A Multi-Laboratory, Multi-Platform Analysis of the Multi-Attribute Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
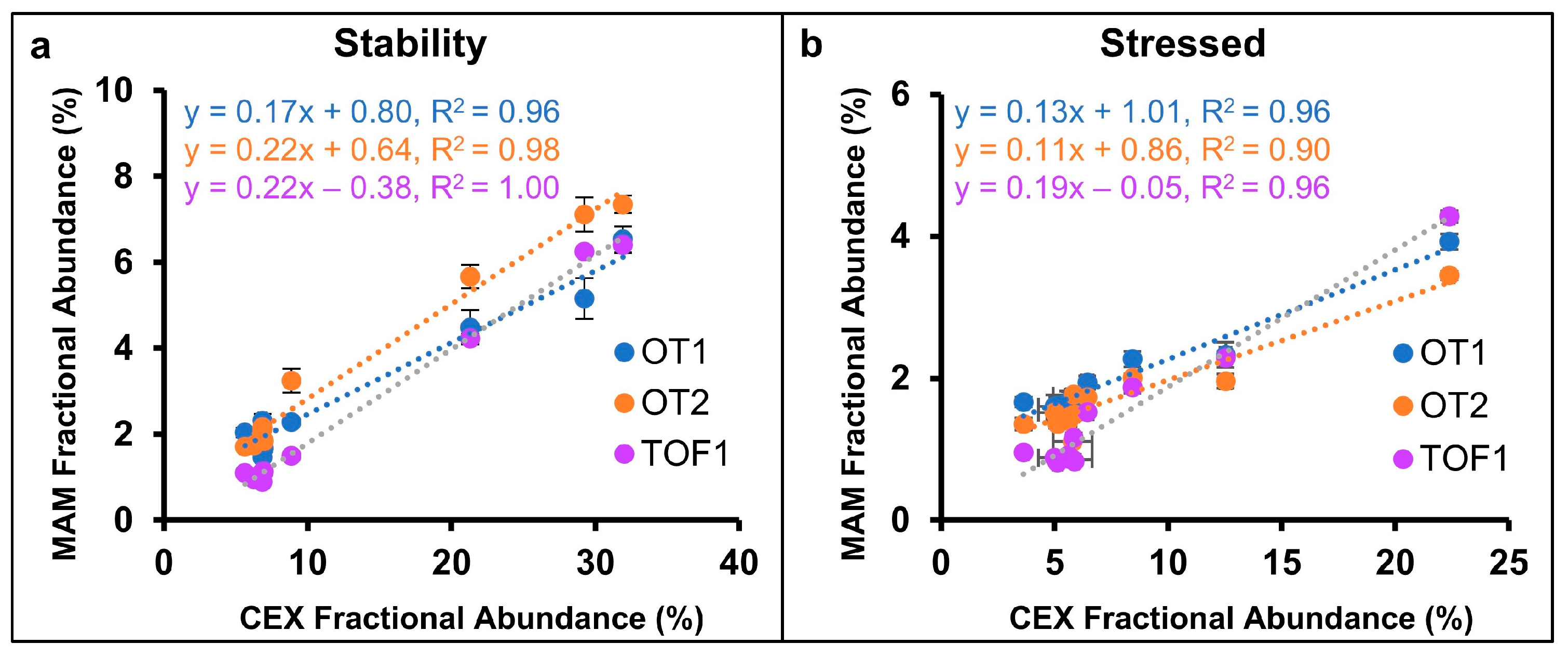
2.1. Overview and System Comparison
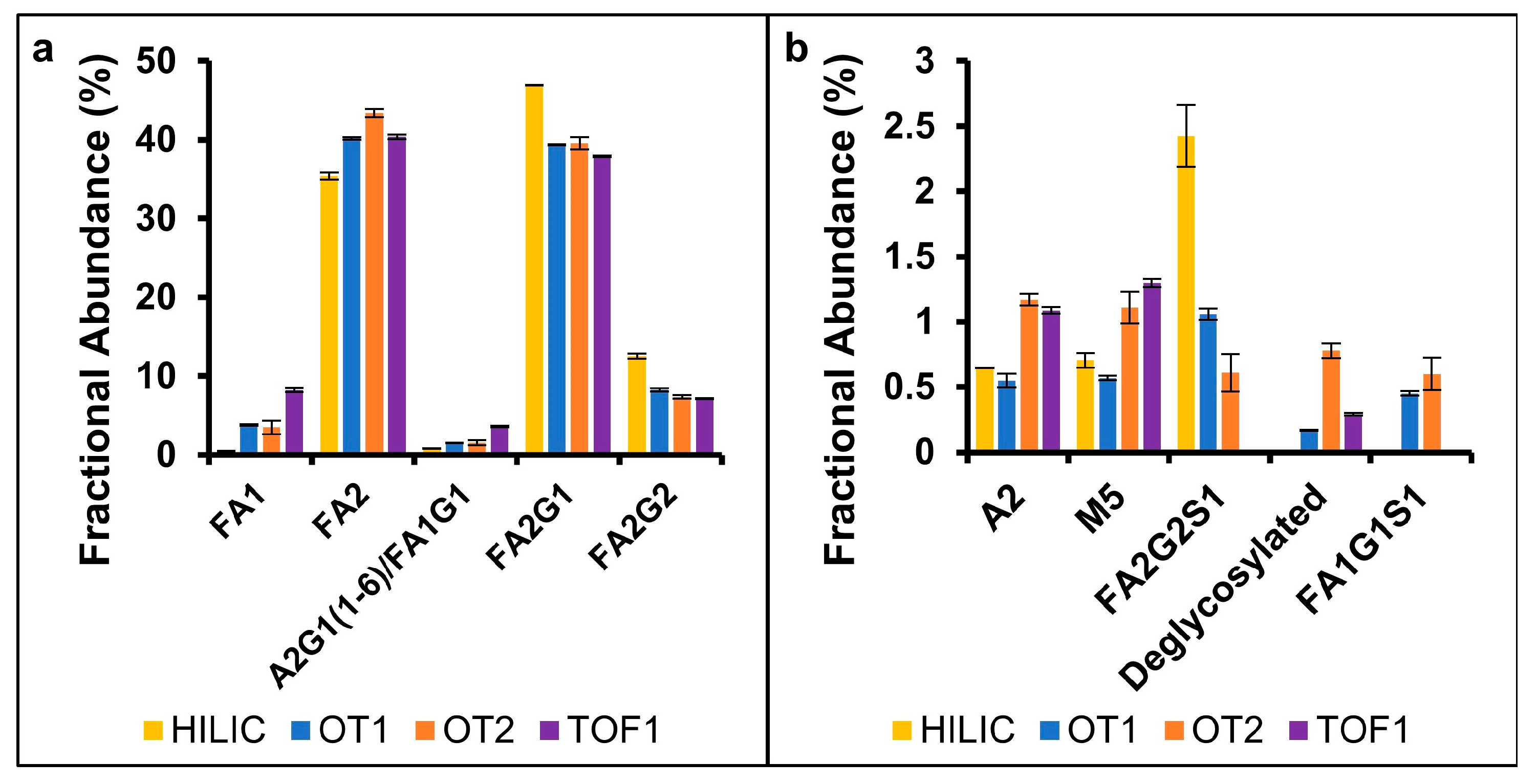
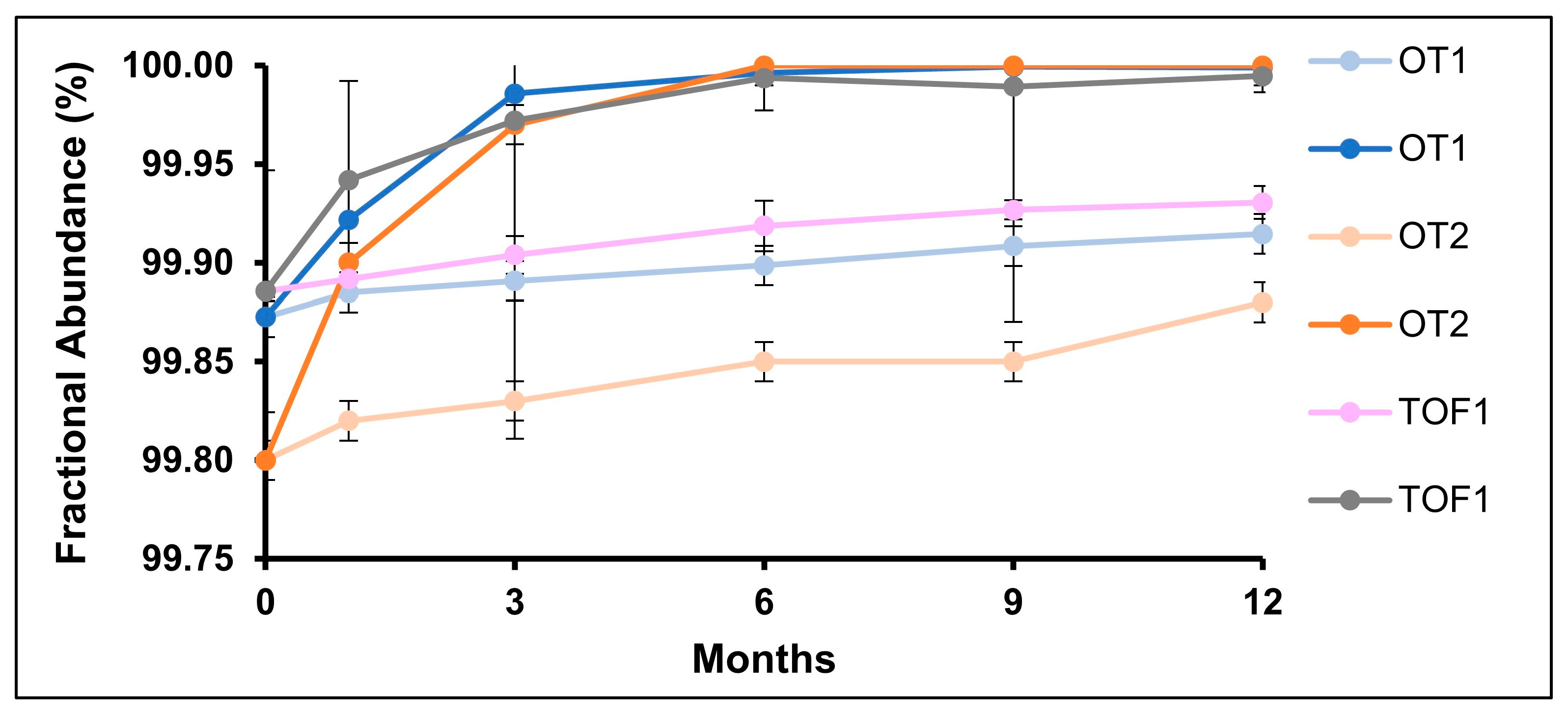
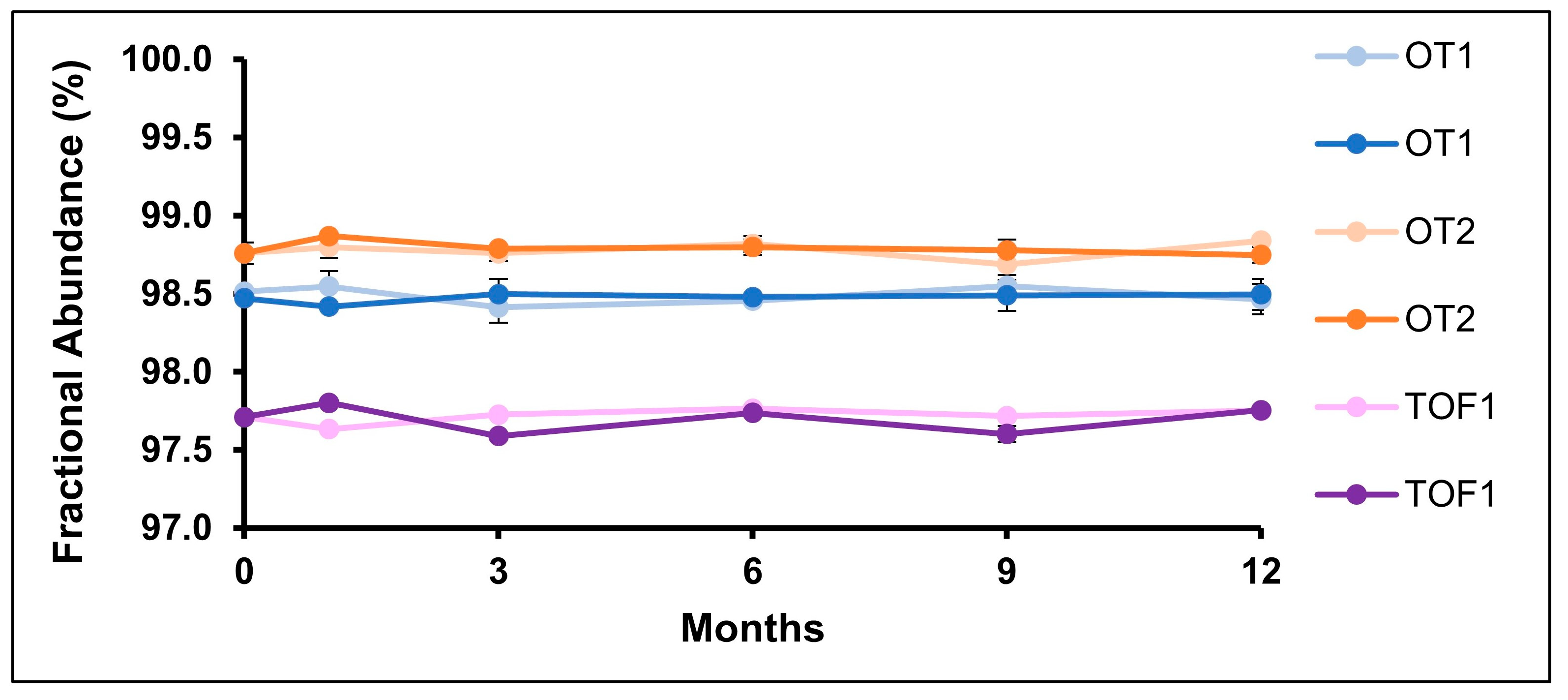
2.2. N-Linked Glycans
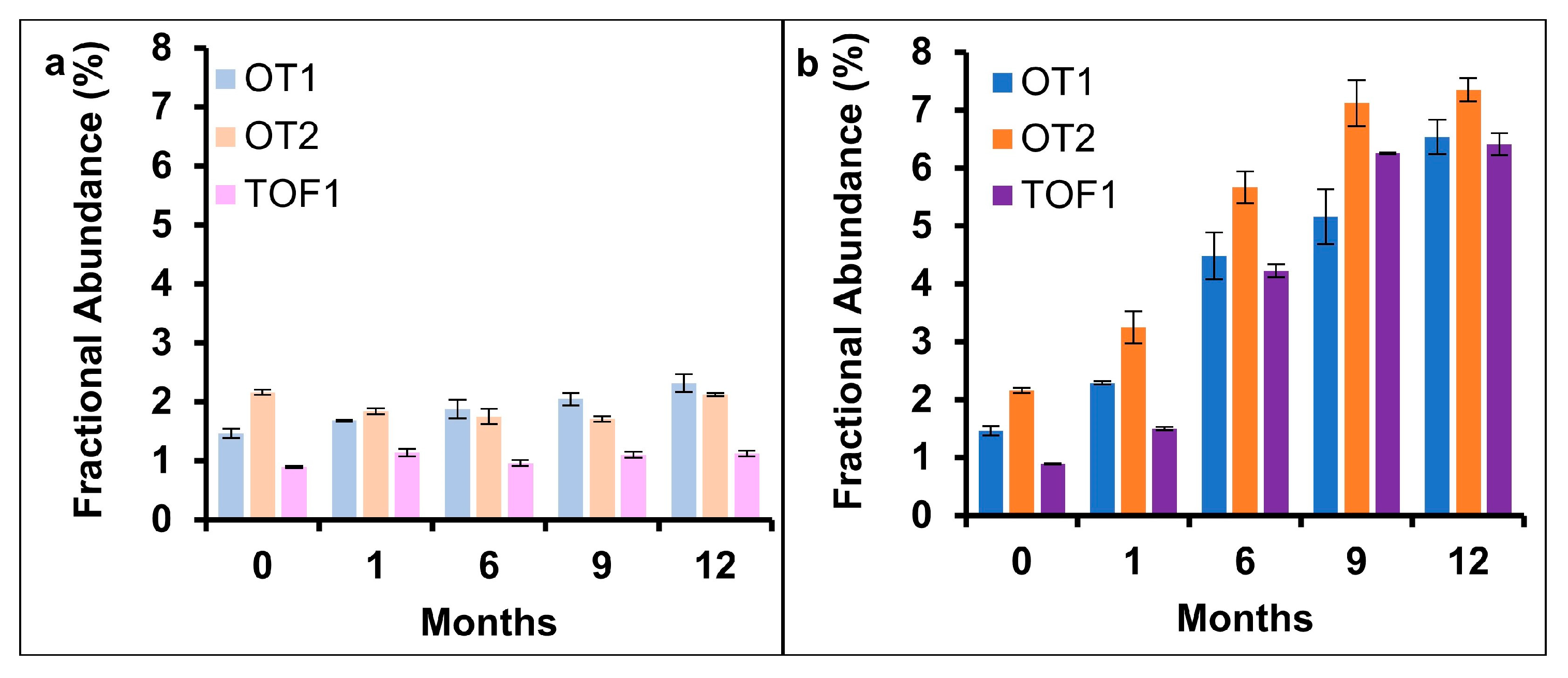
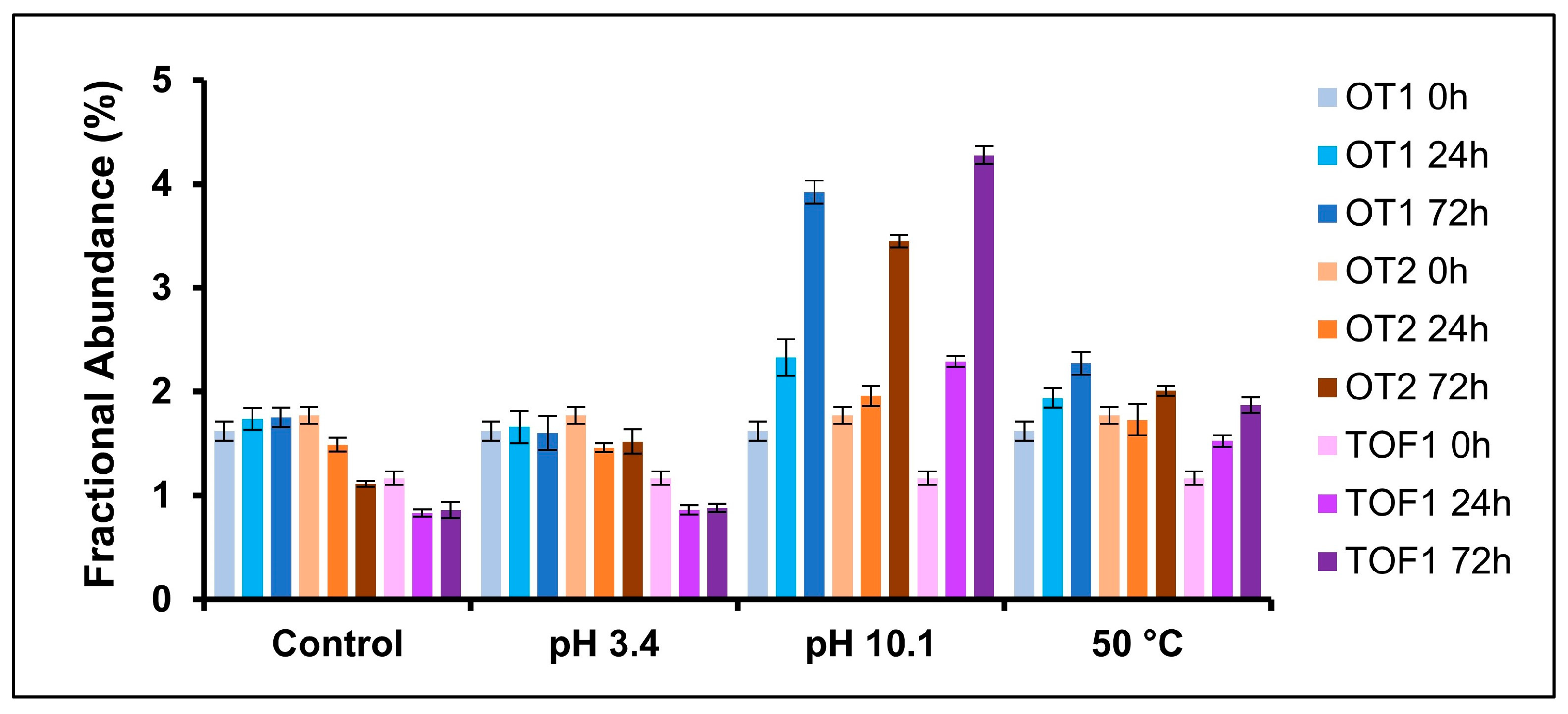
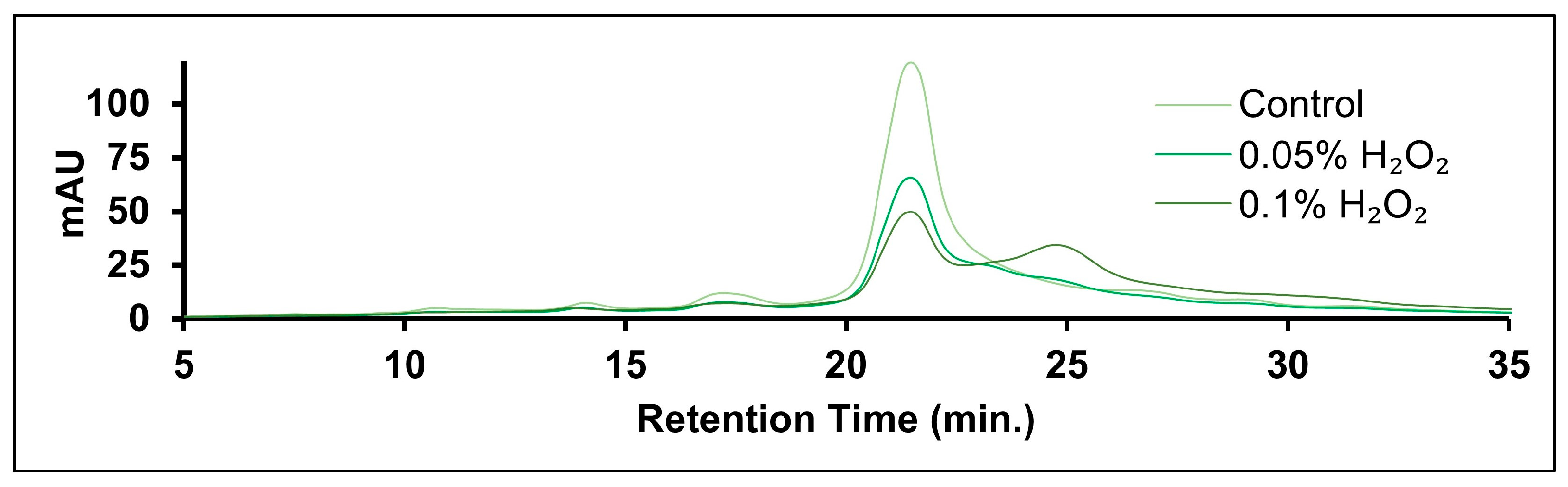
2.3. Deamidation
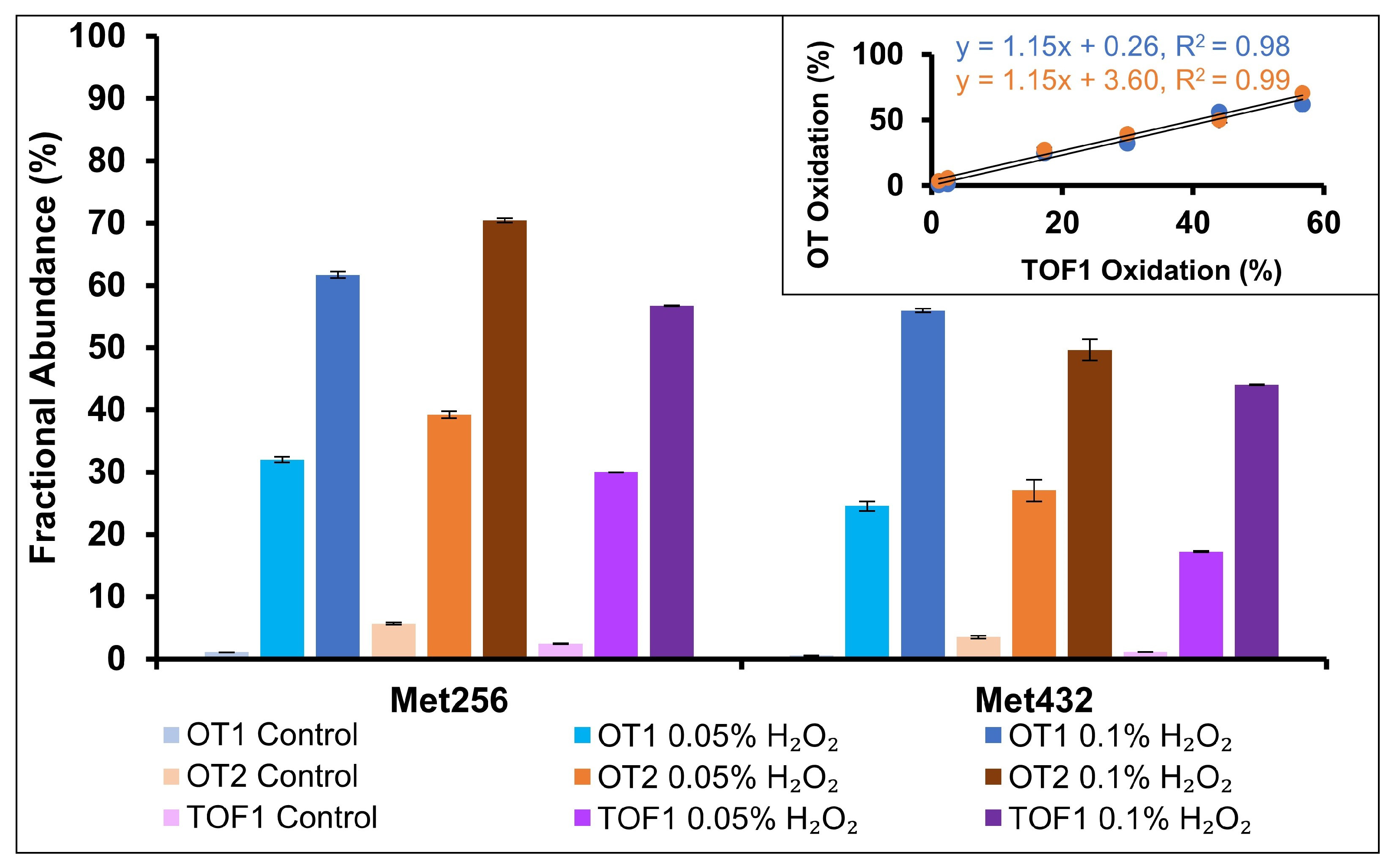
2.4. Oxidation
2.5. C- and N-Terminal Variants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. MAM Peptide Mapping with LC-MS
4.3. Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography–Fluorescence Detection (HILIC-FLD)
4.4. Cation Exchange Chromatography–Ultraviolet Detection (CEX-UV)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-AB | 2-aminobenzamide |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| ADC | Antibody–drug conjugate |
| AEX | Anion exchange chromatography |
| BLA | Biologics License Application |
| CEX | Cation exchange chromatography |
| CGE | Capillary gel electrophoresis |
| CQA | Critical quality attributes |
| CZE | Capillary zone electrophoresis |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| ESI | Electrospray ionization |
| FA | Formic acid |
| FLD | Fluorescence detection |
| FWHM | Full width at half maximum |
| GdnHCl | Guanidinium hydrochloride |
| HIC | Hydrophobic interaction chromatography |
| HILIC | Hydrophilic interaction chromatography |
| HPAEC-PAD | High-performance anion exchange chromatography combined with pulsed amperometric detection |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| IAA | Iodoacetic acid |
| ICH | International Council for Harmonisation |
| IEC | Ion exchange chromatography |
| IgG1 | Immunoglobulin G1 |
| IM | Ion mobility |
| IND | Investigational new drug |
| LC | Liquid chromatography |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibody |
| MAM | Multi-attribute method |
| MPA | Mobile Phase A |
| MPB | Mobile Phase B |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| MWCO | Molecular weight cut-off |
| NH4HCO3 | Ammonium bicarbonate |
| NPD | New peak detection |
| OT | Orbitrap |
| PQA | Product quality attributes |
| PRTC | Pierce Retention Time Calibration |
