Pfaffia glomerata Ameliorates BPA-Induced Reproductive Impairments in Mice by Suppressing Apoptosis via PI3K/AKT Signaling Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Ingredients of Pg
2.2. Generation of Drug-Disease Venn Diagram
2.3. Ingredient-Target-Disease Network Analysis
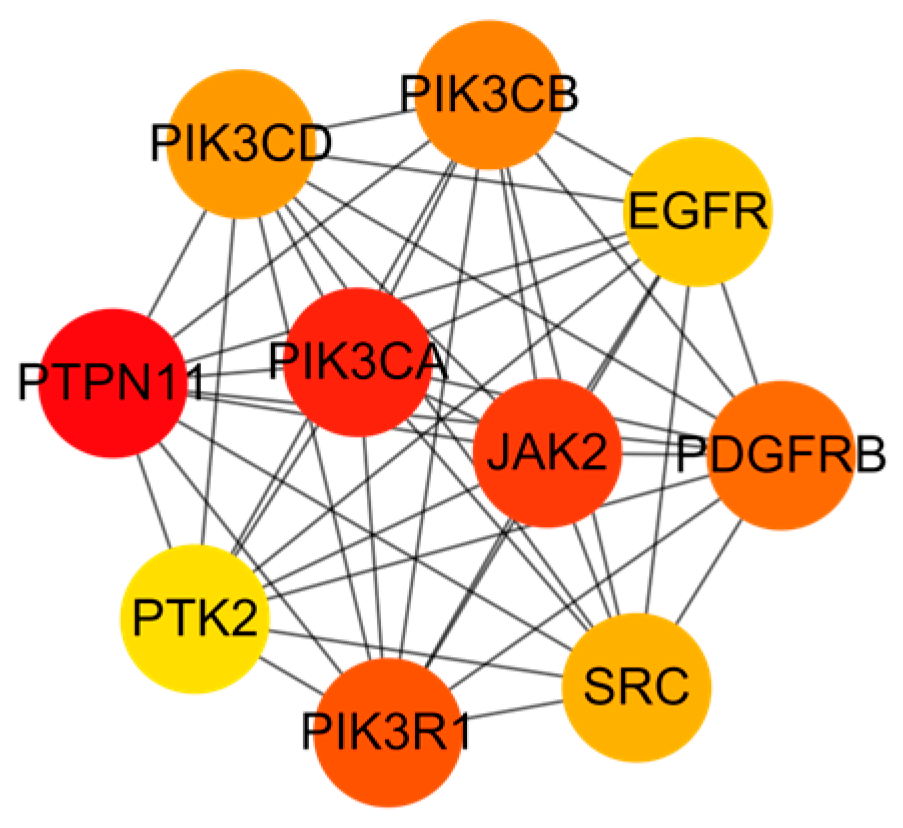
2.4. PPI Network Analysis
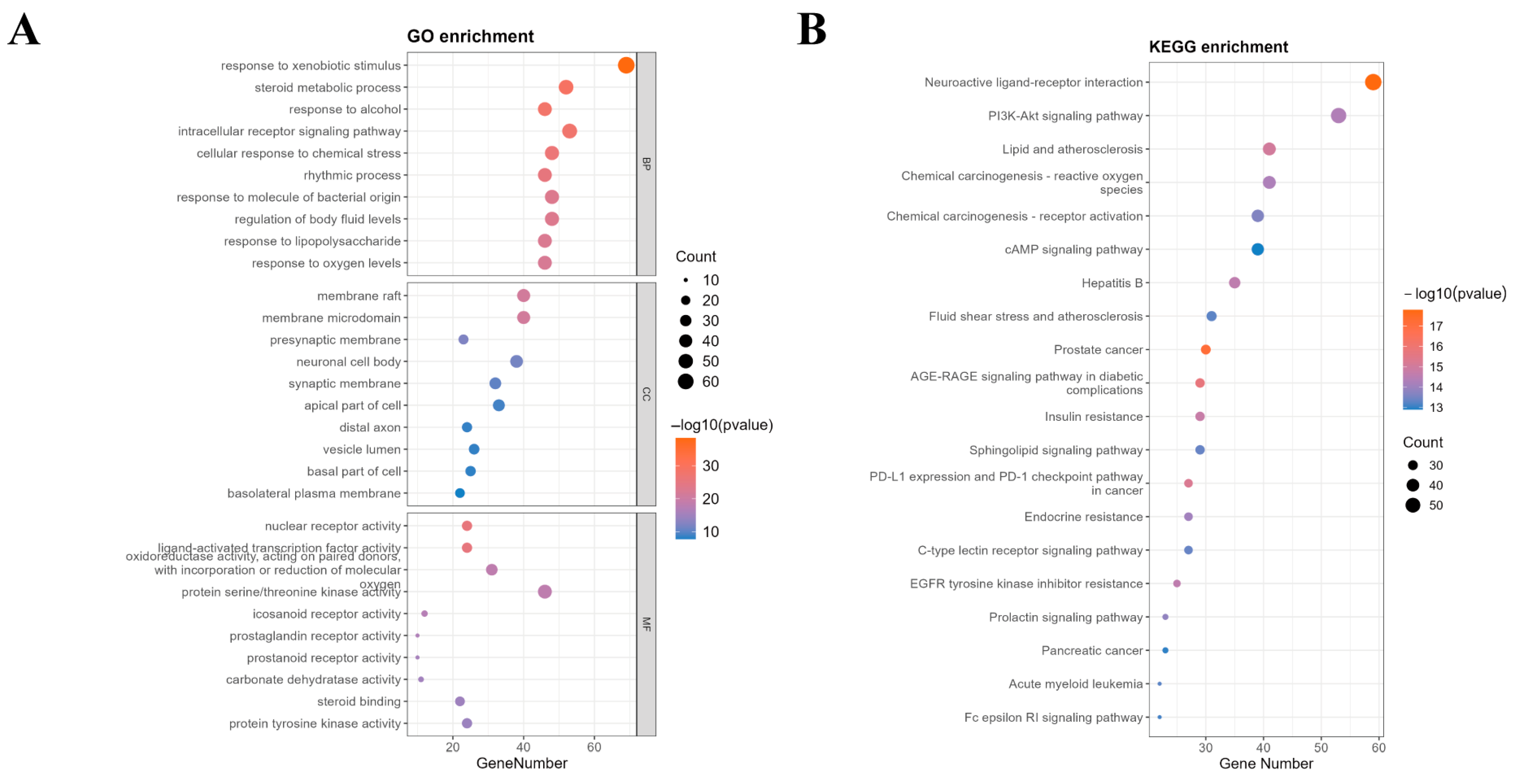
2.5. GO/KEGG Enrichment Analysis
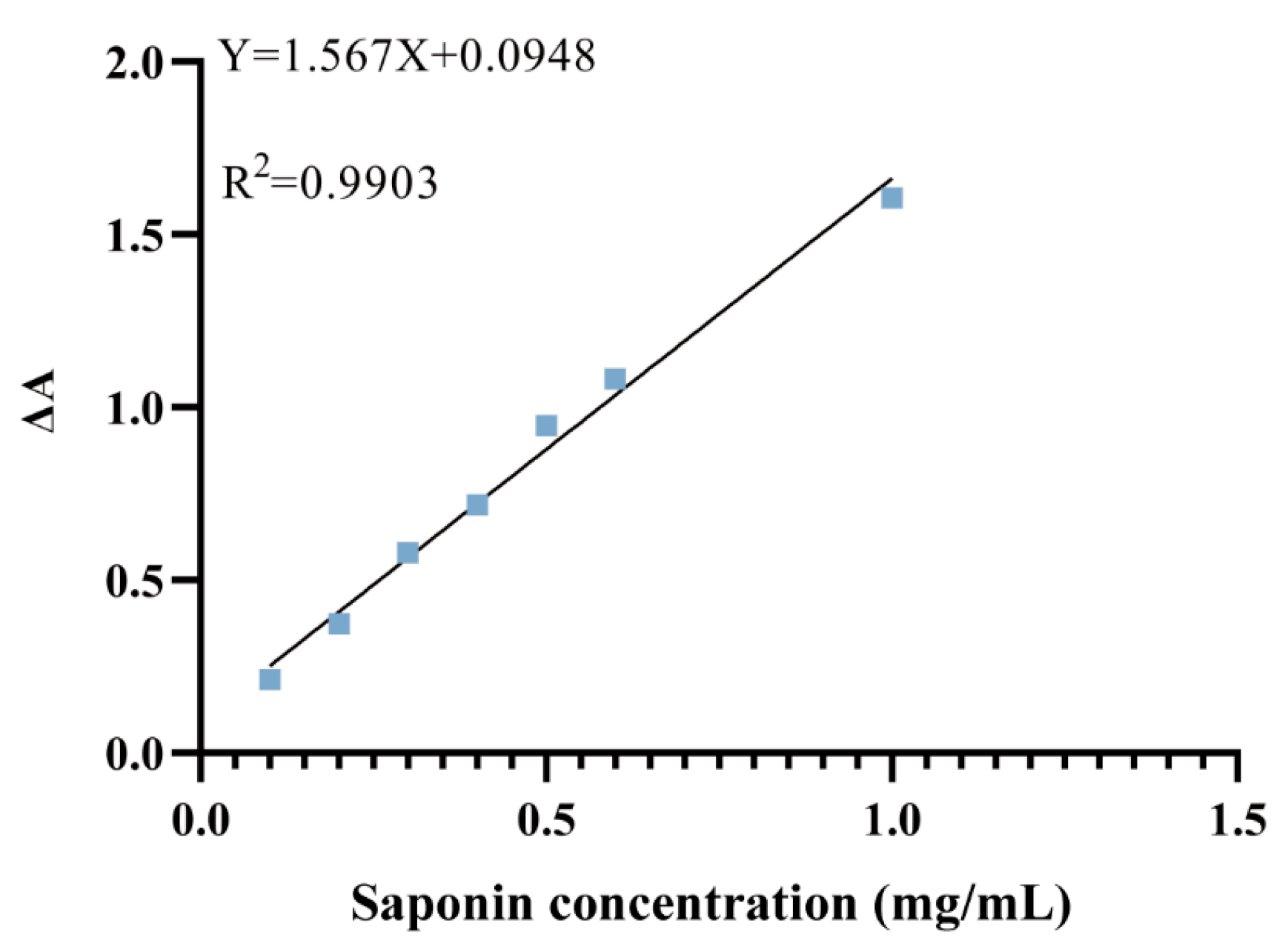
2.6. Quantification of Total Saponins in Pg
2.7. Pg Attenuates BPA-Induced Sperm Abnormalities
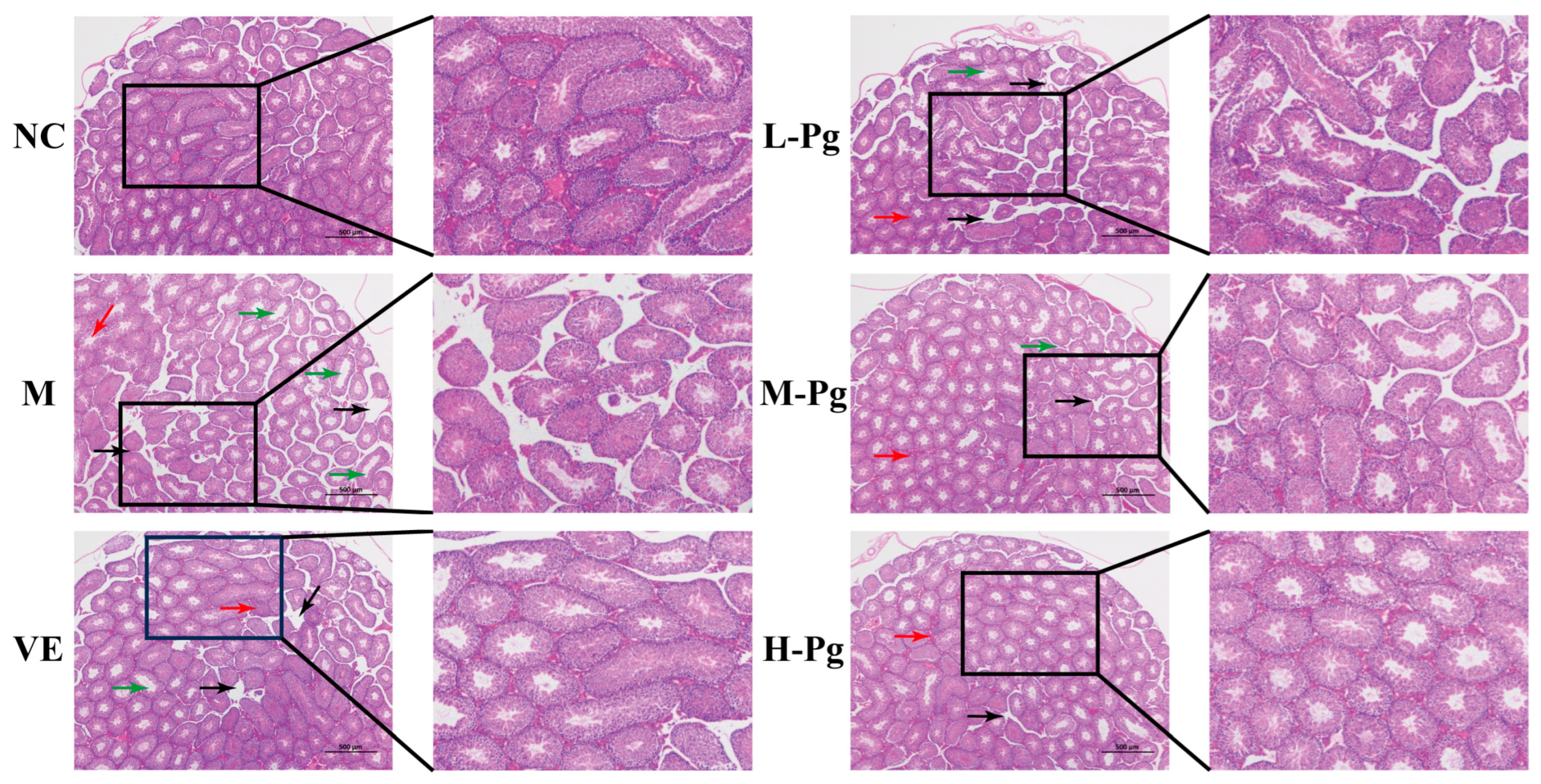
2.8. Pg Improves BPA-Induced Injury to Testicular Tissue Structure
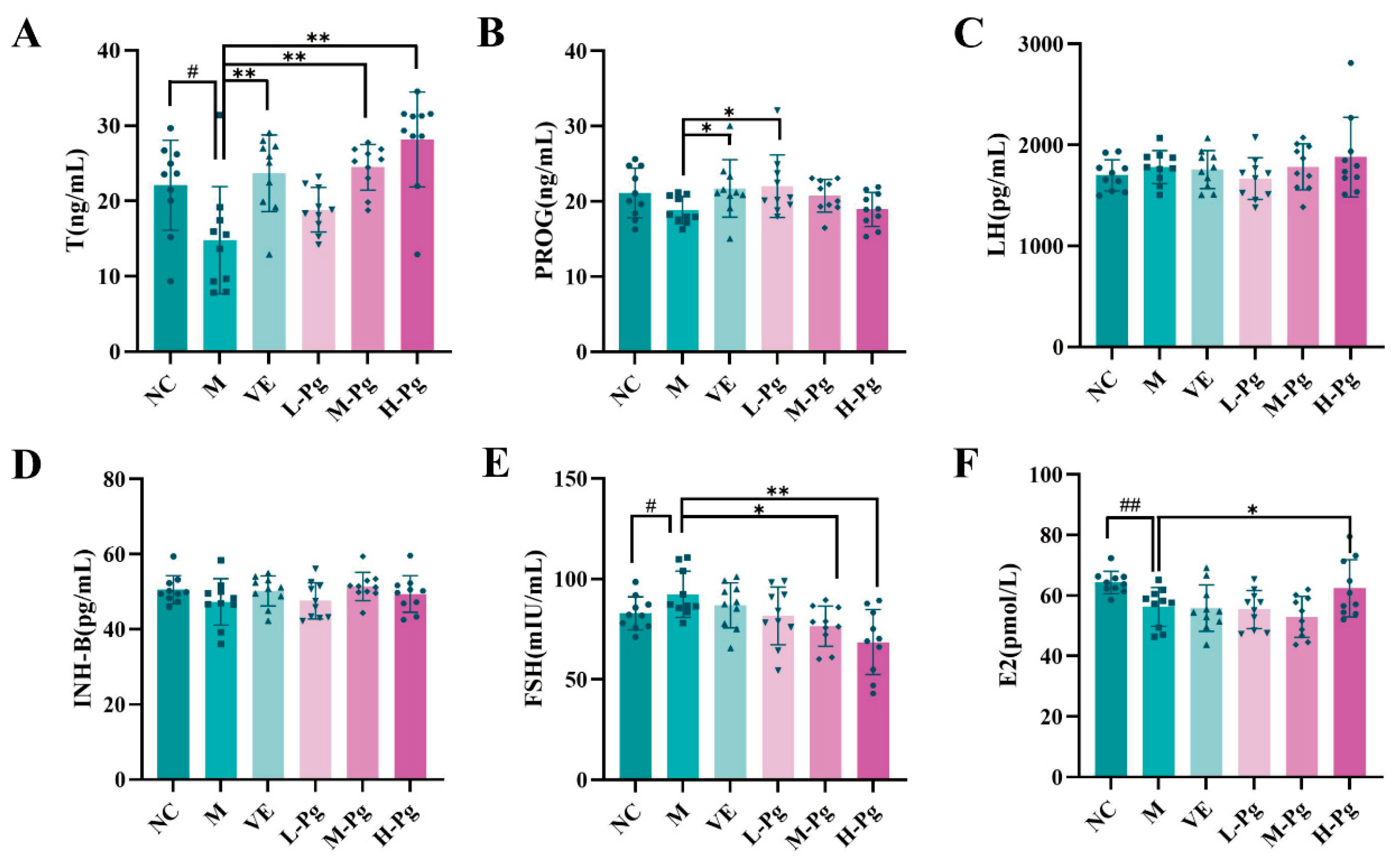
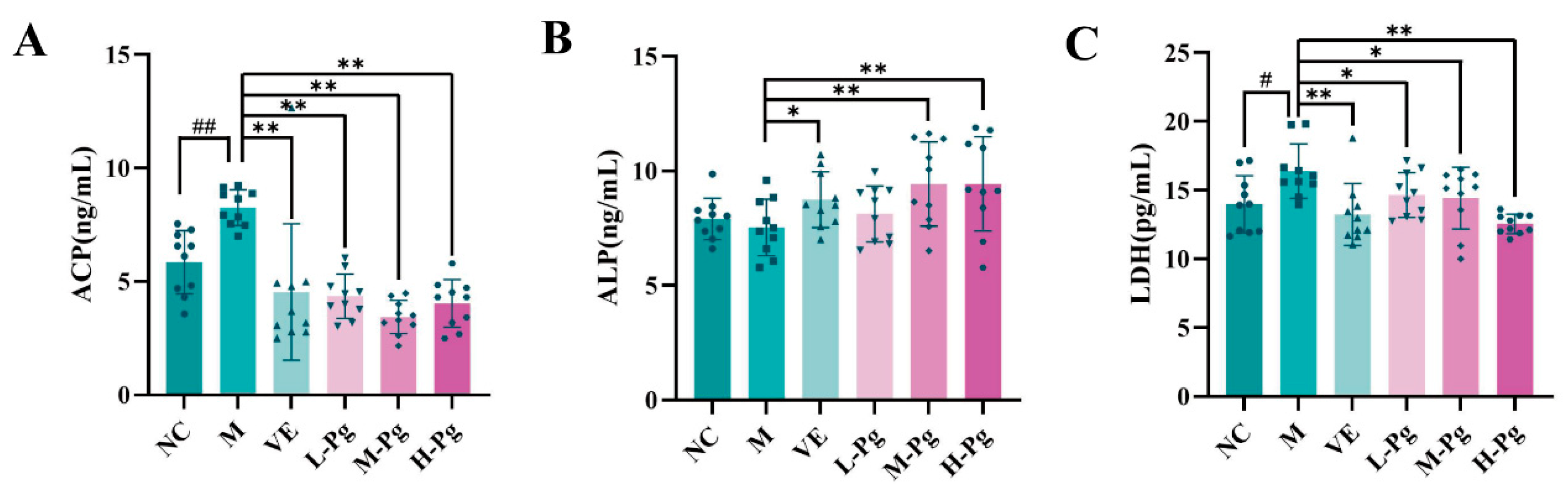
2.9. Sex Hormone Panel and Testicular Biomarkers Analysis
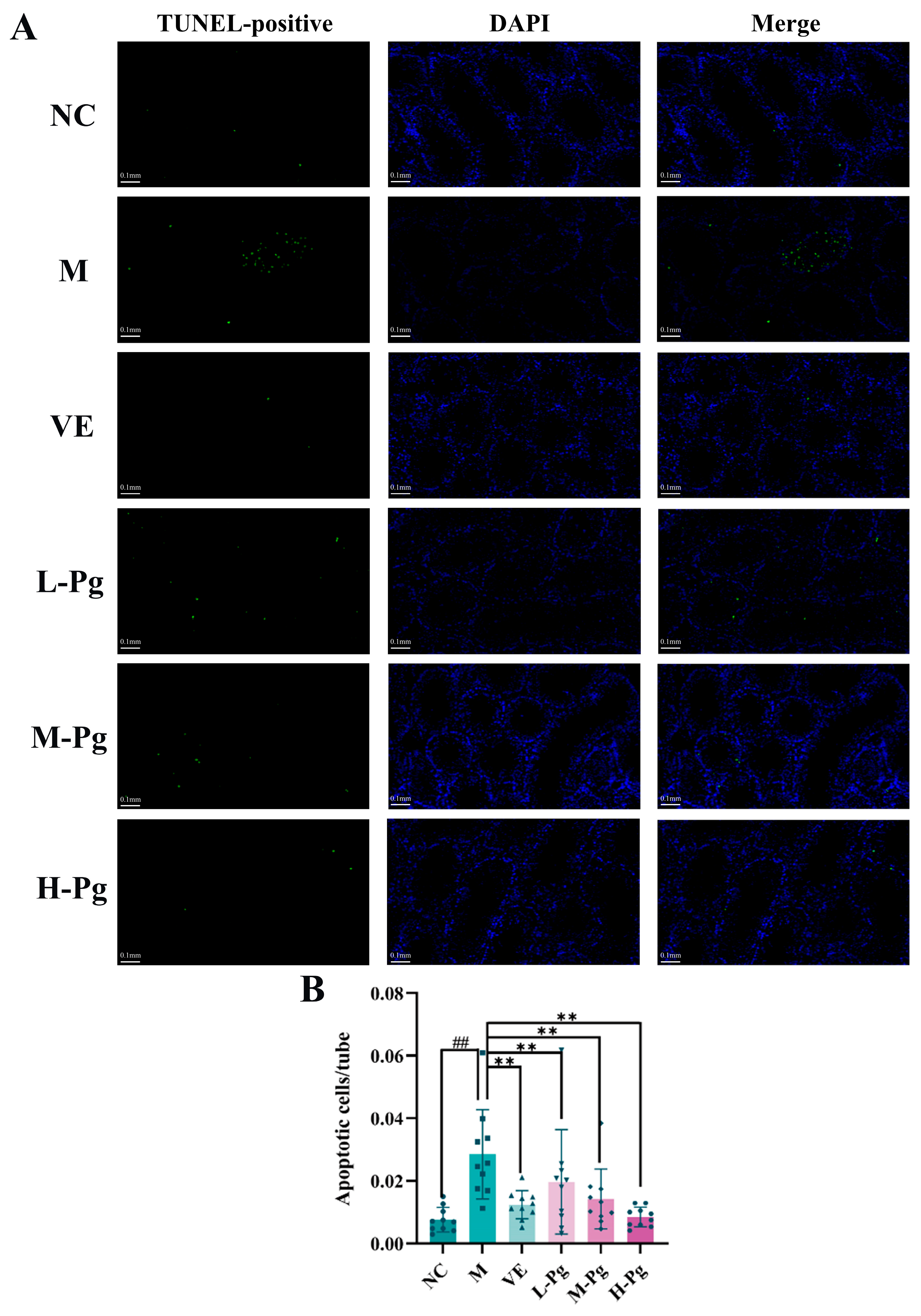
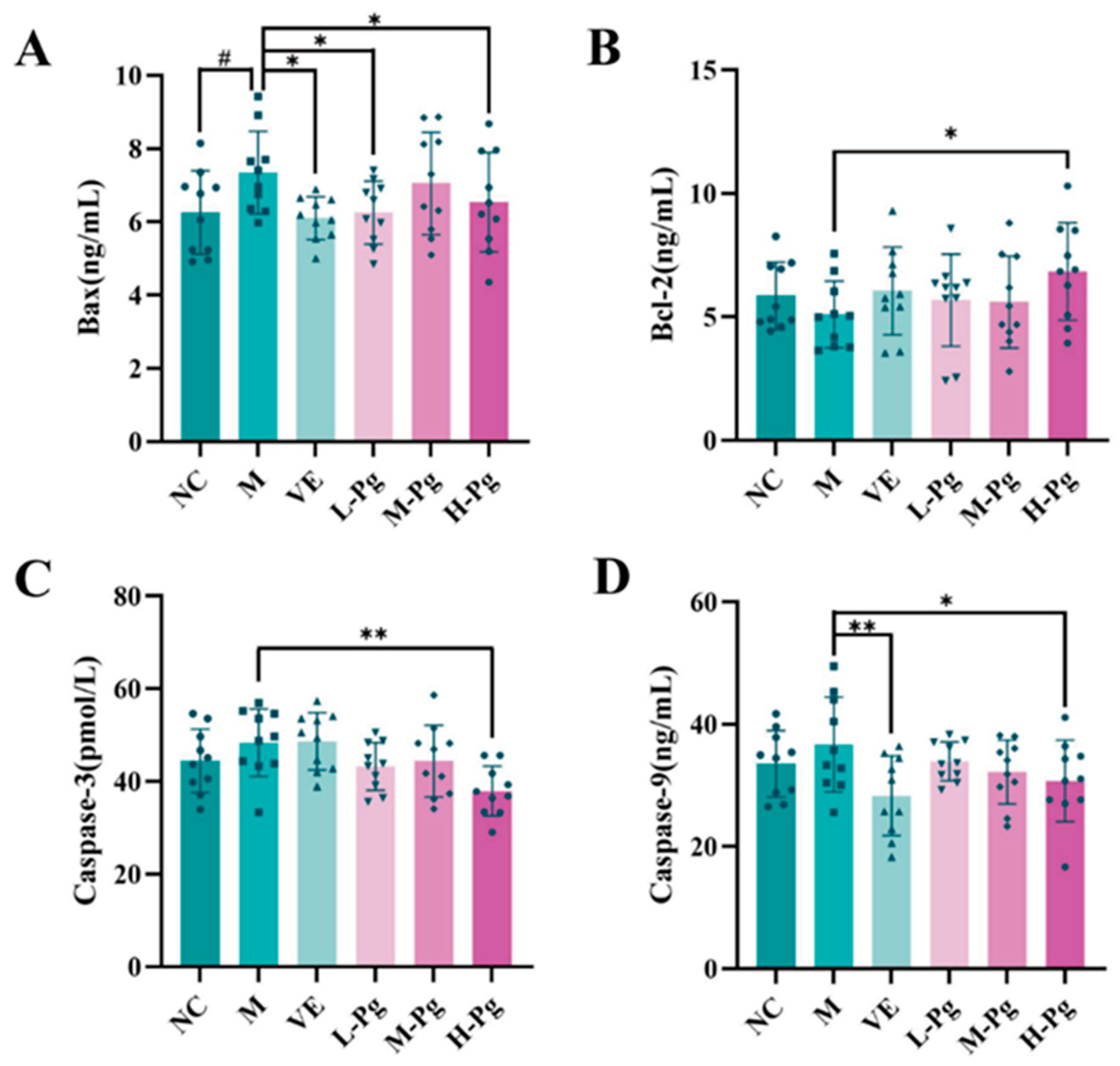
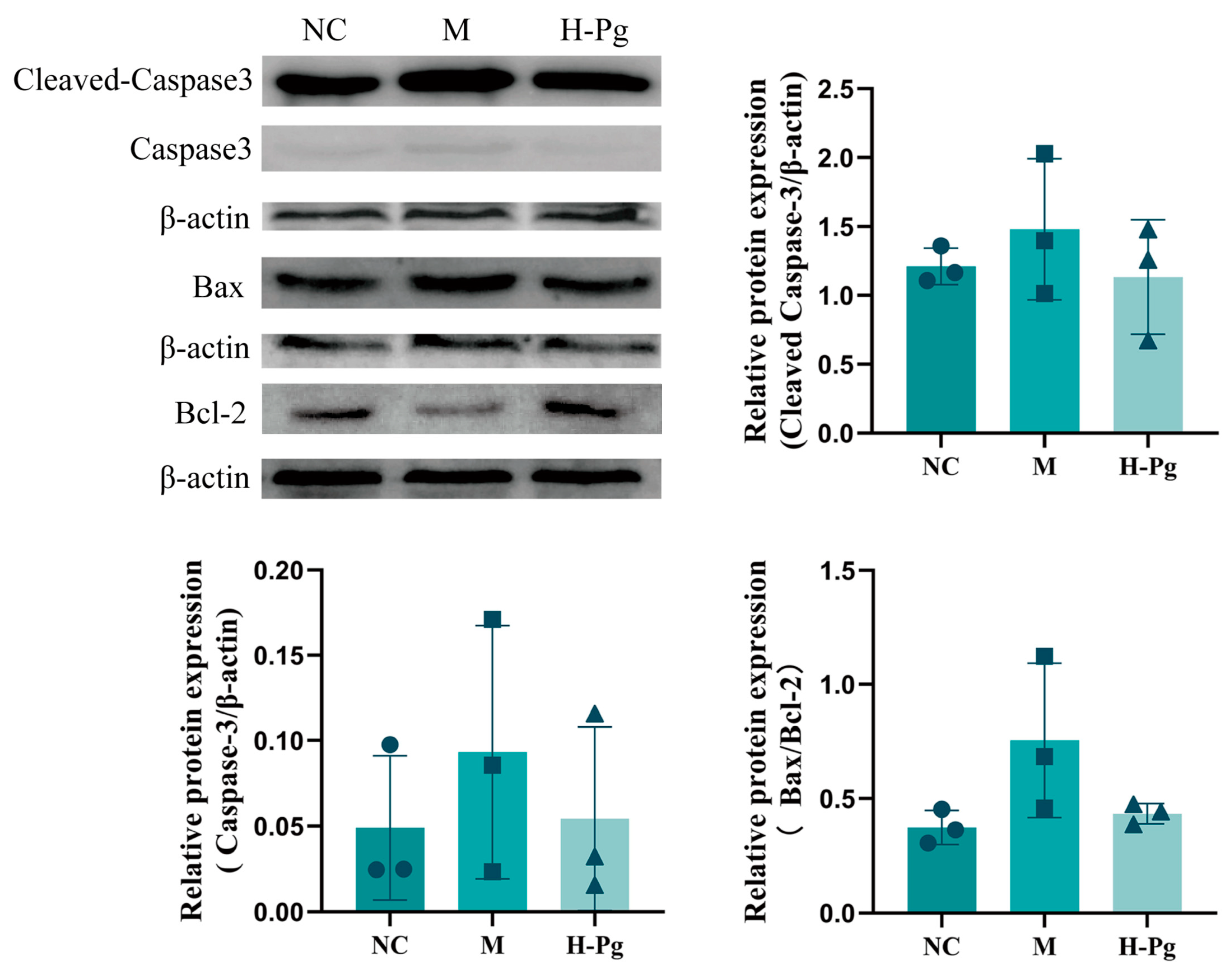
2.10. Cell Apoptosis-Related Indicator Testing
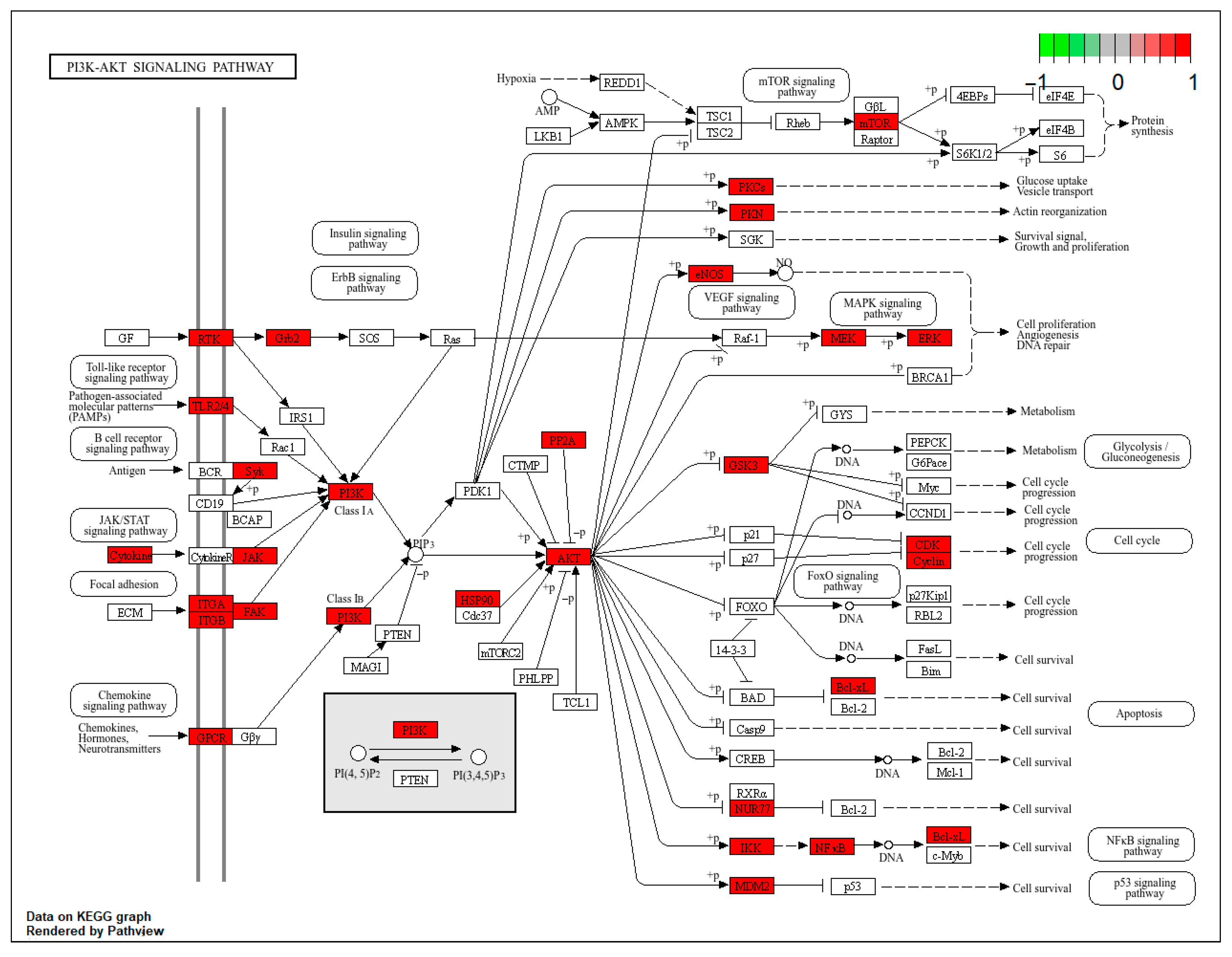
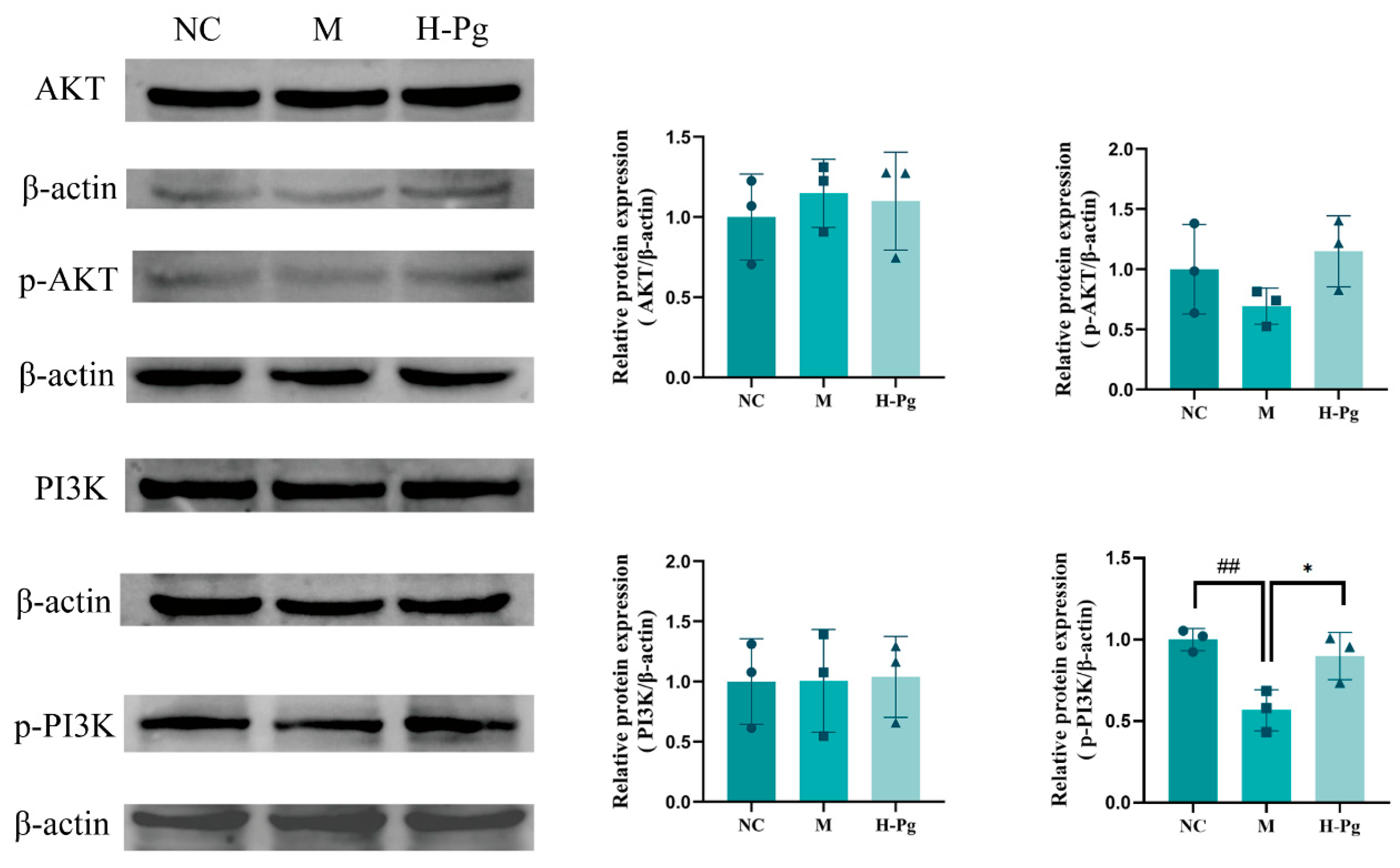
2.11. Pg Attenuates Testicular Injury by Inhibiting Apoptosis via Suppression of the BPA-Induced PI3K/AKT Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.1.1. Acquisition of Pg Bioactive Constituents and Target Prediction
4.1.2. Screening for Reproductive System Injury Targets
4.1.3. Construction of “Component-Target-Disease” Network
4.1.4. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Construction and Core Target Identification
4.1.5. Functional Enrichment Analysis
4.2. Experimental Materials and Instruments
4.3. Preparation and Content Determination of Pg Extract
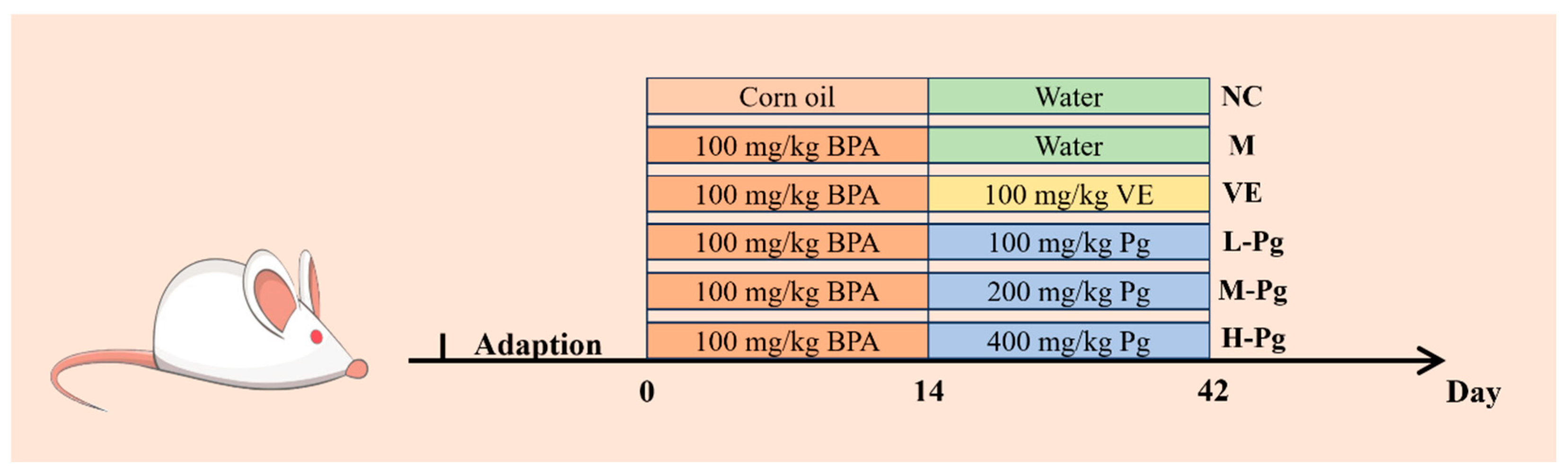
4.4. Animals and Grouping
4.5. Sperm Morphology Assessment
4.6. Histopathological Observation
4.7. TUNEL Staining
4.8. Six-Item Sex Hormone Panel
4.9. Measurement of Apoptosis
4.10. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
4.11. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kiess, W.; Haeusler, G. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 35, 101566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, B.; Terekeci, H.; Sandal, S.; Kelestimur, F. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Exposure, Effects on Human Health, Mechanism of Action, Models for Testing and Strategies for Prevention. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano, L.; Pironti, C.; Pinto, G.; Ricciardi, M.; Buono, A.; Brogna, C.; Venier, M.; Piscopo, M.; Amoresano, A.; Motta, O. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in the Environment: Occupational and Exposure Events, Effects on Human Health and Fertility. Toxics 2022, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, G.R.; Flaws, J.A. Bisphenol A and Phthalates: How Environmental Chemicals Are Reshaping Toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 166, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.-L.; Li, D.-Q.; Zhuo, M.-N.; Liao, Y.-S.; Xie, Z.-Y.; Guo, T.