Histone Deacetylases in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Their Potential Role as Therapeutic Targets: Shedding Light on Astrocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. HDACs Superfamily: Structural and Catalytic Framework
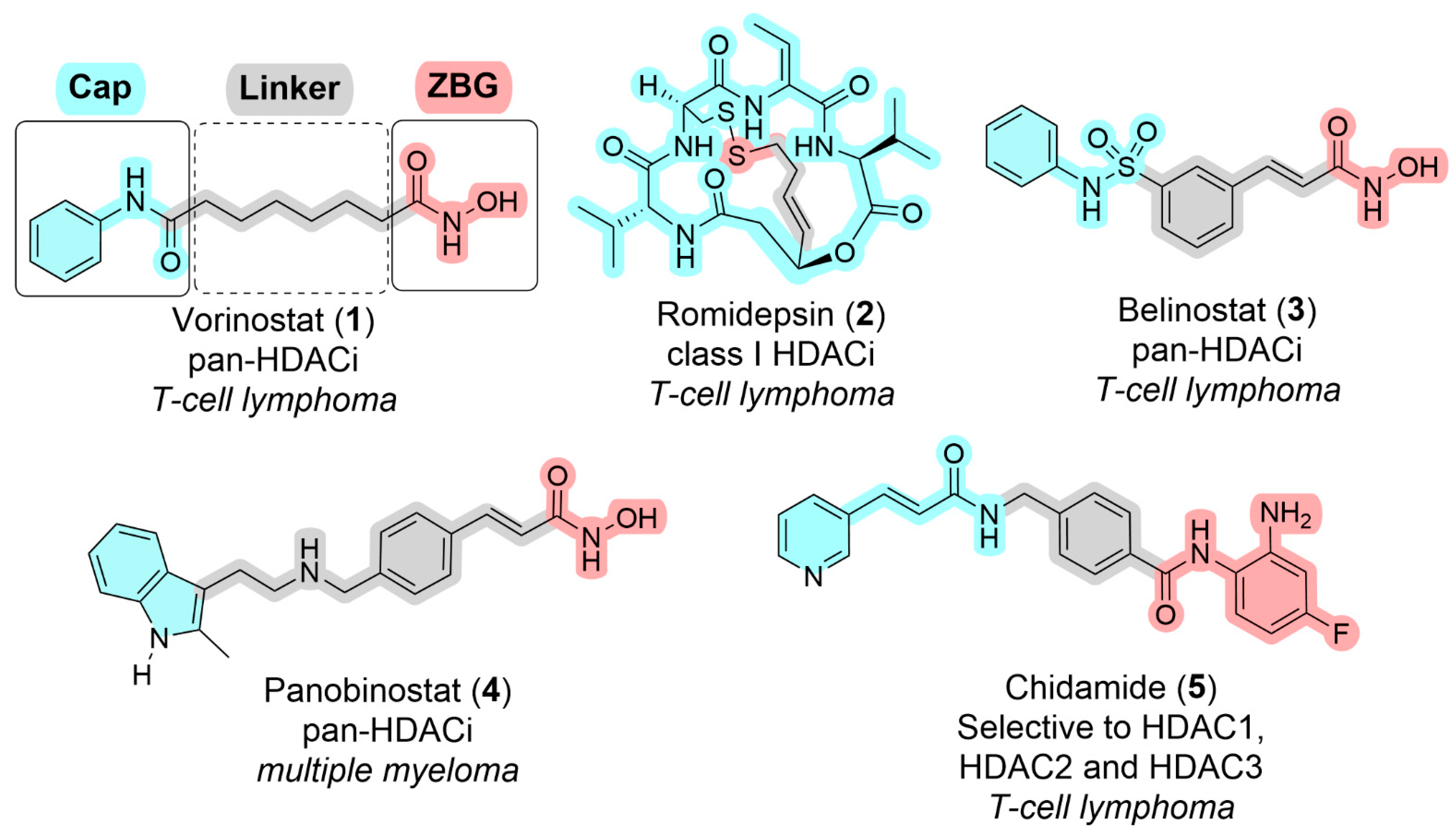
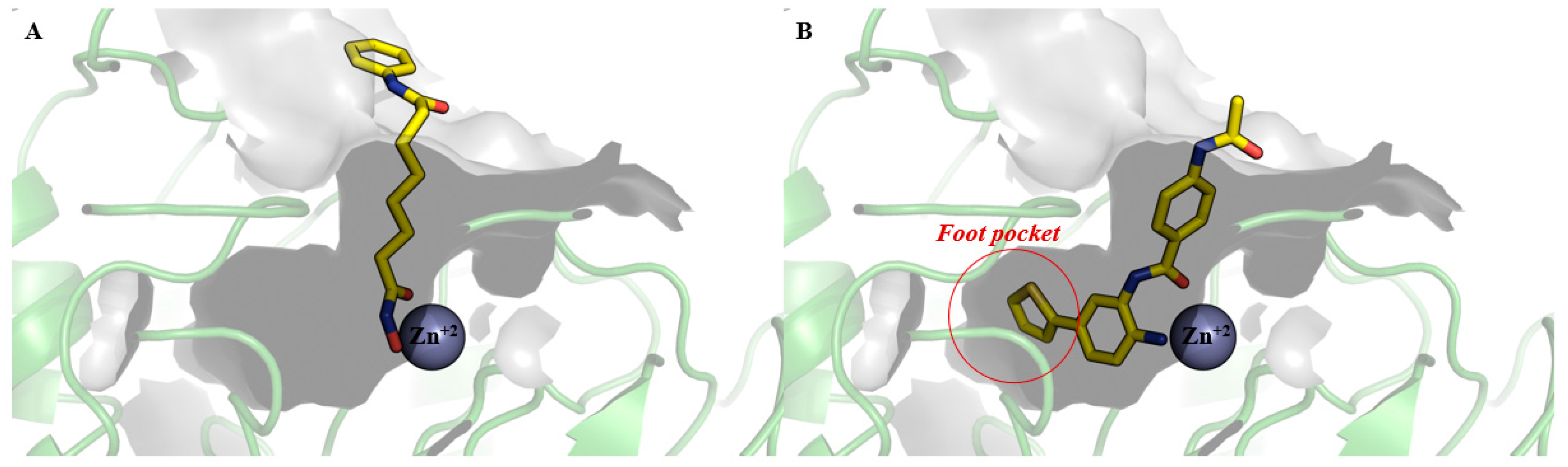
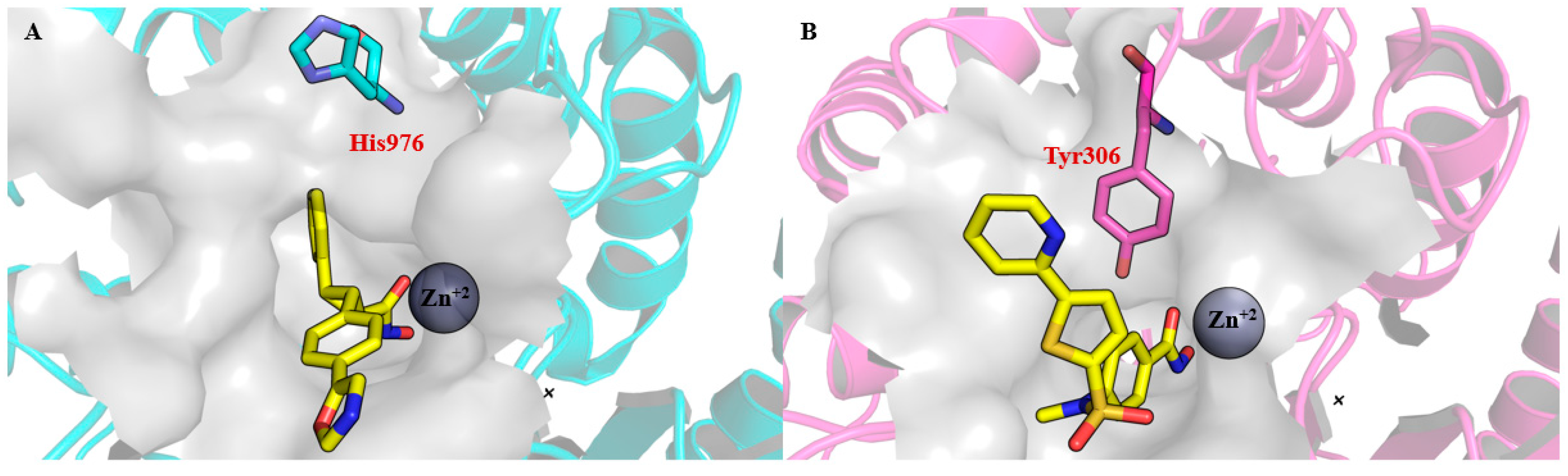
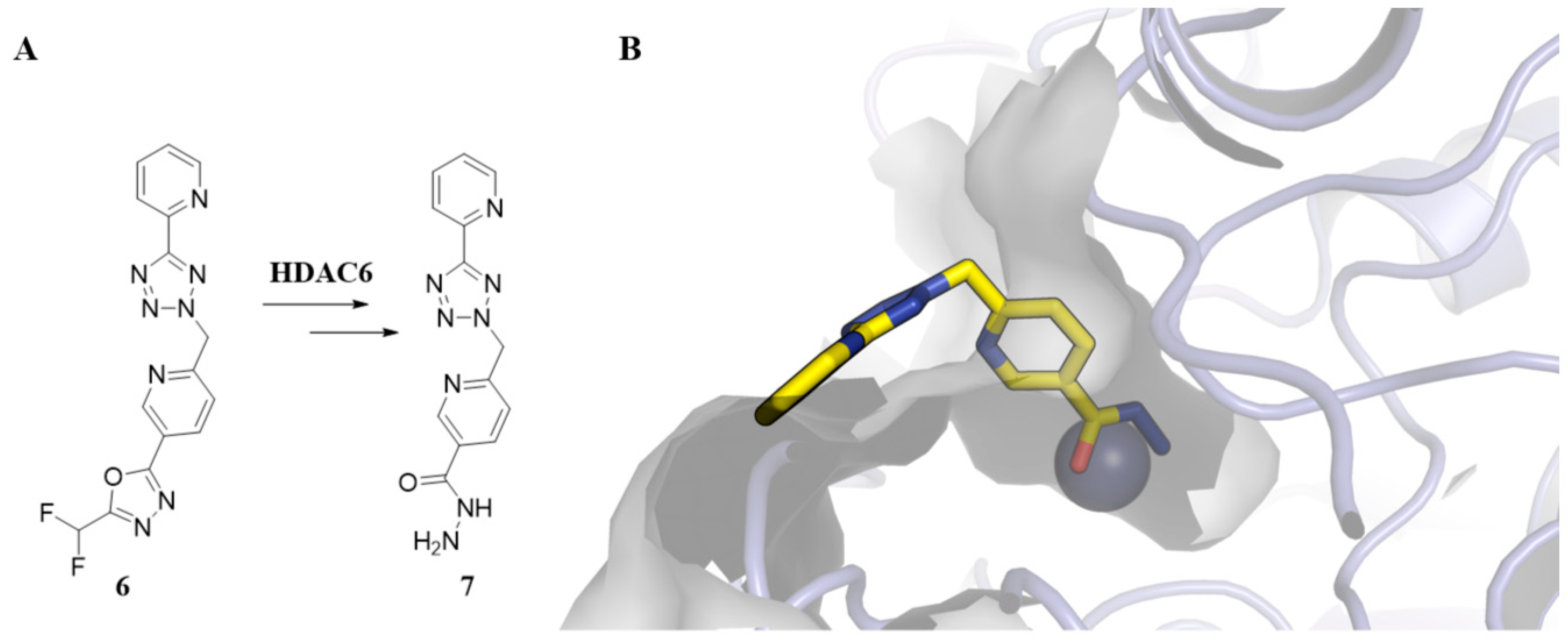
3. Pharmacophoric Features of HDACi
4. Implications of HDACs/HDACi in NDDs
5. HDACs and Astrocytes
5.1. Astrocytes in the Health and Injured CNS
5.2. HDACs, HDACi and Astrocytes
6. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APDA | autophagy-dysregulated astrocytes |
| APOE | apolipoprotein E |
| Aβ | amyloid-beta peptides |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| C3 | complement component 3 |
| CD | catalytic domain |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CFDA | China Food and Drug Administration |
| DAA | disease-associated astrocytes |
| DMF | dimethyl fumarate |
| FDA U.S. | Food and Drug Administration |
| FGF21 | fibroblast growth factor 21 |
| GCIs | glial cytoplasmic inclusions |
| FRDA | Friendeich’s ataxia |
| FXN | frataxin |
| GDNF | glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor |
| GFAP | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| GSK3β | glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta |
| HDACs | histone deacetylases |
| HDACi | histone deacetylase inhibitors |
| HATs | histone acetyltransferases |
| H4 | histone 4 |
| HD | Huntington’s disease |
| Hsp90 | heat shock protein 90 |
| LARA | lipid-accumulated reactive astrocyte |
| LBs | Lewy bodies |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MPTP | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine |
| NAD+ | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NDDs | neurodegenerative diseases |
| NES | nuclear export signal |
| NRF2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| PBA | Phenylbutyrate |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| PDEs | phosphodiesterases |
| SAHA | suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid |
| TFEB | transcription factor EB |
| TLE | temporal lobe epilepsy |
| TSA | trichostatin A |
| TSP | thrombospondins |
| VPA | valproic acid |
| ZBG | zinc-binding group |
References
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Recent Advances in Alzheimer’s Disease: Mechanisms, Clinical Trials and New Drug Development Strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, C.; Kabra, U.D. A Comprehensive Review of Multi-Target Directed Ligands in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 144, 107152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.; Cruz, M.T.; Fortuna, A.; Bicker, J. Restoring the Epigenome in Alzheimer’s Disease: Advancing HDAC Inhibitors as Therapeutic Agents. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 104052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsi, A.; Shahwan, M.; Zuberi, A.; Altwaijry, N. Identification of Potential Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase 6 Through Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Approach: Implications in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Chung, W.-S. Astrocytic Crosstalk with Brain and Immune Cells in Healthy and Diseased Conditions. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2024, 84, 102840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S.; Deneen, B. The Emerging Nature of Astrocyte Diversity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 42, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, L.P.; Matias, I.C.P.; Garcia, M.N.; Gomes, F.C.A. Astrocytic Control of Neural Circuit Formation: Highlights on TGF-Beta Signaling. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 78, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, B.L.L.; Liddelow, S.A. Heterogeneity of Astrocyte Reactivity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2025, 48, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, I.; Morgado, J.; Gomes, F.C.A. Astrocyte Heterogeneity: Impact to Brain Aging and Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, L.P.; Morgado, J.; Bergamo Araujo, A.P.; da Silva Antônio, L.M.; Mota-Araujo, H.P.; de Sena Murteira Pinheiro, P.; Sagrillo, F.S.; Cesar, G.V.; Ferreira, S.T.; Figueiredo, C.P.; et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibition Mitigates Cognitive Deficits and Astrocyte Dysfunction Induced by Amyloid-β (Aβ) Oligomers. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 4028–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, B.L.L.; Kristell, J.D.; Allan, K.C.; Cohn, E.F.; Karl, M.; Jerome, A.D.; Garrison, E.; Maeno-Hikichi, Y.; Sturno, A.M.; Kerr, A.; et al. A Phenotypic Screening Platform for Identifying Chemical Modulators of Astrocyte Reactivity. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoretti, I.; Lee, Y.-M.; Goodson, H.V. Molecular Evolution of the Histone Deacetylase Family: Functional Implications of Phylogenetic Analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witt, O.; Deubzer, H.E.; Milde, T.; Oehme, I. HDAC Family: What Are the Cancer Relevant Targets? Cancer Lett. 2009, 277, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.A.; Thota, S.; Fraga, C.A.M. Beyond the Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 6. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, P.D.S.M.; Rodrigues, D.A.; Sant’Anna, C.M.R.; Fraga, C.A.M. Modeling Zinc-oxygen Coordination in Histone Deacetylase: A Comparison of Semiempirical Methods Performance. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2018, 118, e25720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagger, G. Essential Function of Histone Deacetylase 1 in Proliferation Control and CDK Inhibitor Repression. