Phytochemical Screening by HRLC–MS/MS (Q-TOF) and Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Thottea sivarajanii Leaf Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phytochemical Characterization
2.2. In Vitro Antioxidant Capacity
2.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity in RAW 264.7 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Collection and Extraction
4.2. Cell Lines and Maintenance
4.3. Total Phenol Content
4.4. Total Flavonoid Content
4.5. HRLC–MS/MS (Q-TOF) Analysis
4.6. In Vitro Antioxidant Studies
4.6.1. DPPH
4.6.2. ABTS
4.6.3. FRAP
4.7. Anti-Inflammatory Studies in RAW 264.7 Cells
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TSL | Thottea sivarajanii leaf methanol extract |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| ABTS | 2,2′-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) |
| FRAP | Ferric reducing antioxidant power |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| BER | Berbamine |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| LC | Liquid chromatography |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
References
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Valko, R.; Liska, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Flavonoids and their role in oxidative stress, inflammation, and human diseases. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2025, 413, 111489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averill-Bates, D. Reactive oxygen species and cell signaling. Review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Mol. Cell Res. 2024, 1871, 119573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomova, K.; Raptova, R.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Chronic diseases and aging. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2499–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozougwu, J.C. The role of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in oxidative stress. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Biosci. 2016, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S. Chapter Two—Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Disease. In Oxidative Stress and Biomaterials; Dziubla, T., Butterfield, D.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 35–58. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Anil Kumar, N.V.; Zucca, P.; Varoni, E.M.; Dini, L.; Panzarini, E.; Rajkovic, J.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Azzini, E.; Peluso, I.; et al. Lifestyle, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Back and Forth in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirończuk-Chodakowska, I.; Witkowska, A.M.; Zujko, M.E. Endogenous non-enzymatic antioxidants in the human body. Adv. Med. Sci. 2018, 63, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.; Duennwald, M.L. Nrf2 and Oxidative Stress: A General Overview of Mechanisms and Implications in Human Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Yu, W.; Liu, J.; Tang, D.; Yang, L.; Chen, X. Oxidative cell death in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Buttari, B.; Panieri, E.; Profumo, E.; Saso, L. An Overview of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Inflammation. Molecules 2020, 25, 5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, N.; Kurata, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Morikawa, S.; Masumoto, J. The role of interleukin-1 in general pathology. Inflamm. Regen. 2019, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, J.K.; Günther, S.; Sundberg, E.J. Structural Basis of IL-1 Family Cytokine Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K. Does the Interdependence between Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Explain the Antioxidant Paradox? Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5698931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yue, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, K.; Chen, S.; Du, Z.J. Curcumin, inflammation, and chronic diseases: How are they linked? Molecules 2015, 20, 9183–9213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyane, T.S.; Jere, S.W.; Houreld, N.N. Oxidative stress in ageing and chronic degenerative pathologies: Molecular mechanisms involved in counteracting oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Kandeel, M.; Metwally, E.; Murtaza, G.; Kalhoro, D.H.; Yin, Y.; Tan, B.; Chughtai, M.I.; Yaseen, A.; Afzal, A.; et al. Unraveling the harmful effect of oxidative stress on male fertility: A mechanistic insight. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1070692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsas, A.; Zikopoulos, A.; Moustakli, E.; Zachariou, A.; Tsirka, G.; Tsiampali, C.; Palapela, N.; Sofikitis, N.; Dimitriadis, F. The Silent Threat to Women’s Fertility: Uncovering the Devastating Effects of Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfahuneygn, G.; Gebreegziabher, G.J. Medicinal plants used in traditional medicine by Ethiopians: A review article. J. Respir. Med. Lung Dis. 2019, 4, 1040. [Google Scholar]
- Velu, G.; Palanichamy, V.; Rajan, A.P. Phytochemical and Pharmacological Importance of Plant Secondary Metabolites in Modern Medicine. In Bioorganic Phase in Natural Food: An Overview; Roopan, S.M., Madhumitha, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 135–156. [Google Scholar]
- Wink, M. Modes of Action of Herbal Medicines and Plant Secondary Metabolites. Medicines 2015, 2, 251–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishnav, P.; Demain, A.L. Unexpected applications of secondary metabolites. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwozo, O.S.; Effiong, E.M.; Aja, P.M.; Awuchi, C.G. Antioxidant, phytochemical, and therapeutic properties of medicinal plants: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.S.; Osman, W.J.; Garelnabi, E.A.; Osman, Z.; Osman, B.; Khalid, H.S.; Mohamed, M.A. Secondary metabolites as anti-inflammatory agents. J. Phytopharm. 2014, 3, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, B.; Sharma, J.; Kumar, P.; Shourie, A. Phytochemical properties and pharmacological role of plants: Secondary metabolites. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2021, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, A.K.; Bansal, P.; Kumar, S. Plants-herbal wealth as a potential source of ayurvedic drugs. Asian J. Tradit. Med. 2009, 4, 152–170. [Google Scholar]
- Lerma-Herrera, M.A.; Beiza-Granados, L.; Ochoa-Zarzosa, A.; López-Meza, J.E.; Navarro-Santos, P.; Herrera-Bucio, R.; Aviña-Verduzco, J.; García-Gutiérrez, H.A. Biological Activities of Organic Extracts of the Genus Aristolochia: A Review from 2005 to 2021. Molecules 2022, 27, 3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaiju, P.N.; Athira, M.; Suja, S.R. In Vitro Anti-inflammatory Activity of the Root of Thottea siliquosa (Lam) Rottb., a Medicinal Undershrub in Western Ghats, India. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharma Res. 2021, 11, L135–L142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusaiba, S.A.W.; Murugan, K.J. In vitro analysis on bactericidal screening and antioxidant potentiality of leaf and root extracts of Thottea siliquosa (Lam.) Ding Hou. An ethnobotanical plant. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koottasseri, A.; Babu, A.; Augustin, A.; Job, J.T.; Narayanankutty, A. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of the methanolic extract of Thottea siliquosa: An in vitro and in silico study. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrine Raju, M.R.; Ramesh, B. Phytochemical investigation and pharmacological activity in the roots of Thottea siliquosa Lam. Asian J. Biol. Life Sci. 2012, 1, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Tom, A.; Job, J.T.; Rajagopal, R.; Alfarhan, A.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, Y.O.; Na, S.W.; Narayanankutty, A.J.P.; Pathology, M.P. Thottea siliquosa (Lam.) Ding Hou leaf methanolic extract inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced TLR4 activation and cytokine production as well as ethyl methyl sulfonate induced genotoxicity. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 117, 101772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renny, A.; Sidhic, J.; Tom, A.; Kuttithodi, A.M.; Job, J.T.; Rajagopal, R.; Alfarhan, A.; Narayanankutty, A. Methanol Extract of Thottea siliquosa (Lam.) Ding Hou Leaves Inhibits Carrageenan- and Formalin-Induced Paw Edema in Mice. Molecules 2024, 29, 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adna, J.; Elza, J.A.; Haneef, F.K.; Radhamany, P. GC-MS analysis and in silico molecular docking studies of anti-inflammatory compounds from Thottea barberi (Gamble) Ding Hou root. Med. Plants—Int. J. Phytomed. Relat. Ind. 2019, 11, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, K.; Punitha, T.; Vinodhini, R.; Mickymaray, S.; Shonga, A.; Tomass, Z.; Thajuddin, N.J. Efficacy of different solvent extracts of Aristolochia krisagathra and Thottea ponmudiana for potential antimicrobial activity. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 9, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- John, J.A.; Jose, J.O.; George, V.; Pradeep, N.S.; Sethuraman, M.G. Volatile Constituents and Antibacterial Activity of Leaf Oil of Thottea ponmudiana Sivar. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2008, 20, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, R.; Das, A.K.; Paul, S.B.; Raaman, N.; Sharma, G.D.; Adhikari, P.P. Evaluation of bioavailability of three extracts of a less known ethno-medicinal plant, Thottea tomentosa from Assam. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2022, 21, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, E.S.; Khan, A.S.; Binu, S. A new species of Thottea Rottb.(Aristolochiaceae) from Kerala, South India. Rheedea 2000, 10, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, S.; Mehta, A.; Bajpai, V.K.; Shukla, S. In vitro antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of ethanolic leaf extract of Stevia rebaudiana Bert. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2338–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y.; Blachier, F.; Tossou, M.C.B.; Rahu, N. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: What Polyphenols Can Do for Us? Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7432797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.; Green, I.R.; Ali, I.; Khan, I.A.; Ali, Z.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Ahmed, I. Ursolic acid derivatives for pharmaceutical use: A patent review (2012–2016). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017, 27, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonowicz, M.; Kalinowska, M.; Gryko, K. Enhanced Antioxidant Activity of Ursolic Acid by Complexation with Copper (II): Experimental and Theoretical Study. Materials 2021, 14, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento, P.G.G.; Lemos, T.L.G.; Bizerra, A.M.C.; Arriaga, Â.M.C.; Ferreira, D.A.; Santiago, G.M.P.; Braz-Filho, R.; Costa, J.G.M. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of Ursolic Acid and Derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiruvengadam, M.; Venkidasamy, B.; Subramanian, U.; Samynathan, R.; Ali Shariati, M.; Rebezov, M.; Girish, S.; Thangavel, S.; Dhanapal, A.R.; Fedoseeva, N.; et al. Bioactive Compounds in Oxidative Stress-Mediated Diseases: Targeting the NRF2/ARE Signaling Pathway and Epigenetic Regulation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, S.J. Oxidative stress and inflammation. Open J. Immunol. 2019, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitaka, Y.; Hamada, H.; Uesugi, D.; Kuboki, A.; Shimoda, K.; Iwaki, T.; Kiriake, Y.; Saikawa, T. Synthesis of Daidzein Glycosides, α-Tocopherol Glycosides, Hesperetin Glycosides by Bioconversion and Their Potential for Anti-Allergic Functional-Foods and Cosmetics. Molecules 2019, 24, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Flores, Y.K.; Martínez-Galero, E.; Correa-Basurto, J.; Sixto-López, Y.; Villegas, I.; Rosillo, M.Á.; Cárdeno, A.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C. Daidzein and Equol: Ex Vivo and In Silico Approaches Targeting COX-2, iNOS, and the Canonical Inflammasome Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijiti, N.; Someya, A.; Nagaoka, I. Effects of isoflavone derivatives on the production of inflammatory cytokines by synovial cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.-J.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.-Q.; Zhang, D.-J. Berbamine Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects via Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 2307–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathem, S.H.; Abdulsahib, W.K.; Zalzala, M.H. Berbamine and Thymoquinone Exert Protective Effects against Immune-Mediated Liver Injury via NF-κB-Dependent Pathway. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 960981. [Google Scholar]
- Sundur, S.; Shrivastava, B.; Sharma, P.; Raj, S.S.; Jayasekhar, V.J. A review article of pharmacological activities and biological importance of Calophyllum inophyllum. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2014, 2, 599–603. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, T.; Shimosaka, S.; Sasaki, H.; Matsumura, T.; Tukiyama, T.; Tokiwa, T. (+)-Syringaresinol-di-O-β-d-glucoside, a phenolic compound from Acanthopanax senticosus Harms, suppresses proinflammatory mediators in SW982 human synovial sarcoma cells by inhibiting activating protein-1 and/or nuclear factor-κB activities. Toxicol. Vitr. 2007, 21, 1530–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, I.Z. Free Radicals and Oxidative Stress: Signaling Mechanisms, Redox Basis for Human Diseases, and Cell Cycle Regulation. Curr. Mol. Med. 2023, 23, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroux, F.S.; Pavlick, K.P.; Hines, I.N.; Kawachi, S.; Harada, H.; Bharwani, S.; Hoffman, J.M.; Grisham, M.B. Role of nitric oxide in inflammation. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2001, 173, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacique, A.P.; Barbosa, É.S.; de Pinho, G.P.; Silvério, F.O. Miniaturized Methodologies for Determining the Total Phenol and Flavonoid Concentrations and the Antioxidant Activity. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, N.; Shah, M.H.; Khan, N.; Al-Hashimi, A.; Elshikh, M.S.; Iqbal, A.; Ahmad, S.; Abbasi, A.M. Variations in Total Phenolic, Total Flavonoid Contents, and Free Radicals’ Scavenging Potential of Onion Varieties Planted under Diverse Environmental Conditions. Plants 2022, 11, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, İ.; Alwasel, S.H. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay. Processes 2023, 11, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.M.