Coaxial Electrospun Nanofibers of Shikonin and Cresol as Antibacterial Wound Dressing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
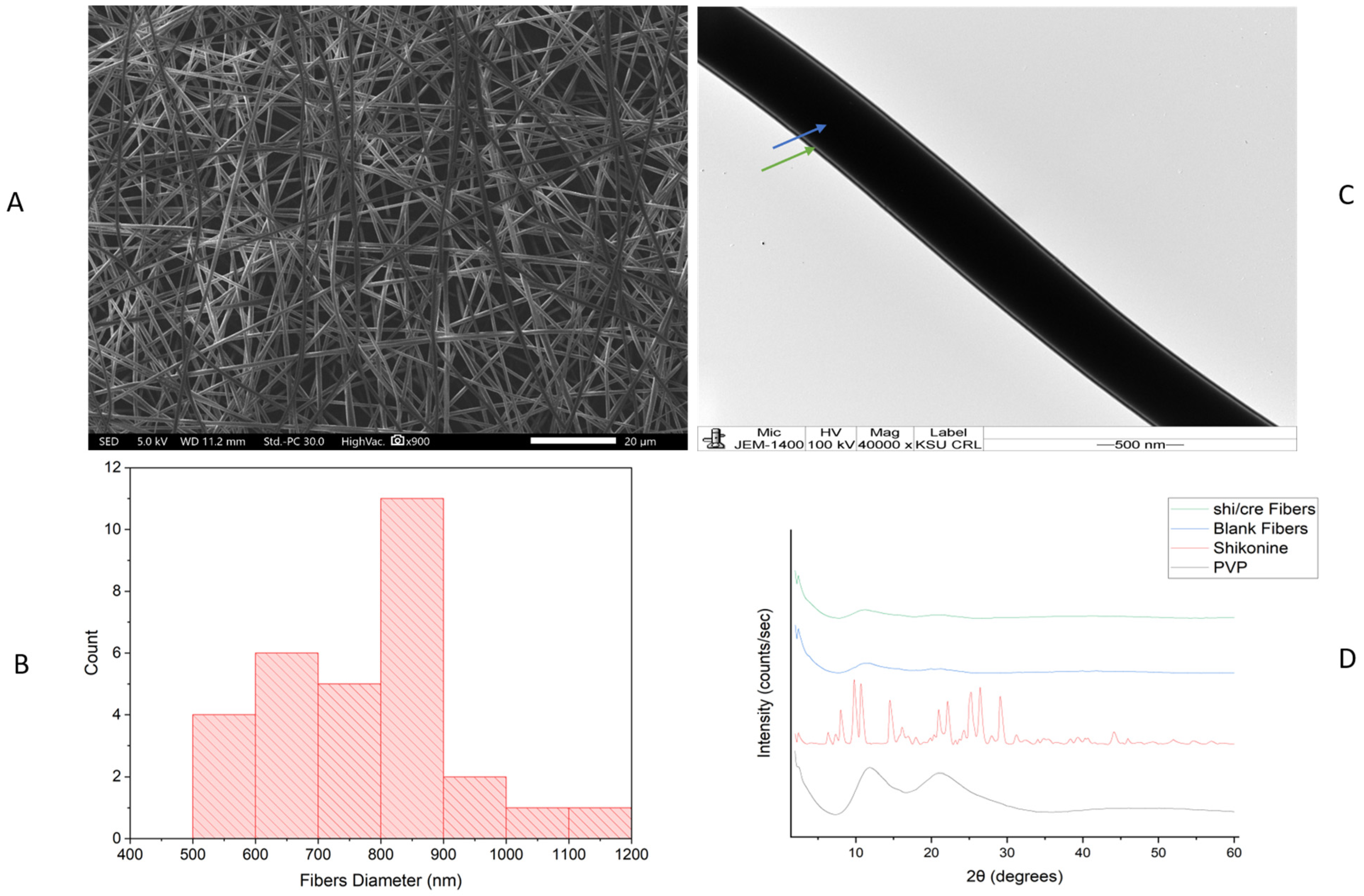
2.1. Morphology Assessment of the Drug-Loaded Coaxial Nanofibers
2.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Assessment
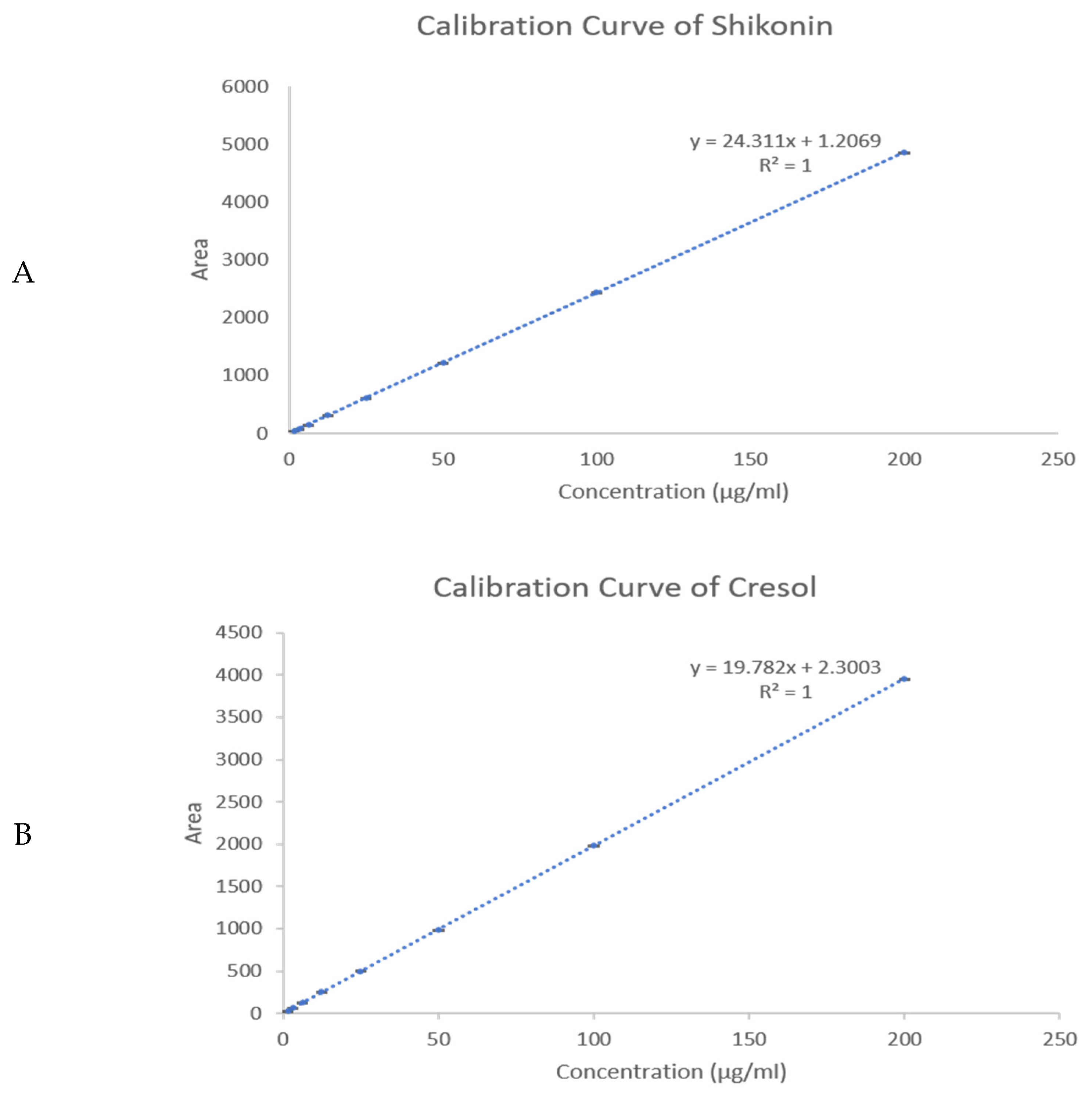
2.3. Drug Loading (DL) and Encapsulation Efficiency (EE) % Determination
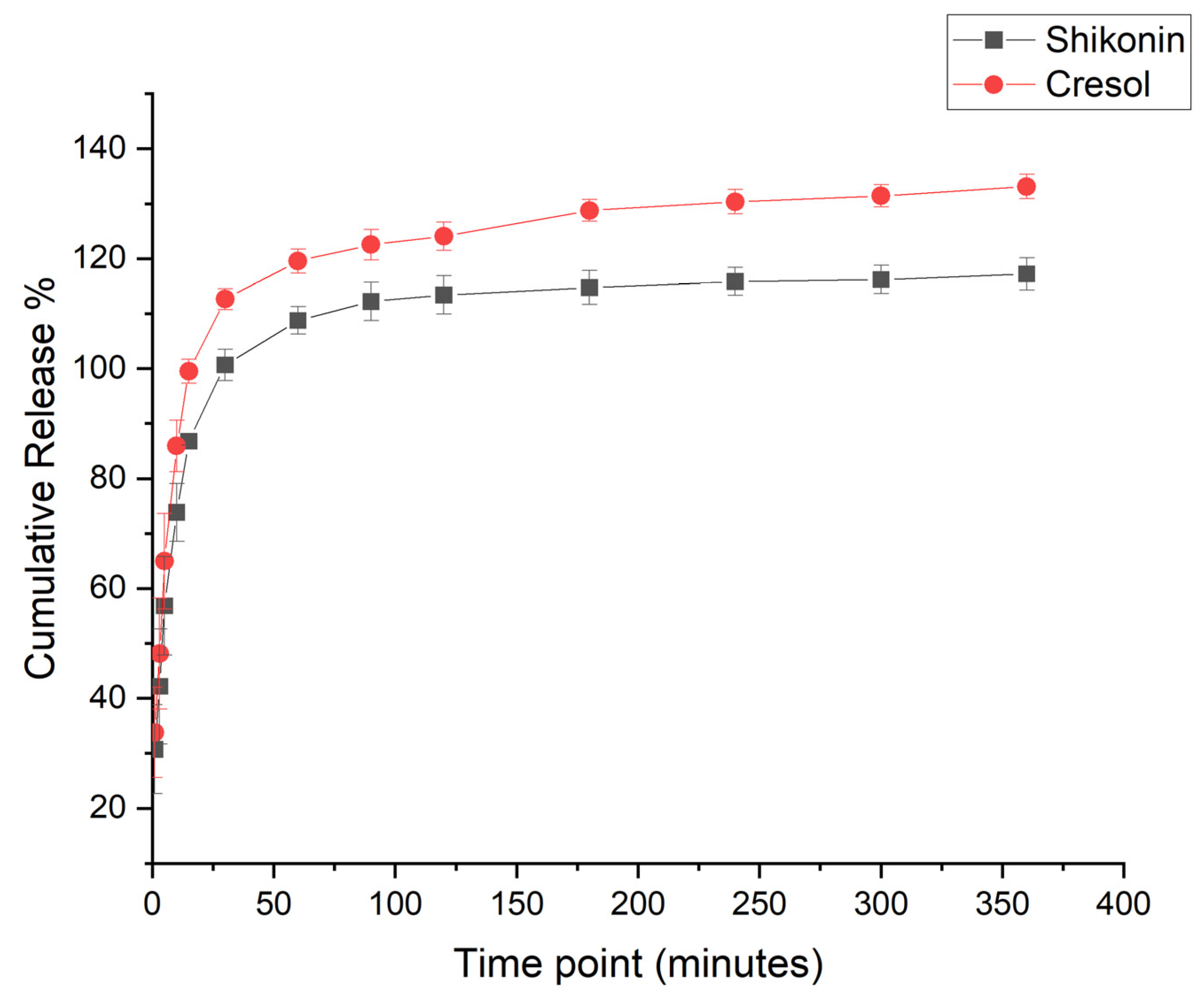
2.4. In Vitro Drug Release Assessment
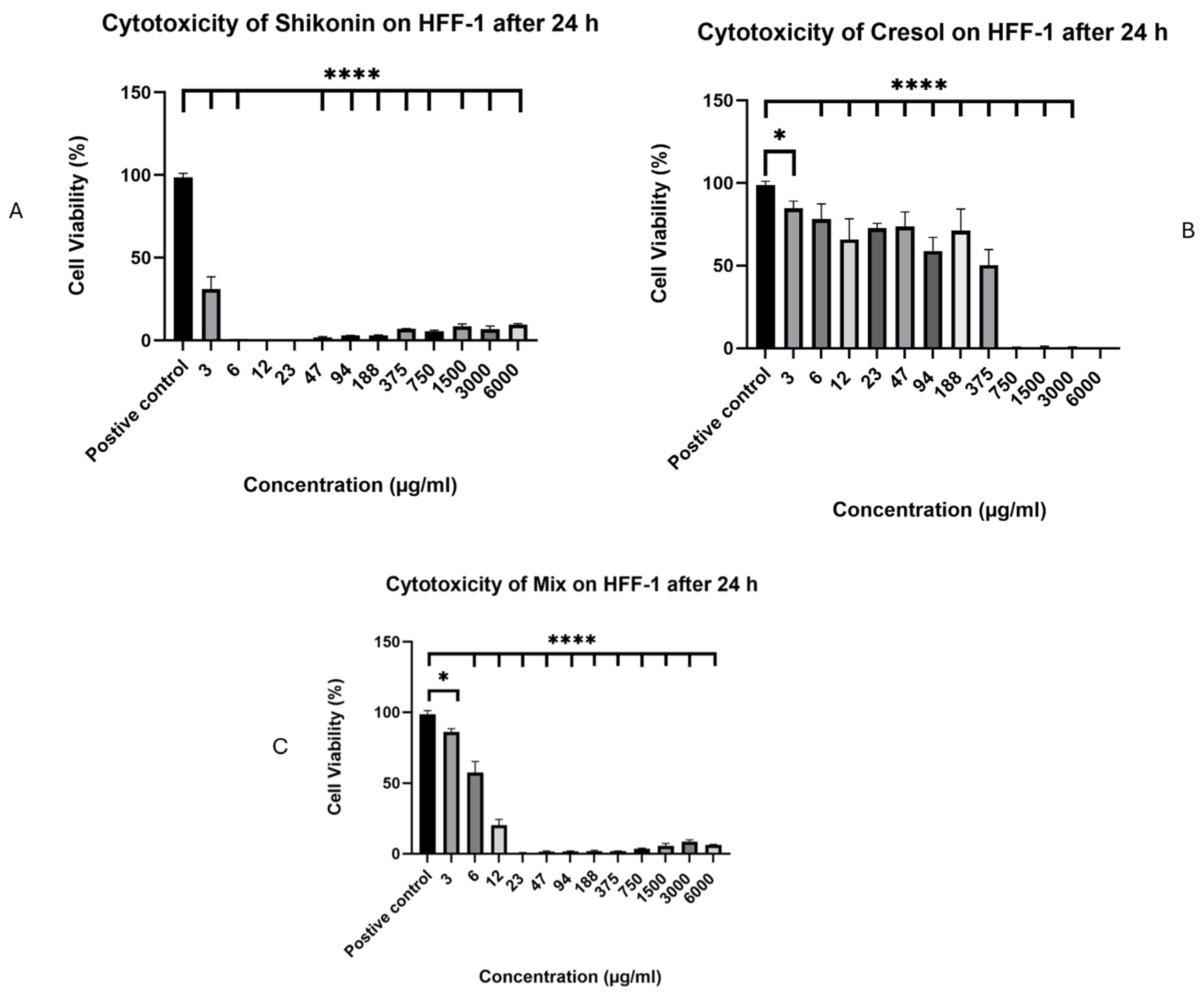
2.5. In Vitro Cell Viability Assessment
2.6. Antibacterial Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assessment
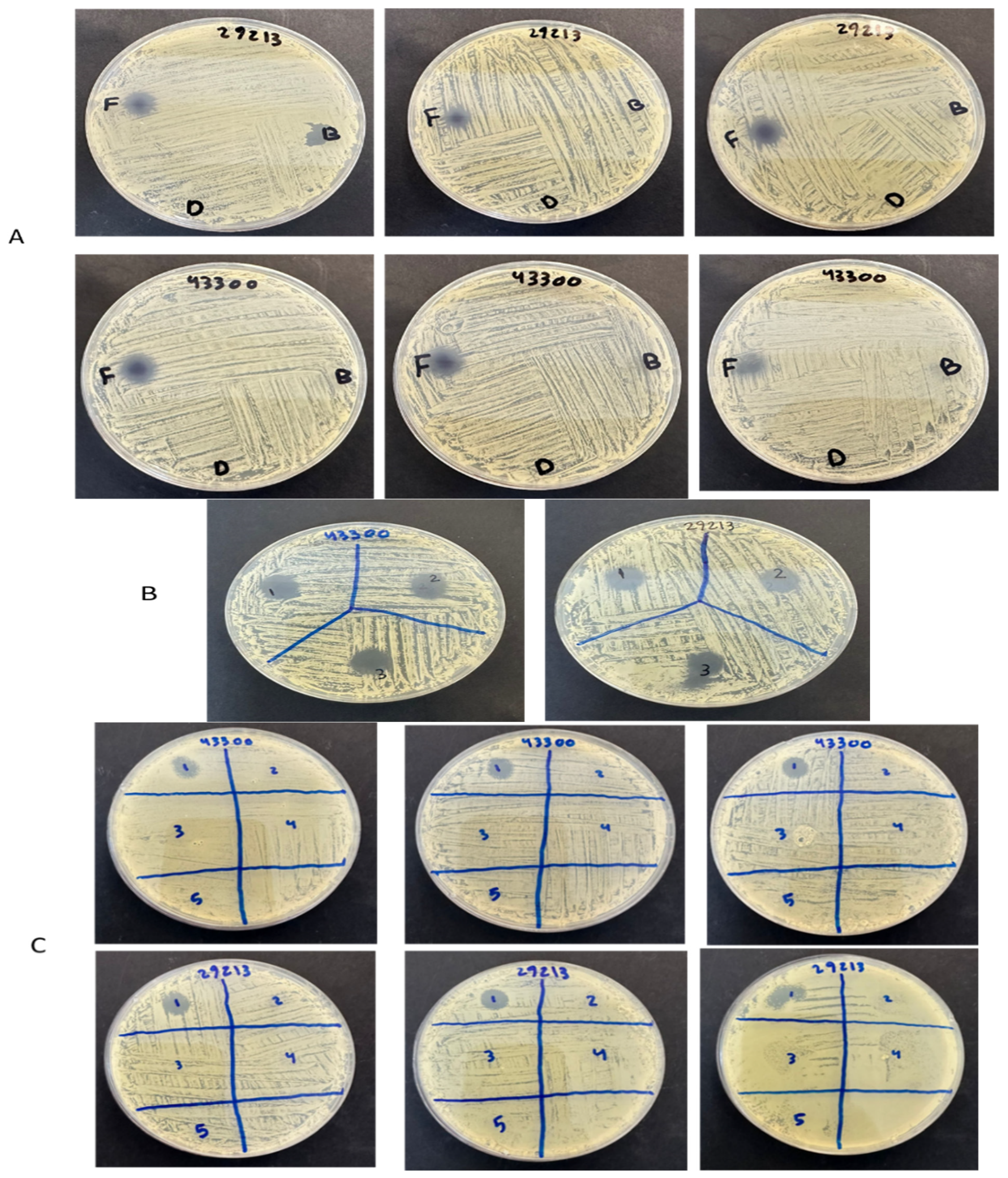
2.7. Antibacterial Zone of Inhibition Assessment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Drug-Loaded Coaxial PVP Fibers
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Assessment
3.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Assessment
3.5. X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) Assessment
3.6. Quantification Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Determination
3.7. Drug Loading (DL) and Encapsulation Efficiency (EE) % Determination
3.8. In Vitro Drug Release Assessment
3.9. In Vitro Cell Viability Assessment
3.10. Antibacterial Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assessment
3.11. Antibacterial Zone of Inhibition Assessment
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.; Li, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B. Multifunctional Chitosan/Polycaprolactone Nanofiber Scaffolds with Varied Dual-Drug Release for Wound-Healing Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 4666–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazarlu, O.; Iranshahi, M.; Kashani, H.R.K.; Reshadat, S.; Habtemariam, S.; Iranshahy, M.; Hasanpour, M. Perspective on the application of medicinal plants and natural products in wound healing: A mechanistic review. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 174, 105841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J.; Wilkinson, H.N. Wound healing: Cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourian Dehkordi, A.; Mirahmadi Babaheydari, F.; Chehelgerdi, M.; Raeisi Dehkordi, S. Skin tissue engineering: Wound healing based on stem-cell-based therapeutic strategies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rensburg, J.J.; Lin, H.; Gao, X.; Toh, E.; Fortney, K.R.; Ellinger, S.; Zwickl, B.; Janowicz, D.M.; Katz, B.P.; Nelson, D.E.; et al. The human skin microbiome associates with the outcome of and is influenced by bacterial infection. MBio 2015, 6, e01315-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negut, I.; Grumezescu, V.; Grumezescu, A.M. Treatment strategies for infected wounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirhaj, M.; Labbaf, S.; Tavakoli, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Emerging treatment strategies in wound care. Int. Wound J. 2022, 19, 1934–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellingeri, A.; Falciani, F.; Traspedini, P.; Moscatelli, A.; Russo, A.; Tino, G.; Chiari, P.; Peghetti, A. Effect of a wound cleansing solution on wound bed preparation and inflammation in chronic wounds: A single-blind RCT. J. Wound Care 2016, 25, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolimi, P.; Narala, S.; Nyavanandi, D.; Youssef, A.A.A.; Dudhipala, N. Innovative Treatment Strategies to Accelerate Wound Healing: Trajectory and Recent Advancements. Cells 2022, 11, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gushiken, L.F.S.; Beserra, F.P.; Bastos, J.K.; Jackson, C.J.; Pellizzon, C.H. Cutaneous wound healing: An update from physiopathology to current therapies. Life 2021, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y.; States, U.; States, U. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers. Methods Mater. Appl. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburayan, W.S.; Booq, R.Y.; BinSaleh, N.S.; Alfassam, H.A.; Bakr, A.A.; Bukhary, H.A.; Alyamani, E.J.; Tawfik, E.A. The delivery of the novel drug ‘halicin’ using electrospun fibers for the treatment of pressure ulcer against pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhaj, S.; Conway, B.R.; Ghori, M.U. Nanofibres in Drug Delivery Applications. Fibers 2023, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahtani, M.E.; Aodah, A.H.; Abu Asab, O.A.; Basit, A.W.; Orlu, M.; Tawfik, E.A. Fabrication and characterization of fast-dissolving films containing escitalopram/quetiapine for the treatment of major depressive disorder. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Li, Q.; Sun, Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, X. Promising Nanomedicines of Shikonin for Cancer Promising Nanomedicines of Shikonin for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 1195–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.-L.; Lin, C.-H.; Li, C.-H.; Tsai, C.-H.; Ho, J.-D.; Chiou, G.C.Y.; Kang, J.-J.; Cheng, Y.-W. Anti-inflammatory properties of shikonin contribute to improved early-stage diabetic retinopathy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ding, Q.; Hao, Y.; Cui, B.; Ding, C.; Gao, F. Pharmacological Effects of Shikonin and Its Potential in Skin Repair: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 7950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Chen, T.X.; Branford-White, C.J.; Zhu, L.M. Electrospun shikonin-loaded PCL/PTMC composite fiber mats with potential biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 382, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arampatzis, A.S.; Kontogiannopoulos, K.N.; Theodoridis, K.; Aggelidou, E.; Rat, A.; Willems, A.; Tsivintzelis, I.; Papageorgiou, V.P.; Kritis, A.; Assimopoulou, A.N. Electrospun wound dressings containing bioactive natural products: Physico-chemical characterization and biological assessment. Biomater. Res. 2021, 25, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arampatzis, A.S.; Giannakoula, K.; Kontogiannopoulos, K.N.; Theodoridis, K.; Aggelidou, E.; Rat, A.; Kampasakali, E.; Willems, A.; Christofilos, D.; Kritis, A.; et al. Novel electrospun poly-hydroxybutyrate scaffolds as carriers for the wound healing agents alkannins and shikonins. Regen. Biomater. 2021, 8, rbab011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, M.B.; Durães, A.F.S.; Silvério, F.O.; Pinho, G.P. Determination of three cresol isomers in sewage sludge by solid-liquid extraction with low temperature purification and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2020, 55, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, R.C.; Sheskey, P.J.; Owen, S.C. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 5th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK; Chicago, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Prestinaci, F.; Pezzotti, P.; Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial resistance: A global multifaceted phenomenon. Pathog. Glob. Health 2015, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Yang, L.; Wan, Y.; Zhao, W.E.; Li, S.W. Small Molecules Accelerate Skin Wound Healing: Shikonin Efficacy and Mechanism of Action in Mice. Int. J. Morphol. 2024, 42, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Tariq, M.; Syed, N.A.; Rizvi, G. Towards Analysis and Optimization of Electrospun PVP (Polyvinylpyrrolidone) Nanofibers. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 9, 4090747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaya, H.A.; Alfahad, A.J.; Alsulaihem, F.M.; Aodah, A.H.; Alshehri, A.A.; Almughem, F.A.; Alfassam, H.A.; Aldossary, A.M.; Halwani, A.A.; Bukhary, H.A.; et al. Fast-Dissolving Nifedipine and Atorvastatin Calcium Electrospun Nanofibers as a Potential Buccal Delivery System. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, D.; Alsulami, K.; Alsulaihem, F.M.; Bakr, A.; Booq, R.Y.; Alfahad, A.J.; Aodah, A.H.; Alsudir, S.; Fathaddin, A.; Alyamani, E.J.; et al. Dual Drug-Loaded Coaxial Nanofiber Dressings for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 11, 5681–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; You, L.; Sun, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, P. Heliyon Shikonin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: A promising strategy for psoriasis treatment. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameh, E.S. A review of basic crystallography and x-ray diffraction applications. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 3289–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, H.; Khorashadizadeh, M.; Haseloer, A.; Klein, A. Characterization and Release Behavior of a Thiosemicarbazone from Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol Core-Shell Nanofibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontogiannopoulos, K.N.; Assimopoulou, A.N.; Tsivintzelis, I.; Panayiotou, C.; Papageorgiou, V.P. Electrospun fiber mats containing shikonin and derivatives with potential biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 409, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriyanti, I.; Edikresnha, D.; Rahma, A.; Munir, M.; Rachmawati, H.; Khairurrijal, K. Mangosteen pericarp extract embedded in electrospun PVP nanofiber mats: Physicochemical properties and release mechanism of α-mangostin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 31, 4927–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Xie, Y.; Dong, Y.; Su, Y.; Upton, Z. Investigating the potential of Shikonin as a novel hypertrophic scar treatment. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, S.; Lan, W.; Huang, C.; Lin, C.; Chan, C.; Chang, M.; Jeng, J. Scavenging property of three cresol isomers against H2O2, hypochlorite, superoxide and hydroxyl radicals. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Chang, H.; Chan, C.; Yeung, S. p-Cresol Affects Reactive Oxygen Species Generation, Cell Cycle Arrest, Cytotoxicity and Inflammation/Atherosclerosis-Related Modulators Production in Endothelial Cells and Mononuclear Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Zahrani, N.A.; Alshabibi, M.A.; Bakr, A.A.; Almughem, F.A.; Alshehri, A.A.; Al-Ghamdi, H.A.; Tawfik, E.A.; Damiati, L.A. Molecular Hybrids of Thiazolidinone: Bridging Redox Modulation and Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Xu, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Yin, L.; Peng, X.; Fu, H.; Chang, L.-J.; et al. Preparation of shikonin liposome and evaluation of its in vitro antibacterial and in vivo infected wound healing activity. Phytomedicine 2022, 99, 154035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Sharma, R.; Singh, A.; Attri, S.; Arora, S.; Kaur, S.; Bedi, N. Pharmacological and analytical aspects of alkannin / shikonin and their derivatives: An update from 2008 to 2022. Chin. Herb. Med. 2022, 14, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.-Y.; Wang, P.-F.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Luo, Y.-L.; Hu, D.-Q.; Qi, J.-L.; Lu, G.-H.; Pang, Y.-J.; Yang, R.-W.; Zhu, H.-L.; et al. Shikonin derivatives as inhibitors of tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 83003–83010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andújar, I.; Ríos, J.L.; Giner, R.M.; Recio, M.C. Pharmacological properties of shikonin—A review of literature since 2002. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.; Kou, M.; Shi, C.; Peng, X.; Wang, X. Control of Foodborne Staphylococcus aureus by Shikonin, a Natural Extract. Foods 2021, 10, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S. In Vitro Effects of Essential Oils from Ostericum koreanum against Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella spp. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2005, 28, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drug Bank. Cresol 2015. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB11143 (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Bagheri, F.; Tahvilian, R.; Karimi, N.; Chalabi, M.; Azami, M. Shikonin production by callus culture of onosma bulbotrichom as active pharmaceutical ingredient. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.G.; Shin, S.-Y.; Shin, H.-J.; Huh, Y.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.-O.; Han, S.B.; Lee, J.; et al. Determination of three preservatives, cresol, chlorocresol and benzethonium, in drugs by high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet (HPLC-UV) detection. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 42, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albreht, A.; Vovk, I.; Simonovska, B. Addition of β-lactoglobulin produces water-soluble shikonin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, S.A.; Sheppard, B.L.; McGuinness, E.P.J.; Gleeson, N.C.; Yoneda, M.; Bonnar, J. The MTS assay as an indicator of chemosensitivity/resistance in malignant gynaecological tumours. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2003, 27, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI M07; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically Standard, Approval CDM-A. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; p. 91.
