Emodin Enhances Rosiglitazone’s Therapeutic Profile by Dual Modulation of SREBP1-Mediated Adipogenesis and PPARγ-Driven Thermogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
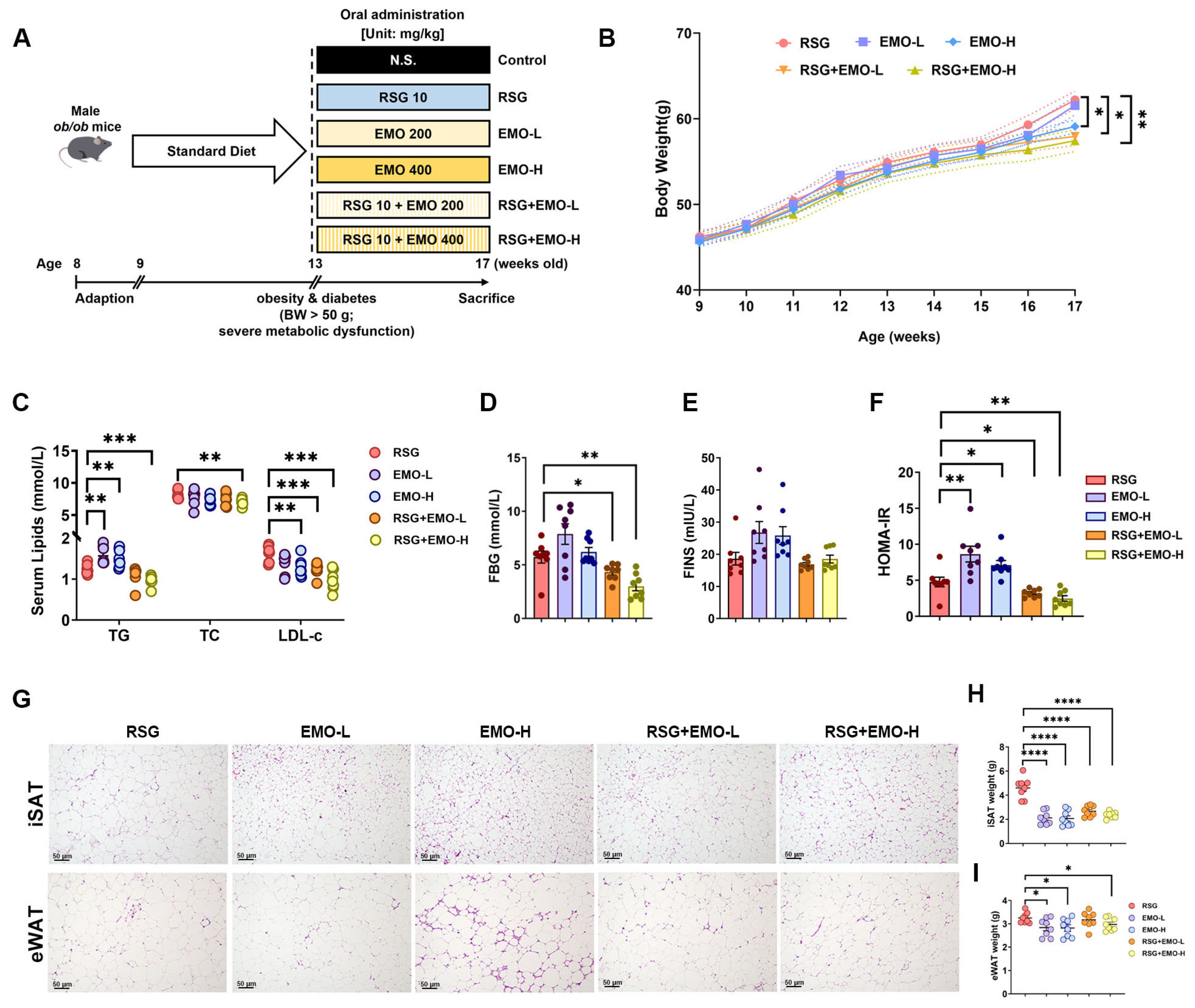
2.1. EMO Enhances RSG-Induced Insulin Sensitization and Attenuates Pro-Obesity Effects
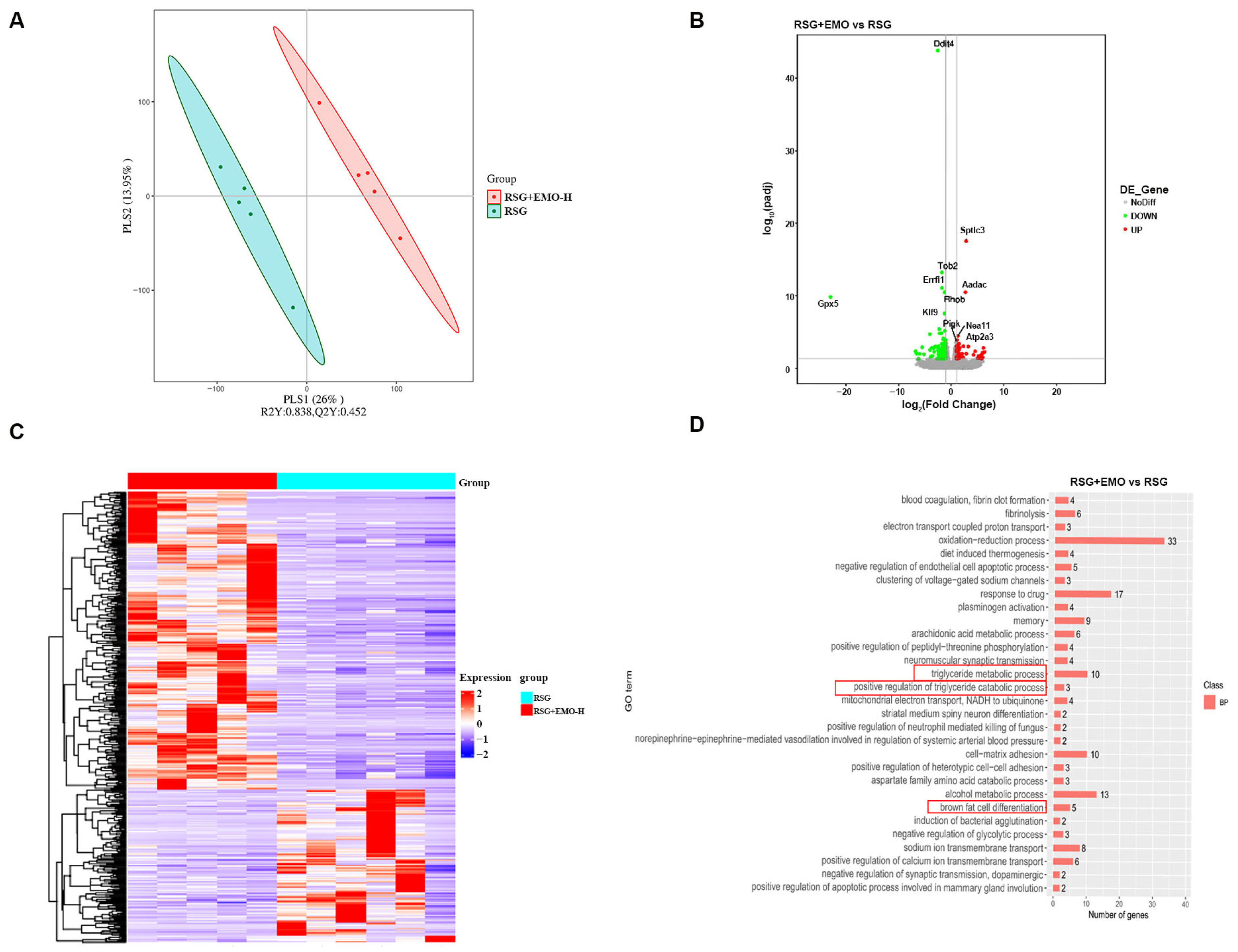
2.2. EMO Modulates Adipogenesis and Thermogenesis Pathways in iSAT of RSG-Induced Obesity
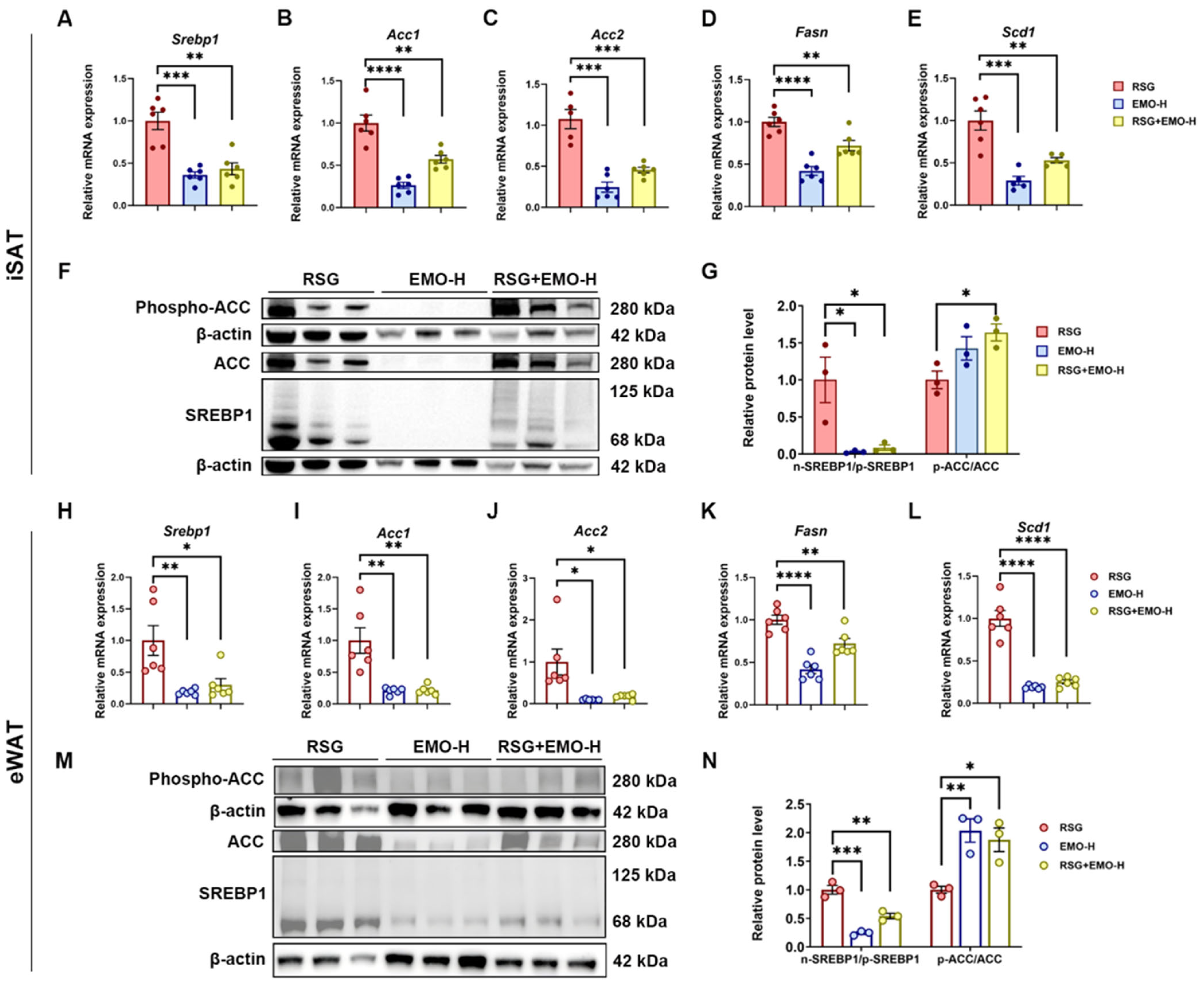
2.3. EMO Inhibits RSG-Induced Adipogenesis via the SREBP1 Pathway in Ob/Ob Mice
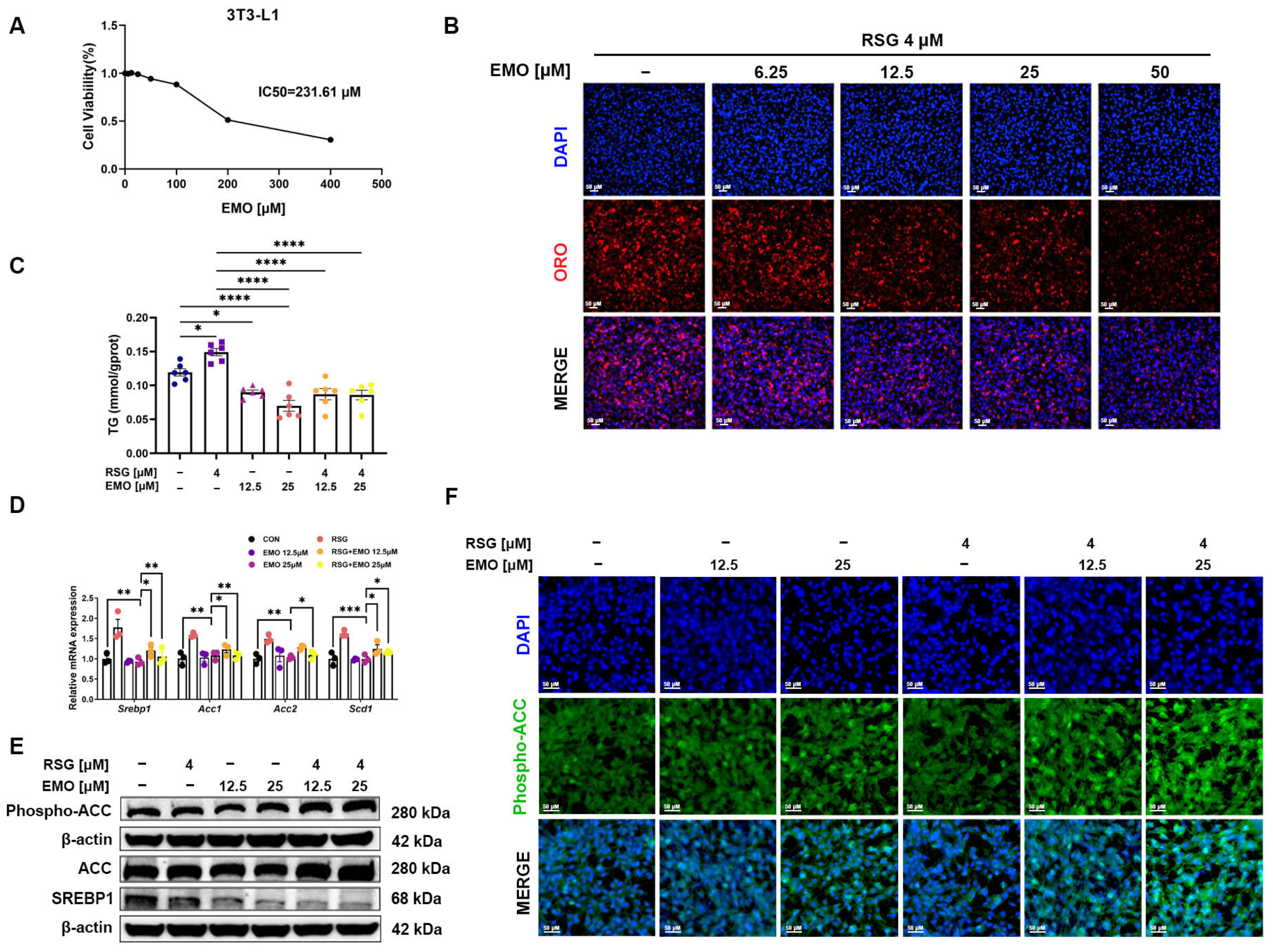
2.4. EMO Attenuates RSG-Induced Adipogenesis via the SREBP1 Pathway in 3T3-L1 Cells
2.5. EMO Enhances RSG-Mediated PPARγ Activation in 3T3-L1 Cells
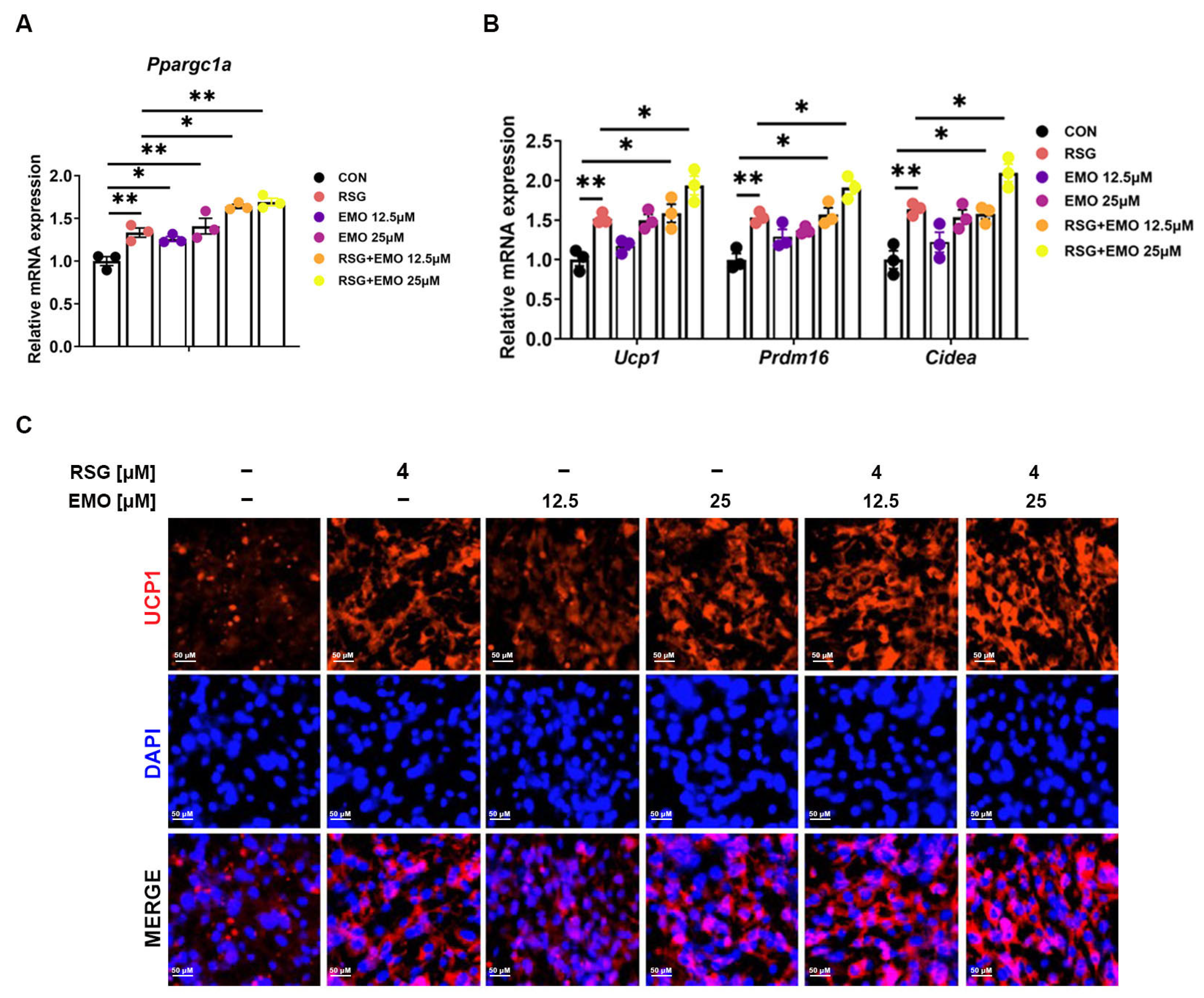
2.6. EMO Amplifies RSG-Mediated Thermogenesis via the PPARγ-PGC-1α Axis in Adipose Tissues
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Animal Study Design
4.3. Biochemical Analysis
4.4. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
4.5. 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Differentiation
4.6. Cell Viability Assay
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.10. RNA Sequencing Analysis
4.11. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.12. Molecular Docking
4.13. Statistical Analysis
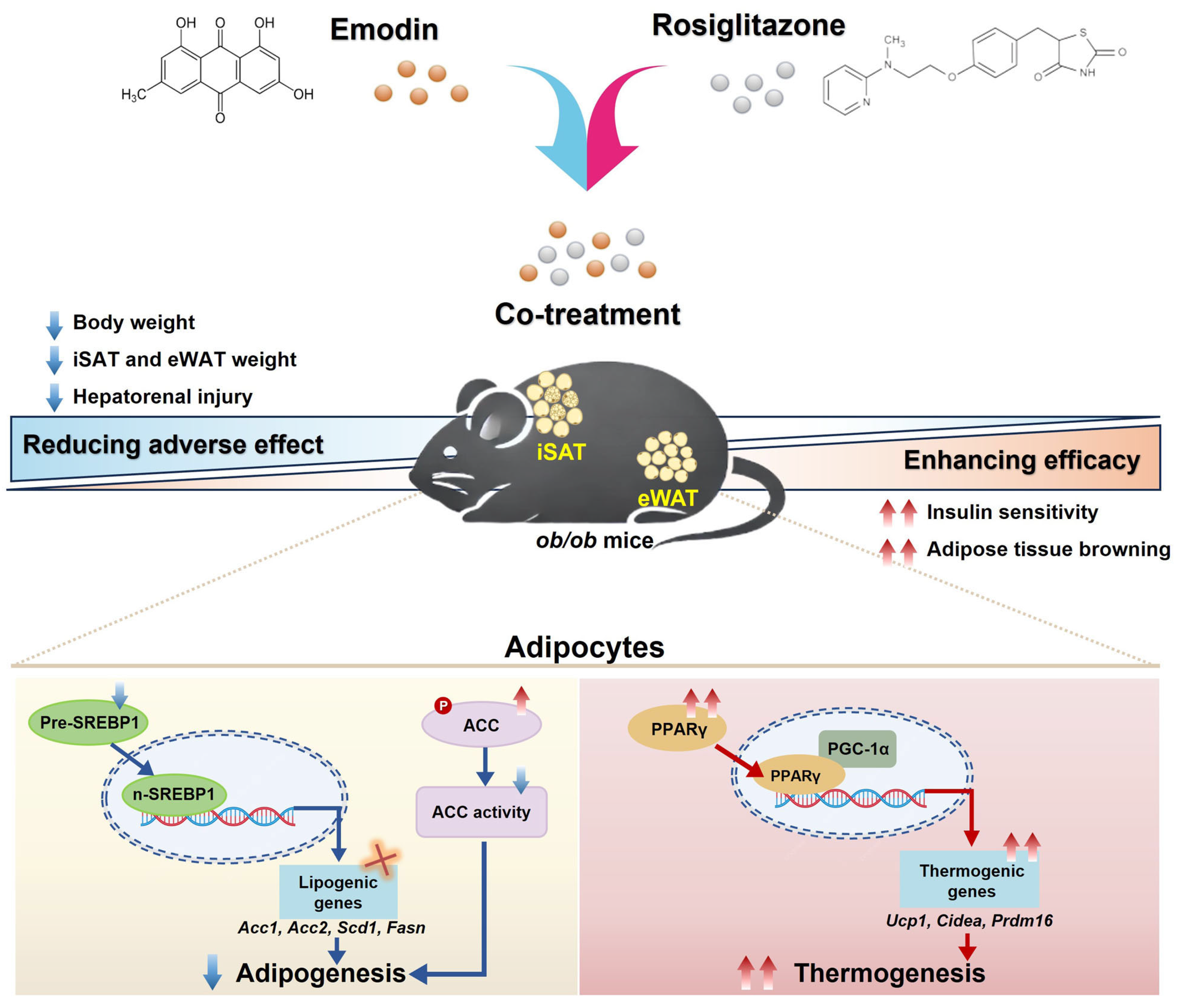
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| BAT | brown adipose tissue |
| CCK-8 | cell counting kit-8 |
| CIDEA | cell death-inducing DNA fragmentation factor-like effector A |
| CMC-Na | sodium carboxy methylcellulose |
| CREA | creatinine |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EMO | emodin |
