The Effect of Chronic Immunosuppressive Regimen Treatment on Apoptosis in the Heart of Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
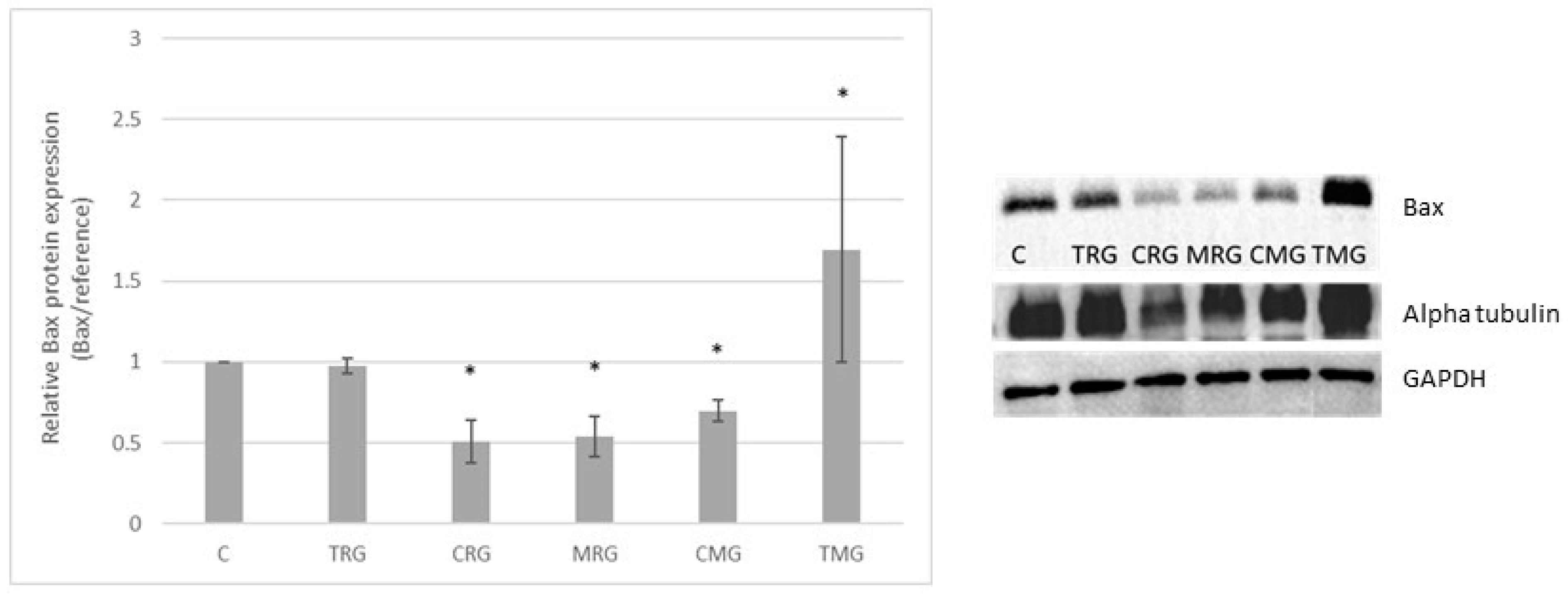
2.1. Bax Protein Expression
2.2. Bcl-2 Protein Expression
2.3. Caspaze 3 Expression
2.4. Caspaze 9 Expression
2.5. TUNEL Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
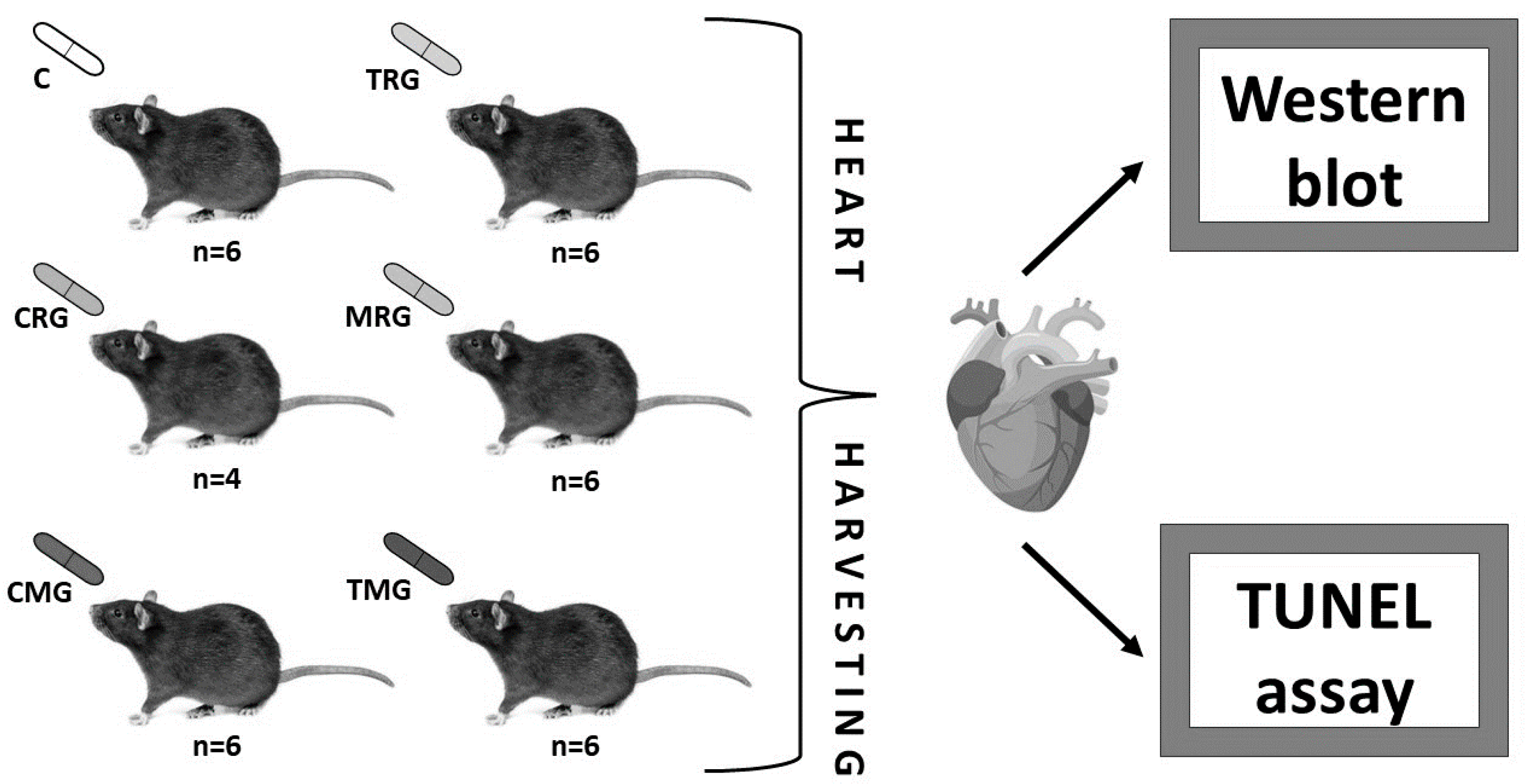
4.1. Animals
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Western Blot Analysis
Statistical Analysis for the Western Blot Analysis
4.2.2. TUNEL Assay Result
Quantitative Analysis of TUNEL-Positive Cells
Statistical Analysis for the TUNEL Assay
5. Conclusions
Strengths and Limitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saidi, R.F.; Hejazii Kenari, S.K. Challenges of Organ Shortage for Transplantation: Solutions and Opportunities. Int. J. Organ Transplant. Med. 2014, 5, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beyar, R. Challenges in Organ Transplantation. Rambam Maimonides Med. J. 2011, 2, e0049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R. Modern Immunosuppressive Therapy in Kidney Transplantation. Open J. Organ Transpl. Surg. 2013, 3, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taylor, A.L.; Watson, C.J.E.; Bradley, J.A. Immunosuppressive agents in solid organ transplantation: Mechanisms of action and therapeutic efficacy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2005, 56, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilch, N.A.; Bowman, L.J.; Taber, D.J. Immunosuppression trends in solid organ transplantation: The future of individualization, monitoring, and management. Pharmacotherapy 2021, 41, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Egashira, N.; Masuda, S. Recent Topics on The Mechanisms of Immunosuppressive Therapy-Related Neurotoxicities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggiani, F.; Moroni, G.; Ponticelli, C. Cardiovascular Risk after Kidney Transplantation: Causes and Current Approaches to a Relevant Burden. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elezaby, A.; Dexheimer, R.; Sallam, K. Cardiovascular effects of immunosuppression agents. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 981838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Böhm, M.; Marx, N. Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease. Circulation 2021, 143, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, D.C.; Katelaris, C.H. Long-Term Management of Patients Taking Immunosuppressive Drugs. Aust. Prescr. 2009, 32, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, J.M.M.; Christiaans, M.H.L.; van Hooff, J.P. Effect of Immunosuppressive Agents on Long-Term Survival of Renal Transplant Recipients. Drugs 2004, 64, 2047–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellström, B. Risk Factors for and Management of Post-Transplantation Cardiovascular Disease. BioDrugs 2001, 15, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surówka, A.; Prowans, P.; Żołnierczuk, M.; Miśkiewicz, M.; Wawrowski, T.; Skodda, M.; Markowska, M.; Kędzierska-Kapuza, K. The Effect of Calcineurin Inhibitors on MMPs Activity in Heart and Their Side Effects—A Review of Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirali, A.C.; Bia, M.J. Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Renal Transplant Recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A Review of Programmed Cell Death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J.C. Mechanisms of Apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1415–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy, M.S. Cell death: A review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, R.; Chaudhry, G. Understanding Apoptosis and Apoptotic Pathways Targeted Cancer Therapeutics. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, S.A.; Epelman, S. Chronic Heart Failure and Inflammation. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.M.; Izumo, S. Apoptosis and Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Empel, V.P.M.; Bertrand, A.T.A.; Hofstra, L.; Crijns, H.J.; Doevendans, P.A.; De Windt, L.J. Myocyte apoptosis in heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 67, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaddy, R.E. Apoptosis in heart transplantation. Coron Artery Dis. 1997, 8, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teringova, E.; Tousek, P. Apoptosis in ischemic heart disease. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, P.M.; Izumo, S. Apoptosis in heart: Basic mechanisms and implications in cardiovascular diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2003, 9, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surówka, A.; Żołnierczuk, M.; Prowans, P.; Grabowska, M.; Kupnicka, P.; Markowska, M.; Olejnik-Wojciechowska, J.; Szlosser, Z.; Wilk, A.; Szumilas, K.; et al. The Effects of Chronic Immunosuppressive Treatment on Morphological Changes in Cardiac Tissue and the Balance between Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) and Their Inhibitors in the Rat Heart. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surówka, A.; Szumilas, K.; Wilk, A.; Misiakiewicz-Has, K.; Ciechanowski, K.; Kędzierska-Kapuza, K. The Effect of Chronic Immunosuppressive Regimens Treatment on Aortal Media Morphology and the Balance between Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) and Their Inhibitors in the Abdominal Aorta of Rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surówka, A.; Wilk, A.; Szumilas, K.; Kędzierska-Kapuza, K. The Effect of Immunosuppressive Drugs on MMPs Activity in The Walls of Blood Vessels—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, J. Caspases in apoptosis and beyond. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6194–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvesen, G.S. Caspases and apoptosis. Hooper NM, editor. Essays Biochem. 2002, 38, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Riedl, S.J.; Shi, Y. Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawen, A. Apoptosis—An introduction. BioEssays 2003, 25, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Lessene, G.; Strasser, A.; Adams, J.M. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinou, J.C.; Youle, R.J. Mitochondria in Apoptosis: Bcl-2 family Members and Mitochondrial Dynamics. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häcker, G. The morphology of apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2000, 301, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayer, S.; Joannes, A.; Jaillet, M.; Gregianin, E.; Mahmoudi, S.; Sommé, J.M.; Fabre, A.; Mordant, P.; Cazes, A.; Crestani, B.; et al. The pro-apoptotic BAX protein influences cell growth and differentiation from the nucleus in healthy interphasic cells. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, K.C.; Green, D.R. How cells die: Apoptosis pathways. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108 (Suppl. 4), S99–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadiullina, R.; Mirgayazova, R.; Davletshin, D.; Khusainova, E.; Chasov, V.; Bulatov, E. Assessment of Thermal Stability of Mutant p53 Proteins via Differential Scanning Fluorimetry. Life 2023, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, T.J. Targeting the extrinsic apoptosis signaling pathway for cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 60, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, G.M.; Newbold, A.; Johnstone, R.W. Chapter Five—Intrinsic and Extrinsic Apoptotic Pathway Signaling as Determinants of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Antitumor Activity. In Advances in Cancer Research. Volime 116: Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Cancer Therapeutics; Grant, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 165–197. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123943873000057 (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Safarini, O.A.; Keshavamurthy, C.; Patel, P. Calcineurin Inhibitors. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558995/ (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Martinez-Martinez, S.; Redondo, J.M. Inhibitors of the Calcineurin/NFAT Pathway. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.N.; Metcalfe, M.S.; Nicholson, M.L. Rapamycin in transplantation: A review of the evidence. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Park, S.R.; Yoon, Y.J. An overview of rapamycin: From discovery to future perspectives. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulton, B.; Markham, A. Mycophenolate Mofetil. Drugs 1996, 51, 278–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwerner, J.; Fiorentino, D. Mycophenolate mofetil. Dermatol. Ther. 2007, 20, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remiszewski, P. Immunosuppressive therapy after human lung transplantation—Drugs presentation. Pneumonol. Alergol. Pol. 2005, 73, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Chien, C.T.; Yu, S.L.; Lee, Y.T.; Chen, W.J. Cyclosporine A regulate oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes: Mechanisms via ROS generation, iNOS and Hsp70. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 137, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, D.; Ammirati, E. Cyclosporine in transplantation—A history of converging timelines. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2011, 25, 493–504. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, C.M.; Goa, K.L.; Gillis, J.C. Tacrolimus. An update of its pharmacology and clinical efficacy in the management of organ transplantation. Drugs 1997, 54, 925–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, D.; Haragsim, L. Cyclosporine: A Review. J. Transplant. 2012, 2012, 230386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, S.; Leu, S.; Sheu, J.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, L.T.; Kao, Y.H.; Yen, C.H.; Tsai, T.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Chang, H.W.; et al. Intra-coronary administration of tacrolimus markedly attenuates infarct size and preserves heart function in porcine myocardial infarction. J. Inflamm. 2012, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yu, J.; Chen, R.; Wu, J.; Fei, J.; Bo, Q.; Xue, L.; Li, D. Mycophenolate mofetil attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via regulation of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Pharm. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 69, 850–855. [Google Scholar]
- Diepstraten, S.T.; Anderson, M.A.; Czabotar, P.E.; Lessene, G.; Strasser, A.; Kelly, G.L. The manipulation of apoptosis for cancer therapy using BH3-mimetic drugs. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, H.U.; Haj-Yehia, A.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 2000, 5, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waehre, A.; Halvorsen, B.; Yndestad, A.; Husberg, C.; Sjaastad, I.; Nygård, S.; Louch, W.; Reims, H.M.; Roald, B.; Dahl, C.P.; et al. Abstract 3395: The Homeostatic Chemokine CXCL13 and Its Receptor CXCR5 Are Regulated in Heart Failure and Are Involved in Cardiac Remodelling. Circulation 2009, 120 (Suppl. 18), S801. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, R.; Wang, D.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. Suppression of apoptosis in vascular endothelial cell, the promising way for natural medicines to treat atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 168, 105599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedzierska, K.; Sporniak-Tutak, K.; Kolasa, A.; Domanski, L.; Domański, M.; Sindrewicz, K.; Smektała, T.; Bober, J.; Safranow, K.; Osekowska, B.; et al. The effect of immunosuppressive therapy on renal cell apoptosis in native rat kidneys. Histol. Histopathol. 2015, 30, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durlik, M.; Danielewicz, R. Zalecenia: Dotyczące Leczenia Immunosupresyjnego po Przeszczepieniu Narządów Unaczynionych. Fundacja Zjednoczeni dla Transplantacji: Warsaw, Poland, 2021; Available online: https://p-t-t.org/artykul/zalecenia-dotyczace-leczenia-immunosupresyjnego-po-przeszczepieniu-narzadow-unaczynionych (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- van Westrhenen, R.; Aten, J.; Hajji, N.; de Boer, O.J.; Kunne, C.; de Waart, D.R.; Krediet, R.T. Cyclosporin A induces peritoneal fibrosis and angiogenesis during chronic peritoneal exposure to a glucose-based, lactate-buffered dialysis solution in the rat. Blood Purif. 