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 2672–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longworth, M.S.; Laimins, L.A. Histone Deacetylase 3 Localizes to the Plasma Membrane and Is a Substrate of Src. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4495–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberland, M.; Mokalled, M.H.; Montgomery, R.L.; Olson, E.N. Epigenetic Control of Skull Morphogenesis by Histone Deacetylase 8. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberland, M.; Montgomery, R.L.; Olson, E.N. The Many Roles of Histone Deacetylases in Development and Physiology: Implications for Disease and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijter, A.J.M.D.; Gennip, A.H.V.; Caron, H.N.; Kemp, S.; Kuilenburg, A.B.P.V. Histone Deacetylases (HDACs): Characterization of the Classical HDAC Family. Biochem. J. 2003, 370, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantscheff, M.; Hopf, C.; Savitski, M.M.; Dittmann, A.; Grandi, P.; Michon, A.-M.; Schlegl, J.; Abraham, Y.; Becher, I.; Bergamini, G.; et al. Chemoproteomics Profiling of HDAC Inhibitors Reveals Selective Targeting of HDAC Complexes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-J.; Grégoire, S. Class II Histone Deacetylases: From Sequence to Function, Regulation, and Clinical Implication. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 2873–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.Y.; Zhang, J.; Miska, E.A.; Guenther, M.G.; Kouzarides, T.; Lazar, M.A. Nuclear Receptor Corepressors Partner with Class II Histone Deacetylases in a Sin3-Independent Repression Pathway. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahm, A.; Paolini, C.; Pallaoro, M.; Nardi, M.C.; Jones, P.; Neddermann, P.; Sambucini, S.; Bottomley, M.J.; Lo Surdo, P.; Carfí, A.; et al. Unraveling the Hidden Catalytic Activity of Vertebrate Class IIa Histone Deacetylases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17335–17340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, Y.; Christianson, D.W. Histone Deacetylase 6 Structure and Molecular Basis of Catalysis and Inhibition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Fernández, A.; Cabrero, J.R.; Serrador, J.M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. HDAC6: A Key Regulator of Cytoskeleton, Cell Migration and Cell–Cell Interactions. Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Li, H.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, T. The Role of HDAC6 in Autophagy and NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 763831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, R.J.; Franzoni, I.; Mann, M.K.; Szewczyk, M.M.; Mirabi, B.; Ferreira De Freitas, R.; Owens, D.D.G.; Ackloo, S.; Scheremetjew, A.; Juarez-Ornelas, K.A.; et al. Discovery and Characterization of a Chemical Probe Targeting the Zinc-Finger Ubiquitin-Binding Domain of HDAC6. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 10273–10288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira De Freitas, R.; Harding, R.J.; Franzoni, I.; Ravichandran, M.; Mann, M.K.; Ouyang, H.; Lautens, M.; Santhakumar, V.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; Schapira, M. Identification and Structure–Activity Relationship of HDAC6 Zinc-Finger Ubiquitin Binding Domain Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 4517–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, K.; Sun, S.; Jia, G.; Qin, M.; Hou, X.; Chou, C.J.; Huang, C.; Li, X. First-in-Class Hydrazide-Based HDAC6 Selective Inhibitor with Potent Oral Anti-Inflammatory Activity by Attenuating NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 12140–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. The Development Prospection of HDAC Inhibitors as a Potential Therapeutic Direction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2017, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.G. Targeting Huntington’s Disease through Histone Deacetylases. Clin. Epigenet. 2011, 2, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Taliyan, R. Targeting Histone Deacetylases: A Novel Approach in Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Dis. 2015, 2015, 303294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraco, G.; Cavone, L.; Chiarugi, A. The Therapeutic Potential of HDAC Inhibitors in the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokmanovic, M.; Clarke, C.; Marks, P.A. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Overview and Perspectives. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenberg, K.J.; Johnstone, R.W. Histone Deacetylases and Their Inhibitors in Cancer, Neurological Diseases and Immune Disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolden, J.E.; Peart, M.J.; Johnstone, R.W. Anticancer Activities of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Kuljaca, S.; Tee, A.; Marshall, G.M. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Multifunctional Anticancer Agents. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2006, 32, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaler, F.; Mercurio, C. Towards Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase Isoforms: What Has Been Achieved, Where We Are and What Will Be Next. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnock-Jones, K.P. Panobinostat: First Global Approval. Drugs 2015, 75, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, R.M. Belinostat: First Global Approval. Drugs 2014, 74, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.A.; Witter, D.J.; Belvedere, S. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 5097–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, N.O.; Pirone, A.; Lynch, B.A.; Hewitt, M.C.; Quinton, M.S.; McKee, T.D.; Ivarsson, M. CoREST Complex-Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Show Prosynaptic Effects and an Improved Safety Profile To Enable Treatment of Synaptopathies. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Reid, R.C.; Iyer, A.; Sweet, M.J.; Fairlie, D.P. Towards Isozyme-Selective HDAC Inhibitors For Interrogating Disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1479–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, J.C.; Jennings, A.J.; Skene, R.; Wu, Y.; Melkus, R.; Jong, R.D.; O’Connell, S.; Grimshaw, C.E.; Navre, M.; Gangloff, A.R. Exploration of the HDAC2 Foot Pocket: Synthesis and SAR of Substituted N-(2-Aminophenyl)Benzamides. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3142–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauffer, B.E.L.; Mintzer, R.; Fong, R.; Mukund, S.; Tam, C.; Zilberleyb, I.; Flicke, B.; Ritscher, A.; Fedorowicz, G.; Vallero, R.; et al. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitor Kinetic Rate Constants Correlate with Cellular Histone Acetylation but Not Transcription and Cell Viability. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26926–26943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürli, R.W.; Luckhurst, C.A.; Aziz, O.; Matthews, K.L.; Yates, D.; Lyons, K.A.; Beconi, M.; McAllister, G.; Breccia, P.; Stott, A.J.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Potent and Selective Class IIa Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors as a Potential Therapy for Huntington’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9934–9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, P.; Smil, D.V.; Wahhab, A.; Leit, S.; Rahil, J.; Li, Z.; Déziel, R.; Besterman, J.M. Diphenylmethylene Hydroxamic Acids as Selective Class IIa Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5684–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannini, A.; Volpari, C.; Filocamo, G.; Casavola, E.C.; Brunetti, M.; Renzoni, D.; Chakravarty, P.; Paolini, C.; De Francesco, R.; Gallinari, P.; et al. Crystal Structure of a Eukaryotic Zinc-Dependent Histone Deacetylase, Human HDAC8, Complexed with a Hydroxamic Acid Inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15064–15069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbert, C.; Guardiola, A.; Shao, R.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Ito, A.; Nixon, A.; Yoshida, M.; Wang, X.-F.; Yao, T.-P. HDAC6 Is a Microtubule-Associated Deacetylase. Nature 2002, 417, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggarty, S.J.; Koeller, K.M.; Wong, J.C.; Grozinger, C.M.; Schreiber, S.L. Domain-Selective Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6)-Mediated Tubulin Deacetylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4389–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, J.J.; Murphy, P.J.M.; Gaillard, S.; Zhao, X.; Wu, J.-T.; Nicchitta, C.V.; Yoshida, M.; Toft, D.O.; Pratt, W.B.; Yao, T.-P. HDAC6 Regulates Hsp90 Acetylation and Chaperone-Dependent Activation of Glucocorticoid Receptor. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.E.; Wagner, F.F.; Kaya, T.; Gale, J.P.; Aidoud, N.; Davoine, E.L.; Lazzaro, F.; Weïwer, M.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Holson, E.B. Discovery of the First Histone Deacetylase 6/8 Dual Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 4816–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, F.F.; Olson, D.E.; Gale, J.P.; Kaya, T.; Weïwer, M.; Aidoud, N.; Thomas, M.; Davoine, E.L.; Lemercier, B.C.; Zhang, Y.-L.; et al. Potent and Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) Does Not Require a Surface-Binding Motif. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1772–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, N.J.; Mahendran, A.; Breslow, R.; Christianson, D.W. Unusual Zinc-Binding Mode of HDAC6-Selective Hydroxamate Inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13459–13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osko, J.D.; Christianson, D.W. Structural Determinants of Affinity and Selectivity in the Binding of Inhibitors to Histone Deacetylase 6. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Kozikowski, A.P. Why Hydroxamates May Not Be the Best Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors—What Some May Have Forgotten or Would Rather Forget? ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, B.; Hansen, F.K. 2-(Difluoromethyl)-1,3,4-Oxadiazoles: The Future of Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 Modulation? ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2024, 7, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellupica, E.; Caprini, G.; Cordella, P.; Cukier, C.; Fossati, G.; Marchini, M.; Rocchio, I.; Sandrone, G.; Vanoni, M.A.; Vergani, B.; et al. Difluoromethyl-1,3,4-Oxadiazoles Are Slow-Binding Substrate Analog Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase 6 with Unprecedented Isotype Selectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripa, L.; Sandmark, J.; Hughes, G.; Shamovsky, I.; Gunnarsson, A.; Johansson, J.; Llinas, A.; Collins, M.; Jung, B.; Novén, A.; et al. Selective and Bioavailable HDAC6 2-(Difluoromethyl)-1,3,4-Oxadiazole Substrate Inhibitors and Modeling of Their Bioactivation Mechanism. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 14188–14207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, B.; Watson, P.R.; Reßing, N.; Cragin, A.D.; Schäker-Hübner, L.; Christianson, D.W.; Hansen, F.K. Difluoromethyl-1,3,4-Oxadiazoles Are Selective, Mechanism-Based, and Essentially Irreversible Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase 6. