The Immunomodulatory Effects of Apigenin and Quercetin on Cytokine Secretion by the Human Gingival Fibroblast Cell Line and Their Potential Link to Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
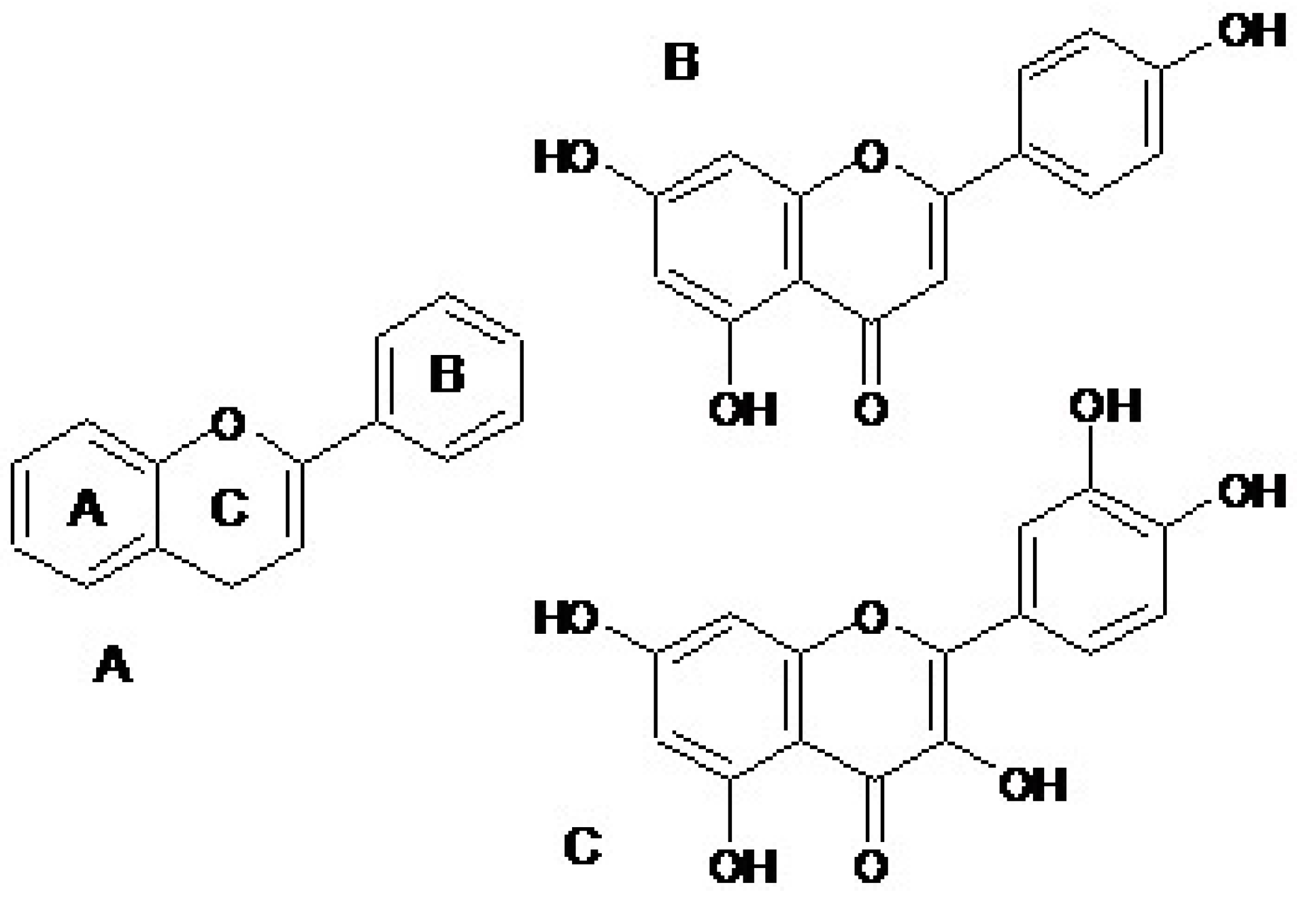
1. Introduction
2. Results
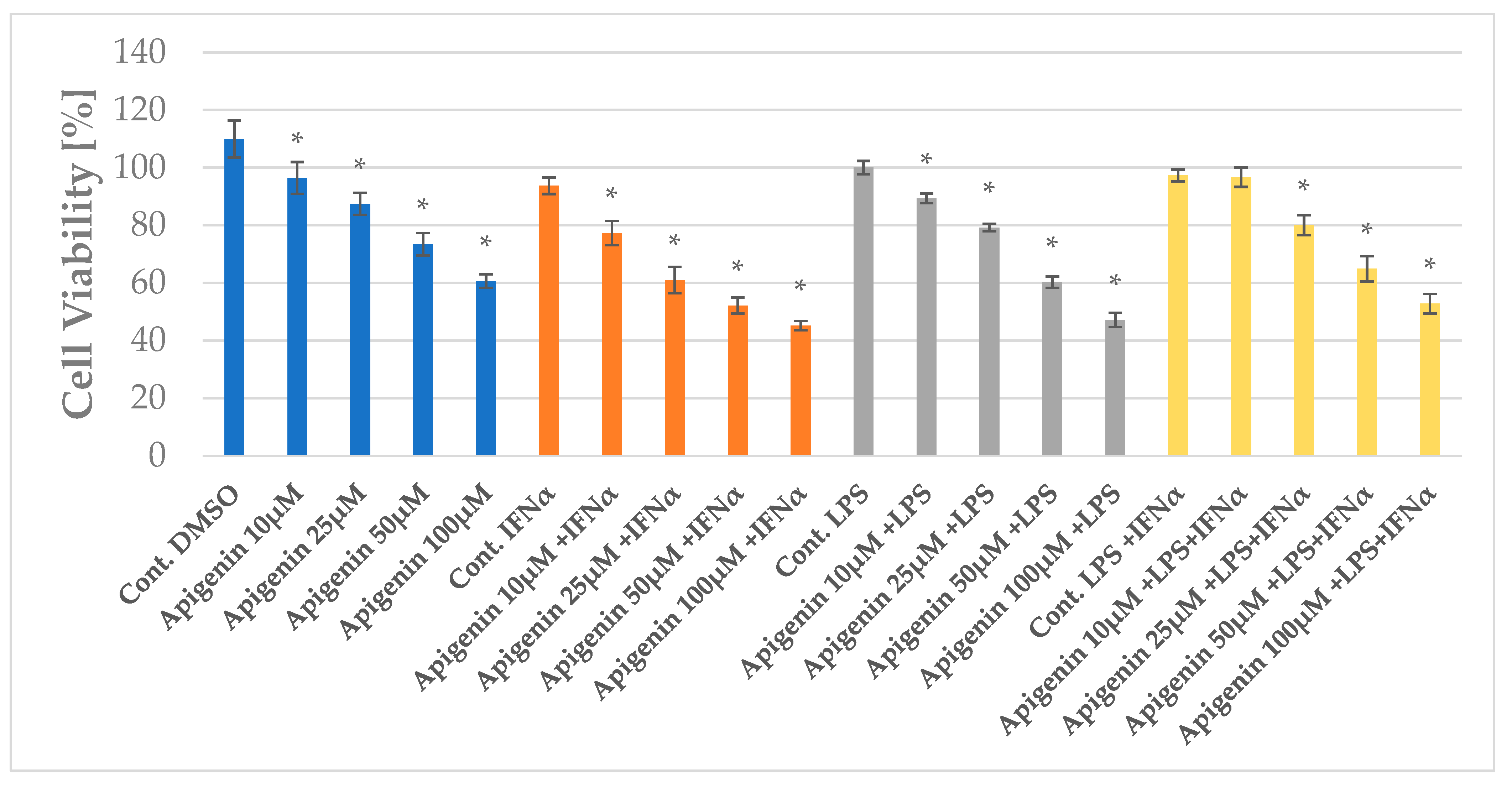
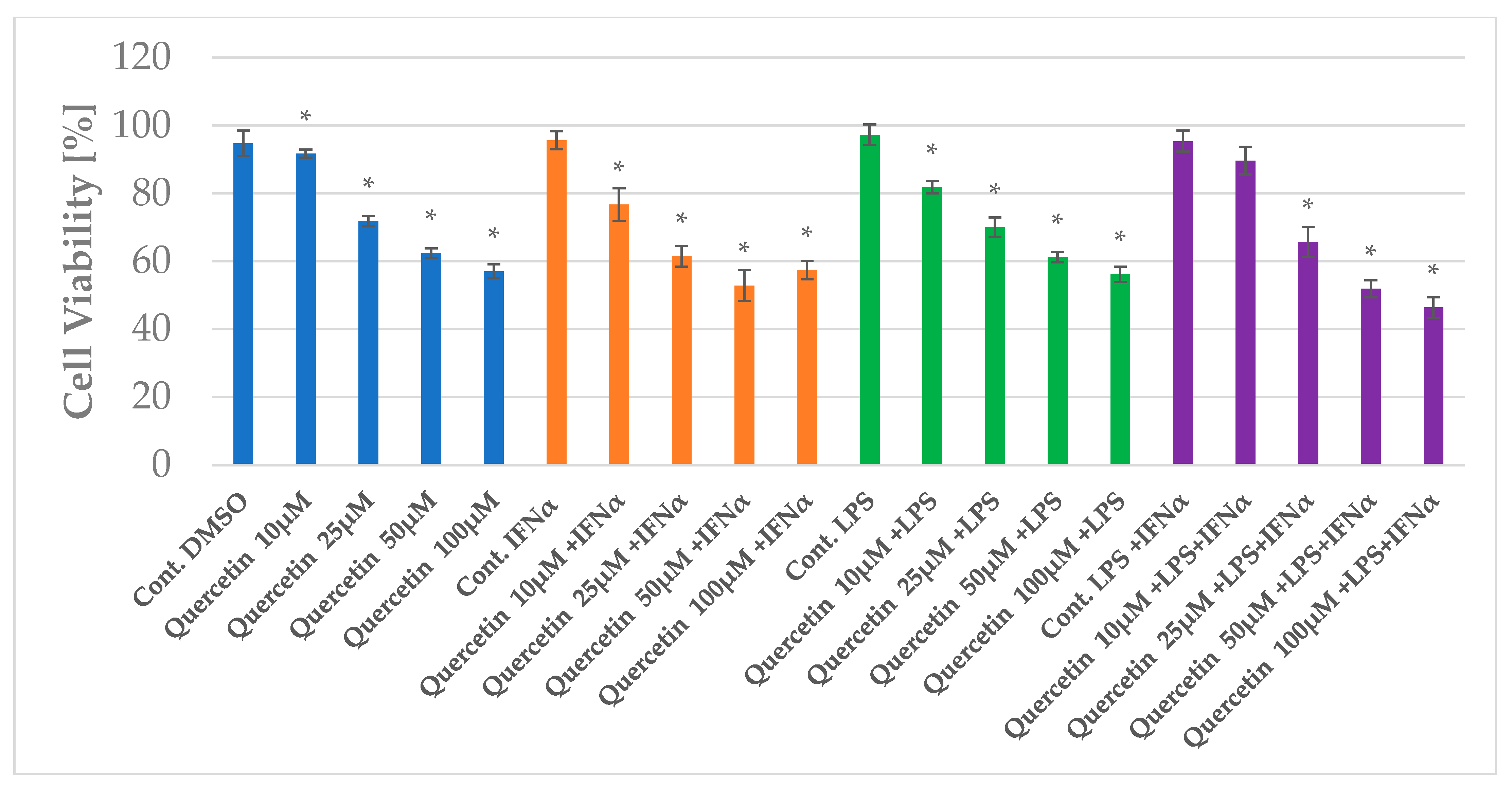
2.1. The Impact of Apigenin and Quercetin on the Viability of HGF-1
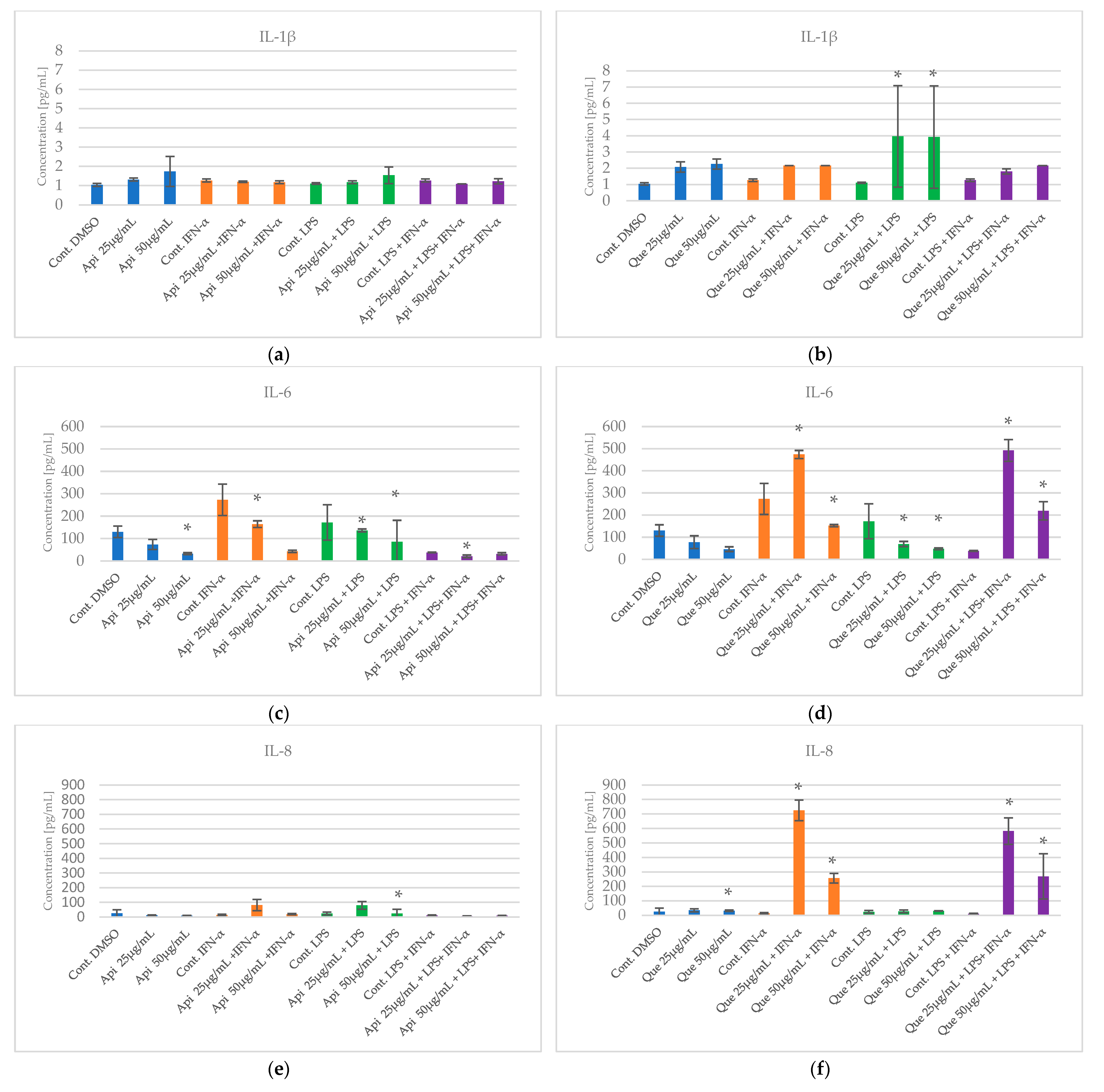
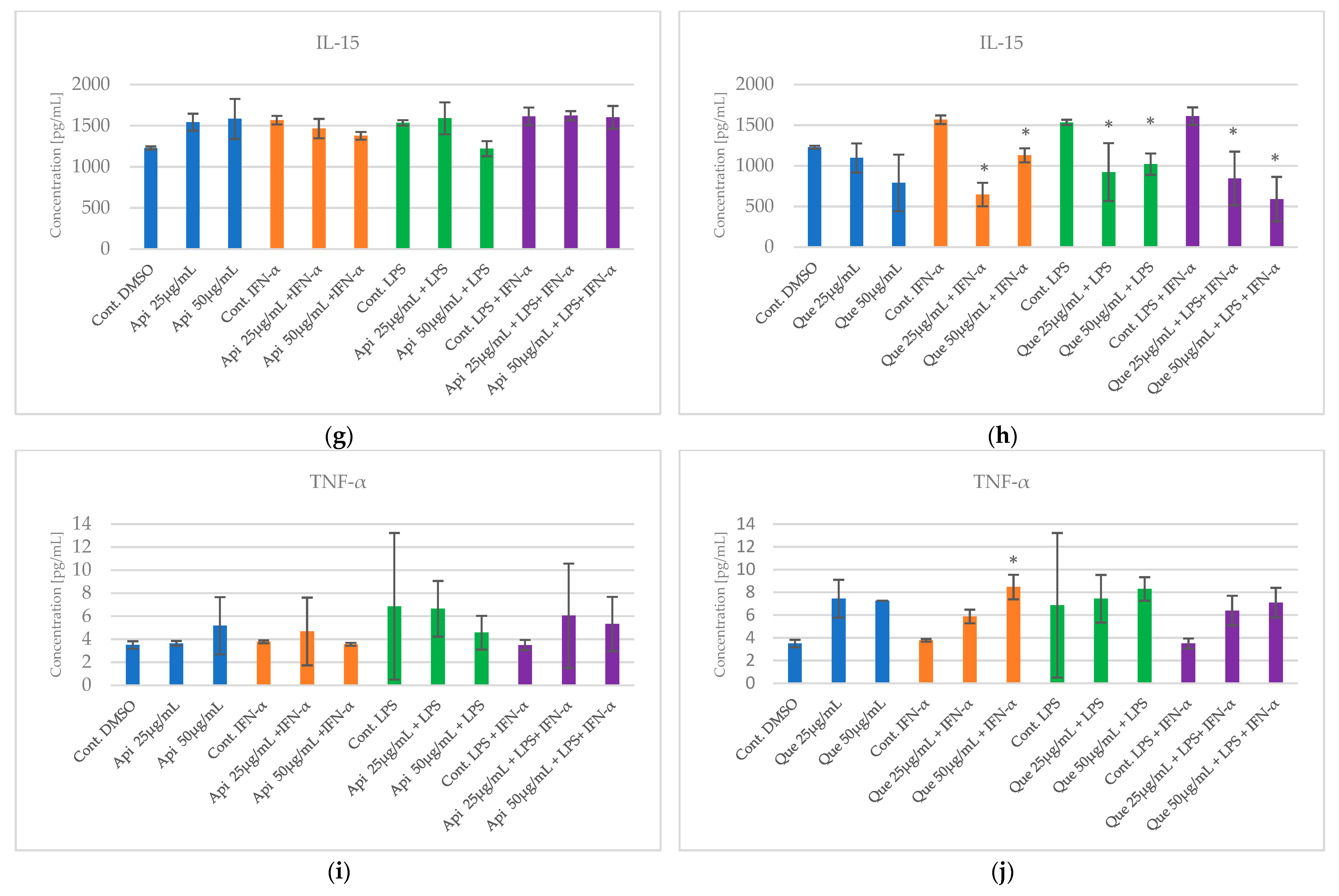
2.2. The Impact of Apigenin and Quercetin on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Secretion by HGF-1 Followed by LPS and/or IFN-α Stimulation
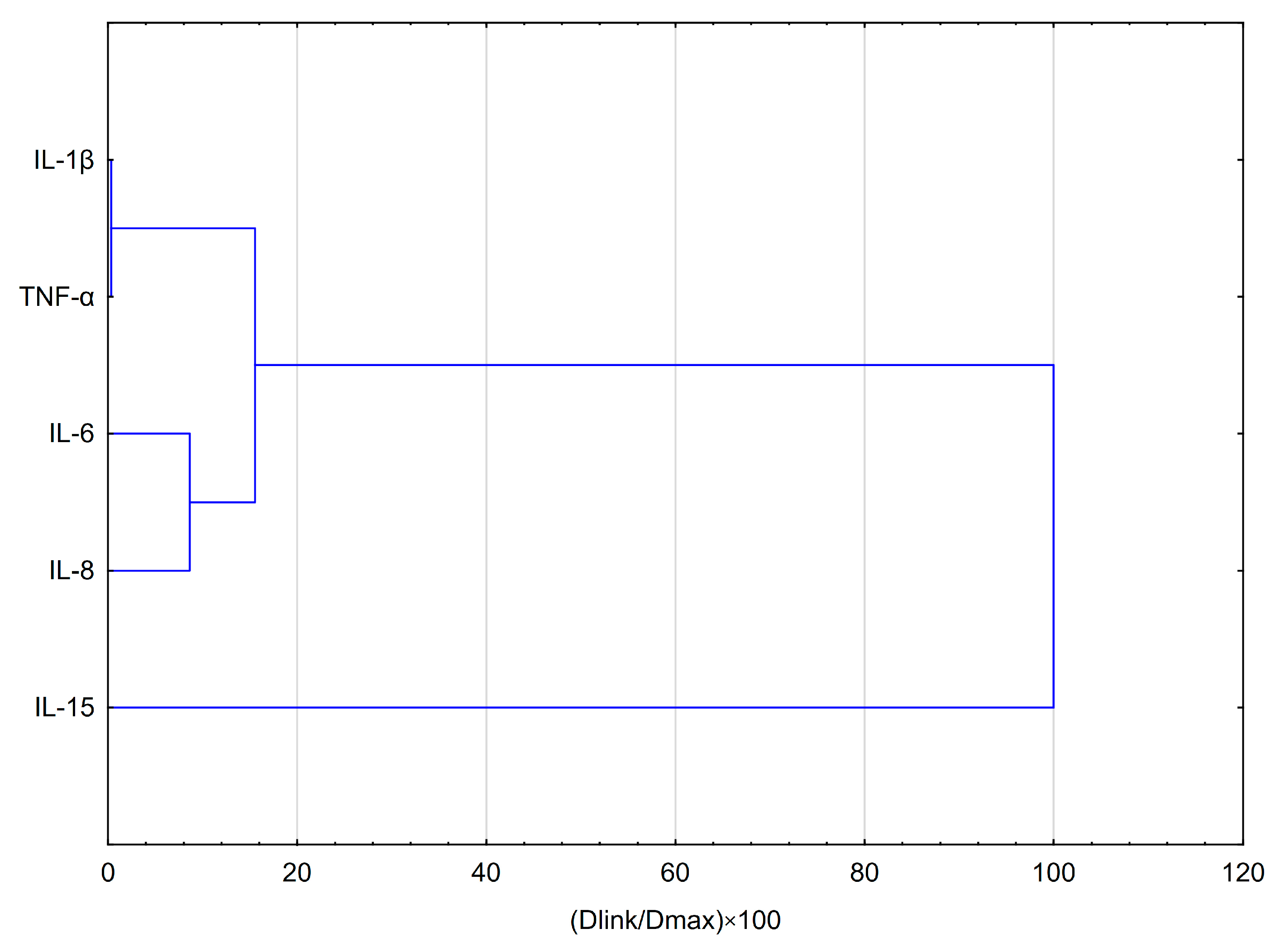
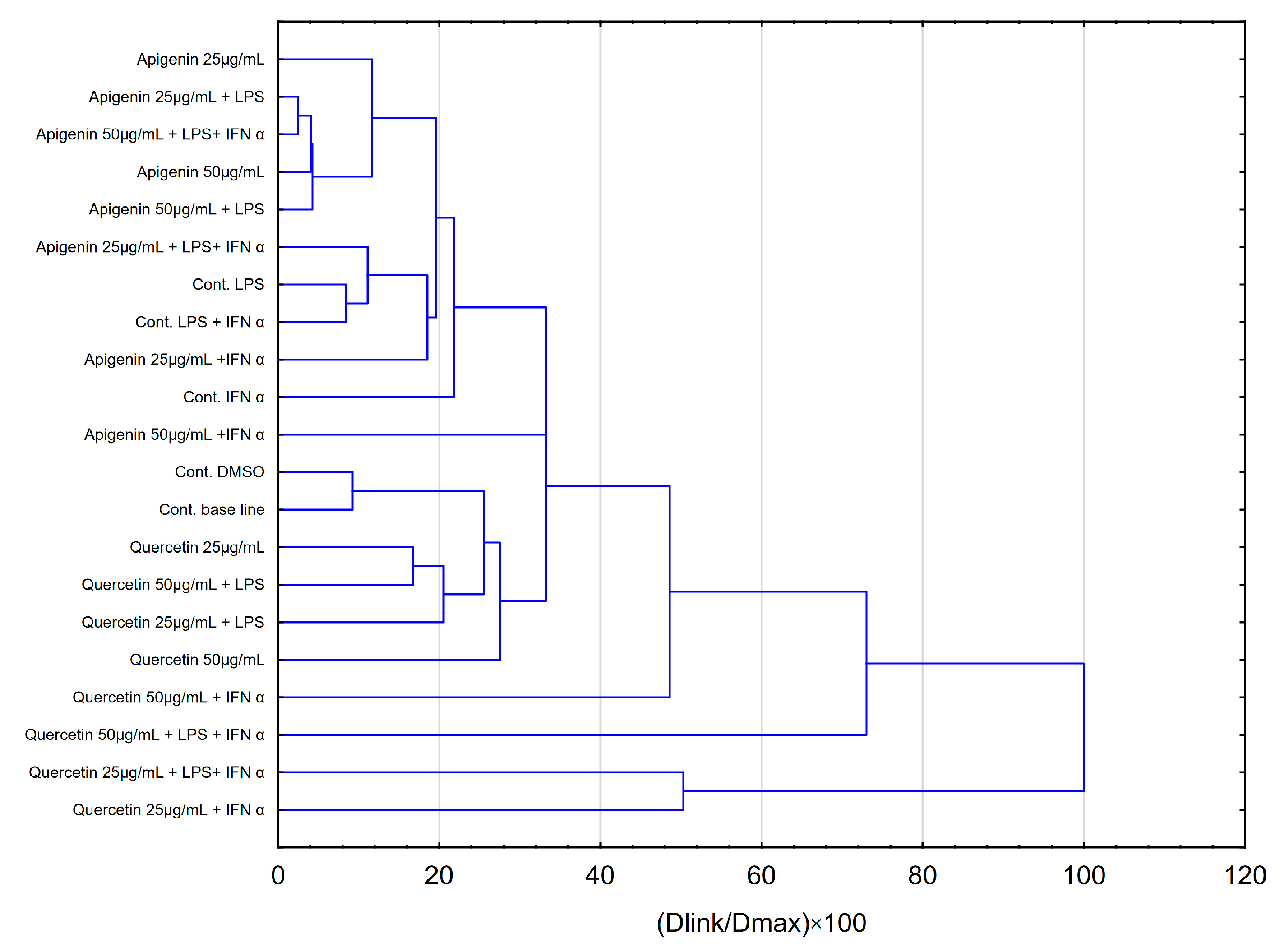
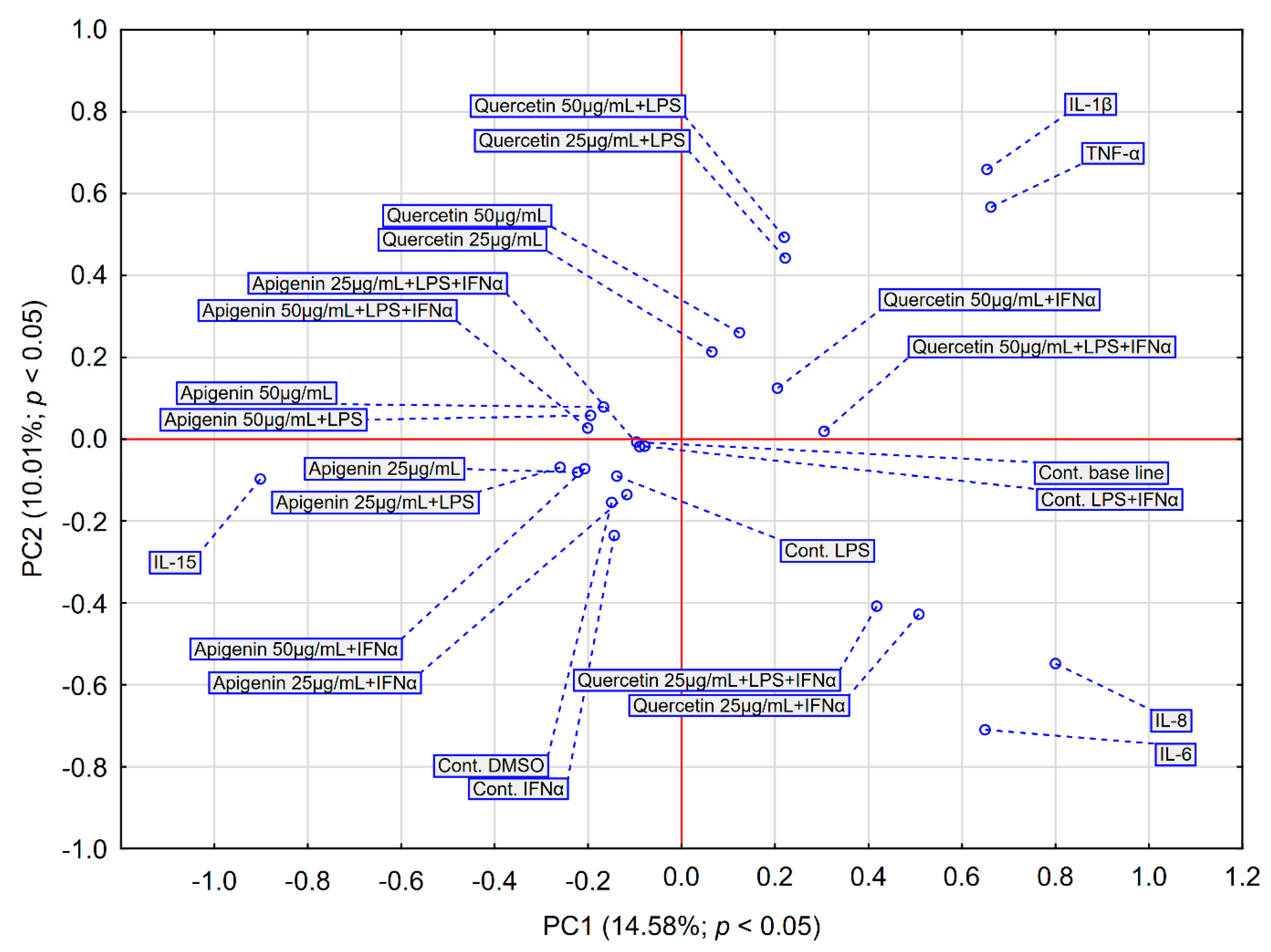
2.3. Statistical Analysis Comparing Effects of Apigenin and Quercetin on the Production of Selected Cytokines in LPS, IFN-α and LPS+IFN-α Stimulated HGF-1 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. HGF-1 Collection
4.3. The Cytotoxicity Assay–MTT Assay
4.4. Multiplex Bead-Based Cytokine Assay
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, A.K. Chemistry and Biological Activities of Flavonoids: An Overview. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 162750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, H.; Chen, X. A Review of Classification, Biosynthesis, Biological Activities and Potential Applications of Flavonoids. Molecules 2023, 28, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Fu, Q.; Deng, C.; Luo, L.; Xiang, T.; Zhao, H. Immunomodulatory Potential of Flavonoids for the Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases and Tumour. Scand. J. Immunol. 