Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction Alleviates Asthma via Spatial Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Treg Cell Promotion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
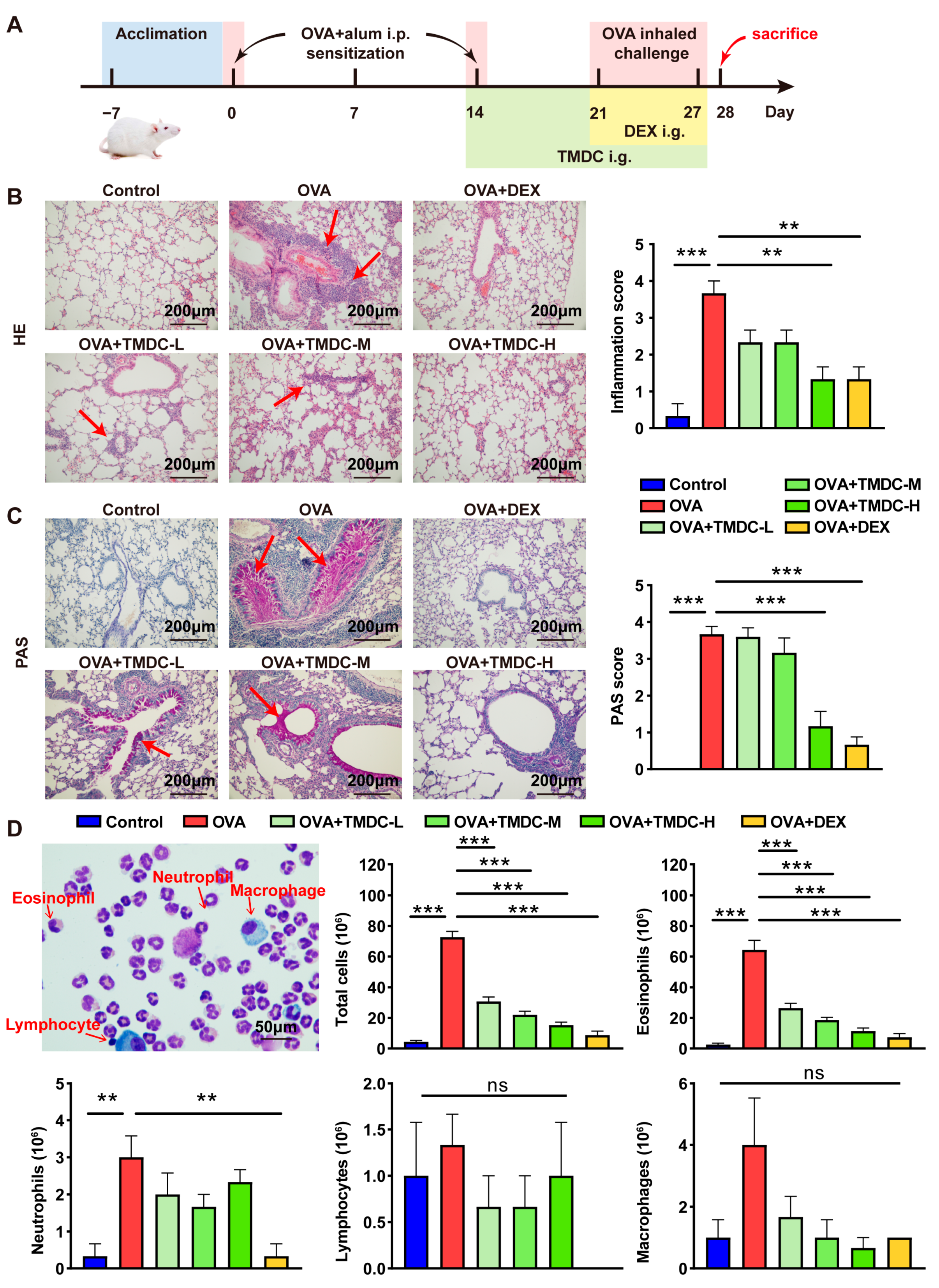
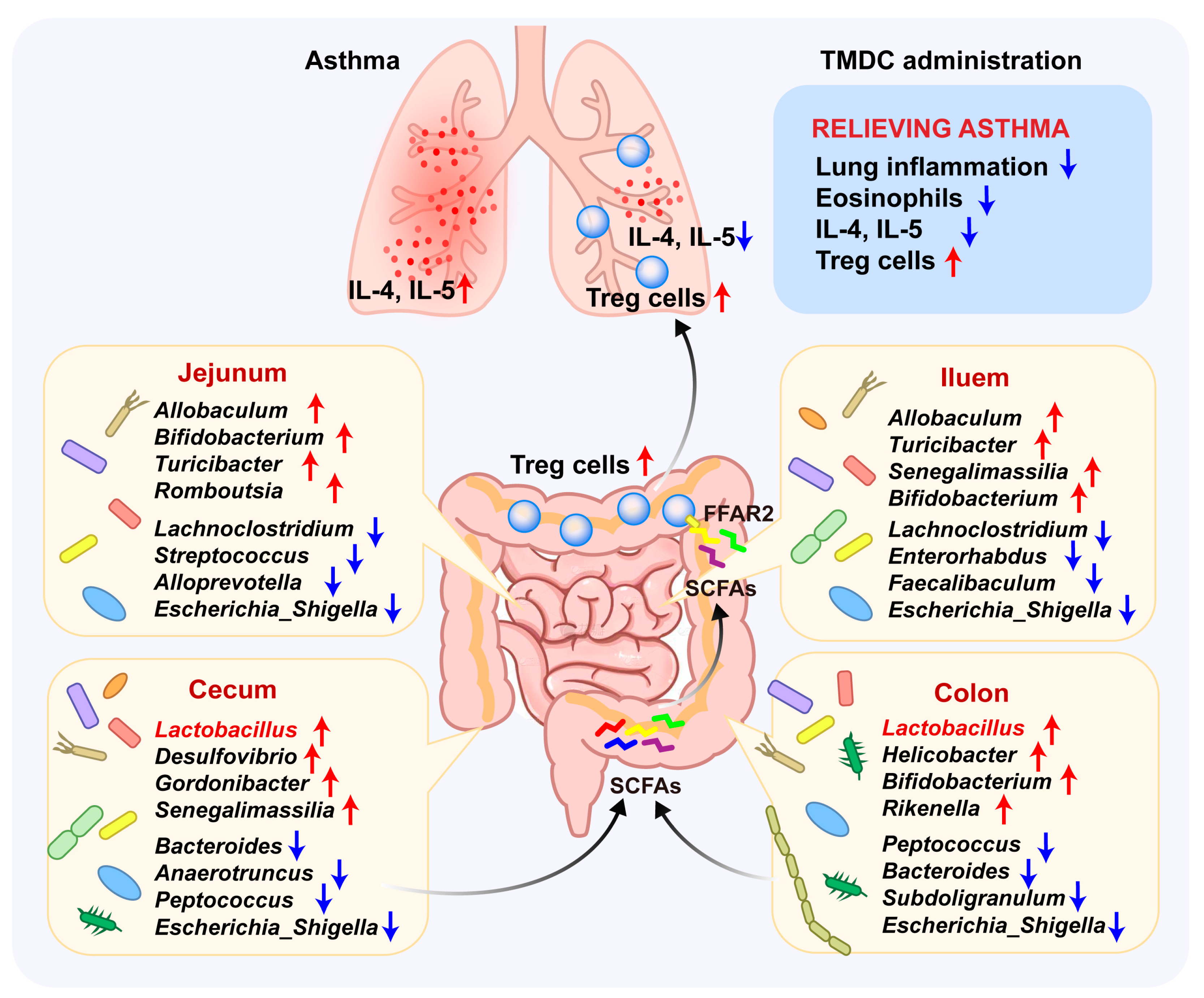
2.1. TMDC Alleviated the Lung Inflammation of Asthmatic Mice
2.2. TMDC Reduced the Type 2 Cytokine by Promoting Treg Cells
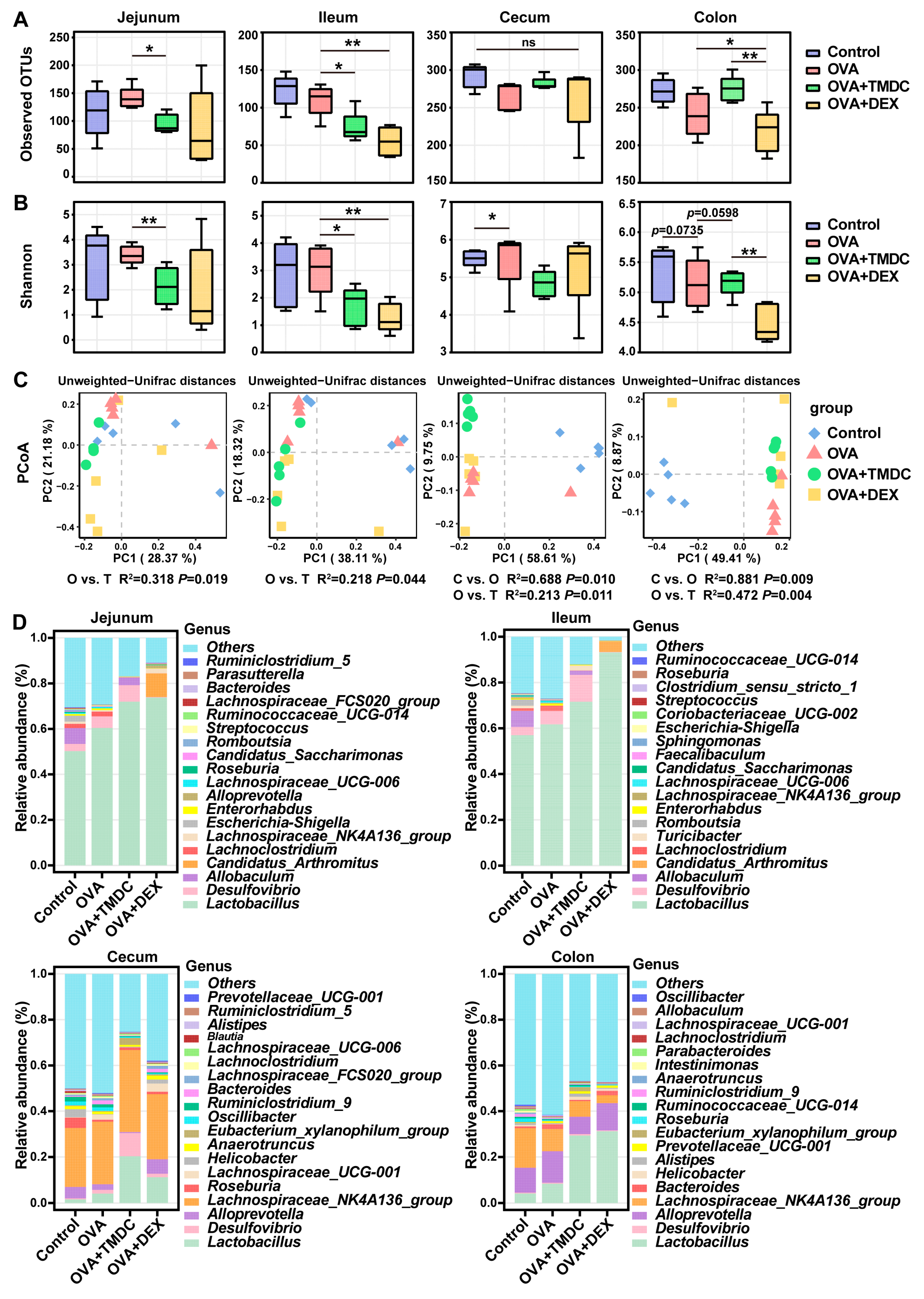
2.3. TMDC Improved the Microbial Composition Across Different Gut Segments
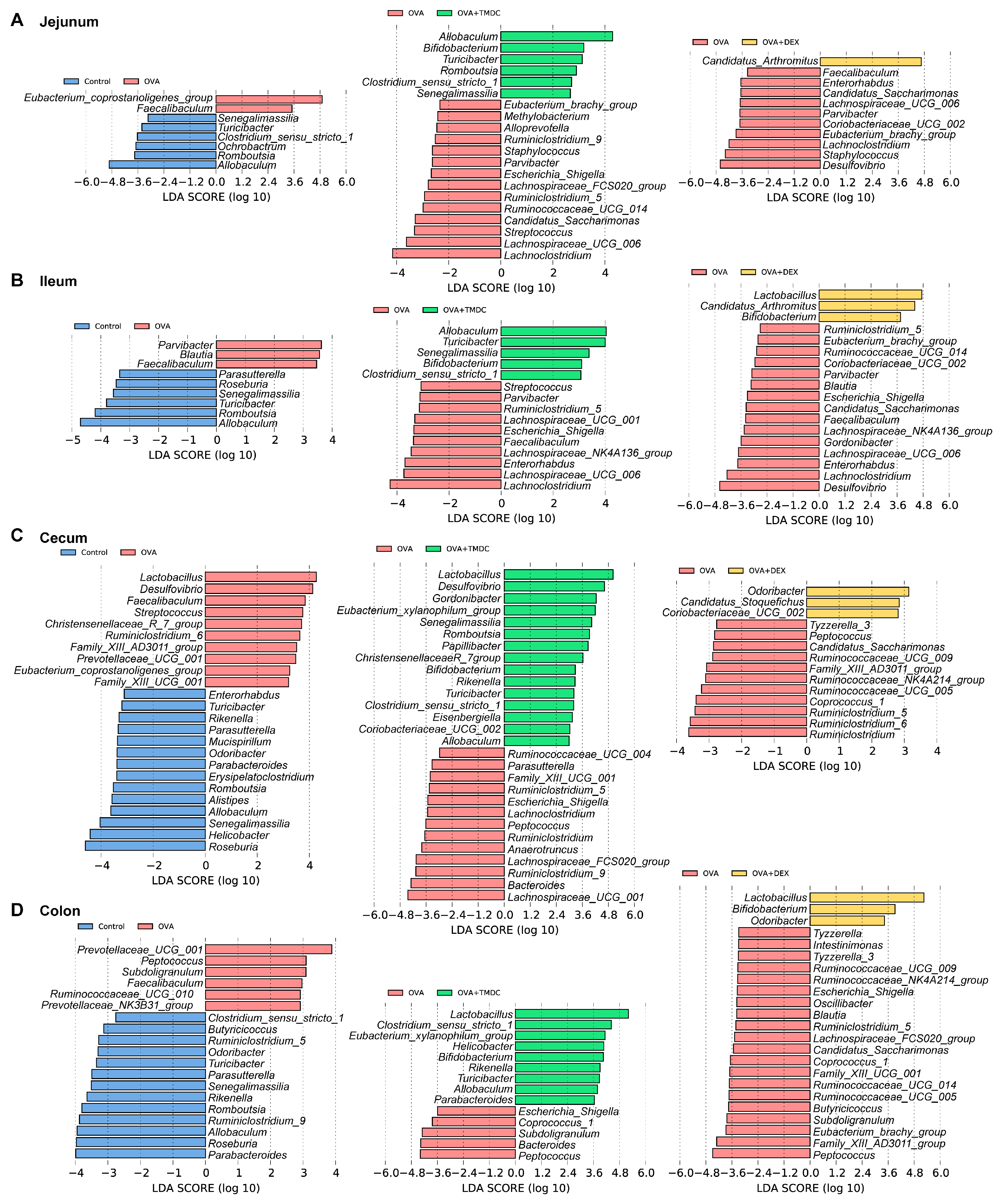
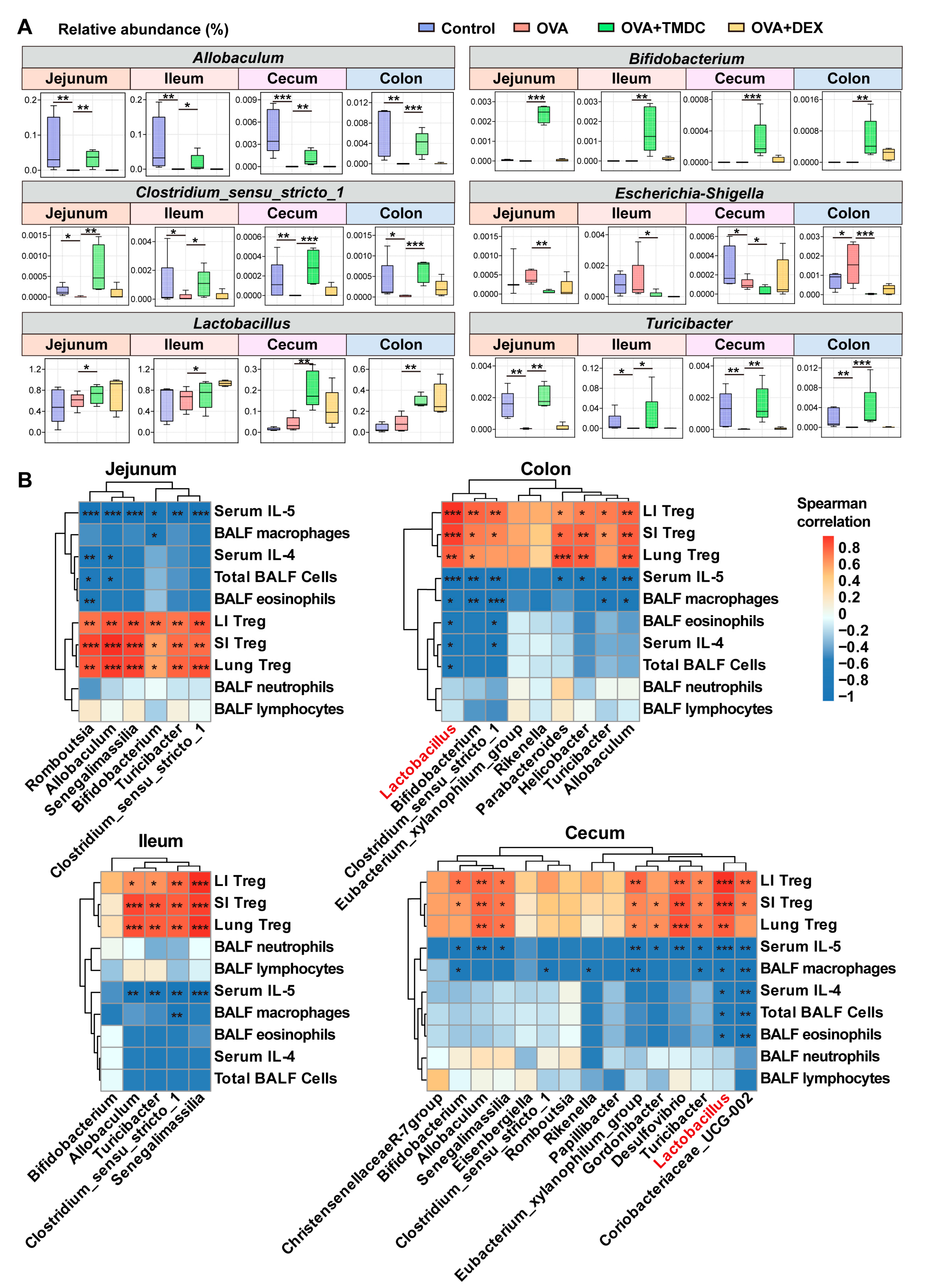
2.4. Specific Microbes Affected by TMDC Across Different Gut Segments
2.5. Lactobacillus Exhibited Significant Correlations to Inflammatory Cells and Cytokines
2.6. Lactobacillus Supplementation Restores Antibiotic-Induced Diminished Therapeutic Effect of TMDC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Preparation of TMDC Decoction
= (clinical dose × conversion coefficient)/gavage volume
= (156 g × 0.0026)/0.2 mL = 2.028 g/mL
4.3. Establishment of OVA-Induced Asthmatic Mouse Model
4.4. Antibiotic Treatment and LGG Treatment in an Asthmatic Mouse Model
4.5. Collection of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) for Diff-Quick Staining
4.6. Tissue Histology and Analysis
4.7. Detection of Cytokine Levels by ELISA
4.8. Preparation of Single-Cell Suspensions of Lung, SI, and Colon
4.9. Analysis of Treg Cells by Flow Cytometry
4.10. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Raw Data Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHR | airway hyperresponsiveness |
| BALF | bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| DEX | dexamethasone |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| LC-MS | liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| LI | large intestine |
| OTU | operational taxonomic unit |
| OVA | ovalbumin |
