Mammea siamensis Flower Extract-Induced Cell Death Apoptosis in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells via Vacuolar-Type H+-ATPase Inhibition Associated with GSK-3β/β-Catenin, PI3K/Akt/NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. 1H NMR Analysis of MS Methanolic Extract
2.2. MS Extract Increased Cell Toxicity in HCT116 Cells
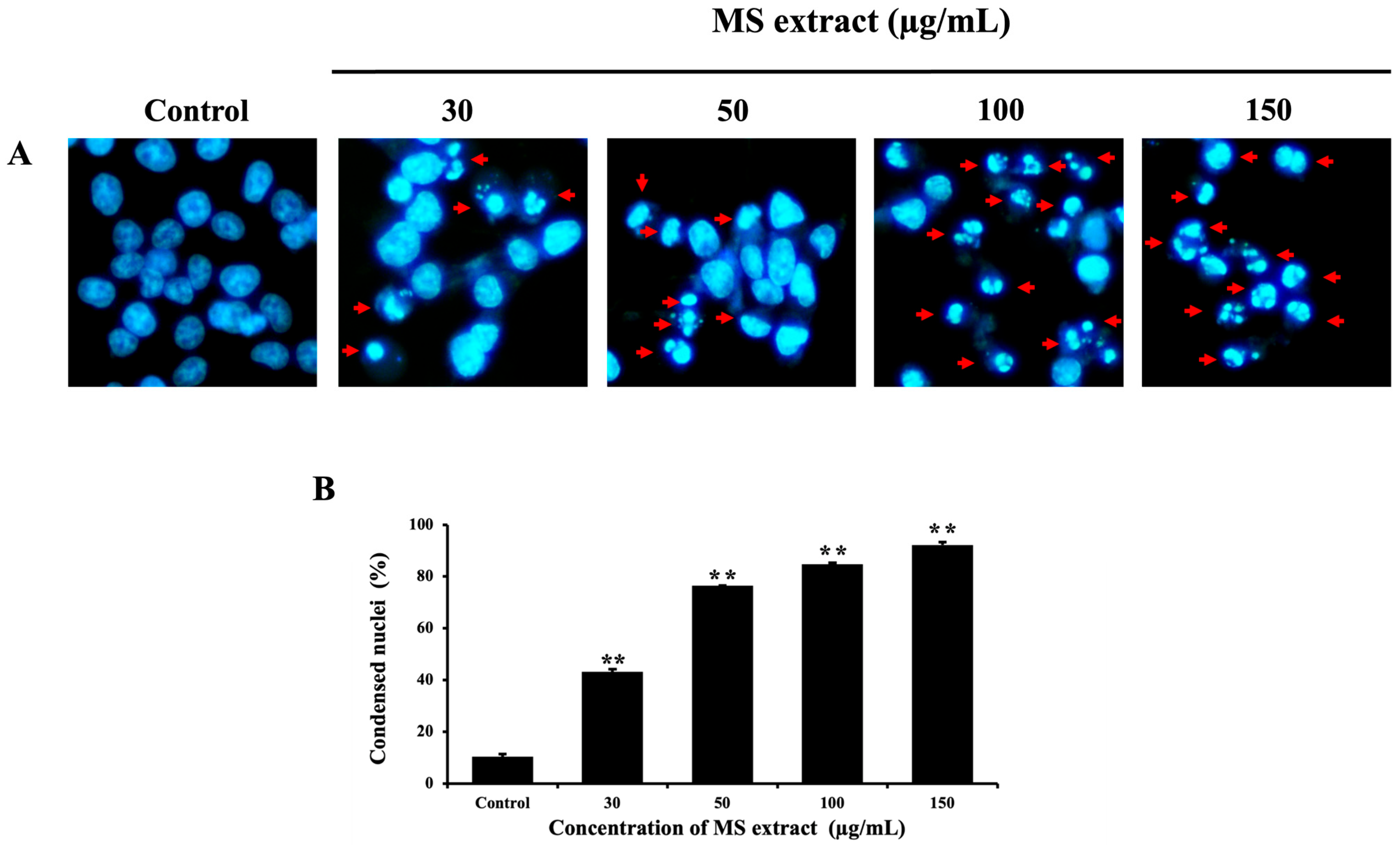
2.3. MS Extract Induced Nuclear Morphological Change in HCT116 Cells
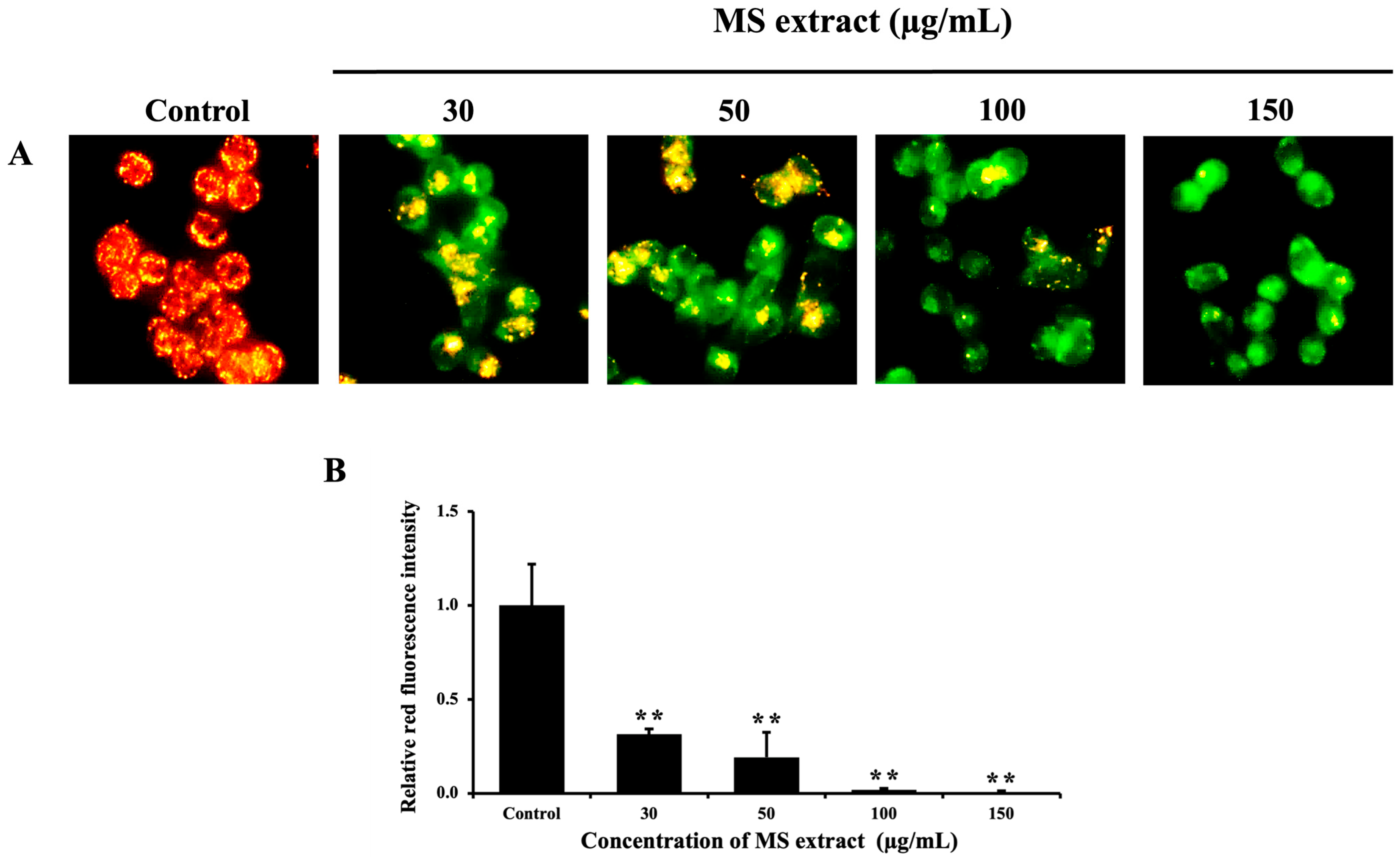
2.4. MS Extract Reduced Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm) in HCT116 Cells
2.5. MS Extract Increased the Population of Sub-G1 Apoptotic HCT116 Cells
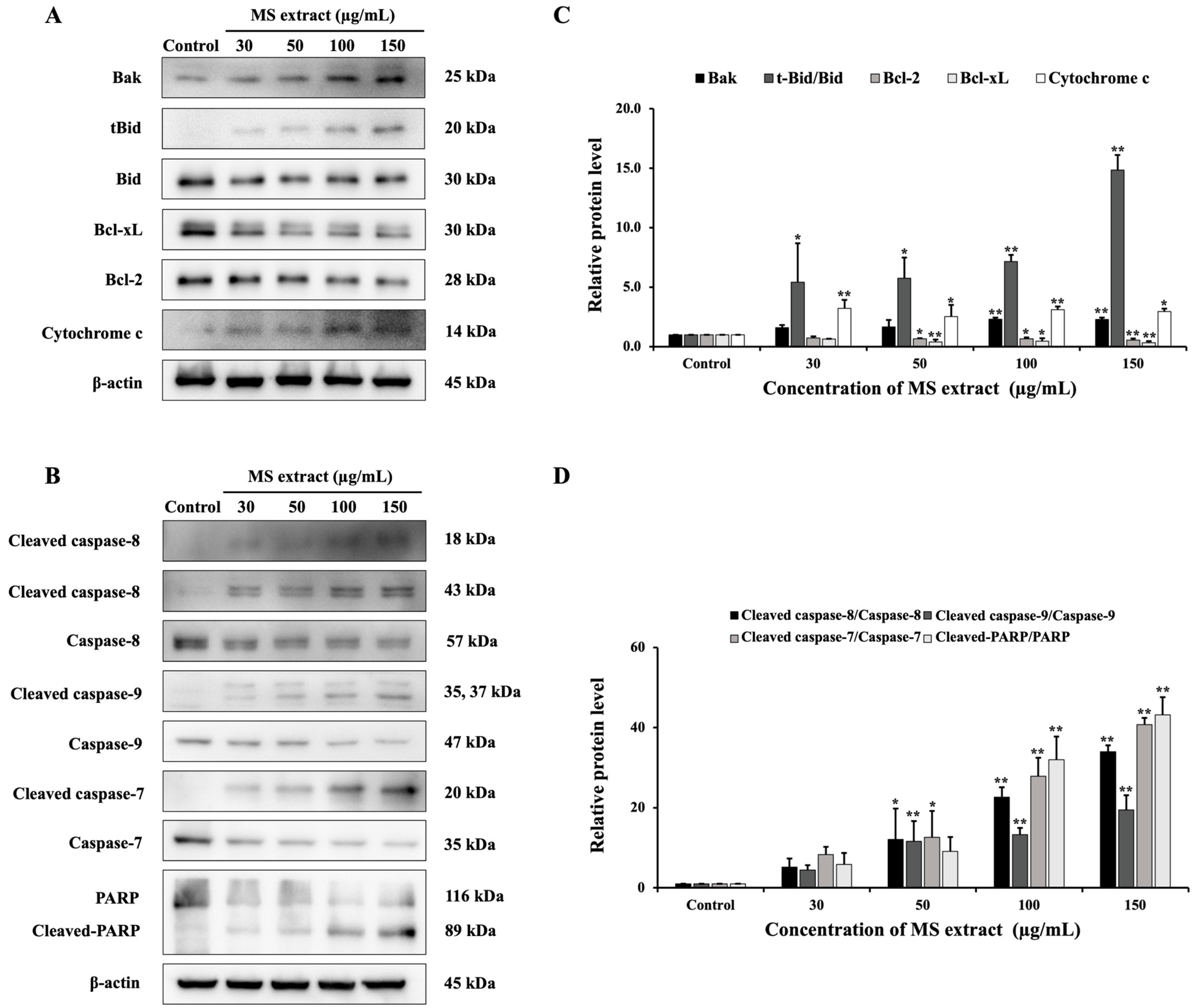
2.6. MS Extract Stimulated Apoptosis Pathways in HCT116 Cells
2.7. MS Extract Inhibited V-ATPase Activity in HCT116 Cells
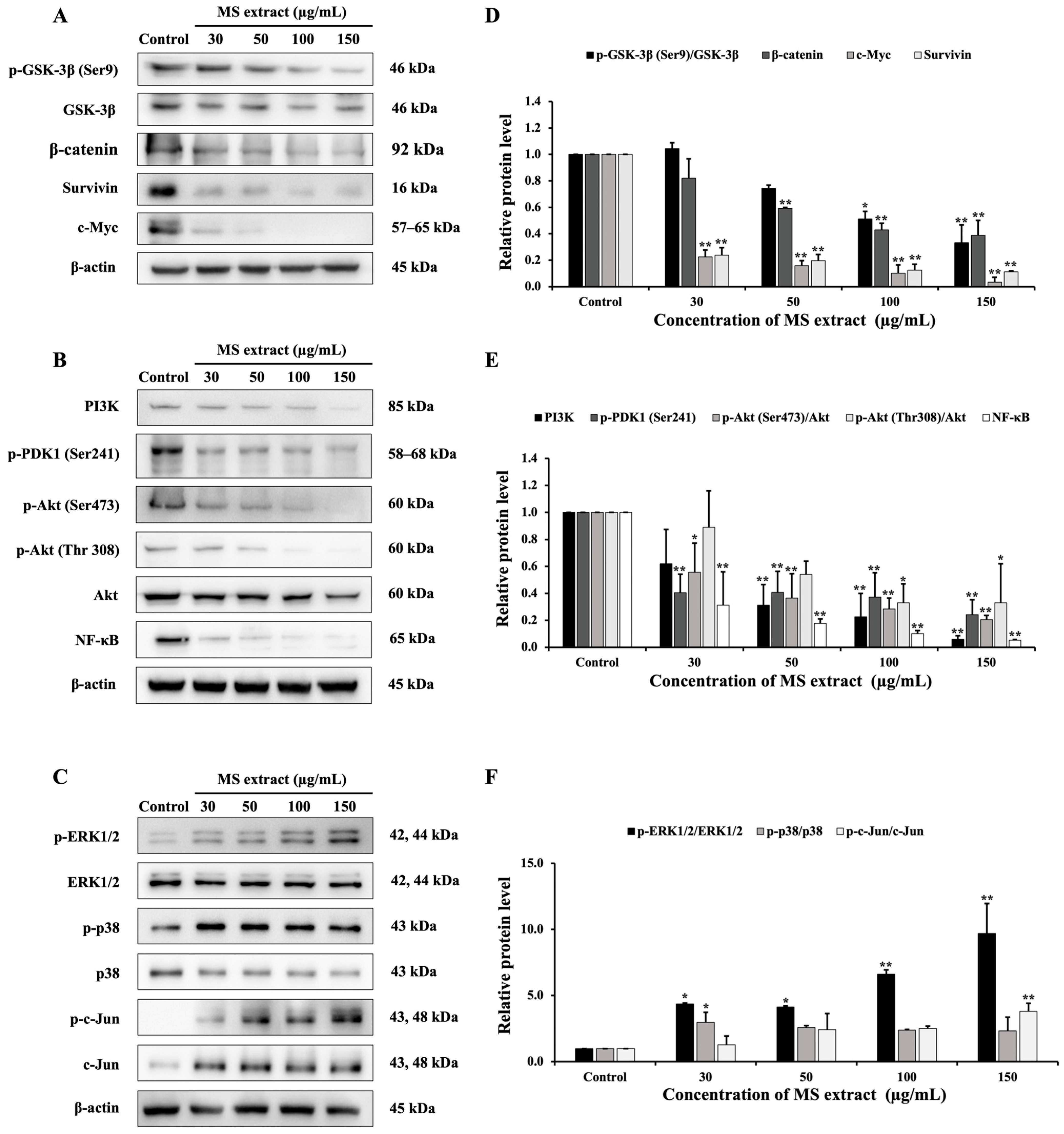
2.8. MS Extract Relegated the GSK-3β/β-Catenin, PI3K/Akt/NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling Pathways in HCT116 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Plant Extraction
4.3. 1H NMR Analysis
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.6. Hoechst33342 Staining
4.7. JC-1 Staining
4.8. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.9. Acridine Orange (AO) Staining
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Yusoff, M.M.; Maniam, G.P.; Ichwan, S.J.; Soundharrajan, I.; Govindan, N. Nutraceuticals as potential therapeutic agents for colon cancer: A review. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badavenkatappa Gari, S.; Nelson, V.K.; Peraman, R. Tinospora sinensis (Lour.) Merr alkaloid rich extract induces colon cancer cell death via ROS mediated, mTOR dependent apoptosis pathway: “an in-vitro study”. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.; Sugita, H.; Muraki, K.; Saeki, S.; Chaipech, S.; Pongpiriyadacha, Y.; Muraoka, O.; Morikawa, T. Anti-proliferative activities of coumarins from the Thai medicinal plant Mammea siamensis (Miq.) T. Anders. against human digestive tract carcinoma cell lines. Fitoterapia 2021, 148, 104780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Manse, Y.; Chaipech, S.; Pongpiriyadacha, Y.; Muraoka, O.; Morikawa, T. Structures of Mammeasins P and Q, Coumarin-Related Polysubstituted Benzofurans, from the Thai Medicinal Plant Mammea siamensis (Miq.) T. Anders.: Anti-Proliferative Activity of Coumarin Constituents against Human Prostate Carcinoma Cell Line LNCaP. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaniad, P.; Chukaew, A.; Payaka, A.; Phuwajaroanpong, A.; Techarang, T.; Plirat, W.; Punsawad, C. Antimalarial potential of compounds isolated from Mammea siamensis T. Anders. flowers: In vitro and molecular docking studies. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaniad, P.; Chukaew, A.; Na-Ek, P.; Yusakul, G.; Chuaboon, L.; Phuwajaroanpong, A.; Plirat, W.; Konyanee, A.; Septama, A.W.; Punsawad, C. In vivo antimalarial effect of 1-hydroxy-5,6,7-trimethoxyxanthone isolated from Mammea siamensis T. Anders. flowers: Pharmacokinetic and acute toxicity studies. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinrut, L.; Itharat, A.; Ruangnoo, S. Free radical scavenging and lipid peroxidation of Thai medicinal plants used for diabetic treatment. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2011, 94 (Suppl. S7), S178–S182. [Google Scholar]
- Sukkasem, K.; Panthong, S.; Itharat, A. Antimicrobial Activities of Thai Traditional Remedy “Kheaw-Hom” and Its Plant Ingredients for Skin Infection Treatment in Chickenpox. J. Med. Assoc. Thai 2016, 99 (Suppl. S4), 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Noysang, C.; Mahringer, A.; Zeino, M.; Saeed, M.; Luanratana, O.; Fricker, G.; Bauer, R.; Efferth, T. Cytotoxicity and inhibition of P-glycoprotein by selected medicinal plants from Thailand. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uto, T.; Tung, N.H.; Thongjankaew, P.; Lhieochaiphant, S.; Shoyama, Y. Kayeassamin A Isolated from the Flower of Mammea siamensis Triggers Apoptosis by Activating Caspase-3/-8 in HL-60 Human Leukemia Cells. Pharmacogn. Res. 2016, 8, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, P.; Itharat, A.; Thongdeeying, P.; Tuy-on, T.; Kuropakornpong, P.; Pipatrattanaseree, W.; Mingmalairak, C.; Davies, N.M. Ethnopharmacological nexus between the traditional Thai medicine theory and biologically based cancer treatment. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 287, 114932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, C.M.; Singh, A.T.K. Apoptosis: A Target for Anticancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Kavanagh, J.J. Anticancer therapy targeting the apoptotic pathway. Lancet Oncol. 2003, 4, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Park, S.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, G.