The Association Between Serum Drug Concentration and a Flare in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Tapering TNF Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients
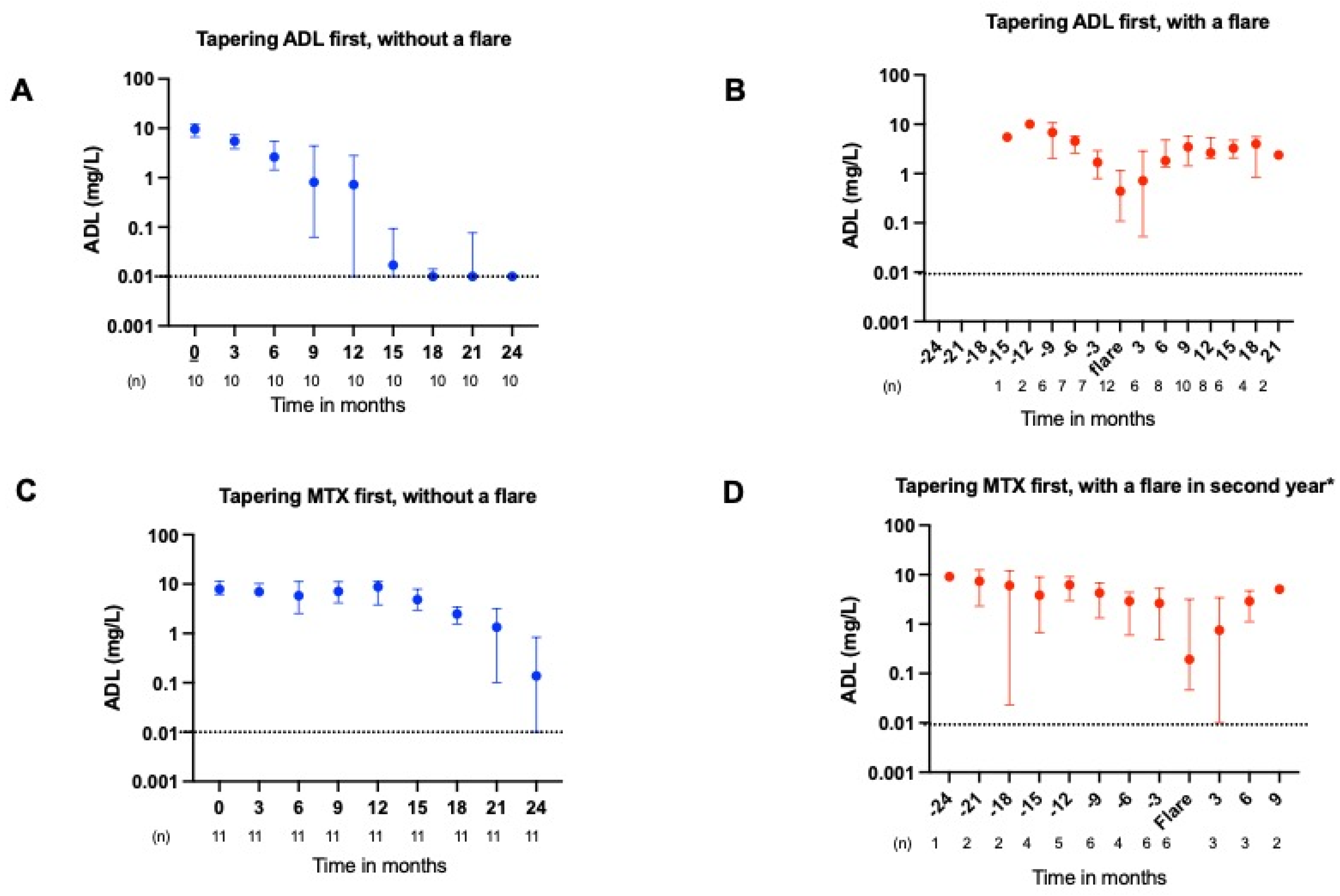
2.2. ADL and ETN Serum Concentrations During Tapering
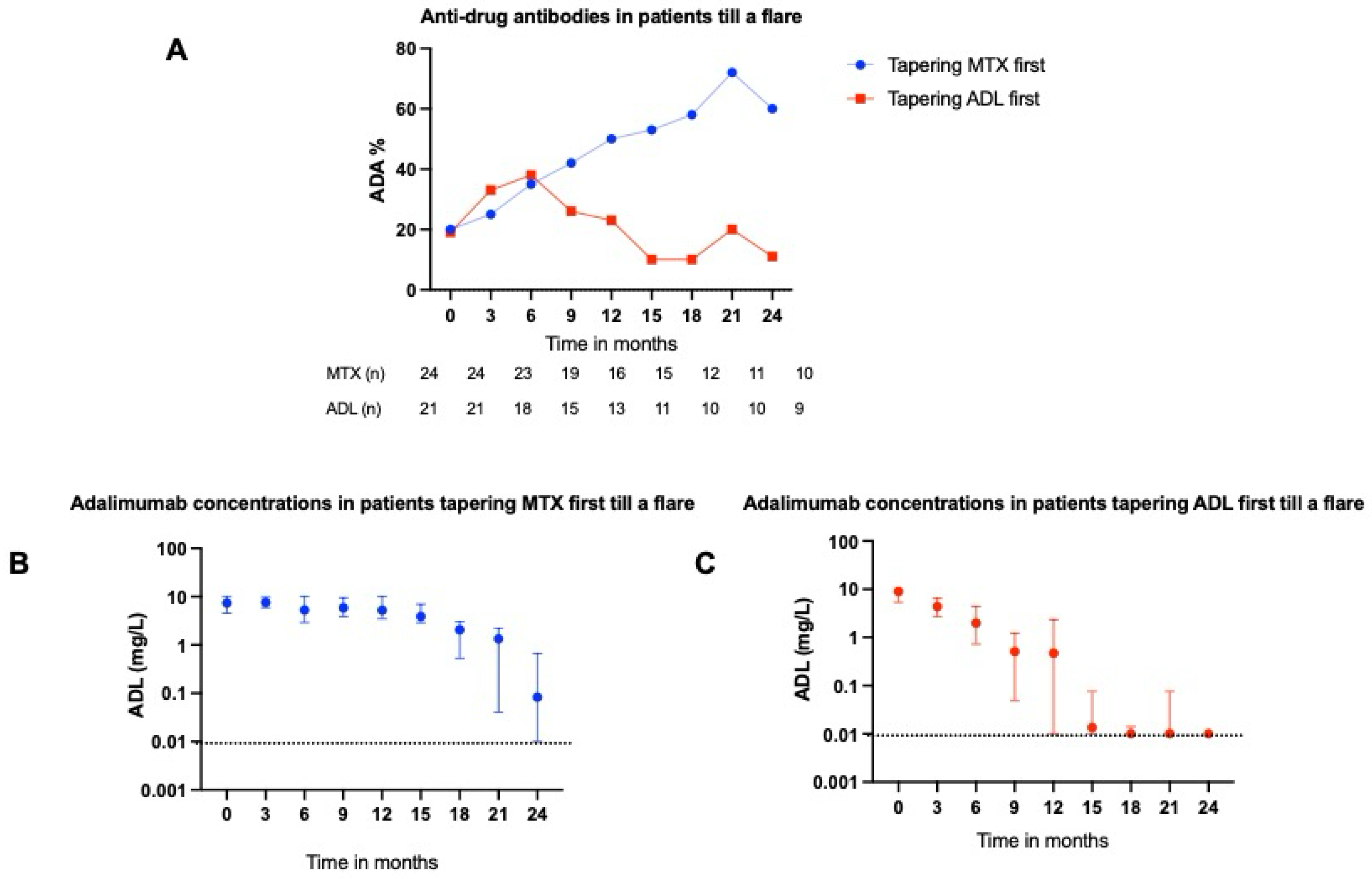
2.3. ADL and ETN Serum Concentrations During a Flare
2.4. ADAs Targeting ADL
3. Discussion
3.1. Main Findings
3.2. Pharmacokinetics
3.3. Immunogenicity
3.4. Strengths and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Outcome Measures and Assessments
4.3. Measurement of Serum Drug Concentrations
4.4. Measurement of Anti-Drug Antibodies (ADAs)
4.5. Statistics
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TNFi | Tumor necrosis factor inhibitor |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| ADAs | Anti-drug antibodies |
| ADL | Adalimumab |
References
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review. JAMA 2018, 320, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiti Moghadam, M.; Vonkeman, H.E.; Ten Klooster, P.M.; Tekstra, J.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Starmans-Kool, M.; Brouwer, E.; Bos, R.; Lems, W.F.; Colin, E.M.; et al. Stopping Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Treatment in Patients With Established Rheumatoid Arthritis in Remission or With Stable Low Disease Activity: A Pragmatic Multicenter, Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henaux, S.; Ruyssen-Witrand, A.; Cantagrel, A.; Barnetche, T.; Fautrel, B.; Filippi, N.; Lukas, C.; Raffeiner, B.; Rossini, M.; Degboé, Y.; et al. Risk of losing remission, low disease activity or radiographic progression in case of bDMARD discontinuation or tapering in rheumatoid arthritis: Systematic analysis of the literature and meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schett, G.; Emery, P.; Tanaka, Y.; Burmester, G.; Pisetsky, D.S.; Naredo, E.; Fautrel, B.; van Vollenhoven, R. Tapering biologic and conventional DMARD therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: Current evidence and future directions. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1428–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Herwaarden, N.; van der Maas, A.; Minten, M.J.; van den Hoogen, F.H.; Kievit, W.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Bijlsma, J.W.; van den Bemt, B.J.; den Broeder, A.A. Disease activity guided dose reduction and withdrawal of adalimumab or etanercept compared with usual care in rheumatoid arthritis: Open label, randomised controlled, non-inferiority trial. BMJ 2015, 350, h1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Mulligen, E.; Weel, A.; Kuijper, T.M.; Hazes, J.M.W.