| PAS | periodic acid-Schiff |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PTS | phosphotransferase system |
| SI | small intestine |
| TCM | traditional Chinese medicine |
| TMDC | Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan decoction |
References
- Wenzel, S.E. Asthma: Defining of the persistent adult phenotypes. Lancet 2006, 368, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatz, M.; Rosenwasser, L. The allergic asthma phenotype. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2014, 2, 645–648; quiz 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, R.; Ip, M.; Kulkarni, T.; Kim, S.; Perng, D.; Yao, X.; Iwanaga, T.; Koh, M.S. Challenges faced in managing adult asthma: A perspective from Asian countries. Respirology 2020, 25, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J. Mechanistic analysis of Th2-type inflammatory factors in asthma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 6898–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlBloushi, S.; Al-Ahmad, M. Exploring the immunopathology of type 2 inflammatory airway diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1285598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramori, G.; Nucera, F.; Mumby, S.; Bello, F.L.; Adcock, I.M. Corticosteroid resistance in asthma: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Mol. Asp. Med. 2022, 85, 100969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamar, M.; Chen, Q.; Martinez-Blanco, M.; Chatila, T.A. Regulatory T cells in allergic inflammation. Semin. Immunol. 2023, 70, 101847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A. Regulatory T cells mediated immunomodulation during asthma: A therapeutic standpoint. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcik, W.; Boutin, R.C.T.; Sokolowska, M.; Finlay, B.B. The Role of Lung and Gut Microbiota in the Pathology of Asthma. Immunity 2020, 52, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, F.; Liang, B.; Liang, Y.; Chen, S.; Mo, X.; Ju, Y.; Zhao, H.; Jia, H.; Spector, T.D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in asthma in UK adults. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, K.E.; Sitarik, A.R.; Havstad, S.; Lin, D.L.; Levan, S.; Fadrosh, D.; Panzer, A.R.; LaMere, B.; Rackaityte, E.; Lukacs, N.W.; et al. Neonatal gut microbiota associates with childhood multisensitized atopy and T cell differentiation. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, K.E.; Rackaityte, E.; LaMere, B.; Fadrosh, D.W.; Fujimura, K.E.; Panzer, A.R.; Lin, D.L.; Lynch, K.V.; Halkias, J.; Mendoza, V.F.; et al. Heritable vaginal bacteria influence immune tolerance and relate to early-life markers of allergic sensitization in infancy. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durack, J.; Kimes, N.E.; Lin, D.L.; Rauch, M.; McKean, M.; McCauley, K.; Panzer, A.R.; Mar, J.S.; Cabana, M.D.; Lynch, S.V. Delayed gut microbiota development in high-risk for asthma infants is temporarily modifiable by Lactobacillus supplementation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-F.; Chie, W.-C.; Wang, I.J. Efficacy of Lactobacillus Administration in School-Age Children with Asthma: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori-Andrade, A.C.M.; Nolasco, A.E.; Malacco, N.L.S.O.; Vaz, L.G.; Afonso, L.C.C.; Russo, R.C.; Vieira, L.Q.; Dos Santos, L.M. Lactobacillus delbrueckii UFV-H2b20 increases IFN-γ production and CD39+CD73+ Treg cell numbers in lungs, and protects mice against experimental allergic asthma. Immunobiology 2022, 227, 152284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Yu, J.; Jeong, S.K.; Hong, S.-J. Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus on allergic march model by suppressing Th2, Th17, and TSLP responses via CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) Tregs. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 153, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Lv, M.; Jiang, Z.