Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a prevalent metabolic disease with global implications, necessitating effective management strategies. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4) inhibitors have shown promise as potent agents for T2DM treatment. Methods: This study combines chemical synthesis, molecular modelling, and inhibitory activity assays to characterise the structure–activity relationship of novel isomeric 1,2,4-oxadiazole-substituted derivatives of the 2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane scaffold acylated with (R)-3-amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic acid. Results: In this article, we demonstrate the efficacy of new compounds as robust inhibitors of DPP-4. The attempts to further modify neogliptin (our lead compound described previously) resulted in a more potent DPP-4 inhibitor 9a (IC50 = 4.3 nM), which did not mediate any substantial inhibition of DPP-8 and DPP-9. Conclusions: This study demonstrates that pseudo peptides incorporating (R)-3-amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic acid, a 2-aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane moiety, and 1,2,4-oxadiazole substituents act as potent and selective DPP-4 inhibitors. By the stereochemical refinement of oxadiazole derivatives of neogliptin, we discovered compound 9a, a strong candidate for further development in T2DM treatment.
1. Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a complex chronic metabolic disease characterised by hyperglycaemia arising from both insulin resistance [1] and impaired insulin production [2]. T2DM affects millions of people worldwide and is associated with various complications (cardiovascular, nephro-, neuro-, and retinopathy, and foot ulcers) [3]. To effectively manage T2DM and its complications, early diagnosis, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions are required [4]. Multiple antihyperglycemic treatment options are approved to provide personalised diabetes care, with ongoing clinical investigations exploring novel drugs [5].
Among those, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, commonly called gliptins, have garnered considerable attention; these orally administered small-molecule agents prevent the fast enzymatic degradation of incretin hormones by inhibiting DPP-4. This therapeutic approach augments the levels of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) that stimulate insulin synthesis and suppress glucagon secretion [6]. DPP-4 inhibitors have demonstrated their efficacy in reducing glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) levels as monotherapy and in combination with other antidiabetic agents [5]. Notably, DPP-4 inhibitors are suitable for patients intolerant to metformin [7] and less likely to cause hypoglycaemia. In other words, their favourable safety profile makes DPP-4 inhibitors ideal for a diverse patient population [8]. Several structures with target-specific interaction with DPP-4 have received official approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), including sitagliptin [9], saxagliptin [10], alogliptin [11], and linagliptin [12] (Figure 1). Although the FDA has not yet approved some other gliptins (e.g., vildagliptin, teneligliptin, trelagliptin), at least eight additional DPP-4 inhibitors have received approval from different regulatory agencies worldwide and are widely prescribed for T2DM treatment, coinciding with ongoing efforts yielding at least ten novel DPP-4 inhibitors in clinical development [5]. Previously, we developed and discussed neogliptin, a novel DPP-4 inhibitor that demonstrated superior potency to sitagliptin, one of the most common DPP-4 inhibitors [13]. In this article, we utilised neogliptin as a template for further drug development, which yielded a novel compound 9a with enhanced DPP-4 inhibiting activity, supported by structure–activity relationship (SAR) models and in vitro enzymatic assays.
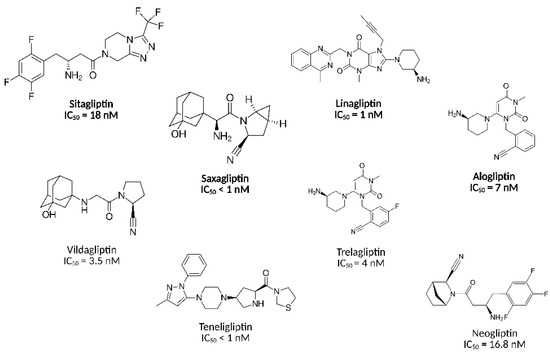
Figure 1.
Structures and DPP-4 inhibitory activities of selected compounds. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs are shown in bold.
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Synthesis
5-phenyl-substituted 1,2,4-oxadiazoles 3a and 3b were synthesised from the corresponding nitriles 1a,b (1:1 mixture of isomers) [13] by standard synthetic procedures from corresponding nitrile and acid components (Figure 2). Nitriles were converted into amidoximes and subsequently cyclised with benzoic acid to afford a mixture of intermediates 2a,b, which were further separated by column chromatography, where diastereomer 2b formed an upper spot on a TLC plate (as well as on the silica gel column) and was less soluble in Et2O or Et2O/n–hexane mixture than its counterpart 2a. Moreover, 2b was isolated as a crystalline powder, whereas 2a was obtained as a solid foam. After Boc-deprotection and another column chromatography step, target compounds 3a and 3b were received as free amines.
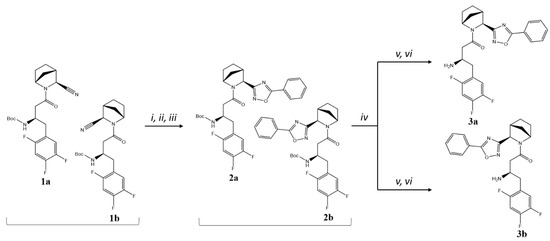
Figure 2.
Synthesis of compounds 3a,b. Reagents and conditions: (i) NH2OH×HCl, K2CO3, EtOH, overnight at t = 65–70 °C; (ii) PhCOOH, DIC, DCM, for 2 h at RT; (iii) Py, overnight at t = 110 °C; (iv) column chromatography on silica gel, Et2O/n–hexane 2:1; (v) TsOH, CH3CN, overnight at RT; (vi) column chromatography on silica gel, 1→10% EtOH in CHCl3.
For the synthesis of 3-phenyl substituted 1,2,4-oxadiazoles 9a and 9b, another strategy was applied (Figure 3). Initially, starting from acids 4a,b (1:1 mixture of isomers) [13], we prepared a mixture of isomeric amino-intermediates 6a,b that were further acylated with Boc-protected (R)-3-amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic acid 7 using standard conditions. Diastereomer separation was performed by analogy with 2a,b, and the separated intermediates 8a and 8b were subjected to Boc-deprotection, affording the corresponding target products 9a and 9b.
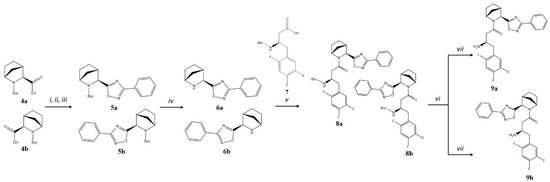
Figure 3.