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 13821–13837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depetter, Y.; Geurs, S.; De Vreese, R.; Goethals, S.; Vandoorn, E.; Laevens, A.; Steenbrugge, J.; Meyer, E.; De Tullio, P.; Bracke, M.; et al. Selective Pharmacological Inhibitors of HDAC6 Reveal Biochemical Activity but Functional Tolerance in Cancer Models. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyault, C.; Sadoul, K.; Pabion, M.; Khochbin, S. HDAC6, at the Crossroads between Cytoskeleton and Cell Signaling by Acetylation and Ubiquitination. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5468–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.A.; Pinheiro, P.D.S.M.; Sagrillo, F.S.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Fraga, C.A.M. Histone Deacetylases as Targets for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders: Challenges and Future Opportunities. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 2177–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarev, A.D.; Attwood, M.M.; Jonsson, J.; Chubarev, V.N.; Tarasov, V.V.; Schiöth, H.B. Recent Developments of HDAC Inhibitors: Emerging Indications and Novel Molecules. Brit. J. Clin. Pharma 2021, 87, 4577–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganoni, S.; Macklin, E.A.; Hendrix, S.; Berry, J.D.; Elliott, M.A.; Maiser, S.; Karam, C.; Caress, J.B.; Owegi, M.A.; Quick, A.; et al. Trial of Sodium Phenylbutyrate–Taurursodiol for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClarty, B.M.; Rodriguez, G.; Dong, H. Class 1 Histone Deacetylases Differentially Modulate Memory and Synaptic Genes in a Spatial and Temporal Manner in Aged and APP/PS1 Mice. Brain Res. 2024, 1837, 148951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, N.O.; Lowe, J.A., III. Bicyclic Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase. U.S. Patent 20200148678A1, 3 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jefson, M.R.; Lowe, J.A., III; Dey, F.; Bergmann, A.; Schoop, A.; Fuller, N.O. Hetero-Halo Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase. U.S. Patent 20180194769A1, 12 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Laria, J.C.P.; Gómez, J.C.; Iglesias, R.R.I. New Heteroaryl Amide Derivatives as Selective Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 (HDAC1-2). ZA202000727B, 27 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hecklau, K.; Mueller, S.; Koch, S.P.; Mehkary, M.H.; Kilic, B.; Harms, C.; Boehm-Sturm, P.; Yildirim, F. The Effects of Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 1 and 3 in Huntington’s Disease Mice. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 616886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, F.; Parvizi, P.; Senger, G.; Tuncbag, N.; Rosenmund, C.; Yildirim, F. Impaired Inhibitory GABAergic Synaptic Transmission and Transcription Studied in Single Neurons by Patch-Seq in Huntington’s Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020293118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, T.H.; Huot, P.; Damude, S.; Fox, S.H.; Jones, S.W.; Rusche, J.R.; Brotchie, J.M. RGFP109, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Attenuates l-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia in the MPTP-Lesioned Marmoset: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Park. Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Soragni, E.; Chou, C.J.; Barnes, G.; Jones, S.; Rusche, J.R.; Gottesfeld, J.M.; Pandolfo, M. Two New Pimelic Diphenylamide HDAC Inhibitors Induce Sustained Frataxin Upregulation in Cells from Friedreich’s Ataxia Patients and in a Mouse Model. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codazzi, F.; Hu, A.; Rai, M.; Donatello, S.; Salerno Scarzella, F.; Mangiameli, E.; Pelizzoni, I.; Grohovaz, F.; Pandolfo, M. Friedreich Ataxia-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons Show a Cellular Phenotype That Is Corrected by a Benzamide HDAC Inhibitor. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 4847–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soragni, E.; Miao, W.; Iudicello, M.; Jacoby, D.; De Mercanti, S.; Clerico, M.; Longo, F.; Piga, A.; Ku, S.; Campau, E.; et al. Epigenetic Therapy for F Riedreich Ataxia. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tago, T.; Toyohara, J.; Ishii, K. Preclinical Evaluation of an18 F-Labeled SW-100 Derivative for PET Imaging of Histone Deacetylase 6 in the Brain. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tago, T.; Sakata, M.; Kanazawa, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Ishii, K.; Toyohara, J. Preclinical Validation of a Novel Brain-Penetrant PET Ligand for Visualization of Histone Deacetylase 6: A Potential Imaging Target for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2024, 51, 2193–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tago, T.; Toyohara, J. Step-by-Step Optimisation of the Radiosynthesis of the Brain HDAC6 Radioligand [18F]FSW-100 for Clinical Applications. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2024, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoal, T.A.; Chamoun, M.; Lax, E.; Wey, H.-Y.; Shin, M.; Ng, K.P.; Kang, M.S.; Mathotaarachchi, S.; Benedet, A.L.; Therriault, J.; et al. [11C]Martinostat PET Analysis Reveals Reduced HDAC I Availability in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wei, Y.; Lautrup, S.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y.; Cordonnier, S.; Mattson, M.P.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. NAD+ Supplementation Reduces Neuroinflammation and Cell Senescence in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease via cGAS–STING. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2011226118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mary, A.; Eysert, F.; Checler, F.; Chami, M. Mitophagy in Alzheimer’s Disease: Molecular Defects and Therapeutic Approaches. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöndorf, D.C.; Ivanyuk, D.; Baden, P.; Sanchez-Martinez, A.; De Cicco, S.; Yu, C.; Giunta, I.; Schwarz, L.K.; Di Napoli, G.; Panagiotakopoulou, V.; et al. The NAD+ Precursor Nicotinamide Riboside Rescues Mitochondrial Defects and Neuronal Loss in iPSC and Fly Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2976–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Süssmuth, S.D.; Haider, S.; Landwehrmeyer, G.B.; Farmer, R.; Frost, C.; Tripepi, G.; Andersen, C.A.; Di Bacco, M.; Lamanna, C.; Diodato, E.; et al. An Exploratory Double-blind, Randomized Clinical Trial with Selisistat, a SIRT1 Inhibitor, in Patients with H Untington’s Disease. Brit. J. Clin. Pharma 2015, 79, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Ran, Y.; Xie, F.; Liu, Y.; Wei, C.; Luan, X.; Wu, J. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel N-Benzyl Piperidine Derivatives as Potent HDAC/AChE Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2023, 80, 117178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sena Murteira Pinheiro, P.; Franco, L.S.; Montagnoli, T.L.; Fraga, C.A.M. Molecular Hybridization: A Powerful Tool for Multitarget Drug Discovery. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2024, 19, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Qiu, W.; Tang, X.; Guo, H.; Yang, P.; Chen, Y.; Sun, H. Design, Synthesis, and Proof of Concept of Balanced Dual Inhibitors of Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) and Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 3226–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado-Tejedor, M.; Garcia-Barroso, C.; Sánchez-Arias, J.A.; Rabal, O.; Pérez-González, M.; Mederos, S.; Ugarte, A.; Franco, R.; Segura, V.; Perea, G.; et al. A First-in-Class Small-Molecule That Acts as a Dual Inhibitor of HDAC and PDE5 and That Rescues Hippocampal Synaptic Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabal, O.; Sánchez-Arias, J.A.; Cuadrado-Tejedor, M.; De Miguel, I.; Pérez-González, M.; García-Barroso, C.; Ugarte, A.; Estella-Hermoso De Mendoza, A.; Sáez, E.; Espelosin, M.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of First-in-Class Dual Acting Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) and Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) Inhibitors for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 8967–9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabal, O.; Sánchez-Arias, J.A.; Cuadrado-Tejedor, M.; De Miguel, I.; Pérez-González, M.; García-Barroso, C.; Ugarte, A.; Estella-Hermoso De Mendoza, A.; Sáez, E.; Espelosin, M.; et al. Multitarget Approach for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Inhibition of Phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9) and Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) Covering Diverse Selectivity Profiles. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 4076–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, A.; La Pietra, V.; Betari, N.; Petragnani, N.; Conte, M.; Daniele, S.; Pietrobono, D.; Martini, C.; Petralla, S.; Casadei, R.; et al. Discovery of the First-in-Class GSK-3β/HDAC Dual Inhibitor as Disease-Modifying Agent To Combat Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ran, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, J.; Yu, C.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, A.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Dual-Function Inhibitors Targeting NMDAR and HDAC for Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 103, 104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, P.D.S.M.; De Chirico, F.; Loi, M.; Trazzi, S.; Ciani, E.; Rodrigues, D.A.; Alves, M.A.; Lima, L.M.; Milelli, A.; Monti, B.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Multitarget GPR40 Agonists/HDAC6 Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 296, 117868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; An, B.; Pan, T.; Li, Z.; Huang, L.; Li, X. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Possessing Glutathione Peroxidase-like and Antioxidant Activities against Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 5718–5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hösli, L.; Zuend, M.; Bredell, G.; Zanker, H.S.; Porto De Oliveira, C.E.; Saab, A.S.; Weber, B. Direct Vascular Contact Is a Hallmark of Cerebral Astrocytes. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacVicar, B.A.; Newman, E.A. Astrocyte Regulation of Blood Flow in the Brain. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stackhouse, T.L.; Mishra, A. Neurovascular Coupling in Development and Disease: Focus on Astrocytes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 702832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, G.; Bataveljic, D.; Visser, J.; Kumar, N.; Moulard, J.; Dallérac, G.; Mozheiko, D.; Rollenhagen, A.; Ezan, P.; Mongin, C.; et al. Physiological Synaptic Activity and Recognition Memory Require Astroglial Glutamine. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, H.; Dulla, C.G.; Farzampour, Z.