-Y.; Choi, Y.W.; Kim, B.W.; Choi, Y.H. Induction of apoptosis by a hexane extract of aged black garlic in the human leukemic U937 cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2014, 8, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; El-Deiry, W.S. Overview of cell death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvandi, P.; Geoerger, B.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Hagan, S.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitton, B.; Okamoto, H.; Packham, G.; Crabb, S.J. Vacuolar ATPase as a potential therapeutic target and mediator of treatment resistance in cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 3800–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotter, K.; Stransky, L.; McGuire, C.; Forgac, M. Recent Insights into the Structure, Regulation, and Function of the V-ATPases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Kang, R.; Liu, J.; Tang, D. The V-ATPases in cancer and cell death. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennoune, S.R.; Martinez-Zaguilan, R. Plasmalemmal vacuolar H+-ATPases in angiogenesis, diabetes and cancer. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2007, 39, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.R.; Devkota, H.P.; Nakamura, T.; Watanabe, T.; Yahara, S. Chemical constituents and their DPPH radical scavenging activity of Nepalese crude drug Begonia picta. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2015, 9, 446. [Google Scholar]
- Kuerban, M.; Ma, F.; Shan, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, G. Comparative discriminant analysis of Mesua ferrea L. and its adulterants. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesca, D.; Mazumder, S.; Almasan, A. DNA damage response and apoptosis. Methods Enzymol. 2008, 446, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Fei, Z.; Qin, L. Anticancer effects of α-mangostin in OVACAR-3 human ovarian carcinoma cells are mediated via involvement of reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial -mediated apoptosis, suppression of cell migration and invasion and m-TOR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. BUON 2020, 25, 2293–2300. [Google Scholar]
