Py-CoMSIA: An Open-Source Implementation of Comparative Molecular Similarity Indices Analysis in Python
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
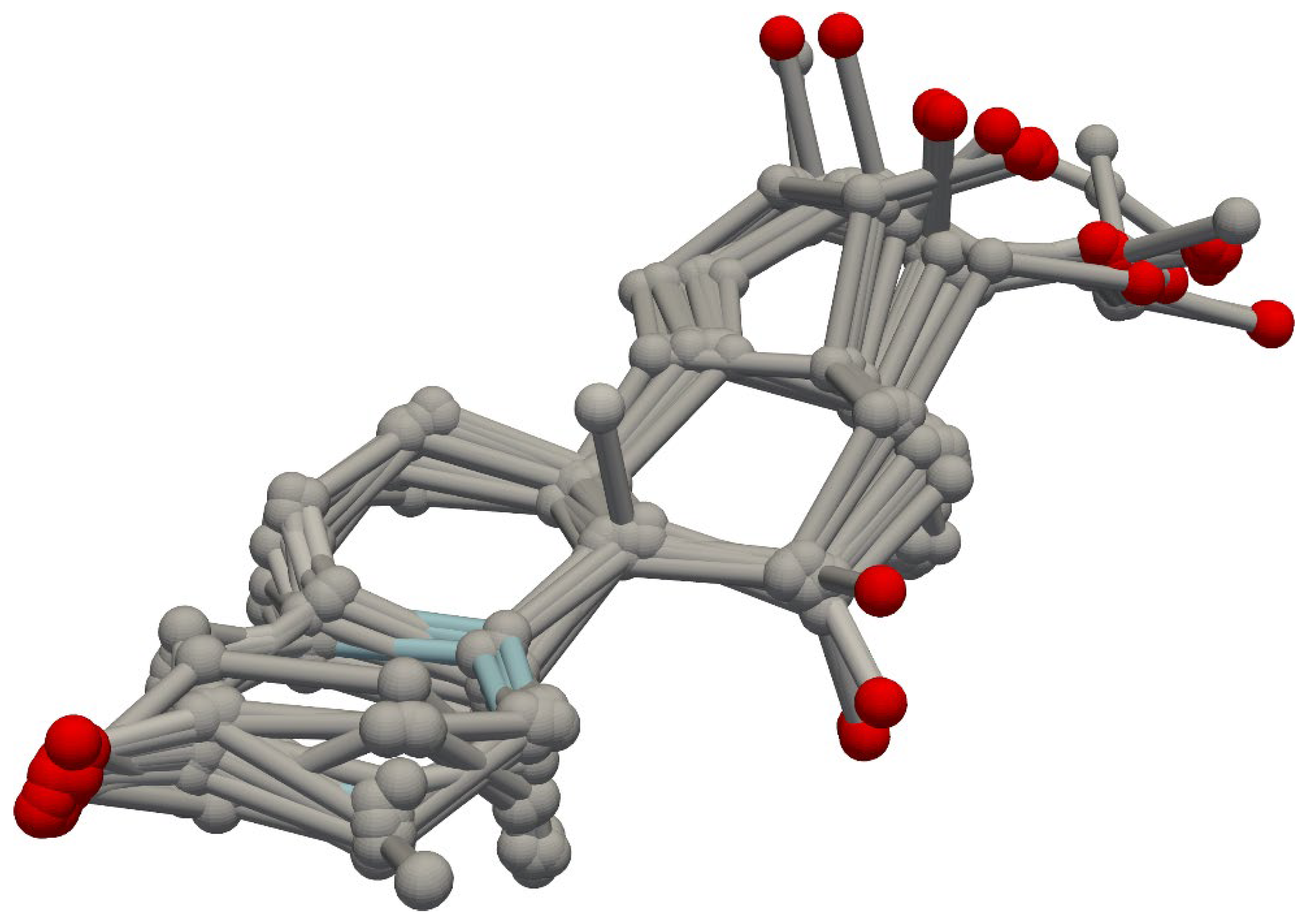
2.1. Steroid Benchmark Test Case
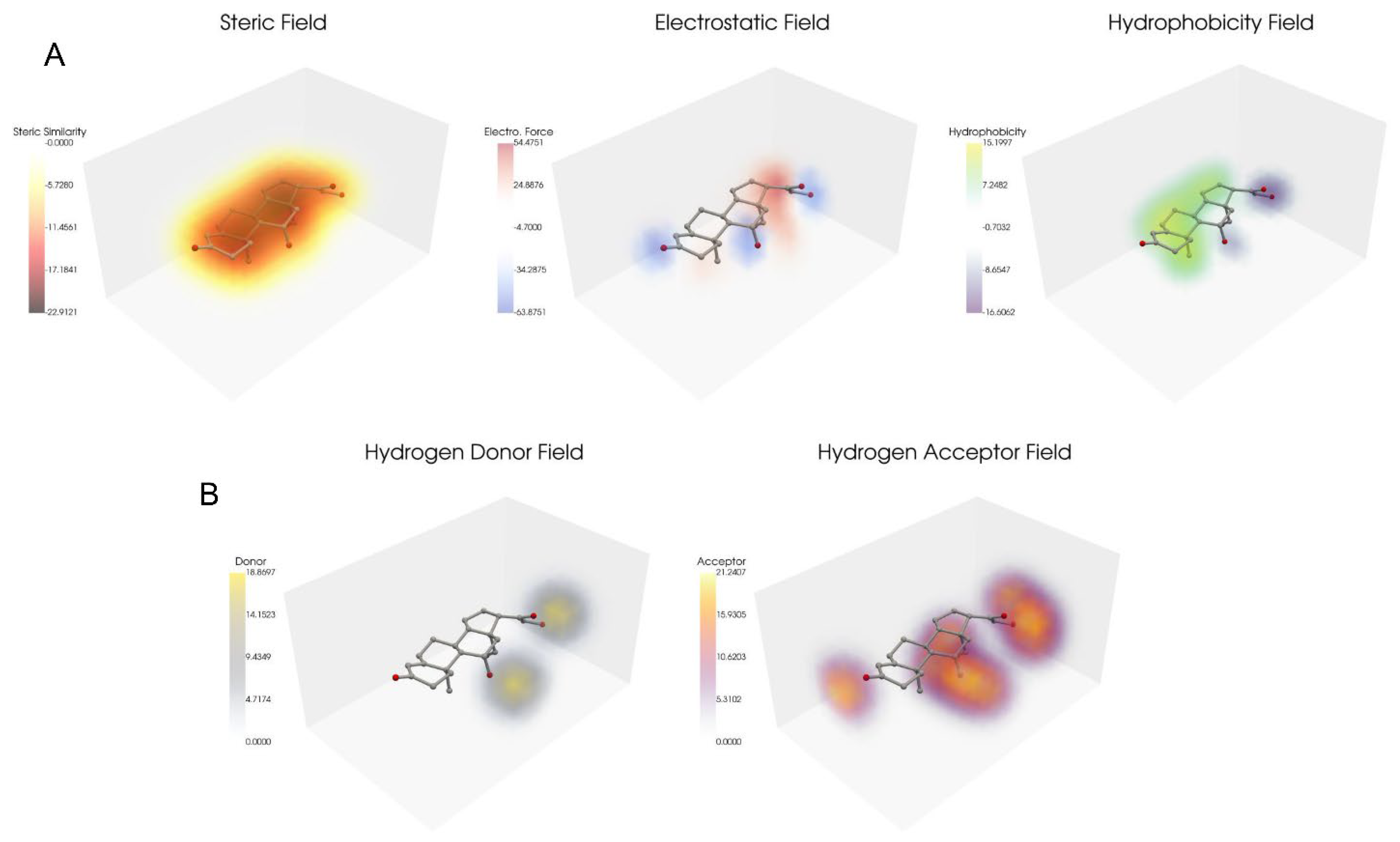
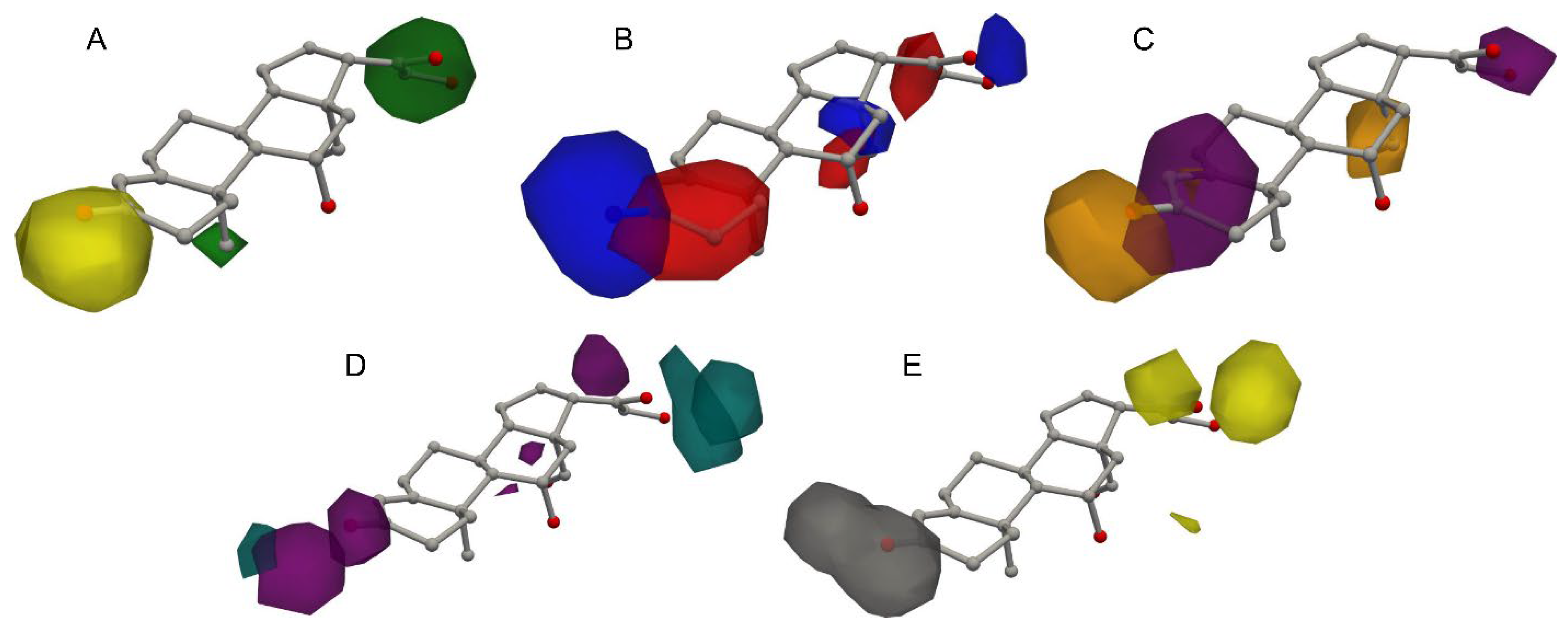
2.2. Steroid Dataset Contour Plots
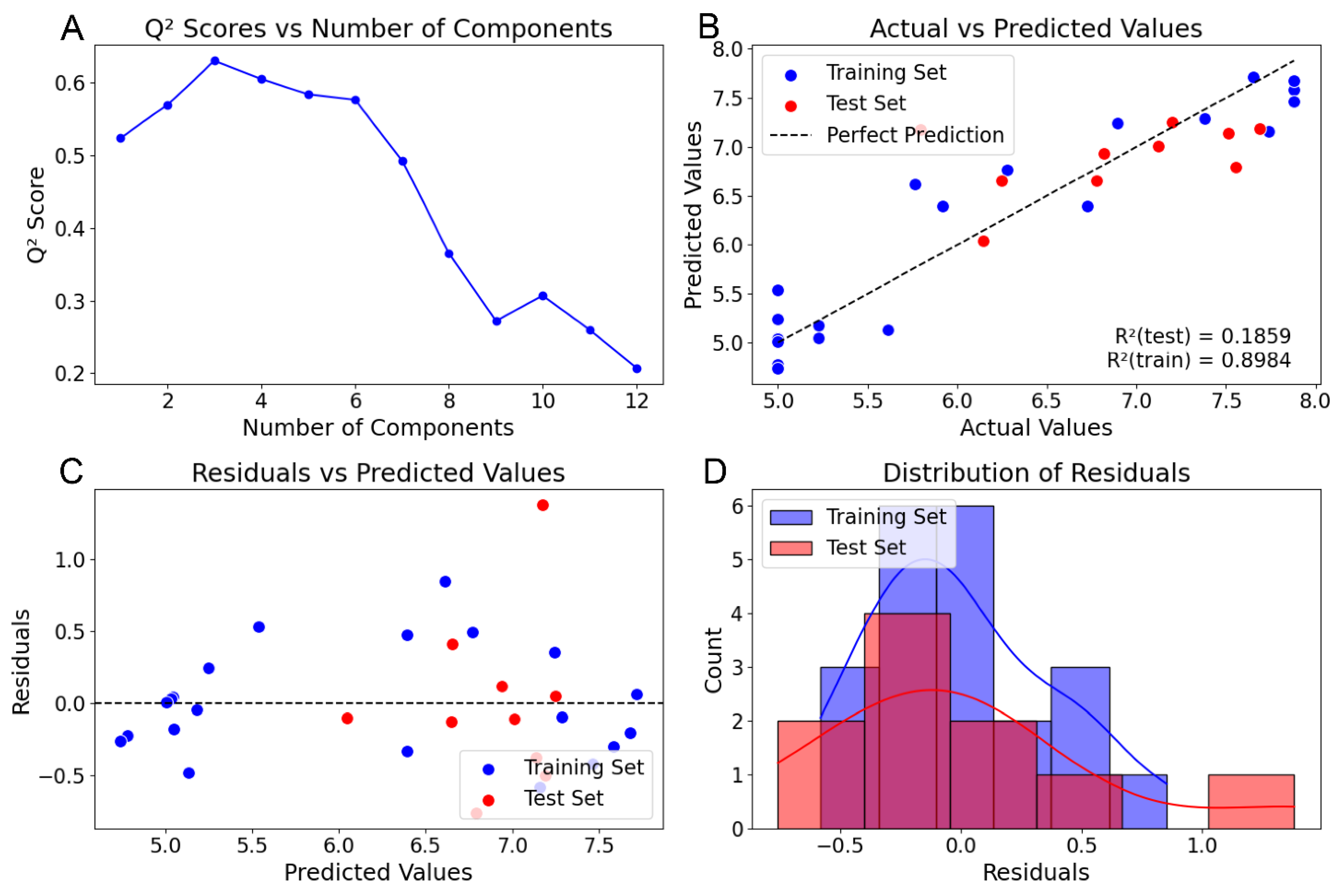
2.3. Additional Benchmark Datasets
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Software Packages
4.2. Datasets
4.3. Molecular Alignment
4.4. Molecular Grid Generation
4.5. Steric, Electrostatic, Hydrophobic, Hydrogen Donor, and Acceptor Field Calculations
4.6. Data Processing
4.7. Partial Least Squares Regression
4.8. Contour Plots
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klebe, G. Comparative Molecular Similarity Indices Analysis: CoMSIA. Perspect. Drug Discov. Des. 1998, 12, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebe, G.; Abraham, U.; Mietzner, T. Molecular Similarity Indices in a Comparative Analysis (CoMSIA) of Drug Molecules to Correlate and Predict Their Biological Activity. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 4130–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, R.D.; Patterson, D.E.; Bunce, J.D. Comparative Molecular Field Analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of Shape on Binding of Steroids to Carrier Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 5959–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Das, R.N. A Review on Principles, Theory and Practices of 2D-QSAR. Available online: http://www.eurekaselect.com (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Lewis, R.A.; Wood, D. Modern 2D QSAR for Drug Discovery. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2014, 4, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucholtz, E.; Tropsha, A. The Effect of Region Size on CoMFA Analyses. Med. Chem. Res. 1999, 9, 675–685. [Google Scholar]
- Basics Manual Sybl-X 1.1; Tripos A Certara Company: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2010.
