Screening Novel Furoxan Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors Targeting Thioredoxin Glutathione Reductase of Fasciola gigantica
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
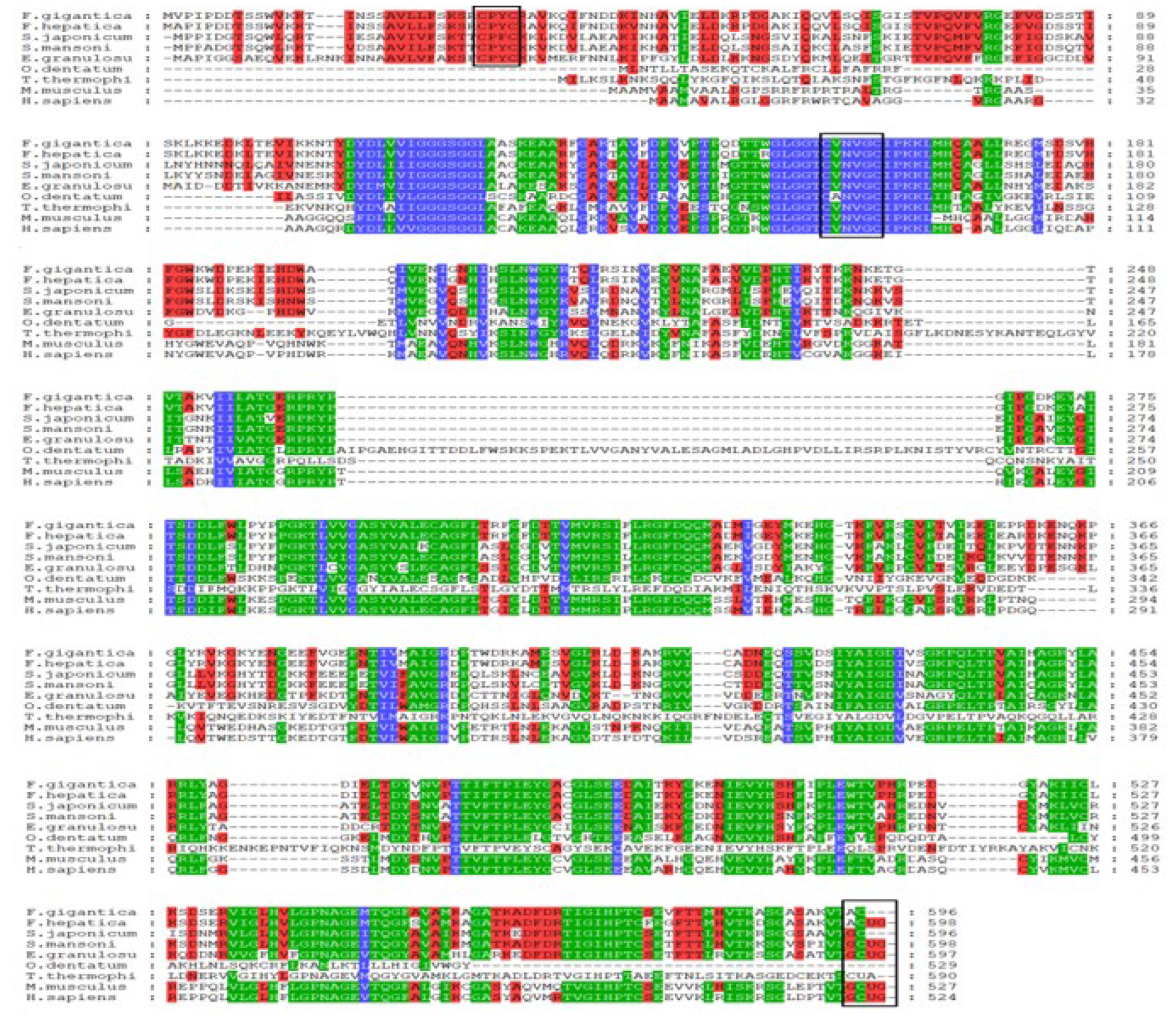
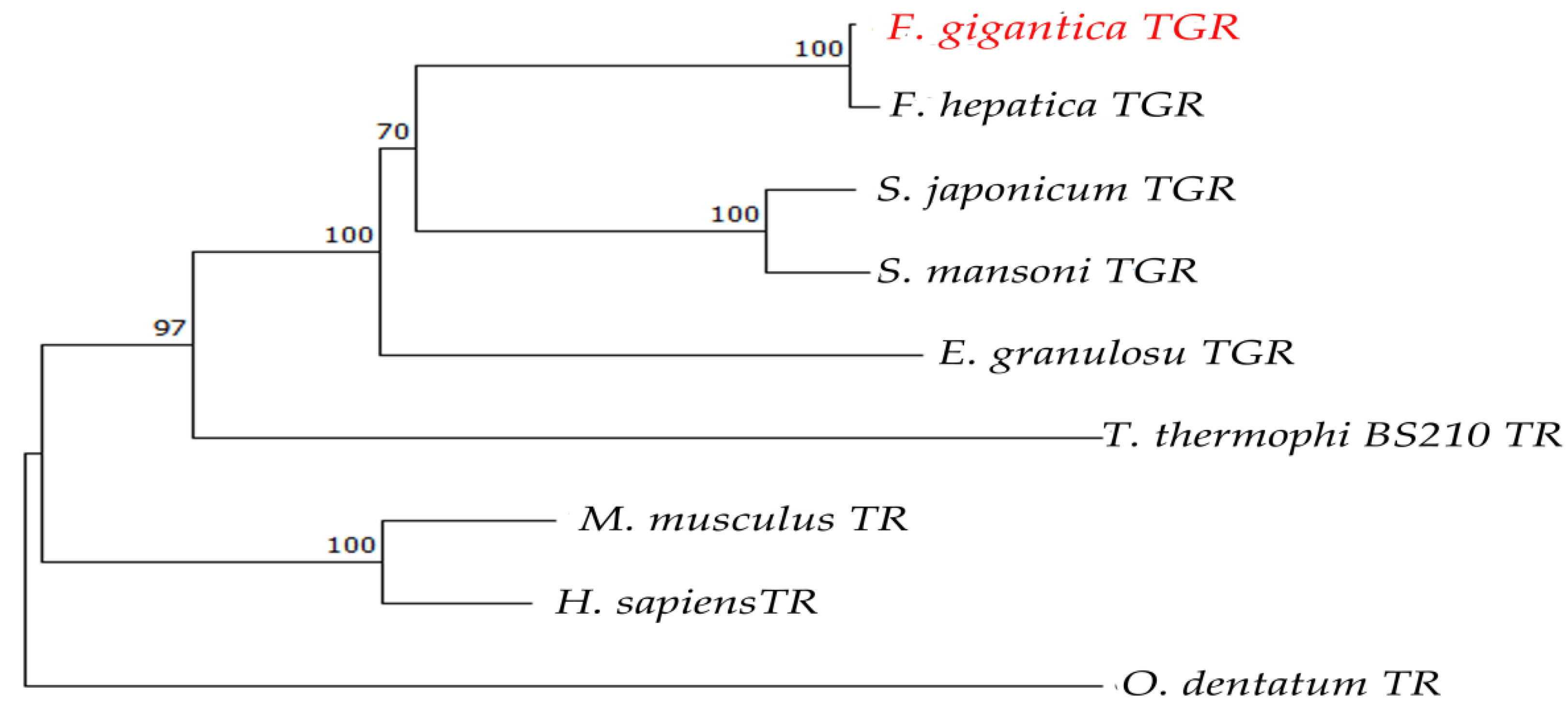
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis of FgTGR
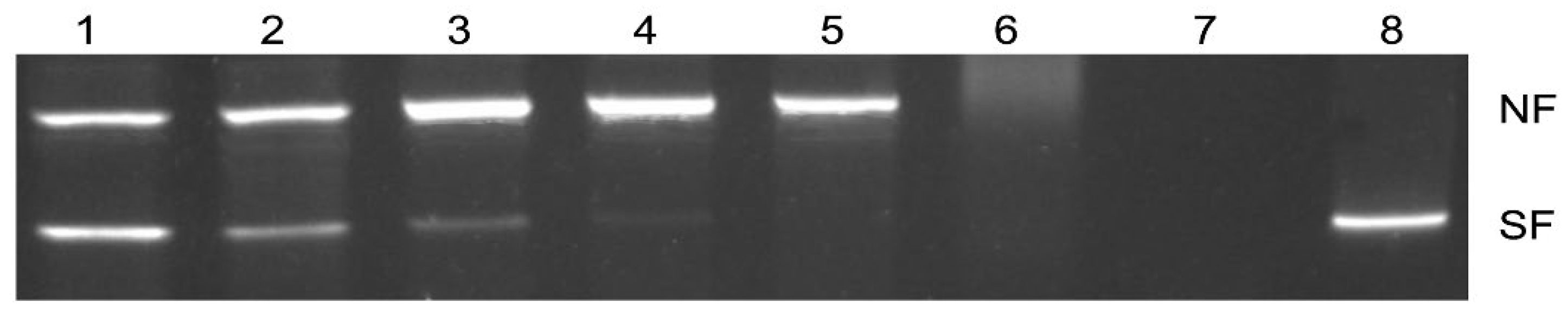
2.2. Supercoiled DNA Protection Activity of FgTGR
2.3. Immunolocalization Analysis of FgTGR
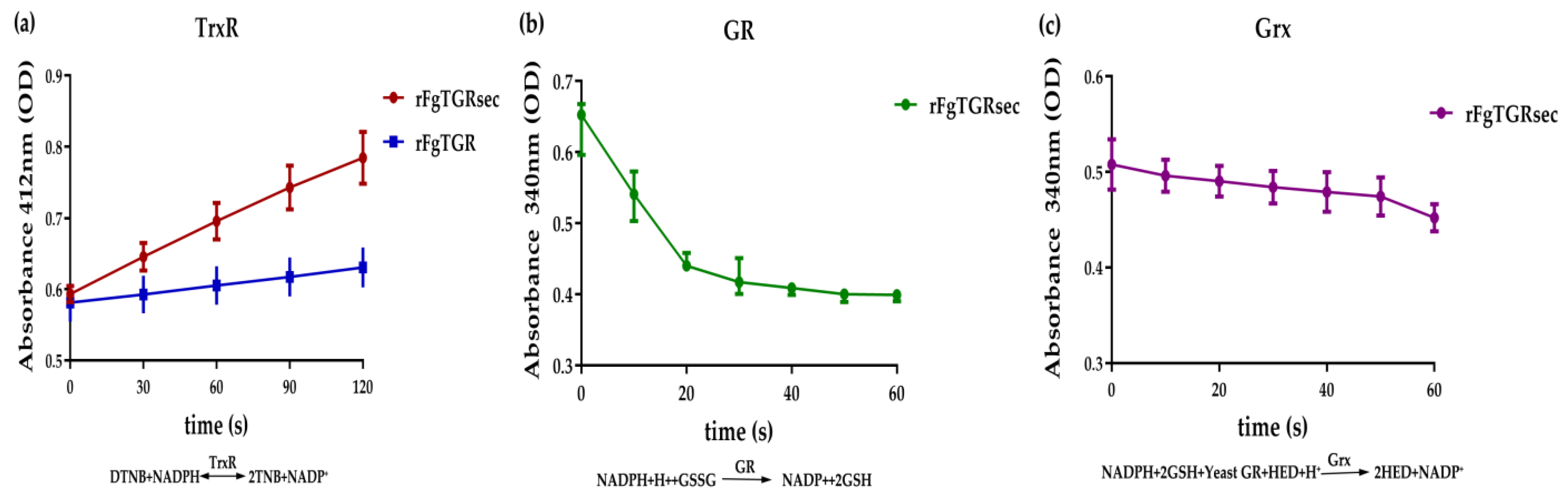
2.4. Enzymatic Activities of FgTGRsec and FgTGR
2.5. Inhibtion of Catalytic Activity of FgTGRsec by Furoxan Derivatives
3. Discussion
3.1. Role of FgTGR in Antioxidant Defense and Redox Homeostasis
3.2. Structural and Functional Characteristics of FgTGR
3.3. Comparative Enzymatic Activities of FgTGR and FgTGRsec
3.4. Inhibitory Effects of Furoxan Derivatives on FgTGRsec
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Parasites, Proteins, and Antibodies
4.2. Sequence and Phylogenetic Analyses of FgTGR
4.3. Localization of FgTGR Protein by Immunolocalization
4.4. Antioxidant Activity of FgTGR
4.5. Enzymatic Assays
4.5.1. TrxR Activity Assay of FgTGRsec
4.5.2. GR Assay of FgTGRsec
4.5.3. Grx Assay of FgTGRsec
4.6. Compound Inhibition of FgTGRsec
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renslo, A.R.; McKerrow, J.H. Drug discovery and development for neglected parasitic diseases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.W.; Dalton, J.P. Zoonotic helminth infections with particular emphasis on fasciolosis and other trematodiases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2763–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, F.; Corvo, I.; Bergalli, L.; Ilarraz, A.; Cabrera, M.; Gil, J.; Susuki, B.M.; Caffrey, C.R.; Timson, D.J.; Robert, X.; et al. Novel and selective inactivators of Triosephosphate isomerase with anti-trematode activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, J.M.; Elliott, T.P.; Beddoe, T.; Anderson, G.; Skuce, P.; Spithill, T.W. Current Threat of Triclabendazole Resistance in Fasciola hepatica. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakare, R.; Dasgupta, A.; Chopra, S. Triclabendazole for the treatment of fascioliasis. Drugs Today 2019, 55, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaechea, F.; Lovera, V.; Larroza, M.; Raffo, F.; Cabrera, R. Resistance of Fasciola hepatica against triclabendazole in cattle in Patagonia (Argentina). Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 178, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabada, M.M.; Lopez, M.; Cruz, M.; Delgado, J.R.; Hill, V.; White, A.C., Jr. Treatment Failure after Multiple Courses of Triclabendazole among Patients with Fascioliasis in Cusco, Peru: A Case Series. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, T.; Suttiprapa, S.; Sripa, B. Unusual thiol-based redox metabolism of parasitic flukes. Parasitol. Int. 2017, 66, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, M.; Denicola, A.; Marino, S.M.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Salinas, G. Linked thioredoxin-glutathione systems in platyhelminth parasites: Alternative pathways for glutathione reduction and deglutathionylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 4959–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, G.; Selkirk, M.E.; Chalar, C.; Maizels, R.M.; Fernandez, C. Linked thioredoxin-glutathione systems in platyhelminths. Trends Parasitol. 2004, 20, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Li, J.; Xie, S.; Qian, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yin, X.; Hua, Z.; Yu, C. Thioredoxin glutathione reductase as a novel drug target: Evidence from Schistosoma japonicum. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntz, A.N.; Davioud-Charvet, E.; Sayed, A.A.; Califf, L.L.; Dessolin, J.; Arner, E.S.; Williams, D.L. Thioredoxin glutathione reductase from Schistosoma mansoni: An essential parasite enzyme and a key drug target. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Fu, Z.; Lin, J. Characterization of thioredoxin glutathione reductase in Schiotosoma japonicum. Parasitol. Int. 2012, 61, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Guo, Q.; Feng, C.; Chen, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, S.; Hong, Y.; Sun, D. Synthesis of oxadiazole-2-oxide derivatives as potential drug candidates for schistosomiasis targeting SjTGR. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yue, Y.; Shi, B.; Zhao, X.; Hong, Y. Characterization and enzymatic function of thioredoxin glutathione reductase in Orientobilharzia turkestanicum isolated from Xizang. BMC Vet. Res. 2025, 21, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changklungmoa, N.; Kueakhai, P.; Sangpairoj, K.; Chaichanasak, P.; Jaikua, W.; Riengrojpitak, S.; Sobhon, P.; Chaithirayanon, K. Molecular cloning and characterization of Fasciola gigantica thioredoxin-glutathione reductase. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 2119–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Fu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Han, H.; Lu, K.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Lin, J. Inhibitory effects and analysis of RNA interference on thioredoxin glutathione reductase expression in Schistosoma japonicum. J. Parasitol. 