-L.; Li, J.-J.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Liang, Z.-Q. Organophosphorus Flame Retardants and Plasticizers: Sources, Occurrence, Toxicity and Human Exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, K.; Gong, A. Research Progress of the Application of Reference Materials in the Detection of Bisphenols in Plastic Packaged Food and Beverages. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2022, 13, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Qin, R.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Q. Determination of BPA in Sports Drink by HPLC. Food Res. Dev. 2017, 38, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Gao, J.; Gao, Y. Research on the Determination of Bisphenol A in the Electronic and Electrical Product by Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography(HPLC). Inf. Technol. Stand. 2024, 10, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Rochester, J.R.; Bolden, A.L. Bisphenol S and F: A Systematic Review and Comparison of the Hormonal Activity of Bisphenol A Substitutes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Kannan, K.; Tan, H.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.; Widelka, M. Bisphenol Analogues Other Than BPA: Environmental Occurrence, Human Exposure, and Toxicity-A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5438–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrer, C.; Roiss, T.; Von Goetz, N.; Gramec Skledar, D.; Peterlin Mašič, L.; Hungerbühler, K. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling of the Bisphenols BPA, BPS, BPF, and BPAF with New Experimental Metabolic Parameters: Comparing the Pharmacokinetic Behavior of BPA with Its Substitutes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 077002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, J.S.; Yin, L.; Measel, E.; Liang, S.; Yu, X. Effects of Bisphenol A and Its Analogs on Reproductive Health: A Mini Review. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 79, 96–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Chen, S.; Zeng, C.; Fan, Y.; Ge, W.; Chen, W. Estrogenic and Non-Estrogenic Effects of Bisphenol A and Its Action Mechanism in the Zebrafish Model: An Overview of the Past Two Decades of Work. Environ. Int. 2023, 176, 107976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanojević, M.; Sollner Dolenc, M. Mechanisms of Bisphenol A and Its Analogs as Endocrine Disruptors via Nuclear Receptors and Related Signaling Pathways. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 2397–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, D.-Y.; Pang, W.-K.; Adegoke, E.O.; Rahman, M.S.; Park, Y.-J.; Pang, M.-G. Bisphenol-A Disturbs Hormonal Levels and Testis Mitochondrial Activity, Reducing Male Fertility. Hum. Reprod. Open 2023, 2023, hoad044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, L.K.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, M.Y.; Guo, C.R.; Zhu, X.D.; Jiang, H.B.