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Huguenard, J.R.; Reimer, R.J. A Local Glutamate-Glutamine Cycle Sustains Synaptic Excitatory Transmitter Release. Neuron 2014, 81, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopherson, K.S.; Ullian, E.M.; Stokes, C.C.A.; Mullowney, C.E.; Hell, J.W.; Agah, A.; Lawler, J.; Mosher, D.F.; Bornstein, P.; Barres, B.A. Thrombospondins Are Astrocyte-Secreted Proteins That Promote CNS Synaptogenesis. Cell 2005, 120, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukdereli, H.; Allen, N.J.; Lee, A.T.; Feng, A.; Ozlu, M.I.; Conatser, L.M.; Chakraborty, C.; Workman, G.; Weaver, M.; Sage, E.H.; et al. Control of Excitatory CNS Synaptogenesis by Astrocyte-Secreted Proteins Hevin and SPARC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E440–E449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, L.P.; Almeida, J.C.; Tortelli, V.; Vargas Lopes, C.; Setti-Perdigão, P.; Stipursky, J.; Kahn, S.A.; Romão, L.F.; De Miranda, J.; Alves-Leon, S.V.; et al. Astrocyte-Induced Synaptogenesis Is Mediated by Transforming Growth Factor β Signaling through Modulation of d-Serine Levels in Cerebral Cortex Neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 41432–41445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.J.; Bennett, M.L.; Foo, L.C.; Wang, G.X.; Chakraborty, C.; Smith, S.J.; Barres, B.A. Astrocyte Glypicans 4 and 6 Promote Formation of Excitatory Synapses via GluA1 AMPA Receptors. Nature 2012, 486, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauch, D.H.; Nägler, K.; Schumacher, S.; Göritz, C.; Müller, E.-C.; Otto, A.; Pfrieger, F.W. CNS Synaptogenesis Promoted by Glia-Derived Cholesterol. Science 2001, 294, 1354–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buosi, A.S.; Matias, I.; Araujo, A.P.B.; Batista, C.; Gomes, F.C.A. Heterogeneity in Synaptogenic Profile of Astrocytes from Different Brain Regions. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Qin, S.; Huang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Tan, Z.; Gu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wang, D.; Lian, X.-F.; He, C.; et al. Region-Restrict Astrocytes Exhibit Heterogeneous Susceptibility to Neuronal Reprogramming. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.-S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic Reactive Astrocytes Are Induced by Activated Microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Barres, B.A. Reactive Astrocytes: Production, Function, and Therapeutic Potential. Immunity 2017, 46, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, L.E.; Liddelow, S.A.; Chakraborty, C.; Münch, A.E.; Heiman, M.; Barres, B.A. Normal Aging Induces A1-like Astrocyte Reactivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1896–E1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttenplan, K.A.; Weigel, M.K.; Adler, D.I.; Couthouis, J.; Liddelow, S.A.; Gitler, A.D.; Barres, B.A. Knockout of Reactive Astrocyte Activating Factors Slows Disease Progression in an ALS Mouse Model. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, X.; Cisternas, P.; Jury, N.; Martinez, P.; Huang, X.; You, Y.; Redding-Ochoa, J.; Vidal, R.; Zhang, J.; Troncoso, J.; et al. Activated Endothelial Cells Induce a Distinct Type of Astrocytic Reactivity. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoettels, B.A.; Wertz, T.S.; Birk, D.E.; Oxford, J.T.; Beard, R.S. The Extracellular Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Is Upregulated by Endothelial Cells During Inflammation and Contributes to Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 682.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Jung, Y.-J.; Park, Y.R.; Lim, S.; Choi, Y.-J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Mun, J.Y.; Chung, W.-S. A Distinct Astrocyte Subtype in the Aging Mouse Brain Characterized by Impaired Protein Homeostasis. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 726–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadick, J.S.; O’Dea, M.R.; Hasel, P.; Dykstra, T.; Faustin, A.; Liddelow, S.A. Astrocytes and Oligodendrocytes Undergo Subtype-Specific Transcriptional Changes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 2022, 110, 1788–1805.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Miranda, F.; Araujo, A.P.B.; Medinas, D.B.; Gomes, F.C.A. Astrocytic Hevin/SPARCL-1 Regulates Cognitive Decline in Pathological and Normal Brain Aging. Aging Cell 2025, 24, e14493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.; McCabe, C.; Medina, S.; Varshavsky, M.; Kitsberg, D.; Dvir-Szternfeld, R.; Green, G.; Dionne, D.; Nguyen, L.; Marshall, J.L.; et al. Disease-Associated Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease and Aging. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.; Holtzman, D.M.; Apostolova, L.G.; Cruchaga, C.; Masters, C.L.; Hardy, J.; Villemagne, V.L.; Bell, J.; Cho, M.; Hampel, H. Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s Disease Trajectories and the next-Generation Clinical Care Pathway. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 1236–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-P.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Fang, W.; Wang, Z.; Ye, H.; Wang, M.-J.; Ke, L.; Huang, T.; Lv, P.; et al. Lipid-Accumulated Reactive Astrocytes Promote Disease Progression in Epilepsy. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Miranda, F.; Matias, I.; Gomes, F.C.A. Astrocytic Proteostasis in the Tale of Aging and Neurodegeneration. Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 103, 102580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chun, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.; Park, U.; Chu, J.; Bhalla, M.; Choi, S.-H.; Yousefian-Jazi, A.; Kim, S.; et al. Astrocytic Autophagy Plasticity Modulates Aβ Clearance and Cognitive Function in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Domenico, A.; Carola, G.; Calatayud, C.; Pons-Espinal, M.; Muñoz, J.P.; Richaud-Patin, Y.; Fernandez-Carasa, I.; Gut, M.; Faella, A.; Parameswaran, J.; et al. Patient-Specific iPSC-Derived Astrocytes Contribute to Non-Cell-Autonomous Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
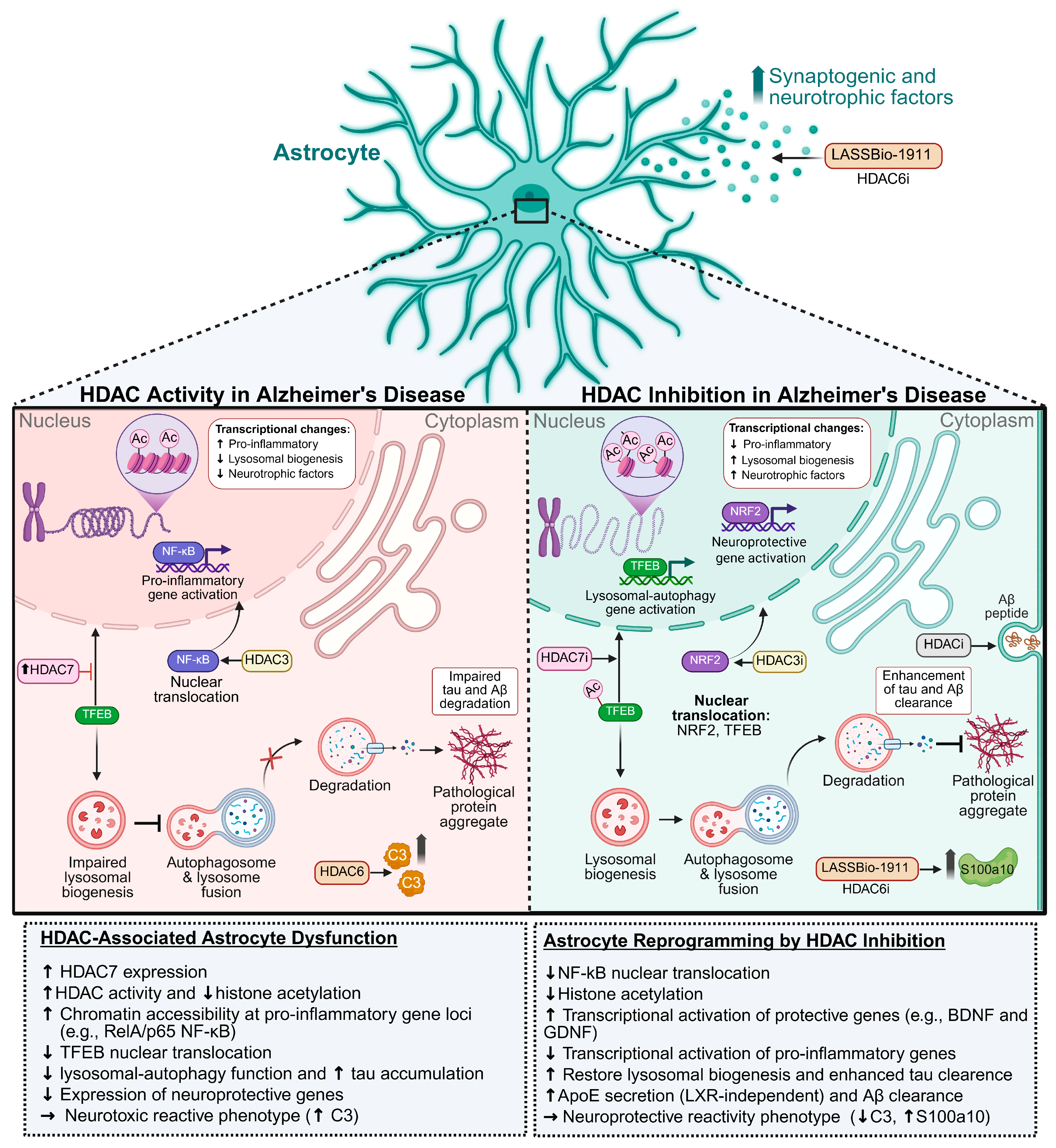