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Cui, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction Alleviate Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Asthma by Inhibiting Mast Cell Degranulation and Down-Regulating the Differential Expression Proteins. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 725953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, T.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-asthmatic Effects of TMDCT Decoction in Eosinophilic Asthma Through Treg/Th17 Balance. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 819728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropini, C.; Earle, K.A.; Huang, K.C.; Sonnenburg, J.L. The Gut Microbiome: Connecting Spatial Organization to Function. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Guryn, K.; Leone, V.; Chang, E.B. Regional Diversity of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zuo, B.; Huang, S.; Zeng, B.; Han, D.; Li, T.; Liu, T.; Wu, Z.; Wei, H.; Zhao, J.; et al. Spatial heterogeneity of bacterial colonization across different gut segments following inter-species microbiota transplantation. Microbiome 2020, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikiy, S.; Rudensky, A.Y. Principles of regulatory T cell function. Immunity 2023, 56, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skuljec, J.; Chmielewski, M.; Happle, C.; Habener, A.; Busse, M.; Abken, H.; Hansen, G. Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Redirected Regulatory T Cells Suppress Experimental Allergic Airway Inflammation, a Model of Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harb, H.; Stephen-Victor, E.; Crestani, E.; Benamar, M.; Massoud, A.; Cui, Y.; Charbonnier, L.-M.; Arbag, S.; Baris, S.; Cunnigham, A.; et al. A regulatory T cell Notch4-GDF15 axis licenses tissue inflammation in asthma. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, X.-L.; Luo, Z.