Interferon Lambda: The Next Frontier in Antiviral Therapy?
Abstract
1. Introduction
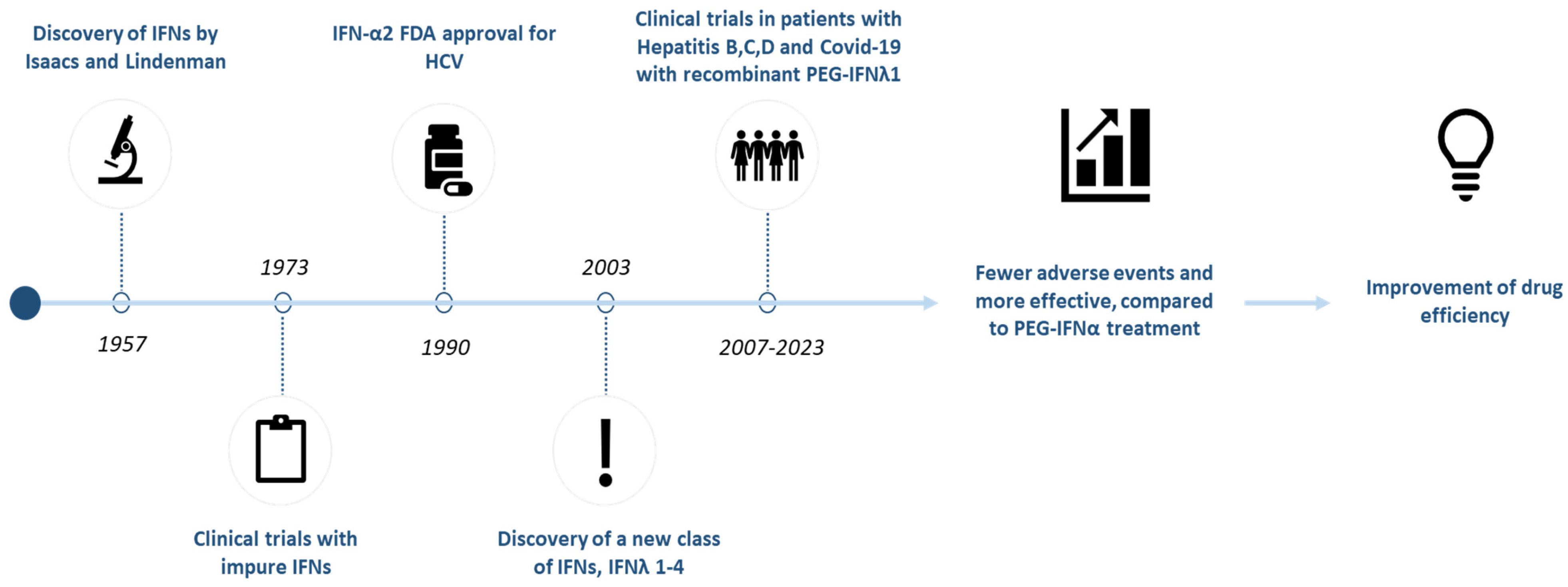
1.1. Discovery and Classification of Interferon Lambda (IFN-λ)
1.2. Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Potential of IFN-λ
2. Biological Background
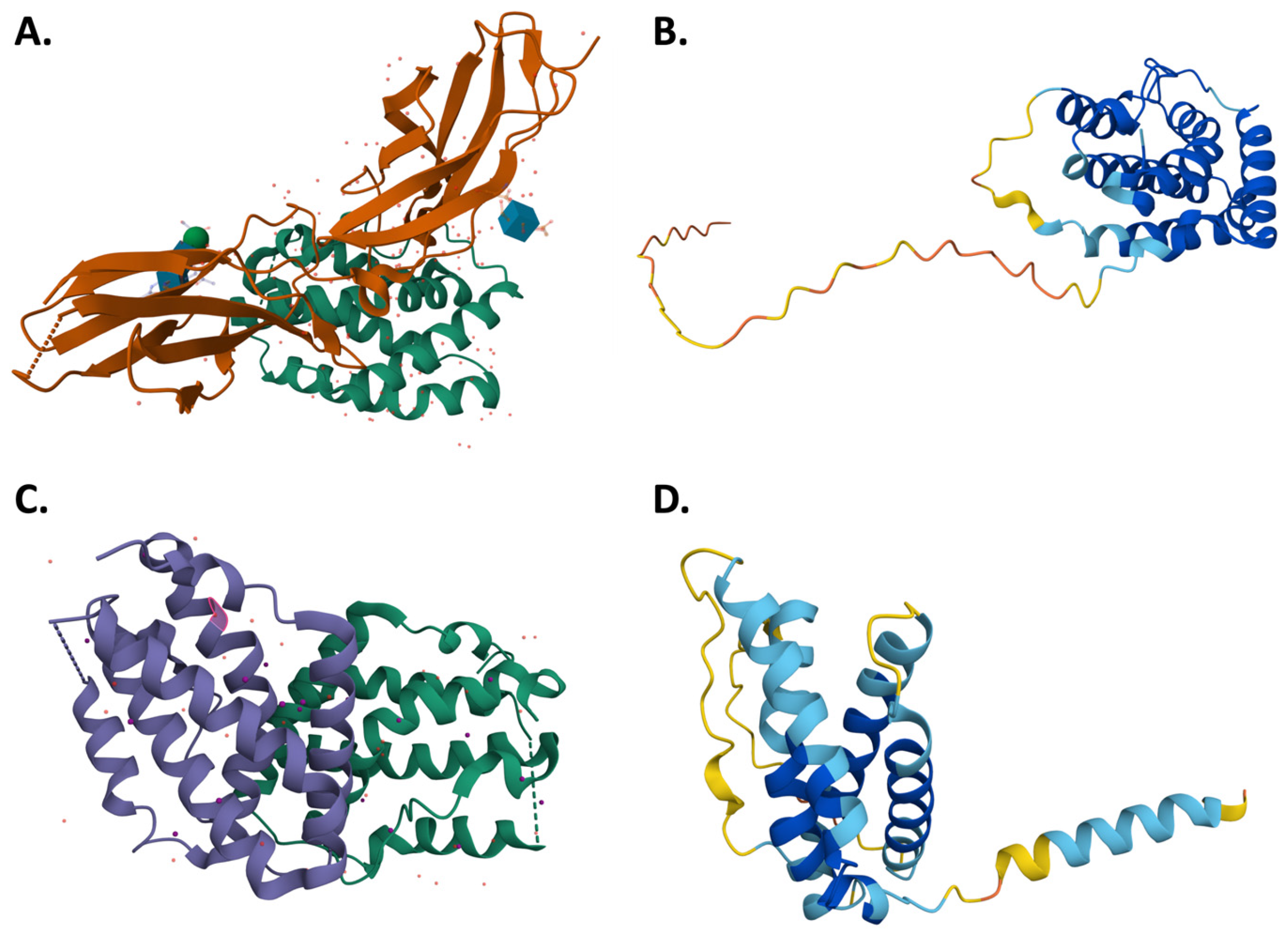
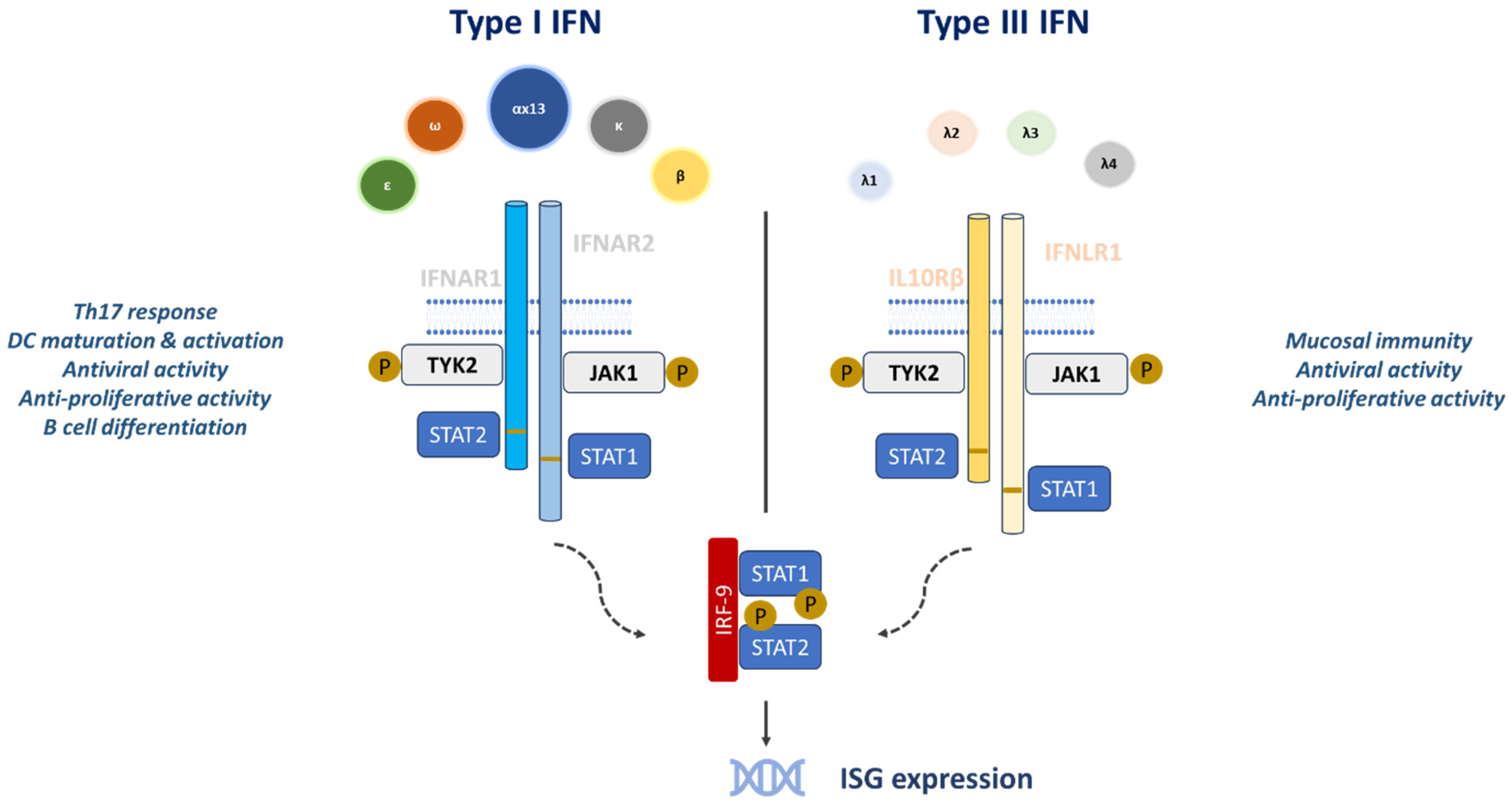
2.1. Molecular Structure, Signaling Mechanism and Common Aspects of Type III Interferons with Other Interferons
2.2. Development and Engineering of Recombinant IFN-λ
3. Therapeutic Applications—Ongoing Research
3.1. Antiviral Properties of IFN-λ and Clinical Trials
3.1.1. Hepatitis B
3.1.2. Hepatitis C
3.1.3. Hepatitis D
3.1.4. Hepatitis E
3.1.5. COVID-19
3.2. Other Potential Applications
3.2.1. Cancer
3.2.2. Autoimmune Diseases
3.2.3. Bacterial Infections
4. Future Perspectives and Innovations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEG-IFNα2a | Pegylated interferon alfa 2a |
| PEG-IFNλ | Pegylated interferon lambda |
| PEG-IFNα | Pegylated interferon alfa |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| IFNLR1 | Interferon lambda receptor 1 |
| IL-10Rβ | Interleukin-10 receptor β chain |
| IFNAR | Receptor for type I Interferons |
| IFNLR | Interferon lambda receptor |
| ISGF3 | Interferon stimulated gene factor 3 |
| NRTIs | Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors |
| ISGs | Interferon stimulated genes |
| DAAs | Direct acting antivirals |
| HBeAg | Hepatitis B e antigen |
| IFNs | Interferons |
| IFNα | Interferon alfa |
| IFN-λ | Interferon lambda |
| IRF9 | Interferon regulatory factor 9 |
| STAT | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| TYK | Tyrosine kinase |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HDV | Hepatitis D virus |
| HEV | Hepatitis E virus |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| SVR | Sustained virologic response |
| RBV | Ribavirin |
| DCV | Daclatasvir |
| TVR | Telaprevir |
| CHD | Chronic hepatitis D |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| LNF | Lonafarnib |
| RTV | Ritonavir |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| GT | Genotype |
References
- Sheppard, P.; Kindsvogel, W.; Xu, W.; Henderson, K.; Schlutsmeyer, S.; Whitmore, T.E.; Kuestner, R.; Garrigues, U.; Birks, C.; Roraback, J.; et al. IL-28, IL-29 and Their Class II Cytokine Receptor IL-28R. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotenko, S.V.; Gallagher, G.; Baurin, V.V.; Lewis-Antes, A.; Shen, M.; Shah, N.K.; Langer, J.A.; Sheikh, F.; Dickensheets, H.; Donnelly, R.P. IFN-Lambdas Mediate Antiviral Protection through a Distinct Class II Cytokine Receptor Complex. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, H.; Meyer, J.; Freeman, J.; Doyle, S.E.; Klucher, K.; Miller, D.M.; Hausman, D.; Hillson, J.L. Peginterferon Lambda-1a, a New Therapeutic for Hepatitis C Infection, from Bench to Clinic. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2013, 1, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fensterl, V.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Sen, G.C. No Love Lost Between Viruses and Interferons. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2015, 2, 549–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.Y.; Ho, J.X.; Kow, A.S.F.; Liang, G.; Tham, C.L.; Ho, Y.C.; Lee, M.T. Interferon Therapy and Its Association with Depressive Disorders—A Review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1048592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.Z.; Jackson, S.S.; O’Brien, T.R. IFNL4: Notable Variants and Associated Phenotypes. Gene 2020, 730, 144289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Su, S.B. Interferon-Λs: The Modulators of Antivirus, Antitumor, and Immune Responses. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syedbasha, M.; Egli, A. Interferon Lambda: Modulating Immunity in Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol 2017, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.G.; Jin, S.W.; Zhang, S.S.; Xia, T.J.; Liao, Y.H.; Pan, R.L.; Yan, M.Z.; Chang, Q. Interferon Lambda in Respiratory Viral Infection: Immunomodulatory Functions and Antiviral Effects in Epithelium. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1338096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.M.; Badiger, R.; Alazawi, W.; Foster, G.R.; Mitchell, J.A. Pharmacology and Therapeutic Potential of Interferons. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 135, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Schnepf, D.; Staeheli, P. Interferon-λ Orchestrates Innate and Adaptive Mucosal Immune Responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, J.L.; Schneider, W.M.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Vercauteren, K.; Jude, K.M.; Xiong, A.; Moraga, I.; Horton, T.M.; Glenn, J.S.; de Jong, Y.P.; et al. The IFN-λ-IFN-ΛR1-IL-10Rβ Complex Reveals Structural Features Underlying Type III IFN Functional Plasticity. Immunity 2017, 46, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Nice, T.J.; Diamond, M.S. Interferon-λ: Immune Functions at Barrier Surfaces and Beyond. Immunity 2015, 43, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François-Newton, V.; de Freitas Almeida, G.M.; Payelle-Brogard, B.; Monneron, D.; Pichard-Garcia, L.; Piehler, J.; Pellegrini, S.; Uzé, G. USP18-Based Negative Feedback Control Is Induced by Type I and Type III Interferons and Specifically Inactivates Interferon α Response. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Finotto, S. Role of Interferon-λ in Allergic Asthma. J. Innate. Immun. 2015, 7, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Schoggins, J.W.; Diamond, M.S. Shared and Distinct Functions of Type I and Type III Interferons. Immunity 2019, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Upadhyay, V.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Singh, S.M.; Panda, A.K. Protein Recovery from Inclusion Bodies of Escherichia Coli Using Mild Solubilization Process. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bourayne, M.; Meunier, S.; Bitoun, S.; Correia, E.; Mariette, X.; Nozach, H.; Maillère, B. Pegylation Reduces the Uptake of Certolizumab Pegol by Dendritic Cells and Epitope Presentation to T-Cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 808606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaak, J.F. Current Therapy of Chronic Viral Hepatitis B, C and D. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Guo, H. Hepatitis B Virus CccDNA: Formation, Regulation and Therapeutic Potential. Antivir. Res. 2020, 180, 104824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, C.; Mason, W.S. Molecular Biology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Virology 2015, 479, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Liang, T.J. Development of Direct-Acting Antiviral and Host-Targeting Agents for Treatment of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, H.; Block, T.; Brown, N.; Brownstein, A.; Brosgart, C.; Chang, K.M.; Chen, P.J.; Chisari, F.V.; Cohen, C.; El-Serag, H.; et al. A Research Agenda for Curing Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.L.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Chang, T.T.; Peng, C.Y.; Wong, D.; Coffin, C.S.; Lim, S.G.; Chen, P.J.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Marcellin, P.; et al. Peginterferon Lambda for the Treatment of HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B: A Randomized Phase 2b Study (LIRA-B). J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.; Mistry, S.; Riva, A.; Cooksley, H.; Hadzhiolova-Lebeau, T.; Plavova, S.; Katzarov, K.; Simonova, M.; Zeuzem, S.; Woffendin, C.; et al. Peg-Interferon Lambda Treatment Induces Robust Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaminza, P.; Dryden, K.A.; Boyd, B.; Wood, M.R.; Law, M.; Yeager, M.; Chisari, F.V. Ultrastructural and Biophysical Characterization of Hepatitis C Virus Particles Produced in Cell Culture. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10999–11009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, Q.