2022, 95, e13106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandra Domańska, A.M. Flavonoids as Anti-Inflammatory Agents in Theraphy of Parodontium Diseases. Postep. Fitoter. 2008, 1, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kurek-Górecka, A.; Walczy’nska, K.; Felitti, R.; Baron, S.; Olczyk, P. Propolis and Diet Rich in Polyphenols as Cariostatic Agents Reducing Accumulation of Dental Plaque. Molecules 2022, 27, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janabi, A.H.W.; Kamboh, A.A.; Saeed, M.; Xiaoyu, L.; BiBi, J.; Majeed, F.; Naveed, M.; Mughal, M.J.; Korejo, N.A.; Kamboh, R.; et al. Flavonoid-Rich Foods (FRF): A Promising Nutraceutical Approach against Lifespan-Shortening Diseases. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, M.; Sip, A.; Mrówczynska, L.; Broniarczyk, J.; Wa’skiewicz, A.; Ratajczak, I. Biological Activity and Chemical Composition of Propolis from Various Regions of Poland. Molecules 2023, 28, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S.; Choi, J.S.; Islam, M.N.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.P. Inhibition of 5-Lipoxygenase and Skin Inflammation by the Aerial Parts of Artemisia Capillaris and Its Constituents. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2011, 34, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Nurul Islam, M.; Yousof Ali, M.