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M.; de Jong, P.H.P. The impact of a disease flare during tapering of DMARDs on the lives of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Mulligen, E.; Weel, A.E.; Hazes, J.M.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.; de Jong, P.H.P. Tapering towards DMARD-free remission in established rheumatoid arthritis: 2-year results of the TARA trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieckaert, C.L.; van Tubergen, A.; Gehin, J.E.; Hernández-Breijo, B.; Le Mélédo, G.; Balsa, A.; Böhm, P.; Cucnik, S.; Elkayam, O.; Goll, G.L.; et al. EULAR points to consider for therapeutic drug monitoring of biopharmaceuticals in inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouw, M.F.; Krieckaert, C.L.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van der Kleij, D.; Aarden, L.; Rispens, T.; Wolbink, G. Key findings towards optimising adalimumab treatment: The concentration-effect curve. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’AMi, M.J.; Krieckaert, C.L.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Rispens, T.; Boers, M.; Wolbink, G.J. Successful reduction of overexposure in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with high serum adalimumab concentrations: An open-label, non-inferiority, randomised clinical trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.S.; Borazan, N.; Barroso, N.; Duan, L.; Taroumian, S.; Kretzmann, B.; Bardales, R.; Elashoff, D.; Vangala, S.; Furst, D.E. Comparative Immunogenicity of TNF Inhibitors: Impact on Clinical Efficacy and Tolerability in the Management of Autoimmune Diseases. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BioDrugs 2015, 29, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneiro, J.R.; Salgado, E.; Gomez-Reino, J.J. Immunogenicity of monoclonal antibodies against tumor necrosis factor used in chronic immune-mediated Inflammatory conditions: Systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelds, G.M.; Krieckaert, C.L.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van Schouwenburg, P.A.; Lems, W.F.; Twisk, J.W.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Aarden, L.; Wolbink, G.J. Development of antidrug antibodies against adalimumab and association with disease activity and treatment failure during long-term follow-up. JAMA 2011, 305, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss, S.L.; Klein, C.E.; Jin, Z.; Locke, C.S.; Rodila, R.C.; Kupper, H.; Burmester, G.-R.; Awni, W.M. Methotrexate Dose in Patients With Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Impacts Methotrexate Polyglutamate Pharmacokinetics, Adalimumab Pharmacokinetics, and Efficacy: Pharmacokinetic and Exposure-response Analysis of the CONCERTO Trial. Clin. Ther. 2018, 40, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jani, M.; Chinoy, H.; Warren, R.B.