- Ye, J.; Zhong, S.; Wan, H.; Guo, X.; Yao, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.-Z.; Xiao, S. Upregulated Astrocyte HDAC7 Induces Alzheimer-like Tau Pathologies via Deacetylating Transcription Factor-EB and Inhibiting Lysosome Biogenesis. Mol. Neurodegener. 2025, 20, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano-Kobayashi, A.; Canela, A.; Yoshihara, T.; Hagiwara, M. Astrocyte-Targeting Therapy Rescues Cognitive Impairment Caused by Neuroinflammation via the Nrf2 Pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2303809120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, M.R.; Johnson, D.A.; Sirkis, D.W.; Messing, A.; Johnson, J.A. Nrf2 Activation in Astrocytes Protects against Neurodegeneration in Mouse Models of Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 13574–13581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltan, S.; Bachleda, A.; Morrison, R.S.; Murphy, S.P. Expression of Histone Deacetylases in Cellular Compartments of the Mouse Brain and the Effects of Ischemia. Transl. Stroke Res. 2011, 2, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.; Nakashima, K.; Kuwabara, T.; Mejia, E.; Gage, F.H. Histone Deacetylase Inhibition-Mediated Neuronal Differentiation of Multipotent Adult Neural Progenitor Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16659–16664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, X.; Liu, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; He, D.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, X.; Hassan, A.; et al. Hdac3 Interaction with P300 Histone Acetyltransferase Regulates the Oligodendrocyte and Astrocyte Lineage Fate Switch. Dev. Cell 2016, 36, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin-Husstege, M.; Muggironi, M.; Liu, A.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. Histone Deacetylase Activity Is Necessary for Oligodendrocyte Lineage Progression. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 10333–10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shin, D.; Kwon, S.H. Histone Deacetylase 6 Plays a Role as a Distinct Regulator of Diverse Cellular Processes. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 775–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, G.S.; Ju, S.M.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J. HDAC 6 Mediates HIV-1 Tat-induced Proinflammatory Responses by Regulating MAPK-NF-kappa B/AP-1 Pathways in Astrocytes. Glia 2015, 63, 1953–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beurel, E. HDAC6 Regulates LPS-Tolerance in Astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhong, S.; Deng, Y.; Yao, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.-Z.; Xiao, S. HDAC7 Activates IKK/NF-κB Signaling to Regulate Astrocyte-Mediated Inflammation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 6141–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanski, R.; Sneeboer, M.A.M.; van Bodegraven, E.J.; Sluijs, J.A.; Kropff, W.; Vermunt, M.W.; Creyghton, M.P.; De Filippis, L.; Vescovi, A.; Aronica, E.; et al. Histone Acetylation in Astrocytes Suppresses GFAP and Stimulates a Reorganization of the Intermediate Filament Network. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 4368–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, Z.S.; Grinter, M.B.; VandeVord, P.J. Astrocyte Reactivity Following Blast Exposure Involves Aberrant Histone Acetylation. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, S.; Boraso, M.; Galmozzi, A.; Serafini, M.M.; De Fabiani, E.; Crestani, M.; Viviani, B. Dose-Dependent Dual Effects of HDAC Inhibitors on Glial Inflammatory Response. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashioka, S.; Klegeris, A.; McGeer, P.L. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid Attenuates Human Astrocyte Neurotoxicity Induced by Interferon-γ. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresselhaus, E.; Duerr, J.M.; Vincent, F.; Sylvain, E.K.; Beyna, M.; Lanyon, L.F.; LaChapelle, E.; Pettersson, M.; Bales, K.R.; Ramaswamy, G. Class I HDAC Inhibition Is a Novel Pathway for Regulating Astrocytic apoE Secretion. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, H.; Rao, R. Amyloid Clearance Defect in ApoE4 Astrocytes Is Reversed by Epigenetic Correction of Endosomal pH. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6640–E6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinova, Z.; Leng, Y.; Leeds, P.; Chuang, D.-M. Histone Deacetylase Inhibition Alters Histone Methylation Associated with Heat Shock Protein 70 Promoter Modifications in Astrocytes and Neurons. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liao, H.-M.; Wei, M.; Leeds, P.; Chuang, D.-M. Valproic Acid and Other HDAC Inhibitors Upregulate FGF21 Gene Expression and Promote Process Elongation in Glia by Inhibiting HDAC2 and 3. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19, pyw035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniura, S.; Kamitani, H.; Watanabe, T.; Eling, T.E. Transcriptional Regulation of Cyclooxygenase-1 by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Normal Human Astrocyte Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 16823–16830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasipura, S.D.; Kim, S.; Al-Harthi, L. Epigenetic Regulation of HIV-1 Latency in Astrocytes. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3031–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, S.; Polak, P.E.; Lin, S.X.; Braun, D.; Guizzetti, M.; Zhang, X.; Rubinstein, I.; Feinstein, D.L. Dimethyl Fumarate Regulates Histone Deacetylase Expression in Astrocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 263, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltan, S.; Murphy, S.P.; Danilov, C.A.; Bachleda, A.; Morrison, R.S. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Preserve White Matter Structure and Function during Ischemia by Conserving ATP and Reducing Excitotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 3990–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chen, P.S.; Dallas, S.; Wilson, B.; Block, M.L.; Wang, C.