Synthesis of compounds 9a,b. Reagents and conditions: (i) PhCN, NH2OH×HCl, K2CO3, EtOH, overnight at t = 65-70 °C; (ii) DIC, DCM, for 2 h at RT; (iii) Py, overnight at t = 110 °C; (iv) TsOH, CH3CN, overnight at RT; (v) BOP, DIPEA, DCM overnight at RT; (vi) column chromatography on silica gel, Et2O/n–hexane 2:1; Et2O/CHCl3 0→2%; Et2O/DCM 2→5%; (vii) TsOH, CH3CN, overnight at RT, column chromatography on silica gel, 1 → 10% EtOH in CHCl3.
tert-Butyl {(2R)-4-[(3S)-3-(5-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl]-4-oxo-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-yl}carbamate (2a) and tert-Butyl {(2R)-4-[(3R)-3-(5-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl]-4-oxo-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-yl}carbamate (2b)
To a solution of nitrile mixture 1a,b (1 g, 2.3 mmol) in EtOH (30 mL), NH2OHxHCl (0.7 g, 10 mmol) and K2CO3 (0.83 g, 6 mmol) were added. The mixture was stirred overnight at 65–70 °C and then cooled to RT. After that, DCM (50 mL) was added, the precipitate was filtered, the solvent was evaporated, and the crude residue was used further.
To a solution of benzoic acid (0.31 g, 2.5 mmol) in DCM (20 mL), DIC (0.63 g, 5 mmol) was added. The mixture was stirred for 1 h at RT, and then the crude residue from the previous step was added, followed by another 1 h of stirring at RT. DCM was evaporated, and the residue was dissolved in pyridine (25 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred overnight at 110 °C, cooled to RT, and evaporated. The residue was dissolved in DCM (30 mL) and washed with 5% citric acid (3 × 10 mL) and 10% NaHCO3 (3 × 10 mL). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, evaporated to 1–2 mL, and subjected to silica gel column chromatography purification (eluent: Et2O/n–hexane 2:1), leading to pure isomers 2a (0.4 g) and 2b (0.47 g). The total yield was 68%.
2a TLC (Et2O/n–hexane 3:1): Rf 0.4. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 8.11, 8.06 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms, Ph), 7.76–7.56 (m overlapped, 3H, Ph), 7.94–7.36 (m, 1H, trifluoro-Ph), 7.32–7.22 (m, 1H, trifluoro-Ph), 6.70, 6.59, 6.35, 6.20 (4 m, 1H, NH-Boc, rotameric forms), 4.78, 4.65 (2 m, 1H, CHCN, 2 rotameric forms), 4.48, 4.42 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 4.08–3.97 (m, 1H), 2.93–2.54 (m overlapped, 4H), 2.33, 2.18–2.10 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 1.97–1.91, 1.85–1.57 (2 m, 5H), 1.47, 1.36 (2 m 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 1.26, 1.21 (2 s, 9H, Boc, 2 rotameric forms). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 175.51, 174.83, 170.61, 170.51, 168.75, 167.98, 157.37–157.29, 154.95–154.85, 154.77, 154.70, 149.02–148.83, 146.76–146.58, 144.50–144.37, 133.51, 133.34, 129.60, 127.96, 127.80, 123.42, 123.35, 123.01–122.80, 119.67–119.20, 105.73–105.23, 77.65, 77.61, 58.95, 58.49, 57.89, 55.94, 47.40, 47.04, 43.34, 42.18, 38.40, 35.14, 33.34, 33.02, 32.74, 31.07, 29.52, 28.12, 28.06, 27.81, 26.80, 26.31. LC-MS: m/z 557 [M+H]+, 501 [M − t-Bu + H]+. Anal. calcd for C29H31F3N4O4: C, 62.58; H, 5.61; N, 10.07. Found: C, 62.76; H, 5.85; N, 9.84%.
The isomeric compound 2a (0.2 g, 63%) was also prepared from pure isomer 1a (0.25 g, 0.57 mmol) by the same procedure described above for 2a,b. 1H NMR and LC-MS data, as well as Rf, are identical to those described above for 2a.
2b TLC (Et2O/n–hexane 3:1): Rf 0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 8.12, 8.06 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms, Ph), 7.75–7.58 (m overlapped, 3H, Ph), 7.47–7.23, 7.22–7.12 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms, trifluoro-Ph), 6.80–6.69, 6.44–6.34 (2 m, 1H, NH-Boc, 2 rotameric forms), 4.97, 4.63 (2 m, 1H, CHCN, 2 rotameric forms), 4.48, 4.47 (2 m overlapped, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 4.02 (m, 1H), 2.90–2.31 (m overlapped, 4H), 2.23–2.09 (m, 1H), 1.86–1.54 (m overlapped, 5H), 1.47, 1.35 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 1.26, 1.24 (2 s, 9H, Boc, 2 rotameric forms). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 175.50, 174.80, 170.92, 170.47, 169.19, 168.23, 157.30–157.21, 154.82–154.76, 149.01–148.83, 146.89–146.57, 144.52–144.40, 133.50, 133.27, 129.64, 129.56, 127.92, 127.76, 123.45, 123.32, 123.06–122.75, 119.39–119.07, 105.59–105.22, 77.67, 77.50, 59.17, 58.56, 57.72, 55.89, 48.22, 47.47, 42.91, 42.15, 35.22, 33.32, 33.17, 32.87, 31.01, 29.72, 28.08, 28.05, 27.87–27.49, 26.82, 26.12. LC-MS: m/z 557 [M+H]+, 501 [M − t-Bu + H]+, 457 [M − Boc + H]+. Anal. calcd for C29H31F3N4O4: C, 62.58; H, 5.61; N, 10.07. Found: C, 62.77; H, 5.67; N, 9.76%.
