2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Tablets
Experimental campaigns were conducted to elucidate the lubricant and glidant effects on process CPPs and tablet CQAs. The powder blends contained microcrystalline cellulose Avicel PH200 (MCC) from IMCD Group US (Westlake, OH, USA), 10% w/w acetaminophen (APAP) from Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals (Dublin, Ireland), and varying concentrations of MgSt or CS (0–2% w/w, or 0–0.2% w/w, respectively). One-kilogram blends with MgSt (Spectrum Chemical, Gardena, CA, USA) were mixed in a 5 L Tote blender (Tote Systems International, Fort Worth, TX, USA) for 11–30 min, and one-kilogram blends with CS (Cabot Corporation, Tuscula, IL, USA) were mixed for 10–30 min. Although practical mixing times may be shorter than 20 min, experimental data were collected up to 30 min to model the potential effects of over-lubrication. Tablets were fabricated using a Natoli-NP400 tablet press and D-type tooling, with a shallow cup depth of mm and an in-die thickness of 2.44 mm. A dosing position ranging from 9 to 13 mm and a turret speed varying from 11 to 22 rpm were used for blends with MgSt, and a dosing position ranging from 7 to 11 mm and a turret speed varying from 25 to 35 rpm were used for blends with CS.
The MATLAB R2021a function
lhsdesign was used to generate a Latin hypercube design [
24] that samples the turret speed, dosing position, MgSt/CS concentration, and mixing time. In this work, since there are four input variables, the full factorial experimental design used in prior work [
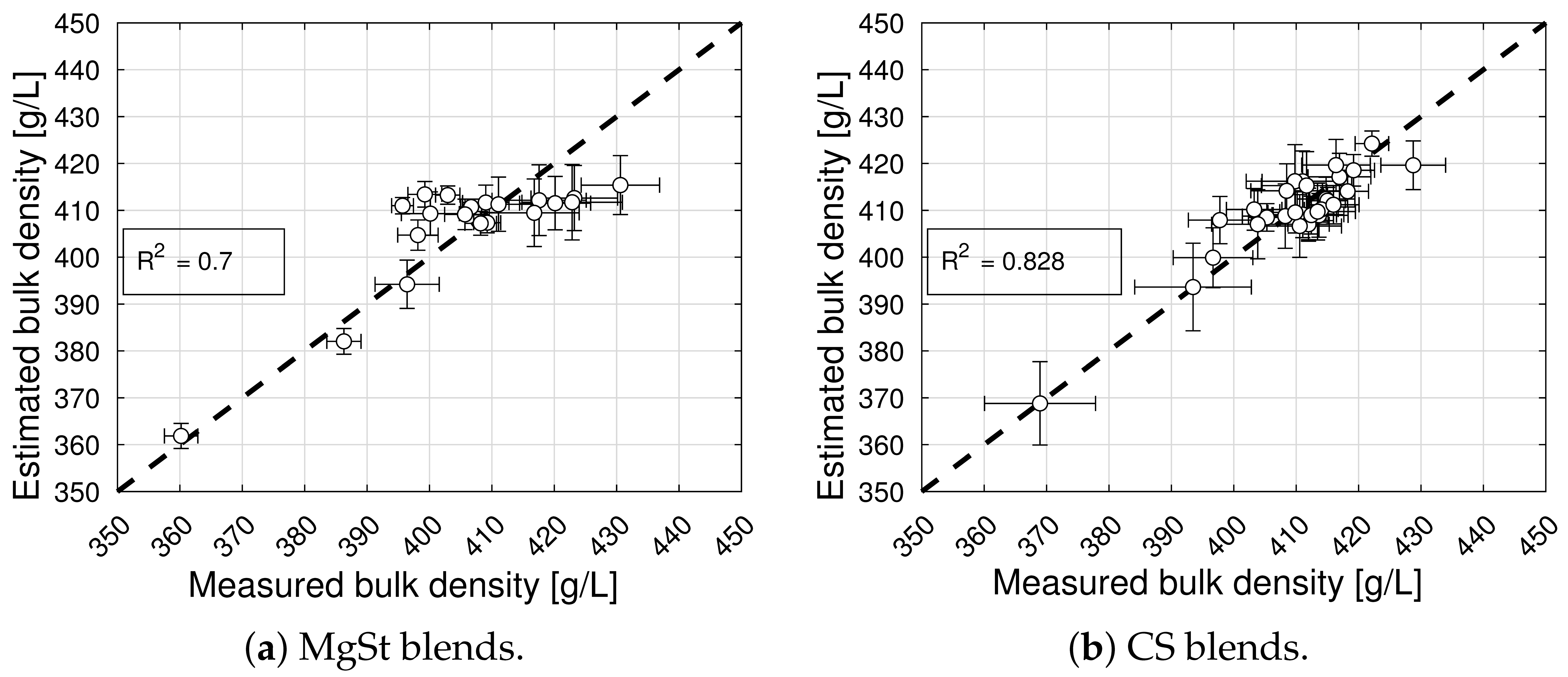
22] is infeasible. In order to maximize the design space coverage while controlling the number of experiments, we chose the Latin Hypercube design for the design of experiment, which is a statistical technique used to generate samples from multiple input variables while ensuring good coverage of the entire design space. The experimental campaigns in this work comprised 20 experiments for blends with MgSt, and of 30 experiments for blends with CS. The bulk density of each one-kilogram blend was determined using a half-kilogram sample, which was divided into eight equal parts using a Retsch PT100 spin riffler (RETSCH GmbH, Haan, Germany) to measure the weight and volume of each sub-sample.
At the start of each experimental run, the tablet press hopper was filled with 0.5 kg of the blend to ensure enough powder was available to maintain steady-state conditions. During each run, a SOTAX AT4 tablet tester (SOTAX Corp, Westborough, MA, USA) was used to measure the thickness, diameter, weight, and hardness of 50 tablets under steady-state manufacturing conditions. Using these measurements, the pre-compression (