-L.; Kuo, G.; Weiner, A.J.; Overby, L.R.; Bradley, D.W.; Houghton, M. Isolation of a CDNA Clone Derived from a Blood-Borne Non-A, Non-B Viral Hepatitis Genome. Science 1989, 244, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, J.P.; Humphreys, I.; Flaxman, A.; Brown, A.; Cooke, G.S.; Pybus, O.G.; Barnes, E. Global Distribution and Prevalence of Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes. Hepatology 2014, 1, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanaway, J.D.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Fitzmaurice, C.; Vos, T.; Abubakar, I.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Assadi, R.; Bhala, N.; Cowie, B.; et al. The Global Burden of Viral Hepatitis from 1990 to 2013: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2016, 388, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.M.; Jacobson, I.M.; Rice, C.M.; Zeuzem, S. Emerging Therapies for the Treatment of Hepatitis C. Embo Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHutchison, J.G.; Gordon, S.C.; Schiff, E.R.; Schiffman, M.L.; Lee, W.M.; Rustgi, V.K.; Goodman, Z.D.; Ling, M.H.; Cort, S.; Albrecht, J.K. Interferon Alfa-2b alone or in combination with Ribavirin as Initial Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis C. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeuzem, S.; Feinman, S.V.; Rasenack, J.; Heathcote, E.J.; Lai, M.Y.; Gane, E.; O’Grady, J.; Reichen, J.; Diago, M.; Lin, A.; et al. Peginterferon Alfa-2a in patients with chronic Hepatitis C. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1666–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichael, M.; Ried, W.F.; Hiffman, I.L.S.; Ajender, K.R.; Eddy, R.; Oleman, C.; Mith, S.; Eorge, G.; Arinos, M.; Ernando, F.; et al. Peginterferon Alfa-2a plus Ribavirin for Chronic Hepatitis C virus infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.M.; Klucher, K.M.; Freeman, J.A.; Hausman, D.F.; Fontana, D.; Williams, D.E. Interferon Lambda as a Potential New Therapeutic for Hepatitis C. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1182, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidlaw, S.M.; Dustin, L.B. Interferon Lambda: Opportunities, Risks, and Uncertainties in the Fight Against HCV. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.J.; Shiffman, M.L.; Zaman, A.; Yoffe, B.; De La Torre, A.; Flamm, S.; Gordon, S.C.; Marotta, P.; Vierling, J.M.; Lopez-Talavera, J.C.; et al. Phase 1b Study of Pegylated Interferon Lambda 1 with or without Ribavirin in Patients with Chronic Genotype 1 Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Hepatology 2010, 52, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.J.; Arora, S.; Everson, G.; Flisiak, R.; George, J.; Ghalib, R.; Gordon, S.C.; Gray, T.; Greenbloom, S.; Hassanein, T.; et al. A Randomized Phase 2b Study of Peginterferon Lambda-1a for the Treatment of Chronic HCV Infection. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R.; Chayama, K.; Chuang, W.L.; Fainboim, H.; Farkkila, M.; Gadano, A.; Gaeta, G.B.; Hézode, C.; Inada, Y.; Heo, J.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Study of Peginterferon Lambda-1a/Ribavirin ± Daclatasvir for Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 2 or 3. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flisiak, R.; Shiffman, M.; Arenas, J.; Cheinquer, H.; Nikitin, I.; Dong, Y.; Rana, K.; Srinivasan, S. A Randomized Study of Peginterferon Lambda-1a Compared to Peginterferon Alfa-2a in Combination with Ribavirin and Telaprevir in Patients with Genotype-1 Chronic Hepatitis C. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.; Rubio, R.; Lazzarin, A.; Romanova, S.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Conway, B.; Molina, J.M.; Xu, D.; Srinivasan, S.; Portsmouth, S. Safety and Efficacy of Pegylated Interferon Lambda, Ribavirin, and Daclatasvir in HCV and HIV-Coinfected Patients. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2017, 37, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagostino, E.; Pol, S.; Olveira, A.; Reesink, H.W.; van Erpecum, K.; Bogomolov, P.; Xu, D.; Critelli, L.; Srinivasan, S.; Cooney, E. Daclatasvir/Peginterferon Lambda-1a/Ribavirin in Patients with Chronic HCV Infection and Haemophilia Who Are Treatment Naïve or Prior Relapsers to Peginterferon Alfa-2a/Ribavirin. Haemophilia 2016, 22, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Palmer, J.; Cerri, K.; Valentine, W. Achieving Sustained Virologic Response in Hepatitis C: A Systematic Review of the Clinical, Economic and Quality of Life Benefits. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzetto, M.; Canese, M.G.; Arico, S.; Trepo, C.; Bonino, F.; Verme, G. Immunofluorescence Detection of New Antigen-Antibody System (S/Anti-5) Associated to Hepatitis B Virus in Liver and in Serum of HBsAg Carriers. Gut 1977, 18, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureau, C.; Negro, F. The Hepatitis Delta Virus: Replication and Pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S102–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattovich, G.; Giustina, G.; Christensen, E.; Pantalena, M.; Zagni, I.; Realdi, G.; Schalm, S.W. Influence of Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection on Morbidity and Mortality in Compensated Cirrhosis Type B. The European Concerted Action on Viral Hepatitis (Eurohep). Gut 2000, 46, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, B.; Yurdaydin, C.; Kabaçam, G.; Ratsch, B.A.; Zachou, K.; Bremer, B.; Dalekos, G.N.; Erhardt, A.; Tabak, F.; Yalcin, K.; et al. Late HDV RNA Relapse after Peginterferon Alpha-Based Therapy of Chronic Hepatitis Delta. Hepatology 2014, 60, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentha, N.; Clément, S.; Negro, F.; Alfaiate, D. A Review on Hepatitis D: From Virology to New Therapies. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 17, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, S.; Etzion, O.; Lurie, Y.; Bader, N.; Yardeni, D.; Channa, S.M.; Mawani, M.; Parkash, O.; Martins, E.B.; Gane, E.J. Discussion a Phase 2 randomized clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Pegylated interferon lambda monotherapy in patients with chronic hepatitis delta Virus Infection: Interim results from the limt hdv study. In Proceedings of the AASLD Liver Meeting 2017, Washington, DC, USA, 20–24 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Etzion, O.; Hamid, S.; Lurie, Y.; Gane, E.J.; Yardeni, D.; Duehren, S.; Bader, N.; Nevo-Shor, A.; Channa, S.M.; Cotler, S.J.; et al. Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis D with Peginterferon Lambda—the Phase 2 LIMT-1 Clinical Trial. Hepatology 2023, 77, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.; Hercun, J.; Rahman, F.; Huang, A.; Da, B.; Surana, P.; Kapuria, D.; Rotman, Y.; Vittal, A.; Gilman, C.A.; et al. A Phase 2 Study of Peginterferon Lambda, Lonafarnib and Ritonavir for 24 Weeks: End-of-Treatment Results from the LIFT HDV Study. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaiate, D.; Clément, S.; Gomes, D.; Goossens, N.; Negro, F. Chronic Hepatitis D and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worm, H.C.; Van Der Poel, W.H.M.; Brandstätter, G. Hepatitis E: An Overview. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Izopet, J.; Nicot, F.; Simmonds, P.; Jameel, S.; Meng, X.J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; et al. Update: Proposed Reference Sequences for Subtypes of Hepatitis E Virus (Species Orthohepevirus A). J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenfak-Foguena, A.; Schöni-Affolter, F.; Bürgisser, P.; Witteck, A.; Darling, K.E.A.; Kovari, H.; Kaiser, L.; Evison, J.-M.; Elzi, L.; De La Fuente, V.G.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus Seroprevalence and Chronic Infections in Patients with HIV, Switzerland. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavitian, S.; Péron, J.M.; Huynh, A.; Mansuy, J.M.; Ysebaert, L.; Huguet, F.; Vinel, J.P.; Attal, M.; Izopet, J.; Récher, C. Hepatitis E Virus Excretion Can Be Prolonged in Patients with Hematological Malignancies. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 49, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, G.; Mulders, C.E.; Zhu, J.; van Oord, G.W.; Feng, Z.; Kreeft-Voermans, J.J.C.; Boonstra, A.; Vanwolleghem, T. Treatment Induced Clearance of Hepatitis E Viruses by Interferon-Lambda in Liver-Humanized Mice. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2866–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Elbaz, J.; Jilg, N.; Gustafson, J.L.; Xu, M.; Hatipoglu, D.; Nohelty, E.; Kim, A.Y.; Chung, R.T. Peginterferon Lambda for the Treatment of Hospitalized Patients with Mild COVID-19: A Pilot Phase 2 Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1095828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Srivastava, Y.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Singh, S.K.; Verma, G.; Tiwari, S.; Tandel, N.; Beura, S.K.; Panigrahi, A.R.; Maji, S.; et al. Understanding Mutations in Human SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein: A Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis. Viruses 2023, 15, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felgenhauer, U.; Schoen, A.; Gad, H.H.; Hartmann, R.; Schaubmar, A.R.; Failing, K.; Drosten, C.; Weber, F. Inhibition of SARS–CoV-2 by Type I and Type III Interferons. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 13958–13964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, P.; Andrews, J.R.; Bonilla, H.; Hedlin, H.; Jacobson, K.B.; Balasubramanian, V.; Purington, N.; Kamble, S.; de Vries, C.R.; Quintero, O.; et al. Peginterferon Lambda-1a for Treatment of Outpatients with Uncomplicated COVID-19: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, J.J.; Kandel, C.; Biondi, M.J.; Kozak, R.A.; Zahoor, M.A.; Lemieux, C.; Borgia, S.M.; Boggild, A.K.; Powis, J.; McCready, J.; et al. Peginterferon Lambda for the Treatment of Outpatients with COVID-19: A Phase 2, Placebo-Controlled Randomised Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, G.; Moreira Silva, E.A.S.; Medeiros Silva, D.C.; Thabane, L.; Campos, V.H.S.; Ferreira, T.S.; Santos, C.V.Q.; Nogueira, A.M.R.; Almeida, A.P.F.G.; Savassi, L.C.M.; et al. Early Treatment with Pegylated Interferon Lambda for Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadeh, V.R.; Lew, J.M.; Zahoor, M.A.; Santer, D.; Feld, J.J.; Falzarano, D. Combination Therapy Enhances the Antiviral Activity of IFN-λ against SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV. Virus Res. 2025, 355, 199560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasfar, A.; Abushahba, W.; Balan, M.; Cohen-Solal, K.A. Interferon Lambda: A New Sword in Cancer Immunotherapy. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2011, 2011, 349575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, H.C.; Gamero, A.M. Interferon-Lambda as a Potential Therapeutic Agent in Cancer Treatment. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010, 30, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeberg, U.R.; Suciu, S.; Bröcker, E.B.; Ruiter, D.J.; Chartier, C.; Liénard, D.; Marsden, J.; Schadendorf, D.; Eggermont, A.M.M. Final Results of the EORTC 18871/DKG 80-1 Randomised Phase III Trial: RIFN-A2b versus RIFN-γ versus ISCADOR M® versus Observation after Surgery in Melanoma Patients with Either High-Risk Primary (Thickness >3 Mm) or Regional Lymph Node Metastasis. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, Y.; Endo, S.; Matsui, A.; Sato, A.; Saito, K.; Semba, K.; Takahashi, M.; Murakami, T. Potential Anti-Tumor Effect of IFN-Λ2 (IL-28A) against Human Lung Cancer Cells. Lung Cancer 2012, 78, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushahba, W.; Balan, M.; Castaneda, I.; Yuan, Y.; Reuhl, K.; Raveche, E.; De La Torre, A.; Lasfar, A.; Kotenko, S.V. Antitumor Activity of Type I and Type III Interferons in BNL Hepatoma Model. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2010, 59, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kawamura, K.; Ma, G.; Iwata, F.; Numasaki, M.; Suzuki, N.; Shimada, H.; Tagawa, M. Interferon-λ Induces G1 Phase Arrest or Apoptosis in Oesophageal Carcinoma Cells and Produces Anti-Tumour Effects in Combination with Anti-Cancer Agents. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkart, C.; Arimoto, K.; Tang, T.; Cong, X.; Xiao, N.; Liu, Y.C.; Kotenko, S.V.; Ellies, L.G.; Zhang, D.E. Usp18 Deficient Mammary Epithelial Cells Create an Antitumour Environment Driven by Hypersensitivity to IFN-λ and Elevated Secretion of Cxcl10. Embo Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1035–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes, F.; Young, A.; Mittal, D.; Martinet, L.; Bruedigam, C.; Takeda, K.; Andoniou, C.E.; Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Hill, G.R.; Smyth, M.J. NK Cells Require IL-28R for Optimal in Vivo Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2376–E2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Ohtsuki, M.; Hata, M.; Kobayashi, E.; Murakami, T. Antitumor Activity of IFN-λ in Murine Tumor Models. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 7686–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numasaki, M.; Tagawa, M.; Iwata, F.; Suzuki, T.; Nakamura, A.; Okada, M.; Iwakura, Y.; Aiba, S.; Yamaya, M. IL-28 Elicits Antitumor Responses against Murine Fibrosarcoma. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5086–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasfar, A.; De La Torre, A.; Abushahba, W.; Cohen-Solal, K.A.; Castaneda, I.; Yuan, Y.; Reuhl, K.; Zloza, A.; Raveche, E.; Laskin, D.L.; et al. Concerted Action of IFN-α and IFN-λ Induces Local NK Cell Immunity and Halts Cancer Growth. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 49259–49267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uggenti, C.; Lepelley, A.; Crow, Y.J. Self-Awareness: Nucleic Acid-Driven Inflammation and the Type I Interferonopathies. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 37, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, V.; Gunnarsson, I.; Dorschner, J.; Eketjäll, S.; Zickert, A.; Niewold, T.B.; Svenungsson, E. High Levels of Circulating Interferons Type I, Type II and Type III Associate with Distinct Clinical Features of Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Wang, C.M.; Chen, T.D.; Jan Wu, Y.J.; Lin, J.C.; Lu, L.Y.; Wu, J. Interferon-Λ3/4 Genetic Variants and Interferon-Λ3 Serum Levels Are Biomarkers of Lupus Nephritis and Disease Activity in Taiwanese. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.J.; Lv, C.; Zhao, F.; Xu, T.S.; Li, P. Elevated Serum Levels of Interleukin-29 Are Associated with Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibodies. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2017, 241, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazek, K.; Eames, H.L.; Weiss, M.; Byrne, A.J.; Perocheau, D.; Pease, J.E.; Doyle, S.; McCann, F.; Williams, R.O.; Udalova, I.A. IFN-λ Resolves Inflammation via Suppression of Neutrophil Infiltration and IL-1β Production. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggi, A.; Tan, Y.; Granucci, F.; Zanoni, I. IFN-λ Suppresses Intestinal Inflammation by Non-Translational Regulation of Neutrophil Function. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.R.; Kotenko, S.V.; Kaplan, M.J. Interferon Lambda in Inflammation and Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.W.; Constant, D.A.; Nice, T.J. Interferon Lambda in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 767505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.; Carbonetti, N. Roles and Effects of Interferon Lambda Signaling in the Context of Bacterial Infections. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2023, 43, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, S.; Parker, D. IL-1β Activation in Response to Staphylococcus Aureus Lung Infection Requires Inflammasome-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, T.S.; Prince, A.S. Bacterial Pathogens Activate a Common Inflammatory Pathway through IFNλ Regulation of PDCD4. PLoS Pathog 2013, 9, e1003682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.; Wickersham, M.; Riquelme, S.; Prince, A. The Effects of IFN-λ on Epithelial Barrier Function Contribute to Klebsiella Pneumoniae ST258 Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 60, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardanuy, J.; Scanlon, K.; Skerry, C.; Fuchs, S.Y.; Carbonetti, N.H. Age-Dependent Effects of Type I and Type III IFNs in the Pathogenesis of Bordetella Pertussis Infection and Disease. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 2192–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhao, M.; Dong, L.; Zhao, L.; Zou, M.; Sun, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Zou, Z. Design and Evaluation of Novel Interferon Lambda Analogs with Enhanced Antiviral Activity and Improved Drug Attributes. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbalaei, M.; Rezaee, S.A.; Farsiani, H. Pichia Pastoris: A Highly Successful Expression System for Optimal Synthesis of Heterologous Proteins. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5867–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Pal, M.; Sharma, R.K. Pichia as Yeast Cell Factory for Production of Industrially Important Bio-Products: Current Trends, Challenges, and Future Prospects. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2023, 8, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanath, V. A Short Communication on Pichia Pastoris vs. E. Coli: Efficient Expression System. Ann. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 5, 049–050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronopoulou, S.; Tsochantaridis, I.; Tokamani, M.; Kokkinopliti, K.D.; Tsomakidis, P.; Giannakakis, A.; Galanis, A.; Pappa, A.; Sandaltzopoulos, R. Expression and Purification of Human Interferon Alpha 2a (IFNα2a) in the Methylotrophic Yeast Pichia Pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2023, 211, 106339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltà-Foix, R.; Garcia-Fruitós, E.; Arís, A. Time to Consider Ruling out Inclusion Bodies Denaturing Protocols for Spontaneous Solubilization of Biologically Active Proteins. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigata, M.; Meinert, C.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Bock, N. Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of Current Characterization and Evaluation Techniques. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mooney, D.J. Designing Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater 2016, 1, 16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaciu, A.; Munteanu, R.A.; Moldovan, A.I.; Moldovan, C.S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Hydrogels Based Drug Delivery Synthesis, Characterization and Administration. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Minhas, M.U.; Ahmad, M.; Sohail, M.; Khalid, Q.; Abdullah, O. Synthesis and Evaluation of Topical Hydrogel Membranes; a Novel Approach to Treat Skin Disorders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Xu, X.; Song, J.; Luo, F.; Qian, Z. Synthesis, Characterization, and Acute Oral Toxicity Evaluation of PH-Sensitive Hydrogel Based on MPEG, Poly(ε-Caprolactone), and Itaconic Acid. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 239838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiancich, C.; Bianco, J.; Vanvarenberg, K.; Ucakar, B.; Joudiou, N.; Gallez, B.; Bastiat, G.; Lagarce, F.; Préat, V.; Danhier, F. Injectable Nanomedicine Hydrogel for Local Chemotherapy of Glioblastoma after Surgical Resection. J. Control. Release 2017, 264, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nice, T.J.; Baldridge, M.T.; McCune, B.T.; Norman, J.M.; Lazear, H.M.; Artyomov, M.; Diamond, M.S.; Virgin, H.W. Interferon-λ Cures Persistent Murine Norovirus Infection in the Absence of Adaptive Immunity. Science 2015, 347, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Daniels, B.P.; Pinto, A.K.; Huang, A.C.; Vick, S.C.; Doyle, S.E.; Gale, M.; Klein, R.S.; Diamond, M.S. Interferon-λ Restricts West Nile Virus Neuroinvasion by Tightening the Blood-Brain Barrier. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 284ra57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, A.; Lennemann, N.J.; Ouyang, Y.; Bramley, J.C.; Morosky, S.; Marques, E.T.D.A.; Cherry, S.; Sadovsky, Y.; Coyne, C.B. Type III Interferons Produced by Human Placental Trophoblasts Confer Protection against Zika Virus Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galani, I.E.; Triantafyllia, V.; Eleminiadou, E.E.; Koltsida, O.; Stavropoulos, A.; Manioudaki, M.; Thanos, D.; Doyle, S.E.; Kotenko, S.V.; Thanopoulou, K.; et al. Interferon-λ Mediates Non-Redundant Front-Line Antiviral Protection against Influenza Virus Infection without Compromising Host Fitness. Immunity 2017, 46, 875–890.