- Coats, E.A. The CoMFA Steroids as a Benchmark Dataset for Development of 3D QSAR Methods. Perspect. Drug Discov. Des. 1998, 12, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub. Datasets/Coates_CoMFA/Coats_CoMFA_steroidsBenchmarkDataset.sdf at Master·exeResearch/Datasets. Available online: https://github.com/exeResearch/datasets/blob/master/Coates_CoMFA/Coats_CoMFA_steroidsBenchmarkDataset.sdf (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Kubinyi, H. QSAR and 3D QSAR in Drug Design Part 1: Methodology. Drug Discov. Today 1997, 2, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, J.J.; O’Brien, L.A.; Weaver, D.F. A Comparison of Methods for Modeling Quantitative Structure−Activity Relationships. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 5541–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, A.; Malde, A.; Jain, R.; Coutinho, E. 3D-QSAR Study of Ring-Substituted Quinoline Class of Anti-Tuberculosis Agents. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aher, Y.D.; Agrawal, A.; Bharatam, P.V.; Garg, P. 3D-QSAR Studies of Substituted 1-(3, 3-Diphenylpropyl)-Piperidinyl Amides and Ureas as CCR5 Receptor Antagonists. J. Mol. Model. 2007, 13, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragno, R. www.3d-Qsar.Com: A Web Portal That Brings 3-D QSAR to All Electronic Devices—The Py-CoMFA Web Application as Tool to Build Models from Pre-Aligned Datasets. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2019, 33, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. arXiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Python Software Foundation. Available online: https://docs.python.org/3.11/reference/index.html (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Landrum, G.; Tosco, P.; Kelley, B.; Rodriguez, R.; Cosgrove, D.; Vianello, R.; sriniker; Gedeck, P.; Jones, G.; Schneider, N.; et al. Rdkit/Rdkit: 2024_09_5 (Q3 2024) Release. 2025. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14779836 (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array Programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C.B.; Kaszynski, A.A. PyVista: 3D Plotting and Mesh Analysis through a Streamlined Interface for the Visualization Toolkit (VTK). J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Weininger, D. SMILES, a Chemical Language and Information System. 1. Introduction to Methodology and Encoding Rules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1988, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative Partial Equalization of Orbital Electronegativity—A Rapid Access to Atomic Charges. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildman, S.A.; Crippen, G.M. Prediction of Physicochemical Parameters by Atomic Contributions. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1999, 39, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J.E.J.; Dean, P.M. Three-Dimensional Hydrogen-Bond Geometry and Probability Information from a Crystal Survey. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 1996, 10, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, Y.C.; Bures, M.G.; Danaher, E.A.; DeLazzer, J.; Lico, I.; Pavlik, P.A. A Fast New Approach to Pharmacophore Mapping and Its Application to Dopaminergic and Benzodiazepine Agonists. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 1993, 7, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Sjöström, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-Regression: A Basic Tool of Chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
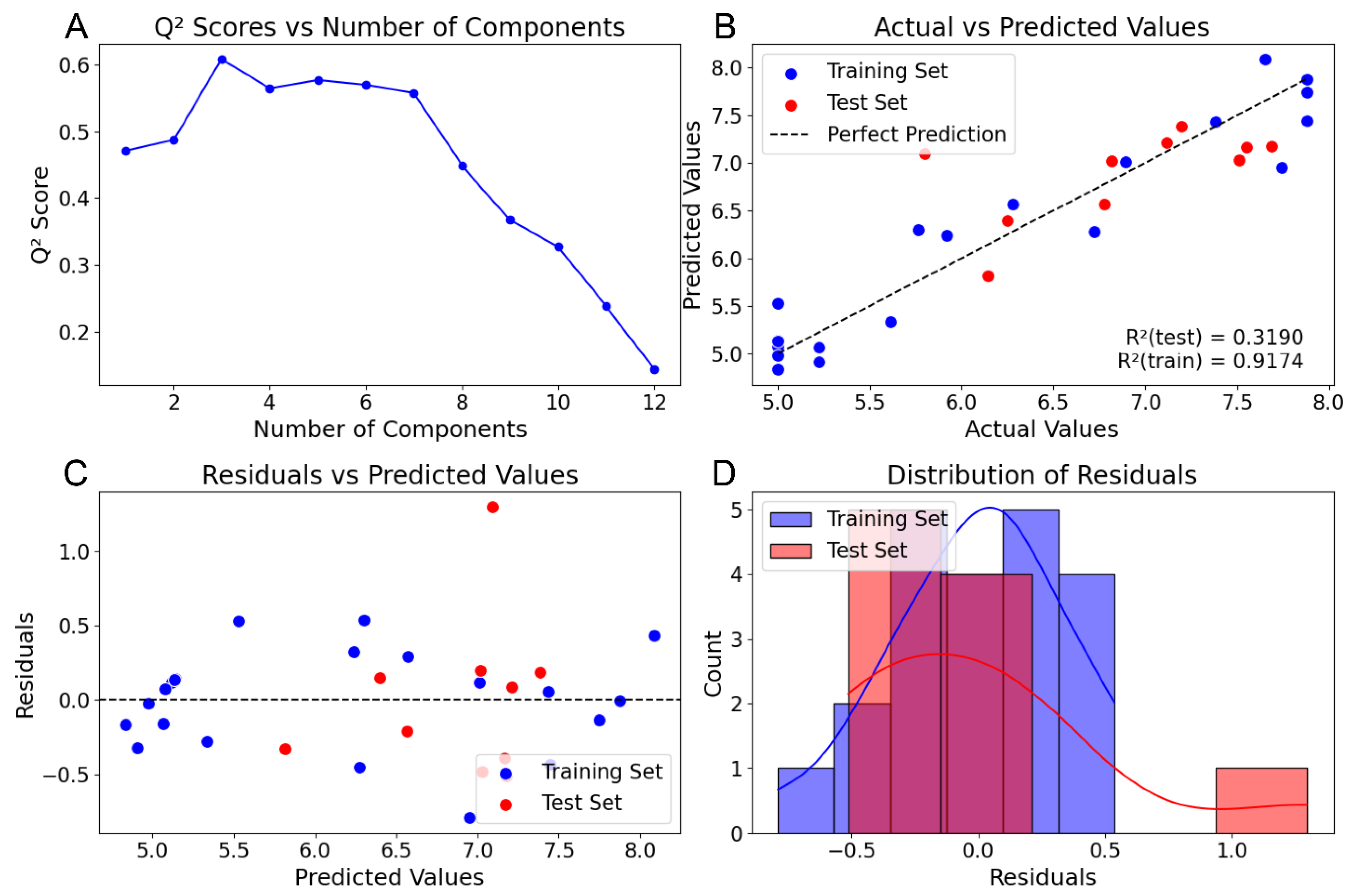
| Published (SEH) | Py-CoMSIA (SEH) | Py-CoMSIA (SEHAD) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| q2 | 0.665 | 0.609 | 0.630 |
| SPRESS | 0.759 | 0.718 | 0.698 |
| r2 | 0.937 | 0.917 | 0.898 |
| S | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.366 |
| no. comp | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| Field Contributions | |||
| steric | 0.073 | 0.149 | 0.065 |
| electrostatic | 0.513 | 0.534 | 0.258 |
| hydrophobic | 0.415 | 0.316 | 0.154 |
| hydrogen donor | 0.274 | ||
| hydrogen acceptor | 0.248 | ||
| Steroid | pKi | CoMSIA (SEH Published) | Py-CoMSIA (SEH) | Py-CoMSIA (SEHAD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | ||||
| aldosterone | 6.28 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.49 |
| androstanediol | 5 | −0.08 | 0.12 | 0.05 |
| androstenediol | 5 | 0.21 | −0.17 | −0.22 |
| androstenedione | 5.76 | −0.43 | 0.54 | 0.85 |
| androsterone | 5.61 | 0.41 | −0.27 | −0.48 |
| corticosterone | 7.88 | 0.14 | 0.00 | −0.30 |
| cortisol | 7.88 | 0.16 | −0.43 | −0.42 |
| cortisone | 6.89 | −0.19 | 0.12 | 0.35 |
| dehydroepiandrostrone | 5 | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.03 |
| deoxycorticosterone | 7.65 | −0.04 | 0.43 | 0.07 |
| deoxycortisol | 7.88 | 0.08 | −0.14 | −0.20 |
| dihydrotestosterone | 5.92 | −0.46 | 0.32 | 0.47 |
| estradiol | 5 | −0.04 | 0.08 | 0.01 |
| estriol | 5 | 0.2 | −0.03 | −0.26 |
| estrone | 5 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.25 |
| etiocholanolone | 5.26 | −0.36 | −0.16 | −0.05 |
| pregnenolone | 5.26 | −0.59 | −0.32 | −0.18 |
| hydroxypregnenlone | 5 | 0.35 | 0.53 | 0.54 |
| progesterone | 7.38 | −0.32 | 0.06 | −0.09 |
| hydroxyprog | 7.74 | 0.04 | −0.79 | −0.58 |
| testosterone | 6.72 | 0.36 | −0.45 | −0.33 |
| Mean | 6.15 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Standard Deviation | 1.17 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.37 |
| Test Set | ||||
| prednisolone | 7.51 | −0.11 | −0.48 | −0.37 |
| cortisol-21-acetate | 7.55 | −0.13 | −0.39 | −0.76 |
| 4-pregnene-3,11,20-trione | 6.78 | 0.26 | −0.21 | −0.13 |
