Targeting Amyloid-β Proteins as Potential Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics: Anti-Amyloid Drug Discovery, Emerging Therapeutics, Clinical Trials and Implications for Public Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis
2.1. Amyloid-β (Aβ) Plaques
2.2. Neurofibrillary Tangles (NFTs)
2.3. Neuroinflammatory Processes in AD
2.4. Oxidative Stress
2.5. Potential Therapeutic Targets in AD
3. The Amyloid-Premise
3.1. Historical Background, Biochemical and Pathological Evidence
3.2. Role of Amyloid-β (Aβ) Peptides in AD
4. Clinically Approved Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics
5. Amyloid-Targeting Therapies
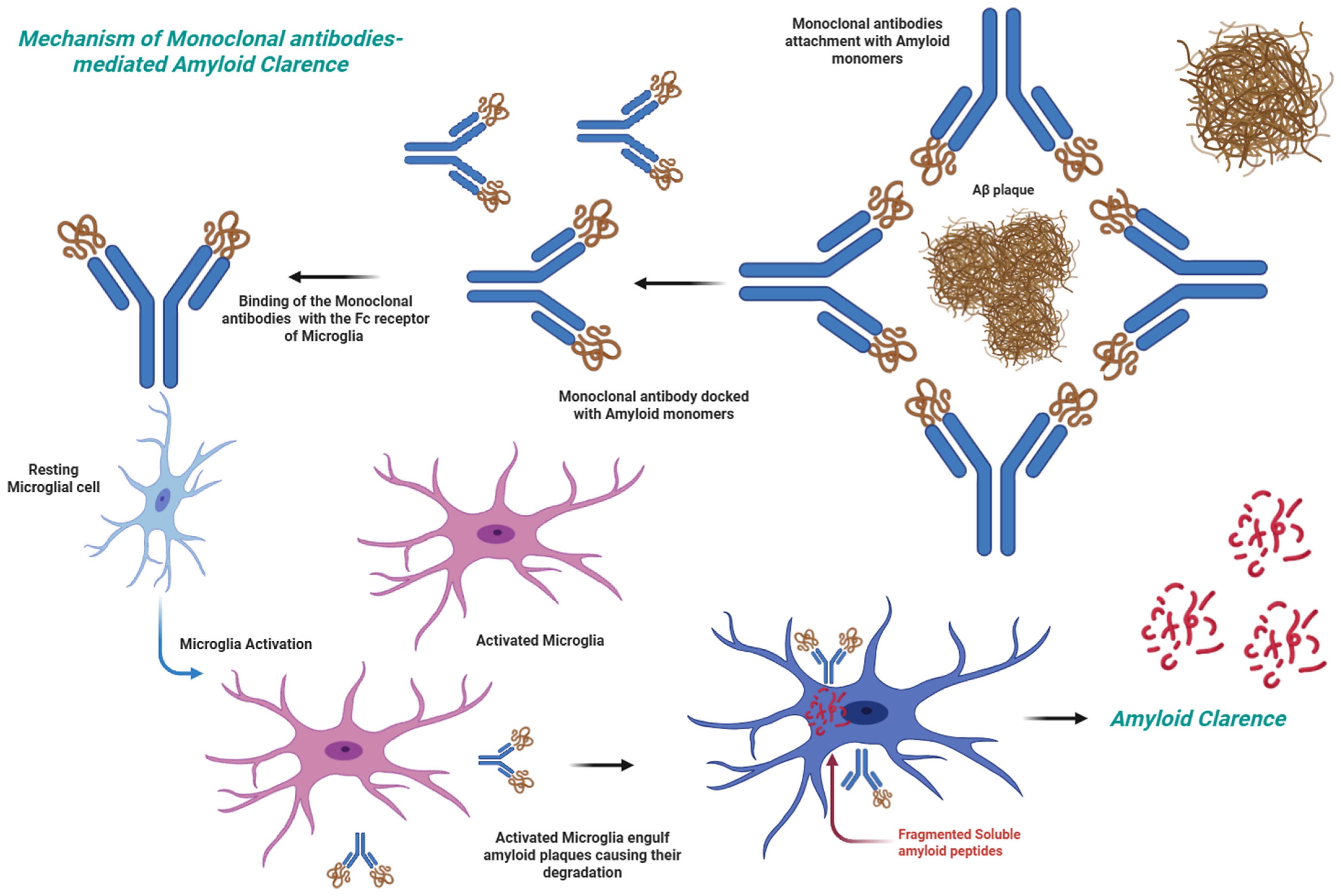
5.1. Anti-Aβ Antibodies
5.2. Clinically Approved Anti-Aβ Antibodies
5.2.1. Lecanemab
5.2.2. Aducanumab
5.2.3. Donanemab
6. Anti-Amyloid Antibodies in the Pipeline
6.1. Bapineuzumab
6.2. Solanezumab
6.3. Gantenerumab
6.4. Crenezumab
6.5. Remternetug
6.6. ABBV-916
6.7. Trontinemab
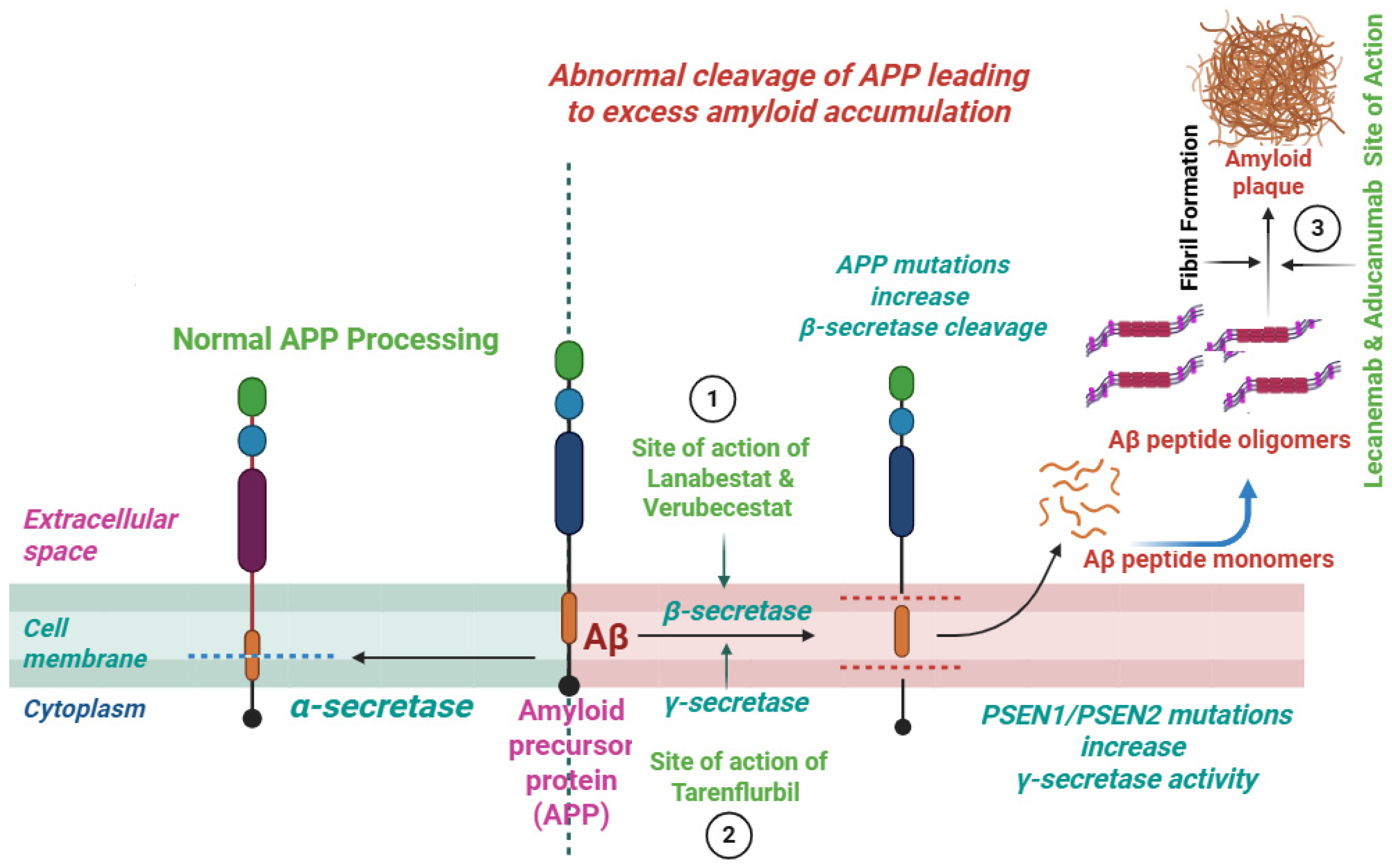
7. β-Secretase (BACE-1) and γ-Secretase Inhibitors
8. Inhibitors of the Aβ Aggregation
9. Other Innovative Approaches in Alzheimer’s Disease
9.1. Tau-Targeting Therapies
9.2. Immunotherapies
9.3. Stem Cell Therapies
9.4. Gene Therapies
9.5. Neutrophins-Based Gene Therapies
9.6. Epigenetic Therapies
9.7. Multi-Target Approaches
9.8. Digital Therapeutics
9.9. Nano-Enabled Anti-AD Therapeutics
10. Challenges and Implications for Public Health
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selkoe, D.J. Resolving controversies on the path to Alzheimer’s therapeutics. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Better, M.A. 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 1598–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s disease: The amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Progress Report on the United Nations Decade of Healthy Ageing, 2021–2023; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Jiang, C.; Liu, X.; Shi, W.; Bai, J.; Mubarik, S.; Wang, F. Epidemiological and sociodemographic transitions in the global burden and risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: A secondary analysis of GBD 2021. Int. J. Equity Health 2025, 24, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, W.S. World Alzheimer Report 2022-How strong are global health systems: Lessons learned and case studies from across the globe. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, e073714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, L.; Maslow, K. Centers For Disease Control And Prevention’s Healthy Brain Initiative: A Public Health Approach To Cognitive Health. Innov. Aging 2018, 2 (Suppl. S1), 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, E.M.; O’Brien, K.; McGuire, L.C.; Baumgart, M.; Gore, J.; Brandt, K.; Levey, A.I.; Lamont, H. Promoting healthy aging: Public health as a leader for reducing dementia risk. Public Policy Aging Rep. 2023, 33, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Cheng, F. Global and regional economic costs of dementia: A systematic review. Lancet 2017, 390, S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, J.S.; Dementia, C.; Group, C.I. Cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 2006, CD005593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, S.; Kishi, T.; Iwata, N. Memantine monotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyck, C.H.; Swanson, C.J.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Chen, C.; Gee, M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Li, D.; Reyderman, L.; Cohen, S.; et al. Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd Haeberlein, S.; Aisen, P.S.; Barkhof, F.; Chalkias, S.; Chen, T.; Cohen, S.; Dent, G.; Hansson, O.; Harrison, K.; von Hehn, C.; et al. Two randomized phase 3 studies of aducanumab in early Alzheimer’s disease. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 9, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golde, T.E.; Schneider, L.S.; Koo, E.H. Anti-Aβ therapeutics in Alzheimer’s disease: The need for a paradigm shift. Neuron 2011, 69, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahnashi, M.H.; Ayaz, M.; Ghufran, M.; Almazni, I.A.; Alqahtani, O.; Alyami, B.A.; Alqahtani, Y.S.; Khan, H.A.; Sadiq, A.; Waqas, M. Phytochemicals-based β-amyloid cleaving enzyme-1 and MAO-B inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Molecular simulations-based predictions. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 8359–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrup, K. The case for rejecting the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karran, E.; Hardy, J. A critique of the drug discovery and phase 3 clinical programs targeting the amyloid hypothesis for Alzheimer disease. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittner, L.M.; Götz, J. Amyloid-β and tau—A toxic pas de deux in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, G.S. Amyloid-β and tau: The trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzi, R.E.; Bertram, L. Twenty years of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid hypothesis: A genetic perspective. Cell 2005, 120, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevigny, J.; Chiao, P.; Bussière, T.; Weinreb, P.H.; Williams, L.; Maier, M.; Dunstan, R.; Salloway, S.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y. The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2016, 537, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowitzki, S.; Lasser, R.A.; Dorflinger, E.; Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F.; Nikolcheva, T.; Ashford, E.; Retout, S.; Hofmann, C.; Delmar, P.; et al. A phase III randomized trial of gantenerumab in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan Butterfield, D. Amyloid β-peptide (1-42)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: Implications for neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease brain. A review. Free Radic. Res. 2002, 36, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, R.H. Mitochondria and mitochondrial cascades in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J. Soluble oligomers of the amyloid β-protein impair synaptic plasticity and behavior. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 192, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elawad, M.A.; Ayaz, M.; Mosa, O.F.; Usman, A.; Hamdoon, A.A.E.; Almawash, S.; Salim, L.H.M.; Ahmed, A.; Elkhalifa, M.E.M. Polyphenols and Their Biogenic Nano-Formulations Targeting BACE1 as Anti-Amyloid Therapies; Meeting the Challenges of Bioavailability, Safety, and Specificity for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, 2400525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, S.Y.; Sadeghi, L.; Dehghan, G. Investigation of amyloid-β peptide production and clearance pathways in different stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2024, 84, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauk, A. Why is the amyloid beta peptide of Alzheimer’s disease neurotoxic? Dalton Trans. 2008, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurcău, M.C.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L.; Jurcău, A.; Marcu, F.; Ţiț, D.M.; Pașcalău, N.; Nistor-Cseppentö, D.C. The link between oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease: Therapeutic implications and future perspectives. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasoff-Conway, J.M.; Carare, R.O.; Osorio, R.S.; Glodzik, L.; Butler, T.; Fieremans, E.; Axel, L.; Rusinek, H.; Nicholson, C.; Zlokovic, B.V. Clearance systems in the brain—Implications for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, G. Clearance systems in the brain, from structure to function. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 729706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brion, J.-P.; Anderton, B.H.; Authelet, M.; Dayanandan, R.; Leroy, K.; Lovestone, S.; Octave, J.-N.; Pradier, L.; Touchet, N.; Tremp, G. Neurofibrillary tangles and tau phosphorylation. In Proceedings of the Biochemical Society Symposia, York, UK, 17–18 December 2001; Portland Press Limited: London, UK, 2001; pp. 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, R.A. Plaques and tangles and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Folia Neuropathol. 2006, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Onyango, I.G.; Jauregui, G.V.; Čarná, M.; Bennett, J.P., Jr.; Stokin, G.B. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, D.; Sharma, V.; Deshmukh, R. Activation of microglia and astrocytes: A roadway to neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christen, Y. Oxidative stress and Alzheimer disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 621S–629S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalifa, A.E.; Alkhalifa, O.; Durdanovic, I.; Ibrahim, D.R.; Maragkou, S. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease: Insights into Pathophysiology and Treatment. J. Dement. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2025, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhapola, R.; Beura, S.K.; Sharma, P.; Singh, S.K.; HariKrishnaReddy, D. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: Current knowledge of signaling pathways and therapeutics. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappolla, M.A.; Martins, R.N.; Poeggeler, B.; Omar, R.A.; Perry, G. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: The shortcomings of antioxidant therapies. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 101, S155–S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-S.; Jo, S.A. Mechanisms of amyloid-β peptide clearance: Potential therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Hatta, T.; Ito, M.; Kusakabe, K.-I. Anti-amyloid-β antibodies and anti-tau therapies for Alzheimer’s disease: Recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 72, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.N.; Singh, C.; Singh, A.; Singh, M.; Singh, B.K. Mitochondrial dysfunction: A potential therapeutic target to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 3075–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Peng, G. Neuroinflammation as a potential therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Interv. Aging 2022, 17, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Allsop, D. Amyloid deposition as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1991, 12, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenner, G.G.; Wong, C.W. Alzheimer’s disease: Initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984, 120, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goate, A.; Chartier-Harlin, M.-C.; Mullan, M.; Brown, J.; Crawford, F.; Fidani, L.; Giuffra, L.; Haynes, A.; Irving, N.; James, L.; et al. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 1991, 349, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, P.; Seeman, N. Alzheimer’s disease: β-amyloid plaque formation in human brain. Synapse 2011, 65, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, D.W. The pathogenesis of senile plaques. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 56, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.-C.; Yu, J.-T.; Wang, H.-F.; Tan, M.-S.; Meng, X.-F.; Wang, C.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, X.-C.; Tan, L. Efficacy and safety of donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine, and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 41, 615–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Li, X.; Ayaz, M.; Ullah, F.; Sadiq, A.; Ovais, M.; Shahid, M.; Khayrullin, M.; Hazrat, A. Neuroprotective studies on Polygonum hydropiper L. essential oils using transgenic animal models. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 580069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Zeb, A.; Ayaz, M.; Murkovic, M. Characterization of phenolic compounds using UPLC–HRMS and HPLC–DAD and anti-cholinesterase and anti-oxidant activities of Trifolium repens L. leaves. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Ali, G.; Nawaz, A.; AlOmar, T.S.; Rauf, A.; Ayaz, M.; Ahmad, S.; Almasoud, N.; AlOmar, A.S.; Khalil, A.A.; et al. Neuroprotective evaluation of diospyrin against drug-induced Alzheimer’s disease. Fitoterapia 2023, 171, 105703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidul Islam, M.; Mohammed Al-Majid, A.; Nageh Sholkamy, E.; Yousuf, S.; Ayaz, M.; Nawaz, A.; Wadood, A.; Rehman, A.U.; Prakash Verma, V.; Motiur Rahman, A.; et al. Synthesis of spiro-oxindole analogs engrafted pyrazole scaffold as potential Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics: Anti-oxidant, enzyme inhibitory and molecular docking approaches. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202203047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, M.; Ali, T.; Sadiq, A.; Ullah, F.; Naseer, M.I. Current trends in medicinal plant research and neurodegenerative disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 922373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, A.; Hassan, M.; Ayaz, M. Carotenoid and Phenolic Profiles and Antioxidant and Anticholinesterase Activities of Leaves and Berries of Phytolacca acinosa. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.M.; Keating, G.M. Memantine: A review of its use in Alzheimer’s disease. Drugs 2006, 66, 1515–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Jin, H.; Xue, Y.