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Yan, H. Metabolomics Reveals That Ferroptosis Participates in Bisphenol A-Induced Testicular Injury. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Liu, S.; Tan, L.; Gao, X.; Fan, W.; Ding, C.; Li, M.; Tang, Z.; Shi, X.; Luo, Y.; et al. Testicular Toxicity of Bisphenol Compounds: Homeostasis Disruption of Cholesterol/Testosterone via PPARα Activation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkowska, K.; Kratz, E.M.; Sawicka, E.; Piwowar, A. The Impact of Metalloestrogens on the Physiology of Male Reproductive Health as a Current Problem of the XXI Century. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, P.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.; Li, J.; Song, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Prenatal Bisphenol A Exposure Causes Sperm Quality and Functional Defects via Leydig Cell Impairment and Meiosis Arrest in Mice Offspring. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Du, L.; Zhang, P.; Guo, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Wu, P.; Lei, X.; Qu, B. BPA Induces Testicular Damage in Male Rodents via Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 193, 114984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundakovic, M.; Champagne, F.A. Epigenetic Perspective on the Developmental Effects of Bisphenol A. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, T.; Burdeos, G.C.; Itaya, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyazawa, T. Vitamin E: Regulatory Redox Interactions. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsemeh, A.E.; Ahmed, M.M.; Fawzy, A.; Samy, W.; Tharwat, M.; Rezq, S. Vitamin E Rescues Valproic Acid-Induced Testicular Injury in Rats: Role of Autophagy. Life Sci. 2022, 296, 120434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, D.G.; Ramos, L.d.P.; Attik, N.; Pereira, T.C.; de Oliveira, L.D.; Marcucci, M.C.; Rodrigues, F.P.; Back Brito, G.N.; Carrouel, F. Pfaffia paniculata Extract, a Potential Antimicrobial Agent against Candida spp., Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, and Streptococcus Mutans Biofilms. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinello, K.C.; Fonseca, E.d.S.M.; Akisue, G.; Silva, A.P.; Salgado Oloris, S.C.; Sakai, M.; Matsuzaki, P.; Nagamine, M.K.; Palermo Neto, J.; Dagli, M.L.Z. Effects of Pfaffia paniculata (Brazilian ginseng) Extract on Macrophage Activity. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.A.R.A.; Tanimoto, A.; Quaglio, A.E.V.; Almeida, L.D.J.; Severi, J.A.; Di Stasi, L.C. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Brazilian ginseng (Pfaffia paniculata) on TNBS-Induced Intestinal Inflammation: Experimental Evidence. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, M.; Liu, Y.; Qin, M.; Lan, M.; Wu, W.; Chen, L. Pharmacognostical Study on Domestic Pfaffia glomerata. Biot. Resour. 2021, 43, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotto, L.M.; Herrig, S.P.R.; Nunes, M.G.I.F.; Sakai, O.A.; Barros, B.C.B. Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Pfaffia glomerata Leaves and Evaluation of Composition, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2025, 97, e20240317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrim Ribeiro, S.T.; Gancedo, N.C.; Braz de Oliveira, A.J.; Correia Gonçalves, R.A. A Comprehensive Review of Pfaffia glomerata Botany, Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, Biological Activities, and Biotechnology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 328, 118003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Yan, D.; Tang, L.; Xu, L.; Huang, L.; Li, B. Optimization of Pfaffia paniculata Compound Extraction Process Based on Multiple Indicators and Its Anti-Fatigue Study. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2022, 45, 2452–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dere, E.; Anderson, L.M.; Hwang, K.; Boekelheide, K. Biomarkers of Chemotherapy-Induced Testicular Damage. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 100, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Yu, R.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, J.; Huang, L.; Zhu, W.; Liu, H. Excavation of the Core Efficacy of Pfaffia paniculata Based on Network Pharmacology. World Sci. Technol.-Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 23, 4146–4155. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Ma, X.; Wen, X.; Chen, D.; Si, J. Chemical Constituents from Pfaffia paniculata. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2009, 40, 522–525. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J. Studies on Chemical Constituents of Polar Parts of Pfaffia glomerata and Its Antitumor Activity in Vitro. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dorta de Oliveira, C.B.; Cardozo Filho, L.; Palazzo de Mello, J.C.; Valarini Júnior, O.; Calaça, G.N.; Alonso Rocha, S.; Sato, F.; Sakai, O.A. Pressurized Liquid Extraction Followed by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for Determination of Beta-Ecdysone Extracted from Pfaffia glomerata (Spreng.) Pedersen. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felipe, D.F.; Brambilla, L.Z.S.; Porto, C.; Pilau, E.J.; Cortez, D.A.G. Phytochemical Analysis of Pfaffia glomerata Inflorescences by LC-ESI-MS/MS. Molecules 2014, 19, 15720–15734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bardelli, A.; Silliman, N.; Ptak, J.; Szabo, S.; Yan, H.; Gazdar, A.; Powell, S.M.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. High Frequency of Mutations of the PIK3CA Gene in Human Cancers. Science 2004, 304, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Qin, J.; Zhou, J.; Lu, Y.; Yang, N.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Li, C. Pachymic Acid Promotes Ferroptosis and Inhibits Gastric Cancer Progression by Suppressing the PDGFRB-Mediated PI3K/Akt Pathway. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaryouh, H.; De Pauw, I.; Baysal, H.; Peeters, M.; Vermorken, J.B.; Lardon, F.; Wouters, A. Recent Insights in the PI3K/Akt Pathway as a Promising Therapeutic Target in Combination with EGFR-Targeting Agents to Treat Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 112–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, L.; Stanton, P.; de Kretser, D.M. Endocrinology of the Male Reproductive System and Spermatogenesis. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Ahmed, S.F., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Das, N.; Kumar, T.R. Molecular Regulation of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Synthesis, Secretion and Action. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 60, R131–R155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lin, W.; Wang, Z.; Huang, R.; Xia, H.; Li, Z.; Deng, J.; Ye, T.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y. Hormone Regulation in Testicular Development and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemes, H. The Phagocytic Function of Sertoli Cells: A Morphological, Biochemical, and Endocrinological Study of Lysosomes and Acid Phosphatase Localization in the Rat Testis. Endocrinology 1986, 119, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.C.; Millán, J.L. Developmental Expression of Alkaline Phosphatase Genes; Reexpression in Germ Cell Tumours and in Vitro Immortalized Germ Cells. Eur. Urol. 1993, 23, 38–44; discussion 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyovwi, M.O.; Nwangwa, E.K.; Ben-Azu, B.; Rotue, R.A.; Edesiri, T.P.; Emojevwe, V.; Igweh, J.C.; Uruaka, C.I. Prevention and Reversal of Chlorpromazine Induced Testicular Dysfunction in Rats by Synergistic Testicle-Active Flavonoids, Taurine and Coenzyme-10. Reprod. Toxicol. 2021, 101, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotta, C.; Cattaneo, M.G.; Molteni, R.; De Palma, C. Autophagy in the Regulation of Tissue Differentiation and Homeostasis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 602901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, R.; Viggiano, A.; Urbanek, K.; Cappetta, D.; Troisi, J.; Scafuro, M.; Guida, M.; Esposito, G.; Ciuffreda, L.P.; Rossi, F.; et al. Chronic Exposure to Low Dose of Bisphenol A Impacts on the First Round of Spermatogenesis via SIRT1 Modulation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; Chianese, R.; Troisi, J.; Richards, S.; Nori, S.L.; Fasano, S.; Guida, M.; Plunk, E.; Viggiano, A.; Pierantoni, R.; et al. Neuro-Toxic and Reproductive Effects of BPA. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 1109–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, F. Chronic Exposure of BPA Impairs Male Germ Cell Proliferation and Induces Lower Sperm Quality in Male Mice. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. Shenhuang Liuwei Powder Alleviates Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Ulcers in Rats through the Inhibition of the AGE/RAGE Signaling Pathway and Promotion of Antibacterial Activity and Angiogenesis via Activation of the PI3K/Akt/eNOS/HIF-1α Pathway. Comb. Chem. High. Throughput Screen. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnero, A.; Blanco-Aparicio, C.; Renner, O.; Link, W.; Leal, J.F.M. The PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signalling Pathway in Cancer, Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Bisphenol A and Male Murine Reproductive System: Finding a Link between Plasticizer and Compromised Health. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 183, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. Echinacoside and Cistanche Tubulosa (Schenk) R. Wight Ameliorate Bisphenol A-Induced Testicular and Sperm Damage in Rats through Gonad Axis Regulated Steroidogenic Enzymes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, S.; Sengul, E.; Yildirim, S.; Aksu, E.H.; Bolat, İ.; Çınar, B.; Shadidizaji, A.; Çelebi, F.; Warda, M. Molecular Insights into the Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of P-Coumaric Acid against Bisphenol A-Induced Testicular Injury: In Vivo and in Silico Studies. Reprod. Toxicol. 2024, 125, 108579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grami, D.; Rtibi, K.; Hammami, I.; Selmi, S.; De Toni, L.; Foresta, C.; Marzouki, L.; Sebai, H. Protective Action of Eruca Sativa Leaves Aqueous Extracts Against Bisphenol A-Caused In Vivo Testicular Damages. J. Med. Food 2020, 23, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalet, S.M. Normal Testicular Function and Spermatogenesis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 53, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufau, M.L. The Luteinizing Hormone Receptor. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1998, 60, 461–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedara, I.A.; Subair, T.I.; Ego, V.C.; Oyediran, O.; Farombi, E.O. Chemoprotective Role of Quercetin in Manganese-Induced Toxicity along the Brain-Pituitary-Testicular Axis in Rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 263, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.S. LDH-C4: A Target with Therapeutic Potential for Cancer and Contraception. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2012, 371, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzynkiewicz, Z.; Galkowski, D.; Zhao, H. Analysis of Apoptosis by Cytometry Using TUNEL Assay. Methods 2008, 44, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenhong, L.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, B.; Rongxian, L.; Shiyan, G.; Zuoshun, H. Cadmium Treatment Induces Oxidative Damage and Apoptosis in Vitro Skeletal Muscle Cells. Toxicology 2025, 515, 154139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Ge, X.; Zhang, F. Puerarin Attenuates Neurological Deficits via Bcl-2/Bax/Cleaved Caspase-3 and Sirt3/SOD2 Apoptotic Pathways in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Ray, S.; Hussein, M.A.; Srkalovic, G.; Almasan, A. Role of Apo2L/TRAIL and Bcl-2-Family Proteins in Apoptosis of Multiple Myeloma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2003, 44, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghav, P.K.; Verma, Y.K.; Gangenahalli, G.U. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Bcl-2 Protein to Predict the Structure of Its Unordered Flexible Loop Domain. J. Mol. Model. 2012, 18, 1885–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.E.; Hohorst, L.; García-Sáez, A.J. Expanding Roles of BCL-2 Proteins in Apoptosis Execution and Beyond. J. Cell Sci. 2023, 136, jcs260790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, E.; Eaves, C.J. Paradoxical Roles of Caspase-3 in Regulating Cell Survival, Proliferation, and Tumorigenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 221, e202201159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.G.; Jänicke, R.U. Emerging Roles of Caspase-3 in Apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. The Effects of Hormone-Mediated PI3K/AKT Signaling on Spermatogenesis in Sertoli Cells. Biocell 2023, 47, 1709–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppers, A.J.; Mitchell, L.A.; Wang, P.; Lin, M.; Aitken, R.J. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Signalling Pathway Involvement in a Truncated Apoptotic Cascade Associated with Motility Loss and Oxidative DNA Damage in Human Spermatozoa. Biochem. J. 2011, 436, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hers, I.; Vincent, E.E.; Tavaré, J.M. Akt Signalling in Health and Disease. Cell Signal 2011, 23, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Peng, C.; Liu, Y. Regulation of Ferroptosis by PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway: A Promising Therapeutic Axis in Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1372330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, R.; Wang, X.; Peng, J.; Chen, X. Research Progress of Pfaffia paniculata on Chemical Compositions and Pharmacological Actions. Inf. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 35, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, T.M.; Boeff, D.D.; de Oliveira Carvalho, L.; Ritter, M.R.; Konrath, E.L. The Traditional Use of Native Brazilian Plants for Male Sexual Dysfunction: Evidence from Ethnomedicinal Applications, Animal Models, and Possible Mechanisms of Action. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen, 6th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; ISBN 978-92-4-003078-7. [Google Scholar]
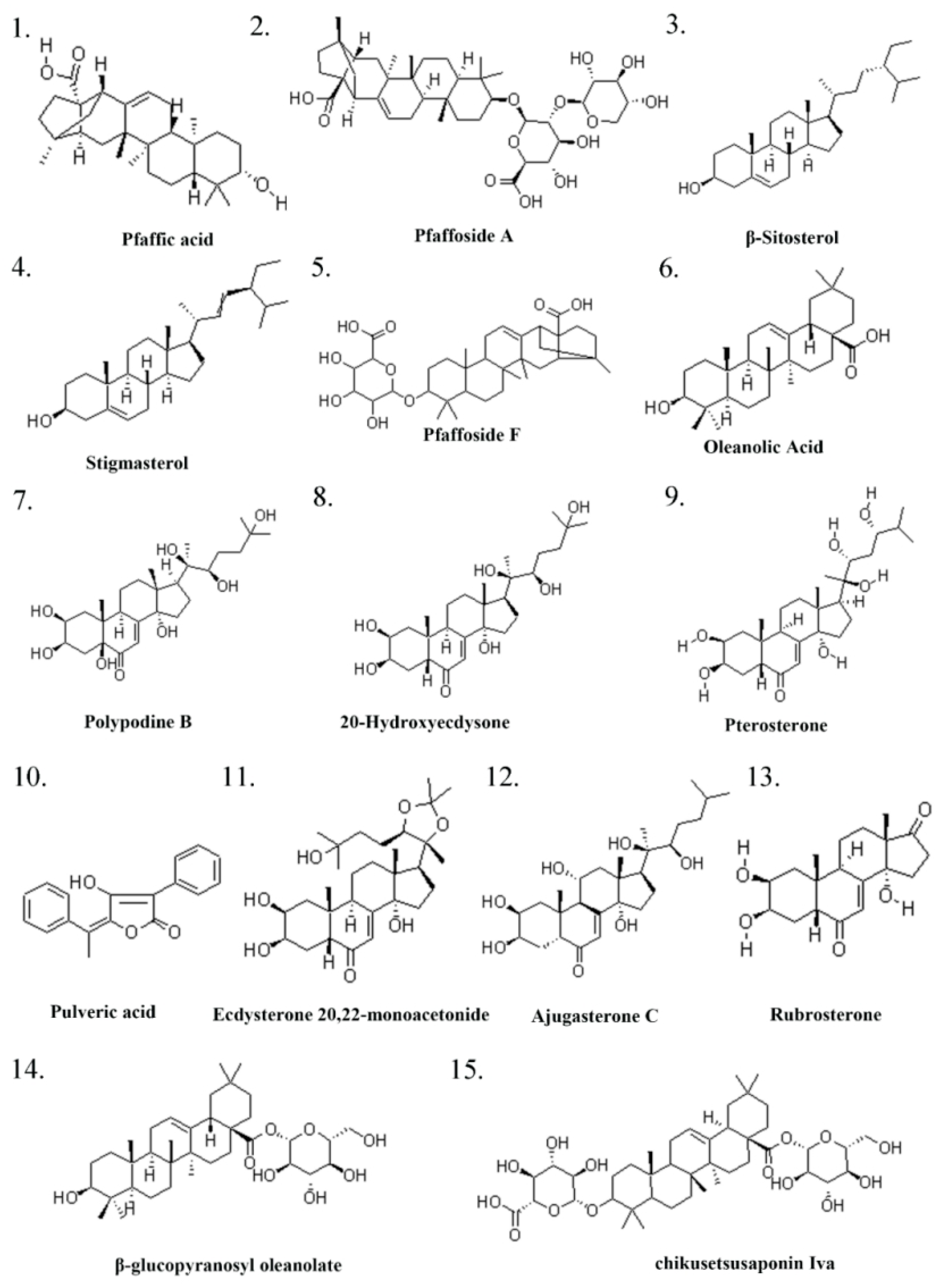
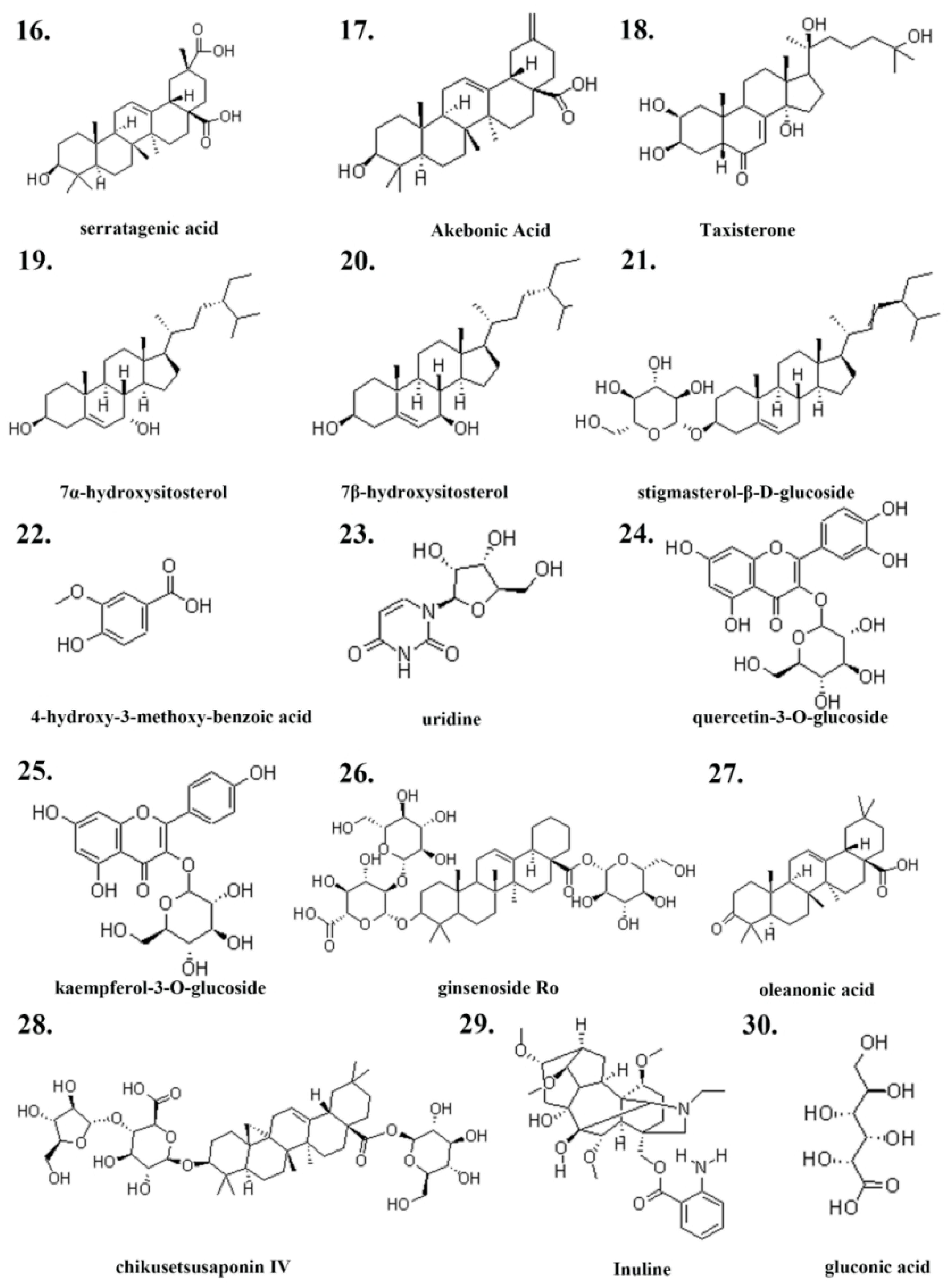
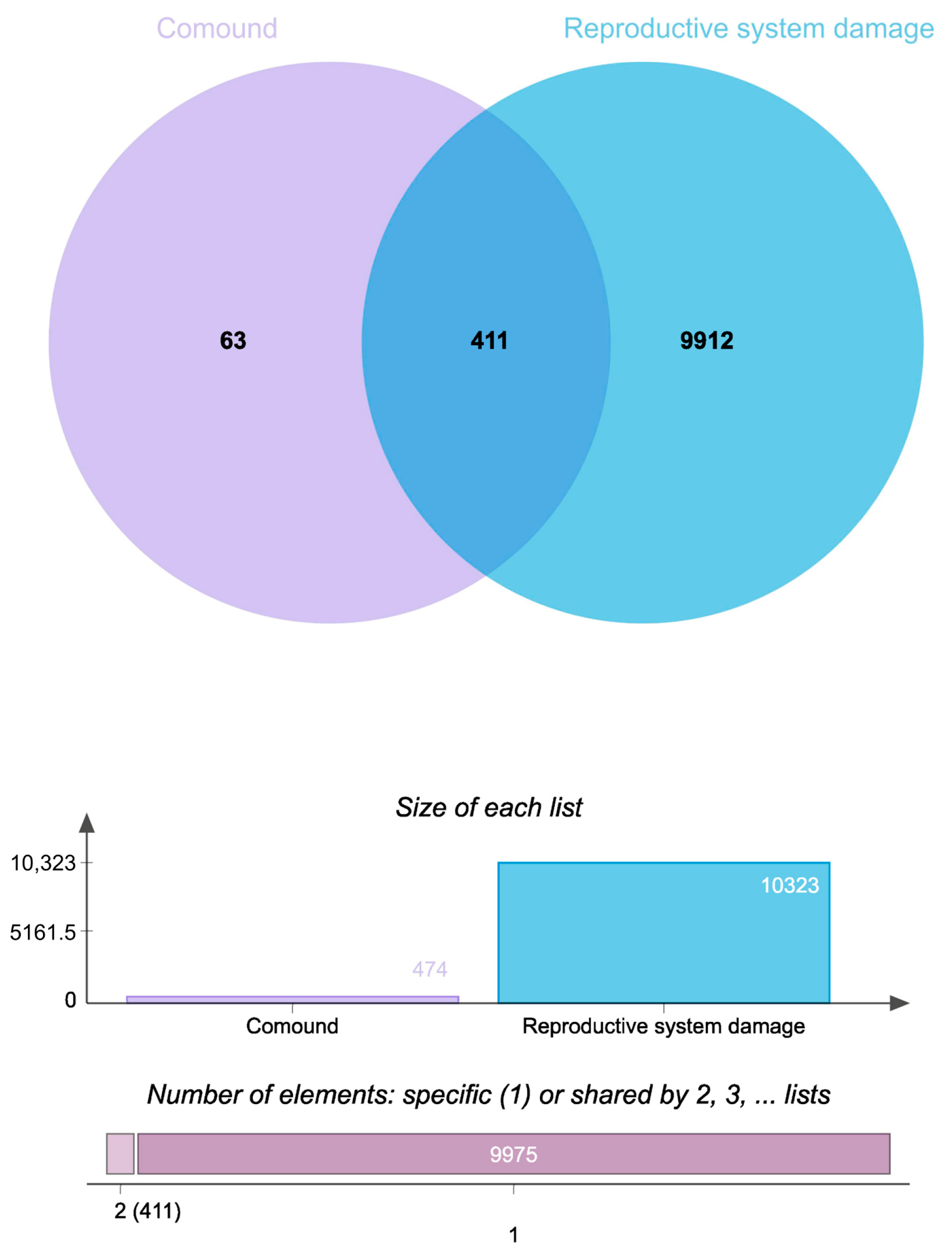
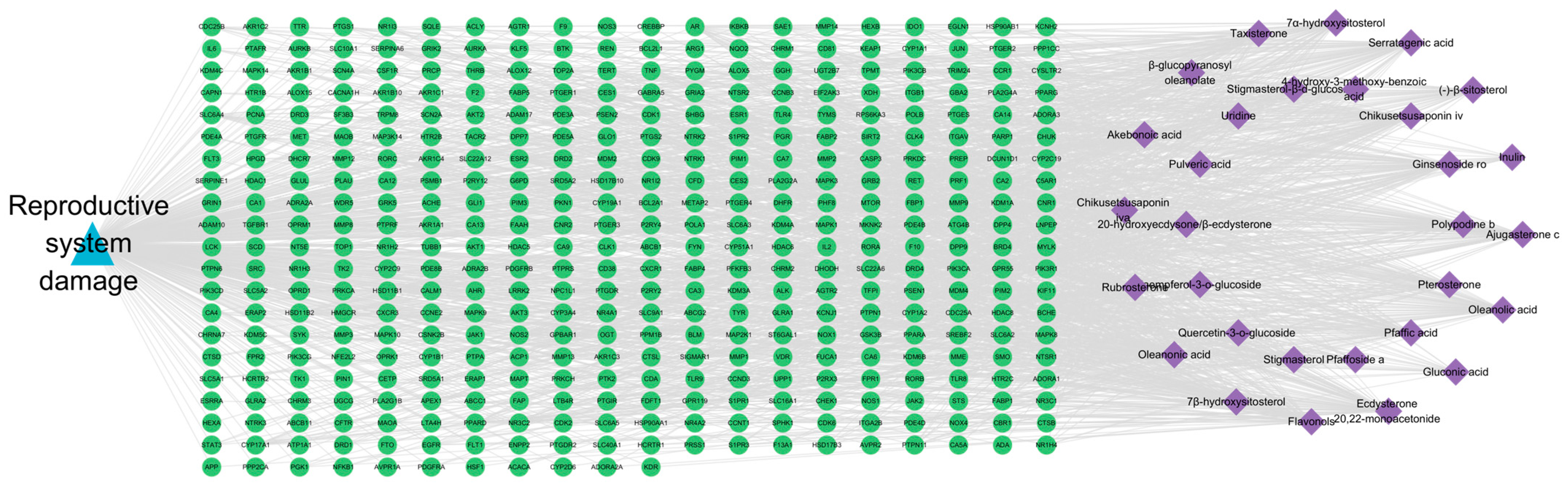


| Serial Number | Ingredient Name | CAS Number | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pfaffic acid | 86432-14-6 | [32] |
| 2 | Pfaffoside A | 90745-17-8 | [32] |
| 3 | (-)-β-Sitosterol | 83-46-5 | [32] |
| 4 | Stigmasterol | 83-48-7 | [32] |
| 5 | Flavonols | 577-85-5 | [32] |