(3R)-3-Amino-1-[(3S)-3-(5-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-2-azabicyclo [2.2.1]heptan-2-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one (3a)
To a solution of Boc-protected isomer 2a (0.3 g, 0.54 mmol) in CH3CN (20 mL), p-TSAxH2O (0.21 g, 1.1 mmol) was added, and the resulting mixture was stirred overnight. After that, CH3CN was evaporated, and the residue was dissolved in CHCl3 and subjected to silica gel column chromatography purification (eluent: 0 → 10% EtOH in CHCl3), leading to 3a in a free base form (0.22 g), yield 89%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 8.11, 8.05 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms, Ph), 7.74–7.58 (m, 3H, Ph), 7.48–7.38, 7.38–7.30 (2 m overlapped, 2H, 2 rotameric forms, trifluoro-Ph), 4.75, 4.65 (2 m, 1H, CHCN, 2 rotameric forms), 4.49, 4.46 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 3.4–3.2 (br, 2H, NH2), 3.29–3.22 (m, 1H), 2.75–2.69 (m, 1H), 2.64–2.52 (m overlapped, 2H, 2 rotameric forms), 2.37–2.21, 2.13–2.07 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms), 1.97–1.53 (m overlapped, 5H, 2 rotameric forms), 1.44, 1.35 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 175.45, 174.79 (NC=O), 170.72, 170.54, 169.99, 169.22 (two carbons of oxadiazole), 157.13–157.01, 154.72–154.60, 148.99–148.72, 147.06–146.91, 146.55–146.27, 144.66–144.51 (three quaternary CF-carbons of trifluorophenyl), 133.47, 133.26 (para-carbon of phenyl), 129.60, 129.56 (meta-carbon of phenyl), 127.91, 127.75 (ortho-carbon of phenyl), 123.84–123.55 (quaternary ipso-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 123.41, 123.29 (quaternary ipso-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 119.52–119.27 (ortho-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 105.72–105.22 (meta-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 79.23 (imp. of CHCl3), 59.03, 58.44, 57.69, 55.78 (two CH-carbons of azanorbornane), 49.85, 48.92, 48.30 (CHNH2-carbon), 43.25, 42.11, 41.74, 41.36, 35.36, 35.21, 35.11 (PhCH2 and COCH2 carbon of propane and CH-carbon of azanorbornane), 33.31, 31.10, 29.64, 28.58, 26.78, 26.28, 23.70 (three CH2-carbons of azanorbornane). LC-MS: m/z 457 [M+H]+. Anal. calcd for C24H23F3N4O2 ×0.6 CHCl3 × 0.3 C6H13NO (N-tert-butylacetamide): C, 56.36; H, 4.93; N, 10.70. Found: C, 56.51; H, 4.68; N, 10.46%.
(3R)-3-Amino-1-[(3R)-3-(5-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one (3b)
3b (0.25 g, 88%) as free base was prepared from 2b (0.35 g, 0.63 mmol) by analogy with 3a. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 8.11–8.05 (m, 2H, Ph), 7.75–7.59 (m, 3H, Ph), 7.48–7.40, 7.30–7.19 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms, trifluoro-Ph), 4.89, 4.64 (2 m, 1H, CHCN, 2 rotameric forms), 4.50, 4.48 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 3.3–3.2 (br, 2H, NH2), 3.26–3.21, 3.19–3.13 (2 m overlapped, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 2.75–2.66 (m, 1H), 2.65–2.56, 2.48–2.43 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms), 2.26–2.07, 1.98–1.84 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms), 1.82–1.51 (m overlapped, 5H), 1.45, 1.34 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 175.41, 174.79 (NC=O), 170.78, 170.52, 170.29, 169.26 (two carbons of oxadiazole), 157.10–157.00, 154.69–154.57, 148.84–148.70, 147.00–146.88, 146.53–146.26, 144.60–144.48 (three quaternary CF-carbons of trifluorophenyl), 133.42, 133.24 (para-carbon of phenyl), 129.54 (meta-carbon of phenyl), 127.83, 127.72 (ortho-carbon of phenyl), 123.82–123.42 (quaternary ipso-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 123.40, 123.21 (quaternary ipso-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 119.45–119.04 (ortho-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 105.68–104.79 (meta-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 79.20 (imp. of CHCl3), 59.00, 58.46, 57.80, 55.70 (two CH-carbons of azanorbornane), 49.22 (CHNH2-carbon), 43.19, 42.07, 41.79, 41.13, 35.78, 35.33, 35.06 (PhCH2 and COCH2 carbon of propane and CH-carbon of azanorbornane), 33.31, 31.02, 29.70, 26.74, 26.24 (three CH2-carbons of azanorbornane). LC-MS: m/z 457 [M+H]+. Anal. calcd for C24H23F3N4O2 ×0.5 CHCl3: C, 57.01; H, 4.59; N, 10.85. Found: C, 57.24; H, 4.38; N, 10.45%.
tert-Butyl (3S)-3-(5-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxylate (5a,b)
The isomeric mixture 5a,b (1.5 g, 66%) was prepared from 4a,b (1.6 g, 6.6 mmol) and benzonitrile (1.0 g, 10 mmol) by analogy with 2a and 2b. DCM/Et2O 3:1 was used as eluent for column chromatography purification. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 8.02–7.98 (m, 2H, Ph), 7.62–7.54 (m, 3H, Ph), 4.68, 4.67 (2 m, 1H, CHCN, 2 rotameric forms), 4.31, 4.22 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 2.80–2.73 (2 m overlapped, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 2.05–1.96 (m, 1H), 1.81–1.56 (m overlapped, 4H), 1.43 (m, 1H), 1.41, 1.18 (2 s, 9H, Boc, 2 rotameric forms). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 179.31, 179.08, 167.74, 167.72, 153.68, 152.08, 131.77, 131.75, 129.44, 129.39, 127.13, 127.08, 126.14, 126.13, 79.64, 79.25, 58.69, 58.48, 57.37, 55.95, 43.32, 42.85, 35.38, 34.71, 30.08, 29.87, 28.16, 27.81, 26.79, 26.68. LC-MS: m/z 286 [M − t-Bu + H]+, 242 [M − Boc + H]+. Anal. calcd for C19H23N3O3: C, 66.84; H, 6.79; N, 12.31. Found: C, 66.52; H, 6.75; N, 12.20%.
(3S)-3-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane and (3R)-3-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane (6a,b)
6a,b (0.8 g, 94%), obtained as a mixture of free base form isomers, was prepared from the Boc-protected mixture 5a,b (1.2 g, 3.5 mmol) by analogy with the procedure described above for 3a. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 8.01–7.97 (m, 2H, Ph), 7.61–7.53 (m, 3H, Ph), 4.14 (m, 1H, CHCN), 3.44 (m, 1H), 2.77 (br, 1H, NH), 2.70 (m, 1H), 1.73–1.47 (m overlapped, 5H), 1.29 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 182.00, 167.38, 131.47, 129.26, 127.03, 126.47, 56.61, 55.32, 41.80, 35.44, 31.94, 27.85. LC-MS: m/z 242 [M+H]+. Anal. calcd for C14H15N3O: C, 69.69; H, 6.27; N, 17.41. Found: C, 69.90; H, 5.98; N, 17.20%.
tert-Butyl {(2R)-4-[(3S)-3-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl]-4-oxo-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-yl}carbamate (8a) and tert-Butyl {(2R)-4-[(3R)-3-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl]-4-oxo-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-yl}carbamate (8b)
To the solution of acid 7 (0.73 g, 2.2 mmol) in DCM (30 mL), the following reagents were added: DIPEA (0.29 g, 2.2 mmol), BOP-reagent (0.98 g, 2.2 mmol), and amino-component 6a,b (0.53 g, 2.2 mmol). The mixture was stirred overnight at RT and then washed with 5% citric acid (3 × 10 mL) and 10% NaHCO3 (3 × 10 mL). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, evaporated to 1–2 mL, and subjected to silica gel column chromatography purification (eluent: Et2O/n–hexane 2:1), followed by two more column chromatography separations (eluents: 0 → 2% Et2O in CHCl3 and 2 → 5% Et2O in DCM), leading to pure isomers 8a (0.43 g) and 8b (0.5 g). The total yield was 76%.