| eWAT | epididymal white adipose tissue |
| FASN | fatty acid synthase |
| FBG | fasting blood glucose |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| FC | fold change |
| FINS | fasting insulin |
| H&E | hematoxylin-eosin |
| HDL-c | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| IBMX | 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| iSAT | interscapular subcutaneous adipose tissue |
| LDL-c | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| MASLD | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| ORO | oil red o |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| PGC-1α | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α |
| PRDM16 | PR domain containing 16 |
| P/S | penicillin/streptomycin |
| RSG | rosiglitazone |
| SCD1 | stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 |
| SREBP1 | sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| TC | total cholesterol |
| TZD | thiazolidinedione |
| TBIL | total bilirubin |
| TG | triglyceride |
| TBA | total bile acid |
| UCP1 | uncoupling protein 1 |
| UN | urea nitrogen |
| WAT | white adipose tissue |
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Yki-Jarvinen, H.; Scherer, P.E. Why does obesity cause diabetes? Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Cule, M.; Thanaj, M.; Basty, N.; Hashemloo, M.A.; Sorokin, E.P.; Whitcher, B.; Burgess, S.; Bell, J.D.; Sattar, N.; et al. Genetic Evidence for Distinct Biological Mechanisms That Link Adiposity to Type 2 Diabetes: Toward Precision Medicine. Diabetes 2024, 73, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Ye, H.; Xie, L.; Ouyang, S. Advances in small-molecule insulin secretagogues for diabetes treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebovitz, H.E. Thiazolidinediones: The Forgotten Diabetes Medications. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soccio, R.E.; Chen, E.R.; Lazar, M.A. Thiazolidinediones and the promise of insulin sensitization in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Colhoun, H.M.; Deanfield, J.; Emerson, S.S.; Esbjerg, S.; Hardt-Lindberg, S.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kahn, S.E.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marassi, M.; Fadini, G.P. The cardio-renal-metabolic connection: A review of the evidence. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, O.E.; Zsiros, N.; Olsson, I.A. Estimating the predictive validity of diabetic animal models in rosiglitazone studies. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, F.; Liu, Q.; Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Yi, W. Structure-based screening, optimization and biological evaluation of novel chrysin-based derivatives as selective PPARgamma modulators for the treatment of T2DM and hepatic steatosis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 276, 116728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Huang, J.; Wen, M.; Zhang, X.; Lyu, D.; Li, S.; Xiao, H.; Li, M.; Shen, C.; Huang, H. Gentiopicroside ameliorates glucose and lipid metabolism in T2DM via targeting FGFR1. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Herrera-Bravo, J.; Kamiloglu, S.; Petroni, K.; Mishra, A.P.; Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Sureda, A.; Martorell, M.; Aidarbekovna, D.S.; Yessimsiitova, Z.; et al. Recent advances in the therapeutic potential of emodin for human health. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Fu, J.; Yin, X.; Cao, S.; Li, X.; Lin, L.; Huyiligeqi; Ni, J. Emodin: A Review of its Pharmacology, Toxicity and Pharmacokinetics. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Liu, R. Advances in the study of emodin: An update on pharmacological properties and mechanistic basis. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, S.; Shang, F.; Ning, Y.; Huang, Z.; He, R.; Sun, J.; Dong, S. Emodin Improves Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Obese Mice via Activating Brown Adipose Tissue and Inducing Browning of White Adipose Tissue. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 618037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ding, L.; Song, B.; Xiao, X.; Qi, M.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Tang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L. Emodin improves lipid and glucose metabolism in high fat diet-induced obese mice through regulating SREBP pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 770, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Ding, W.; Liu, Y. Anti-diabetic effects of emodin involved in the activation of PPARgamma on high-fat diet-fed and low dose of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Lang, D.Q.; Liu, L.; Yi, Y.K.; Liu, Q.; Shen, C.Y. Natural bioactive constituents from herbs and nutraceuticals promote browning of white adipose tissue. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 178, 106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, R.B.; Semwal, D.K.; Combrinck, S.; Viljoen, A. Emodin—A natural anthraquinone derivative with diverse pharmacological activities. Phytochemistry 2021, 190, 112854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martinez, B.I.; Ruiz-Ramos, M.