| pyro-Q | Pyroglutamic acid |
| QC | Quality control |
| rCE-SDS | Reduced capillary electrophoresis sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| RH | Relative humidity |
| RT | Retention time |
| SEC | Size-exclusion chromatography |
| TOF | Time-of-flight |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Dykstra, A.B.; Flick, T.G.; Lee, B.; Blue, L.E.; Angell, N. Chip-Based Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Mass Spectrometry for Rapid Resolution and Quantitation of Critical Quality Attributes in Protein Biotherapeutics. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2021, 32, 1952–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykstra, A.B.; Lubinsky, T.G.; Vitrac, H.; Campuzano, I.D.G.; Bondarenko, P.V.; Simone, A.R. Utilization of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry and High-Resolution Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry to Characterize Therapeutically Relevant Peptides with Asparagine Deamidation and Isoaspartate. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowska, I.; Mo, J.; Rahimi Pirkolachahi, F.; McVean, C.; Meijer, L.A.T.; Switzar, L.; Balog, C.; Lewis, M.J.; Hu, P. Implementation of a High-Resolution Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Method in Quality Control Laboratories for Release and Stability Testing of a Commercial Antibody Product. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 2369–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Buettner, A.; Vosika, E.; Sadek, M.; Hao, Z.; Reusch, D.; Koenig, M.; Chan, W.; Bathke, A.; et al. Mass spectrometry-based multi-attribute method in protein therapeutics product quality monitoring and quality control. mAbs 2023, 15, 2197668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buettner, A.; Maier, M.; Bonnington, L.; Bulau, P.; Reusch, D. Multi-Attribute Monitoring of Complex Erythropoetin Beta Glycosylation by GluC Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Peptide Mapping. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7574–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Recent applications of quantitative mass spectrometry in biopharmaceutical process development and manufacturing. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 234, 115581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, C.; Millan-Martin, S.; Carillo, S.; Fussl, F.; MacHale, C.; Bones, J. Implementation of a LC-MS based multi-attribute method (MAM) and intact multi-attribute method (iMAM) workflow for the characterisation of a GLP-Fc fusion protein. Anal. Biochem. 2024, 693, 115585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Fernandez, J.; Vellala, P.; Kulkarni, T.A.; Aguilar, I.; Ritz, D.; Lan, K.; Patel, P.; et al. A Fully Integrated Online Platform For Real Time Monitoring Of Multiple Product Quality Attributes In Biopharmaceutical Processes For Monoclonal Antibody Therapeutics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.E.; Dubois, H.; Hoffmann, M.; DEri, S.; Fromentin, Y.; Wiesner, J.; Pfenninger, A.; Clavier, S.; Pieper, A.; Duhau, L.; et al. Automated mass spectrometry multi-attribute method analyses for process development and characterization of mAbs. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1166, 122540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, A.R.; Edgeworth, M.; Devine, P.W.A.; Shepherd, S.; Chatterton, N.; Turner, C.; Lilley, K.S.; Chen, X.; Bond, N.J. Multi-Attribute Monitoring Method for Process Development of Engineered Antibody for Site-Specific Conjugation. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2023, 34, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Kwofie, F.; Attanasio, N.; Haas, M.; Higgins, J.; Kosanam, H. Exploring the Correlation between LC-MS Multi-Attribute Method and Conventional Chromatographic Product Quality Assays through Multivariate Data Analysis. AAPS J. 2024, 27, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, L.; Fu, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Qian, W.; Zhou, X.; et al. Mass spectrometry-based multi-attribute method for mutation analysis in the early development of therapeutic proteins. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 220, 115018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.R.; Mulholland, J.; Lewis, M.J.; Hu, P. Targeted CQA analytical control strategy for commercial antibody products: Replacing ion-exchange chromatography methods for charge heterogeneity with multi-attribute monitoring. mAbs 2024, 16, 2341641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mans, J.; Oyugi, M.; Asmelash, B.; Sommers, C.; Rogstad, S. The Use of Mass Spectrometry in Therapeutic Protein Biologics License Applications: A Retrospective Review Revisited. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2023, 34, 2575–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogstad, S.; Faustino, A.; Ruth, A.; Keire, D.; Boyne, M.; Park, J. A Retrospective Evaluation of the Use of Mass Spectrometry in FDA Biologics License Applications. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2017, 28, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butre, C.I.; D’Atri, V.; Diemer, H.; Colas, O.; Wagner, E.; Beck, A.; Cianferani, S.; Guillarme, D.; Delobel, A. Interlaboratory Evaluation of a User-Friendly Benchtop Mass Spectrometer for Multiple-Attribute Monitoring Studies of a Monoclonal Antibody. Molecules 2023, 28, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitasuwan, P.; Powers, T.W.; Medwid, T.; Huang, Y.; Bare, B.; Lee, L.A. Enhancing the multi-attribute method through an automated and high-throughput sample preparation. mAbs 2021, 13, 1978131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.; Zhang, Z. Fully Unattended Online Protein Digestion and LC-MS Peptide Mapping. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 15514–15521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pierson, N.A.; Hua, X.; Patel, B.A.; Olma, M.H.; Strulson, C.A.; Letarte, S.; Richardson, D.D. Analytical Performance Evaluation of Identity, Quality-Attribute Monitoring and new Peak Detection in a Platform Multi-Attribute Method Using Lys-C Digestion for Characterization and Quality Control of Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchahoir, T.; Schiel, J.E.; Rogers, R.; Heckert, A.; Place, B.J.; Ammerman, A.; Li, X.; Robinson, T.; Schmidt, B.; Chumsae, C.M.; et al. New Peak Detection Performance Metrics from the MAM Consortium Interlaboratory Study. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2021, 32, 913–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyugi, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Wu, D.; Rogstad, S. Method validation and new peak detection for the liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry multi-attribute method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 234, 115564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Validation