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Jung, H.A. Effects of C-Glycosylation on Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Apigenin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 64, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, A.W.; Haenen, G.R.M.M.; Bast, A. Health Effects of Quercetin: From Antioxidant to Nutraceutical. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 585, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, S.H.; Ko, W.C.; Ko, F.N.; Teng, C.M. Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation by Some Flavonoids. Thromb. Res. 1991, 64, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Aliaga, K.; Bermejo-Bescós, P.; Benedí, J.; Martín-Aragón, S. Quercetin and Rutin Exhibit Antiamyloidogenic and Fibril-Disaggregating Effects in Vitro and Potent Antioxidant Activity in APPswe Cells. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Ullah, H.; Aschner, M.; Cheang, W.S.; Akkol, E.K. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, R.; Li, X.X.; Li, J.F.; Zhang, L. Neuroprotective, Anti-Amyloidogenic and Neurotrophic Effects of Apigenin in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Molecules 2013, 18, 9949–9965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twarowski, B.; Herbet, M. Inflammatory Processes in Alzheimer’s Disease-Pathomechanism, Diagnosis and Treatment: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhapola, R.; Hota, S.S.; Sarma, P.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Medhi, B.; Reddy, D.H.K. Recent Advances in Molecular Pathways and Therapeutic Implications Targeting Neuroinflammation for Alzheimer’s Disease. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 1669–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominy, S.S.; Lynch, C.; Ermini, F.; Benedyk, M.; Marczyk, A.; Konradi, A.; Nguyen, M.; Haditsch, U.; Raha, D.; Griffin, C.; et al. Porphyromonas Gingivalis in Alzheimer’s Disease Brains: Evidence for Disease Causation and Treatment with Small-Molecule Inhibitors. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, F.Q.; Almeida-da-Silva, C.L.C.; Huynh, B.; Trinh, A.; Liu, J.; Woodward, J.; Asadi, H.; Ojcius, D.M. Association between Periodontal Pathogens and Systemic Disease. Biomed. J. 2019, 42, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek-Górecka, A.; Kłósek, M.; Pietsz, G.; Czuba, Z.P.; Kolayli, S.; Can, Z.; Balwierz, R.; Olczyk, P. The Phenolic Profile and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Ethanolic Extract of Polish Propolis on Activated Human Gingival Fibroblasts-1 Cell Line. Molecules 2023, 28, 7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansores-España, D.; Carrillo-Avila, A.; Melgar-Rodriguez, S.; Díaz-Zuñiga, J.; Martínez-Aguilar, V. Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s Disease. Med. Oral. Patol. Oral. Cir. Bucal 2021, 26, e43–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagasingam, S.; Chukkapalli, S.S.; Welbury, R.; Singhrao, S.K. Porphyromonas Gingivalis Is a Strong Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. Rep. 2020, 4, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachiega, T.F.; Orsatti, C.L.; Pagliarone, A.C.; Sforcin, J.M. The Effects of Propolis and Its Isolated Compounds on Cytokine Production by Murine Macrophages. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Shao, M.; Hu, T. Interleukin-1β Is a Potential Therapeutic Target for Periodontitis: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 12, aau3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornman, K.S.; Crane, A.; Wang, H.Y.; Giovlne, F.S.D.; Newman, M.G.; Pirk, F.W.; Wilson, T.G., Jr.; Higginbottom, F.L.; Duff, G.W. The Interleukin-1 Genotype as a Severity Factor in Adult Periodontal Disease. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1997, 24, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, J.; Samojedny, A.; Paul, M.; Pietsz, G.; Wilczok, T. Effect of apigenin, kaempferol and resveratrol on the expression of interleukin-1b and tumor necrosis factor-a genes in J774. 2 macrophages. Pharmacol. Rep. 2005, 57, 390–394. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, J.L.; Assunção, A.K.M.; Da Silva, M.C.P.; Reis, A.S.D.; Costa, G.C.; Arruda, D.D.S.; Rocha, B.A.; Vaz, M.M.D.O.L.L.; Paes, A.M.D.A.; Guerra, R.N.M.; et al. Brazilian Green Propolis: Anti-Inflammatory Property by an Immunomodulatory Activity. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2012, 2012, 157652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarrenho, L.G.; de Lima, M.H.F.; Hori, J.I.; Lima, J.A.; Ambrósio, S.R.; Bastos, J.K.; De Jong, D.; Berretta, A.A. Effects of Three Different Brazilian Green Propolis Extract Formulations on Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Secretion by Macrophages. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Yue, Y.; Li, J.; He, T.; He, Y. The inhibitory effect of quercetin on IL-6 production by LPS-stimulated neutrophils. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2005, 2, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshidi, S.; Sofiabadi, M.; Eslami, M.; Foroughi, F. Apigenin Acts as Anti-inflammatory Compound through Reducing IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in LPS-induced Inflammation; in-vivo Study. Research Square 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.C.; Heneka, M.T. The endotoxin hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bester, J.; Soma, P.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Viscoelastic and ultrastructural characteristics of whole bloodand plasma in Alzheimer-type dementia, and the possible role of bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Oncotarget 2015, 3, 35284–35303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Crincoli, V.; Laino, L.; Alovisi, M.; Sovereto, D.; Mastrangelo, F.; Lo Russo, L.; Lo Muzio, L. The Role of Periodontitis and Periodontal Bacteria in the Onset and Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cojocaru, I.M.; Miu, G.; Sapira, V. Study of Interleukin-6 Production in Alzheimer’s Disease. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 49, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Charrière, K.; Schneider, V.; Perrignon-Sommet, M.; Lizard, L.; Benani, A.; Jacquin-Piques, A.; Vejux, A. Exploring the Role of Apigenin in Neuroinflammation: Insights and Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginwala, R.; Bhavsar, R.; Chigbu, D.G.I.; Jain, P.; Khan, Z.K. Potential Role of Flavonoids in Treating Chronic Inflammatory Diseases with a Special Focus on the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Apigenin. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. Available online: https://nhiso.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/ISO-10993-5-2009.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Suni, J.; Valkama, S.; Peltola, E. Save Your Tears for the Toxicity Assays—Carbon Nanotubes Still Fooling Scientists. ACS Omega 2025, 3, 5554–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakas, D.; Ari, F.; Ulukaya, E. The MTT viability assay yields strikingly false-positive viabilities although the cells are killed by some plant extracts. Turk. J. Biol. 2017, 18, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balez, R.; Steiner, N.; Engel, M.; Muñoz, S.S.; Lum, J.S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Vallotton, P.; Sachdev, P.; O’Connor, M.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of apigenin against inflammation, neuronal excitability and apoptosis in an induced pluripotent stem cell model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, H.; Arango, D.; Nicholas, C.; Duarte, S.; Nuovo, G.J.; He, W.; Voss, O.H.; Gonzalez-Mejia, M.E.; Guttridge, D.C.; Grotewold, E.; et al. Dietary Apigenin Exerts Immune-Regulatory Activity in Vivo by Reducing NF-?B Activity, Halting Leukocyte Infiltration and Restoring Normal Metabolic Function. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klósek, M.; Sedek, L.; Lewandowska, H.; Czuba, Z.P. The Effect of Ethanolic Extract of Brazilian Green Propolis and Artepillin C on AFGF-1, Eselectin, and CD40L Secreted by Human Gingival Fibroblasts. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 46, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurek-Górecka, A.; Kłósek, M.; Balwierz, R.; Pietsz, G.; Czuba, Z.P. The Immunomodulatory Effects of Apigenin and Quercetin on Cytokine Secretion by the Human Gingival Fibroblast Cell Line and Their Potential Link to Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050628
Kurek-Górecka A, Kłósek M, Balwierz R, Pietsz G, Czuba ZP. The Immunomodulatory Effects of Apigenin and Quercetin on Cytokine Secretion by the Human Gingival Fibroblast Cell Line and Their Potential Link to Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(5):628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050628
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurek-Górecka, Anna, Małgorzata Kłósek, Radosław Balwierz, Grażyna Pietsz, and Zenon P. Czuba. 2025. "The Immunomodulatory Effects of Apigenin and Quercetin on Cytokine Secretion by the Human Gingival Fibroblast Cell Line and Their Potential Link to Alzheimer’s Disease" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 5: 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050628
APA StyleKurek-Górecka, A., Kłósek, M., Balwierz, R., Pietsz, G., & Czuba, Z. P. (2025). The Immunomodulatory Effects of Apigenin and Quercetin on Cytokine Secretion by the Human Gingival Fibroblast Cell Line and Their Potential Link to Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals, 18(5), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050628