| epicorticosterone | 7.2 | −0.55 | 0.19 | 0.05 |
| 19-nortestosterone | 6.14 | 0.3 | −0.33 | −0.10 |
| 16a,17-dihydroxy-4-pregnene-3,20-dione | 6.25 | −0.93 | 0.15 | 0.41 |
| 16a-methyl-4-pregnene-3,20-dione | 7.12 | −0.23 | 0.09 | −0.11 |
| 19-norprogesterone | 6.82 | −0.08 | 0.20 | 0.12 |
| 11b,17,21-trihydroxy-2a-methyl-4-pregnen-3,20-dione | 7.69 | 0.03 | −0.51 | −0.50 |
| 11b,17,21-trihydroxy-2a-methyl-9a-fluoro-4-pregnen-3,20-dione | 5.8 | −2.02 | 1.30 | 1.38 |
| Mean | 6.89 | −0.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.65 | 0.69 | 0.51 | 0.56 |
| Dataset | Fields | r2train | r2train Published | r2test | r2test Published | q2 | q2 Published | SPRESS | SPRESS Published | Strain | Strain Published | Stest | Stest Published | No. Comps | No. Comps Published |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE | SEH | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.57 | 0.49 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 1.38 | 1.36 | 1.14 | 1.15 | 1.38 | 1.48 | 3 | 2 |
| AChE | SEHAD | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.57 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.49 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.51 | 0.45 | 0.84 | 0.98 | 6 | 4 |
| ATA | SEHAD | 0.74 | 0.86 | −0.77 | −0.41 | 0.29 | 0.46 | 1.10 | N/A | 0.65 | N/A | 1.28 | N/A | 5 | 6 |
| CCR5 | SEHAD | 0.93 | 0.94 | N/A | N/A | 0.81 | 0.78 | 0.38 | N/A | 0.22 | N/A | 0.84 | N/A | 5 | 5 |
| THER | SEAD | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.43 | 0.53 | 0.63 | 0.51 | 1.15 | 1.35 | 0.66 | 0.91 | 1.65 | 1.6 | 4 | 3 |
| THR | SEHAD | 0.84 | 0.89 | 0.51 | 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 0.32 | 0.77 | 0.69 | 3 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haga, C.L.; Le, C.N.; Yang, X.D.; Phinney, D.G. Py-CoMSIA: An Open-Source Implementation of Comparative Molecular Similarity Indices Analysis in Python. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030440
Haga CL, Le CN, Yang XD, Phinney DG. Py-CoMSIA: An Open-Source Implementation of Comparative Molecular Similarity Indices Analysis in Python. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(3):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030440
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaga, Christopher L., Crystal N. Le, Xue D. Yang, and Donald G. Phinney. 2025. "Py-CoMSIA: An Open-Source Implementation of Comparative Molecular Similarity Indices Analysis in Python" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 3: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030440
APA StyleHaga, C. L., Le, C. N., Yang, X. D., & Phinney, D. G. (2025). Py-CoMSIA: An Open-Source Implementation of Comparative Molecular Similarity Indices Analysis in Python. Pharmaceuticals, 18(3), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030440