- Yokomakura, A.; Hong, J.; Ohuchi, K.; Oh, S.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Mano, N.; Takahashi, T.; Hwang, G.W.; Naganuma, A. Increased production of reactive oxygen species by the vacuolar-type (H(+))-ATPase inhibitors bafilomycin A1 and concanamycin A in RAW 264 cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 37, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; Estanqueiro, M.; Oliveira, M.B.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Main Benefits and Applicability of Plant Extracts in Skin Care Products. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, N.H.; Uto, T.; Sakamoto, A.; Hayashida, Y.; Hidaka, Y.; Morinaga, O.; Lhieochaiphant, S.; Shoyama, Y. Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of compounds from the flower of Mammea siamensis (Miq.) T. Anders. on human cancer cell lines. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuy-on, T.; Maki, P.; Itharat, A. Factors influencing decision for Thai traditional medicine treatment for cancer, treatment results and patient quality of life at the Jitmetta Mercy Foundation for Cancer Patients of Thailand (JFCT) in Petchaburi province. J. Thai Khadi Res. Inst. 2021, 18, 229–262. (In Thai) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ye, J.; Guo, J. Vitexin exerts anti-tumor and anti-angiogensis effects on cervical cancer through VEGFA/VEGFR2 pathway. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2022, 43, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Min, J.-W.; Kong, W.-L.; He, X.-H.; Li, J.-X.; Peng, B.-W. A review on the pharmacological effects of vitexin and isovitexin. Fitoterapia 2016, 115, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, K.; Xu, B. Molecular targets of vitexin and isovitexin in cancer therapy: A critical review. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2017, 1401, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, H.; Luo, S. Vitexin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial pathway and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, Z.T.; Gonzalvez, F.; Houtkooper, R.H.; Vaz, F.M.; Gottlieb, E. BID is cleaved by caspase-8 within a native complex on the mitochondrial membrane. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Wu, Y.; Wen, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Yuan, J.; Zhou, B. Potential Molecular Mechanism of Illicium simonsii Maxim Petroleum Ether Fraction in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, F.; Comità, S.; Venneri, G.; Rago, V.; Naimo, G.D.; De Amicis, F.; De Bartolo, A.; Tundis, R.; Mauro, L.; Panno, M.L. Poncirus trifoliata (L.) Raf. Seed Extract Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in the Androgen Receptor Positive LNCaP Prostate Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhorova, E.A.; Zamaraev, A.V.; Kopeina, G.S.