), main-compression (
), and after-ejection (
) tablet relative densities were calculated following Bachawala et al. [
23]. Specifically, for a given filling weight
W and a true density
of the blend, these relative densities are given by
where the corresponding tablet volumes are given by
with
mm being the die diameter, and
the corresponding thicknesses (see
Figure 1). The tensile strength
for the convex tablets is obtained from Pitt’s model [
25] using the measured hardness
F, i.e.,
with
. It bears emphasis that not all measurements are available on-line to implement real-time control under the QbC paradigm [
16].
2.2. Tableting Reduced-Order Models
Tableting consists of four main stages, namely die-filling, pre-compression, main-compression, and tablet ejection. Powders are first filled into a die cavity which is confined on the bottom by a punch tip (see schematic A in
Figure 1). During pre-compression, a relatively small force is exerted by the upper punch to remove air and prevent capping of the tablet during ejection. In the main-compaction stage, a larger force is applied on the powder bed to reach the desired in-die tablet thickness (see schematic B in
Figure 1). The tablet undergoes elastic recovery during the unloading and ejection stages (see schematics C and D in
Figure 1). It is worth noting that the axially compacted powder creates a residual stress in the radial direction and, in turn, an ejection force needs to be exerted by the bottom punch in order to overcome tablet/die friction.
The development of mechanistic and semi-mechanistic reduced-order models (ROMs), resulting from a trade-off between complexity and performance, but still based on product and process understanding, forms an essential cornerstone for process design, optimization, and control in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Here, we adopt semi-mechanistic formulae which are in remarkable agreement with the particle-level calculations that use the particle mechanics approach for modeling the consolidation and compaction of powders under large deformations [
26]. These semi-mechanistic ROMs have also been used by Bachawala et al. [
23] to integrate tableting with dry granulation. Specifically, mathematical expressions for the die-filling efficacy coefficient
, the Kawakita’s compaction force
, the elastic recovery
, the tablet density
, and the Leunberger’s tablet tensile strength
are listed below.