8a TLC (Et2O/n–hexane 3:1): Rf 0.4. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 8.00, 7.96 (2 m overlapped, 2H, 2 rotameric forms, Ph), 7.63–7.50 (m overlapped, 3H, Ph), 7.48–7.36 (m, 1H, trifluoro-Ph), 7.35–7.21 (m, 1H, trifluoro-Ph), 6.71, 6.61, 6.37 (3 m, 1H, NH-Boc, rotameric forms), 5.04, 4.80 (2 m, 1H, CHCN, 2 rotameric forms), 4.50, 4.49 (2 m overlapped, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 4.07–3.96 (m, 1H), 2.94–2.81 (m, 1H), 2.76 (m, 1H), 2.68–2.53 (m, 2H), 2.14–2.07 (m, 1H), 1.85–1.37 (m overlapped, 6H), 1.25, 1.20, 1.18 (3 s, 9H, Boc, rotameric forms). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 178.74, 178.34, 168.84, 168.10, 167.71, 167.57, 157.37–157.27, 154.94–154.76, 154.84, 149.03–148.84, 146.91–146.58, 144.51–144.39, 131.79, 131.67, 129.27, 127.18, 127.04, 126.14, 125.98, 122.90–122.70, 119.43–119.18, 105.73–105.23, 77.66, 58.69, 58.02, 57.85, 56.05, 47.36, 46.95, 43.78, 42.37, 38.32, 35.76, 33.88, 33.03, 32.84, 30.81, 28.10, 28.05, 27.79, 26.66, 26.09. LC-MS: m/z 557 [M+H]+, 501 [M − t-Bu + H]+, 457 [M − Boc + H]+. Anal. calcd for C29H31F3N4O4: C, 62.58; H, 5.61; N, 10.07. Found: C, 62.32; H, 5.56; N, 9.69%.
The isomeric compound 8a (0.12 g, 49% over 3 steps) was prepared from pure isomeric acid 4a (0.11 g, 4.6 mmol) by the same three-step procedure described above for 8a,b. 1H NMR and LC-MS data, as well as Rf, are identical to those described above for 8a.
8b TLC (Et2O/n–hexane 3:1): Rf 0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 8.02, 7.96 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms, Ph), 7.65–7.49 (m overlapped, 3H, Ph), 7.49–7.40, 7.39–7.34 (2 m overlapped, 1H, 2 rotameric forms, trifluoro-Ph), 7.34–7.22, 7.22–7.13 (2 m overlapped, 1H, 2 rotameric forms, trifluoro-Ph), 6.82–6.74, 6.46–6.40 (2 m, 1H, NH-Boc, 2 rotameric forms), 5.20, 4.77 (2 m, 1H, CHCN, 2 rotameric forms), 4.55, 4.52 (2 m overlapped, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 4.07–3.95 (m, 1H), 2.95–2.67 (m overlapped, 3H), 2.64–2.55, 2.46–2.34 (2 m overlapped, 2H, 2 rotameric forms), 2.17–2.08 (m, 1H), 1.84–1.38 (m overlapped, 5H), 1.25, 1.23, 1.17 (3 s, 9H, Boc, rotameric forms). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 178.66, 178.62, 169.28, 168.31, 167.80, 167.59, 157.36–157.18, 154.94–154.82, 154.86, 154.77, 149.21–148.88, 146.91–146.54, 144.40–144.37, 131.83, 131.64, 129.35, 129.26, 127.19, 127.04, 126.20, 125.96, 123.06–122.74, 119.41–119.12, 105.75–105.14, 77.69, 77.59, 58.95, 58.12, 57.74, 56.01, 48.21, 47.47, 43.49, 42.40, 35.86, 33.94, 33.17, 32.97, 30.76, 29.56, 28.09, 28.06, 27.75, 26.72, 25.99. LC-MS: m/z 557 [M+H]+, 501 [M − t-Bu + H]+, 457 [M − Boc + H]+. Anal. calcd for C29H31F3N4O4: C, 62.58; H, 5.61; N, 10.07. Found: C, 62.29; H, 5.28; N, 9.70%.
(3R)-3-Amino-1-[(3S)-3-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one (9a)
9a as free base (0.24 g, 89%) was prepared from 8a (0.33 g, 0.6 mmol) by analogy with 3a. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 8.01, 7.96 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms, Ph), 7.63–7.50 (m, 3H, Ph), 7.47–7.31 (m overlapped, 2H, trifluoro-Ph), 5.04, 4.80 (2 m, 1H, CHCN, 2 rotameric forms), 4.52 (m, 1H), 3.4–3.2 (br, 2H, NH2), 3.29–3.22 (m, 1H), 2.87, 2.75 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 2.73–2.52 (m overlapped, 2H, 2 rotameric forms), 2.38–2.23 (m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 2.11–2.07 (m, 1H), 1.87–1.56 (m overlapped, 5H), 1.52–1.39 ppm (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 178.77, 178.50 (NC=O), 170.05, 169.35, 167.73, 167.57 (two carbons of oxadiazole), 157.11–157.01, 154.72–154.60, 149.02–148.75, 147.07–146.91, 146.57–146.30, 144.68–144.52 (three quaternary CF-carbons of trifluorophenyl), 131.80, 131.64 (para-carbon of phenyl), 129.33, 129.28 (meta-carbon of phenyl), 127.16, 127.04 (ortho-carbon of phenyl), 126.15, 125.95 (quaternary ipso-carbon of phenyl), 123.76–123.47 (quaternary ipso-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 119.53–119.28 (ortho-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 105.76–105.26 (meta-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 79.24 (imp. of CHCl3), 58.75, 57.98, 57.68, 55.90 (two CH-carbons of azanorbornane), 49.86, 48.87, 48.20 (CHNH2-carbon), 43.75, 42.37, 41.54, 41.25, 35.77, 35.34, 35.16 (PhCH2 and COCH2 carbon of propane and CH-carbon of azanorbornane), 33.91, 30.84, 29.48, 28.59, 26.68, 26.08 (three CH2-carbons of azanorbornane). LC-MS: m/z 457 [M+H]+. Anal. calcd for C24H23F3N4O2 × 0.46 CHCl3 × 0.31 C6H13NO (N-tert-butylacetamide): C, 57.78; H, 5.06; N, 11.03. Found: C, 57.50; H, 5.30; N, 10.91%.