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Lavrik, I.N. Role of the nucleus in apoptosis: Signaling and execution. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 4593–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafech, A.; Stéphanou, A. On the Importance of Acidity in Cancer Cells and Therapy. Biology 2024, 13, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayek, S.R.; Rane, H.S.; Parra, K.J. Reciprocal Regulation of V-ATPase and Glycolytic Pathway Elements in Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stransky, L.; Cotter, K.; Forgac, M. The Function of V-ATPases in Cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1071–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Schwarzenberg, K.; Wiedmann, R.M.; Oak, P.; Schulz, S.; Zischka, H.; Wanner, G.; Efferth, T.; Trauner, D.; Vollmar, A.M. Mode of Cell Death Induction by Pharmacological Vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) Inhibition*. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Song, L.; Zhang, S.; Lin, W.; Cao, Y.; Xu, F.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; et al. Bafilomycin A1 targets both autophagy and apoptosis pathways in pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2015, 100, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanapokasin, R.; Innajak, S.; Nilwarangoon, S. PO-230 Effect of C. cochinchinense extract on V-ATPase inhibition triggering apoptosis in human cancer cell lines. ESMO Open 2018, 3, A110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hao, H.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Z. Inhibition of the mTORC1/NF-κB Axis Alters Amino Acid Metabolism in Human Hepatocytes. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 8621464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Chu, L. V-ATPase B2 promotes microglial phagocytosis of myelin debris by inactivating the MAPK signaling pathway. Neuropeptides 2024, 106, 102436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Choi, M.Y.; Yu, J.; Castro, J.E.; Kipps, T.J.; Carson, D.A. Salinomycin inhibits Wnt signaling and selectively induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13253–13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Deng, K. Blocking the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to treat colorectal