The model parameters have the following mechanistic interpretation:
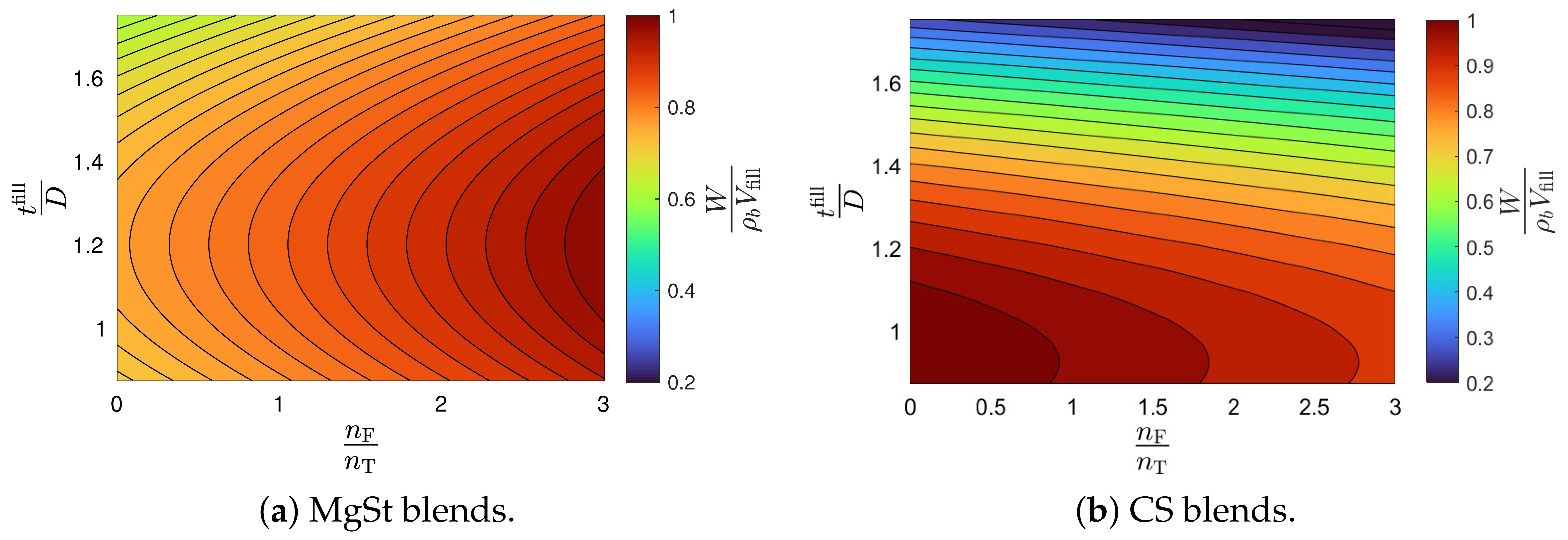
The filling efficacy coefficient is typically less than one due to the tablet press inefficiencies in the feed-frame, turret and die-filling dynamics; that is, the tablet weight
W is typically less than the bulk density
times the fill volume of the die
—which is given by
with
h being the cup depth.