-R.; Yu, J.; Tong, Z.-R.; Li, Q.-Q.; Wu, J.-H.; Tao, Y.; Feng, P.-S.; Lan, J.-P.; Wang, P. Pi-Pa-Run-Fei-Tang alleviates lung injury by modulating IL-6/JAK2/STAT3/IL-17 and PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway and balancing Th17 and Treg in murine model of OVA-induced asthma. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 317, 116719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Jia, J.; Cao, B.; Liu, M.; Guo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; et al. Ephedrae Herba polysaccharides inhibit the inflammation of ovalbumin induced asthma by regulating Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg cell immune imbalance. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 152, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Dong, R.; Ge, D.; Peng, G. Gegen Qinlian Decoction Alleviates Experimental Colitis and Concurrent Lung Inflammation by Inhibiting the Recruitment of Inflammatory Myeloid Cells and Restoring Microbial Balance. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 1273–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Ge, D.; Peng, G.; Zhou, M. Dachengqi Decoction alleviates intestinal inflammation in ovalbumin-induced asthma by reducing group 2 innate lymphoid cells in a microbiota-dependent manner. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2023, 13, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Kong, J.; Dong, R.; Ge, D.; Li, J.; Peng, G. Xuanbai Chengqi Decoction Ameliorates Pulmonary Inflammation via Reshaping Gut Microbiota and Rectifying Th17/Treg Imbalance in a Murine Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2021, 16, 3317–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, W.; Lee, Y.K.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H. Spatial Heterogeneity and Co-occurrence of Mucosal and Luminal Microbiome across Swine Intestinal Tract. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-L.; Lu, C.