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Iqbal, Y.; Hussain, A.I.; Khan, I.; Xie, F. Recent trends in extraction, purification, and antioxidant activity evaluation of plant leaf-extract polysaccharides. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2022, 16, 1820–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Joshi, A.; Arora, B.; Bhowmik, A.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, P. Significance of FRAP, DPPH, and CUPRAC assays for antioxidant activity determination in apple fruit extracts. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.; Lu, J. Anti-inflammatory effects of ononin on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 83, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
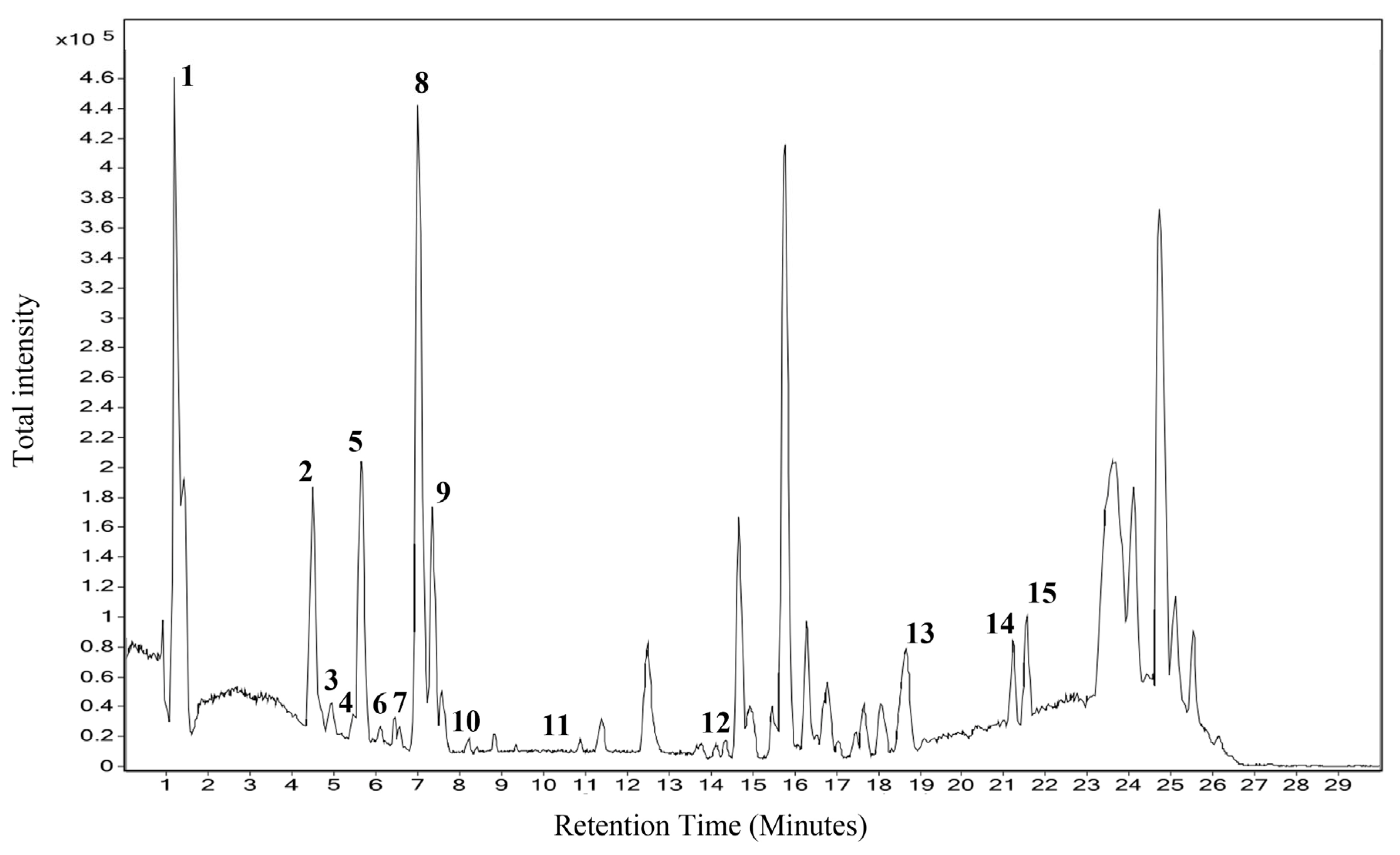



| Sl. No | RT | Name | Formula | Mass | m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1.276 | Anthranilic acid | C7H7NO2 | 137.047 | 138.0542 |
| 2. | 4.407 | N-Feruloyltyramine | C18H19NO4 | 313.1301 | 314.1373 |
| 3. | 5.262 | Caseadine | C20H23NO4 | 341.1626 | 342.17 |
| 4. | 5.35 | Batatasin II | C16H18O4 | 274.1217 | 297.111 |
| 5. | 5.743 | Calophyllin B | C18H16O4 | 296.1043 | 297.1116 |
| 6. | 6.536 | Daidzein 4’,7-diglucoside | C27H30O14 | 578.1667 | 577.1585 |
| 7. | 6.993 | Nummularine F | C23H32N4O4 | 428.2422 | 487.2561 |
| 8. | 7.145 | Syringaresinol O-beta-D-glucoside | C28H36O13 | 580.2226 | 579.2149 |
| 9. | 7.609 | Berbamine | C37H40N2O6 | 08.2887 | 607.2821 |
| 10. | 8.41 | Epi-Tulipinolide diepoxide | C17H22O6 | 322.1413 | 345.1305 |
| 11. | 10.222 | 1-Dehydro-[6]gingerdione | C17H22O4 | 290.1506 | 313.1399 |
| 12. | 14.692 | (S)-Nerolidol 3-O-[a-L-Rhamnopyranosyl-(1->4)-a-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->2)-b-Dglucopyranoside] | C33H56O14 | 676.3747 | 14.692 |
| 13. | 19.037 | Ursolic acid | C30H48O3 | 456.3656 | 455.3584 |
| 14. | 21.156 | Ganosporelactone A | C30H40O7 | 512.2793 | 535.2688 |
| 15. | 21.499 | Omega-hydroxy behenic | C22H44O3 | 356.3335 | 355.3262 |
| Assay | IC50/EC50 Value (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| T. sivarajanii | Standard (Ascorbic Acid) | |
| DPPH | 184.5 ± 2.4 | 65 ± 1.3 |
| ABTS | 24.15 ± 0.13 | 2.1 ± 0.03 |
| FRAP | 4.94 ± 0.32 | 0.93 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Padmalayam, P.M.; Kuttithodi, A.M.; Tom, A.; Job, J.T.; George, S.; Narayanankutty, A. Phytochemical Screening by HRLC–MS/MS (Q-TOF) and Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Thottea sivarajanii Leaf Extract. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121794
Padmalayam PM, Kuttithodi AM, Tom A, Job JT, George S, Narayanankutty A. Phytochemical Screening by HRLC–MS/MS (Q-TOF) and Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Thottea sivarajanii Leaf Extract. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(12):1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121794
Chicago/Turabian StylePadmalayam, Pooja Mohan, Aswathi Moothakoottil Kuttithodi, Alby Tom, Joice Tom Job, Satheesh George, and Arunaksharan Narayanankutty. 2025. "Phytochemical Screening by HRLC–MS/MS (Q-TOF) and Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Thottea sivarajanii Leaf Extract" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 12: 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121794
APA StylePadmalayam, P. M., Kuttithodi, A. M., Tom, A., Job, J. T., George, S., & Narayanankutty, A. (2025). Phytochemical Screening by HRLC–MS/MS (Q-TOF) and Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Thottea sivarajanii Leaf Extract. Pharmaceuticals, 18(12), 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121794