(3R)-3-Amino-1-[(3R)-3-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one (9b)
9b as free base (0.23 g, 88%) was prepared from 8b (0.32 g, 0.58 mmol) by analogy with 3a. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 7.97 (m, 2H, Ph), 7.64–7.51 (m, 3H, Ph), 7.50–7.39, 7.32–7.15 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms, trifluoro-Ph), 5.17, 4.78 (2 m, 1H, CHCN, 2 rotameric forms), 4.55, 4.52 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 3.40–3.20 (br, 2H, NH2), 3.27–3.20 (m, 1H), 2.88, 2.77–2.66 (2 m, 2H, 2 rotameric forms), 2.63–2.53 (m, 1H), 2.32–2.23, 2.22–2.15 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms), 2.13–2.05 (m, 1H), 1.94–1.59 (m overlapped, 5H), 1.51, 1.40 (2 m, 1H, 2 rotameric forms). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ (ppm): 178.78, 178.60 (NC=O), 170.37, 169.37, 167.68, 167.56 (two carbons of oxadiazole), 157.13–157.04, 154.72–154.61, 148.89–148.75, 147.06–146.94, 146.43–146.29, 144.66–144.54 (three quaternary CF-carbons of trifluorophenyl), 131.79, 131.67 (para-carbon of phenyl), 129.30, 127.10 (meta-carbon of phenyl), 127.02 (ortho-carbon of phenyl), 126.14, 125.87 (quaternary ipso-carbon of phenyl), 123.74–123.46 (quaternary ipso-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 119.51–119.04 (ortho-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 105.78–105.28 (meta-carbon of trifluorophenyl), 79.24 (imp. of CHCl3), 58.81, 58.00, 57.75, 55.84 (two CH-carbons of azanorbornane), 49.29, 49.03 (CHNH2-carbon), 43.63, 42.33, 41.55, 40.98, 35.75, 35.33 (PhCH2 and COCH2 carbon of propane and CH-carbon of azanorbornane), 33.94, 30.76, 29.57, 28.60, 26.66, 26.05 (three CH2-carbons of azanorbornane). LC-MS: m/z 457 [M+H]+. Anal. calcd for C24H23F3N4O × 0.16 CHCl3 × 0.21 C6H13NO (N-tert-butylacetamide): C, 61.09; H, 5.22; N, 11.80. Found: C, 61.30; H, 5.27; N, 11.60%.
2.2. Molecular Modelling
The molecular docking analysis of compounds 3a, 3b, 9a, and 9b revealed that 9a exhibited the highest potency against DPP-4, as indicated by the docking score (GScore) in Table 1. This observation was further supported by the consistent alignment of pharmacophore characteristics with those of the reference compound, trelagliptin (Figure 4). Compound 9a exhibits a more densely populated network of lipophilic contacts, as evidenced by lower values of the corresponding increment in the scoring function. Upon complex formation, the trifluorophenyl group in 9a establishes tighter interactions with Trp627/629, and contact with Tyr752 becomes apparent, accounting for the increased lipophilic contact. Notably, the oxadiazole scaffold in 9a undergoes a 90-degree rotation relative to its analogous counterpart in 3a, facilitating the formation of a new hydrogen bond with Tyr662. It is also noteworthy that compounds 3b and 9b exhibited a distinct binding pose compared to 9a and trelagliptin, along with inferior GScore values and strain energy parameters in the ligand–protein complex (ΔG strain). It was revealed that 9a induces minimal structural rearrangements in the DPP-4 protein compared to its isomers.

Table 1.
The scoring outcomes of 3a, 3b, 9a, and 9b in comparison with trelagliptin. The lead compound is highlighted in green.
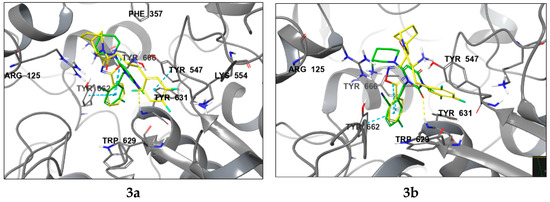
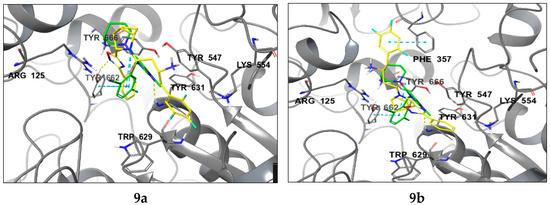
Figure 4.
The binding poses of compounds 3a, 3b, 9a, and 9b (shown in yellow) in contrast to trelagliptin (green) when bound to DPP-4. Dashed lines represent various interactions: pi-stacking (blue), hydrogen bonds (yellow), and strained contacts (orange). Detailed high-quality figures are available in the Supplementary Information (SI).
Compounds 3a and 9a showcase an increased prevalence of aromatic substituents, thereby intensifying the involvement of stacking interactions within the molecular system. As shown in Figure 5, these interactions simultaneously involve three tyrosine residues: Tyr547, Tyr662, and Tyr666. A notable repositioning of the trifluorophenyl fragment is observed, facilitating interactions with Trp629 and Tyr547 upon incorporating a phenyl substituent into the oxadiazole heterocycle. This spatial rearrangement results in the mediation of additional lipophilic contacts, consequently enhancing the site specificity and affinity of compounds 3a and 9a compared to neogliptin (refer to the Supplementary Materials for a detailed comparison of binding poses). Furthermore, interactions with charged amino acid residues, specifically Arg125 and Arg669, oriented towards the electron density of the heterocycle, are maintained. This preservation ensures optimal molecular recognition of lipophilic cavities, thereby contributing to the overall binding effectiveness of the compounds.
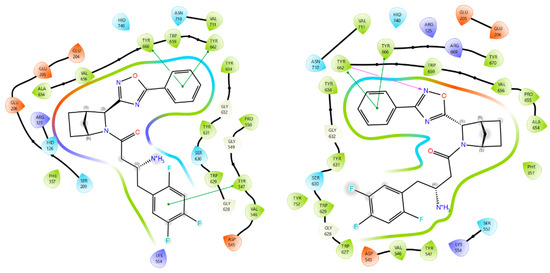
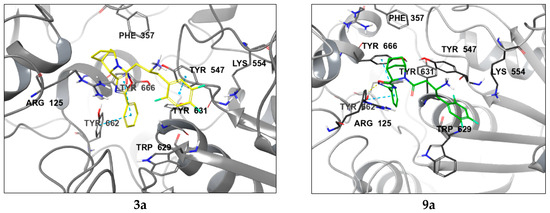
Figure 5.