-C.; Lai, W.-F.; Wu, T.-S.; Lu, J.-J.; Chen, Y.-M.; Tzeng, C.-M.; Liu, H.-T.; Wei, H.; Lai, H.-C. Role of gut microbiota in identification of novel TCM-derived active metabolites. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y. Treating asthma patients with probiotics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Hosp. 2023, 40, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rose, M.A.; Stieglitz, F.; Köksal, A.; Schubert, R.; Schulze, J.; Zielen, S. Efficacy of probiotic Lactobacillus GG on allergic sensitization and asthma in infants at risk. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabana, M.D.; McKean, M.; Caughey, A.B.; Fong, L.; Lynch, S.; Wong, A.; Leong, R.; Boushey, H.A.; Hilton, J.F. Early Probiotic Supplementation for Eczema and Asthma Prevention: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20163000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.T.; Lin, F.H.; Lee, Y.T.; Ku, M.S.; Lue, K.H. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG immunopathologic changes in chronic mouse asthma model. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voo, P.-Y.; Wu, C.-T.; Sun, H.-L.; Ko, J.-L.; Lue, K.-H. Effect of combination treatment with Lactobacillus rhamnosus and corticosteroid in reducing airway inflammation in a mouse asthma model. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. = Wei Mian Yu Gan Ran Za Zhi 2022, 55, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spacova, I.; Petrova, M.I.; Fremau, A.; Pollaris, L.; Vanoirbeek, J.; Ceuppens, J.L.; Seys, S.; Lebeer, S. Intranasal administration of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevents birch pollen-induced allergic asthma in a murine model. Allergy 2019, 74, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.M.; Yu, M.; Darby, T.M.; Vaccaro, C.; Li, J.-Y.; Owens, J.A.; Hsu, E.; Adams, J.; Weitzmann, M.N.; Jones, R.M.; et al. The Microbial Metabolite Butyrate Stimulates Bone Formation via T Regulatory Cell-Mediated Regulation of WNT10B Expression. Immunity 2018, 49, 1116–1131.