-C.; Kinyamu, H.; Lu, N.; Gao, X.; Leng, Y.; et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Up-Regulate Astrocyte GDNF and BDNF Gene Transcription and Protect Dopaminergic Neurons. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 11, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.-S.; Choi, S.; Khattar, P.; Choi, N.; Lee, S.C. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Suppress the Expression of Inflammatory and Innate Immune Response Genes in Human Microglia and Astrocytes. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010, 5, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Niu, F.; Huang, R.; Xu, Y. Enhancement of Glutamate Uptake in 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium-Treated Astrocytes by Trichostatin A. NeuroReport 2008, 19, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.A.H.; Thakore, N.; Singh, S.; Guzman, W.; Mehrotra, S.; Gangaraju, V.; Husain, S. Histone Deacetylases Regulation by δ-Opioids in Human Optic Nerve Head Astrocytes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltan, O.M.; Abdelrahman, K.S.; Bass, A.K.A.; Takizawa, K.; Narumi, A.; Konno, H. Design of Multi-Target Drugs of HDACs and Other Anti-Alzheimer Related Targets: Current Strategies and Future Prospects in Alzheimer’s Diseases Therapy. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 151, 107651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artetxe-Zurutuza, A.; Iturrioz-Rodriguez, N.; Elizazu, J.; Toledano-Pinedo, M.; Porro-Pérez, A.; De Goñi, I.; Elua-Pinin, A.; Schäker-Hübner, L.; Azkargorta, M.; Elortza, F.; et al. Generation and Validation of a Novel Multitarget Small Molecule in Glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Guo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, D.; Yu, J.; Liu, P. Study on Multi-Target Effects of the Novel HDAC6 Inhibitor W5 on Aβ/Cu2+-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Model of Rats. Brain Res. 2024, 1832, 148847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
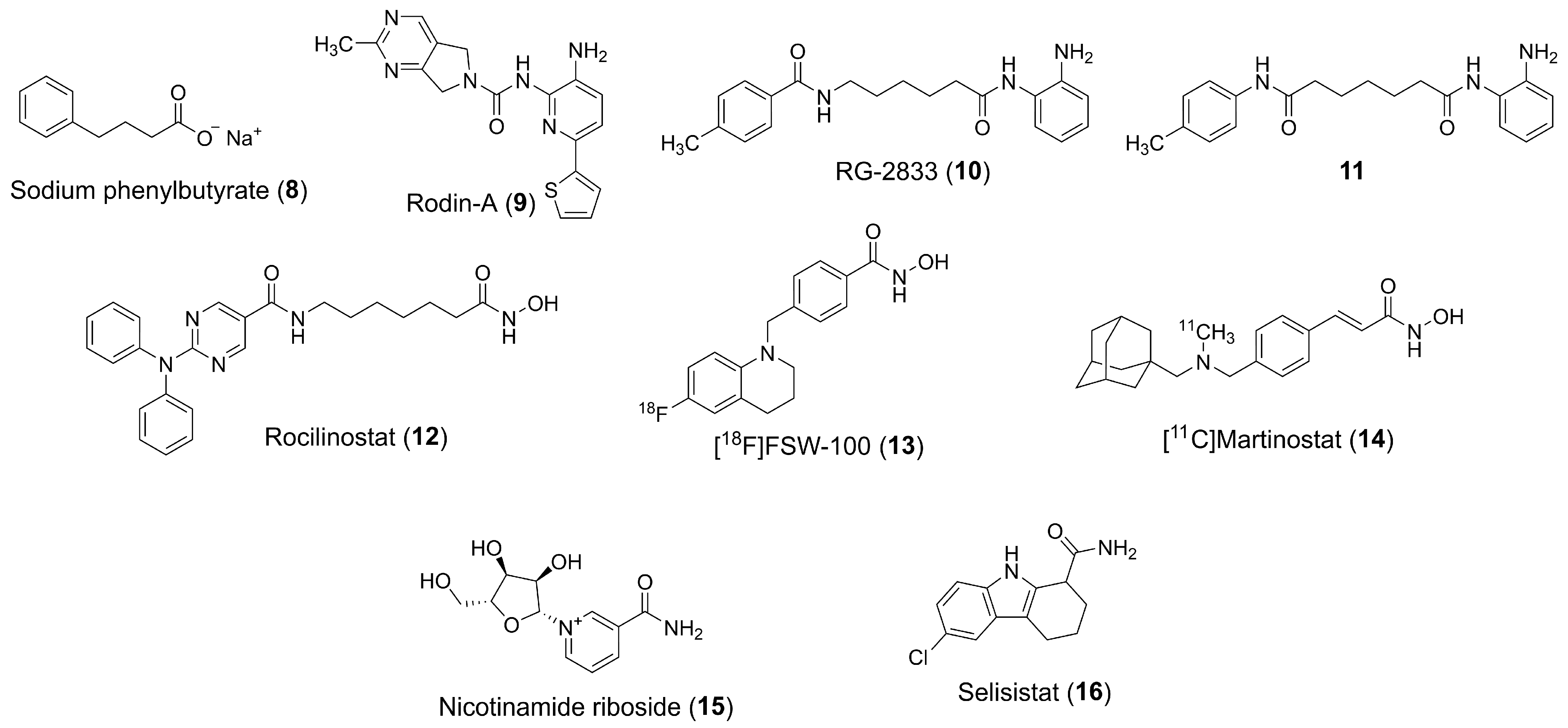
| Class | Members | Cofactor | Localization | Key Features/Functions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | HDACs 1, 2, 3, 8 | Zn2+ | Nucleus | Strong deacetylase activity; transcriptional repression; complexes with CoREST, NuRD, Sin3 |
| IIa | HDACs 4, 5, 7, 9 | Zn2+ | Nucleus ↔ Cytoplasm | Low catalytic activity; shuttle between compartments; scaffold proteins |
| IIb | HDACs 6, 10 | Zn2+ | Predominantly cytoplasmic | HDAC6: dual catalytic domains, ubiquitin-binding; regulates α-tubulin, Hsp90, protein degradation |
| III | Sirtuins 1–7 | NAD+ | Nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria | Metabolism-linked; roles in stress response, longevity, neuroprotection |
| Study ID (NCT) | Compound/HDACi | Target/HDACs | Disease/Indication | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03056495 | Vorinostat (1) | Pan-HDAC (hydroxamic acid) | AD | Phase I |
| NCT02124083 | Vorinostat (1) | Pan-HDAC | Niemann-Pick disease | Phase I/II |
| NCT03127514 | Phenylbutyrate (8) + Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (AMX0035) | Modest HDAC inhibition | ALS | Phase II |
| NCT05619783 | Phenylbutyrate (8) + Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (AMX0035) | Modest HDAC inhibition | ALS | Phase III |
| NCT03533257 | Phenylbutyrate (8) | Modest HDAC inhibition | AD | Phase II |
| NCT00212316 | Phenylbutyrate (8) | Modest HDAC inhibition | HD | Phase II |
| NCT03963973 | RDN-929 | HDAC-CoREST selective | AD, PD | Early clinical trials |
| NCT05019105 | ALKS-1140 | HDAC-CoREST selective | - | Phase I |
| NCT06469853 | MBF-015 | HDAC1/2 | HD | Phase II |
| - | RG-2833 (10) | HDAC1/3 | Friedreich’s ataxia | Phase I |
| NCT05526742 | CKD-510 | HDAC6 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease | Phase I |
| NCT04746287 | CKD-510 | HDAC6 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease | Phase I |
| NCT02149160 | EVP-0334 (FRM-0334) | Brain-penetrant HDACi | Frontotemporal dementia (granulin mutation) | Phase II |
| NCT03176472 | Rocilinostat (12) | HDAC6 | Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy | Phase II |
| NCT03721211 | [11C]Martinostat (14) | HDACs | Brain imaging | Phase I |
| NCT05617508 | Nicotinamide riboside (15) | Sirtuin | AD | Phase I |
| NCT03482167 | Nicotinamide riboside (15) | Sirtuin | Mild cognitive impairment | Phase I/II |
| NCT03816020 | Nicotinamide riboside (15) | Sirtuin | PD | Phase I |
| NCT01521585 | Selisistat (16) | Sirtuin | HD | Phase II |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinheiro, P.d.S.M.; Diniz, L.P.; Franco, L.S.; Siqueira, M.; Gomes, F.C.A. Histone Deacetylases in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Their Potential Role as Therapeutic Targets: Shedding Light on Astrocytes. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101471
Pinheiro PdSM, Diniz LP, Franco LS, Siqueira M, Gomes FCA. Histone Deacetylases in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Their Potential Role as Therapeutic Targets: Shedding Light on Astrocytes. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101471
Chicago/Turabian StylePinheiro, Pedro de Sena Murteira, Luan Pereira Diniz, Lucas S. Franco, Michele Siqueira, and Flávia Carvalho Alcantara Gomes. 2025. "Histone Deacetylases in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Their Potential Role as Therapeutic Targets: Shedding Light on Astrocytes" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101471
APA StylePinheiro, P. d. S. M., Diniz, L. P., Franco, L. S., Siqueira, M., & Gomes, F. C. A. (2025). Histone Deacetylases in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Their Potential Role as Therapeutic Targets: Shedding Light on Astrocytes. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101471