Ligand interaction diagrams and the binding poses of compounds 3a and 9a in the active cavity of DPP-4. Dashed lines represent various interactions: pi-stacking (blue), hydrogen bonds (yellow), and strained contacts (orange). Detailed high-quality figures are available in the Supplementary Information (SI).
2.3. X-Ray Diffraction Study
The stereoselective synthesis of the respective starting materials, 1a and 4a, which correspond to the target compounds, 3a and 9a, was conducted to establish precise structural assignments for the isolated isomeric compounds. These starting compounds were synthesised following the methodology outlined in [13]. In the case of 1a, single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis were successfully grown. The crystallographic analysis validated the structure of the intended isomer (Figure 6).
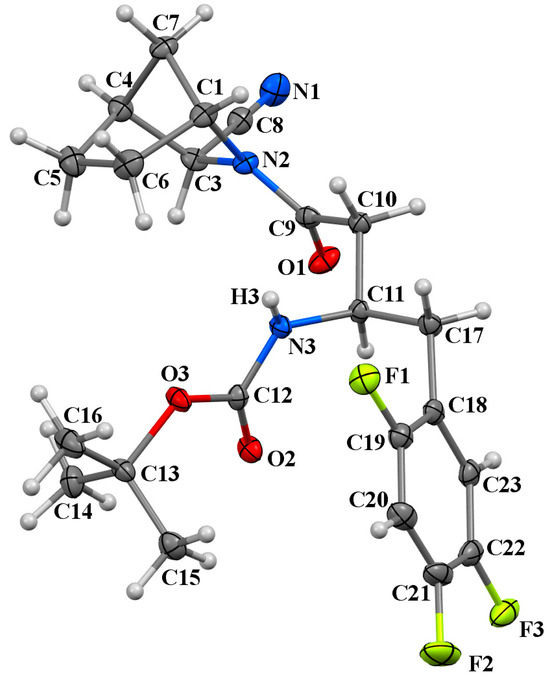
Figure 6.
The molecular structure of 1a showing the labelling scheme: non-hydrogen atoms (C1-23 are carbons shown in grey, N1-3 are nitrogen atoms shown in blue, O1-3 are oxygen atoms shown in red, F1-3 are fluorine atoms shown in lime) are represented as 30% probability displacement ellipsoids. Hydrogen atoms are depicted as small white spheres with arbitrary radii.
2.4. Inhibitory Activity Assays
The assessment of DPP-4 enzyme inhibitory activities for the synthesised compounds was performed using protocols similar to those previously described in the literature [13,14]. For the determination of IC50 values, inhibitory assays were conducted employing recombinant DPP-4 enzyme D4943, the chromogenic substrate Gly-Pro-pNA, and a buffer system (50 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM NaCl, 0.01% Triton, pH = 7.6). Following a brief incubation period (37 °C for 30 min), absorbance at 405 nm was measured. Initial optimisation of the procedure utilised reference compounds. Each inhibitor was analysed in a dilution range spanning from 10−4 to 10−11 M. Certified samples of commercially available DPP-4 inhibitors (vildagliptin, sitagliptin, alogliptin, and linagliptin) with known IC50 values, as well as precursor nitriles (including neogliptin), were utilised as reference compounds [13]. Correspondingly, the analysis of inhibition activity for related enzymes was executed using DPP-8 and DPP-9 inhibition assays, where the compounds were studied in the dilution range 10−2 to 10−8 M (Table 2).

Table 2.
DPP-4-, DPP-8-, and DPP-9-inhibitory activities of target compounds 3a, 3b, 9a, and 9b in comparison with neogliptin.
3. Discussion
Oxadiazoles are heterocyclic compounds that have gathered substantial attention in medicinal chemistry due to their diverse pharmacological activities and structural versatility. Various agents bearing oxadiazole moieties have been explored as potential drug candidates in different therapeutic areas, including antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer agents [15,16,17,18]. The considerable potential of oxadiazole-containing scaffolds for DPP-4 inhibition was previously demonstrated by Nordhoff et al. [14,19], where such oxadiazole-containing DPP-4 inhibitors exhibited improved potency and metabolic stability. Following this approach, we modified the nitrile group of neogliptin, resulting in four isomeric oxadiazole derivatives. Similarly to the findings of Nordhoff et al. [14], some of the synthesised oxadiazoles were shown to be potent inhibitors of DPP-4, outperforming their precursor nitriles. Some differences among the synthesised diastereomers were observed, with RS-stereoisomers (3a and 9a) being more potent over RR-isomers (3b and 9b). Interestingly, closely related oxadiazole-substituted pyrrolidines, studied as novel anthelmintics, demonstrated that only the S-enantiomer of 3-phenyl-5-(pyrrolidine-2-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazole derivative exhibited the inhibitory activity on nematode motility and development, whereas the R-enantiomer remained inactive [20]. Our study revealed that only 9a exhibited a higher DPP-4 inhibitory activity than neogliptin, suggesting the importance of the 3-phenyl substitution in the 1,2,4-oxadiazole heteroatom orientation.
While DPP-4 inhibitors are generally well tolerated and effective in managing T2DM, inhibiting DPP-8 and DPP-9 has raised concerns. DPP-8 and DPP-9 have broader substrate specificities compared to DPP-4 and are involved in various biological processes, including immune response regulation. The previous literature suggests that inhibiting DPP-8 and DPP-9 may be associated with some adverse effects, such as haematological and gastrointestinal issues [9,21]. In our study, all of the tested oxadiazole-derivatives showed feeble DPP-8 and DPP-9 inhibitory activity in the concentration range 10−3–10−6 M. This is below the estimated therapeutic range and is consistent with the data in the literature for already known DPP-4 inhibitor compounds, making it possible to predict the absence of side effects associated with the undesirable inhibition of homologous enzymes DPP-8 and DPP-9.
It is also crucial to highlight that we used distinct diastereomers to measure the DPP-4 inhibitory activity of the synthesised compounds. Acid 4a is a precursor in the synthetic route leading to 1a [13]; therefore, we can reasonably infer the same isomeric structure for 4a, as confirmed by the X-ray diffraction study for 1a. These distinct diastereomers served as precursors for the syntheses of 3a and 9a, employing methodologies analogous to those delineated in Figure 1 and Figure 2. A compelling indication of the exclusive production of the targeted diastereomers was validated through the absence of corresponding spots on the TLC plate for 2b and 8b, which were perfectly visible in diastereomeric mixtures These observations and NMR results further support the successful synthesis of the intended isomers 3a and 9a.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Synthesis
All starting reagents were obtained from reliable commercial vendors, mostly Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, United States), Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), and Acros (Geel, Belgium), and used without further purification. Intermediates and final compounds were isolated using column chromatography on silica gel. Compounds were only used for biological evaluation if the purity was ≥95%.
