Review of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Epidemiology, Aetiology, Pathology, and Pharmacological Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
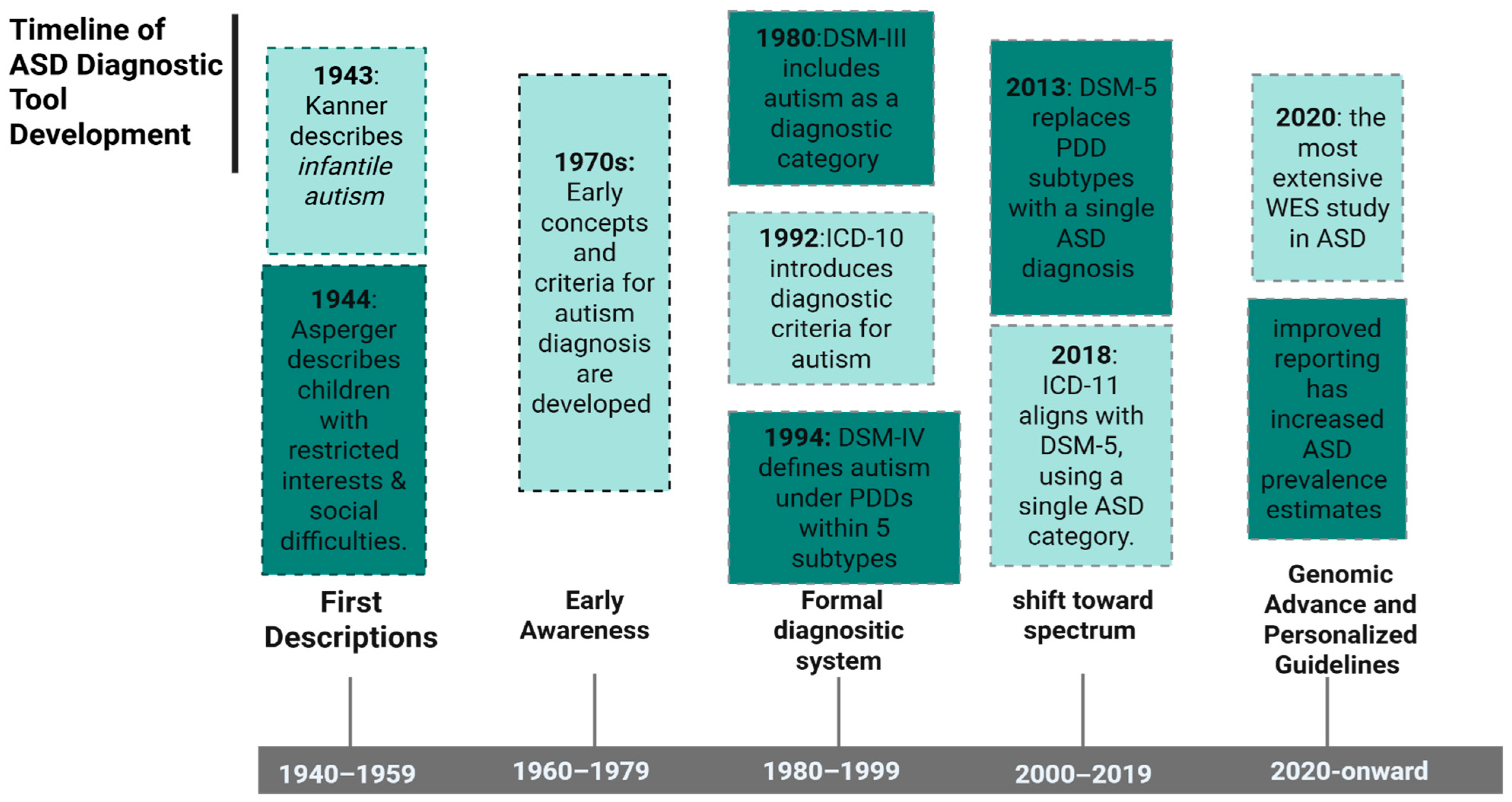
2. History of ASD Diagnosis
3. ASD Prevalence
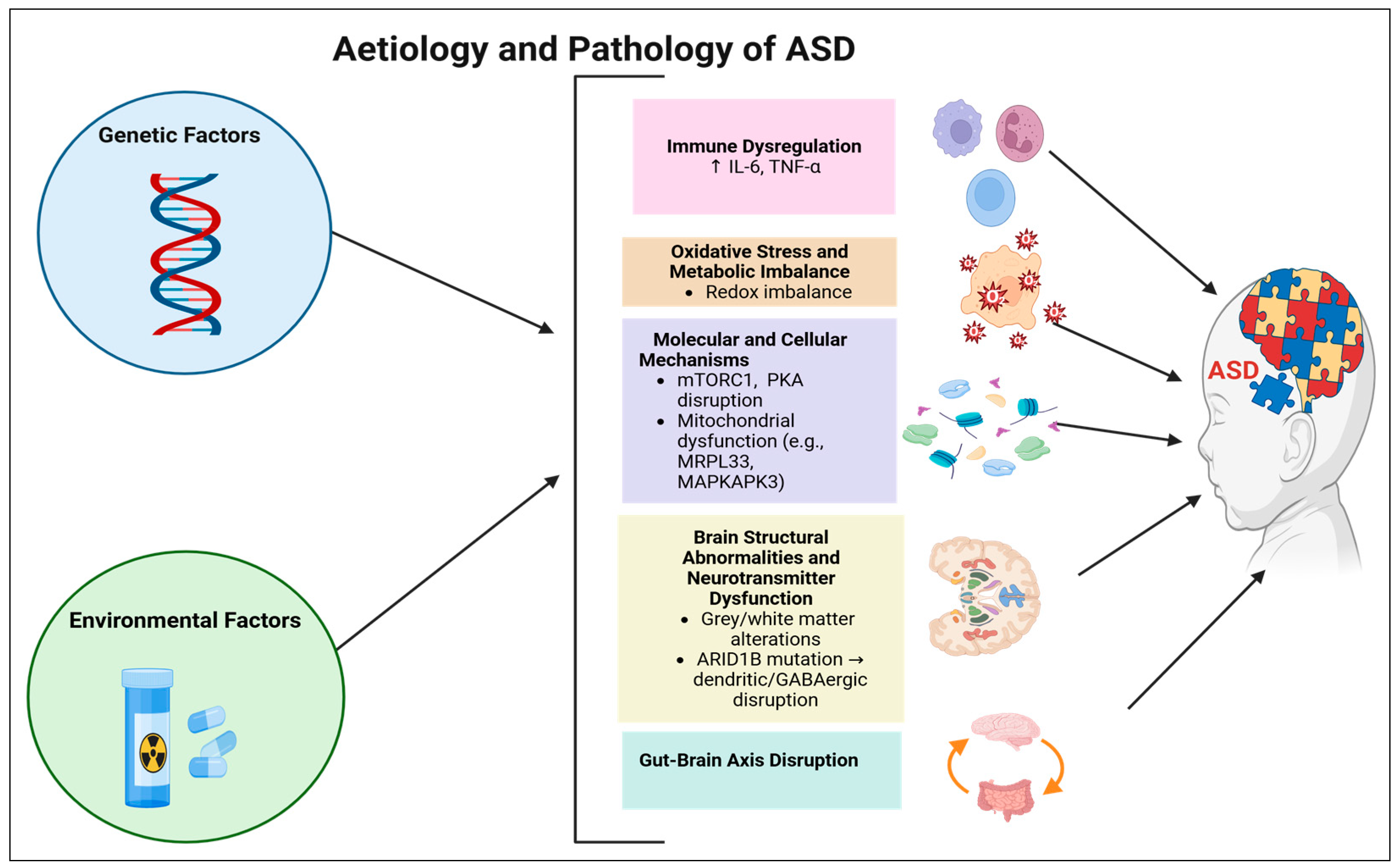
4. ASD Aetiology
5. ASD Pathology
6. ASD Pharmacological Treatment
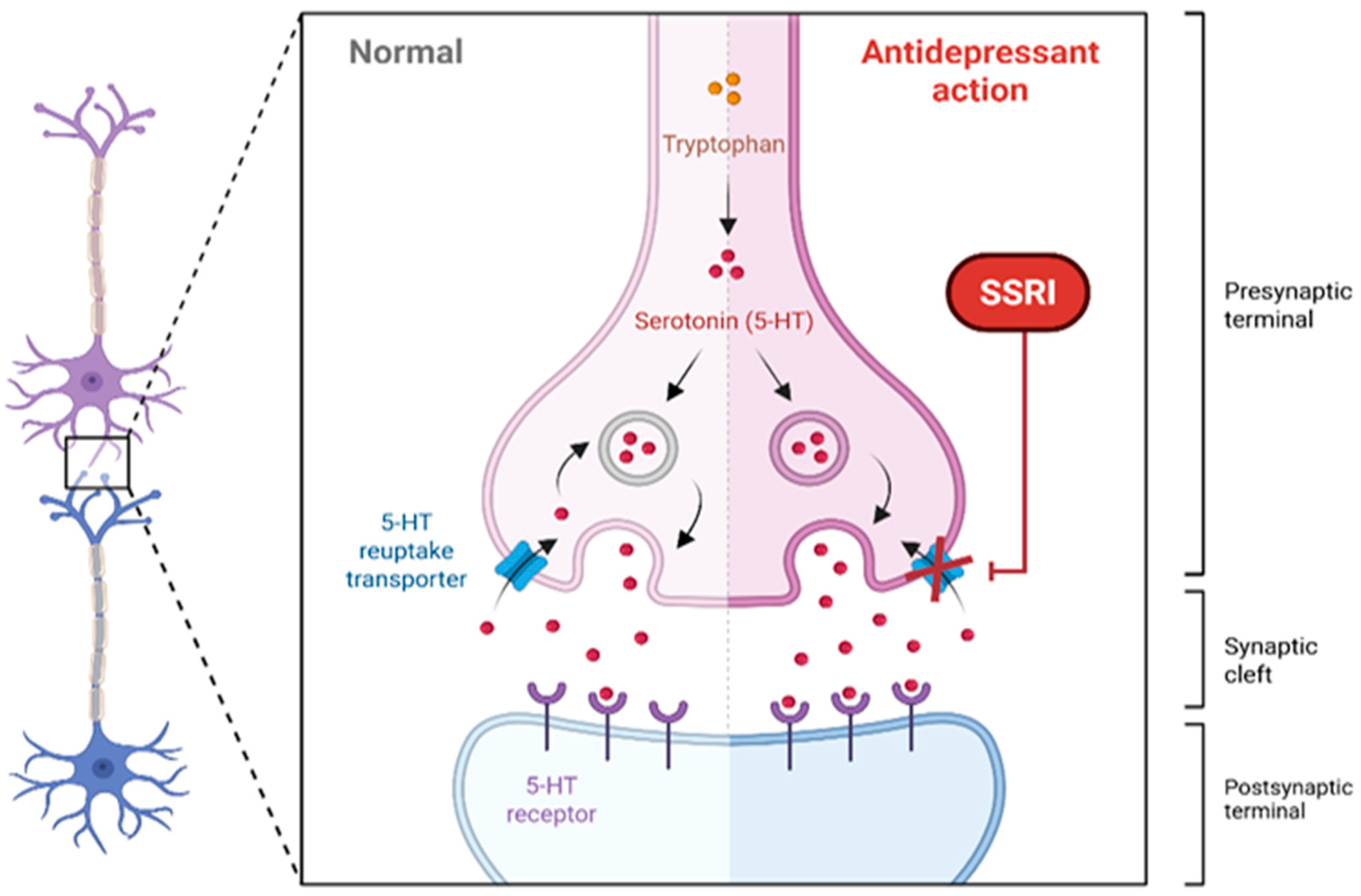
6.1. SSRIs
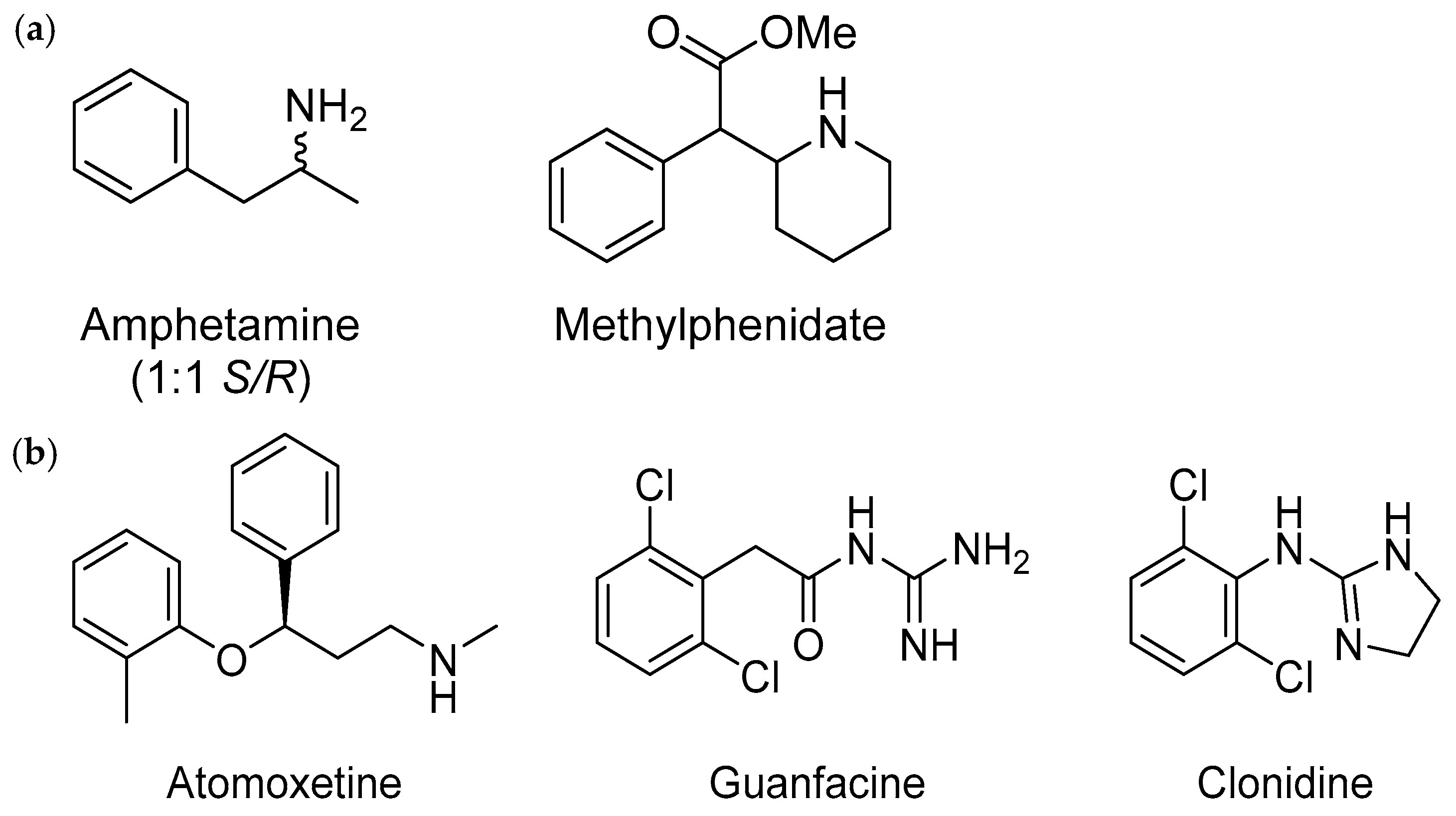
6.2. ADHD Medications
6.3. Mood Stabilizers
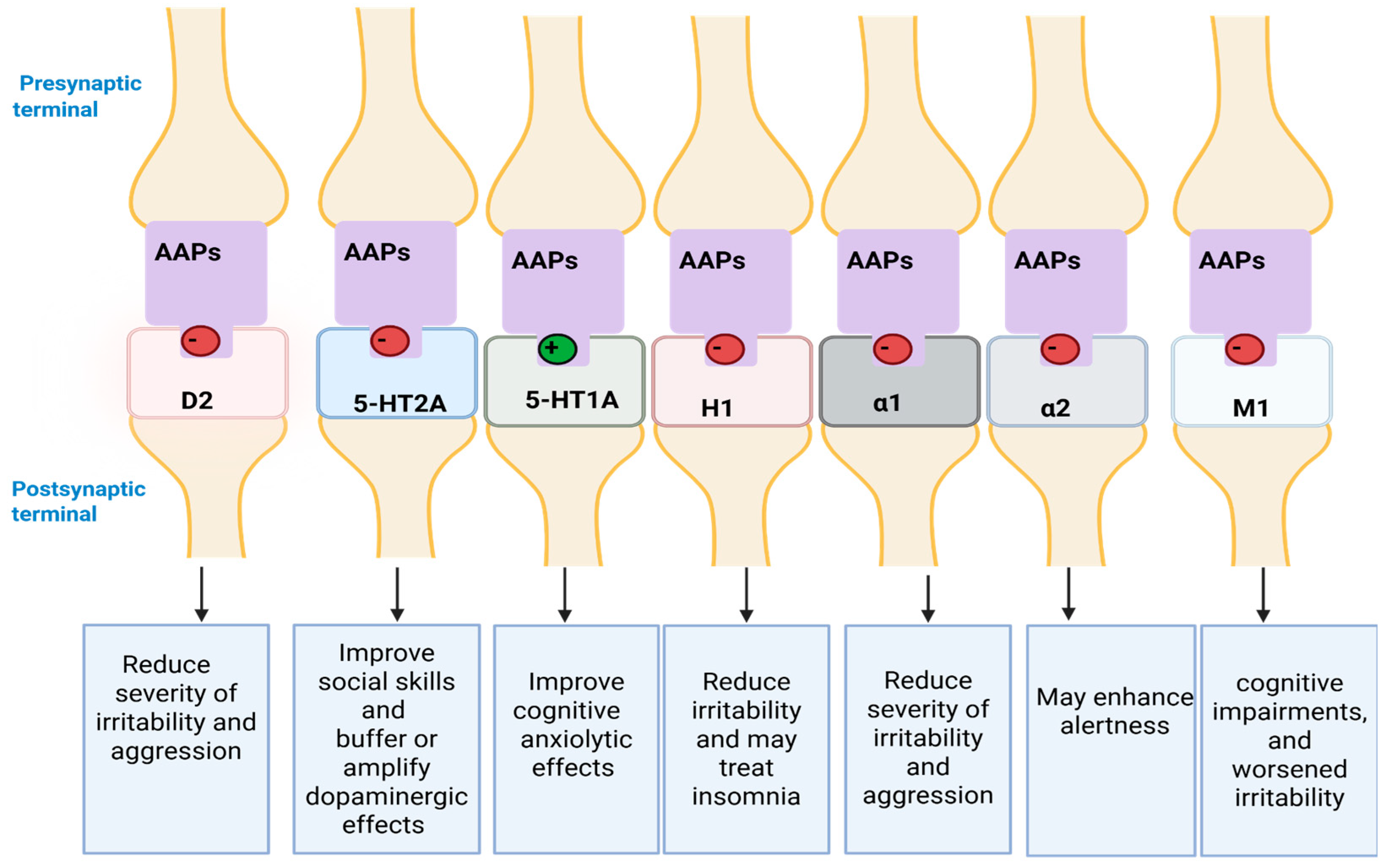
6.4. AAPs
6.4.1. Clinical Indications
Core Features
Irritability, Aggression, and Self-Injury
Comorbidities with ASD
6.4.2. Dosages for ASD in Paediatrics
6.4.3. Mechanism of Action (MoA)
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAPs | Atypical antipsychotics | H1, H1R | Histamine 1 Receptor |
| ABC-I | Aberrant Behavioural Checklist–Irritability | HCPs | Health care professionals |
| ADDM | Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring | HPT | Hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid |
| ADHD | Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder | ICD-10/11 | International Classification of Diseases, 10th/11th edition |
| ADI-R | Autism Diagnostic Interview—Revised | IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| ADRs | Adverse drug reactions | M1 | Muscarinic acetylcholine |
| ADOS | Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule | MAPKAPK3 | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Activated Protein Kinase 3 |
| ARID1B | AT-Rich Interaction Domain 1B | MAO | Monoamine oxidase |
| ASD | Autism spectrum disorder | MoA | Mechanism of Action |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor | mTORC1 | Mechanistic target of the rapamycin complex 1 |
| BMI | Body mass index | MRDBPC | Multicentre randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled |
| CDD | Childhood disintegrative disorder | MRPL33 | Mitochondrial Ribosomal Protein L33 |
| CGI-I | Clinical Global Impressions—Improvement | OR | Odds ratio |
| Cmax | Maximum plasma concentration | PDD | Pervasive Developmental Disorder |
| CNS | Central nervous system | PDD-NOS | Pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease | PI3 | Phosphatidylinositol-3 |
| Cl | Confidence interval | PKA/B | Protein kinase A/B |
| CREB | Response element-binding protein | PPB | Plasma protein binding |
| D2 | Dopamine D2 | PRR | Proportional reporting ratio |
| D2R, DRD2 | Dopamine receptor D2 | RCTs | Randomized controlled trials |
| DDIs | Drug–drug interactions | SCN3A | sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 3 |
| DSM-III | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders—Third Edition | SFARI | Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative |
| DSM-IV | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders—Fourth Edition | SMD | Standardized mean difference |
| DSM-5 | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders—Fifth Edition | SNO | S-nitrosylation |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram | SSRIs | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors |
| FAERS | FDA Adverse Event Reporting System | SV2A | Synaptic vesicle membrane protein 2A |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration | t1/2 | Half-life |
| FMR1 | Fragile X syndrome | TNF-α | Tumour necrosis factor-alpha |
| G6Pase | Glucose-6-Phosphatase | TRAF7 | TNF receptor associated factor 7 |
| GABA | Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid | TSC1/TSC2 | Tuberous sclerosis complex |
| GABA-T | GABA transaminase | VMAT-2 | Vesicular monoamine transporter 2 |
| GAD | Glutamic acid decarboxylase | WES | Whole exome sequencing |
| GBD | Global Burden of Disease | α1/α2 | alpha-1/2 adrenergic |
| GSK3β | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta | 5-HT1A/2A | Serotonin receptors (1A/2A subtype) |
References
- GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moitra, M.; Owens, S.; Hailemariam, M.; Wilson, K.S.; Mensa-Kwao, A.; Gonese, G.; Kamamia, C.K.; White, B.; Young, D.M.; Collins, P.Y. Global mental health: Where we are and where we are going. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2023, 25, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldelli-Maia, J.M.; Bhugra, D. Analysis of global prevalence of mental and substance use disorders within countries: Focus on sociodemographic characteristics and income levels. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2022, 34, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiukwu, F.; de Filippis, R.; Orsolini, L.; Gashi Bytyçi, D.; Shoib, S.; Ransing, R.; Slaih, M.; Jaguga, F.; Handuleh, J.I.; Ojeahere, M.I. Scaling up global mental health services during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond. Psychiatr. Serv. 2022, 73, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, J.; Huang, Y.; Han, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, X. Alarming changes in the global burden of mental disorders in children and adolescents from 1990 to 2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 31, 1827–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeshaft, A.; Blakey, R.; Kwong, A.S.; Riglin, L.; Smith, G.D.; Stergiakouli, E.; Tilling, K.; Thapar, A. Mental-health before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in adults with neurodevelopmental disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 159, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K.; Gupta, J.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Kumar, R.; Meena, A.K.; Madaan, P.; Sharawat, I.K.; Gulati, S. Psychological and behavioral impact of lockdown and quarantine measures for COVID-19 pandemic on children, adolescents and caregivers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2021, 67, fmaa122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieling, C.; Buchweitz, C.; Caye, A.; Silvani, J.; Ameis, S.H.; Brunoni, A.R.; Cost, K.T.; Courtney, D.B.; Georgiades, K.; Merikangas, K.R. Worldwide prevalence and disability from mental disorders across childhood and adolescence: Evidence from the global burden of disease study. JAMA Psychiatry 2024, 81, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hus, Y.; Segal, O. Challenges surrounding the diagnosis of autism in children. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2021, 17, 3509–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wang, H.; Ning, W.; Cui, M.; Wang, Q. New advances in the diagnosis and treatment of autism spectrum disorders. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dakroury, W.A.; Alnemary, F.M.; Alnemary, F. Autism in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Current situation and future perspectives for services and research. Perspect. ASHA Spec. Interest 2022, 7, 2104–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buescher, A.V.; Cidav, Z.; Knapp, M.; Mandell, D.S. Costs of autism spectrum disorders in the United Kingdom and the United States. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringsheim, T.; Panagiotopoulos, C.; Davidson, J.; Ho, J.; CAMESA Guideline Group. Evidence-based recommendations for monitoring safety of second-generation antipsychotics in children and youth. Paediatr. Child Health 2011, 16, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.P.N.; Itria, A.; Lopes, L.C. Budget Impact Analysis of Risperidone Use and Adverse Event Monitoring in Autism Spectrum Disorder in Brazil: Assessment of Theoretical Versus Real Data. PharmacoEconom.-Open 2023, 7, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.E. Social skills deficits in autism spectrum disorder: Potential biological origins and progress in developing therapeutic agents. CNS Drugs 2018, 32, 713–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, N.E.; Lord, C.; Volkmar, F.R. The diagnosis of autism: From Kanner to DSM-III to DSM-5 and beyond. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 4253–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asperger, H. Die “Autistischen psychopathen” im kindesalter. Arch. Psychiatr. Nervenkr. 1944, 117, 76–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joon, P.; Kumar, A.; Parle, M. What is autism? Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 73, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.C. DSM-IV: Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. JAMA 1994, 272, 828–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetit, R.; Hillary, R.F.; Price, D.J.; Lawrie, S.M. The neuropathology of autism: A systematic review of post-mortem studies of autism and related disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 129, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Dell’Aquila, A. The diagnosis of “pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified”: A systematic literature review. Children 2023, 10, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Garikipati, A.; Ciobanu, M.; Singh, N.; Browning, E.; DeCurzio, J.; Barnes, G.; Dinenno, F.; Mao, Q.; Das, R. Machine learning differentiation of autism spectrum sub-classifications. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2024, 54, 4216–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlani, V.; Motlani, G.; Thool, A.; Thool, A.R. Asperger syndrome (AS): A review article. Cureus 2022, 14, e31395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Arnfred, S.; Carlsson, J.; Nylander, L.; Pedersen, L.; Mortensen, E.L.; Handest, P. Self-disorders in asperger syndrome compared to schizotypal disorder: A clinical study. Schizophr. Bull. 2020, 46, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M. Clinical Diagnosis of Autism: An Evaluation of the Developmental Protocol. Ph.D. Thesis, Divine Mercy University, Sterling, VA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rudin, I.V. Speech disorders of genetic origin in teaching practice. Educ. Pedagog. J. 2021, 1, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sarma, J.; Nayak, D.; Dabria, T. A Case Report on Rett’s Syndrome. Indian J. Private Psychiatry 2024, 18, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.J.; Larsen, K.; Havighurst, S.S. Childhood Disintegrative Disorder (CDD): Symptomatology of the Norwegian patient population and parents’ experiences of patient regression. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2022, 52, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vara, S.; Guerrera, S.; Valeri, G.; Vicari, S. Later onset of childhood disintegrative disorder (CDD): A case report. Neurocase 2022, 28, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, N.L.; Fial, A.; Van Hecke, A.V.; Whitmore, K.; Meyer, K.; Pena, S.; Carlson, M.; Koth, K.A. A scoping review of diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in primary care. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2023, 37, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Posar, A.; Visconti, P. Autism Spectrum Disorder and the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders—Fifth Edition (DSM-5): The Experience of 10 Years. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2023, 58, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp-Becker, I. Autism spectrum disorder in ICD-11—A critical reflection of its possible impact on clinical practice and research. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterstrom, F.K.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Wang, J.; Breen, M.S.; De Rubeis, S.; An, J.-Y.; Peng, M.; Collins, R.; Grove, J.; Klei, L. Large-scale exome sequencing study implicates both developmental and functional changes in the neurobiology of autism. Cell 2020, 180, 568–584.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.-C.; Lin, L.-S.; Long, S.; Ke, X.-Y.; Fukunaga, K.; Lu, Y.-M.; Han, F. Signalling pathways in autism spectrum disorder: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidan, J.; Fombonne, E.; Scorah, J.; Ibrahim, A.; Durkin, M.S.; Saxena, S.; Yusuf, A.; Shih, A.; Elsabbagh, M. Global prevalence of autism: A systematic review update. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosvenor, L.P.; Croen, L.A.; Lynch, F.L.; Marafino, B.J.; Maye, M.; Penfold, R.B.; Simon, G.E.; Ames, J.L. Autism diagnosis among US children and adults, 2011–2022. JAMA Netw Open. 2024, 7, e2442218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciver, D.; Roy, A.S.; Johnston, L.; Boilson, M.; Curnow, E.; Johnstone-Cooke, V.; Rutherford, M. Waiting times and influencing factors in children and adults undergoing assessment for autism, ADHD, and other neurodevelopmental differences. Autism Res. 2025, 18, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, R.; Lindenbaum, A.; Ravi, M.; Robsky, W.; Flahive, J.; Garrison, W. Improving early identification and access to diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in toddlers in a culturally diverse community with the rapid interactive screening test for autism in toddlers. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 3937–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A. Arab views on autism. In Encyclopedia of Autism Spectrum Disorders; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 302–305. [Google Scholar]
- AlBatti, T.H.; Alsaghan, L.B.; Alsharif, M.F.; Alharbi, J.S.; BinOmair, A.I.; Alghurair, H.A.; Aleissa, G.A.; Bashiri, F.A. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among Saudi children between 2 and 4 years old in Riyadh. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2022, 71, 103054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Nions, E.; Petersen, I.; Buckman, J.E.; Charlton, R.; Cooper, C.; Corbett, A.; Happé, F.; Manthorpe, J.; Richards, M.; Saunders, R. Autism in England: Assessing underdiagnosis in a population-based cohort study of prospectively collected primary care data. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2023, 29, 100626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maenner, M.J. Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2020. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2023, 72, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saure, E.; Castrén, M.; Mikkola, K.; Salmi, J. Intellectual disabilities moderate sex/gender differences in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2023, 67, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canitano, R.; Bozzi, Y. Autism Spectrum Disorder with Epilepsy: A Research Protocol for a Clinical and Genetic Study. Genes 2023, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougeard, C.; Picarel-Blanchot, F.; Schmid, R.; Campbell, R.; Buitelaar, J. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder and co-morbidities in children and adolescents: A systematic literature review. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 744709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, A.K.; Stanton, J.; Hans, S.; Grabrucker, A. Chapter 1: Autism spectrum disorders: Etiology and patholog. In Autism Spectrum Disorders [Internet]; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2021; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lunina, D. A Meta-analysis of Syndromic Autism Genes. Int. J. High Sch. Res. 2023, 5, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sarraj, Y.; Taha, R.Z.; Al-Dous, E.; Ahram, D.; Abbasi, S.; Abuazab, E.; Shaath, H.; Habbab, W.; Errafii, K.; Bejaoui, Y. The genetic landscape of autism spectrum disorder in the Middle Eastern population. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1363849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baris, R.O.; Sahin, N.; Bilgic, A.D.; Ozdemir, C.; Edgunlu, T.G. Molecular and in silico analyses of SYN III gene variants in autism spectrum disorder. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 192, 2887–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- database SFARISg. Gene Scoring Module. Available online: https://gene.sfari.org/database/gene-scoring/ (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Mitchell, R.A.; Mitchell, M.; Williams, K. The autism spectrum disorder phenotype in children with tuberous sclerosis complex: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2022, 64, 1214–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehesh, T.; Mosleh-Shirazi, M.A.; Jafari, S.; Abolhadi, E.; Dehesh, P. A assessment of the effects of parental age on the development of autism in children: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. BMC Psychol. 2024, 12, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tioleco, N.; Silberman, A.E.; Stratigos, K.; Banerjee-Basu, S.; Spann, M.N.; Whitaker, A.H.; Turner, J.B. Prenatal maternal infection and risk for autism in offspring: A meta-analysis. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 1296–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.L.; Paraíso-Luna, J.; Bustos-Martínez, I.; Barco, Á. Targeting epigenetic dysregulation in autism spectrum disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 1028–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beversdorf, D.Q.; Anagnostou, E.; Hardan, A.; Wang, P.; Erickson, C.A.; Frazier, T.W.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J. Precision medicine approaches for heterogeneous conditions such as autism spectrum disorders (The need for a biomarker exploration phase in clinical trials-Phase 2m). Front. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 1079006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Liang, Z.; Ma, G.; Qureshi, A.; Ran, X.; Feng, C.; Liu, X.; Yan, X.; Shen, L. Autism spectrum disorder: Pathogenesis, biomarker, and intervention therapy. MedComm 2024, 5, e497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencer, S.; Kartawy, M.; Lendenfeld, F.; Soluh, H.; Tripathi, M.K.; Khaliulin, I.; Amal, H. Proteomics of autism and Alzheimer’s mouse models reveal common alterations in mTOR signaling pathway. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.D.; Jha, N.K.; Ojha, S.; Sadek, B. mTOR Signaling Disruption and Its Association with the Development of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Molecules 2023, 28, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, M.; Zerbi, V.; Gini, S.; Alvino, F.; Banerjee, A.; Barberis, A.; Basson, M.A.; Bozzi, Y.; Galbusera, A.; Ellegood, J.; et al. Biological subtyping of autism via cross-species fMRI. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; He, X.; Qian, L.; Zhao, B.; Fan, Y.; Gao, F.; Yan, B.; Zhu, F.; Ma, X. Association between plasma proteome and childhood neurodevelopmental disorders: A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. EBioMedicine 2022, 78, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román, P.; Ruiz-González, C.; Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Cardona, D.; Requena, M.; Alarcón, R. Exposure to Environmental Pesticides and the Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Medicina 2024, 60, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Membrino, V.; Di Paolo, A.; Alia, S.; Papiri, G.; Vignini, A. The role of oxidative stress in autism spectrum disorder: A narrative literature review. Oxygen 2023, 3, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długosz, A.; Wróblewski, M.; Błaszak, B.; Szulc, J. The Role of Nutrition, Oxidative Stress, and Trace Elements in the Pathophysiology of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevi, F.; Belardo, A.; Zolla, L. A metabolomics approach to investigate urine levels of neurotransmitters and related metabolites in autistic children. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwierz, M.; Suprunowicz, M.; Mrozek, K.; Pietruszkiewicz, J.; Oracz, A.J.; Konarzewska, B.; Waszkiewicz, N. Vitamin B12 and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Review of Current Evidence. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, M.L.; McAllister, A.K. Immune mediators in the brain and peripheral tissues in autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, S.F.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Sarawi, W.; Attia, S.M.; Bakheet, S.A.; Alqarni, S.A.; Ali, N.; AsSobeai, H.M. Imbalance in pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines milieu in B cells of children with autism. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 141, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Microglia and astrocytes underlie neuroinflammation and synaptic susceptibility in autism spectrum disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1125428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, N.; Sarajlija, A. Neuroglial Dysregulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Pathogenetic Insights, Genetic Threads, and Therapeutic Horizons. Neuroglia 2025, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Li, T.; Qin, R.; Li, L.; Yuan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Gray matter asymmetry alterations in children and adolescents with comorbid autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2024, 33, 2593–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Hiremath, C.; Khokhar, S.K.; Bansal, E.; Sagar, K.J.V.; Padmanabha, H.; Girimaji, A.S.; Narayan, S.; Kishore, M.T.; Yamini, B. Altered cerebellar lobular volumes correlate with clinical deficits in siblings and children with ASD: Evidence from toddlers. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamanna, J.; Meldolesi, J. Autism Spectrum disorder: Brain areas involved, neurobiological mechanisms, diagnoses and therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffat, J.J.; Smith, A.L.; Jung, E.-M.; Ka, M.; Kim, W.-Y. Neurobiology of ARID1B haploinsufficiency related to neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Gomez, D.A.; Garcia-Guaqueta, D.P.; Charry-Sánchez, J.D.; Sarquis-Buitrago, E.; Blanco, M.; Velez-van-Meerbeke, A.; Talero-Gutiérrez, C. A systematic review of common genetic variation and biological pathways in autism spectrum disorder. BMC Neurosci. 2021, 22, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Bowirrat, A.; Sunder, K.; Thanos, P.K.; Hanna, C.; Gold, M.S.; Dennen, C.A.; Elman, I.; Murphy, K.T.; Makale, M.T. Dopamine dysregulation in reward and autism spectrum disorder. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascucci, T.; Colamartino, M.; Fiori, E.; Sacco, R.; Coviello, A.; Ventura, R.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; Turriziani, L.; Persico, A.M. P-cresol Alters Brain Dopamine Metabolism and Exacerbates Autism-like Behaviors in the BTBR Mouse. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiCarlo, G.E.; Aguilar, J.I.; Matthies, H.J.; Harrison, F.E.; Bundschuh, K.E.; West, A.; Hashemi, P.; Herborg, F.; Rickhag, M.; Chen, H.; et al. Autism-linked dopamine transporter mutation alters striatal dopamine neurotransmission and dopamine-dependent behaviors. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3407–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandic-Maravic, V.; Grujicic, R.; Milutinovic, L.; Munjiza-Jovanovic, A.; Pejovic-Milovancevic, M. Dopamine in autism spectrum disorders—Focus on D2/D3 partial agonists and their possible use in treatment. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 787097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, M.; Kumar, A. Correlation of mutated gene and signalling pathways in ASD. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2023, 14, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico, D.; Mapelli, L. Dopaminergic Modulation of Prefrontal Cortex Inhibition. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, L.; van Wingen, G.; Cerliani, L. Atypically high influence of subcortical activity on primary sensory regions in autism. NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 32, 102839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Mao, X.; Zhu, C.; Zou, X.; Peng, F.; Yang, W.; Li, B.; Li, G.; Ge, T.; Cui, R. GABAergic System Dysfunction in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 781327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marilovtseva, E.V.; Abdurazakov, A.; Kurishev, A.O.; Mikhailova, V.A.; Golimbet, V.E. The Role of GABA Pathway Components in Pathogenesis of Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, E.W.; Hammill, C.; Taylor, M.J.; Near, J.; Schachar, R.; Crosbie, J.; Arnold, P.D.; Anagnostou, E.; Lerch, J.P. Cerebellar gamma-aminobutyric acid: Investigation of group effects in neurodevelopmental disorders. Autism Res. 2023, 16, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, M.H.; Bote, V.; Serra, L.A.; Cendros, M.; Salazar, J.; Mestres, C.; Guijarro, S.; Alvarez, A.; Lamborena, C.; Mendez, I.; et al. CES1 and SLC6A2 Genetic Variants as Predictors of Response to Methylphenidate in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2022, 15, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koevoet, D.; Deschamps, P.K.H.; Kenemans, J.L. Catecholaminergic and cholinergic neuromodulation in autism spectrum disorder: A comparison to attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1078586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Duan, M.; Guo, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, H. Changes in the gut microbiota of children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2020, 13, 1614–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Fang, X.; Liang, L.; Li, H.; Dong, Z.; Fan, S.; et al. Gut microbial GABA imbalance emerges as a metabolic signature in mild autism spectrum disorder linked to overrepresented Escherichia. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 101919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Niu, B.; Ma, J.; Ge, Y.; Han, Y.; Wu, W.; Yue, C. Intervention and research progress of gut microbiota-immune-nervous system in autism spectrum disorders among students. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1535455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, R.; Risoleo, M.C.; Messina, G.; Parisi, L.; Carotenuto, M.; Vetri, L.; Roccella, M. The Neurochemistry of Autism. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Iakoucheva, L.M. Therapeutic strategies for autism: Targeting three levels of the central dogma of molecular biology. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, H.; Zhang, C.; Wan, L.; Yang, G. Prevalence Trends and Treatment Patterns of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children and Adolescents in the United States from 2017 to 2020. Neurol. Ther. 2024, 13, 1685–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denucci, B.L.; de Lima, L.S.; Mota, I.F.L.; Azevedo, J.R.M.; Veras, L.G.; Bicca, J.V.M.L.; de Miranda Santana, B.; Pinheiro, G.B.; Coelho, G.G.; Mortari, M.R. Current knowledge, challenges, new perspectives of the study, and treatments of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Reprod. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D. The metamorphosis of autism: A history of child development in britain by bonnie evans. Bull. Hist. Med. 2019, 93, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, J.H.; Yang, H.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Cortese, S.; Smith, L.; Koyanagi, A.; Dragioti, E.; Radua, J.; Fusar-Poli, P. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for irritability in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis with the GRADE assessment. Mol. Autism 2024, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, N.; Rojas, V.; Liquitay, C.M.E.; Pérez, I.; Johnson, F.A.; Osorio, C.A.; Irarrázaval, M.; Madrid, E.; Franco, J.V.A. Non-pharmacological interventions for autism spectrum disorder in children: An overview of systematic reviews. BMJ Evid. Based Med. 2023, 28, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, M.; Moradi, A.; Tehrani-Doost, M.; Hassanabadi, H.; Khosroabadi, R. Effects of combining medication and pivotal response treatment on aberrant behavior in children with autism spectrum disorder. Children 2018, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsayouf, H.A.; Talo, H.; Biddappa, M.L. Core Signs and Symptoms in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Improved after Starting Risperidone and Aripiprazole in Combination with Standard Supportive Therapies: A Large, Single-Center, Retrospective Case Series. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramerman, L.; de Kuijper, G.; Scheers, T.; Vink, M.; Vrijmoeth, P.; Hoekstra, P.J. Is risperidone effective in reducing challenging behaviours in individuals with intellectual disabilities after 1 year or longer use? A placebo-controlled, randomised, double-blind discontinuation study. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2019, 63, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davico, C.; Secci, I.; Vendrametto, V.; Vitiello, B. Pharmacological treatments in autism spectrum disorder: A narrative review. J. Psychopathol. 2023, 29, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manter, M.A.; Birtwell, K.B.; Bath, J.; Friedman, N.D.; Keary, C.J.; Neumeyer, A.M.; Palumbo, M.L.; Thom, R.P.; Stonestreet, E.; Brooks, H. Pharmacological treatment in autism: A proposal for guidelines on common co-occurring psychiatric symptoms. BMC Med. 2025, 23, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishworiya, R.; Valica, T.; Hagerman, R.; Restrepo, B. An Update on Psychopharmacological Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Focus 2024, 22, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H. Pediatric and Neurological assessments. In Textbook of Autism Spectrum Disorders, 2nd ed.; Hollander, H., Ed.; Am Psychiatric Assoc Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; pp. 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hellings, J. Pharmacotherapy in autism spectrum disorders, including promising older drugs warranting trials. World J. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonoff, E.; Mowlem, F.; Pearson, O.; Anagnostou, E.; Donnelly, C.; Hollander, E.; King, B.H.; McCracken, J.T.; Scahill, L.; Sikich, L. Citalopram did not significantly improve anxiety in children with autism spectrum disorder undergoing treatment for core symptoms: Secondary analysis of a trial to reduce repetitive behaviors. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 32, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, A.M.; Ricciardello, A.; Lamberti, M.; Turriziani, L.; Cucinotta, F.; Brogna, C.; Vitiello, B.; Arango, C. The pediatric psychopharmacology of autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review-Part I: The past and the present. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 110, 110326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncrieff, J.; Cooper, R.E.; Stockmann, T.; Amendola, S.; Hengartner, M.P.; Horowitz, M.A. The serotonin theory of depression: A systematic umbrella review of the evidence. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 3243–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Santiago, C.; Rodríguez-Pinacho, C.V.; Pérez-Sánchez, G.; Acosta-Cruz, E. Effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on endocrine system. Biomed. Rep. 2024, 21, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, J.; Knight, D.; Nemeroff, C. Second generation SSRIS: Human monoamine transporter binding profile of escitalopram and R-fluoxetine. L’encephale 2002, 28, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancu, G.; Uilăcan, A.; Blebea, N.M. Chirality in Modern Antidepressants: A Comprehensive Review of Stereochemical Impacts on Pharmacology and Therapeutics. Drugs Drug Candidates 2024, 3, 654–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-C.; Sun, W.; Lv, X.-Q.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Shi, J.-N. Escitalopram-induced sinus bradycardia in coronary heart disease combined with depression: A case report and review of literature. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 10, 1133662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Y.S.; Khoodoruth, M.A.S.; Albobali, Y.; Haddad, P.M. SSRI withdrawal syndrome in children and adolescents: A narrative literature review. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2023, 22, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohel, A.J.; Shutter, M.C.; Patel, P.; Molla, M. Fluoxetine. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.-C.; Sun, C.-K.; Fan, H.-Y.; Chung, W.; Tzang, R.-F.; Hung, K.-C.; Chiu, H.-J.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Yeh, P.-Y. Therapeutic effects of antidepressants for global improvement and subdomain symptoms of autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2022, 47, E299–E310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.; Vanwong, N.; Sukasem, C. Pharmacogenomics and non-genetic factors affecting drug response in autism spectrum disorder in Thai and other populations: Current evidence and future implications. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 14, 1285967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodnyy, A.Y.; Kondaurova, E.M.; Tsybko, A.S.; Popova, N.K.; Kudlay, D.A.; Naumenko, V.S. The brain serotonin system in autism. Rev. Neurosci. 2024, 35, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, J.; Rasga, C.; Santos, J.X.; Martiniano, H.; Marques, A.R.; Oliveira, G.; Vicente, A.M. Bridging Genetic Insights with Neuroimaging in Autism Spectrum Disorder—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachar, R.J.; Dupuis, A.; Arnold, P.D.; Anagnostou, E.; Kelley, E.; Georgiades, S.; Nicolson, R.; Townes, P.; Burton, C.L.; Crosbie, J. Autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Shared or unique neurocognitive profiles? Res. Child. Adolesc. Psychopathol. 