cancer: Strategies to improve current therapies (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2023, 62, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Guttridge, D.C.; You, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fribley, A.; Mayo, M.W.; Kitajewski, J.; Wang, C.Y. Wnt-1 signaling inhibits apoptosis by activating beta-catenin/T cell factor-mediated transcription. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Song, Y.; Yao, J.; Huang, K.; Zhu, X. Apigenin suppresses colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 3075–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sun, M.M.; Zhang, G.G.; Yang, J.; Chen, K.S.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, K.C.; Singh, H.; Krishnan, R.; Seow, H.F. GSK-3β phosphorylation and alteration of β-catenin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2003, 199, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rascio, F.; Spadaccino, F.; Rocchetti, M.T.; Castellano, G.; Stallone, G.; Netti, G.S.; Ranieri, E. The Pathogenic Role of PI3K/AKT Pathway in Cancer Onset and Drug Resistance: An Updated Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Jin, X. Vitexin induces G2/M-phase arrest and apoptosis via Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human glioblastoma cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4599–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Ueno, L.; Vogt, P.K. Akt-mediated regulation of NFkappaB and the essentialness of NFkappaB for the oncogenicity of PI3K and Akt. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 2863–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Shen, S.; Verma, I.M. NF-κB, an active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.B.; Meng, F.R.; Fang, Y.X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, C.W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, G.Q.; Feng, F.B.; Qiu, H.Y. Inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation and angiogenesis of human fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine 2018, 97, e10920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhou, J. The protective activity of natural flavonoids against osteoarthritis by targeting NF-κB signaling pathway. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1117489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidya Priyadarsini, R.; Senthil Murugan, R.; Maitreyi, S.; Ramalingam, K.; Karunagaran, D.; Nagini, S. The flavonoid quercetin induces cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells through p53 induction and NF-κB inhibition. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.J.T.; Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; McCubrey, J.A. Akt inactivates ERK causing decreased response to chemotherapeutic drugs in advanced CaP cells. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, J.; López, J.M. Understanding MAPK Signaling Pathways in Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.D.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.P.; Xu, Y.J.; Yu, Y.; Ding, Y.J.; Yu, W.L.; Zhang, R.X.; Zhang, H.M.; Du, H.Y. Vitexin suppresses autophagy to induce apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma via activation of the JNK signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 84520–84532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.Y.; Lee, W.S.; Lu, J.N.; Kang, M.H.; Ryu, C.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Kang, H.S.; Shin, S.C.; Choi, Y.H. Induction of apoptosis in human colon cancer HCT-116 cells by anthocyanins through suppression of Akt and activation of p38-MAPK. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 35, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnol, S.; Chambard, J.-C. ERK and cell death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death—Apoptosis, autophagy and senescence. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Shen, T.; Wang, S.; Ren, D. Morusin induces apoptosis and autophagy via JNK, ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling in human lung carcinoma cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 331, 109279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazim, U.M.; Rasheduzzaman, M.; Lee, Y.J.; Seol, D.W.; Park, S.Y. Enhancement of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by 5-fluorouracil requires activating Bax and p53 pathways in TRAIL-resistant lung cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 18095–18105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.Y.; Zhou, B.F.; Xie, Y.Y.; Lou, J.; Li, K.Q. Bufalin and 5-fluorouracil synergistically induce apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 8019–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.I.; Othman, I.; Abas, F.; Lajis, N.; Naidu, R. Mechanism of Apoptosis Induced by Curcumin in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhu, G.; Xu, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, H.; Feng, F.; Wen, Z.