Wang, J.; Shi, L.; Ma, J.; Liang, Z.; Fan, W. Investigating the inflammatory mechanism of notoginsenoside R1 in Diabetic nephropathy via ITGB8 based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Yu, X.; Xie, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Pan, S.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z. Phillygenin improves diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis via regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2025, 136, 156314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Li, P.; Liu, C.; Yin, F.; Han, J.; Sun, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Guan, S.; Wang, X. Exploring the molecular mechanisms for renoprotective effects of Huangkui capsule on diabetic nephropathy mice by comprehensive serum metabolomics analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 340, 119223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Chong, N.; Chen, D.; Shu, J.; Sun, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y. GDF-15 alleviates diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting NEDD4L-mediated IKK/NF-κB signalling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 128, 111427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.M.; Elshaer, S.L.; Gangaraju, R.; Abdelaziz, R.R.; Nader, M.A. Ameliorative effect of montelukast against STZ induced diabetic nephropathy: Targeting HMGB1, TLR4, NF-κB, NLRP3 inflammasome, and autophagy pathways. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 32, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, C.; Liu, J.; Pan, C.; Guo, J. Astragaloside IV attenuates podocyte apoptosis via regulating TXNIP/NLRP3/GSDMD signaling pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamahara, K.; Yasuda, M.; Kume, S.; Koya, D.; Maegawa, H.; Uzu, T. The role of autophagy in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 193757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Hou, L. IL-6 and diabetic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1465625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, S.; Shi, Q. Isoliquiritigenin attenuates high glucose-induced proliferation, inflammation, and extracellular matrix deposition in glomerular mesangial cells by suppressing JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, M.; Lan, S.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Li, W. Integrated network pharmacology and pharmacological investigations to discover the active compounds of Toona sinensis pericarps against diabetic nephropathy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 333, 118441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhang, L. DNA PAMPs as Molecular Tools for the cGAS-STING Signaling Pathways. Methods Mol. Biol. 2025, 2854, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Tang, K.; Li, J.; Tan, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, Z.; Tao, A.; Tan, N. Mailuoning oral liquid ameliorates vasculitis in thromboangiitis obliterans rats via inactivating cGAS-STING-IRF3 and TLR4-MAPKs/NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 337, 118707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xu, P. Cellular functions of cGAS-STING signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2023, 33, 630–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Huang, J.; Tang, X.; Du, B.; Yang, B. Semen Strychni Pulveratum and vomicine alleviate neuroinflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis through cGAS-STING-TBK1 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 336, 118741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Shen, W.; Tao, W.; Peng, J.; Pan, M.; Qi, X.; Feng, W.; Wei, N.; Zheng, S.; Jin, H. Curcumol ameliorates alcohol and high-fat diet-induced fatty liver disease via modulation of the Ceruloplasmin/iron overload/mtDNA signaling pathway. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2025, 136, 109807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xia, Y.; Ma, Y.; Gao, M.; Hou, S.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y. Inhibition of the cGAS–STING pathway: Contributing to the treatment of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 20, 1900–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, W.; Wu, J.; Hong, H.; Quan, W.; Qiao, X.; Cui, C.; Qiao, C.; Zhao, W.; et al. The cGAS-STING-interferon regulatory factor 7 pathway regulates neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2025, 20, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy, G.; Flannery, S.M.; Almine, J.F.; Connolly, D.J.; Paulus, C.; Jønsson, K.L.; Jakobsen, M.R.; Nevels, M.M.; Bowie, A.G.; Unterholzner, L. Non-canonical Activation of the DNA Sensing Adaptor STING by ATM and IFI16 Mediates NF-κB Signaling after Nuclear DNA Damage. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Scores Groups | CON | MOD | SIN-L | SIN-M | SIN-H | CaD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| glomerular sclerosis | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Tubular atrophy | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Inflammatory cell infiltration | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Overall score | 0 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
| Primer Name | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (3′-5′) |
|---|---|---|
| M-cGAS | CACGAGGAAATCCGCTGAGTC | CACGAGGAAATCCGCTGAGTC |
| M-TBK1 | GCAGTGCTAAGAAAGGACCATCA | TGCCTGAAGACCCTGAGAAAGAC |
| M-IRF3 | CTACGGCAGGACGCACAGAT | GCAGCTAACCGCAACACTTCT |
| M-STING | TCGGGTTTATTCCAACAGCG | GTTTAGCCTGCTCAAGCCGAT |
| M-GAPDH | CCTCGTCCCGTAGACAAAATG | TGAGGTCAATGAAGGGGTCGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, X.; He, T.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Cong, B.; Gao, W. Research on Sinomenine Inhibiting the cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway to Alleviate Renal Inflammatory Injury in db/db Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070934
Jin X, He T, Zhang T, Wang X, Chen X, Cong B, Gao W. Research on Sinomenine Inhibiting the cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway to Alleviate Renal Inflammatory Injury in db/db Mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070934
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Xiaofei, Tongtong He, Tianci Zhang, Xiaorong Wang, Xiangmei Chen, Bin Cong, and Weijuan Gao. 2025. "Research on Sinomenine Inhibiting the cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway to Alleviate Renal Inflammatory Injury in db/db Mice" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070934
APA StyleJin, X., He, T., Zhang, T., Wang, X., Chen, X., Cong, B., & Gao, W. (2025). Research on Sinomenine Inhibiting the cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway to Alleviate Renal Inflammatory Injury in db/db Mice. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070934