2023, 51, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayouf, H.A. Growing evidence of pharmacotherapy effectiveness in managing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in young children with or without autism spectrum disorder: A minireview. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1408876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, S. Evidence-based prescribing of medications for ADHD: Where are we in 2023? Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2023, 24, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugaya, L.S.; Farhat, L.C.; Califano, P.; Polanczyk, G.V. Efficacy of stimulants for preschool attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JCPP Adv. 2023, 3, e12146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, S.; Adamo, N.; Del Giovane, C.; Mohr-Jensen, C.; Hayes, A.J.; Carucci, S.; Atkinson, L.Z.; Tessari, L.; Banaschewski, T.; Coghill, D. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of medications for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children, adolescents, and adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, L.; You, C.; Liu, C.; Dong, P.; Xu, X.; Zhang, K. Efficacy and safety of methylphenidate and atomoxetine in medication-naive children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in a real-world setting. Drugs R&D 2024, 24, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, S.; Bai, Y.; Leng, Y.; Chang, E.; Huang, L. Safety profiles of methylphenidate, amphetamine, and atomoxetine: Analysis of spontaneous reports submitted to the food and drug administration adverse event reporting system. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1208456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, N.; Steward, C.; Marshall, F.; Fone, K.; Marsden, C. Effects of amphetamine isomers, methylphenidate and atomoxetine on synaptosomal and synaptic vesicle accumulation and release of dopamine and noradrenaline in vitro in the rat brain. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechler, K.; Banaschewski, T.; Hohmann, S.; Häge, A. Evidence-based pharmacological treatment options for ADHD in children and adolescents. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 230, 107940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraone, S.V. The pharmacology of amphetamine and methylphenidate: Relevance to the neurobiology of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and other psychiatric comorbidities. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 87, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhao, D.; Lan, Y.; Jin, L.; Yang, L. Comparison of serious adverse effects of methylphenidate, atomoxetine and amphetamine in the treatment of ADHD: An adverse event analysis based on the FAERS database. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2025, 26, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuchat, E.E.; Bocklud, B.E.; Kingsley, K.; Barham, W.T.; Luther, P.M.; Ahmadzadeh, S.; Shekoohi, S.; Cornett, E.M.; Kaye, A.D. The role of alpha-2 agonists for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children: A review. Neurol. Int. 2023, 15, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, F.M.; Groen, Y.; Fuermaier, A.B.; Tucha, O. The female side of pharmacotherapy for ADHD—A systematic literature review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, S.L.; Levy, S.E.; Myers, S.M.; Kuo, D.Z.; Apkon, S.; Davidson, L.F.; Ellerbeck, K.A.; Foster, J.E.; Noritz, G.H.; Leppert, M.O.C. Identification, evaluation, and management of children with autism spectrum disorder. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20193447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesso, G.; Bargnesi, F.; Mutti, G.; Berloffa, S.; Viglione, V.; Fantozzi, P.; Tolomei, G.; Guccione, F.; Muratori, P.; Milone, A. Extended-Release Lithium Treatment for Adolescents with Bipolar Disorder with or Without Comorbid Autism Spectrum Disorder: Protocol of a Longitudinal Prospective Naturalistic Study for the Assessment of Efficacy and Tolerability. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlattani, T.; D’Amelio, C.; Cavatassi, A.; De Luca, D.; Di Stefano, R.; Di Berardo, A.; Mantenuto, S.; Minutillo, F.; Leonardi, V.; Renzi, G. Autism spectrum disorders and psychiatric comorbidities: A narrative review. J. Psychopathol. 2023, 29, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, S.M.; Varshney, A.; Ravi, D.; Moncy, A.M. Efficacy and Safety of Antiepileptic Drugs in the Management of Behavioral Issues in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Psychiatry Spectrum. 2025, 4, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anukirthiga, B.; Mishra, D.; Pandey, S.; Juneja, M.; Sharma, N. Prevalence of epilepsy and inter-ictal epileptiform discharges in children with autism and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Indian. J. Pediatr. 2019, 86, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canitano, R.; Palumbi, R.; Scandurra, V. Autism with epilepsy: A neuropsychopharmacology update. Genes 2022, 13, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugino, T.A.; Samsock, T.C. Levetiracetam in autistic children: An open-label study. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2002, 23, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, S.; Iyengar, R.; Chaplin, W.F.; Watner, D.; Waldoks, S.E.; Anagnostou, E.; Soorya, L.; Hollander, E. Levetiracetam versus placebo in childhood and adolescent autism: A double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 21, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.M.; Adams, J.B.; Anderson, A.L.; Frye, R.E. Rating of the effectiveness of 26 psychiatric and seizure medications for autism spectrum disorder: Results of a national survey. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, G.; Nöhles, V.B.; Ostuzzi, G.; Barbui, C.; Tedeschi, F.; Heuer, F.H.; Keller, A.; DelBello, M.P.; Welge, J.A.; Blom, T.J. Systematic review and network meta-analysis: Efficacy and safety of antipsychotics vs antiepileptics or lithium for acute mania in children and adolescents. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2024, 64, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, P.R.; do Nascimento Gonzaga, T.K.; Maia, R.E.; da Silva, B.A. Ionic channels as potential targets for the treatment of autism spectrum disorder: A review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 1834–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wei, Z.-H.; Qiao, X.-Z.; Deng, Y.-C. Genetic variations of GABA metabolism pathway and epilepsy. Ann. Genet. Genom. 2021, 2, 1006. [Google Scholar]
- Badawy, A.A.; Elghaba, R.; Soliman, M.; Hussein, A.M.; AlSadrah, S.A.; Awadalla, A.; Abulseoud, O.A. Chronic valproic acid administration increases plasma, liver, and brain ammonia concentration and suppresses glutamine synthetase activity. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, X.; Zhou, D. The efficacy of lamotrigine after failure of the first administration of valproate in treating epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2022, 11, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buraniqi, E.; Dabaja, H.; Wirrell, E.C. Impact of antiseizure medications on appetite and weight in children. Pediatr. Drugs 2022, 24, 335–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakami, T. Neuropharmacology of antiseizure drugs. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2021, 41, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-García, I.J.; Gómez-Lira, G.; Phillips-Farfán, B.V.; Pichardo-Macías, L.A.; García-Cruz, M.E.; Chávez-Pacheco, J.L.; Mendoza-Torreblanca, J.G. Synaptic vesicle protein 2a expression in glutamatergic terminals is associated with the response to levetiracetam treatment. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Incal, C.; Broos, J.; Torfs, T.; Kooy, R.F.; Vanden Berghe, W. Towards kinase inhibitor therapies for fragile X syndrome: Tweaking twists in the autism spectrum kinase signaling network. Cells 2022, 11, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanaatfar, F.; Ghanaatfar, A.; Isapour, P.; Farokhi, N.; Bozorgniahosseini, S.; Javadi, M.; Gholami, M.; Ulloa, L.; Coleman-Fuller, N.; Motaghinejad, M. Is lithium neuroprotective? An updated mechanistic illustrated review. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutalib, N.A.; Rafi, M.A.A.M.; Latip, N.A. Revisiting cyp2c9-mediated drug-drug interactions: A review. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2021, 14, 6166–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Mei, S.; Feng, W. Population pharmacokinetics of topiramate in Chinese children with epilepsy. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 79, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauzin, M.; Tréluyer, J.M.; Nabbout, R.; Billette de Villemeur, T.; Desguerre, I.; Aboura, R.; Gana, I.; Zheng, Y.; Benaboud, S.; Bouazza, N. Dosing recommendations for lamotrigine in children: Evaluation based on previous and new population pharmacokinetic models. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 61, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauzin, M.; Tréluyer, J.M.; Nabbout, R.; Chemaly, N.; Billette de Villemeur, T.; Desguerre, I.; Lui, G.; Gana, I.; Boujaafar, S.; Zheng, Y. Predictive performance of population pharmacokinetic models of levetiracetam in children and evaluation of dosing regimen. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 61, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatza, E.; Sinha, J.; Maglalang, P.D.; Edginton, A.; Gonzalez, D. Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Total and Unbound Valproic Acid to Evaluate Dosing in Children With and Without Hypoalbuminemia. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2024, 63, 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Zhou, W.; Hu, K.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.; Shao, F. Population Pharmacokinetics of Lithium in Young Pediatric Patients With Intellectual Disability. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 650298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.; Carmo, F.; Martel, F. Metabolic effects of atypical antipsychotics: Molecular targets. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2023, 35, e13347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Hao, S.; Williamson, T.; McMorris, C.A.; Bousman, C.A. Psychotropic prescribing rates and pharmacogenomic testing implications for autism in the Canadian primary care sentinel surveillance network. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2022, 32, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alò, G.L.; De Crescenzo, F.; Amato, L.; Cruciani, F.; Davoli, M.; Fulceri, F.; Minozzi, S.; Mitrova, Z.; Morgano, G.P.; Nardocci, F. Impact of antipsychotics in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2021, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.S.; Nasir, M.; Farhat, L.C.; Kook, M.; Artukoglu, B.B.; Bloch, M.H. Meta-analysis: Pharmacologic treatment of restricted and repetitive behaviors in autism spectrum disorders. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 60, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pablo, G.S.; Jorda, C.P.; Vaquerizo-Serrano, J.; Moreno, C.; Cabras, A.; Arango, C.; Hernández, P.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J.; Simonoff, E.; Fusar-Poli, P. Systematic review and meta-analysis: Efficacy of pharmacological interventions for irritability and emotional dysregulation in autism spectrum disorder and predictors of response. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2023, 62, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Policy and Global Affairs; Committee on Women in Science, Engineering, and Medicine; Committee on Improving the Representation of Women and Underrepresented Minorities in Clinical Trials and Research. Improving Representation in Clinical Trials and Research: Building Research Equity for Women and Underrepresented Groups; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, J.Y.; Liu, M.F. Culturally tailored interventions for ethnic minorities: A scoping review. Nurs. Open 2021, 8, 2078–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, E.; Wasserman, S.; Swanson, E.N.; Chaplin, W.; Schapiro, M.L.; Zagursky, K.; Novotny, S. ADouble-blind placebo-controlled pilot study of olanzapine in childhood/adolescent pervasive developmental disorder. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 16, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loebel, A.; Brams, M.; Goldman, R.S.; Silva, R.; Hernandez, D.; Deng, L.; Mankoski, R.; Findling, R.L. Lurasidone for the treatment of irritability associated with autistic disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findling, R.L.; McNamara, N.K.; Gracious, B.L.; O’Riordan, M.A.; Reed, M.D.; Demeter, C.; Blumer, J.L. Quetiapine in nine youths with autistic disorder. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2004, 14, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubchik, P.; Sever, J.; Weizman, A. Low-dose quetiapine for adolescents with autistic spectrum disorder and aggressive behavior: Open-label trial. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2011, 34, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tololeski, B.P.; Radobuljac, M.D. Quetiapine treatment in pediatric scenarios. In Diagnosis, Management and Modeling of Neurodevelopmental Disorders; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 395–404. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, N.; Torrents, R.; Azorin, J.-M. Comorbidities and the right dose: Antipsychotics. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2022, 18, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasser, R.; Modesto, B.; Penido, A.L.R.; Palma, S.M.M. Lurasidone in the Management of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A review. Braz. J. Glob. Health. 2021, 1, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominick, K.; Wink, L.K.; McDougle, C.J.; Erickson, C.A. A retrospective naturalistic study of ziprasidone for irritability in youth with autism spectrum disorder. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-H. Pharmacokinetic Prediction of Immediate-and Extended-Release Tablets for Patients with Liver Disease Using Whole Body Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling for the Antipsychotic Drug Quetiapine. AAPS PharmSciTech 2025, 26, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifu, S.; Trifu, A.D. Receptor profiles of atypical antipsychotic molecules. UPB Sci. Bull. Ser. B Chem. Mater. Sci. 2020, 82, 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, M.; Vanwong, N.; Sukasem, C. Pharmacogenomics in clinical practice to prevent risperidone-induced hyperprolactinemia in autism spectrum disorder. Pharmacogenomics 2022, 23, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Program NIoMHPDS. PDSP Ki Database. Available online: https://pdsp.unc.edu/databases/kidb.php (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Mano-Sousa, B.J.; Pedrosa, A.M.; Alves, B.C.; Galduróz, J.C.F.; Belo, V.S.; Chaves, V.E.; Duarte-Almeida, J.M. Effects of risperidone in autistic children and young adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 538–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J.; Folawemi, O.; Bittla, P.; Kaur, S.; Sojitra, V.; Zahra, A.; Khan, S. The Effects of Risperidone on Cognition in People with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e45524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanth, M. Benzisoxazole Derivatives: Synthesis and Their Therapeutic Significance in Medicinal Chemistry. In Recent Developments in Chemistry and Biochemistry Research; BP International: Hooghly, India, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Issifou, H.S.T. Molecular Modelling of Interactions Between Antipsychotic Drugs and Receptors Mediating Antipsychotic Effects and Important Side Effects. Master’s Thesis, UiT Norges arktiske universitet, Alta, Norway, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Avramets, D.; Jeon, B.; Choo, H. Modulation of serotonin receptors in neurodevelopmental disorders: Focus on 5-HT7 receptor. Molecules 2021, 26, 3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, S.; Takao, C.; Matsudaira, K.; Sato, N.; Tu, T.T.H.; Niwa, S.-I.; Uchida, K.; Toyofuku, A. Case report: Treatment of persistent atypical odontalgia with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder with risperidone and atomoxetine. Front. Pain. Res. 2022, 3, 926946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrico, T.; Kahlon, A. Pathophysiology and management of risperidone-induced sialorrhea: Case report. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1185750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlambo, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Tan, S.; Chen, C. Receptors involved in mental disorders and the use of clozapine, chlorpromazine, olanzapine, and aripiprazole to treat mental disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Kong, J.; Tan, Q.-R.; Li, X.-M. Neuroprotective effect of atypical antipsychotics in cognitive and non-cognitive behavioral impairment in animal models. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2009, 3, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneller, L.A.; Abad-Santos, F.; Hempel, G. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling to describe the pharmacokinetics of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone according to cytochrome P450 2D6 phenotypes. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 59, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamnanphon, M.; Vanwong, N.; Prommas, S.; Koomdee, N.; Sukprasong, R.; Rachanakul, J.; Nuntharadthanaphong, N.; Hongkaew, Y.; John, S.; Ngamsamut, N. Risperidone plasma concentrations are associated with hyperprolactinemia in autism spectrum disorder children: The impact of CYP2D6 polymorphisms. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2022, 96, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustapha, M.E.; Geesi, M.H.; Farag, Z.R.; Anouar, E.H. Electrophilic aromatic synthesis of radioiodinated aripiprazole: Experimental and DFT investigations. Curr. Org. Synth. 2020, 17, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bon, E.; Rai, K. The Place of Antipsychotics in The Treatment of Anxiety Disorders. Int. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2024, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doutor, G.C.; Leão Filho HRd, S.; Santos, T.S.B.; Silva, V.R.A.; Nascimento, L.L.; Guimarães, L.C.K.; Marques, I.E.; Caetano FOd, C.; Bertoloni, V.F.; Ribeiro, G. Efetividade e segurança da risperidona e aripiprazol no tratamento do transtorno do espectro autista: Uma revisão narrativa. Rev. Med. 2025, 104, 227101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, H.; Mishra, A.; Mishra, A.K. Aripiprazole: An FDA approved bioactive compound to treat schizophrenia—A mini review. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2020, 17, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Moura, A.C.H.V. Antipsicóticos Atípicos no Tratamento da Irritabilidade Severa em Crianças e Adolescentes com Perturbação do Espectro do Autismo: Uma Revisão. Master’s Thesis, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2020. Available online: https://repositorio-aberto.up.pt/handle/10216/128754 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Bartram, L.A.; Lozano, J.; Coury, D.L. Aripiprazole for treating irritability associated with autism spectrum disorders. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2019, 20, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preda, A.; Shapiro, B.B. A safety evaluation of aripiprazole in the treatment of schizophrenia. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2020, 19, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneller, L.A.; Zubiaur, P.; Koller, D.; Abad-Santos, F.; Hempel, G. Influence of CYP2D6 phenotypes on the pharmacokinetics of aripiprazole and dehydro-aripiprazole using a physiologically based pharmacokinetic approach. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 60, 1569–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolli, P.; Kelley, G.; Rosales, M.; Faden, J.; Serdenes, R. Olanzapine pharmacokinetics: A clinical review of current insights and remaining questions. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2023, 16, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, M.; Nikolic, T.; Turnic, M.; Djuric, D.; Mitrović, M.; Nikolić, T.; Turnić, M.; Đurić, D. Olanzapine-Focus on the Cardiometabolic Side Effects. Serbian J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2021, 22, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohith, A.N.; Ramesh, P.; Vaidya, B.P.; Shenoy, S.; Sharma, P.S.V.N. Olanzapine-associated chronic urinary retention and ciliochoroidal effusion: Rare adverse effects of a commonly prescribed antipsychotic. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2023, 45, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.; Castellani, L.N.; Kowalchuk, C.; Alganem, K.; Zhang, X.; Ryan, W.G.; Singh, R.; Wu, S.; Au, E.; Asgariroozbehani, R. Olanzapine’s effects on hypothalamic transcriptomics and kinase activity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2024, 163, 106987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado, B.; Dunn, J.; Veronin, M.A.; Reinert, J.P. Efficacy and safety considerations with second-generation antipsychotics as adjunctive analgesics: A review of literature. J. Pharm. Technol. 2021, 37, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, M.; Paletta, S.; Maffini, M.; Colasanti, A.; Dragogna, F.; Di Pace, C.; Altamura, A. Clinical pharmacology of atypical antipsychotics: An update. EXCLI J. 2014, 13, 1163–1191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lerond, J.; Lothe, A.; Ryvlin, P.; Bouvard, S.; d’Amato, T.; Ciumas, C.; Daléry, J.; Poulet, E.; Saoud, M. Effects of aripiprazole, risperidone, and olanzapine on 5-HT1A receptors in patients with schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 33, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, D.E.; Richards, B.L. A brief review of quetiapine. Am. J. Psychiatry Resid. J. 2022, 18, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, S.; Parvataneni, T.; Makani, R.; Patel, R.S. Efficacy and safety of quetiapine for pediatric bipolar depression: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Cureus 2020, 12, e8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Muñoz, F.; Álamo, C. Active metabolites as antidepressant drugs: The role of norquetiapine in the mechanism of action of quetiapine in the treatment of mood disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2013, 4, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amerio, A.; Giacomini, C.; Fusar-Poli, L.; Aguglia, A.; Costanza, A.; Serafini, G.; Aguglia, E.; Amore, M. Efficacy and safety of lurasidone in children and adolescents: Recommendations for clinical management and future research. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 4062–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzelska-Górka, J.; Mikulska, J.; Wiszniewska, A.; Biała, G. New atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia and depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, F.; Arone, A.; Gurrieri, R.; Weiss, F.; Russomanno, G.; Marazziti, D. Third-Generation Antipsychotics: The Quest for the Key to Neurotrophism. Life 2025, 15, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, V.; De Berardis, D.; Maina, G. Third-generation antipsychotics and lurasidone in the treatment of substance-induced psychoses: A narrative review. Healthcare 2024, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živković, N.; Mrkalić, E.; Jelić, R.; Tomović, J.; Odović, J.; Serafinović, M.Ć.; Sovrlić, M. The Molecular Recognition of Lurasidone by Human Serum Albumin: A Combined Experimental and Computational Approach. Molecules 2025, 30, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čarapić, M.; Marković, B.; Pavlovic, M.; Agbaba, D.; Nikolic, K. Comparative study of performances of UHPLC-MS/MS and HPLC/UV methods for analysis of ziprasidone and its main impurities. Acta Chromatogr. 2023, 35, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.C.; Miners, J.O.; McKinnon, R.A.; Langmead, C.J.; Gregory, K.J.; Copolov, D.; Chan, S.K.W.; Bastiampillai, T. Binding of SEP-363856 within TAAR1 and the 5HT1A receptor: Implications for the design of novel antipsychotic drugs. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman-Tancredi, A.; Kleven, M.S. Comparative pharmacology of antipsychotics possessing combined dopamine D 2 and serotonin 5-HT 1A receptor properties. Psychopharmacology 2011, 216, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foresteire, N.P.; Howard, C.; Szustkiewicz, K. Tricyclic Antidepressant and Antipsychotic Toxicity: Clomipramine and Ziprasidone Overdose. Cureus 2024, 16, e63691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalari, V.K.; Morrison, P.E.; Budman, C.L. Atypical antipsychotics for treatment of Tourette syndrome. In International Review of Movement Disorders; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 4, pp. 203–235. [Google Scholar]