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Resveratrol induces human colorectal cancer cell apoptosis by activating the mitochondrial pathway via increasing reactive oxygen species. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.-Y.; Shi, C.-B.; Wen, H.; Li, F.-L.; Wang, B.-L.; Wang, J. Upregulation of p53 Expression in Patients with Colorectal Cancer by Administration of Curcumin. Cancer Investig. 2011, 29, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitthisuk, P.; Innajak, S.; Poorahong, W.; Samosorn, S.; Dolsophon, K.; Watanapokasin, R. Effect of Acacia concinna Extract on Apoptosis Induction Associated with Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Modulated Intracellular Signaling Pathway in Human Colon HCT116 Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sitthisuk, P.; Poorahong, W.; Innajak, S.; Krajarng, A.; Samosorn, S.; Watanapokasin, R. Mammea siamensis Flower Extract-Induced Cell Death Apoptosis in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells via Vacuolar-Type H+-ATPase Inhibition Associated with GSK-3β/β-Catenin, PI3K/Akt/NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040441
Sitthisuk P, Poorahong W, Innajak S, Krajarng A, Samosorn S, Watanapokasin R. Mammea siamensis Flower Extract-Induced Cell Death Apoptosis in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells via Vacuolar-Type H+-ATPase Inhibition Associated with GSK-3β/β-Catenin, PI3K/Akt/NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040441
Chicago/Turabian StyleSitthisuk, Pornnapa, Watcharaporn Poorahong, Sukanda Innajak, Aungkana Krajarng, Siritron Samosorn, and Ramida Watanapokasin. 2025. "Mammea siamensis Flower Extract-Induced Cell Death Apoptosis in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells via Vacuolar-Type H+-ATPase Inhibition Associated with GSK-3β/β-Catenin, PI3K/Akt/NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling Pathway" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040441
APA StyleSitthisuk, P., Poorahong, W., Innajak, S., Krajarng, A., Samosorn, S., & Watanapokasin, R. (2025). Mammea siamensis Flower Extract-Induced Cell Death Apoptosis in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells via Vacuolar-Type H+-ATPase Inhibition Associated with GSK-3β/β-Catenin, PI3K/Akt/NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040441