-H.; Chen, Q.; Yao, S.-Y.; Du, M.-Q.; Liu, S. Current and future therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease: An overview of drug development bottlenecks. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1206572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L. A resurrection of aducanumab for Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdsson, E.M. Tau Immunotherapies for Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Tauopathies: Status of Trials and Insights from Preclinical Studies. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 101, S129–S140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breukink, F. Immunotherapy as a Treatment Strategy for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Bachelor’s Thesis, Faculty of Science and Engineering, Rijksuniversiteit Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Gettman, L. Lecanemab-irmb (Leqembi™) for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Sr. Care Pharm. 2024, 39, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbins, A.; Davies, M.; Lynn, E.; Roy, D.; Yeomans, A.; Shakir, S.A. Safety and effectiveness of the anti-amyloid monoclonal antibody (mAb) drug lecanemab for early Alzheimer’s disease: The pharmacovigilance perspective. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2025, 91, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeberlein, S.B.; von Hehn, C.; Tian, Y.; Chalkias, S.; Muralidharan, K.K.; Chen, T.; Wu, S.; Skordos, L.; Nisenbaum, L.; Rajagovindan, R.; et al. Emerge and Engage topline results: Phase 3 studies of aducanumab in early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16, e047259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Aducanumab: First approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintun, M.A.; Lo, A.C.; Duggan Evans, C.; Wessels, A.M.; Ardayfio, P.A.; Andersen, S.W.; Shcherbinin, S.; Sparks, J.; Sims, J.R.; Brys, M. Donanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1691–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.R.; Zimmer, J.A.; Evans, C.D.; Lu, M.; Ardayfio, P.; Sparks, J.; Wessels, A.M.; Shcherbinin, S.; Wang, H.; Nery, E.S.M. Donanemab in early symptomatic Alzheimer disease: The TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashad, A.; Rasool, A.; Shaheryar, M.; Sarfraz, A.; Sarfraz, Z.; Robles-Velasco, K.; Cherrez-Ojeda, I. Donanemab for Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review of clinical trials. Healthcare 2022, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Misra, S. Evidences and therapeutic advantages of donanemab in the treatment of early Alzheimer’s disease. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2024, 35, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Frisardi, V.; Imbimbo, B.P.; D ‘Onofrio, G.; Pietrarossa, G.; Seripa, D.; Pilotto, A.; Solfrizzi, V. Bapineuzumab: Anti-β-amyloid monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of Alzheimer‘s disease. Immunotherapy 2010, 2, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salloway, S.; Sperling, R.; Fox, N.C.; Blennow, K.; Klunk, W.; Raskind, M.; Sabbagh, M.; Honig, L.S.; Porsteinsson, A.P.; Ferris, S.; et al. Two phase 3 trials of bapineuzumab in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushouk, A.I.; Elmaraezy, A.; Aglan, A.; Salama, R.; Fouda, S.; Fouda, R.; AlSafadi, A.M. Bapineuzumab for mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbimbo, B.P.; Ottonello, S.; Frisardi, V.; Solfrizzi, V.; Greco, A.; Seripa, D.; Pilotto, A.; Panza, F. Solanezumab for the treatment of mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 8, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doody, R.S.; Thomas, R.G.; Farlow, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Vellas, B.; Joffe, S.; Kieburtz, K.; Raman, R.; Sun, X.; Aisen, P.S.; et al. Phase 3 trials of solanezumab for mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, R.J.; Cummings, J.; Schobel, S.; Salloway, S.; Vellas, B.; Boada, M.; Black, S.E.; Blennow, K.; Fontoura, P.; Klein, G.; et al. Gantenerumab: An anti-amyloid monoclonal antibody with potential disease-modifying effects in early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Solfrizzi, V.; Imbimbo, B.P.; Giannini, M.; Santamato, A.; Seripa, D.; Logroscino, G. Efficacy and safety studies of gantenerumab in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2014, 14, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyck, C.H. Anti-amyloid-β monoclonal antibodies for Alzheimer’s disease: Pitfalls and promise. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowitzki, S.; Bittner, T.; Sink, K.M.; Mackey, H.; Rabe, C.; Honig, L.S.; Cassetta, E.; Woodward, M.; Boada, M.; van Dyck, C.H. Evaluating the safety and efficacy of crenezumab vs placebo in adults with early Alzheimer disease: Two phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trials. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Osse, A.M.L.; Cammann, D.; Powell, J.; Chen, J. Anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. BioDrugs 2024, 38, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.-K.; Kuan, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-W.; Hu, C.-J. Clinical trials of new drugs for Alzheimer disease: A 2020–2023 update. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.; Lee, G.; Ritter, A.; Sabbagh, M.; Zhong, K. Alzheimer’s disease drug development pipeline: 2020. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2020, 6, e12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, H.P.; Schumacher, V.; Schäfer, M.; Imhof-Jung, S.; Freskgård, P.-O.; Brady, K.; Hofmann, C.; Rüger, P.; Schlothauer, T.; Göpfert, U.; et al. Delivery of the Brainshuttle™ amyloid-beta antibody fusion trontinemab to non-human primate brain and projected efficacious dose regimens in humans. MAbs 2023, 15, 2261509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehlin, D.; Hultqvist, G.; Michno, W.; Aguilar, X.; Dahlén, A.D.; Cerilli, E.; Bucher, N.M.; van den Broek, S.L.; Syvänen, S. Bispecific brain-penetrant antibodies for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2025, 12, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, C.; Demos, C.M.; Jagannatha Rao, K.; Pappolla, M.A.; Sambamurti, K. Beta-secretase: Structure, function, and evolution. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets 2008, 7, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, M.F.; Kost, J.; Voss, T.; Mukai, Y.; Aisen, P.S.; Cummings, J.L.; Tariot, P.N.; Vellas, B.; Van Dyck, C.H.; Boada, M.; et al. Randomized trial of verubecestat for prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1408–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, J.R.; Resende, R.; Custódio, J.B.; Salvador, J.A.; Santos, A.E. BACE1 inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease: Current challenges and Future perspectives. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 101, S53–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbimbo, B.P.; Panza, F.; Frisardi, V.; Solfrizzi, V.; D’Onofrio, G.; Logroscino, G.; Seripa, D.; Pilotto, A. Therapeutic intervention for Alzheimer’s disease with γ-secretase inhibitors: Still a viable option? Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2011, 20, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weggen, S.; Beher, D. Molecular consequences of amyloid precursor protein and presenilin mutations causing autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2012, 4, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Strooper, B. Lessons from a failed γ-secretase Alzheimer trial. Cell 2014, 159, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyn, J. What lessons can be learned from failed Alzheimer’s disease trials? Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 8, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaurin, J.; Cecal, R.; Kierstead, M.; Tian, X.; Phinney, A.L.; Manea, M.; French, J.; Lambermon, M.H.; Darabie, A.A.; Brown, M.E.; et al. Therapeutically effective antibodies against amyloid-β peptide target amyloid-β residues 4–10 and inhibit cytotoxicity and fibrillogenesis. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Arendash, G.W.; Hou, H.; Fernandez, F.; Jensen, M.; Runfeldt, M.; Shytle, R.D.; Tan, J. Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reduces β-amyloid mediated cognitive impairment and modulates tau pathology in Alzheimer transgenic mice. Brain Res. 2008, 1214, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarretta, K.L.; Gordon, D.J.; Meredith, S.C. Peptide-based inhibitors of amyloid assembly. Methods Enzymol. 2006, 413, 273–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congdon, E.E.; Sigurdsson, E.M. Tau-targeting therapies for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congdon, E.E.; Ji, C.; Tetlow, A.M.; Jiang, Y.; Sigurdsson, E.M. Tau-targeting therapies for Alzheimer disease: Current status and future directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 19, 715–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovestone, S.; Boada, M.; Dubois, B.; Hüll, M.; Rinne, J.O.; Huppertz, H.