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Santiago-Osorio, E.; Mendoza-Nunez, V.M. Hypoglycemic Effect of Resveratrol: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.B.; Song, J.Y.; Xu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Xie, S.; Teng, C.L. Interventional effects of Pueraria oral liquid on T2DM rats and metabolomics analysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefterova, M.I.; Haakonsson, A.K.; Lazar, M.A.; Mandrup, S. PPARgamma and the global map of adipogenesis and beyond. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Gan, M.; Wang, X.; Liao, T.; Chen, Q.; Lei, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, L.; et al. The global perspective on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) in ectopic fat deposition: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakers, A.; De Siqueira, M.K.; Seale, P.; Villanueva, C.J. Adipose-tissue plasticity in health and disease. Cell 2022, 185, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punthakee, Z.; Almeras, N.; Despres, J.P.; Dagenais, G.R.; Anand, S.S.; Hunt, D.L.; Sharma, A.M.; Jung, H.; Yusuf, S.; Gerstein, H.C. Impact of rosiglitazone on body composition, hepatic fat, fatty acids, adipokines and glucose in persons with impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance: A sub-study of the DREAM trial. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, S.; Hu, N.; Gu, M.; Chu, C.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Huang, C. Rhein Reduces Fat Weight in db/db Mouse and Prevents Diet-Induced Obesity in C57Bl/6 Mouse through the Inhibition of PPARgamma Signaling. PPAR Res. 2012, 2012, 374936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, K.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Ding, Z.; et al. A promising drug combination of mangiferin and glycyrrhizic acid ameliorates disease severity of rheumatoid arthritis by reversing the disturbance of thermogenesis and energy metabolism. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ma, D.; Xu, W.; Shao, S.; Yu, X. Effect and cardiovascular safety of adding rosiglitazone to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Investig. 2015, 6, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauzá-Thorbrügge, M.; Amengual-Cladera, E.; Galmés-Pascual, B.M.; Morán-Costoya, A.; Gianotti, M.; Valle, A.; Proenza, A.M.; Lladó, I. Impact of Sex on the Therapeutic Efficacy of Rosiglitazone in Modulating White Adipose Tissue Function and Insulin Sensitivity. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, E.Y.; Ha, N.H.; Song, M.G.; Choi, S.H.; Chun, B.G.; Kim, D.H. The effect of Korean Red Ginseng extract on rosiglitazone-induced improvement of glucose regulation in diet-induced obese mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S.; Guo, H.; Dong, S.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z. Emodin ameliorates hepatic steatosis through endoplasmic reticulum-stress sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c pathway in liquid fructose-feeding rats. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, E105–E117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Eid, S.; Adams, M.; Scherer, T.; Torres-Gomez, H.; Hackl, M.T.; Kaplanian, M.; Riedl, R.; Luger, A.; Furnsinn, C. Emodin, a compound with putative antidiabetic potential, deteriorates glucose tolerance in rodents. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 798, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, K.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Dang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, W. Cholesterol overload in macrophages drives metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis via inhibiting 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase in mice. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebisch, K.; Voigt, V.; Wabitsch, M.; Brandsch, M. Protocol for effective differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells to adipocytes. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 425, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, M.; Sheng, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, G.; Zhang, L. High dietary Fructose Drives Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via Activating ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2/11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 Pathway in Mice. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 3480–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.D.; Guan, X.Q.; Chen, J.; Peng, S.; Finel, M.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Wang, R.M.; Bi, H.C.; Lei, M.; Wang, D.D.; et al. Neobavaisoflavone Induces Bilirubin Metabolizing Enzyme UGT1A1 via PPARalpha and PPARgamma. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 628314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.Y.; Bae, H.; Lee, Y.J.; Choi, Y.I.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.B.; Suh, S.W.; Kim, S.W.; Han, B.W. Structural Basis for the Enhanced Anti-Diabetic Efficacy of Lobeglitazone on PPARγ. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Wang, Y.-R.; Wang, X.; Xiao, X.-L.; Sun, Y.-H.; Zhang, S.-A.; Dang, Y.-Q.; Wang, K.; Zhou, W.-J. Emodin Enhances Rosiglitazone’s Therapeutic Profile by Dual Modulation of SREBP1-Mediated Adipogenesis and PPARγ-Driven Thermogenesis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121810
Li M, Wang Y-R, Wang X, Xiao X-L, Sun Y-H, Zhang S-A, Dang Y-Q, Wang K, Zhou W-J. Emodin Enhances Rosiglitazone’s Therapeutic Profile by Dual Modulation of SREBP1-Mediated Adipogenesis and PPARγ-Driven Thermogenesis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(12):1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121810
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Meng, Yi-Rong Wang, Xue Wang, Xiao-Li Xiao, Yun-Hong Sun, Sheng-An Zhang, Yan-Qi Dang, Kai Wang, and Wen-Jun Zhou. 2025. "Emodin Enhances Rosiglitazone’s Therapeutic Profile by Dual Modulation of SREBP1-Mediated Adipogenesis and PPARγ-Driven Thermogenesis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 12: 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121810
APA StyleLi, M., Wang, Y.-R., Wang, X., Xiao, X.-L., Sun, Y.-H., Zhang, S.-A., Dang, Y.-Q., Wang, K., & Zhou, W.-J. (2025). Emodin Enhances Rosiglitazone’s Therapeutic Profile by Dual Modulation of SREBP1-Mediated Adipogenesis and PPARγ-Driven Thermogenesis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(12), 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121810