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Plant, D.; Fu, B.; Morgan, A.W.; Wilson, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D.; Hyrich, K.; et al. Clinical utility of random anti-tumor necrosis factor drug-level testing and measurement of antidrug antibodies on the long-term treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanmarti, R.; Inciarte-Mundo, J.; Estrada-Alarcon, P.; Garcia-Manrique, M.; Narvaez, J.; Rodriguez-Moreno, J.; Gomez-Centeno, A.; Pascal, M.; Yagüe, J. Towards optimal cut-off trough levels of adalimumab and etanercept for a good therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis. Results of the INMUNOREMAR study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-Y.; Chen, Y.-M.; Hsieh, T.-Y.; Hung, W.-T.; Hsieh, C.-W.; Chen, H.-H.; Tang, K.-T.; Lan, J.-L. Drug trough levels predict therapeutic responses to dose reduction of adalimumab for rheumatoid arthritis patients during 24 weeks of follow-up. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-Y.; Chen, Y.-M.; Tsai, W.-C.; Tseng, J.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Hsieh, C.-W.; Hung, W.-T.; Lan, J.-L. Significant associations of antidrug antibody levels with serum drug trough levels and therapeutic response of adalimumab and etanercept treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, D.; Klareskog, L.; Sasso, E.H.; Salfeld, J.G.; Tak, P.P. Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: A comprehensive review. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 117, 244–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestorov, I.; Zitnik, R.; DeVries, T.; Nakanishi, A.M.; Wang, A.; Banfield, C. Pharmacokinetics of subcutaneously administered etanercept in subjects with psoriasis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 62, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, S. TNF inhibitor therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed. Rep. 2013, 1, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korth-Bradley, J.M.; Rubin, A.S.; Hanna, R.K.; Simcoe, D.K.; Lebsack, M.E. The pharmacokinetics of etanercept in healthy volunteers. Ann. Pharmacother. 2000, 34, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisman, M.H.; Moreland, L.W.; Furst, D.E.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Keystone, E.C.; Paulus, H.E.; Teoh, L.S.; Velagapudi, R.B.; Noertersheuser, P.A.; Granneman, G.; et al. Efficacy, pharmacokinetic, and safety assessment of adalimumab, a fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha monoclonal antibody, in adults with rheumatoid arthritis receiving concomitant methotrexate: A pilot study. Clin. Ther. 2003, 25, 1700–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternant, D.; Ducourau, E.; Fuzibet, P.; Vignault, C.; Watier, H.; Lequerré, T.; Le Loët, X.; Vittecoq, O.; Goupille, P.; Mulleman, D.