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; Van Der Veeken, J.; DeRoos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J.; et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.M.; Howitt, M.R.; Panikov, N.; Michaud, M.; Gallini, C.A.; Bohlooly-Y, M.; Glickman, J.N.; Garrett, W.S. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science 2013, 341, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, X.; Zhao, W.; Liu, W.-H.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Hong, Y.; Cui, J.; Shang, X.; Feng, H.; Hung, W.-L.; et al. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BL-99 ameliorates colitis-related lung injury in mice by modulating short-chain fatty acid production and inflammatory monocytes/macrophages. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Guan, X.; Chen, D.; Ma, W. The Th17/Treg Cell Balance: A Gut Microbiota-Modulated Story. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Cui, J.; Xu, G.; Li, N.; Peng, G. Intestinal IL-17 family orchestrates microbiota-driven histone deacetylation and promotes Treg differentiation to mediate the alleviation of asthma by Ma-Xing-Shi-Gan decoction. Phytomedicine 2025, 156656, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, T.; Pu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhang, W.; Xue, F.; Shan, Z.; Liu, J.; et al. Hypoxic hUCMSC-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate allergic airway inflammation and airway remodeling in chronic asthma mice. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Component | Chinese Name | Amount (g) |
|---|---|---|
| Gypsum fibrosum [Sulfates] | Shi Gao | 30 |
| Prunus mume (Siebold) Siebold & Zucc [Rosaceae] | Wu Mei | 20 |
| Fagopyrum cymosum (Trevir.) Meisn. [Polygonaceae] | Jin Qiao Mai | 15 |
| Reynoutria multiflora (Thunb.) Moldenke [Polygonaceae] | Shou Wu Teng | 15 |