of Analytical Procedures Q2 (R2); ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline; International Conference on Harmonization (ICH): Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Analytical Procedure Development Q14; ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline; International Conference on Harmonization (ICH): Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Evans, A.R.; Hebert, A.S.; Mulholland, J.; Lewis, M.J.; Hu, P. ID-MAM: A Validated Identity and Multi-Attribute Monitoring Method for Commercial Release and Stability Testing of a Bispecific Antibody. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 9166–9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chan, P.K.; Richardson, J.; Shah, B. An evaluation of instrument types for mass spectrometry-based multi-attribute analysis of biotherapeutics. mAbs 2020, 12, 1783062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.; Jiang, X.G.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z. LC-MS/MS peptide mapping with automated data processing for routine profiling of N-glycans in immunoglobulins. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2014, 25, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwald-Gruber, C.; Thader, A.; Maresch, D.; Dalik, T.; Altmann, F. Determination of true ratios of different N-glycan structures in electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 2519–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Vallejo, D.; Hageman, T.S.; White, D.R.; Benet, A.; Coghlan, J.; Sen, K.I.; Ford, M.; Saveliev, S.; et al. Multifaceted assessment of rituximab biosimilarity: The impact of glycan microheterogeneity on Fc function. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 146, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montacir, O.; Montacir, H.; Eravci, M.; Springer, A.; Hinderlich, S.; Saadati, A.; Parr, M.K. Comparability study of Rituximab originator and follow-on biopharmaceutical. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 140, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remoroza, C.A.; Burke, M.C.; Mak, T.D.; Sheetlin, S.L.; Mirokhin, Y.A.; Cooper, B.T.; Goecker, Z.C.; Lowenthal, M.S.; Yang, X.; Wang, G.; et al. Comparison of N-Glycopeptide to Released N-Glycan Abundances and the Influence of Glycopeptide Mass and Charge States on N-Linked Glycosylation of IgG Antibodies. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 1443–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhu, X.; Wu, W.; Ludwig, R.; Song, H.; Li, R.; Zhou, J.; Tao, L.; Leone, A.M. Subunit mass analysis for monitoring multiple attributes of monoclonal antibodies. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2019, 33, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chu, L.; Li, W.; Lawson, K.; Apostol, I.; Eris, T. Application of a Quantitative LC-MS Multiattribute Method for Monitoring Site-Specific Glycan Heterogeneity on a Monoclonal Antibody Containing Two N-Linked Glycosylation Sites. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3562–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Liu, T.; Xu, J.; Guo, Q.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhuang, H.; Pan, Z.; Fu, R.; Zhao, X.; et al. Rapid Mass Spectrometry-Based Multiattribute Method for Glycation Analysis with Integrated Afucosylation Detection Capability. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2024, 35, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carillo, S.; Perez-Robles, R.; Jakes, C.; Ribeiro da Silva, M.; Millan Martin, S.; Farrell, A.; Navas, N.; Bones, J. Comparing different domains of analysis for the characterisation of N-glycans on monoclonal antibodies. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipman, J.; Karfunkle, M.; Zhu, H.; Zhuo, Y.; Chen, K.; Patabandige, M.; Wu, D.; Oyugi, M.; Kerr, R.; Yang, K.; et al. Assessment of monoclonal antibody glycosylation: A comparative study using HRMS, NMR, and HILIC-FLD. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Machiesky, L.A.; De Mel, N.; Du, Q.; Xu, W.; Washabaugh, M.; Jiang, X.R.; Wang, J. Characterization of IgG1 Fc Deamidation at Asparagine 325 and Its Impact on Antibody-dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity and FcγRIIIa Binding. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camperi, J.; Goyon, A.; Guillarme, D.; Zhang, K.; Stella, C. Multi-dimensional LC-MS: The next generation characterization of antibody-based therapeutics by unified online bottom-up, middle-up and intact approaches. Analyst 2021, 146, 747–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gstottner, C.; Klemm, D.; Haberger, M.; Bathke, A.; Wegele, H.; Bell, C.; Kopf, R. Fast and Automated Characterization of Antibody Variants with 4D HPLC/MS. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Savane, T.S.; Rathore, A.S. Multiattribute Monitoring of Aggregates and Charge Variants of Monoclonal Antibody through Native 2D-SEC-MS-WCX-MS. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2023, 34, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotti-Ciarlet, A.; Wang, W.; Lownes, R.; Pristatsky, P.; Fang, Y.; McKelvey, T.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Drummond, J.; Prueksaritanont, T.; et al. Impact of methionine oxidation on the binding of human IgG1 to FcRn and Fcγ receptors. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1878–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Chen, K.; Chu, L.; Kinderman, F.; Apostol, I.; Huang, G. Methionine oxidation in human IgG2 Fc decreases binding affinities to protein A and FcRn. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumsae, C.; Gaza-Bulseco, G.; Sun, J.; Liu, H. Comparison of methionine oxidation in thermal stability and chemically stressed samples of a fully human monoclonal antibody. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 850, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshima, G.; Li, M.X.; Danishmand, R.; Obi, C.; To, R.; Huang, C.; Kung, J.; Lahidji, V.; Freeberg, J.; Thorner, L.; et al. Separation of oxidized variants of a monoclonal antibody by anion-exchange. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2091–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyon, A.; Excoffier, M.; Janin-Bussat, M.C.; Bobaly, B.; Fekete, S.; Guillarme, D.; Beck, A. Determination of isoelectric points and relative charge variants of 23 therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1065–1066, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, L.W., Jr.; Qiu, D.; Mahon, D.; Adamo, M.; Cheng, K.C. C-terminal lysine variants in fully human monoclonal antibodies: Investigation of test methods and possible causes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 100, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.S.; Nightlinger, N.S.; Livingston, B.; Campbell, P.; Bailey, R.; Balland, A. Development of a quantitative mass spectrometry multi-attribute method for characterization, quality control testing and disposition of biologics. mAbs 2015, 7, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mass Spectrometry-Based Multi Attribute Method for Therapeutic Proteins<1060>; USP: Rockville, MD, USA, 2025.