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odendall, C.; Voak, A.A.; Kagan, J.C. Type III IFNs Are Commonly Induced by Bacteria-Sensing TLRs and Reinforce Epithelial Barriers during Infection. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3270–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Interferon Type | Drug Brand Name | Manufacturing Company | Market Entry Date | Disease |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFNα-2a | Pegasys | Pharmaand GmbH | 16 October 2002 | Chronic hepatitis B and C |
| IFNα-2b | Besremi | PharmaEssentia USA Corporation | 12 November 2021 | Polycythemia vera |
| IFNα-n3 | Alferon N | AIM ImmunoTech Inc. | 10 October 1989 | Condyloma acuminate |
| IFNβ-1a | Avonex | Biogen Inc. | 23 May 2003 | Multiple sclerosis |
| Rebif | EMD Serono, Inc. | 7 March 2002 | Multiple sclerosis | |
| Plegridy | Biogen Inc. | 15 August 2014 | Multiple sclerosis | |
| IFNβ-1b | Betaseron | Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. | 11 August 2009 | Multiple sclerosis |
| Betaferon | BayerPharma | 30 November 1995 | Multiple sclerosis | |
| IFNγ-1b | Actimmune | Horizon Therapeutics Ireland DAC Dublin, Ireland | 1 December 2013 | Malignant osteopetrosis; Chronic granulomatous disease |
| Condition | Clinical Trial Number | Trial Phase | Number of Participants Treated | Intervention | Publication Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDV infection | NCT02765802 | Phase 2 | 33 | 120 μg or 180 μg PEG-IFNλ | 2023 |
| HDV infection | NCT03600714 | Phase 2 | 26 | 180 μg PEG-IFNλ + LNF + RTV | 2020 |
| HBV infection | NCT01204762 | Phase 2 | 163 | 180 μg PEG-IFNλ or 180 μg PEG-IFNα2a | 2015 |
| HCV (GT 1-4) + HIV infection | NCT01866930 | Phase 3 | 300 | 180 μg PEG-IFNλ + RBV + DCV | 2016 |
| HCV infection GT 2 or 3 | NCT01616524 | Phase 3 | 874 | 180 μg PEG-IFNλ + RBV/RBV + DCV or 180 μg PEG-IFNα2a + RBV | 2016 |
| HCV infection GT 1 | NCT01598090 | Phase 3 | 617 | 180 μg PEG-IFNλ + RBV + TVR or 180 μg PEG-IFNα + RBV + TVR | 2016 |
| Hemophilia + HCV infection GT 1-4 | NCT01741545 | Phase 3 | 51 | 180 μg PEG-IFNλ + RBV + DCV | 2016 |
| HCV infection GT 1-4 | NCT01001754 | Phase 2b | 525 | 120/180/240 μg of PEG-IFNλ + RBV or 180 μg PEG-IFNα2a + RBV | 2014 |
| HCV infection GT 1-4 | No NCT number provided | Phase 2a | 55 | 80/120/180/240 μg PEG-IFNλ + RBV or 180 μg PEG-IFNα2a + RBV | 2010 |
| HCV infection GT 1 | No NCT number provided | Phase 1b | 56 | 1.5/3.0 μg/kg * PEG-IFNλ or 0.5–2.25 μg/kg * PEG-IFNλ + RBV or 1.5 μg/kg * + RBV | 2010 |
| Healthy volunteers | No NCT number provided | Phase 1a | 24 | 0.5/1.5/5.0/7.5 μg/kg * PEG-IFNλ or placebo | 2007 |
| Clinical Trial Number | Trial Phase | Number of Participants | Intervention | Publication Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04727424 | Phase 3 | 1951 | 180 μg PEG-IFN-λ or placebo | 2023 |
| NCT04331899 | Phase 2 | 120 | 180 μg PEG-IFN-λ or placebo | 2021 |
| NCT04354259 | Phase 2 | 60 | 180 μg PEG-IFN-λ or placebo | 2021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chronopoulou, S.; Tsochantaridis, I. Interferon Lambda: The Next Frontier in Antiviral Therapy? Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060785
Chronopoulou S, Tsochantaridis I. Interferon Lambda: The Next Frontier in Antiviral Therapy? Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(6):785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060785
Chicago/Turabian StyleChronopoulou, Sofia, and Ilias Tsochantaridis. 2025. "Interferon Lambda: The Next Frontier in Antiviral Therapy?" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 6: 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060785
APA StyleChronopoulou, S., & Tsochantaridis, I. (2025). Interferon Lambda: The Next Frontier in Antiviral Therapy? Pharmaceuticals, 18(6), 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060785