2007, 25, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffe, I.; Katz, I.; Sehgal, S.; Bex, F.; Kharode, Y.; Tamasi, J.; Epstein, S. Lack of change of cancellous bone volume with short-term use of the new immunosuppressant rapamycin in rats. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1993, 53, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolicoeur, E.M.; Qi, S.; Xu, D.; Dumont, L.; Daloze, P.; Chen, H. Combination therapy of mycophenolate mofetil and rapamycin in prevention of chronic renal allograft rejection in the rat. Transplantation 2003, 75, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, I.A.; Takizawa, M.; Jaffe, I.I.; Stein, B.; Fallon, M.D.; Epstein, S. Comparison of the effects of FK506 and cyclosporine on bone mineral metabolism in the rat. A pilot study. Transplantation 1991, 52, 571–574. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Kuzuya, T.; Liu, D.; Nagasaka, T.; Yokoyama, I.; Miwa, Y.; Morozumi, K.; Oikawa, T.; Uchida, K.; et al. Is absorption profile of cyclosporine really important for effective immunosuppression? Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R. Comparing rat’s to human’s age: How old is my rat in people years? Nutrition 2005, 21, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Group | X ± SD | Median (Range) |
|---|---|---|
| C | 10.7 ± 1.4 | 10.7 (7.6–14.8) |
| TRG | 16.7 b ± 2.7 | 17.0 (12.9–23.0) |
| CRG | 18.5 a ± 1.6 | 18.9 (13.9–22.6) |
| MRG | 23.0 a ± 4.0 | 21.4 (16.0–30.9) |
| CMG | 25.5 a ± 4.8 | 24.2 (18.1–35.8) |
| TMG | 27.9 a ± 5.1 | 27.5 (17.8–33.7) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Surówka, A.; Żołnierczuk, M.; Prowans, P.; Grabowska, M.; Kupnicka, P.; Markowska, M.; Szlosser, Z.; Kędzierska-Kapuza, K. The Effect of Chronic Immunosuppressive Regimen Treatment on Apoptosis in the Heart of Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091188
Surówka A, Żołnierczuk M, Prowans P, Grabowska M, Kupnicka P, Markowska M, Szlosser Z, Kędzierska-Kapuza K. The Effect of Chronic Immunosuppressive Regimen Treatment on Apoptosis in the Heart of Rats. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091188
Chicago/Turabian StyleSurówka, Anna, Michał Żołnierczuk, Piotr Prowans, Marta Grabowska, Patrycja Kupnicka, Marta Markowska, Zbigniew Szlosser, and Karolina Kędzierska-Kapuza. 2024. "The Effect of Chronic Immunosuppressive Regimen Treatment on Apoptosis in the Heart of Rats" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091188
APA StyleSurówka, A., Żołnierczuk, M., Prowans, P., Grabowska, M., Kupnicka, P., Markowska, M., Szlosser, Z., & Kędzierska-Kapuza, K. (2024). The Effect of Chronic Immunosuppressive Regimen Treatment on Apoptosis in the Heart of Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091188