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and concentration-effect relationship of adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combe, B. Update on the use of etanercept across a spectrum of rheumatoid disorders. Biologics 2008, 2, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhout, L.C.; L’aMi, M.J.; Ruwaard, J.; Hart, M.H.; Heer, P.O.-D.; Bloem, K.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Boers, M.; Alvarez, D.F.; et al. Dynamics of circulating TNF during adalimumab treatment using a drug-tolerant TNF assay. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaat3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Schouwenburg, P.A.; Rispens, T.; Wolbink, G.J. Immunogenicity of anti-TNF biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schie, K.A.; Hart, M.H.; de Groot, E.R.; Kruithof, S.; Aarden, L.A.; Wolbink, G.J.; Rispens, T. The antibody response against human and chimeric anti-TNF therapeutic antibodies primarily targets the TNF binding region. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schie, K.A.; Kruithof, S.; van Schouwenburg, P.A.; Vennegoor, A.; Killestein, J.; Wolbink, G.; Rispens, T. Neutralizing capacity of monoclonal and polyclonal anti-natalizumab antibodies: The immune response to antibody therapeutics preferentially targets the antigen-binding site. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1035–1037 e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, P.; Vencovský, J.; Sylwestrzak, A.; Leszczyński, P.; Porawska, W.; Baranauskaite, A.; Tseluyko, V.; Zhdan, V.M.; Stasiuk, B.; Milasiene, R.; et al. A phase III randomised, double-blind, parallel-group study comparing SB4 with etanercept reference product in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate therapy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Thaci, D.; Gerdes, S.; Arenberger, P.; Pulka, G.; Kingo, K.; Weglowska, J.; EGALITY Study Group; Hattebuhr, N.; Poetzl, J.; et al. The EGALITY study: A confirmatory, randomized, double-blind study comparing the efficacy, safety and immunogenicity of GP2015, a proposed etanercept biosimilar, vs. the originator product in patients with moderate-to-severe chronic plaque-type psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maini, R.N.; Breedveld, F.C.; Kalden, J.R.; Smolen, J.S.; Davis, D.; Macfarlane, J.D.; Antoni, C.; Leeb, B.; Elliott, M.J.; Woody, J.N.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of multiple intravenous infusions of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody combined with low-dose weekly methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieckaert, C.L.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Wolbink, G.J. Methotrexate reduces immunogenicity in adalimumab treated rheumatoid arthritis patients in a dose dependent manner. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1914–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atiqi, S.; Hooijberg, F.; Loeff, F.C.; Rispens, T.; Wolbink, G.J. Immunogenicity of TNF-Inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagheer, S.; Rasheed, M.S.; Ashraf, F.; Rao, A.; Fatima, M.; Ajmal, M.N.; Ameen, A.; Mohamed, K.; Khan, A.; Ali, F.; et al. Enhancing Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment by Subcutaneous Methotrexate Injectionsand Anti-IL-2 Antibody Synthesis. Int. J. Agric. Biosci. 2024, 13, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Bloem, K.; van Leeuwen, A.; Verbeek, G.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Wolbink, G.J.; van der Kleij, D.; Rispens, T. Systematic comparison of drug-tolerant assays for anti-drug antibodies in a cohort of adalimumab-treated rheumatoid arthritis patients. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 418, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassione, E.B.; Grignaschi, S.; Xoxi, B.; Luvaro, T.; Greco, M.I.; Mazzucchelli, I.; Bugatti, S.; Montecucco, C.; Manzo, A. Insights Into the Concept of Rheumatoid Arthritis Flare. Front. Med. 2022, 17, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Jamnitski, A.; Krieckaert, C.L.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Hart, M.H.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Aarden, L.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Wolbink, G.J. Patients non-responding to etanercept obtain lower etanercept concentrations compared with responding patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schouwenburg, P.A.; Bartelds, G.M.; Hart, M.H.; Aarden, L.; Wolbink, G.J.; Wouters, D. A novel method for the detection of antibodies to adalimumab in the presence of drug reveals “hidden” immunogenicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. J. Immunol. Methods 2010, 362, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moots, R.J.; Xavier, R.M.; Mok, C.C.; Rahman, M.U.; Tsai, W.-C.; Al-Maini, M.H.; Pavelka, K.; Mahgoub, E.; Kotak, S.; Korth-Bradley, J.; et al. The impact of anti-drug antibodies on drug concentrations and clinical outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with adalimumab, etanercept, or infliximab: Results from a multinational, real-world clinical practice, non-interventional study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175207. [Google Scholar]
- van Strien, J.; Dijk, L.; Atiqi, S.; Schouten, R.; Bloem, K.; Wolbink, G.J.; Loeff, F.; Rispens, T. Drug-tolerant detection of anti-drug antibodies in an antigen-binding assay using europium chelate fluorescence. J. Immunol. Methods 2023, 514, 113436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | All RA Patients (N = 111) | Tapering ADL First, Followed by MTX (N = 22) | Tapering MTX First, Followed by ADL (N = 24) | Tapering ETN First, Followed by MTX (N = 32) | Tapering MTX First, Followed by ETN (N = 33) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | |||||