-J.; Calero, M.; Andrés, M.V.; Gómez-Carrillo, B.; León, T.; et al. A phase II trial of tideglusib in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 45, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Ser, T.; Steinwachs, K.C.; Gertz, H.J.; Andres, M.V.; Gomez-Carrillo, B.; Medina, M.; Vericat, J.A.; Redondo, P.; Fleet, D.; Leon, T.; et al. Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease with the GSK-3 inhibitor tideglusib: A pilot study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 33, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-González, M.; Pérez-Piñera, P.; Martínez-Rivera, M.; Lopez Muniz, A.; Vega, J.A. Immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease: Rational basis in ongoing clinical trials. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiukas, Z.; Ephraim, R.; Tangalakis, K.; Davidson, M.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Feehan, J. Immunotherapies for Alzheimer’s disease—A review. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.S.; Cashman, N.R. Passive immunotherapies targeting Aβ and tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 144, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Yang, L.-P.; Zhao, L. Stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. World J. Stem Cells 2020, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.M.; Yeon, B.K.; Cho, S.-J.; Suh, Y.-H. Stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: A review of recent clinical trials. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 54, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, T.; Valenzuela, M. Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, and stem cell therapy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.M.; Fong, H.; Huang, Y. Stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders: Current status and future perspectives. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, C.R.; Volarevic, A.; Djonov, V.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as new remedy for the treatment of neurocognitive disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, S.; Pourmand, S.M.; Motevaseli, E.; Hassanzadeh, G. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and MSC-derived exosomes in animal models of central nervous system diseases: Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome. IUBMB Life 2023, 75, 794–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, N.C.; Khan, N.M.; Islam, M.; Nain, Z.; Roy, R.K.; Haque, A.; Barman, S.K. CRISPR-Cas9: A promising genome editing therapeutic tool for Alzheimer’s disease—A narrative review. Neurol. Ther. 2020, 9, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z. Neprilysin gene transfer: A promising therapeutic approach for A lzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 93, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuszynski, M.H.; Thal, L.; Pay, M.; Salmon, D.P.; U, H.S.; Bakay, R.; Patel, P.; Blesch, A.; Vahlsing, H.L.; Ho, G.; et al. A phase 1 clinical trial of nerve growth factor gene therapy for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, A.; Angelov, B.; Drechsler, M.; Lesieur, S. Neurotrophin delivery using nanotechnology. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, A.; Ahmad, F.; Teoh, S.L.; Kumar, J.; Yahaya, M.F. Neurotrophic factor alpha 1 gene therapy in Alzheimer’s disease: Scope and advancements. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2025, 18, 1518868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toader, C.; Serban, M.; Munteanu, O.; Covache-Busuioc, R.-A.; Enyedi, M.; Ciurea, A.V.; Tataru, C.P. From synaptic plasticity to Neurodegeneration: BDNF as a transformative target in medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Gera, R.; Linderoth, B.; Lind, G.; Wahlberg, L.; Almqvist, P.; Behbahani, H.; Eriksdotter, M. A review of techniques for biodelivery of nerve growth factor (NGF) to the brain in relation to Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1331, 167–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Shi, C.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Tang, R.; Tang, M. Neuroimaging techniques, gene therapy, and gut microbiota: Frontier advances and integrated applications in Alzheimer’s Disease research. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1485657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastroeni, D.; Grover, A.; Delvaux, E.; Whiteside, C.; Coleman, P.D.; Rogers, J. Epigenetic mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 1161–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Thakur, A.; Dwivedi, A.R.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, V. Multi-target-directed ligands as an effective strategy for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 1757–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agis-Torres, A.; Sollhuber, M.; Fernandez, M.; Sanchez-Montero, J.M. Multi-target-directed ligands and other therapeutic strategies in the search of a real solution for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2014, 12, 2–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, R.; Pecic, S. Multi-Target Directed Ligands for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2023, 385, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.B.; Costa, L.; Dias, C.B.; Chen, J.; Hillebrandt, H.; Gardener, S.L.; Brown, B.M.; Loo, R.; Garg, M.; Rainey-Smith, S.R.; et al. Multi-domain interventions for dementia prevention–a systematic review. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2023, 27, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.A.; Mallik, A.; Thomson, Z.; de Raadt St. James, A.; Dupuis, K.; Cohen, D. Developing a music-based digital therapeutic to help manage the neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia. Front. Digit. Health 2023, 5, 1064115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, C.; Silva, A.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Barroso, M.F. Single and multitarget systems for drug delivery and detection: Up-to-date strategies for brain disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovais, M.; Zia, N.; Ahmad, I.; Khalil, A.T.; Raza, A.; Ayaz, M.; Sadiq, A.; Ullah, F.; Shinwari, Z.K. Phyto-therapeutic and nanomedicinal approaches to cure Alzheimer’s disease: Present status and future opportunities. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthivashan, G.; Ganesan, P.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Choi, D.-K. Therapeutic strategies and nano-drug delivery applications in management of ageing Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Gong, B.; Ji, W.; Yin, T.; Gao, C.; Liangwen, D.; Hao, M.; Chen, C.; et al. Biomaterials-based anti-inflammatory treatment strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Purpose of the Therapy | Target | Mechanism of Action | Clinical Trials Stage/Status | Clinical Trial No. | Starting Date | Proposed Completion | Sponsor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aducanumab | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Monoclonal antibodies that target oligomers and Aβ plaques | Discontinued Nov. 2024 | NCT04241068 | Mar-2020 | July-2024 | Biogen |
| NCT05310071 | Jun-2022 | Aug-2024 | Biogen | |||||
| Donanemab | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Monoclonal antibodies explicitly against pyro-glutamate Aβ | Phase-3 | NCT04437511 | Jun-2020 | April-2023 | Eli Lilly |
| NCT05026866 | Aug-2021 | Oct-2027 | ||||||
| NCT05508789 | Oct-2022 | April-2027 | ||||||
| NCT05738486 | Feb-2023 | Mar-2024 | ||||||
| Gantenerumab | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Monoclonal antibodies against Aβ | Phase-3 | NCT01760005 | Dec-2012 | Oct-2027 | Washington Univ. School of Medicine |
| Lecanemab | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Monoclonal antibodies against amyloid proto-fibrils & Aβ | Phase-3 | NCT01760005 | Dec-2012 | Oct-2027 | Washington University School of Medicine & Eisai Inc. |
| NCT03887455 | Mar-2019 | Sep-2027 | ||||||
| NCT04468659 | Jul-2020 | Oct-2027 | ||||||
| NCT05269394 | Dec-2021 | Jul-2027 | ||||||
| Lecanemab | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Monoclonal antibodies against amyloid proto-fibrils and Aβ | Phase-2 | NCT01767311 | Dec-2012 | Feb-2025 | Eisai Inc. |
| Remternetug | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Monoclonal anti-Aβ antibodies | Phase-3 | NCT05463731 | Aug-2022 | Oct-2025 | Eli Lilly |
| Solanezumab | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Monoclonal anti-Aβ antibodies | Phase-3 | NCT01760005 | Dec-2012 | Oct-2027 | Washington Univ. School of Medicine |