| Ganoderma lucidum (Leyss. ex Fr.) Karst. [Polyporaceae] | Ling Zhi | 10 |
| Saposhnikovia divaricata (Turcz. ex Ledeb.) Schischk [Apiaceae] | Fang Feng | 10 |
| Gastrodia elata Blume [Orchidaceae] | Tian Ma | 10 |
| Ephedra sinica Stapf [Ephedraceae] | Ma Huang | 10 |
| Prunus armeniaca L. [Rosaceae] | Xing Ren | 10 |
| Cicadae periostracum [Cicadidae] | Chan Tui | 10 |
| Bombyx batryticatus [Silkworm pilgrimaging] | Jiang Can | 10 |
| Glycyrrhiza glabra L. [Fabaceae] | Sheng Gan Cao | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, N.; Qin, J.; Ge, D.; Peng, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction Alleviates Asthma via Spatial Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Treg Cell Promotion. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050646
Hong Y, Yang Z, Liu Z, Li N, Qin J, Ge D, Peng G, Wang J, Wang Q. Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction Alleviates Asthma via Spatial Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Treg Cell Promotion. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(5):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050646
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Yanfei, Zheng Yang, Zirui Liu, Na Li, Jingbo Qin, Dongyu Ge, Guiying Peng, Ji Wang, and Qi Wang. 2025. "Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction Alleviates Asthma via Spatial Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Treg Cell Promotion" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 5: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050646
APA StyleHong, Y., Yang, Z., Liu, Z., Li, N., Qin, J., Ge, D., Peng, G., Wang, J., & Wang, Q. (2025). Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction Alleviates Asthma via Spatial Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Treg Cell Promotion. Pharmaceuticals, 18(5), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050646