| 57 (11.3) | 59 (8.9) | 52 (10.8) | 58 (10.3) | 58 (13.5) |
| 26 (24–29) | 25 (25–30) | 26 (24–28) | 27 (24–30) | 25 (23–29) |
| 69 (62) | 11 (50) | 17 (70) | 20 (63) | 21 (63) |
| 5.7 (3.9–8.5) | 7.1 (4.2–9.0) | 6.0 (3.1–9.1) | 5.7 (4.0–8.5) | 4.7 (2.5–70 |
| Clinical | |||||
| 56 (50) | 13 (72) | 12 (57) | 16 (55) | 15 (46) |
| 70 (63) | 12 (67) | 15 (71) | 20 (69) | 23 (74) |
| 1.0 (0.49) | 1.0 (0.44) | 1.1 (0.6) | 1.0 (0.53) | 0.9 (0.35) |
| 8 (3–15) | 6 (2–18) | 5.5 (2–12) | 9.5 (4.5–16) | 8 (5–14) |
| 2 (1–5) | 2 (1–5) | 1.8 (1–5) | 2 (1–8) | 3 (1–5) |
| 47 (42) | 12 (54) | 13 (54) | 11 (34) | 11 (33) |
| 20 (15–25) | 15 (14–25) | 15 (10–25) | 22 (15–25) | 25 (15–25) |
| - | 9.5 (5.5–10.5) | 7.4 (4.7–9.8) | 2.3 (1.8–3.0) | 2.4 (1.9–3.2) |
| Adalimumab | Etanercept | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug Level (mg/L) | OR | (95% CI) | p Value | Drug Level (mg/L) | OR | (95% CI) | p Value |
| Low * (<1.81) | - | - | - | Low * (<0.283) | - | - | - |
| Medium (1.81–6.06) | 0.29 | (0.09–0.92) | 0.036 | Medium (0.283–2.24) | 1.35 | (0.47–3.92) | 0.57 |
| High (>6.06) | 0.37 | (0.14–0.98) | 0.046 | High (>2.24) | 2.14 | (0.86–5.32) | 0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Layegh, Z.; Hooijberg, F.; Boekel, L.; Looijen, A.E.M.; van Mulligen, E.; Loeff, F.C.; Dijk, L.; Dolhain, R.J.E.M.; Rispens, T.; Wolbink, G.J.; et al. The Association Between Serum Drug Concentration and a Flare in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Tapering TNF Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101506
Layegh Z, Hooijberg F, Boekel L, Looijen AEM, van Mulligen E, Loeff FC, Dijk L, Dolhain RJEM, Rispens T, Wolbink GJ, et al. The Association Between Serum Drug Concentration and a Flare in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Tapering TNF Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101506
Chicago/Turabian StyleLayegh, Zohra, Femke Hooijberg, Laura Boekel, Agnes E. M. Looijen, Elise van Mulligen, Floris C. Loeff, Lisanne Dijk, Radboud J. E. M. Dolhain, Theo Rispens, Gertjan J. Wolbink, and et al. 2025. "The Association Between Serum Drug Concentration and a Flare in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Tapering TNF Inhibitors" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101506
APA StyleLayegh, Z., Hooijberg, F., Boekel, L., Looijen, A. E. M., van Mulligen, E., Loeff, F. C., Dijk, L., Dolhain, R. J. E. M., Rispens, T., Wolbink, G. J., & de Jong, P. H. P. (2025). The Association Between Serum Drug Concentration and a Flare in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Tapering TNF Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101506