2014, 100, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prum, S.; Plumworasawat, S.; Chaiyadet, S.; Saichua, P.; Thanan, R.; Laha, T.; Laohaviroj, M.; Sripa, B.; Suttiprapa, S. Characterization and in vitro functional analysis of thioredoxin glutathione reductase from the liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini. Acta Trop. 2020, 210, 105621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroli, A.; Simeoni, S.; Lepore, R.; Tramontano, A.; Via, A. Investigation of a potential mechanism for the inhibition of SmTGR by Auranofin and its implications for Plasmodium falciparum inhibition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Flores, A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, J.J.; Herrera-Juarez, A.M.; Rendon, J.L.; Gonzalez-Andrade, M.; Torres Duran, P.V.; Enriquez-Habib, R.G.; Del Arenal Mena, I.P. Effect of curcuminoids and curcumin derivate products on thioredoxin-glutathione reductase from Taenia crassiceps cysticerci. Evidence suggesting a curcumin oxidation product as a suitable inhibitor. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Shukla, H.; Kalita, P.; Tripathi, T. Structural insights into natural compounds as inhibitors of Fasciola gigantica thioredoxin glutathione reductase. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 3067–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, B.J.; Dantas, R.F.; Senger, M.R.; Melo-Filho, C.C.; Valente, W.C.; de Almeida, A.C.; Rezende-Neto, J.M.; Lima, E.F.; Paveley, R.; Furnham, N.; et al. Discovery of New Anti-Schistosomal Hits by Integration of QSAR-Based Virtual Screening and High Content Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7075–7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Ziniel, P.D.; He, P.Q.; Kommer, V.P.; Crowther, G.J.; He, M.; Liu, Q.; Van Voorhis, W.C.; Williams, D.L.; Wang, M.W. High-throughput screening against thioredoxin glutathione reductase identifies novel inhibitors with potential therapeutic value for schistosomiasis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2015, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, H.; Petukhov, P.A.; Banta, P.R.; Jadhav, A.; Lea, W.A.; Cheng, Q.; Arner, E.S.J.; Simeonov, A.; Thatcher, G.R.J.; Angelucci, F.; et al. Characterization of Lead Compounds Targeting the Selenoprotein Thioredoxin Glutathione Reductase for Treatment of Schistosomiasis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, F.; Hernandez, P.; Porcal, W.; Lopez, G.V.; Cerecetto, H.; Gonzalez, M.; Basika, T.; Carmona, C.; Flo, M.; Maggioli, G.; et al. Identification of thioredoxin glutathione reductase inhibitors that kill cestode and trematode parasites. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Flores, A.; Pardo, J.P.; Rendon, J.L. Hysteresis in thioredoxin-glutathione reductase (TGR) from the adult stage of the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol. Int. 2011, 60, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, G.P.; Fairweather, I.; Trudgett, A.; Hoey, E.; Coy, M.; McConville, M.; Meaney, M.; Robinson, M.; McFerran, N.; Ryan, L.; et al. Understanding triclabendazole resistance. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2007, 82, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kesherwani, M.; Velmurugan, D.; Tripathi, T. Fasciola gigantica thioredoxin glutathione reductase: Biochemical properties and structural modeling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.P. Cellular defenses against damage from reactive oxygen species. Physiol. Rev. 1994, 74, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikapitiya, C.; De Zoysa, M.; Whang, I.; Kim, C.G.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of peroxiredoxin 6 from disk abalone Haliotis discus discus and the antioxidant activity of its recombinant protein. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, R.; Howard, O.M.; Dong, H.F.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Bizzarri, C.; Sergi, R.; Caselli, G.; Pagliei, S.; Romines, B.; Wilshire, J.A.; et al. Thioredoxin, a redox enzyme released in infection and inflammation, is a unique chemoattractant for neutrophils, monocytes, and T cells. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Bai, J.; Araya, S.; Kondo, N.; Nishinaka, Y.; Yodoi, J. Circulating thioredoxin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced neutrophil chemotaxis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15143–15148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Feinstein, S.I.; Manevich, Y.; Ho, Y.S.; Fisher, A.B. Peroxiredoxin 6 gene-targeted mice show increased lung injury with paraquat-induced oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2006, 8, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suttiprapa, S.; Loukas, A.; Laha, T.; Wongkham, S.; Kaewkes, S.; Gaze, S.; Brindley, P.J.; Sripa, B. Characterization of the antioxidant enzyme, thioredoxin peroxidase, from the carcinogenic human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2008, 160, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assady, M.; Farahnak, A.; Golestani, A.; Esharghian, M. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Enzyme Activity Assay in Fasciola spp. Parasites and Liver Tissue Extract. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2011, 6, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sangpairoj, K.; Changklungmoa, N.; Vanichviriyakit, R.; Sobhon, P.; Chaithirayanon, K. Analysis of the expression and antioxidant activity of 2-Cys peroxiredoxin protein in Fasciola gigantica. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 140, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaithirayanon, K.; Sobhon, P. Molecular cloning and characterization of two genes encoding 2-Cys peroxiredoxins from Fasciola gigantica. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 125, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioli, G.; Silveira, F.; Martin-Alonso, J.M.; Salinas, G.; Carmona, C.; Parra, F. A recombinant thioredoxin-glutathione reductase from Fasciola hepatica induces a protective response in rabbits. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 129, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alger, H.M.; Sayed, A.A.; Stadecker, M.J.; Williams, D.L. Molecular and enzymatic characterisation of Schistosoma mansoni thioredoxin. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, F.; Miele, A.E.; Boumis, G.; Dimastrogiovanni, D.; Brunori, M.; Bellelli, A. Glutathione reductase and thioredoxin reductase at the crossroad: The structure of Schistosoma mansoni thioredoxin glutathione reductase. Proteins 2008, 72, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, Q.; Yong, C.; Jia, J.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, L.; Tang, W.; Hong, Y.; Fu, Z. Expression, Purification and Preparation of Polyclonal Antibodies of Thioredoxin Glutathione Reductase from Fasciola gigantica. Chin. J. Zoonotic Infect. Dis. 2024, 1–11, (in press). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, P.; Shukla, H.; Shukla, R.; Tripathi, T. Biochemical and thermodynamic comparison of the selenocysteine containing and non-containing thioredoxin glutathione reductase of Fasciola gigantica. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelucci, F.; Dimastrogiovanni, D.; Boumis, G.; Brunori, M.; Miele, A.E.; Saccoccia, F.; Bellelli, A. Mapping the catalytic cycle of Schistosoma mansoni thioredoxin glutathione reductase by X-ray crystallography. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 32557–32567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.L.; Bonilla, M.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Salinas, G. Thioredoxin glutathione reductase-dependent redox networks in platyhelminth parasites. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2013, 19, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkoji, G.M.; Smith, J.M.; Prichard, R.K. Antioxidant systems in Schistosoma mansoni correlation between susceptibility to oxidant killing and the levels of scavengers of hydrogen peroxide and oxygen free radicals. Int. J. Parasitol. 1988, 18, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Han, Y.; Fu, Z.; Han, H.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, J. Characterization and expression of the Schistosoma japonicum thioredoxin peroxidase-2 gene. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arner, E.S.; Sarioglu, H.; Lottspeich, F.; Holmgren, A.; Bock, A. High-level expression in Escherichia coli of selenocysteine-containing rat thioredoxin reductase utilizing gene fusions with engineered bacterial-type SECIS elements and co-expression with the selA, selB and selC genes. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 292, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengby, O.; Johansson, L.; Carlson, L.A.; Serini, E.; Vlamis-Gardikas, A.; Karsnas, P.; Arner, E.S. Assessment of production conditions for efficient use of Escherichia coli in high-yield heterologous recombinant selenoprotein synthesis. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5159–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Arner, E.S.; Ljung, J.; Aslund, F.; Holmgren, A. Rat and calf thioredoxin reductase are homologous to glutathione reductase with a carboxyl-terminal elongation containing a conserved catalytically active penultimate selenocysteine residue. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 8581–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agorio, A.; Chalar, C.; Cardozo, S.; Salinas, G. Alternative mRNAs arising from trans-splicing code for mitochondrial and cytosolic variants of Echinococcus granulosus thioredoxin Glutathione reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12920–12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Flores, A.; Del Arenal, I.P.; Mendoza-Hernandez, G.; Pardo, J.P.; Flores-Herrera, O.; Rendon, J.L. Mitochondrial Thioredoxin-Glutathione Reductase from Larval Taenia crassiceps (Cysticerci). J Parasitol Res. 2010, 2010, 719856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, F.; Sayed, A.A.; Williams, D.L.; Boumis, G.; Brunori, M.; Dimastrogiovanni, D.; Miele, A.E.; Pauly, F.; Bellelli, A. Inhibition of Schistosoma mansoni thioredoxin-glutathione reductase by auranofin: Structural and kinetic aspects. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 28977–28985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Gonzalez, J.J.; Guevara-Flores, A.; Alvarez, G.; Rendon-Gomez, J.L.; Del Arenal, I.P. In vitro killing action of auranofin on Taenia crassiceps metacestode (cysticerci) and inactivation of thioredoxin-glutathione reductase (TGR). Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, G.; Sayed, A.A.; Lea, W.A.; Luecke, H.F.; Chakrapani, H.; Prast-Nielsen, S.; Jadhav, A.; Leister, W.; Shen, M.; Inglese, J.; et al. Structure mechanism insights and the role of nitric oxide donation guide the development of oxadiazole-2-oxides as therapeutic agents against schistosomiasis. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6474–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.J.; Luo, H.; Fan, W.H.; Wang, G.P.; Yin, X.R.; Shen, S.; Wang, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; et al. Oxadiazole-2-oxides may have other functional targets, in addition to SjTGR, through which they cause mortality in Schistosoma japonicum. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hua, W.; Li, J.; Hua, Z. Molecular docking to explore the possible binding mode of potential inhibitors of thioredoxin glutathione reductase. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 5787–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eweas, A.F.; Allam, G. Targeting thioredoxin glutathione reductase as a potential antischistosomal drug target. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2018, 225, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.A.; Simeonov, A.; Thomas, C.J.; Inglese, J.; Austin, C.P.; Williams, D.L. Identification of oxadiazoles as new drug leads for the control of schistosomiasis. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.S.; Cha, M.K.; Kim, H.K.; Uhm, T.B.; Park, J.W.; Kim, K.; Kim, I.H. Removals of hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radical by thiol-specific antioxidant protein as a possible role In Vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 192, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauri, H.; Butterfield, L.; Kim, A.; Shau, H. Antioxidant function of recombinant human natural killer enhancing factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 208, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Property | Substrate | F. gigantica TGRsec | F. hepatica TGR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific actives (U/mg) | DTNB | 54.47 ± 11.66 | 10.2 ± 1.4 |
| GSSG | 71.14 ± 11.48 | 64.5 ± 5.5 | |
| HED | 11.86 ± 1.88 | 55.4 ± 6 | |
| Apparent Km (µM) | DTNB | 189.39 ± 52.90 | 46 ± 12 |
| GSSG | 71.14 ± 11.48 | 30 ± 5 | |
| HED | 11.86 ± 78.93 | — |
| Compounds | Structure | IC50 of rFgTGRsec (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| LGM-1 | 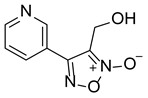 | 6.93 ± 1.74 |
| LGM-2 |  | 15.19 ± 0.80 |
| LGM-35 | 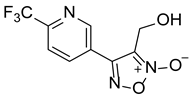 | 4.5 ± 0.35 |
| ZWJ-19 | 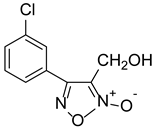 | 3.82 ± 0.33 |
| CH-33 | 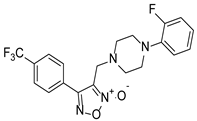 | 18.54 ± 2.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; He, Y.; Guo, Q.; Li, G.; Chen, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, Z.; Oyeyemi, O.T.; Zhu, H.; et al. Screening Novel Furoxan Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors Targeting Thioredoxin Glutathione Reductase of Fasciola gigantica. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111603
Han Y, He Y, Guo Q, Li G, Chen H, Zhao W, Zhou Y, Fu Z, Oyeyemi OT, Zhu H, et al. Screening Novel Furoxan Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors Targeting Thioredoxin Glutathione Reductase of Fasciola gigantica. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111603
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yanhui, Yuting He, Qingqing Guo, Gongming Li, Huan Chen, Wenjiao Zhao, Yan Zhou, Zhiqiang Fu, Oyetunde T. Oyeyemi, Huili Zhu, and et al. 2025. "Screening Novel Furoxan Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors Targeting Thioredoxin Glutathione Reductase of Fasciola gigantica" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111603
APA StyleHan, Y., He, Y., Guo, Q., Li, G., Chen, H., Zhao, W., Zhou, Y., Fu, Z., Oyeyemi, O. T., Zhu, H., Wang, Q., Sun, D., & Hong, Y. (2025). Screening Novel Furoxan Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors Targeting Thioredoxin Glutathione Reductase of Fasciola gigantica. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111603