- Muriithi, B.; Ippoliti, S.; Finny, A.; Addepalli, B.; Lauber, M. Clean and Complete Protein Digestion with an Autolysis Resistant Trypsin for Peptide Mapping. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 5221–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Specifications: Test Procedures and Acceptance Criteria for Biotechnological/Biological Products Q6B. In ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline; International Conference on Harmonization (ICH): Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.

| Condition | Samples | Site Monitored (Heavy Chain) |
|---|---|---|
| Long-term stability, 5 °C | 0, 1, 6, 9, 12 months | N388, N301 glycans, Q1, K451 |
| Accelerated stability, 25 °C/60% RH | 0, 1, 6, 9, 12 months | N388, N301 glycans, Q1, K451 |
| Oxidative stress | 0%, 0.05%, 0.1% H2O2 | M256, M432 |
| pH 3.4 | 0, 24, 72 h | N388 |
| pH 10.0 | 0, 24, 72 h | N388 |
| 50 °C | 0, 24, 72 h | N388 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shipman, J.; Oyugi, M.; Marzan, T.A.; Geerlof-Vidavsky, I.; Kirkpatrick, D.; Zhu, H.; Rasangika, M.; Rogstad, S. A Multi-Laboratory, Multi-Platform Analysis of the Multi-Attribute Method. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111613
Shipman J, Oyugi M, Marzan TA, Geerlof-Vidavsky I, Kirkpatrick D, Zhu H, Rasangika M, Rogstad S. A Multi-Laboratory, Multi-Platform Analysis of the Multi-Attribute Method. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111613
Chicago/Turabian StyleShipman, Joshua, Mercy Oyugi, Tim Andres Marzan, Ilan Geerlof-Vidavsky, Douglas Kirkpatrick, Hongbin Zhu, Milani Rasangika, and Sarah Rogstad. 2025. "A Multi-Laboratory, Multi-Platform Analysis of the Multi-Attribute Method" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111613
APA StyleShipman, J., Oyugi, M., Marzan, T. A., Geerlof-Vidavsky, I., Kirkpatrick, D., Zhu, H., Rasangika, M., & Rogstad, S. (2025). A Multi-Laboratory, Multi-Platform Analysis of the Multi-Attribute Method. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111613