| 6 | Oleanolic Acid | 508-02-1 | [33] |
| 7 | Polypodine B | 18069-14-2 | [32] |
| 8 | 20-Hydroxyecdysone/β-ecdysterone | 5289-74-7 | [34] |
| 9 | Pterosterone | 18089-44-6 | [34] |
| 10 | Pulveric acid | 26548-70-9 | [32] |
| 11 | Ecdysterone 20,22-monoacetonide | 22798-96-5 | [32] |
| 12 | Ajugasterone C | 23044-80-6 | [32] |
| 13 | Rubrosterone | 19466-41-2 | [34] |
| 14 | β-glucopyranosyl oleanolate | 14162-53-9 | [34] |
| 15 | chikusetsusaponin Iva | 51415-02-2 | [34] |
| 16 | serratagenic acid | 6488-64-8 | [34] |
| 17 | akebonoic acid | 104777-60-8 | [34] |
| 18 | Taxisterone | 19536-24-4 | [34] |
| 19 | 7α-hydroxysitosterol | 34427-61-7 | [34] |
| 20 | 7β-hydroxysitosterol | 15140-59-7 | [34] |
| 21 | stigmasterol-β-D-glucoside | 19716-26-8 | [34] |
| 22 | 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-benzoic acid | 121-34-6 | [33] |
| 23 | uridine | 58-96-8 | [32] |
| 24 | Inulin | 22413-78-1 | [35] |
| 25 | quercetin-3-O-glucoside | 482-35-9 | [36] |
| 26 | kaempferol-3-O-glucoside | 480-10-4 | [36] |
| 27 | ginsenoside Ro | 34367-04-9 | [36] |
| 28 | chikusetsusaponin IV | 7518-22-1 | [36] |
| 29 | oleanonic acid | 17990-42-0 | [36] |
| 30 | gluconic acid | 526-95-4 | [36] |
| Molecule Name | Degree | Betweenness Centrality | Closeness Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonols | 87 | 0.020940631 | 0.39269813 |
| Ginsenoside Ro | 86 | 0.01486894 | 0.391304348 |
| Chikusetsusaponin IV | 84 | 0.013922591 | 0.389920424 |
| Oleanonic acid | 82 | 0.010200463 | 0.389920424 |
| Ecdysterone 20,22-monoacetonide | 79 | 0.01687878 | 0.387181738 |
| Ajugasterone c | 73 | 0.011092969 | 0.38381201 |
| Oleanolic acid | 71 | 0.005200213 | 0.382480486 |
| Serratagenic acid | 71 | 0.005753417 | 0.382480486 |
| Rubrosterone | 67 | 0.008512648 | 0.379844961 |
| Pfaffic acid | 67 | 0.004583201 | 0.379844961 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, H.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Pfaffia glomerata Ameliorates BPA-Induced Reproductive Impairments in Mice by Suppressing Apoptosis via PI3K/AKT Signaling Activation. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111614
Xue H, Zhang S, Lu J, Liu J, Li Y, Chen X. Pfaffia glomerata Ameliorates BPA-Induced Reproductive Impairments in Mice by Suppressing Apoptosis via PI3K/AKT Signaling Activation. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111614
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Hongwei, Shuyan Zhang, Juan Lu, Jia Liu, Yihang Li, and Xi Chen. 2025. "Pfaffia glomerata Ameliorates BPA-Induced Reproductive Impairments in Mice by Suppressing Apoptosis via PI3K/AKT Signaling Activation" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111614
APA StyleXue, H., Zhang, S., Lu, J., Liu, J., Li, Y., & Chen, X. (2025). Pfaffia glomerata Ameliorates BPA-Induced Reproductive Impairments in Mice by Suppressing Apoptosis via PI3K/AKT Signaling Activation. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111614