- Radmard, A.; Banga, A.K. Microneedle-Assisted Transdermal Delivery of Lurasidone Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Liu, W.; Duan, C.; Chen, Z.; Han, J.; Song, J.; Zhuang, T.; Zhang, X. Drug-drug solid dispersions of two hydrophobic antipsychotics and DP-VPA-C18 with improved pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 108, 106859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgioni, G.; Bonifazi, A.; Botticelli, L.; Cifani, C.; Matteucci, F.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, E.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Giannella, M.; Piergentili, A.; Piergentili, A. Advances in drug design and therapeutic potential of selective or multitarget 5--HT1A receptor ligands. Med. Res. Rev. 2024, 44, 2640–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, A.; Asati, V.; Kashaw, S.K.; Agarwal, S.; Parwani, D.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mallick, C. The recent development of piperazine and piperidine derivatives as antipsychotic agents. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 362–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacivita, E.; Niso, M.; Mastromarino, M.; Garcia Silva, A.; Resch, C.; Zeug, A.; Loza, M.I.; Castro, M.; Ponimaskin, E.; Leopoldo, M. Knowledge-based design of long-chain arylpiperazine derivatives targeting multiple serotonin receptors as potential candidates for treatment of autism spectrum disorder. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razakarivony, O.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Zimmer, L. Towards in vivo imaging of functionally active 5-HT1A receptors in schizophrenia: Concepts and challenges. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.J.; McCall, W.V. Insomnia and suicide as reported adverse effects of second-generation antipsychotics and mood stabilizers. J. Clin. Sleep. Med. 2022, 18, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, S.; Wang, F.; Angriman, M.; Masi, G.; Bruni, O. Sleep disorders in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: Diagnosis, epidemiology, and management. CNS Drugs 2020, 34, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qassim, M.; Sin, J. Assisting the person with medication. In Working with Serious Mental Illness: A Manual For Clinical Practice, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- FAERS, F. A Comparison of Pediatric and Adult Safety Studies for Antipsychotic and Antidepressant Drugs Submitted to the United States Food and Drug Administration. J. Pediatr. 2019, 208, 236–242.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Tian, H.; Zhuo, C. Exploring the potential pharmacological mechanism of aripiprazole against hyperprolactinemia based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Schizophrenia 2024, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meza, N.; Rees, R.; Liquitay, C.M.E.; Franco, J.V.; Sguassero, Y.; Williams, K.; Pringsheim, T.; Rojas, V.; Madrid, E. Atypical antipsychotics for autism spectrum disorder: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 5, CD014965. [Google Scholar]
- Wannasuphoprasit, Y.; Andersen, S.E.; Arranz, M.J.; Catalan, R.; Jurgens, G.; Kloosterboer, S.M.; Rasmussen, H.B.; Bhat, A.; Irizar, H.; Koller, D. CYP2D6 Genetic variation and antipsychotic-induced weight gain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 2022, 12, 768748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leucht, S.; Priller, J.; Davis, J.M. Antipsychotic drugs: A concise review of history, classification, indications, mechanism, efficacy, side effects, dosing, and clinical application. Am. J. Psychiatry 2024, 181, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykara, H.B.; Güney, S.A.; Avcil, S.; Buran, B.Ş.; Cıray, R.O.; Ermis, C.; Inal, N. Safety of Atypical Antipsychotics in a Child and Adolescent Inpatient Setting: A Naturalistic Study. Psychiatry Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2024, 34, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

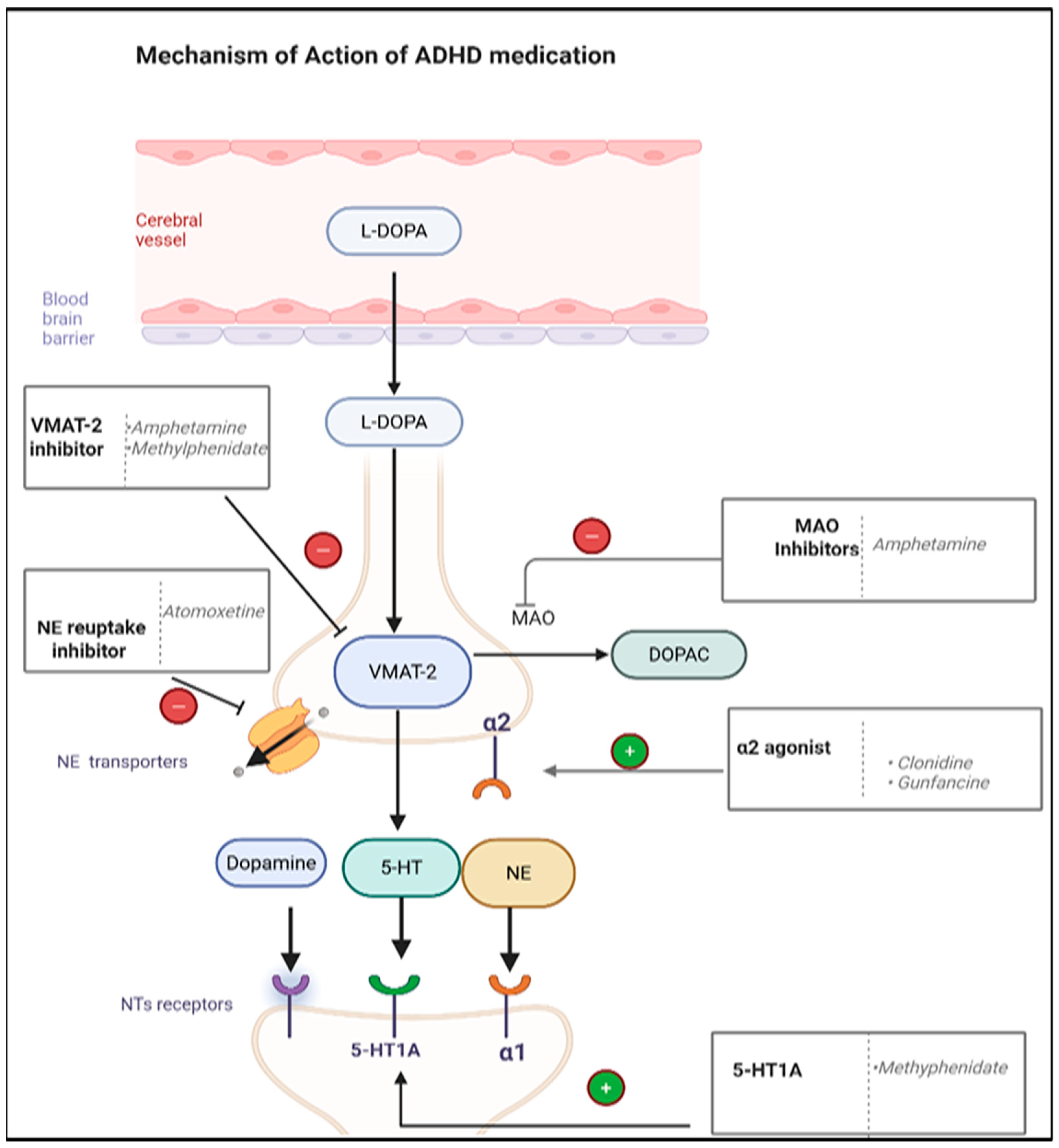
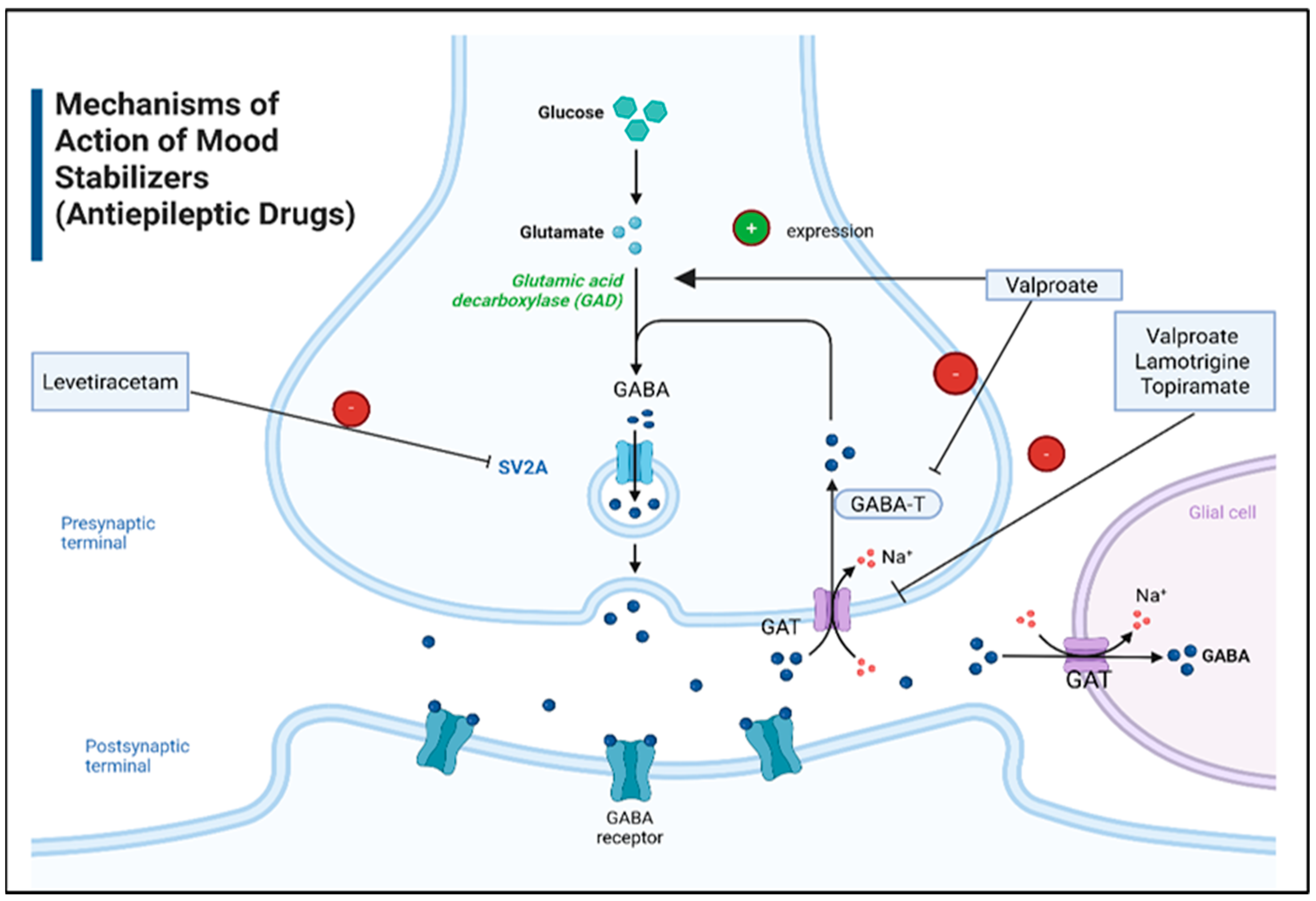
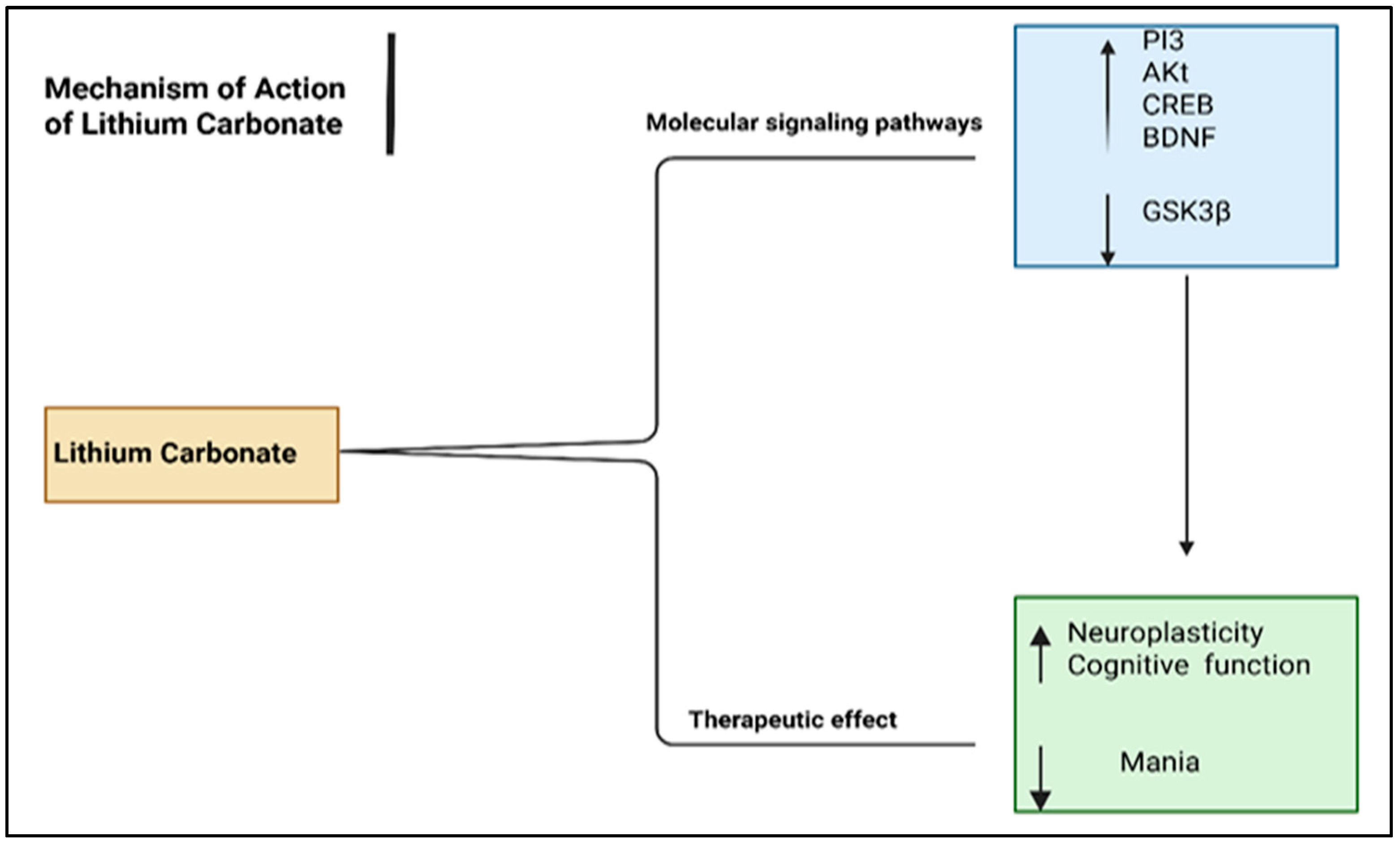
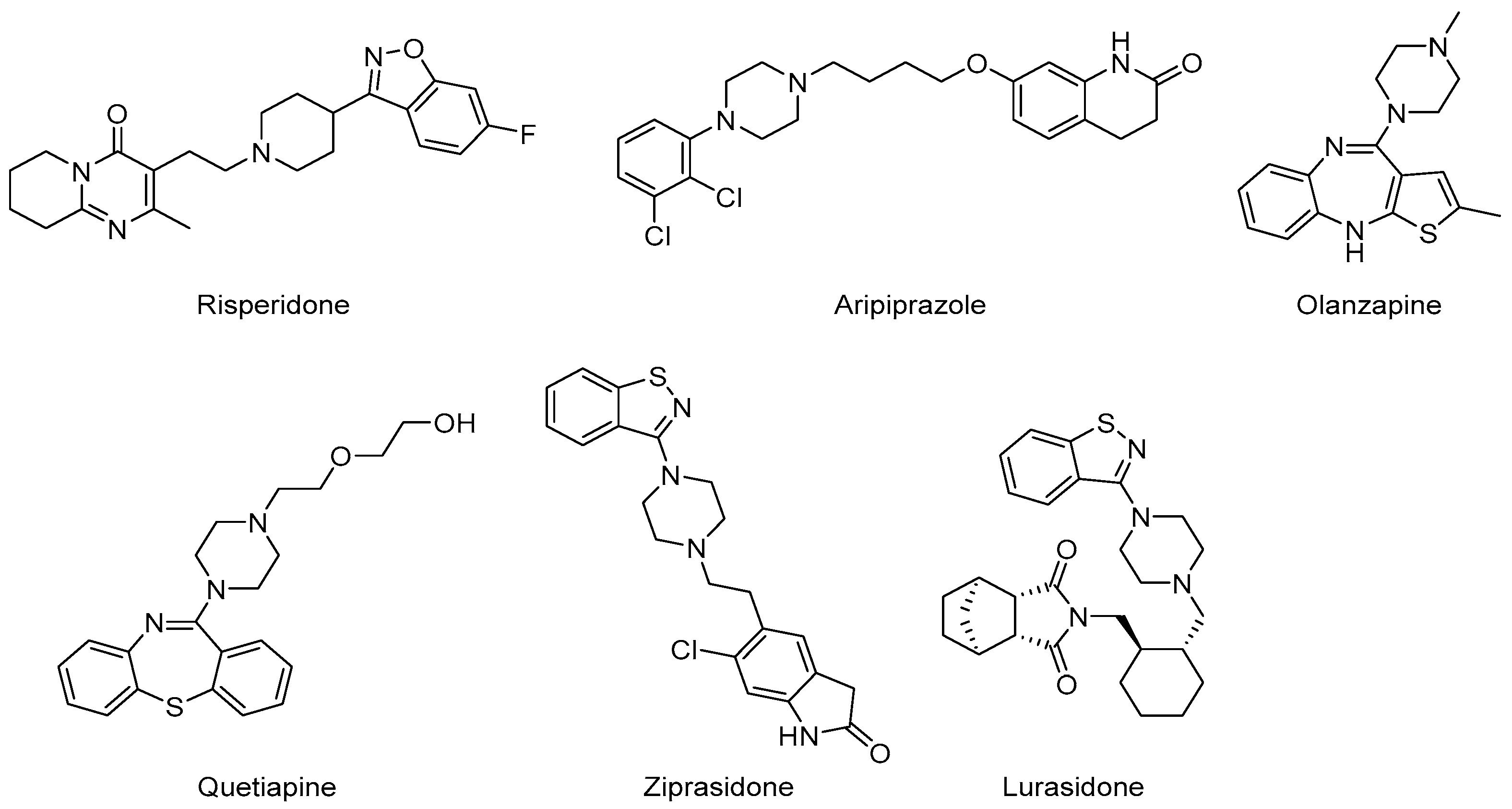
| Disorder | Definition | Clinical Manifestations | Diagnosis Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asperger’s disorder | A neurological disorder that is marked by challenges in interacting with others and repetitive interests without cognitive-linguistic impairment. | Challenges in social interactions, limited verbal communication, and repetitive behaviours and interests |
|
| Autistic disorder | A serious neurodevelopmental disorder marked by difficulties in social interaction and communication, along with limited interests. | Difficulties with social engagement, communication challenges, repetitive behaviours, and heightened sensitivity to sensory inputs. |
|
| Rett’s Disorder | A rare genetic neurodevelopmental disorder associated with a lack of social, speech, and motor skills. | Deterioration of hand movements, motor issues, seizures, trouble with communication, and withdrawal from social engagement. |
|
| Childhood disintegrative disorder (CDD) | A rare neurodevelopmental condition is defined by an impairment of language and social skills in children who initially show typical development during at least the first two years of childhood. | A decline in social and language abilities, and coordination problems. |
|
| Pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS) | A general diagnosis for children who do not clearly fit into other subcategories of PDD. | A decline in social, motor, and language abilities, along with coordination challenges. |
|
| AAP | Age | Dose (Oral) | Renal Impairment | Hepatic Impairment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risperidone | Children ≥ 5 years and Adolescents < 18 years | 0.25–3 mg/day | No dosage adjustment required | No dosage adjustment required |
| Aripiprazole | Children ≥ 6 years and Adolescents < 18 years | 2–15 mg/day | No dosage adjustment required | No dosage adjustment required |
| Olanzapine | Children ≥ 6 years and Adolescents up to 14 years | 2.5–10 mg/day | No dosage adjustment required a | Use with caution b |
| Quetiapine | Children ≥ 10 years and Adolescents < 18 years | 300–750 mg/day | No dosage adjustment required a | 25–50 mg/day and increased based on response and tolerability. |
| Lurasidone | Children ≥ 6 years and Adolescents < 18 years | 20–60 mg/day | No data available | No dosage adjustment required c |
| Ziprasidone | Children ≥ 6 years and Adolescents ≤ 18 years | 20–240 mg/day | No dosage adjustment required | Use with caution |
| AAP | Cmax (nM) | D2 Ki (nM) | 5-HT1A Ki (nM) | 5-HT2A Ki (nM) | H1 Ki (nM) | α1 Ki (nM) | α2 Ki (nM) | M1 Ki (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risperidone | 36.5 | 2.29 | 417 | 0.29 | 18 | 2.5 | 6.55 | >30,000 (6867) |
| Aripiprazole | 240.8 | 1.95 | 5.6 | 13.8 | 28 | 30 | 70 | - |
| Olanzapine | 48 | 20.4 | 2063 | 3.26 | 2.3 | 54.95 | 280 | 4.7 |
| Quetiapine | 1291.4 | 567 | 309 | 200 | 8.7 | 22 | 1000 | 127 |
| Lurasidone | 60.9 | 1.68 | 6.7 | 2 | - | 47.9 | 25.7 | - |
| Ziprasidone | 121 | 3.16 | 2.5 | 0.39 | 44.89 | 10 | 228 | 5100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljead, M.; Qashta, A.; Jalal, Z.; Jones, A.M. Review of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Epidemiology, Aetiology, Pathology, and Pharmacological Treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111644
Aljead M, Qashta A, Jalal Z, Jones AM. Review of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Epidemiology, Aetiology, Pathology, and Pharmacological Treatment. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111644
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljead, Mashal, Aya Qashta, Zahraa Jalal, and Alan M. Jones. 2025. "Review of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Epidemiology, Aetiology, Pathology, and Pharmacological Treatment" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111644
APA StyleAljead, M., Qashta, A., Jalal, Z., & Jones, A. M. (2025). Review of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Epidemiology, Aetiology, Pathology, and Pharmacological Treatment. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111644