4.2. Molecular Modelling
The docking procedure was performed using the Schrödinger Glide module in standard precision mode [22]. The docking grid was calculated according to native ligand dimensions using the DPP-4 PDB model (5KBY) [23]. The docking area was limited per reference ligand size, with 7 Å as a buffer zone. Grid spacing was set at 0.375 Å, VdW radii cut-off 0.8 Å. Several optional constraints were added: nitrile group orientation (reference—trelagliptin), hydrophobic attraction—aromatic and aliphatic moiety (trelagliptin). The generation of docking solutions was performed using the Glide module of Schrödinger Suite (version 2022-4) in standard precision mode with 0.8 Å VdW radius and with the previously mentioned optional constraints. The docking protocol was validated by redocking reference compounds (sitagliptin, trelagliptin, vildagliptin). For each inhibitor, 45 docking solutions were generated, and the best 15 were used for binding mode analysis using GlideScore and EModel values to control target affinity. Optimal binding poses were selected per cluster with an RMSD of less than 1.5 Å. The binding poses and calculated parameters of the reference ligands were taken as a control. Free Gibbs energy (∆G) was calculated using the MM-GBSA method [24], implemented in Schrödinger Suite v.2022-4, module Prime. All results were processed using the Maestro molecular modelling interface (Schrödinger Suite v.2022-4). All protein–ligand complexes were prepared and refined using Schrödinger Protein Prepwizard [25]. This procedure was essential to fix missing amino acid sidechains, incorrect bond orders, and correct protonation states. Optimal binding poses were selected by cluster RMSD less than 1.5 Å. The binding parameters of the reference ligand were chosen as a control.
4.3. Structure and Purity Confirmation
LC/MS analysis was performed on an 1100 LC (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) with ELSD, UV (DAD 200–400 nm) and mass detection (1100 LCMSD, Agilent Technologies, APCI and ES positive ionisation). The most used column was the Onix C18 50 × 4.6 mm; eluent 1—0.1% TFA in water; eluent 2—0.1% TFA in acetonitrile, gradient—eluent 1—2.9 min, eluent 2—0.2 min, eluent 1—rinsing, flow rate 3.75 mL/min. 1H, 13C, COSY and HSQC NMR spectra were registered on the spectrometer Bruker DRX 400 (400.13 MHz for protons, 100.61 MHz for carbons). DMSO-d6 was used as a solvent. Elemental analysis was performed on the Vario MICRO cube CHNS analyser (Elementar Analysensysteme GmbH, Hanau, Germany).
4.4. X-Ray Diffraction Study
Crystals of 1a (C22H26F3N3O3, M = 437.46) are orthorhombic, space group P212121, at 120K a = 5.5917(13), b = 10.260(2), c = 38.079(8) Å, V = 2184.7(9) Å3, Z = 4, dcalc. = 1.330 g/cm3, μ = 1.06 cm−1. Data collection was carried out with a Bruker SMART APEX II diffractometer, λ(MoKα) = 0.71073 Å, ω-scan technique, T = 120(2) K, 5472 independent reflections (Rint = 0.0663) with θmax = 28.346° collected and used in refinement. The structure was solved by direct methods and refined by the full matrix least-squares technique against F2 with the anisotropic thermal parameters for all non-hydrogen atoms. The hydrogen atom of the N-H group was located from the Fourier maps and isotropically refined without restrictions; the remaining hydrogen atoms were placed geometrically and included in the structure factor calculations in a riding motion approximation with isotropic thermal parameters Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for the hydrogen atoms of methyl groups and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for other carbon atoms. The refinement converged to wR2 = 0.0912 and GOF = 1.010 for all independent reflections (R1 = 0.0448 was calculated against F for 4015 observed reflections with I > 2σ(I)). All calculations were performed using the SHELXL programme package [26].
4.5. Inhibitory Activity Evaluation
For the in vitro assays, we used the substrate Gly-Pro-p-nitroanilide (H-Gly-Pro pNA HCl, G0513) and recombinant dipeptidyl peptidase-4 enzyme (D4943), which were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Samples containing DPP-4 (0.0015 U/well) and varying concentrations of test compounds were incubated with the chromogenic peptide substrate, G0513 (90 µg/well), in a total volume of 100 µL of buffer system (50 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM NaCl, 0.01% Triton, pH = 7.6). The mixtures were incubated at 37 ◦C for 30 min, and the absorbance at 405 nm was measured using the microplate reader ChemWell (Awareness Technology Inc., Palm City, FL, USA). The DPP-4 inhibitory activities for each test compound were calculated. IC50 values were obtained using GraphPad Prism 8 software. The inhibition activity analysis of the related enzymes was performed using the “Fluorogenic DPP-8 Assay Kit” and “Fluorogenic DPP-9 Assay Kit”, both purchased from BPS Bioscience (San Diego, CA, USA). The dilution range for every compound was 10−2–10−8 M.
5. Conclusions
In this article, we show that pseudo peptides containing (R)-3-amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoic acid and bicyclic amino moiety (2-aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane) with 1,2,4-oxadiazole substituents are potent DPP-4 inhibitors. The strategic modification of neogliptin and the emphasis on stereochemistry have yielded compound 9a with enhanced inhibitory activity against DPP-4 while minimising the risk of inhibiting DPP-8 and DPP-9. The comprehensive evaluation, combining computational and experimental approaches, provides valuable information for developing DPP-4 inhibitors with improved efficacy and safety profiles. Our study underscores the promising role of 9a with potential applications in managing T2DM as it emerged as the most promising candidate for further optimisation and subsequent animal studies.
6. Patents
Patent (Russian Federation), Issue No. 2018134266, date of issue 28 September 2018, date of registration in the State Register of Inventions (RU) 24 January 2020, date of expiry 28 September 2038. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus, compounds (versions)//Patentee: Neobiotek LLC (Moscow, Russia). Authors: Trukhan V.M., Zinevich T.V., Maslov I.O., Kirichenko O.G.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ph18050642/s1.