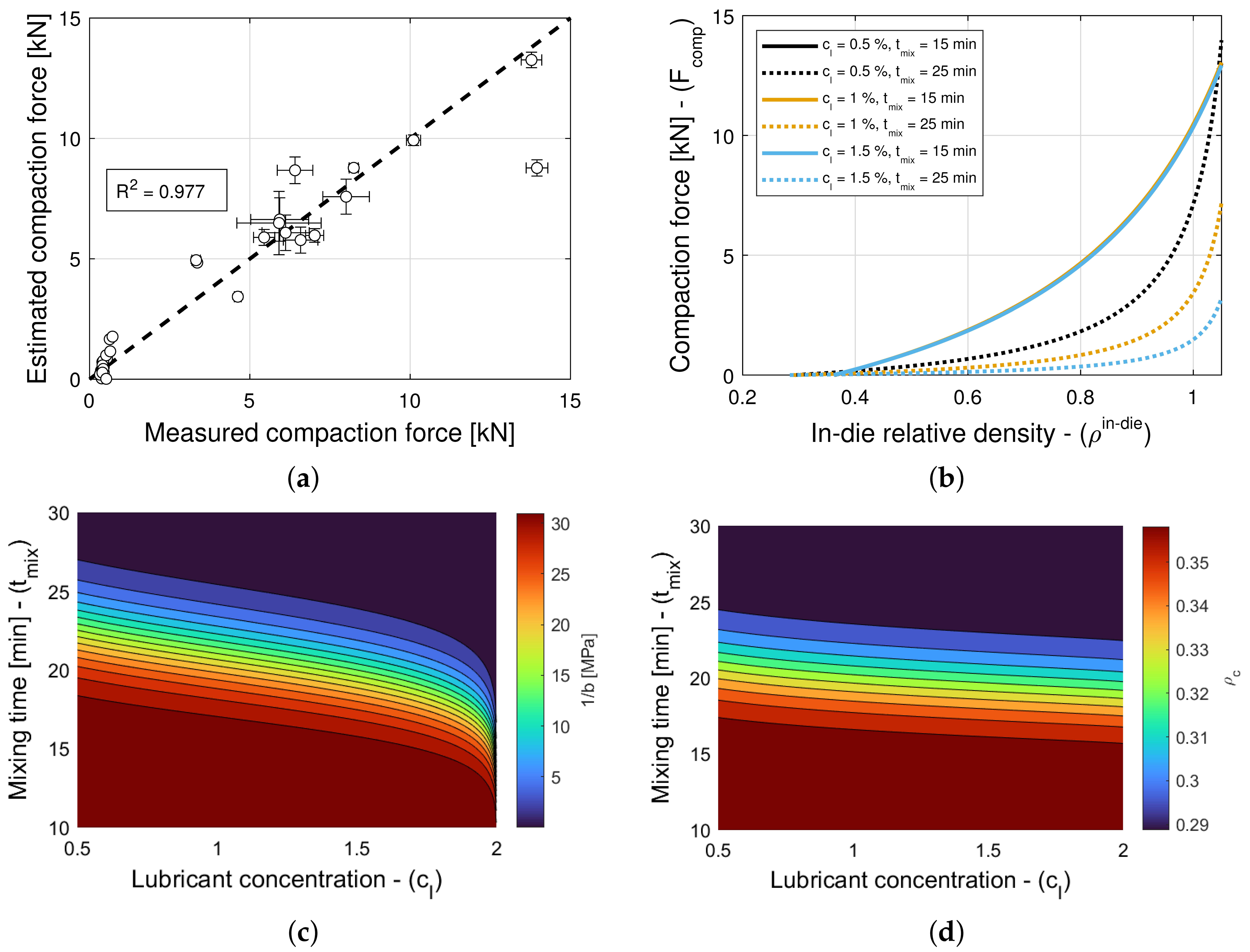
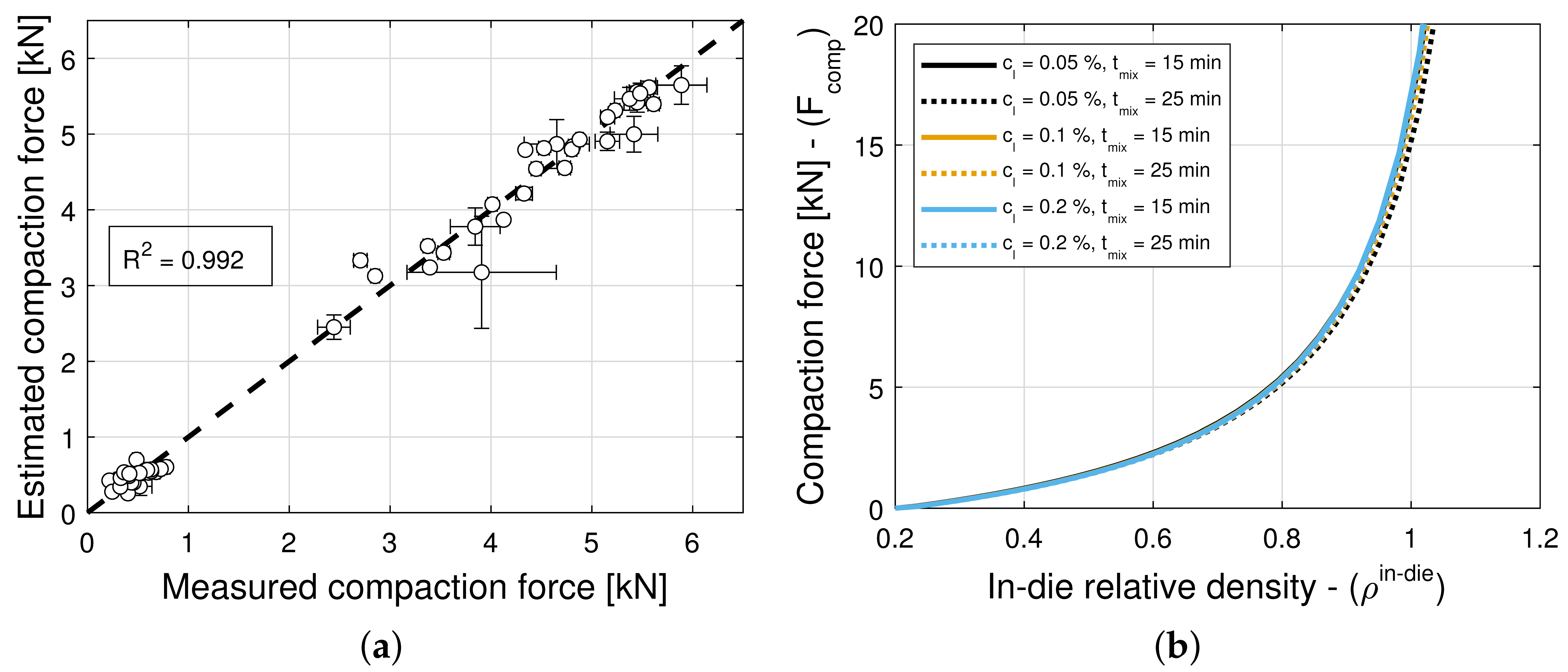
The Kawakita compaction force equation was adapted by Bachawala and Gonzalez [
27] to depend on the in-die tablet relative density
, and the critical in-die relative density
at which jamming occurs and particle-level deformation begins. The parameters
a and
[MPa] represent the total degree of compression or total compressibility of the powder, and the compaction pressure required to reach half of the maximum volume reduction
(i.e., the pressure at a relative in-die density such that
), respectively [
28,
29,
30].
The tablet undergoes elastic recovery during the unloading and ejection stages, and
corresponds to the elastic recovery at full compaction (or zero porosity), while
is the smallest in-die tablet relative density at which elastic recovery is observed. The exponent
n accommodates for nonlinearities and generalizes the otherwise linear trend [
23].
The tablet tensile strength depends on the tablet relative density
after elastic recovery, the tensile strength
of a tablet with a relative density of one (or zero porosity), and the smallest tablet relative density
at which a tablet with adequate strength is formed [
31].
These model parameters are next endowed with dependency on lubricant or glidant mixing conditions.