| ABBV-916 | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Anti-Aβ antibodies | Phase-2 | NCT05291234 | April-2023 | Jun-2024 | AbbVie |
| ACI-24.060 | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Active vaccination stimulating anti-Aβ antibodies | Phase-2 | NCT05462106 | Jun-2022 | Jun-2026 | AC Immune SA |
| ALZN002 | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Autologous Aβ mutant peptide pulsed dendritic cells | Phase-2 | NCT05834296 | Jul-2023 | Mar-2028 | Alzamend Neuro Inc. |
| APH-1105 | Disease modifying small molecule | Aβ | α-secretase modulator | Phase-2 | NCT03806478 | Jun-2023 | Sep-2024 | Aphios |
| MIB-626 | Disease modifying small molecule | Aβ | Sirtuin nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide stimulator to Increase α-secretase activity | Phase-2 | NCT05040321 | Dec-2021 | April-2024 | Brigham & women’s hospital |
| PRI-002 | Disease modifying small molecule | Aβ | Interfere with Aβ42 oligomerization | Phase-2 | NCT06182085 | Dec-2023 | April-2026 | PRInnovation GmbH |
| Trontinemab | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Anti-Aβ and anti-oligomers monoclonal antibodies | Phase-2 | NCT04639050 | Mar-2021 | Sep-2027 | Hoffmann-La Roche |
| Valiltramiprosate | Disease modifying small molecule | Aβ | Inhibitor of Aβ aggregation | Phase-2 | NCT04693520 | Sep-2020 | Jul-2023 | Alzheon Inc. |
| Varoglutamstat | Disease modifying small molecule | Aβ | Reduce the pyroglutamate Aβ formation via inhibition of glutaminyl-cyclase enzyme | Phase-2 | NCT03919162 | Nov-2021 | Nov-2023 | Vivoryon Therapeutics |
| NCT04498650 | Jul-2020 | Jan-2024 | ||||||
| ALN-APP | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | RNAi to reduce APP and down-stream Aβ related events | Phase-1 | NCT05231785 | Feb-2022 | Jul-2025 | Alnylam Pharma |
| ALZ-101 | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Anti-Aβ Vaccine | Phase-1 | NCT05328115 | Sep-2021 | Dec-2023 | Alzinova-AB |
| AV-1959D | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Anti-Aβ Vaccine | Phase-1 | NCT05642429 | Feb-2023 | Feb-2026 | Institute of Medicine |
| BMS-984923 | Disease modifying small molecule | Aβ | Silent allosteric modulator of mGluR5 | Phase-1 | NCT05804383 | Mar-2023 | Oct-2024 | Allyx Therapeutics |
| NCT05817643 | Jan-2023 | Feb-2023 | ||||||
| Remternetug | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Anti-Aβ monoclonal antibodies | Phase-1 | NCT04451408 | Jul-2020 | Aug-2024 | Eli Lilli |
| SHR-1707 | Disease modifying biological agent | Aβ | Anti-Aβ monoclonal antibodies | Phase-1 | NCT06114745 | Jan-2024 | Nov-2025 | Atridia Pty Ltd. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abduljawad, A.A.; Alkinani, K.B.; Zaakan, A.; AlGhamdi, A.S.; Hamdoon, A.A.E.; Alshanbari, B.H.; Alshehri, A.A.; Alluhaybi, B.B.; Alqashi, S.O.I.; Abduljawad, R.A. Targeting Amyloid-β Proteins as Potential Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics: Anti-Amyloid Drug Discovery, Emerging Therapeutics, Clinical Trials and Implications for Public Health. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111731
Abduljawad AA, Alkinani KB, Zaakan A, AlGhamdi AS, Hamdoon AAE, Alshanbari BH, Alshehri AA, Alluhaybi BB, Alqashi SOI, Abduljawad RA. Targeting Amyloid-β Proteins as Potential Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics: Anti-Amyloid Drug Discovery, Emerging Therapeutics, Clinical Trials and Implications for Public Health. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111731
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbduljawad, Asaad Abdulrahman, Khadijah B. Alkinani, Aysha Zaakan, Abeer S. AlGhamdi, Alashary Adam Eisa Hamdoon, Batool H. Alshanbari, Ahmed Abdullah Alshehri, Badria Bakheet Alluhaybi, Shahad Othman Ibrahim Alqashi, and Ryan Abdulrahman Abduljawad. 2025. "Targeting Amyloid-β Proteins as Potential Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics: Anti-Amyloid Drug Discovery, Emerging Therapeutics, Clinical Trials and Implications for Public Health" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111731
APA StyleAbduljawad, A. A., Alkinani, K. B., Zaakan, A., AlGhamdi, A. S., Hamdoon, A. A. E., Alshanbari, B. H., Alshehri, A. A., Alluhaybi, B. B., Alqashi, S. O. I., & Abduljawad, R. A. (2025). Targeting Amyloid-β Proteins as Potential Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics: Anti-Amyloid Drug Discovery, Emerging Therapeutics, Clinical Trials and Implications for Public Health. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111731