Author Contributions
Data curation and investigation, T.V.Z., I.O.M., O.G.K., S.V.S., M.A.G., F.M.D., Y.B.P. and V.M.T.; formal analysis, validation, visualisation, and methodology I.O.M., S.V.S., M.A.G., F.M.D., Y.B.P. and T.V.Z.; resources and funding acquisition, T.V.Z., Y.B.P. and V.M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, T.V.Z. and I.O.M.; writing—review and editing, T.V.Z., I.O.M., S.V.S. and Y.B.P.; conceptualisation, project administration, and supervision, T.V.Z. and V.M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Russian Federation, CITSEP (Centre of Information Technologies and Systems of Executive Power) No. 121031600199-9, scientific code 03-1-21.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article and the Supplementary Materials. CCDC 2307518 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif, accessed on 20 March 2025, or by emailing data_request@ccdc.cam.ac.uk, or by contacting The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, 12 Union Road, Cambridge CB2 1EZ, UK; Fax: +44 1223 336033.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Lomonosov Moscow State University and I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University for the necessary resources, infrastructure, and support. The single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis was performed using IGIC RAS equipment.
Conflicts of Interest
I.O.M., O.G.K., V.M.T. and T.V.Z. are the authors of Patent (Russian Federation), Issue No. 2018134266. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Kahn, S.E.; Hull, R.L.; Utzschneider, K.M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006, 444, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halban, P.A.; Polonsky, K.S.; Bowden, D.W.; Hawkins, M.A.; Ling, C.; Mather, K.J.; Powers, A.C.; Rhodes, C.J.; Sussel, L.; Weir, G.C. β-Cell failure in type 2 diabetes: Postulated mechanisms and prospects for prevention and treatment. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S14–S31. [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Fradkin, J.; Kernan, W.N.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; Rossing, P.; Tsapas, A.; Wexler, D.J.; Buse, J.B. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the european association for the study of diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2669–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlén, A.D.; Dashi, G.; Maslov, I.; Attwood, M.M.; Jonsson, J.; Trukhan, V.; Schiöth, H.B. Trends in Antidiabetic Drug Discovery: FDA Approved Drugs, New Drugs in Clinical Trials and Global Sales. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 807548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J.; Nauck, M.A. The incretin system: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2006, 368, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallwitz, B. Clinical use of DPP-4 inhibitors. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzucchi, S.E.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Buse, J.B.; Diamant, M.; Ferrannini, E.; Nauck, M.; Peters, A.L.; Tsapas, A.; Wender, R.; Matthews, D.R. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2015: A Patient-Centered Approach: Update to a position statement of the american diabetes association and the european association for the study of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornberry, N.; Weber, A. Discovery of JANUVIA™ (Sitagliptin), a Selective Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type2 Diabetes. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augeri, D.J.; Robl, J.A.; Betebenner, D.A.; Magnin, D.R.; Khanna, A.; Robertson, J.G.; Wang, A.; Simpkins, L.M.; Taunk, P.; Huang, Q.; et al. Discovery and preclinical profile of saxagliptin (BMS-477118): A highly potent, long-acting, orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5025–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wallace, M.B.; Stafford, J.A.; Kaldor, S.W.; Kassel, D.B.; Navre, M.; Shi, L.; Skene, R.J.; Asakawa, T.; et al. Discovery of Alogliptin: A Potent, Selective, Bioavailable, and Efficacious Inhibitor of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, M.; Langkopf, E.; Mark, M.; Tadayyon, M.; Thomas, L.; Nar, H.; Pfrengle, W.; Guth, B.; Lotz, R.; Sieger, P.; et al. 8-(3-(R)-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methyl-quinazolin- 2-ylmethyl)-3,7-dihydropurine-2,6-dione (BI 1356), a highly potent, selective, long-acting, and orally bioavailable DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 6450–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslov, I.O.; Zinevich, T.V.; Kirichenko, O.G.; Trukhan, M.V.; Shorshnev, S.V.; Tuaeva, N.O.; Gureev, M.A.; Dahlén, A.D.; Porozov, Y.B.; Schiöth, H.B.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Neogliptin, a Novel 2-Azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-Based Inhibitor of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4). Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordhoff, S.; Bulat, S.; Cerezo-Gálvez, S.; Hill, O.; Hoffmann-Enger, B.; López-Canet, M.; Rosenbaum, C.; Rummey, C.; Thiemann, M.; Matassa, V.G.; et al. The design of potent and selective inhibitors of DPP-4: Optimization of ADME properties by amide replacements. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6340–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneschi, W.; Enes, K.B.; de Mendonça, C.C.; Fernandes, F.d.S.; Miguel, F.B.; Martins, J.d.S.; Le Hyaric, M.; Pinho, R.R.; Duarte, L.M.; de Oliveira, M.A.L.; et al. Synthesis and anticancer evaluation of new lipophilic 1,2,4 and 1,3,4-oxadiazoles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 165, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Wu, K.; Chen, G.S.; Liu, J.R.; Hsieh, C.E.; Chern, J.W. Acrylamide Functional Group Incorporation Improves Drug-like Properties: An Example with EGFR Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glomb, T.; Świątek, P. Antimicrobial activity of 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Varadharaj, S.; Zhao, X.; Parinandi, N.; Flavahan, N.A.; Zweier, J.L. Acetylcholine causes endothelium-dependent contraction of mouse arteries. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordhoff, S.; Cerezo-Gálvez, S.; Deppe, H.; Hill, O.; López-Canet, M.; Rummey, C.; Thiemann, M.; Matassa, V.G.; Edwards, P.J.; Feurer, A. Discovery of β-homophenylalanine based pyrrolidin-2-ylmethyl amides and sulfonamides as highly potent and selective inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4201–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tadesse, S.; Preston, S.; Taki, A.C.; Jabbar, A.; Hofmann, A.; Jiao, Y.; Garcia-Bustos, J.; Harjani, J.; et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship study of pyrrolidine-oxadiazoles as anthelmintics against Haemonchus contortus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 190, 112100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vasconcelos, N.M.; Vliegen, G.; Gonçalves, A.; De Hert, E.; Martín-Pérez, R.; Van Opdenbosch, N.; Jallapally, A.; Geiss-Friedlander, R.; Lambeir, A.-M.; Augustyns, K.; et al. DPP8/DPP9 inhibition elicits canonical Nlrp1b in fl ammasome hallmarks in murine macrophages. Life Sci. Alliance 2019, 2, e201900313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repasky, M.P.; Shelley, M.; Friesner, R.A. Flexible Ligand Docking with Glide. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2007, 18, 8.12.1–8.12.36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimshaw, C.E.; Jennings, A.; Kamran, R.; Ueno, H.; Nishigaki, N.; Kosaka, T.; Tani, A.; Sano, H.; Kinugawa, Y.; Koumura, E.; et al. Trelagliptin (syr-472, zafatek), novel once-weekly treatment for type 2 diabetes, inhibits dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (dpp-4) via a non-covalent mechanism. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suenaga, A.; Okimoto, N.; Hirano, Y.; Fukui, K. An efficient computational method for calculating ligand binding affinities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, G.M.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).