- Pannakal, S.T.; Prasad, A.; Phadke, S.; Sanyal, A.; Butti, S.; Khodr, A.; Morain, C.; Agnaou, R.; Shariff, R.; Benazzouz, A.; et al. Acnocure, a Synergistic Anti-Microbial and Anti-Inflammatory Combination of Thymol and Curcuma Turmerones, Formulation and Time-Kill Studies Against C. acnes. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strains of Bacteria | Shikonin (μg/mL) | Cresol (μg/mL) | Mix (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus—ATCC 29213 | 3 | 1500 | 3 |
| MRSA—ATCC 43300 | 6 | 1500 | 3 |
| E. coli—ATCC 25922 | No inhibition | 750 | 750 |
| E. coli—isolate 1060 | No inhibition | 750 | 1500 |
| A. baumannii—ATCC 747 | No inhibition | 750 | 750 |
| A. baumannii—isolate 3034 | 1500 | 750 | 375 |
| P. aeruginosa—ATCC 27853 | 1500 | 750 | 1500 |
| P. aeruginosa—isolate 7067 | 1500 | 750 | 1500 |
| Strains of Bacteria | Control Drugs (Shi/Cre) | Shi/Cre Fibers | Blank Fibers | Vancomycin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus—ATCC 29213 | 12 mm | 10 mm | 0 mm | 8 mm |
| MRSA—ATCC 43300 | 13 mm | 10 mm | 0 mm | 9 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsulaihem, F.M.; Bakr, A.A.; Alnefaie, M.K.; Alshabibi, M.A.; Alshehri, A.A.; Almughem, F.A.; Alsudir, S.A.; Alamer, A.A.; Alshehri, B.Y.; Alzahrani, D.A.; et al. Coaxial Electrospun Nanofibers of Shikonin and Cresol as Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111642
Alsulaihem FM, Bakr AA, Alnefaie MK, Alshabibi MA, Alshehri AA, Almughem FA, Alsudir SA, Alamer AA, Alshehri BY, Alzahrani DA, et al. Coaxial Electrospun Nanofibers of Shikonin and Cresol as Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111642
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsulaihem, Fatemah M., Abrar A. Bakr, Meshal K. Alnefaie, Manal A. Alshabibi, Abdullah A. Alshehri, Fahad A. Almughem, Samar A. Alsudir, Ali A. Alamer, Bayan Y. Alshehri, Dunia A. Alzahrani, and et al. 2025. "Coaxial Electrospun Nanofibers of Shikonin and Cresol as Antibacterial Wound Dressing" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111642
APA StyleAlsulaihem, F. M., Bakr, A. A., Alnefaie, M. K., Alshabibi, M. A., Alshehri, A. A., Almughem, F. A., Alsudir, S. A., Alamer, A. A., Alshehri, B. Y., Alzahrani, D. A., Aleanizy, F. S., & Tawfik, E. A. (2025). Coaxial Electrospun Nanofibers of Shikonin and Cresol as Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111642