2.3. Rational Function-Based Approach for the Integration of Unit Operations
Multivariate rational functions have been used as surrogate models to successfully interpolate and extrapolate sparse data in many applications [
32,
33]. Bachawala et al. [
22] have proposed a rational function-based approach to systematically and automatically integrate tableting ROMs with upstream unit operations. We adopted this approach to integrate lubricant and glidant mixing with tableting. Therefore, by following the same procedure, we identified the upstream
that describes the coupling, e.g., the glidant
or lubricant
concentration and the total shear imparted to the blend during mixing. Specifically, the coupling is done solely through model parameters
of the tableting reduced-order model
by means of a nonlinear function of upstream
and its parameters
, that is,
Next, we normalized the upstream
to be in the range of
, as shown in
Table 1. In this work,
w/
w and
w/
w are considered for pharmaceutical formulations. Furthermore, in the two experimental campaigns described above, mixing of each one-kilogram blend is done using the same 5 L Tote blender and, in turn, the total shear imparted to the blend
and the total mixing time
are interchangeable upstream CPPs. In contrast, continuous blenders are used in continuous manufacturing operations and, in turn, the total shear imparted depends on the impeller speed, the incoming mass-flowrate, and the equipment design variables, such as the shaft angle, blade width, and weir height [
34,
35]. In this work, a maximum mixing time of
min is considered for normalization purposes.
Bachawala et al. [
23] adopted the following normalized bivariate rational function
to systematically integrate the unit operations
such that
, with
, are the rational function parameters to be estimated, in general. This simple and flexible bivariate rational function has a limiting behavior at the upper and lower bounds that can be easily interpreted physically, that is
There are two distinct limits in the integration of lubricant and glidant mixing with tableting. First, if the blend does not contain any lubricant (glidant), then the tableting ROMs parameters (see
Table 2) ought to be independent of mixing time. Second, if the blend contains lubricant (glidant) but it is not mixed, then the tableting ROMs parameters (see
Table 2) ought to be independent of the lubricant (glidant) concentration. Furthermore, these two limits ought to be the same and equal to the case of 10% APAP and 90% MCC (i.e.,
). Therefore, the generalized bivariate rational function used in the integration of lubricant and glidant mixing with tableting simplifies to
One of the features of (
16) is that the function is monotonic in
X and
Y. However, we observed that the bulk density of the blends with the lubricant had a nonmonotonic trend with respect to the lubricant concentration. Therefore, to capture these nonmonotonic trends in data, in this work, we propose extending the model library to include a different normalized bivariate rational function
and demonstrate that similar limiting behavior is recovered. Specifically, from the more general expression
the limiting behavior is enforced (i.e.,
), and the linear terms are neglected to draw a distinction from (
16), i.e.,
Lastly, a model library
is built by progressively simplifying the bivariate rational functions (
16) and (
18) to fifteen models, as shown in
Table 3. Furthermore, for simplicity and computational efficiency, the model library contains only 43 pairs (one for each model parameter in
; see
Table 2) out of all 225 possible combinations (see
Table 4). For example, in the tensile strength model, the parameters
and
are allowed twenty-five model combinations of the form
, with model number
.
The final step of the rational function-based approach [
23] is to choose the best model combination from the library
, i.e., the combination that provides accurate predictions with the least number of parameters (
). The prediction accuracy is typically measured by the sum of squared errors between the model prediction
and experimental data
. This trade-off between model complexity and accuracy is effectively captured by the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) [
36,
37], defined as
where
n is the number of experimental data points. The model with the lowest
is the best. For small sample sizes, the AIC often leads to overfitting. To improve its performance, a second-order bias correction is introduced.
Model selection and parameter estimation are then automatically realized by solving a nested optimization problem [
23], where the lower subproblem identifies the optimal model parameters for a given model by minimizing the sum of squared errors between the predicted and experimental data, and the upper subproblem selects the best model by minimizing the AIC. In this work, we use MATLAB’s genetic algorithm (
ga),
fmincon, and global search (
GlobalSearch) in that specific order to solve a constrained nonlinear optimization problem and obtain optimal model parameters. This ensures that the estimated parameters are not biased to the initial guess and represent the global solution. The inequality constraints are given by
with
, and
are imposed to ensure the parameters
. The parameters
represent relative quantities and must be in the range
. Furthermore, the onset of critical compaction, elastic recovery, and tablet relative densities occur consecutively, i.e.,
,
, with
and
being the lower bounds of the compaction and elastic recovery critical relative densities, respectively.